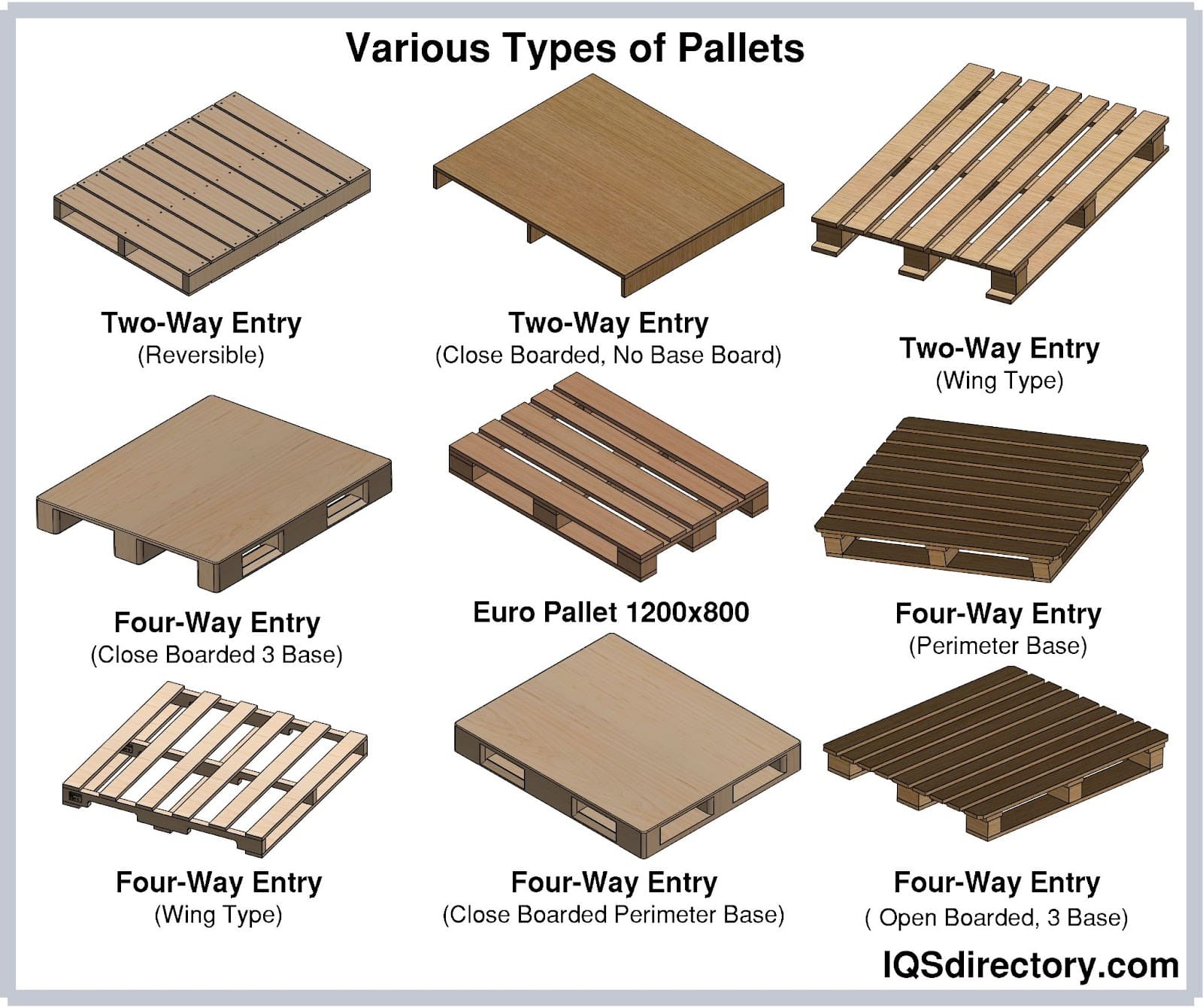
Top 3 Different Types Of Pallets Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for different types of pallets
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing the right types of pallets is essential for optimizing logistics operations and ensuring the safe transport of goods. With increasing competition and the need for efficiency, B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe face the challenge of selecting pallets that align with their specific operational requirements and budget constraints. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse world of pallets, covering various types—including wooden, plastic, metal, and cardboard—as well as their applications across different industries.
By exploring the nuances of pallet dimensions, material properties, and design configurations, this guide empowers international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. It also addresses critical factors such as supplier vetting processes, cost implications, and compliance with international standards, including ISPM 15 for wooden pallets. With insights tailored to the unique needs of buyers in countries like Nigeria and Germany, this resource aims to enhance warehouse efficiency, reduce operational risks, and ultimately improve the bottom line.
Navigating the complexities of pallet selection doesn’t have to be daunting. This guide serves as a vital tool for businesses looking to streamline their supply chain and maximize productivity, ensuring that every load is handled with care and precision.
