Everything You Need to Know About Hydraulic Motor Types Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic motor types
Navigating the complex landscape of hydraulic motor types can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially when seeking reliable solutions that meet specific operational needs. Hydraulic motors play a critical role in converting hydraulic energy into mechanical power, yet the myriad options—including gear, piston, and vane motors—can create confusion in sourcing the right equipment. This guide aims to demystify the selection process by providing in-depth insights into the various types of hydraulic motors, their applications across different industries, and essential criteria for supplier vetting.
As buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including countries like Nigeria and Vietnam) navigate their procurement strategies, understanding the nuances of hydraulic motor performance—including torque, displacement, and efficiency—becomes paramount. Additionally, considerations such as cost, compatibility with existing systems, and the potential for contamination are crucial for informed decision-making.
This comprehensive resource empowers B2B buyers by equipping them with the knowledge necessary to evaluate options effectively, ensuring they can make choices that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. By leveraging the insights presented in this guide, businesses can confidently navigate the global market for hydraulic motors, ultimately leading to smarter investments and improved productivity.
Understanding hydraulic motor types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Motors | Simple design, low cost, durable | Fans, conveyors, agricultural machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, contamination tolerant. Cons: Lower efficiency at high speeds. |
| Vane Motors | Eccentric rotor with sliding vanes | Agricultural equipment, molding machines | Pros: Low noise, high torque at low speeds. Cons: Limited lifespan under high pressures. |
| Radial-Piston Motors | Perpendicular pistons, high torque output | Ground drilling, cranes, winches | Pros: Smooth operation, high torque. Cons: Bulkier design, requires regular maintenance. |
| Axial-Piston Motors | Piston arrangement in circular array, high efficiency | Construction equipment, ship cranes | Pros: Better speed variability, compact design. Cons: Higher initial cost, complex design. |
| Hydraulic Motors | Converts hydraulic energy to mechanical power | Various industrial applications | Pros: Versatile, wide range of applications. Cons: Requires careful selection for optimal performance. |
What Are Gear Motors and Their Applications in B2B?
Gear motors are characterized by their simple design and low manufacturing costs, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to minimize expenses. They are primarily used in applications such as fans, conveyors, and agricultural machinery. While they offer durability and a high tolerance for contamination, buyers should be aware that gear motors may exhibit lower efficiency at high speeds. When selecting gear motors, consider the specific torque and speed requirements of your application, along with the potential for environmental contaminants.
How Do Vane Motors Stand Out in Industrial Settings?
Vane motors feature an eccentric rotor with sliding vanes, allowing them to generate high torque at low speeds, which is particularly beneficial in applications like agricultural equipment and molding machines. They are quieter than other motor types, contributing to a more pleasant working environment. However, their lifespan can be limited under high-pressure conditions, which is a crucial consideration for buyers in demanding industrial sectors. Evaluate the operating pressures and expected maintenance requirements when considering vane motors for your operations.
What Are the Benefits of Radial-Piston Motors for Heavy Machinery?
Radial-piston motors are designed with pistons arranged perpendicularly to the output shaft, providing high torque output and smoother operation. They are commonly used in heavy machinery such as cranes and winches, where reliability is paramount. While they deliver excellent performance, their bulkier design and maintenance needs may pose challenges for some businesses. Buyers should assess the space constraints of their equipment and the frequency of maintenance required to ensure optimal performance.
Why Choose Axial-Piston Motors for Enhanced Efficiency?
Axial-piston motors are known for their circular array of pistons, enabling them to achieve high efficiency and better speed variability. They are ideal for applications in construction equipment and ship cranes, where space and performance are critical. Although they come with a higher initial cost and a more complex design, the long-term efficiency and reliability can justify the investment. Businesses should weigh the upfront costs against the potential for energy savings and performance improvements.
How Do Hydraulic Motors Fit into Various Industrial Applications?
Hydraulic motors serve as a vital component in converting hydraulic energy into mechanical power across diverse industries. Their versatility allows them to be utilized in various applications, from construction to manufacturing. When selecting a hydraulic motor, businesses must consider factors such as torque, speed, and operational conditions to ensure compatibility with their systems. Collaborating with experienced suppliers can enhance decision-making and lead to more efficient operations.
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic motor types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hydraulic motor types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Excavation and earth-moving equipment | High torque for heavy lifting and durability | Ensure compatibility with existing machinery and evaluate local supplier reliability. |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery (e.g., tractors) | Enhanced efficiency and reduced operational costs | Assess the motor’s resistance to dirt and moisture, crucial for outdoor use. |
| Mining | Drilling rigs and conveyors | Reliable performance in harsh environments | Consider motor size and weight for transportation, along with international standards compliance. |
| Manufacturing | Assembly lines and conveyors | Improved productivity and reduced downtime | Evaluate motor speed and torque specifications to match production needs. |
| Marine | Ship cranes and winches | Precision in cargo handling and stability | Focus on corrosion resistance and performance under varying sea conditions. |
How Are Hydraulic Motors Used in Construction Equipment?
