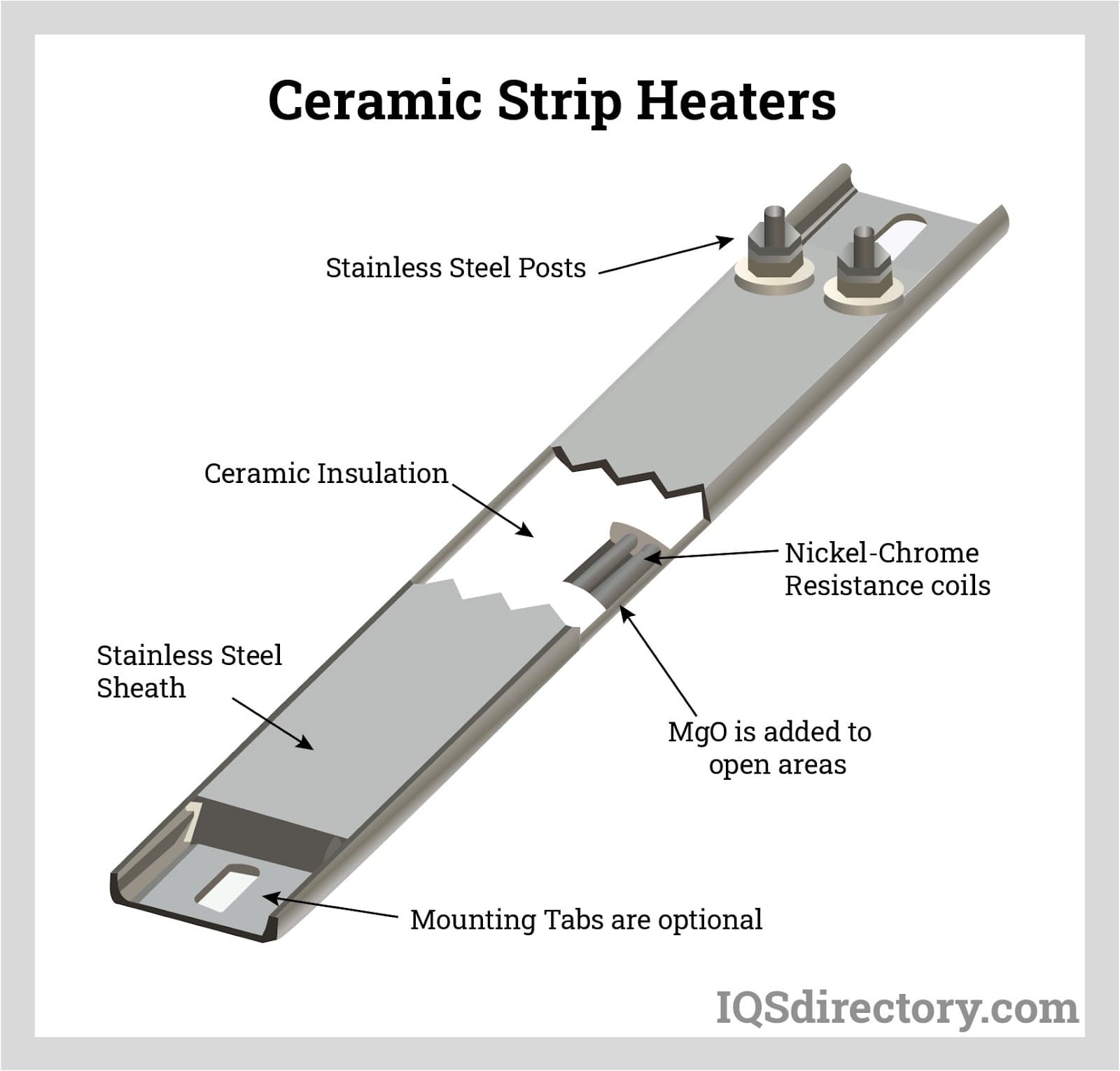
How Does A Ceramic Heater Work: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how does a ceramic heater work
In today’s fast-paced global market, sourcing effective heating solutions like ceramic heaters can be a significant challenge for B2B buyers, especially in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding how a ceramic heater works is crucial not only for optimizing energy efficiency but also for making informed purchasing decisions that align with budgetary constraints and operational needs. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of ceramic heaters, covering their functionality, types, applications, and advantages, as well as essential considerations for supplier vetting and cost analysis.
Ceramic heaters stand out for their eco-friendly attributes and energy efficiency, making them increasingly popular among businesses looking to reduce operating costs while maintaining a comfortable environment. This guide empowers international B2B buyers by elucidating the various types of ceramic heating solutions available, such as convection and radiant heating models, and their respective applications across different industries. Additionally, it offers insights into the latest technological advancements, ensuring that buyers are well-equipped to select the most suitable heating solutions for their specific requirements.