Understanding different types of pallets Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wooden Pallet | Made from timber; most common type; ISPM 15 compliant | General warehousing, shipping, and storage | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to repair; Cons: Susceptible to damage and pests. |
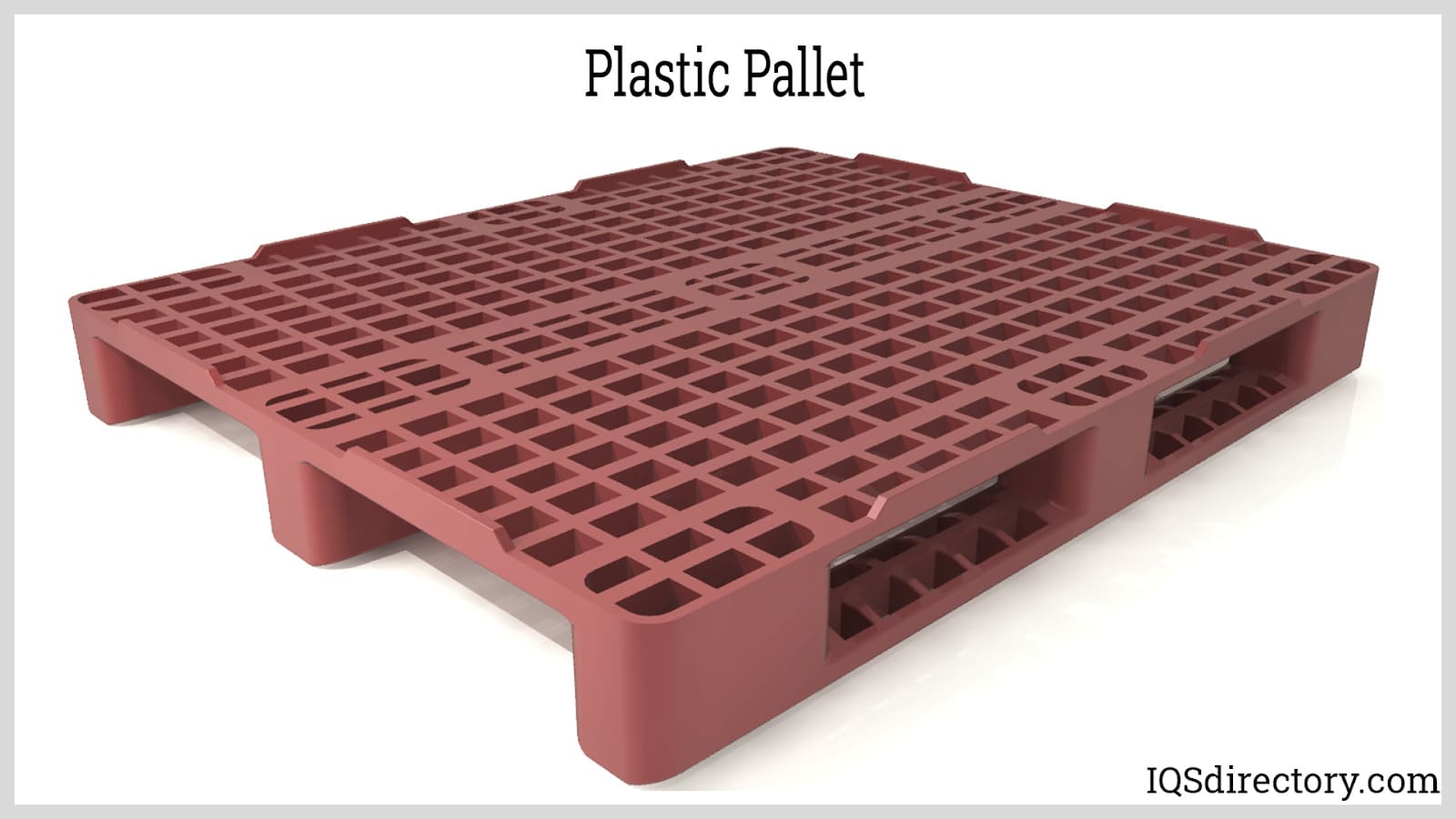
| Plastic Pallet | Lightweight, durable, easy to clean | Food and pharmaceutical industries | Pros: Hygienic, recyclable; Cons: Higher initial cost, may deform under heavy loads. |
| Metal Pallet | Heavy-duty, made from steel or aluminum | Heavy manufacturing, automotive sectors | Pros: Extremely durable, long lifespan; Cons: Heavier, increases transport costs. |
| Cardboard Pallet | Lightweight, disposable, made from corrugated cardboard | Retail and light-duty applications | Pros: Inexpensive, recyclable; Cons: Short lifespan, single-use only. |
| Europallet | Standardized size (1200×800 mm); regulated by EPAL | European logistics and transportation | Pros: Widely accepted, optimizes transport; Cons: Limited to specific dimensions. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Wooden Pallets for B2B Buyers?
Wooden pallets are the most commonly used type in various industries, accounting for 90-95% of the market share. They are typically made from durable timber and must comply with ISPM 15 regulations to ensure they are pest-free for international shipping. B2B buyers appreciate their cost-effectiveness and ease of repair, making them a practical choice for general warehousing and shipping. However, buyers should consider their susceptibility to damage and pests, which may necessitate regular inspections and maintenance.
How Do Plastic Pallets Compare to Other Types?
Plastic pallets are becoming increasingly popular, particularly in sectors like food and pharmaceuticals where hygiene is paramount. They are lightweight and easy to clean, making them suitable for environments that require strict sanitation protocols. While they offer durability and recyclability, B2B buyers should be aware that they can be more expensive than wooden pallets and may deform under excessive loads. This makes them ideal for specific applications but less versatile for heavy-duty needs.
Why Choose Metal Pallets for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Metal pallets, typically constructed from steel or aluminum, are designed for heavy-duty applications in industries such as manufacturing and automotive. Their robustness allows them to support very heavy loads, making them ideal for transporting machinery and equipment. While their durability and lifespan are significant advantages, B2B buyers must consider the increased weight that can lead to higher transport costs. These pallets are best suited for businesses that prioritize strength and longevity over initial investment.
When Should You Use Cardboard Pallets?
Cardboard pallets are primarily designed for light-duty applications and are popular in retail and temporary storage solutions. Their lightweight and disposable nature make them an economical choice for transporting goods that do not require heavy support. While they are inexpensive and recyclable, their short lifespan and single-use nature limit their applicability in long-term logistics strategies. B2B buyers should evaluate whether the cost savings align with their operational needs, particularly for products that require more robust support.