In the construction industry, hydraulic motors are integral to excavation and earth-moving equipment, providing the necessary power to lift and move heavy materials. These motors are designed to deliver high torque, which is essential for tasks such as digging and lifting. Buyers must ensure that the hydraulic motors they source are compatible with their existing machinery and can withstand the operational demands of construction sites, often characterized by rugged terrain and variable weather conditions.
What Role Do Hydraulic Motors Play in Agriculture?
Hydraulic motors are pivotal in agricultural machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, where they enhance operational efficiency. They facilitate various functions, from powering attachments to controlling movement. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, it is essential to consider the motor’s resistance to dirt and moisture, as agricultural equipment is frequently exposed to challenging environmental conditions. This durability directly impacts operational costs and productivity.
How Are Hydraulic Motors Utilized in Mining Operations?
In the mining sector, hydraulic motors power drilling rigs and conveyor systems, ensuring reliable performance in harsh and demanding environments. Their ability to provide consistent torque makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications, such as ore extraction and material transport. Buyers should pay attention to the size and weight of the motors, as well as compliance with international standards, to ensure safe and efficient operation in remote mining locations.
What Benefits Do Hydraulic Motors Provide in Manufacturing?
Within manufacturing, hydraulic motors are commonly used in assembly lines and conveyor systems, where they help streamline production processes. Their ability to deliver precise control over speed and torque enhances productivity and minimizes downtime. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific speed and torque specifications of the motors to ensure they meet the unique demands of their production lines, considering factors such as the type of materials handled and the complexity of operations.
How Are Hydraulic Motors Applied in Marine Industries?
In the marine sector, hydraulic motors are essential for operating ship cranes and winches, providing the necessary precision for cargo handling. The reliability of these motors in varying sea conditions is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operations. Buyers should focus on sourcing motors with high corrosion resistance and robust performance characteristics, as these factors significantly influence operational reliability and maintenance costs in marine environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘hydraulic motor types’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Hydraulic Motor for Unique Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the challenge of selecting the appropriate hydraulic motor type for specific applications. For instance, a construction company in Nigeria might require a motor for a heavy-duty excavator, but lacks clarity on whether to choose a gear motor, piston motor, or vane motor. The stakes are high; an incorrect selection can lead to inefficiencies, increased operational costs, and potential equipment failures, ultimately affecting project timelines and profitability.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their application requirements, including torque, speed, and environmental conditions. Engaging with a hydraulic supplier that specializes in motor applications is vital. Prospective buyers should prepare a detailed specification sheet that outlines these requirements and consult with experts. Suppliers can recommend specific motor types that align with operational needs and even provide performance simulations. Additionally, visiting trade shows or industry forums can offer insights into the latest technologies and practical experiences from peers in similar sectors.
Scenario 2: Managing Contamination and Maintenance Issues with Hydraulic Motors
The Problem: Hydraulic motors are susceptible to contamination from dirt, moisture, or fluid degradation, which can compromise performance and longevity. For example, a mining operation in South America may find that dust and debris frequently infiltrate their hydraulic systems, leading to premature wear and costly repairs. This not only disrupts operations but also strains maintenance budgets and timelines.
The Solution: To combat contamination issues, buyers should invest in high-quality filtration systems and seals designed specifically for their hydraulic motors. Regular maintenance schedules, including oil analysis and filter replacements, are crucial in maintaining optimal performance. Buyers should also consider the environmental factors of their operations when selecting hydraulic motors; for instance, choosing motors with higher tolerance to contaminants can minimize risks. Additionally, providing training for operational staff on proper maintenance practices can significantly extend the life of hydraulic motors and reduce downtime.
Scenario 3: Understanding Performance Metrics and Ratings for Hydraulic Motors
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter confusion surrounding the performance metrics and ratings of hydraulic motors, such as torque and displacement. A manufacturing firm in Europe may be unsure how to interpret these specifications and how they relate to the motor’s capabilities. Misunderstanding these metrics can lead to selecting a motor that underperforms or overburdens the system, resulting in operational inefficiencies and increased energy costs.
The Solution: Buyers should take the initiative to educate themselves on hydraulic motor ratings and their implications for performance. This includes understanding how displacement affects speed and how torque ratings influence the motor’s ability to handle load. Engaging with technical documentation provided by manufacturers can offer insights into these specifications. Furthermore, participating in training sessions or workshops focused on hydraulic systems can enhance understanding. Collaborating with knowledgeable suppliers who can explain these metrics in practical terms can also aid in making informed decisions. By establishing clear performance benchmarks based on application needs, buyers can select motors that align with their operational goals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic motor types
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Hydraulic Motors?
When selecting materials for hydraulic motors, understanding the properties and suitability of various materials is crucial for optimizing performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in hydraulic motor construction: cast iron, aluminum, stainless steel, and composite materials.