By navigating the complexities of the ceramic heater market with this guide, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce energy costs, and ensure compliance with international standards. Whether you are operating in Saudi Arabia or Germany, understanding the intricacies of ceramic heating technology will position your company for success in a competitive marketplace.
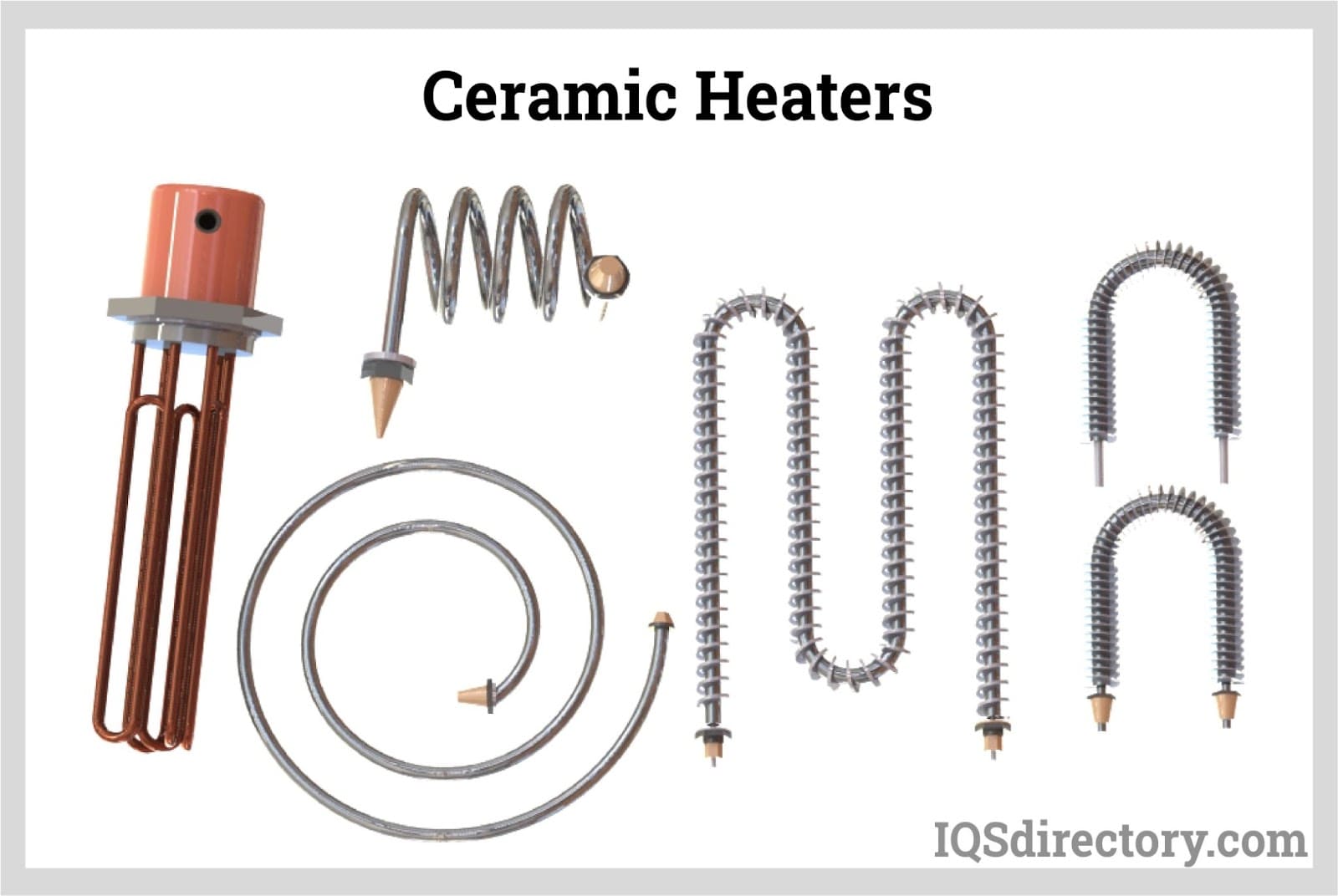
Understanding how does a ceramic heater work Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Band Heaters | Clamps onto objects, providing external heat via conduction. | Manufacturing, plastics processing | Pros: Versatile for various applications; Cons: Limited to flat surfaces. |
| Cartridge Heaters | Cylindrical design for precise internal heating. | Injection molding, automotive | Pros: High precision; Cons: Requires specific installation space. |
| Flexible Heaters | Bendable, suitable for various surfaces. | Medical devices, aerospace | Pros: Adaptable design; Cons: May have lower durability than rigid options. |
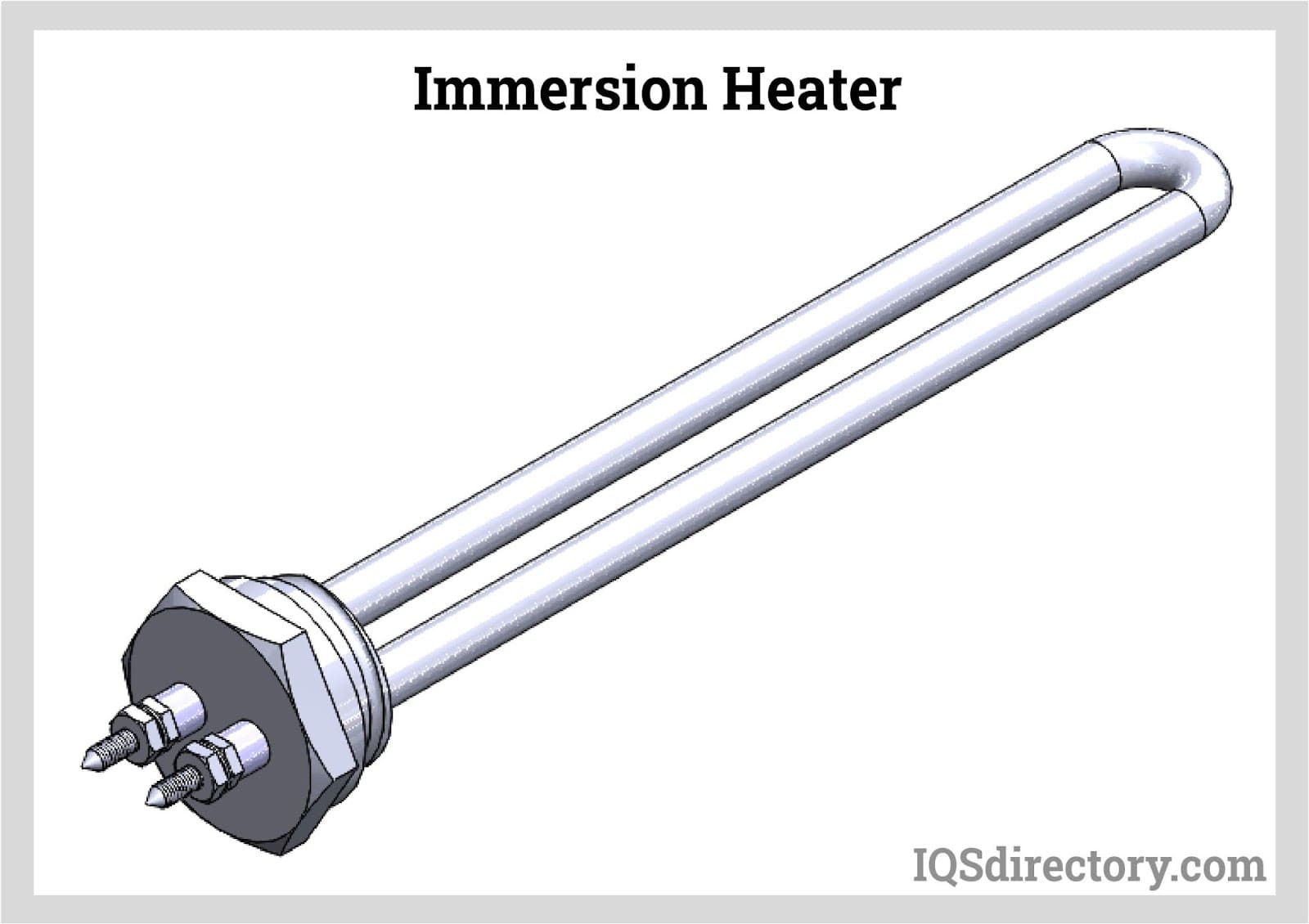
| Immersion Heaters | Directly heats liquids by submersion. | Food processing, chemical industry | Pros: Fast heating; Cons: Limited to liquid applications. |
| Infrared Heaters | Uses infrared radiation for direct heating. | Warehousing, outdoor applications | Pros: Efficient for large spaces; Cons: Less effective in poorly insulated areas. |
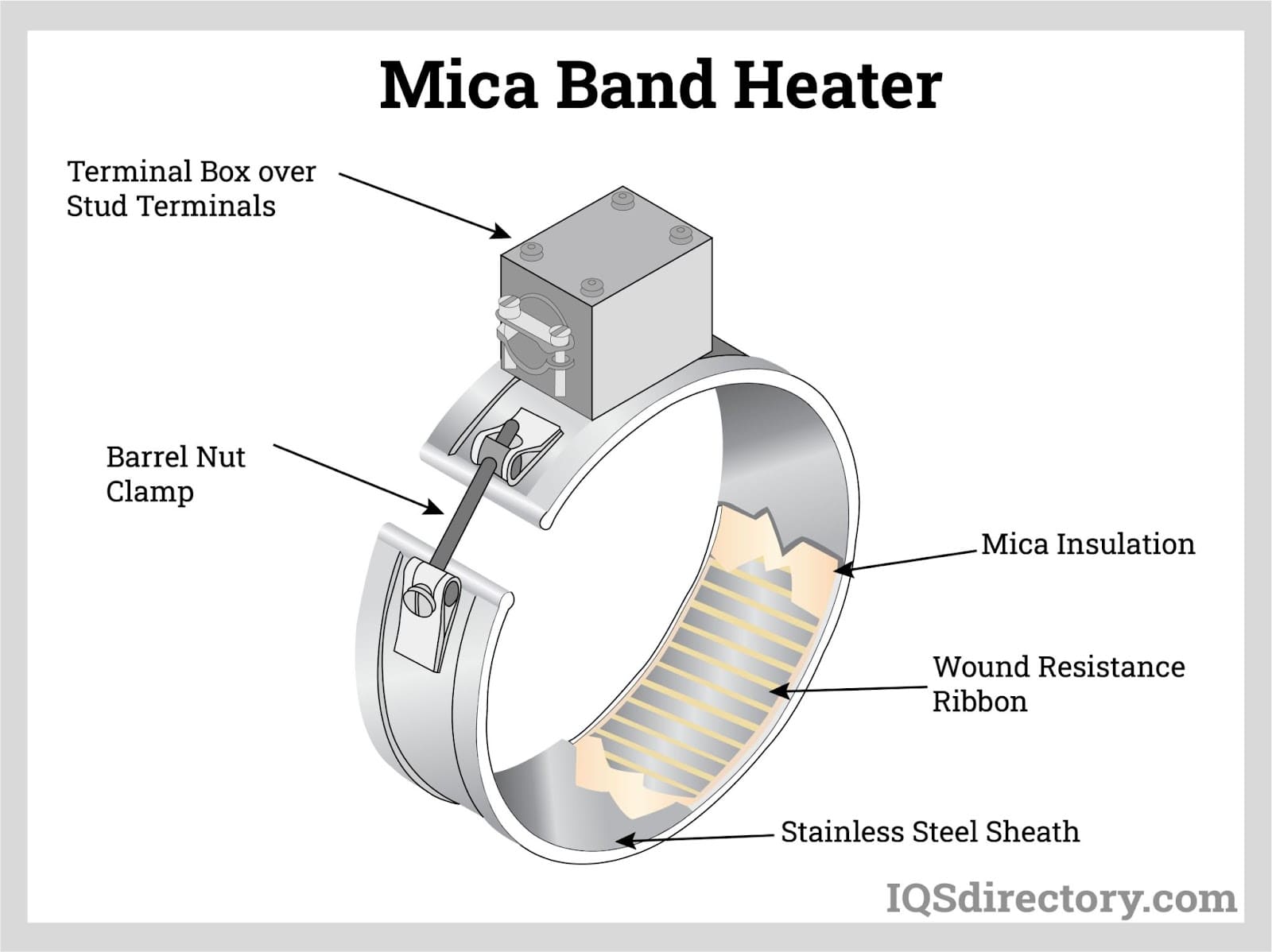
What Are Band Heaters and Their Applications in B2B Settings?