What Are the Benefits of Using Europallets in International Logistics?
Europallets, standardized at 1200×800 mm, are regulated by the European Pallet Association (EPAL), ensuring compatibility across European logistics networks. Their dimensions are designed to optimize space in transport vehicles, making them a preferred choice for international shipping within Europe. While they facilitate efficient handling and storage, B2B buyers should note that their use is limited to specific dimensions, which may not suit all logistics operations. Understanding regional standards is crucial for maximizing transport efficiency.

Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
Key Industrial Applications of different types of pallets
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of different types of pallets | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Use of hygienic plastic pallets for transporting perishable goods | Reduces contamination risk and enhances food safety | Compliance with food safety regulations; durability and ease of cleaning |
| Automotive | Heavy-duty metal pallets for transporting automotive parts | Supports heavy loads and minimizes damage risk | Weight capacity, material strength, and corrosion resistance |
| Pharmaceuticals | Cardboard pallets for lightweight, single-use applications in drug distribution | Cost-effective and compliant with hygiene standards | Sourcing from certified suppliers to ensure compliance with regulations |
| Retail and E-commerce | Wooden pallets for bulk storage and transport of retail products | Cost-effective and versatile for various product types | ISPM 15 compliance for international shipping; availability of repair services |
| Construction and Building | Reusable plastic pallets for transporting construction materials | Reduces waste and improves logistics efficiency | Weight capacity, resistance to weather conditions, and recycling options |
In the Food and Beverage industry, hygienic plastic pallets are essential for transporting perishable goods. These pallets minimize the risk of contamination, ensuring compliance with health regulations. International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and Europe, must prioritize sourcing from suppliers who adhere to food safety standards and offer durable, easy-to-clean pallets.
The Automotive sector relies on heavy-duty metal pallets for the secure transport of automotive parts. These pallets can withstand significant weight and resist damage during transit, ensuring that components arrive in optimal condition. Buyers should consider the weight capacity and corrosion resistance of metal pallets, especially in humid environments common in regions like South America and the Middle East.
In the Pharmaceuticals industry, lightweight cardboard pallets are often used for transporting drugs, offering a cost-effective solution for single-use applications. They meet hygiene standards, which is critical for maintaining drug integrity. Buyers should focus on sourcing from certified suppliers to ensure compliance with strict regulatory requirements, especially in European markets.
For the Retail and E-commerce sector, wooden pallets serve as a versatile solution for bulk storage and transportation of diverse retail products. Their cost-effectiveness and ability to be repaired extend their lifecycle, making them a practical choice. Buyers need to ensure that the pallets comply with ISPM 15 regulations for international shipping to avoid customs issues.
In the Construction and Building industry, reusable plastic pallets are becoming increasingly popular for transporting construction materials. They help reduce waste and improve logistics efficiency by being durable and resistant to weather conditions. Buyers should evaluate the weight capacity and recycling options of these pallets to align with sustainable practices in their operations.

Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘different types of pallets’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Warehouse Operations Due to Pallet Misalignment
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant inefficiencies in their warehouse operations caused by improper pallet alignment and stacking. When pallets are not correctly positioned, it can lead to wasted space, increased handling times, and even accidents. For instance, a buyer in a bustling distribution center may find that their wooden pallets, often used due to cost-effectiveness, warp over time or suffer damage, resulting in unstable stacks that can collapse. This not only disrupts workflow but also poses safety risks for warehouse staff.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should invest in a systematic pallet management strategy. First, conduct a thorough assessment of the types of pallets currently in use and their condition. Transitioning to more durable options like plastic or metal pallets can significantly reduce issues related to warping and damage. Additionally, implementing regular inspections and maintenance protocols ensures that any damaged pallets are identified and replaced promptly. Training staff on proper stacking techniques and using equipment like pallet jacks or forklifts can further enhance safety and efficiency. Adopting a standardized pallet layout—such as using Europallets for European operations—can optimize space and improve the overall flow of goods within the warehouse.
Scenario 2: Regulatory Compliance Challenges with Wooden Pallets
The Problem: Buyers who utilize wooden pallets frequently encounter challenges related to regulatory compliance, particularly when shipping internationally. Many countries require pallets to meet ISPM 15 regulations to prevent the spread of pests and diseases. A buyer in South America, for instance, may face delays and increased costs due to shipments being held at customs because the wooden pallets do not have the required treatment certifications. This not only disrupts the supply chain but can also lead to financial losses.
The Solution: To ensure compliance with international shipping regulations, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing pallets that are certified and clearly marked according to ISPM 15 standards. This involves working closely with suppliers who can provide documentation of treatment and compliance. Buyers should also consider diversifying their pallet options by including plastic or metal pallets, which do not require the same level of treatment and are often easier to manage across borders. Establishing a relationship with a reliable logistics partner who understands these regulations can also streamline the shipping process and reduce the likelihood of customs issues.
Scenario 3: High Costs Associated with Disposable Pallets
The Problem: Many businesses opt for disposable pallets, particularly cardboard, due to their low initial cost. However, B2B buyers often realize that this choice leads to higher long-term costs due to frequent replacements and the environmental impact of waste. For example, a buyer in Nigeria may find that while cardboard pallets are cheaper upfront, the need to constantly replace them for each shipment quickly accumulates expenses and complicates logistics.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should evaluate the long-term cost-benefit of their pallet choices. Transitioning to reusable pallets made from durable materials like plastic or metal can offer substantial savings over time. Although the initial investment is higher, the longevity and recyclability of these materials reduce replacement frequency and waste. Implementing a returnable pallet program can also enhance sustainability while cutting costs. Buyers should engage in discussions with suppliers about bulk purchasing options or rental agreements for reusable pallets, which can further decrease overhead costs while promoting environmentally friendly practices.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for different types of pallets
What Are the Key Properties of Different Pallet Materials?