Cast Iron: A Durable Choice for Hydraulic Motors
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and can handle significant pressure loads.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of cast iron is its durability and strength, making it suitable for high-torque applications. However, it is relatively heavy, which can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a concern. Additionally, cast iron can be prone to corrosion if not properly coated.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is often used in heavy machinery and industrial applications where robustness is required. Its compatibility with various hydraulic fluids makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, as cast iron may require specific treatments to prevent corrosion in humid environments.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and exhibits good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications where weight savings are essential. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 250°F (121°C).
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which facilitates easier installation and reduced energy consumption in hydraulic systems. However, it may not handle high pressures as effectively as cast iron or steel, limiting its use in high-torque applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for mobile applications and equipment where weight is a critical factor, such as in automotive and aerospace industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet international standards, as variations in alloy composition can affect performance in different climates, particularly in hotter regions.
Stainless Steel: High Strength and Corrosion Resistance
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, withstanding temperatures up to 1000°F (538°C) and high pressures.
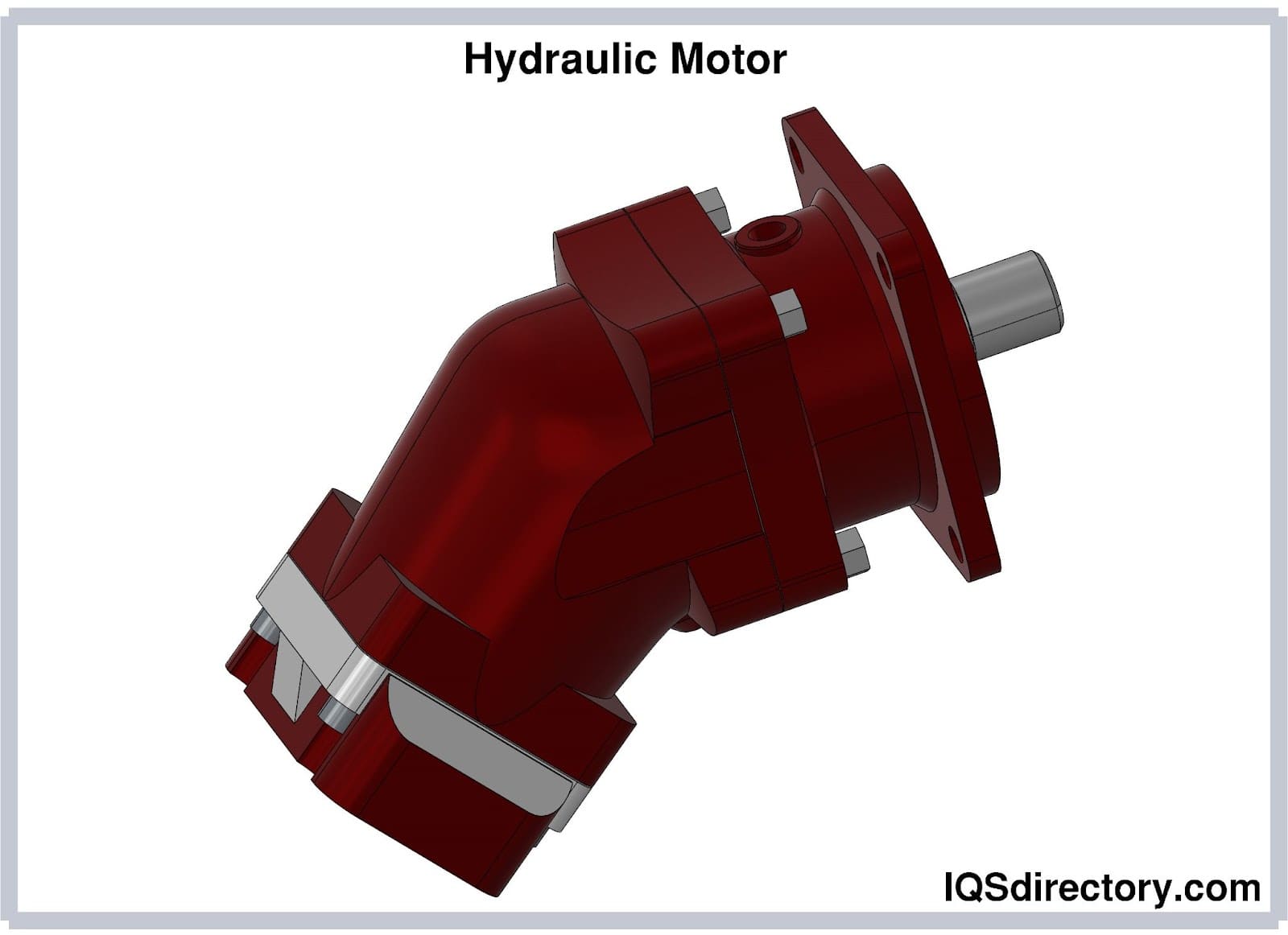
Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for harsh environments. However, it is more expensive than cast iron and aluminum, which could impact budget considerations.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in applications exposed to corrosive fluids or extreme conditions, such as marine environments and food processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers in the Middle East or coastal areas, the corrosion resistance of stainless steel makes it a preferred choice. Compliance with standards such as JIS or ASTM is essential to ensure quality.