Band heaters are designed to provide external heat by clamping onto cylindrical objects, making them ideal for manufacturing settings where precision heating is essential. They utilize conductive heating to maintain optimal temperatures for processes like plastics processing or metalworking. B2B buyers should consider the versatility of band heaters, but they are primarily suited for flat, cylindrical surfaces, limiting their application scope.
How Do Cartridge Heaters Offer Precision Heating?
Cartridge heaters are cylindrical devices that deliver concentrated heat, making them suitable for applications requiring precise temperature control, such as injection molding or automotive manufacturing. Their ability to be inserted into pre-drilled holes allows for internal heating of materials and machinery. When purchasing, businesses should evaluate the required installation space and compatibility with existing systems, as these heaters necessitate specific setups.
What Makes Flexible Heaters Suitable for Diverse Applications?
Flexible heaters are constructed from materials that can bend and conform to various surfaces, making them ideal for applications in medical devices and aerospace industries. Their adaptability allows for efficient heating in complex geometries. However, buyers should note that while flexible heaters are versatile, they may not offer the same durability as rigid heating options, which is crucial for long-term investments.
Why Are Immersion Heaters Essential for Liquid Heating?
Immersion heaters are designed to heat liquids directly by being submerged, making them indispensable in food processing and chemical industries. They provide quick and efficient heating, ensuring that processes run smoothly. Businesses should consider the specific requirements of their liquid heating needs, as immersion heaters are limited to applications involving liquids and may not be suitable for solid materials.
How Do Infrared Heaters Work in Large Spaces?
Infrared heaters utilize electromagnetic waves to directly warm objects, making them effective for large spaces like warehouses or outdoor areas. They provide efficient heating by targeting specific areas rather than heating the air, which can be beneficial in poorly insulated environments. When selecting infrared heaters, B2B buyers should assess the insulation quality of their facilities, as these heaters may be less effective in such conditions.
Key Industrial Applications of how does a ceramic heater work
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how does a ceramic heater work | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Defrosting and heating car windshields | Improves vehicle safety and comfort for passengers | Need for high-temperature resistance and compact design |
| Food and Beverage | Heating food processing equipment | Increases efficiency in food preparation and safety | Compliance with food safety standards and energy efficiency |
| HVAC | Supplementary heating in large commercial spaces | Reduces overall heating costs and improves comfort levels | Compatibility with existing HVAC systems and energy-saving features |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Precise heating in component assembly | Enhances product quality and reduces defects | Temperature control accuracy and reliability under continuous use |
| Medical Devices | Heating elements in medical equipment | Ensures patient safety and effective treatment | Compliance with medical regulations and reliability under varied conditions |
How Are Ceramic Heaters Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, ceramic heaters play a crucial role in defrosting and heating car windshields. By efficiently warming the glass, they improve visibility and safety during adverse weather conditions. For B2B buyers in this field, sourcing high-quality ceramic heaters requires attention to specifications like temperature resistance and compact design, ensuring they can be integrated seamlessly into vehicles. This efficiency not only enhances passenger comfort but also contributes to energy savings.
What Role Do Ceramic Heaters Play in Food and Beverage Processing?
Ceramic heaters are widely used in food processing equipment to maintain optimal temperatures during preparation. Their ability to provide consistent heating enhances food safety and quality, making them indispensable in this industry. When sourcing ceramic heaters, businesses must consider compliance with food safety standards, as well as energy efficiency features that can lower operational costs. This dual focus helps ensure that the equipment not only meets regulatory requirements but also supports sustainable practices.
How Do Ceramic Heaters Benefit HVAC Systems?
In the HVAC sector, ceramic heaters serve as effective supplementary heating solutions for large commercial spaces. They help maintain comfortable temperatures while reducing overall heating costs, particularly in areas where traditional systems may fall short. Buyers need to evaluate compatibility with existing HVAC systems and prioritize energy-saving features that can enhance system performance. This focus on efficiency helps businesses optimize their heating solutions while minimizing energy expenditures.
Why Are Ceramic Heaters Important in Electronics Manufacturing?
Ceramic heaters are essential in the electronics manufacturing industry for providing precise heating during component assembly. Their reliability and temperature control accuracy help reduce defects and improve product quality, which is vital in a competitive market. B2B buyers should look for heaters that can maintain consistent performance under continuous use, ensuring that they meet production demands without compromising quality. This attention to detail can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced product reliability.
How Are Ceramic Heaters Utilized in Medical Devices?
In the medical device sector, ceramic heaters are used to maintain optimal temperatures in various types of equipment, ensuring patient safety and effective treatment outcomes. The sourcing of these heaters must align with stringent medical regulations, requiring a focus on reliability and performance under varied conditions. By investing in high-quality ceramic heating elements, medical device manufacturers can enhance their product offerings, ensuring they meet both safety standards and patient needs effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how does a ceramic heater work’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Energy Efficiency in Ceramic Heaters
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the misconception that all heating solutions are equally efficient. When looking to purchase ceramic heaters, they may not fully grasp how these heaters operate compared to traditional systems. This can lead to poor investment decisions, resulting in higher operational costs and energy waste. For instance, a company in Germany seeking to replace its outdated heating systems might overlook the efficiency benefits of ceramic heaters, instead opting for cheaper alternatives that ultimately cost more in energy bills.
Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should prioritize understanding the operational mechanics of ceramic heaters. They should seek out manufacturers or suppliers who provide detailed insights into how ceramic heating elements store and radiate heat more effectively than conventional metal heating elements. Buyers can request case studies or energy consumption comparisons from vendors to see real-world applications and savings. Additionally, leveraging energy-efficient features such as digital thermostats and timers can help regulate usage. By conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis and focusing on long-term energy savings, businesses can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their sustainability goals.
Scenario 2: Navigating Installation Challenges of Ceramic Heaters
The Problem: Many international B2B buyers face hurdles when integrating new heating solutions into existing infrastructure. For instance, a construction firm in Saudi Arabia might find that the installation of ceramic heaters is more complex than anticipated, leading to delays and increased labor costs. This scenario can be particularly frustrating when buyers are under tight deadlines for project completion or when they are trying to comply with local building regulations.
The Solution: To streamline the installation process, it is crucial for buyers to engage with suppliers who offer comprehensive installation support and clear guidelines. Buyers should request detailed installation manuals and inquire whether the supplier provides on-site assistance or training for their staff. Additionally, it can be beneficial to invest in heaters that are designed for easy installation, such as those that only require plugging into a power source. Networking with other businesses that have successfully integrated ceramic heaters can also yield valuable insights and best practices, allowing for a smoother transition and minimizing downtime.