When selecting pallets for international logistics, understanding the properties of various materials is crucial for optimizing performance and compliance. Here, we analyze four common pallet materials: wood, plastic, metal, and cardboard, focusing on their relevant properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for B2B buyers.
How Do Wooden Pallets Perform in Various Applications?
Wooden pallets are the most prevalent choice in the market, accounting for approximately 90% of pallet usage. Key properties include their ability to support heavy loads (up to 6,000 kg) and their compliance with ISPM 15 regulations, which ensure they are treated to prevent pest infestations.
Pros: They are cost-effective, easy to repair, and can be recycled, making them a sustainable option.
Cons: However, they can suffer from structural damage if mishandled, are more challenging to clean, and may harbor pests if not properly treated.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, wooden pallets are often favored due to their availability and affordability. However, compliance with ISPM 15 is essential to avoid customs issues.
What Advantages Do Plastic Pallets Offer?
Plastic pallets are gaining traction due to their lightweight nature and resistance to moisture and chemicals. They typically support loads similar to wooden pallets but are easier to clean and disinfect, making them suitable for industries with strict hygiene standards, such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Pros: They are durable, resistant to rot, and 100% recyclable.
Cons: Their higher initial cost and susceptibility to deformation under heavy loads can be drawbacks.

Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, the ability to comply with hygiene regulations is a significant advantage, while the higher upfront costs may necessitate a longer-term cost-benefit analysis.
How Do Metal Pallets Compare in Terms of Strength and Durability?
Metal pallets, often made from steel or aluminum, are known for their exceptional strength and durability. They can support very heavy loads and are easy to clean, making them ideal for heavy industries.
Pros: They have a long lifespan and can withstand harsh conditions without damage.
Cons: Their weight increases transport costs, and they are generally more expensive than other pallet types.
International buyers, especially in heavy manufacturing sectors in Germany and the Middle East, may find metal pallets advantageous despite their higher cost due to their longevity and reduced need for replacement.
What Role Do Cardboard Pallets Play in Logistics?
Cardboard pallets are primarily designed for light loads and are often used for single-use applications. They are lightweight and inexpensive, making them suitable for short-term shipping needs.
Pros: They are recyclable and easy to handle, contributing to lower shipping costs.
Cons: Their short lifespan and limited load capacity (usually less than 1,000 kg) restrict their use to specific applications.
For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, cardboard pallets can provide a cost-effective solution for non-critical shipments, but they should be aware of their limitations in durability.
Summary Table of Pallet Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for different types of pallets | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wooden | General warehousing, heavy loads | Cost-effective and repairable | Susceptible to damage and pests | Low |
| Plastic | Food and pharmaceutical industries | Hygienic and moisture-resistant | Higher initial cost | Medium |
| Metal | Heavy manufacturing and industrial applications | Extremely durable and strong | Heavy and costly to transport | High |
| Cardboard | Light, disposable shipping | Lightweight and recyclable | Short lifespan and low capacity | Low |
By understanding the properties and implications of each pallet material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for different types of pallets
What are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Different Types of Pallets?
Manufacturing pallets involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer expectations. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a pivotal role in determining the quality and durability of the pallet.
Material Preparation: What is Involved?
In the initial phase, raw materials are sourced based on the type of pallet being produced. For wooden pallets, this involves selecting high-quality timber that adheres to ISPM 15 regulations, ensuring it is treated to prevent pest infestation. For plastic pallets, manufacturers may opt for high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene, while metal pallets often use steel or aluminum.
The material preparation stage includes cutting the raw materials into the required dimensions and shapes. This is often done using automated machinery that enhances precision and reduces waste. Quality checks at this stage can involve visual inspections and moisture content testing for wooden pallets to ensure they meet specific criteria.
How is the Forming Process Carried Out?
The forming stage varies significantly based on the material used.
- Wooden Pallets: The prepared timber is shaped into boards and blocks, typically through processes like sawing and milling. The pieces are then assembled using nails or screws, with attention to the arrangement for maximum strength and stability.
- Plastic Pallets: These pallets are usually manufactured through injection molding or blow molding processes. The material is heated and molded into the desired shape, ensuring a uniform thickness and structural integrity.
- Metal Pallets: The manufacturing process for metal pallets involves cutting, welding, and sometimes bending the metal into the required shapes. Advanced techniques like laser cutting may be employed for precision.
Each method requires skilled labor and machinery to ensure that the pallets can withstand the intended loads and conditions.
Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
What Does the Assembly Stage Entail?
Once the components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This is where the individual pieces are put together to create the final pallet structure. For wooden pallets, this often involves stacking boards and attaching them to blocks using pneumatic nail guns or similar tools. For plastic and metal pallets, the assembly may include welding or using adhesives to bond parts together.
Quality checks during assembly include verifying the alignment of components, ensuring that the load-bearing capacity is maintained, and confirming that all parts are securely fastened.
How is the Finishing Process Conducted?
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the pallet’s durability and appearance. This may include sanding wooden pallets to remove splinters and applying protective coatings or treatments to increase resistance to moisture and pests. Plastic pallets might undergo surface treatments to improve their grip and durability, while metal pallets are often painted or coated to prevent rust.
Final inspections are crucial during this stage to ensure that the pallets meet customer specifications and industry standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is vital in the manufacturing of pallets, especially for international buyers who need to comply with various regulations. Key international standards include ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles, and industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in Europe.
Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet quality standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during manufacturing to monitor adherence to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspections of finished pallets to ensure they meet all criteria before shipping.