Composite Materials: Innovative and Lightweight Solutions
Key Properties: Composite materials can be engineered for specific applications, offering tailored properties such as high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their versatility and potential for reduced weight. However, they can be more expensive and complex to manufacture, which may limit their application in cost-sensitive projects.
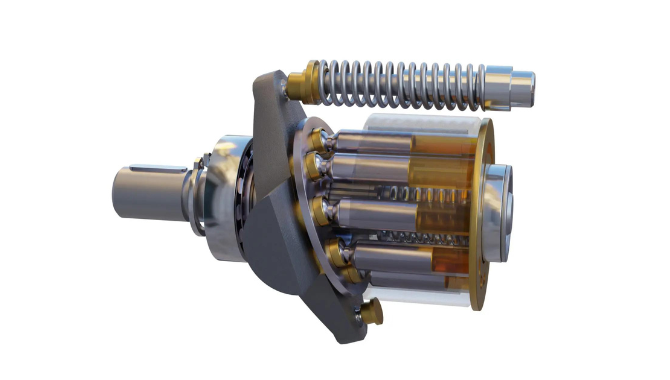
Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in specialized applications, such as aerospace and advanced automotive systems, where performance and weight savings are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards and certifications for composite materials, as these can differ significantly between regions, particularly in Europe and Asia.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Hydraulic Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic motor types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Heavy machinery, industrial applications | Excellent durability and strength | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Mobile applications, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited pressure handling | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Marine environments, food processing | High strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace, advanced automotive systems | Tailored properties and lightweight | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize hydraulic motor performance across diverse applications and environments. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic motor types
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Hydraulic Motors?
The manufacturing process of hydraulic motors involves several critical stages, each ensuring the motor meets the necessary performance and reliability standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
-
Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting high-quality materials that can withstand the operational stresses of hydraulic motors. Common materials include high-grade steel for gears and housings, aluminum for lightweight applications, and various polymers for seals and gaskets. Material testing is crucial to assess properties such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. Suppliers often conduct metallurgical analysis to ensure the materials meet international standards. -
Forming
In this stage, the raw materials undergo various forming processes, which may include machining, forging, and casting. For instance, gear components might be machined from solid blocks of steel, while housings could be cast or forged to enhance structural integrity. Precision is paramount during this phase to ensure that all parts fit together seamlessly, as even minor discrepancies can lead to performance issues. -
Assembly
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the hydraulic motor. This process typically requires skilled labor and advanced machinery to ensure precision alignment and secure fitting. Key components such as pistons, vanes, and gears are assembled within the motor casing. During this phase, manufacturers often employ automated systems to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. -
Finishing
The final stage involves applying surface treatments and coatings that enhance durability and performance. This may include anodizing aluminum parts, applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion, and polishing surfaces for improved aesthetics and reduced friction. Finishing processes are also crucial for ensuring that the components can operate efficiently in various environmental conditions.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Hydraulic Motor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of hydraulic motors, ensuring that each product meets stringent performance and safety standards. The QA process encompasses several international standards, checkpoints, and testing methods.
-
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Manufacturers of hydraulic motors often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Additionally, specific industry standards like CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for products used in the oil and gas sector are critical. Compliance with these standards not only guarantees product reliability but also facilitates smoother international trade. -
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This involves continuous monitoring during manufacturing to catch defects early. Techniques include machine calibration checks and component measurements.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the motors are assembled, they undergo rigorous testing to ensure they perform as expected. This may involve pressure tests, torque tests, and performance evaluations under simulated operational conditions.
- What Common Testing Methods Are Used?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance of hydraulic motors, including:
- Hydraulic Testing: Assessing the motor’s ability to handle pressure and flow rates.
- Torque Testing: Measuring the output torque under different load conditions to ensure the motor meets performance specifications.
- Vibration Analysis: Monitoring vibrations during operation to identify potential mechanical issues.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are some actionable steps to ensure quality compliance:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits
Regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. This includes examining their adherence to international standards and internal QA practices. -
Request Quality Reports
Suppliers should provide comprehensive quality reports that detail their testing processes, results, and any certifications obtained. This documentation can help buyers assess the reliability of the products. -
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services
Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can be conducted at various stages of production to ensure compliance with agreed-upon specifications. -
Understand Regional Quality Nuances
Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that affect product quality. For example, hydraulic motors sold in Europe must comply with CE marking requirements, while those in the Middle East may need to adhere to GCC standards. Understanding these nuances can help buyers navigate potential compliance issues.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Hydraulic Motor Procurement
In the competitive landscape of hydraulic motor procurement, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is paramount for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with the stages of production, relevant international standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source reliable, high-performance hydraulic motors. This knowledge not only mitigates risks but also enhances overall operational efficiency in their respective industries.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘hydraulic motor types’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in procuring hydraulic motors effectively. Understanding the different types of hydraulic motors and the essential steps to evaluate and choose suppliers will empower you to make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and industry standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your procurement process, clearly outline the technical requirements for the hydraulic motor. Identify key factors such as torque, speed, and displacement, as these will dictate the motor’s performance in your specific application. Understanding these specifications ensures that you select a motor that meets your operational demands.