Scenario 3: Evaluating Long-Term Maintenance Needs of Ceramic Heaters
The Problem: Maintenance concerns can deter B2B buyers from choosing ceramic heaters. A facility manager in South America may worry about the potential for higher maintenance costs and downtime associated with ceramic heaters, especially if they are accustomed to the maintenance routines of traditional heating systems. This apprehension could lead to hesitance in adopting more efficient solutions that offer long-term benefits.
Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
The Solution: Buyers should educate themselves on the low-maintenance nature of ceramic heaters. Unlike traditional systems that may require regular bleeding or extensive servicing, ceramic heaters typically need minimal upkeep—often just occasional dusting. To alleviate maintenance concerns, buyers can request warranty information and service packages from suppliers, ensuring they have support in place should any issues arise. Furthermore, establishing a maintenance schedule based on the specific operational conditions of the environment can help in prolonging the life of the heaters while maximizing their efficiency. By understanding the reduced maintenance needs and potential service agreements, buyers can confidently incorporate ceramic heaters into their heating strategy.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how does a ceramic heater work
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Ceramic Heaters?
When considering the functionality and efficiency of ceramic heaters, the materials used in their construction play a crucial role. The primary materials include ceramic composites, metal alloys, and insulating materials. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and disadvantages that can significantly impact performance, cost, and suitability for various applications.
How Do Ceramic Composites Enhance Heater Performance?
Ceramic composites are the most common materials used in the heating elements of ceramic heaters. They possess excellent thermal conductivity and heat retention properties, allowing for rapid heating and prolonged warmth. Additionally, ceramics can withstand high temperatures without degrading, making them ideal for continuous operation.
Pros: Their durability and resistance to thermal shock mean they can operate effectively in high-temperature environments. Ceramic composites are also non-corrosive, enhancing their longevity.
Cons: However, they can be brittle, which poses a risk during manufacturing and transportation. The cost of high-quality ceramic materials can also be relatively high, impacting overall product pricing.
Impact on Application: Ceramic composites are suitable for various heating applications, including industrial and residential heating. They can effectively heat air and surfaces, making them versatile in different settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards such as the European EcoDesign directive, which mandates energy efficiency and environmental considerations in heater design.
Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
What Role Do Metal Alloys Play in Ceramic Heater Functionality?
Metal alloys, particularly those with high resistance, are often used as connectors and in the manufacturing of the heating elements. These materials provide essential electrical conductivity, ensuring efficient energy transfer within the heater.
Pros: Metal alloys are generally more robust than ceramics, offering better mechanical strength and resistance to wear and tear. They are also easier to manufacture, allowing for more complex designs.
Cons: However, they may corrode over time, particularly in humid environments, which can lead to reduced efficiency and lifespan. The cost can vary widely depending on the alloy used.
Impact on Application: Metal alloys are critical for applications requiring high durability and reliability, such as in industrial settings where heaters are subjected to harsh conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of corrosion resistance standards relevant to their region, especially in humid climates like those found in parts of Africa and South America.
How Do Insulating Materials Affect Ceramic Heater Efficiency?
Insulating materials are crucial in ceramic heaters as they minimize heat loss, improving overall efficiency. Common insulating materials include fiberglass and ceramic fiber.
Pros: These materials provide excellent thermal insulation, allowing heaters to maintain their temperature with less energy consumption. They also contribute to safety by preventing overheating.
Cons: The main drawback is that insulating materials can add to the overall weight and bulk of the heater, potentially complicating installation and portability.
Impact on Application: Insulating materials are essential for applications where energy efficiency is paramount, such as in residential heating or energy-sensitive industrial environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for insulation materials that comply with local safety and environmental regulations, particularly in Europe, where stringent standards are in place.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Ceramic Heaters
| Material | Typical Use Case for how does a ceramic heater work | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Composites | Heating elements in residential and industrial heaters | Excellent thermal conductivity | Brittle; higher cost | High |
| Metal Alloys | Connectors and structural components in heaters | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Insulating Materials | Thermal insulation in various heater applications | Reduces heat loss, enhances safety | Can add weight and bulk | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on the specific needs of their operations and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how does a ceramic heater work
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Ceramic Heaters?
The production of ceramic heaters involves several critical stages, ensuring the final product is efficient, reliable, and meets international quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
How Is Material Prepared for Ceramic Heaters?
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of raw materials, typically high-quality ceramic compounds. These materials are then subjected to rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet the required specifications. Once approved, the materials are mixed, often with additives to enhance their thermal properties. This mixture is then granulated to facilitate the forming process.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Ceramic Components?
In the forming stage, the prepared ceramic material is shaped into desired forms using techniques such as pressing, extrusion, or injection molding. Pressing is common for creating heating elements, where the granulated mixture is compacted into molds under high pressure. This ensures uniform density and structural integrity. For more complex shapes, extrusion or injection molding may be employed, allowing for precise dimensions and features.
How Are Ceramic Heaters Assembled and Finished?
Once the ceramic components are formed, the assembly stage begins. This involves integrating the heating elements with electrical components, such as wires, thermostats, and safety features. The assembly process is critical, as any misalignment or poor connections can affect the heater’s efficiency and safety.
After assembly, the heaters undergo a finishing process, which may include surface treatment, painting, or insulation application. This step not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also improves durability and safety, particularly in high-temperature applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented During Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the production of ceramic heaters to ensure they meet both safety and performance standards. Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Additionally, compliance with industry-specific standards like CE marking in Europe or UL certification in the U.S. is crucial for market acceptance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt. Suppliers must provide documentation proving compliance with quality standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to ensure that the processes are within specified tolerances. This includes monitoring the forming, assembly, and finishing stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the complete ceramic heater undergoes rigorous testing for electrical safety, thermal efficiency, and durability. This may involve simulations of real-world conditions to assess performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, particularly in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control practices. This includes reviewing their adherence to ISO standards and other relevant certifications.
-
Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that document the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks. These reports should outline any non-conformities and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control systems and product quality.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods play a crucial role in ensuring that ceramic heaters function safely and effectively. Common testing methods include:
- Electrical Testing: This assesses the heater’s electrical safety and performance, ensuring it meets required voltage and current specifications.
- Thermal Efficiency Testing: Evaluates how efficiently the heater converts electrical energy into heat, often measuring the time taken to reach a set temperature.
- Durability Testing: Simulates prolonged use to ensure that the heater can withstand regular operational stresses without failure.
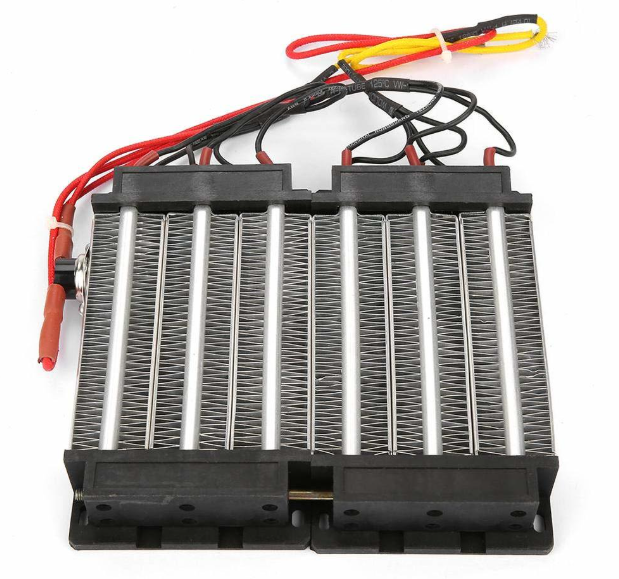
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality certification is essential. Certifications such as CE, UL, or ISO 9001 vary by region and may affect market access. Buyers should be aware of the specific regulations in their target markets, particularly in regions like the European Union, which has stringent safety and environmental standards.

Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
Additionally, consider the implications of local standards in countries like Saudi Arabia, where compliance with Saudi Standards, Metrology and Quality Organization (SASO) regulations is necessary. Understanding these nuances will help buyers make informed decisions and ensure the ceramic heaters they procure are compliant and safe for use in their respective markets.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Ceramic Heater Manufacturing
The manufacturing and quality assurance processes for ceramic heaters are complex but crucial for delivering reliable products to B2B buyers. By understanding these processes, including the manufacturing stages and quality control measures, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and regulatory obligations. This strategic approach not only enhances the reliability of heating solutions but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers committed to quality excellence.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how does a ceramic heater work’
Introduction
Understanding how ceramic heaters work is essential for B2B buyers looking to invest in efficient heating solutions. This guide provides a practical checklist to help you evaluate and procure ceramic heaters effectively, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific technical requirements for the ceramic heaters you need. Consider factors such as heating capacity, energy efficiency ratings, and the type of ceramic materials used in the heating elements.
– Heating Capacity: Ensure the heater can adequately cover the intended area.
– Energy Efficiency Ratings: Look for models compliant with international standards, especially in energy-conscious markets.
Step 2: Research Available Types of Ceramic Heaters
Familiarize yourself with the different types of ceramic heaters available, such as convection and radiant models. Each type has distinct advantages depending on the intended application.
– Convection Heaters: Ideal for larger spaces as they circulate warm air.
– Radiant Heaters: More suitable for localized heating, effectively warming objects and people directly.

Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Credentials
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request documentation such as company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in your sector or region.
– Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or compliance with local standards to ensure quality.
– Experience: Evaluate the supplier’s track record in delivering ceramic heating solutions to similar industries.
Step 4: Assess Energy Efficiency and Cost Implications
Investigate the energy efficiency of the ceramic heaters and their operational costs. Efficient models can significantly reduce energy consumption, translating to lower long-term expenses.
– Operational Cost Estimates: Obtain estimates based on the heater’s wattage and your local energy rates.
– Smart Features: Consider heaters equipped with timers and thermostats that optimize energy use.
Step 5: Check for Maintenance and Warranty Options
Understand the maintenance requirements and warranty provisions for the ceramic heaters you are considering. Reliable warranties and low-maintenance products can save costs and ensure long-term performance.
– Maintenance Needs: Assess how often the heaters require servicing or cleaning.
– Warranty Terms: Look for comprehensive warranties that cover parts and labor.
Step 6: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your purchase, request samples of the ceramic heaters for evaluation. Testing the products in real-world conditions can help confirm their performance meets your expectations.
– Performance Testing: Check how quickly and efficiently the heater warms the space.
– User Feedback: Gather feedback from employees or stakeholders who will be using the heaters.
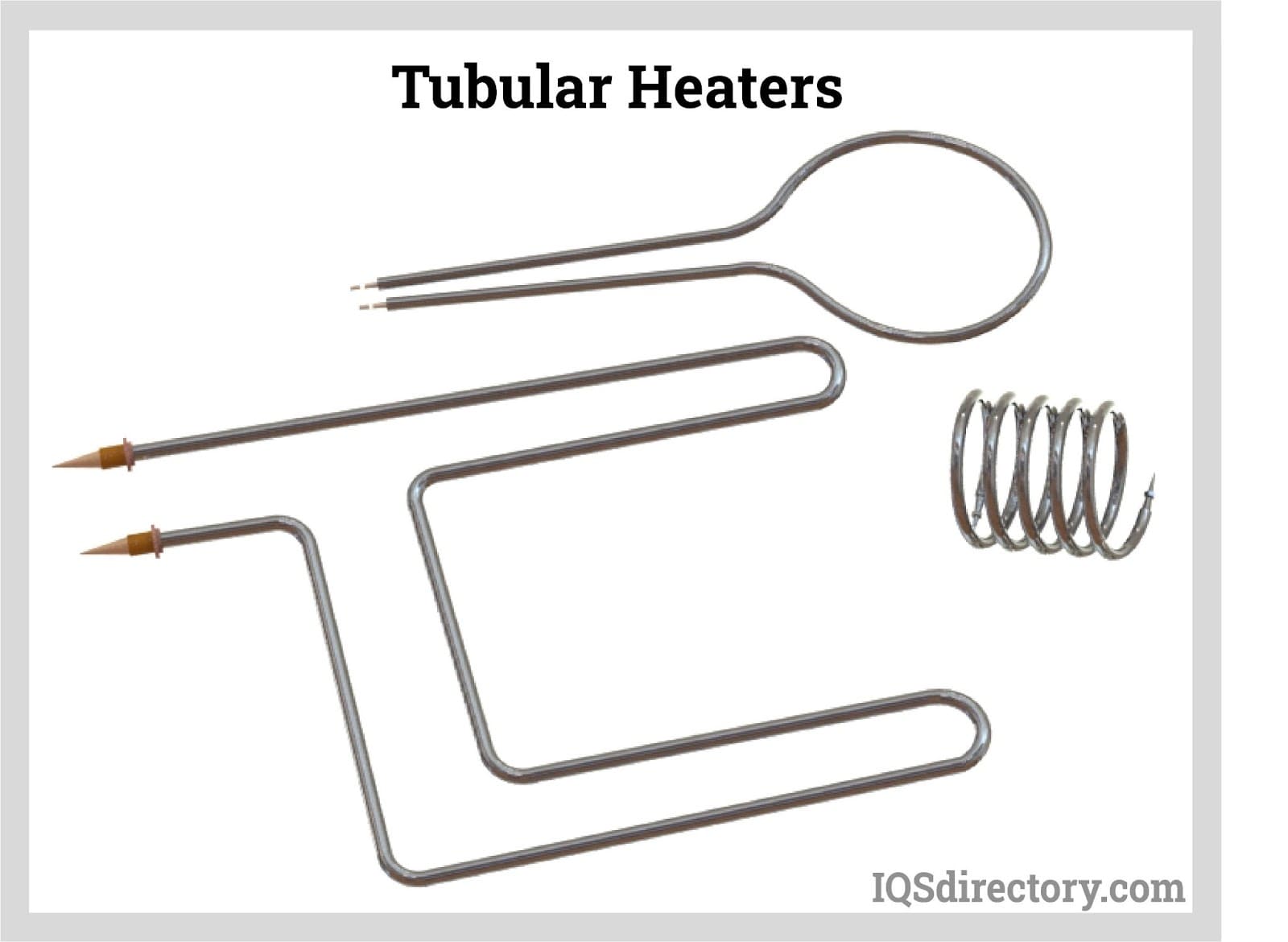
Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
Step 7: Finalize Procurement and Installation Plans
Once you’ve selected a supplier and model, finalize your procurement process. Make sure you have a clear installation plan that includes timelines, necessary tools, and any additional support required.
– Installation Guidelines: Ensure the supplier provides detailed instructions for setup.
– Support Services: Confirm availability of technical support for any installation challenges.
By following this checklist, you can ensure that your procurement process for ceramic heaters is thorough, efficient, and aligned with your operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how does a ceramic heater work Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Ceramic Heaters?