Common testing methods include load testing to verify the pallet’s weight-bearing capacity, dimensional checks to ensure compliance with standards, and visual inspections for defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the supplier’s facilities to ensure compliance with quality standards and practices.
- Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline the results of inspections and tests conducted throughout the manufacturing process.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing processes and quality of the pallets before shipment.
These measures can help mitigate risks associated with purchasing pallets, ensuring that the products meet the necessary quality standards.
What are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing pallets from different regions, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers must be aware of specific quality control and certification nuances. For example, compliance with ISPM 15 is critical for wooden pallets to prevent pest introduction when exporting goods internationally. Buyers should verify that suppliers provide appropriate documentation proving compliance.
Additionally, buyers should consider regional standards and regulations that may differ significantly. Understanding these nuances can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions and ensure that they are sourcing pallets that meet both local and international requirements.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for different types of pallets is crucial for B2B buyers. By being informed about these aspects, buyers can ensure that they select high-quality pallets that meet their operational needs while complying with relevant regulations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘different types of pallets’
When sourcing different types of pallets, it’s essential to follow a systematic approach that ensures you select the right products for your logistics and storage needs. This guide provides a checklist to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions when procuring pallets, considering factors such as material, size, and compliance with international standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical. Consider the dimensions, weight capacity, and material type of the pallets you require. Different industries have unique needs; for example, food and pharmaceuticals may require pallets that are easy to sanitize, while heavy manufacturing might prioritize durability and load capacity.

Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
Step 2: Identify Your Load Requirements
Assess the types of products you will be transporting or storing on the pallets. Understanding the load characteristics—such as weight, volume, and fragility—will help you choose the appropriate pallet type. For instance, heavier loads may necessitate metal pallets, while lighter loads might be efficiently handled with cardboard or plastic options.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, product samples, and references from businesses in similar sectors. It’s essential to ensure the supplier can meet your specific requirements regarding quality, delivery timelines, and after-sales support.
- Check for certifications: Ensure the supplier adheres to relevant international standards such as ISPM 15 for wooden pallets, which ensures they are treated to prevent pest infestations.
- Review production capabilities: Confirm that the supplier can scale production based on your demand, especially for bulk orders.
Step 4: Examine Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and compare pricing structures. Pay attention to additional costs such as shipping, handling, and potential discounts for bulk purchases. Understanding the total cost of ownership will help you make a more informed decision.
- Negotiate terms: Ensure that payment terms are favorable and explore options for long-term partnerships that could yield better pricing over time.
Step 5: Ensure Compliance with Regulations
Check that the pallets meet local and international regulations relevant to your industry. This is particularly important if your products are to be shipped across borders, where specific standards must be adhered to. Non-compliance can lead to costly delays or rejections at customs.
Step 6: Consider Sustainability Practices
With increasing emphasis on sustainability, consider sourcing pallets made from eco-friendly materials or those that are recyclable. Assess the supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices, as this not only enhances your brand image but also aligns with global trends toward environmental responsibility.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Storage
Finally, think about how the pallets will fit into your overall logistics and storage strategy. Consider the space available in your warehouse and how the pallets will be moved and stored. The right pallet configuration can significantly improve warehouse efficiency and reduce handling times.
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the sourcing process for pallets, ensuring that your procurement aligns with your operational needs and strategic goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for different types of pallets Sourcing
When sourcing pallets, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the various cost components, price influencers, and provides actionable tips for negotiating the best deals.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Pallet Sourcing?
1. Material Costs:
The choice of material significantly influences the cost of pallets. Wooden pallets, which hold a dominant market share, are typically the most cost-effective option, priced around $10 to $25 per unit depending on the type and treatment. Plastic pallets, while offering durability and ease of cleaning, can range from $20 to $100 each, depending on the quality and specifications. Metal pallets, known for their strength, can be the most expensive, often exceeding $100 per unit. Cardboard pallets, while inexpensive (around $5 to $10), are designed for single-use applications.
2. Labor Costs:
Labor costs associated with manufacturing pallets vary by region and the complexity of the production process. Automated facilities may have lower labor costs per unit but require significant upfront investment. In contrast, hand-crafted wooden pallets may have higher labor costs due to the skilled labor involved.
Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
3. Manufacturing Overhead:
This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Pallet manufacturers often pass these costs onto buyers, making it a vital component in the pricing structure.
4. Tooling Costs:
For customized pallets, tooling costs can be substantial. Molds or specific machinery required for unique pallet designs add to the initial investment but can be amortized over large production runs.
5. Quality Control (QC):
Ensuring that pallets meet safety and quality standards involves additional QC costs. Compliance with regulations such as ISPM 15 for wooden pallets necessitates inspection and treatment processes, influencing overall pricing.
6. Logistics Costs:
Transportation costs can vary significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and volume. International shipping incurs additional costs related to customs clearance and tariffs, which can impact pricing for buyers in regions like Africa and South America.
7. Profit Margin:
Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and supplier reputation.
What Influences Pallet Pricing?
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ):
Buyers ordering larger quantities often benefit from economies of scale, leading to lower unit costs. Negotiating MOQs can also yield better pricing.
Specifications and Customization:
Custom pallets tailored to specific dimensions or load requirements can significantly increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the associated price increase.
Material Quality and Certifications:
Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., FDA compliance for food-related industries) can elevate costs but may be necessary for specific applications.
Supplier Factors:
The reliability and reputation of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
Incoterms:
Understanding the implications of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) affect total landed costs and should be considered in negotiations.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively for Pallet Pricing?
1. Leverage Volume Discounts:
Negotiate for better pricing by committing to larger orders or exploring long-term contracts that assure suppliers of steady business.
2. Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
Consider not just the initial purchase price but also factors like durability, repair costs, and disposal when evaluating pallet options. A more expensive pallet may offer greater long-term savings.
Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
3. Understand Market Trends:
Stay informed about market trends, including fluctuations in raw material prices and supply chain disruptions, which can impact pallet costs.
4. Build Relationships with Suppliers:
Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Regular communication can help buyers anticipate price changes and secure favorable conditions.
5. Compare Multiple Quotes:
Don’t settle for the first quote. Comparing offers from multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and ensure competitive pricing.
Conclusion
The sourcing of pallets involves a complex interplay of costs and pricing factors that international B2B buyers must navigate carefully. By understanding the cost components and price influencers, and employing effective negotiation strategies, buyers can optimize their procurement processes and achieve significant cost efficiencies. Always remember that prices can fluctuate, and it’s advisable to seek updated quotes and terms before finalizing purchases.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing different types of pallets With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Different Types of Pallets
In the logistics and warehousing sector, selecting the right solution for transporting and storing goods is paramount. While different types of pallets—wooden, plastic, metal, and cardboard—are widely used, various alternative solutions may also serve similar purposes. This analysis aims to compare pallets against two viable alternatives: bulk storage systems and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). Each solution has unique advantages and limitations, impacting performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Different Types Of Pallets | Bulk Storage Systems | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load capacity; versatile for various goods | Excellent for high-density storage; maximizes space | High efficiency in transporting goods; reduces manual labor |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate; varies by material | High initial investment; lower long-term operational costs | High upfront costs; potential ROI through labor savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to implement; requires minimal training | Complex setup; requires planning and design | Requires significant training and integration with existing systems |
| Maintenance | Moderate; wooden pallets require regular checks | Low; mainly involves periodic checks | High; requires regular software updates and maintenance |
| Best Use Case | General warehousing, retail, and distribution | High-volume storage in large warehouses | Automated warehouses needing efficient goods movement |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Bulk Storage Systems
Bulk storage systems are designed to optimize space utilization in warehouses. These systems can significantly increase storage density, allowing businesses to maximize their available square footage. They are particularly effective for high-volume inventory and can accommodate various product types. However, the initial setup costs can be substantial, and the complexity of installation may require specialized expertise. Maintenance is relatively low once established, but the upfront investment and planning may not suit smaller operations or those with diverse product ranges.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs are a modern solution for automating the movement of goods within warehouses. They enhance efficiency by reducing manual handling and speeding up transportation times. Their ability to navigate complex environments and transport various products makes them suitable for large-scale operations. However, AGVs come with high upfront costs and require substantial integration efforts with existing warehouse systems. Maintenance can also be demanding, involving regular software updates and technical support, which may not be ideal for smaller businesses or those with limited budgets.

Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between different types of pallets and alternative solutions like bulk storage systems or AGVs, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals. For businesses with diverse product lines and moderate volume, traditional pallets may offer the best balance of cost and flexibility. Conversely, organizations focused on high-volume storage or automation may find bulk systems or AGVs to be more beneficial despite their higher initial costs. Ultimately, the choice should align with the company’s logistical requirements, workforce capabilities, and future growth plans, ensuring optimal efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for different types of pallets
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Different Types of Pallets?
Understanding the technical properties of pallets is vital for B2B buyers, as these factors significantly affect logistics efficiency, cost management, and product safety. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The grade of the material used in pallets—whether wood, plastic, metal, or cardboard—affects durability, load capacity, and overall cost. For example, wooden pallets typically offer a high load-bearing capacity at a lower cost, making them popular in many industries. In contrast, metal pallets, while more expensive, provide enhanced strength and longevity, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
2. Load Capacity
This specification defines the maximum weight a pallet can safely carry. Load capacities vary by pallet type; for instance, standard wooden pallets can generally support between 1,500 kg and 6,000 kg, depending on their construction. Understanding load capacity is crucial for ensuring safety in transport and storage, as exceeding these limits can lead to accidents or product damage.

Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
3. Dimensions
Standard pallet dimensions are essential for compatibility with storage systems and transportation equipment. Common sizes include the Europallet (1200×800 mm) and the American pallet (1200×1000 mm). Adhering to these dimensions ensures that pallets fit efficiently in shipping containers and warehouse racking systems, optimizing space utilization and logistics operations.