Step 2: Research Different Hydraulic Motor Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of hydraulic motors—gear, vane, and piston motors—and their specific applications.
– Gear Motors: Best for low-cost applications with good contamination tolerance.
– Vane Motors: Ideal for low noise and high torque at low speeds.
– Piston Motors: Suitable for high efficiency and variable speed applications.
This knowledge will help you align your requirements with the most suitable motor type.
Step 3: Assess Supplier Expertise and Experience
Evaluate potential suppliers based on their industry experience and expertise in hydraulic motors. Look for companies with a solid track record in your specific sector, as they are more likely to understand your unique challenges and requirements.
– Request case studies or examples of previous work.
– Inquire about their experience with similar applications or environments.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Standards
Ensure that your selected suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and certifications, such as those from the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). This not only guarantees the quality of the hydraulic motors but also indicates the supplier’s commitment to maintaining high manufacturing standards.
Step 5: Evaluate Technical Support and After-Sales Service
Consider the level of technical support and after-sales services offered by suppliers. Strong post-purchase support can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of your hydraulic motors.
– Inquire about warranty terms and service agreements.
– Ensure availability of spare parts and technical assistance.
Step 6: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you have narrowed down your list of potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include pricing, lead times, and payment terms. Comparing these quotes will help you identify the best value for your investment while ensuring that all technical specifications are met.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
Step 7: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Before finalizing your purchase, perform a risk assessment of the supplier and the hydraulic motors being procured. Consider factors such as delivery reliability, potential for delays, and the supplier’s financial stability. This proactive approach will help mitigate risks associated with your procurement process and ensure a smoother operational flow.
By following these steps, you can make well-informed decisions when sourcing hydraulic motors, ultimately enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of your operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic motor types Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Hydraulic Motors?
When sourcing hydraulic motors, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the durability and performance of hydraulic motors. High-quality metals and specialized components, such as seals and bearings, can significantly increase costs but also enhance longevity and efficiency.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location and the complexity of the motor design. Skilled labor may be required for assembly and quality control, particularly for customized motors.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, depreciation, and factory maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom hydraulic motors. These costs are amortized over production runs, making them a critical consideration for buyers who anticipate large volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that motors meet specified performance standards and certifications. While this adds to the upfront costs, it can prevent costly failures and returns in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary significantly based on the origin of the motors, the shipping method, and the final destination. International buyers should consider the implications of customs duties and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market demand. Understanding this margin can provide leverage during negotiations.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Hydraulic Motors?
Several factors can influence the pricing of hydraulic motors, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize their costs, especially for high-demand applications.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom motors tailored to specific applications can incur additional costs. Buyers must weigh the benefits of customization against standard options that may meet their needs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Motors made from high-grade materials or with certifications (like ISO or CE) may come at a premium. Buyers should assess the trade-off between cost and reliability based on their operational requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their proven track record, but they often provide superior support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can greatly affect the final cost. Understanding the responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs can help buyers estimate total costs accurately.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Hydraulic Motor Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and strategic purchasing can lead to substantial savings. Here are some actionable tips:

Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus not just on the purchase price but also on the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. Presenting a TCO analysis can strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Research and Compare: Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to establish a baseline for pricing. This competitive analysis can provide valuable insights into market rates and help in negotiations.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Long-term partnerships often result in favorable terms and priority during production schedules.
-
Understand Local Market Dynamics: Buyers should be aware of regional economic factors that may impact pricing, such as currency fluctuations and local demand. This knowledge can inform negotiations and purchasing strategies.
-
Be Clear on Expectations: Clearly communicate your requirements and expectations regarding quality and performance. This transparency can lead to better alignment with suppliers and potentially lower costs through streamlined processes.
Conclusion: Why Is It Important to Monitor Pricing Trends in Hydraulic Motors?
Staying informed about pricing trends in hydraulic motors is crucial for making strategic purchasing decisions. Market fluctuations can impact material costs, labor rates, and logistics, affecting overall pricing. By actively monitoring these trends and employing effective negotiation strategies, international buyers can secure favorable terms and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Remember, this analysis serves as a guideline; actual prices may vary based on specific circumstances and supplier negotiations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing hydraulic motor types With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternative Solutions to Hydraulic Motor Types
In the quest for effective mechanical power conversion, hydraulic motors are a popular choice due to their efficiency and versatility. However, various alternative technologies can also perform similar functions, each with unique advantages and disadvantages. This analysis will compare hydraulic motor types with electric motors and pneumatic actuators, providing insights into their performance, cost-effectiveness, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and best use cases.
Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Hydraulic Motor Types | Electric Motors | Pneumatic Actuators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque and efficiency; good for heavy-duty applications | High speed and precision; lower torque | Fast actuation; suitable for lighter loads |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; low operating costs | Varies widely; generally higher upfront costs | Lower initial costs; ongoing air supply costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires hydraulic system setup | Easy installation; compatible with many systems | Simple installation; requires air compressor |
| Maintenance | Requires regular fluid checks and system integrity | Low maintenance; long lifespan with minimal upkeep | Regular checks on air supply and seals needed |
| Best Use Case | Heavy machinery, construction, and agriculture | Manufacturing, robotics, and HVAC systems | Packaging, automotive assembly, and material handling |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Motors
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, offering high precision and speed. They are often more efficient than hydraulic motors in applications requiring rapid movements and lower torque. However, the initial investment can be substantial, especially for high-performance electric motors. Maintenance is minimal, as they have fewer moving parts, but they may require specialized electrical infrastructure, which could complicate installation in some contexts.
Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators use compressed air to produce motion, making them ideal for applications that require quick actuation and lighter loads. They tend to have lower initial costs compared to hydraulic systems, but ongoing costs for compressed air can accumulate, impacting long-term budget considerations. They are relatively easy to install and maintain, yet their performance may be limited in high-torque applications, making them less suitable for heavy machinery.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right solution for mechanical power conversion, B2B buyers should consider the specific application requirements, including torque, speed, and environmental factors. Hydraulic motors are optimal for high-torque, heavy-duty applications, while electric motors excel in precision and speed for lighter tasks. Pneumatic actuators offer a cost-effective option for quick movements in less demanding applications. By carefully evaluating these aspects, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic motor types
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Hydraulic Motors?
When selecting hydraulic motors, understanding critical technical specifications is vital for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Displacement
Displacement measures the volume of hydraulic fluid required for one complete revolution of the motor’s output shaft. It is typically expressed in cubic centimeters per revolution (cc/rev) or cubic inches per revolution (in³/rev). B2B buyers must consider displacement as it directly influences the torque output and speed of the hydraulic motor. A higher displacement generally equates to higher torque but may also affect the overall size and weight of the motor.
2. Torque Rating
Torque rating is a crucial specification that indicates the rotational force produced by the motor, usually measured in Newton-meters (Nm) or inch-pounds (in-lb). This specification is vital for B2B decision-makers because it helps determine if a hydraulic motor can meet the operational demands of specific machinery or equipment. Selecting a motor with adequate torque ensures efficiency and longevity in demanding applications.
3. Pressure Rating
Pressure rating refers to the maximum hydraulic pressure the motor can safely handle, typically expressed in bar or psi. Understanding the pressure rating is essential for ensuring the motor’s reliability and safety in high-stress environments. Choosing a motor with a suitable pressure rating can prevent premature failure and costly downtime.
4. Efficiency
Efficiency indicates how effectively a hydraulic motor converts hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. It is typically expressed as a percentage. Higher efficiency means lower energy consumption and less heat generation, which is critical for maintaining operational costs and extending the motor’s lifespan. B2B buyers should prioritize efficiency to enhance performance and reduce operational expenses.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
5. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range specifies the temperatures within which the hydraulic motor can function optimally. This specification is particularly important for applications in extreme environments, where high or low temperatures can affect performance. Selecting a motor with an appropriate operating temperature range ensures reliability and efficiency, especially in regions with variable climates.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Hydraulic Motor Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation processes in B2B transactions. Here are some common trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for buyers looking to ensure compatibility and quality in hydraulic motors that fit specific machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for B2B buyers to understand as it can influence purchasing decisions, especially for companies with budget constraints or those just starting with hydraulic systems.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting price estimates for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing businesses to compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and freight arrangements. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers negotiate better shipping conditions and clarify liability during the transportation of hydraulic motors.
Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is vital for B2B buyers, especially in industries where equipment availability is critical for project timelines. Knowledge of lead times can help in better planning and resource allocation.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right hydraulic motors for their specific applications and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the hydraulic motor types Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Hydraulic Motor Types Market?
The hydraulic motor types market is witnessing significant growth driven by a surge in industrial automation and the increasing demand for efficient machinery across sectors such as construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. In regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, there is a notable push towards infrastructure development, which boosts the demand for hydraulic systems. Additionally, European markets are adopting advanced hydraulic solutions as part of their commitment to Industry 4.0, integrating IoT technologies that enhance the performance and monitoring of hydraulic motors.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends in this sector. For instance, the rise of smart hydraulics—incorporating sensors and data analytics—enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Furthermore, the shift towards modular systems allows for greater flexibility and customization in hydraulic motor applications, catering to diverse operational needs across different industries.
International B2B buyers, particularly from developing regions, should be aware of the competitive landscape that includes both established manufacturers and new entrants focused on cost-effective solutions. Sourcing strategies that prioritize long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers will be essential for navigating the complexities of global supply chains, particularly in light of geopolitical uncertainties and fluctuating raw material prices.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Hydraulic Motor Types?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration in the hydraulic motor types market, as environmental impact and ethical sourcing gain prominence among B2B buyers. The hydraulic industry is under pressure to minimize its carbon footprint, leading to a growing emphasis on products that utilize eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes. This shift is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where regulatory frameworks are evolving to support sustainable practices.
Ethical supply chains are critical in ensuring that hydraulic motor components are sourced responsibly, reducing the risk of environmental degradation and social injustice. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations are becoming increasingly important for manufacturers looking to establish credibility in global markets.