When sourcing ceramic heaters, a thorough understanding of the cost structure is vital for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
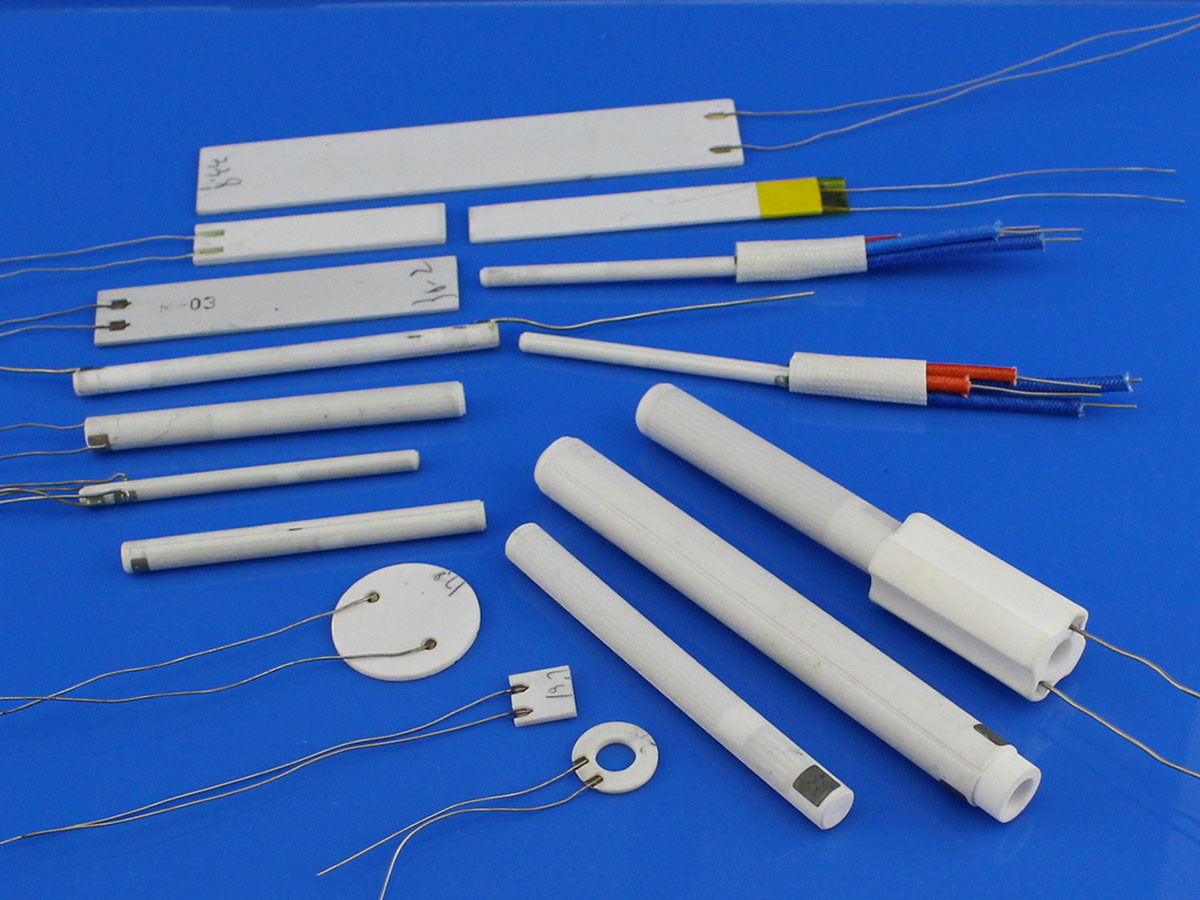
Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
-
Materials: The heating element’s ceramic composition is a significant cost driver. High-quality ceramics, which offer better thermal conductivity and durability, typically come at a higher price. Additionally, other components like electrical wiring and housing materials contribute to the overall material cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the region of manufacture. Skilled labor is required for assembly and quality assurance, particularly in regions with stringent safety and quality standards. Buyers should factor in the labor cost variations when sourcing from different geographical locations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Overhead can significantly impact the total cost, especially if the manufacturing facility is located in an area with high operational costs.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools and molds for ceramic heater production can be substantial. The cost of tooling is often amortized over the production volume, making it crucial to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) when negotiating prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that ceramic heaters meet industry standards requires rigorous testing and quality checks, adding to the overall cost. Certifications such as CE, UL, or ISO can enhance product credibility but may also increase sourcing costs.
-
Logistics: The logistics of transporting ceramic heaters, particularly for international buyers, encompass shipping, customs duties, and insurance. These costs can fluctuate based on the origin and destination, impacting the total cost of ownership.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. Understanding the competitive landscape and market demand can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider When Sourcing Ceramic Heaters?
Several factors can influence the pricing of ceramic heaters. Understanding these can aid buyers in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing often benefits from larger order volumes. Suppliers are more inclined to offer discounts for bulk purchases, which can significantly reduce the per-unit cost.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as size or additional features, may lead to higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications generally command premium prices. Buyers should assess whether the additional cost aligns with their performance requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products but often provide better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs and responsibilities. Understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for budgeting the total acquisition cost.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs and Pricing in Their Ceramic Heater Sourcing?
B2B buyers can implement strategies to optimize costs and ensure favorable pricing when sourcing ceramic heaters.
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage volume purchasing and long-term partnerships to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers may be more amenable to discounts for committed buyers.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase price, consider operational costs, maintenance, and potential energy savings offered by ceramic heaters. This holistic view can help justify higher upfront costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should account for currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions in their pricing evaluations.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of technological advancements and market shifts can provide insights into future pricing trends, enabling buyers to make timely purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides a comprehensive overview of costs and pricing factors for ceramic heaters, actual prices may vary based on specific supplier quotes, market conditions, and individual buyer requirements. Always request detailed quotations to ensure accuracy in cost assessments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how does a ceramic heater work With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of heating solutions, understanding the various technologies available is crucial for B2B buyers. This section compares how ceramic heaters operate against other viable heating alternatives, providing insights into their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases. By examining these aspects, businesses can make informed decisions tailored to their specific heating needs.
| Comparison Aspect | How Does A Ceramic Heater Work | Alternative 1: Immersion Heater | Alternative 2: Infrared Heater |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficiently heats spaces using ceramic elements that retain and radiate heat | Rapidly heats liquids but less effective for air heating | Directly heats objects and people, providing quick warmth |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; low operational costs due to energy efficiency | Generally low initial cost; operational costs vary by usage | Higher initial cost; operational efficiency can offset expenses |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to plug in or hard-wire; minimal installation requirements | Simple installation; requires water source and tank | Easy installation; requires space for installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional dusting required | Requires periodic cleaning and checks for scaling | Minimal maintenance; typically only requires cleaning |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for spaces needing consistent heat, such as offices and homes | Best for heating water in tanks, boilers, or for industrial processes | Excellent for open spaces or areas where targeted heating is needed |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Immersion Heaters?
Immersion heaters are designed to heat liquids efficiently, making them ideal for applications such as water heating in industrial processes or for use in domestic settings. Their primary advantage lies in their low initial cost and rapid heating capabilities. However, immersion heaters require a water source and can incur higher operational costs, particularly if used frequently. They are less suitable for heating air, making them a less versatile option compared to ceramic heaters.
How Do Infrared Heaters Compare?
Infrared heaters utilize electromagnetic radiation to warm objects and people directly, which can create a more immediate sense of warmth. Their installation is generally straightforward, requiring less infrastructure than traditional heating systems. However, they often come with a higher initial investment. Infrared heaters are particularly effective in open spaces and for targeted heating, but they may not provide the consistent ambient warmth that ceramic heaters offer in enclosed environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Heating Needs
When selecting a heating solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific requirements and the environments they operate in. Ceramic heaters stand out for their efficiency and versatility, making them suitable for various applications, from offices to residential spaces. Immersion heaters serve specific needs in liquid heating, while infrared heaters excel in targeted warmth in open environments. Ultimately, the decision should align with factors such as installation ease, maintenance capabilities, and operational costs, ensuring a solution that meets both budgetary and functional expectations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how does a ceramic heater work
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Ceramic Heaters?
When evaluating ceramic heaters for industrial applications, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Composition
Ceramic heaters typically utilize a ceramic heating element, known for its excellent thermal conductivity and durability. The specific type of ceramic material can affect the heater’s efficiency and longevity. For example, high-grade alumina ceramics can withstand higher temperatures and offer better insulation properties, making them ideal for applications in harsh environments.
2. Power Rating (Wattage)
The power rating, measured in watts (W), indicates the heater’s energy consumption and heating capacity. A higher wattage generally translates to faster heating times and the ability to warm larger spaces. Buyers must assess their heating needs against the power rating to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
3. Temperature Range
The operational temperature range indicates the minimum and maximum temperatures a ceramic heater can safely achieve. For B2B buyers, understanding this range is critical, as it determines the heater’s suitability for specific applications, such as in manufacturing processes requiring precise temperature control.