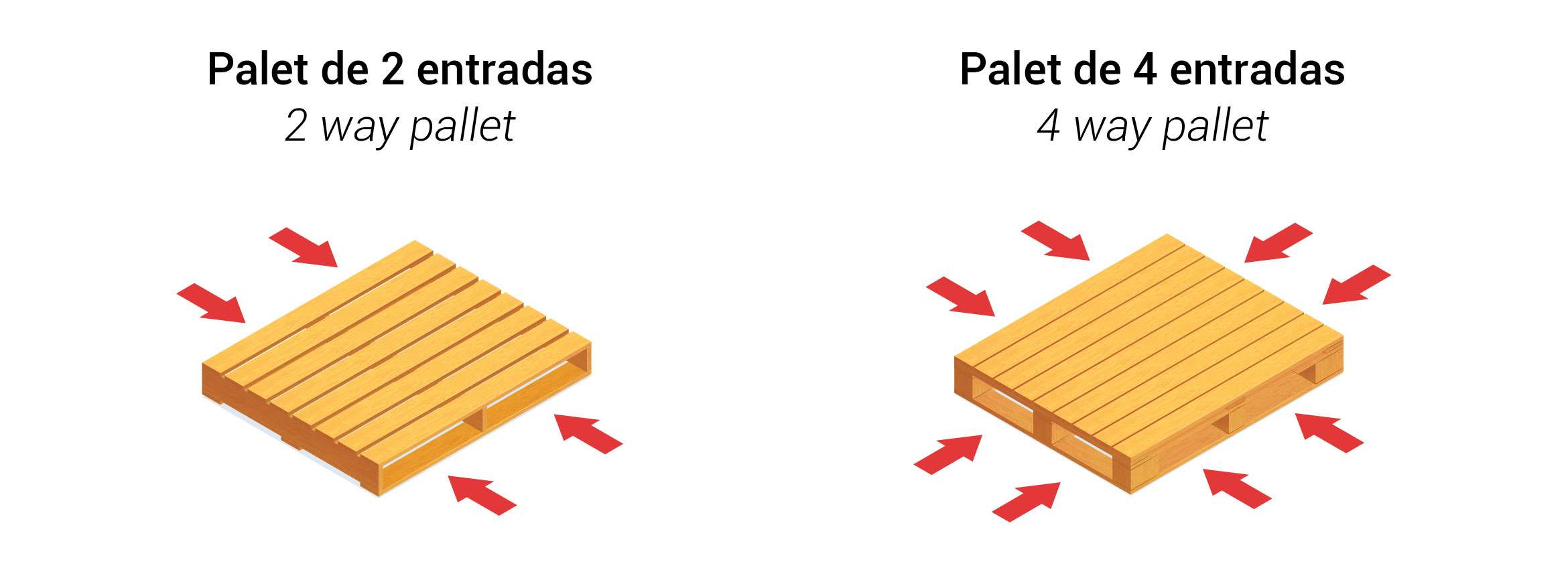
4. Entry Points
The number of entry points refers to how many sides of a pallet can be accessed by forklifts or pallet jacks. Pallets with four entry points offer greater flexibility and ease of handling compared to those with two entry points. This property is vital in high-traffic warehouses where quick and efficient movement of goods is necessary.
5. Heat Treatment Compliance (ISPM 15)
For wooden pallets, compliance with ISPM 15 regulations is critical in international trade. This standard requires that wooden packaging material undergo specific treatments to eliminate pests. Non-compliance can lead to significant delays, fines, or product rejection at borders, making this an essential consideration for global shipping.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Pallet Transactions?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communication and decision-making in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms to understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
In the context of pallets, an OEM refers to a company that manufactures pallets that are then sold under another company’s brand. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking custom pallet solutions tailored to their specific logistics needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of pallets a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for budgeting and inventory management, as it can significantly impact order costs and supply chain efficiency. Buyers must align their needs with suppliers’ MOQs to avoid overstocking or understocking.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting price quotations from suppliers. It typically includes specifications such as material type, dimensions, and load capacity. Submitting an RFQ helps buyers compare options, ensuring they receive competitive pricing and suitable products.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping costs and risk during transit.
5. Recyclability
This term refers to the ease with which a pallet can be recycled after its useful life. With increasing environmental concerns, knowing the recyclability of a pallet type can influence purchasing decisions, aligning with corporate sustainability goals.
By understanding these technical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding their pallet needs, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs in their supply chains.
Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the different types of pallets Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Different Types of Pallets?
The global pallet market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for efficient logistics solutions across various sectors, including retail, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. As international trade expands, the need for standardized pallets, such as the Europallet and American pallet, becomes crucial. These pallets not only facilitate streamlined operations but also optimize space utilization in warehouses and transport vehicles. In regions like Africa and South America, where supply chain infrastructure is rapidly developing, the shift towards reusable and sustainable pallets is gaining traction.
Emerging technologies, such as pallet tracking systems and IoT-enabled pallets, are reshaping sourcing strategies. These innovations enhance visibility and control over inventory, allowing businesses to monitor pallet conditions and streamline logistics operations. International B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer advanced tracking capabilities, as these technologies can significantly reduce costs associated with lost or damaged goods.
Moreover, the rise of e-commerce is pushing companies to adopt more versatile pallet types, such as stackable and reversible pallets, which can adapt to diverse storage and transportation needs. As markets evolve, businesses must remain agile, continuously assessing the changing landscape and aligning their sourcing strategies with current trends.

Illustrative image related to different types of pallets
How is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions for Different Types of Pallets?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the pallet industry. As environmental concerns grow, businesses are compelled to prioritize ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. The production of wooden pallets, for instance, is governed by ISPM 15 regulations, ensuring that wood is treated to prevent pest infestations. However, the market is also witnessing a shift towards eco-friendly alternatives, such as plastic and metal pallets, which offer durability and recyclability.
International B2B buyers are increasingly demanding pallets made from sustainable materials, prompting suppliers to invest in ‘green’ certifications and materials. Certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or recycled content certifications enhance product credibility and appeal to environmentally conscious customers. Furthermore, companies that adopt sustainable practices not only reduce their carbon footprint but also enhance their brand reputation, making them more attractive to potential partners and clients.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now scrutinizing their suppliers’ environmental policies and practices, ensuring that their sourcing decisions align with broader corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals. In this context, suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainability through transparent practices and eco-friendly materials will likely gain a competitive edge in the global market.
What is the Historical Context of Pallet Development and Its Relevance Today?
The history of pallets dates back to the early 20th century, with their modern use gaining momentum during World War II when the military recognized the need for efficient loading and unloading of goods. The introduction of standardized pallet sizes, such as the Europallet and American pallet, revolutionized logistics by facilitating seamless handling and transport across different modes of freight.
Over the decades, the pallet industry has evolved significantly, with advancements in materials and technology shaping its trajectory. Today, pallets are not only seen as mere platforms for transporting goods but also as integral components of supply chain management. The evolution from traditional wooden pallets to innovative materials like plastics and metals reflects the industry’s response to changing market demands, including sustainability and efficiency.
Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as it highlights the adaptability of the pallet market. As businesses continue to seek solutions that enhance operational efficiency and align with sustainable practices, recognizing the evolution of pallets can inform sourcing decisions and strategic planning. This awareness enables buyers to select suppliers that are not only equipped to meet current demands but are also poised for future developments in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of different types of pallets
-
How do I choose the right type of pallet for my products?
Choosing the right type of pallet involves assessing your product’s dimensions, weight, and handling requirements. For heavy loads, consider metal pallets for their durability. If cleanliness is paramount, plastic pallets are easier to sanitize. Additionally, consider regional standards; for example, Europallets are preferred in Europe due to their standard dimensions. Finally, evaluate the logistics involved, including transportation methods and storage conditions, to ensure optimal pallet performance. -
What are the key differences between wooden and plastic pallets?
Wooden pallets are widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of repair, making them suitable for diverse applications. However, they may require compliance with ISPM 15 regulations for international shipping. Plastic pallets, on the other hand, are more hygienic, lightweight, and resistant to moisture and pests, but they typically come at a higher price point. The choice between the two should be influenced by your budget, product type, and specific industry requirements. -
What should I consider when sourcing pallets from international suppliers?
When sourcing pallets internationally, evaluate supplier credentials, including compliance with local and international standards, such as ISPM 15 for wooden pallets. Ensure they provide clear documentation on quality assurance and traceability. Additionally, consider the supplier’s production capacity, lead times, and ability to meet your customization needs. Establishing communication about payment terms and delivery logistics is also crucial to avoid potential delays. -
What are the advantages of using metal pallets over other materials?
Metal pallets offer unparalleled strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy industrial applications. They are resistant to damage and can withstand extreme conditions, which reduces replacement costs over time. Additionally, metal pallets are easy to clean and disinfect, making them suitable for environments requiring high hygiene standards. However, consider their weight and higher shipping costs when evaluating overall logistics. -
How can I ensure the quality of pallets I purchase?
To ensure quality, request samples from potential suppliers and perform physical inspections to assess their durability and construction. Check for certifications that indicate compliance with industry standards. Additionally, consider conducting audits of the supplier’s manufacturing processes and facilities. Establishing a clear return policy and warranty for the pallets can further safeguard your investment against defects. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for pallets?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pallets vary by supplier and type. Generally, wooden pallets have lower MOQs due to their widespread availability, often starting at around 50-100 units. Plastic and metal pallets typically have higher MOQs, sometimes ranging from 200 to 500 units, due to their higher manufacturing costs. Always discuss MOQs upfront with suppliers to align your procurement strategy with their production capabilities. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for my pallet orders?
When managing logistics for pallet orders, consider factors like shipping methods, delivery times, and costs. Work closely with your supplier to determine the best shipping options, whether by sea, air, or land, based on your delivery timeline and budget. Additionally, factor in customs regulations and potential tariffs, especially for international shipments. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can streamline this process and mitigate risks of delays. -
Can pallets be customized to fit specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for pallets, including size adjustments, material choices, and design modifications. Custom pallets can enhance efficiency in your supply chain by ensuring optimal fit for your products and storage systems. When pursuing customization, communicate your specifications clearly to the supplier and inquire about lead times and associated costs to ensure that the final product meets your operational needs effectively.
Top 3 Different Types Of Pallets Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ipla Palletizers – European Pallet Overview
Domain: iplapalletizers.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Different types of pallets and their characteristics include:
1. **European Pallet (Europallet)**:
– Dimensions: 1200 x 800 mm
– Weight: ~21 kg
– Load Capacity: 1400 kg (in motion), 4000 kg (static)
– Usage: Primarily in Europe, compatible with most material handling systems.
2. **American Pallet**:
– Dimensions: 1200 x 1000 mm
– Usage: Most common in North American log…
2. Indoff – Pallet Types and Options
Domain: indoff.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Pallet Types: 1. Wood Pallets – Most common, 58% of pallets in circulation (43% hardwood, 15% softwood). 2. Presswood Pallets – Made from wood fibers, cheaper than plastic, can suffer from water damage. 3. Plywood Pallets – Lightweight, suitable for light to medium loads. Pallet Entry Options: 1. Two-way entry pallets – Stronger, more economical, but less flexible. 2. Four-way entry pallets – Allo…
3. CertifyMe – Pallet Types Explained
Domain: certifyme.net
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Types of pallets discussed include: 1. Wood Pallets: Commonly used for heavier products, strong and durable, cost-effective, quick to build, recyclable, but heavy and hard to clean. 2. Long Pallets: Sub-type of wood pallets for specialized cargo handling, used in warehouses and distribution centers. 3. Lightweight Plywood Pallets: Strong for their weight, smooth surface, moisture-resistant, but no…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for different types of pallets
The landscape of pallet sourcing is evolving, offering significant opportunities for international B2B buyers across diverse markets. Understanding the different types of pallets—wooden, plastic, metal, and cardboard—allows businesses to tailor their logistics strategies to specific needs, enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For instance, while wooden pallets dominate due to their affordability and ease of repair, plastic pallets present advantages in hygiene and durability, particularly in industries like food and pharmaceuticals.
Strategic sourcing of pallets not only involves selecting the right type based on load requirements and environmental considerations but also ensuring compliance with international standards such as ISPM 15 for wooden pallets. This is crucial for avoiding potential trade barriers and ensuring the smooth movement of goods across borders.
As we look ahead, the focus should be on sustainable practices and innovations in pallet design, catering to an increasingly eco-conscious market. International B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to leverage these insights to optimize their supply chains. Embrace strategic sourcing to not only enhance your logistics operations but also position your business as a leader in responsible and efficient trade practices.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.