Moreover, the focus on ‘green’ materials, such as biodegradable hydraulic fluids and recyclable components, is gaining traction. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who not only comply with these standards but also actively promote sustainable practices within their operations. This alignment not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the rising demand from end-users for products that contribute to a circular economy.
What Key Historical Developments Have Influenced the Hydraulic Motor Types Sector?
The evolution of hydraulic motors dates back to the early 20th century when the first hydraulic systems were introduced in industrial machinery. Initially, hydraulic motors were primarily used in heavy equipment due to their ability to generate high torque from relatively compact designs. Over the decades, advancements in materials and engineering have led to the development of more efficient and reliable hydraulic motor types, including gear, piston, and vane motors.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM) revolutionized hydraulic motor production, allowing for more precise engineering and customization. This period also saw the rise of hydraulic systems in automotive applications, leading to an increased demand for more compact and efficient hydraulic motors.
In recent years, the integration of digital technologies and automation has transformed the hydraulic motor landscape, aligning with global trends toward smarter manufacturing and sustainability. As international B2B buyers navigate this dynamic market, understanding the historical context helps in making informed decisions regarding technology adoption and supplier partnerships.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic motor types
-
How do I select the right hydraulic motor type for my application?
Choosing the right hydraulic motor involves evaluating your specific application requirements, including operating speed, torque, and environmental conditions. Consider the type of load your motor will handle and the working environment, such as temperature and potential contamination. Additionally, assess the motor’s efficiency and maintenance needs. Consulting with a reputable hydraulic supplier can provide insights into the best motor type—gear, piston, or vane—based on your operational demands. -
What is the best hydraulic motor type for high-torque applications?
For high-torque applications, low-speed, high-torque (LSHT) hydraulic motors, particularly radial-piston motors, are ideal. They offer substantial torque while maintaining a compact size, which is beneficial for equipment like cranes and winches. Axial-piston motors can also be suitable for applications requiring variable speed and high efficiency. Always evaluate your specific requirements, such as pressure ratings and displacement, to ensure optimal performance. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing hydraulic motors internationally?
When sourcing hydraulic motors internationally, consider factors such as supplier reputation, certifications, and compliance with international quality standards. It’s crucial to assess lead times, shipping logistics, and potential tariffs or import regulations in your region. Additionally, ensure that the supplier offers robust after-sales support and warranties to address any issues that may arise post-purchase. Building a relationship with a reliable supplier can also facilitate smoother transactions and better pricing. -
How can I ensure the quality of hydraulic motors from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, request documentation of certifications such as ISO or ANSI standards from your suppliers. Conduct due diligence by reviewing customer testimonials and case studies. If possible, arrange for a factory visit or ask for samples before placing a large order. Establishing clear quality assurance protocols, including inspection and testing upon arrival, is also essential to verify that the motors meet your specifications and performance standards. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for hydraulic motors?
Minimum order quantities for hydraulic motors can vary widely based on the supplier and the type of motor. Generally, MOQs may range from 5 to 50 units for standard models, while custom designs may have higher requirements. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that suit your purchasing strategy. Consider the cost implications of MOQs in relation to your project requirements and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing hydraulic motors internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on supplier policies and your negotiation outcomes. Common options include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer installment plans for larger orders. It’s advisable to clarify payment terms early in negotiations to avoid misunderstandings later. Ensure that the payment method you choose offers security and protection against potential disputes. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for hydraulic motors?
When managing logistics for hydraulic motors, select a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial equipment. Discuss shipping methods, including air freight for urgent orders or sea freight for cost-effective solutions. Ensure proper packaging to protect motors during transit. Additionally, stay informed about customs requirements in your country to avoid delays and additional costs upon arrival. -
What customization options are available for hydraulic motors?
Customization options for hydraulic motors often include variations in displacement, torque ratings, and mounting configurations to fit specific applications. Some suppliers may also offer tailored designs to meet unique operational requirements. Discuss your needs with potential manufacturers to explore available customization options. Ensure that any modifications align with your operational specifications and performance expectations to achieve optimal results.