4. Heat Retention Capability
Ceramic materials excel in heat retention, allowing heaters to maintain warmth even after the power is turned off. This property is essential for energy efficiency, as it minimizes energy consumption while providing consistent heating. Evaluating heat retention capabilities can lead to cost savings in energy bills.
5. Dimensions and Portability
Ceramic heaters come in various sizes and shapes, affecting their installation options and portability. Compact models are ideal for limited spaces, while larger units may be required for extensive industrial applications. Understanding the dimensions and weight is vital for ensuring the heater fits the intended location and application.
6. Safety Features
Safety is paramount in industrial heating applications. Features such as overheat protection, tip-over switches, and thermal fuses can prevent accidents and ensure reliable operation. B2B buyers should prioritize products with robust safety features to minimize risks in the workplace.
What Are Common Trade Terminology Terms Related to Ceramic Heaters?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and enhance communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are several key terms:
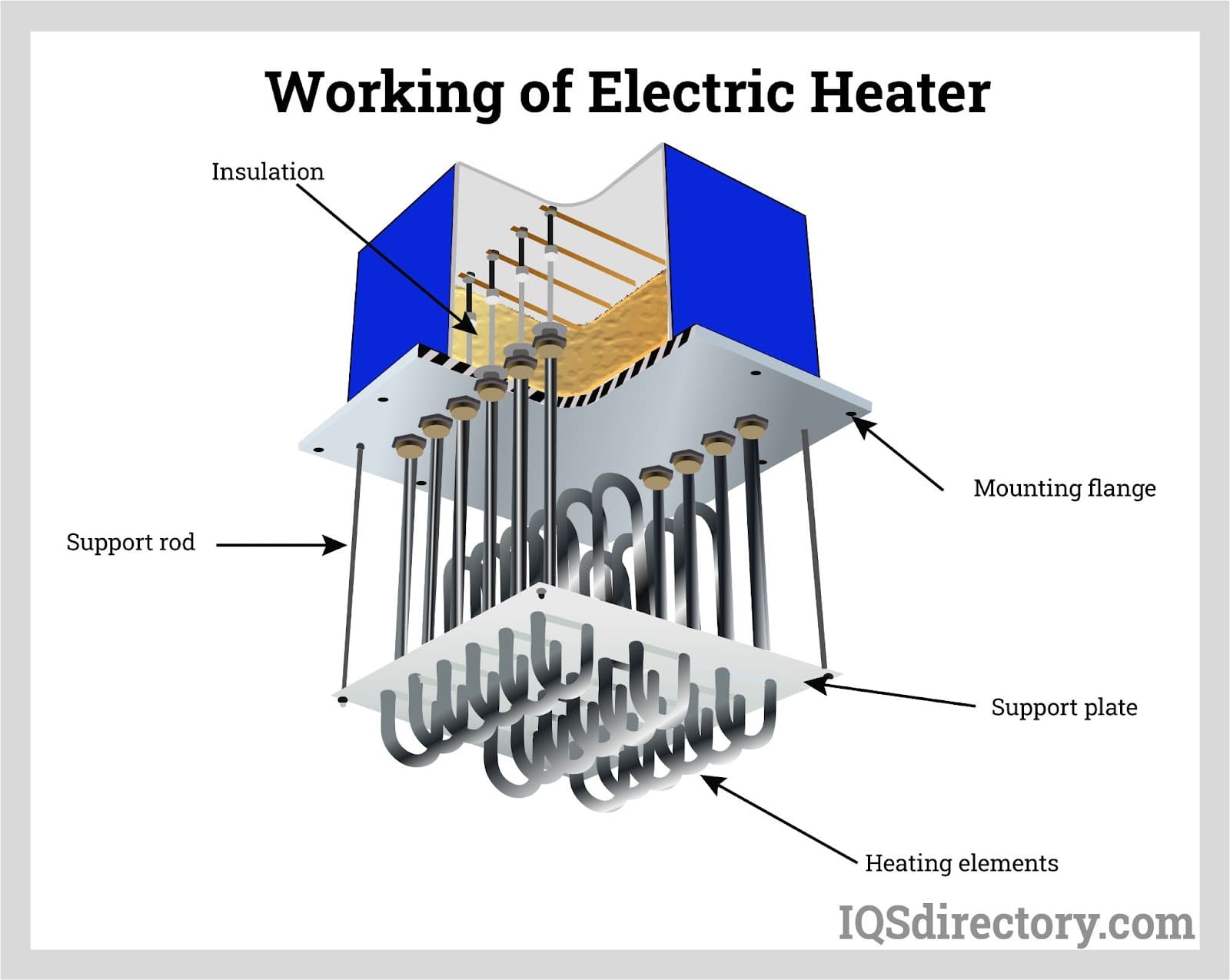
Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of ceramic heaters, partnering with an OEM can provide access to specialized designs and technologies tailored to specific needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it can impact inventory management and overall costs. Negotiating favorable MOQs can lead to better pricing and supply chain efficiency.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process used to invite suppliers to bid on specific products or services. When sourcing ceramic heaters, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and specifications across multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive procurement.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers involved in cross-border purchases of ceramic heaters, as it clarifies the logistics and costs involved.
5. CE Marking
CE marking indicates that a product meets European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For buyers in Europe, ensuring that ceramic heaters carry the CE mark is essential for compliance and marketability within the EU.
6. ERP Lot 20 Compliance
ERP Lot 20 is a European directive focused on energy efficiency for electric heaters. Compliance with this standard is critical for B2B buyers in Europe, as it ensures that products meet strict energy-saving regulations, contributing to sustainability goals.
In conclusion, understanding the technical properties and industry terminology associated with ceramic heaters can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring optimal performance, compliance, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how does a ceramic heater work Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the Ceramic Heater Sector?
The ceramic heater market is experiencing significant growth due to rising energy costs and the need for efficient heating solutions. As global demand for electric heating solutions increases, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers are increasingly looking for options that offer both efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Key trends shaping this market include the integration of advanced technologies such as smart thermostats and energy-saving features, which enhance user experience while reducing operational costs.
Moreover, the shift toward eco-friendly products is becoming a crucial factor for B2B buyers. With an increasing emphasis on sustainability, ceramic heaters are gaining popularity due to their efficient energy consumption and long lifespan. In particular, countries in Europe, such as Germany, are leading the charge in implementing stringent energy efficiency regulations, creating opportunities for manufacturers to innovate and meet these standards. Additionally, the emergence of digital solutions for monitoring energy usage is allowing businesses to manage their heating needs more effectively, further driving demand for ceramic heating solutions.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Ceramic Heater Market?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the ceramic heater industry, with environmental impact becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers. Ceramic heaters are often manufactured using materials that are more environmentally friendly than traditional heating systems. As companies strive to reduce their carbon footprint, they are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and offer green certifications for their products.
Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction among international buyers. Ensuring that materials are sourced from suppliers who prioritize fair labor practices and environmentally responsible methods is essential for companies looking to enhance their brand reputation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ENERGY STAR ratings for energy efficiency are becoming important criteria for evaluating potential suppliers. By choosing manufacturers committed to ethical sourcing and sustainability, businesses can not only comply with regulations but also appeal to a growing consumer base that values environmental responsibility.
What Is the Evolution of Ceramic Heating Technology?
The concept of ceramic heating dates back several decades, initially used in industrial applications due to its efficiency and durability. Over time, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of more compact and efficient ceramic heating solutions suitable for residential and commercial use.
In recent years, technological innovations such as the integration of smart technology have further revolutionized the sector. The introduction of features like programmable timers and energy monitoring systems allows users to optimize their heating needs, reducing waste and enhancing comfort. As the market continues to evolve, the focus remains on creating products that not only meet the heating demands of modern spaces but also adhere to the highest standards of energy efficiency and sustainability.
In conclusion, the ceramic heater market is poised for continued growth, driven by technological advancements and a collective move towards sustainability. For international B2B buyers, understanding these market dynamics and sourcing trends is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how does a ceramic heater work
-
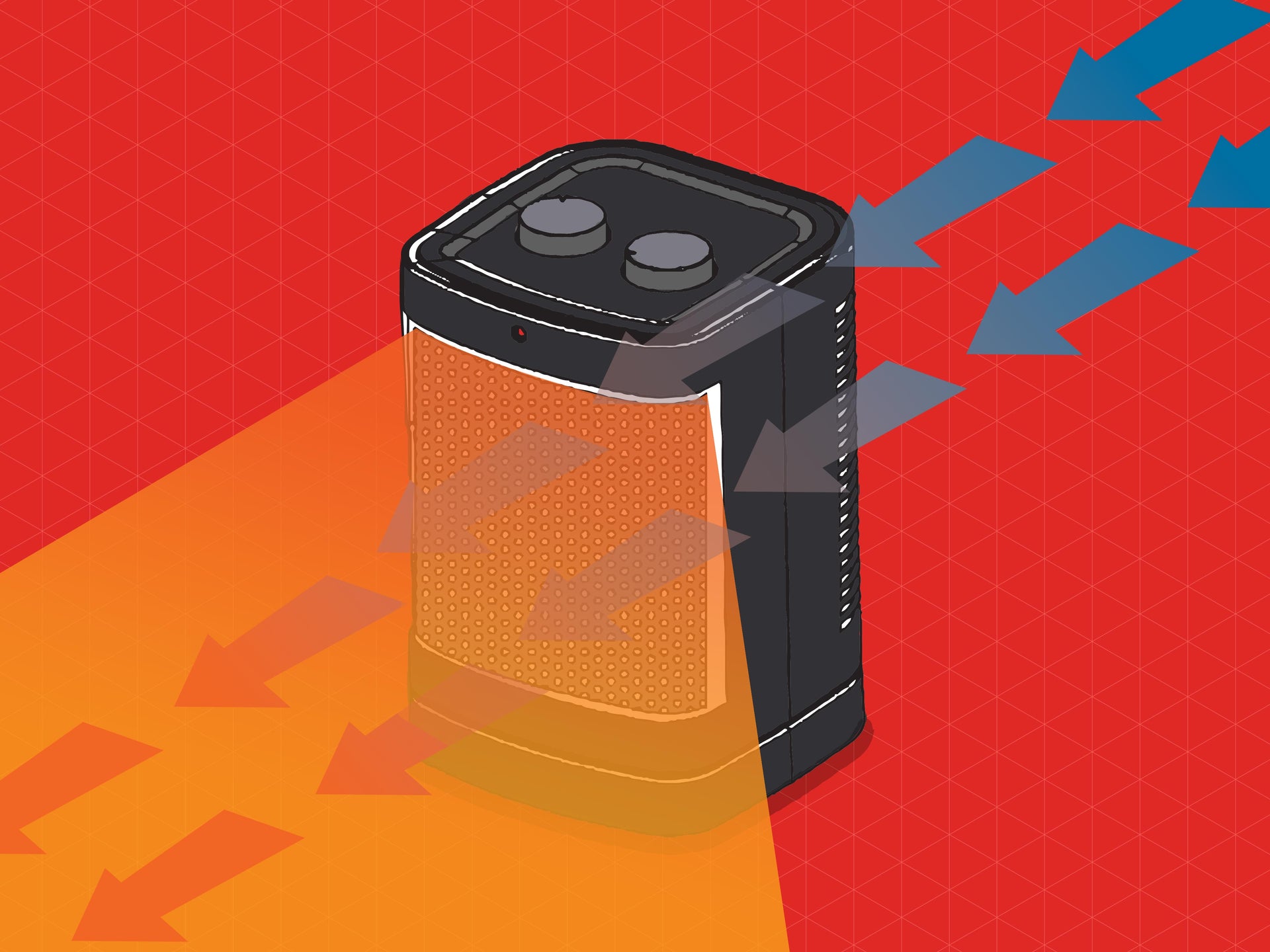
How does a ceramic heater generate heat?
Ceramic heaters generate heat by passing an electric current through a ceramic heating element. The ceramic material, known for its excellent thermal conductivity, resists the flow of electricity, which generates heat through a process called Joule heating. As the ceramic heats up, it stores thermal energy and radiates warmth into the surrounding space, providing efficient and consistent heating. -
What are the advantages of using ceramic heaters in industrial applications?
Ceramic heaters are energy-efficient, compact, and versatile, making them ideal for various industrial applications. They heat up quickly and maintain warmth longer, which reduces energy costs. Additionally, their design allows for both convection and radiant heating, making them suitable for diverse environments, from warehouses to workshops, where efficient heating is crucial. -
How can I customize ceramic heaters for my business needs?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for ceramic heaters, including size, heating capacity, and features such as digital thermostats and timers. When sourcing, communicate your specific requirements to suppliers, such as the intended application, environmental conditions, and energy efficiency standards. This ensures that the heaters meet your operational needs and compliance requirements. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for ceramic heaters?
The MOQ for ceramic heaters varies by supplier and the specific model. Generally, it ranges from a few units for standard models to larger quantities for custom designs. When negotiating with suppliers, consider factors such as pricing, lead times, and shipping costs to determine the best approach for your procurement strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing ceramic heaters internationally?
Payment terms for international orders can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include a deposit upfront with the balance due before shipping, or payment in full upon order confirmation. It’s essential to discuss terms clearly during negotiations and consider options like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. -
How can I ensure the quality of ceramic heaters before purchase?
To ensure quality, request samples before placing a large order and inquire about the manufacturer’s quality assurance (QA) processes. Look for certifications, such as ISO or CE marking, which indicate compliance with international safety and performance standards. Additionally, consider third-party inspections or audits to verify manufacturing practices. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing ceramic heaters?
When importing ceramic heaters, consider shipping methods, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation, such as bills of lading and certificates of origin, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Working with a reliable freight forwarder can also help navigate logistics challenges and ensure timely delivery. -
How do ceramic heaters compare to other heating options in terms of efficiency?
Ceramic heaters are often more efficient than traditional heating systems because they heat up quickly and retain warmth longer. They waste less energy by utilizing a combination of convection and radiant heating, which can lead to reduced energy bills. For businesses looking to minimize operational costs and improve heating performance, ceramic heaters present a compelling alternative to conventional heating methods.
Top 3 How Does A Ceramic Heater Work Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Ceramic Heaters
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Ceramic heaters are electric heaters featuring a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) ceramic element that utilizes resistive heating to produce heat. They are made from ceramic materials known for their electrical resistance and thermal transfer capabilities, making them efficient in conducting heat. Many ceramic heaters are composite materials combining metal and ceramic, enhancing insulation …
2. Reddit – High Rated Ceramic Space Heater
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: High rated ceramic space heater purchased on Amazon for around $30. Rated to heat up a 200 square foot area. User’s trailer is approximately 290 square feet. Features include half power mode to reduce strain on the power outlet and prevent overheating, as well as tilt turn off protection.
3. De’Longhi – Ceramic Heaters
Domain: delonghi.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, De’Longhi – Ceramic Heaters, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how does a ceramic heater work
In conclusion, ceramic heaters represent a significant advancement in efficient heating solutions, particularly appealing to businesses across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Their unique design allows for rapid heat generation and retention, maximizing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs. By leveraging strategic sourcing to obtain high-quality ceramic heaters, companies can enhance their energy management strategies while meeting sustainability goals.
Investing in ceramic heating technology not only provides immediate benefits in terms of cost savings but also supports compliance with stringent energy efficiency regulations, such as the European EcoDesign directive. This positions businesses favorably in competitive markets where environmental responsibility is increasingly prioritized by consumers.
As the demand for innovative and eco-friendly heating solutions continues to rise, now is the time for international B2B buyers to explore partnerships with reliable manufacturers and suppliers. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can ensure access to the latest ceramic heater technologies, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Embrace the future of heating—make ceramic heaters a cornerstone of your energy strategy today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to how does a ceramic heater work
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.