Top 6 Hydraulic Motor Types Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Panagon Systems – Hydraulic Motors
Domain: panagonsystems.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic motors convert hydraulic energy into mechanical power. There are three main types: gear motors, piston motors, and vane motors. Gear motors consist of an idler gear and a driven gear, offering low initial cost and durability, commonly used in fans and conveyors. Vane motors feature an eccentric bore with sliding vanes, providing low noise and high torque at low speeds, used in agricultur…
2. IQS Directory – Hydraulic Motors
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic motors are specialized devices that transform hydraulic pressure or fluid energy into rotational force and angular motion. Key product details include: 1. Motor Displacement: Amount of fluid needed for one complete revolution, expressed in cubic inches or cubic centimeters per revolution. 2. Torque Output: Measured in foot-pounds or inch-pounds, influenced by system pressure and motor di…
3. Harvard Filtration – Hydraulic Motors
Domain: harvardfiltration.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic motors convert hydraulic energy into mechanical energy and are used in various applications such as construction equipment, automotive systems, and aerospace components. There are three main types of hydraulic motors: 1. Vane Motors: Simple design with fewer moving parts, rugged, operates in high-pressure environments, but less efficient. 2. Piston Motors: More complex, highly efficient,…
4. Iron Wing Sales – Hydraulic Motors
Domain: ironwingsales.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic motors are devices that convert hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. There are several types of hydraulic motors, including gear motors, vane motors, and piston motors. Gear motors are known for their simplicity and durability, making them suitable for various applications. Vane motors offer smooth operation and are often used in applications requiring high speed. Piston motors are h…
5. Hosebox – Hydraulic Pumps
Domain: hosebox.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Pumps: 1. Gear Pumps – Commonly used in truck-mounted hydraulic systems, characterized by fewer moving parts, easy serviceability, and tolerance to contamination. They are fixed displacement pumps that produce the same volume of flow with each rotation. 2. Piston Pumps – Suitable for high operating pressures, more complex with stricter filtration requirements, and higher initial costs. T…
6. HidraOil – Hydraulic Motors
Domain: hidraoil.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic motors convert hydraulic energy into mechanical rotational energy (torque and speed). They are used in applications like winches, lawnmowers, mixers, and more. Key types include: 1. Orbital hydraulic motors – fixed displacement, high torque, used in mobile and industrial machinery. Variants include gerotor and geroller types. 2. External gear hydraulic motors – compact, robust, economica…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic motor types
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Hydraulic Motors?
In the competitive landscape of hydraulic motor procurement, understanding the distinct types—gear, vane, and piston motors—is crucial for making informed decisions. Each motor type offers unique advantages tailored to specific applications, from high torque outputs in radial-piston motors to the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of gear motors. Strategic sourcing allows buyers to leverage these insights, ensuring they select the most appropriate hydraulic motor that aligns with their operational needs and budget constraints.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement Process?
Investing time in strategic sourcing not only maximizes efficiency but also fosters long-term supplier relationships that can yield significant cost savings and technical support. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must consider factors like local market conditions, environmental regulations, and supply chain reliability when evaluating potential suppliers.
What’s Next for International Buyers in Hydraulic Motors?
As industries evolve and demand for hydraulic solutions grows, staying ahead of technological advancements and market trends will be key. By partnering with experienced manufacturers and suppliers, you can enhance your operational capabilities and ensure robust performance in your applications. Embrace the opportunity to innovate and optimize your sourcing strategies today—your next step could redefine your hydraulic system’s efficiency and reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
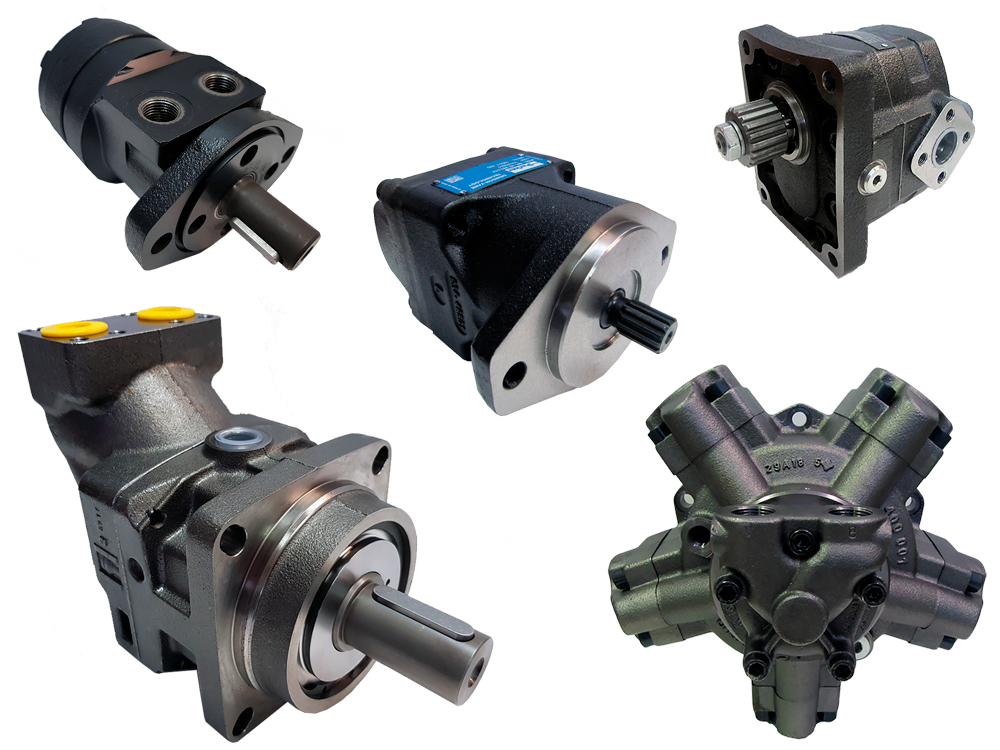
Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor types
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.