How to Source Head Gasket Material Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for head gasket material
In the complex landscape of automotive manufacturing, sourcing the right head gasket material is a critical challenge that can significantly impact engine performance and reliability. As international B2B buyers seek to procure high-quality components, understanding the nuances of head gasket materials is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into the various types of head gasket materials—including Multi-Layer Steel (MLS), graphite, copper, and composite options—each with unique properties suited for specific engine requirements.
Beyond material types, this comprehensive resource covers applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations, equipping buyers with the knowledge necessary to select the best options for their needs. By addressing key factors such as engine specifications, environmental conditions, and performance expectations, this guide empowers businesses from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries such as Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—to navigate the global market with confidence.
With a focus on actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide serves as a valuable tool for enhancing procurement strategies, ensuring that buyers can secure reliable head gasket materials that meet their operational demands while optimizing performance and minimizing risks.
Understanding head gasket material Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) | Composed of 2-5 layers of steel, treated for durability | High-performance engines, modern vehicles | Pros: Excellent sealing, withstands high pressure. Cons: Higher cost, requires precise installation. |
| Graphite | Flexible material that conforms to surface irregularities | Older engine models, thermal cycling environments | Pros: Good heat resistance, cost-effective. Cons: Less durable under extreme conditions, can degrade over time. |
| Copper | Solid construction provides superior strength | Racing applications, high-compression engines | Pros: Exceptional thermal conductivity, leak-proof. Cons: Installation complexity, requires machining. |
| Composite | Made from a blend of materials like graphite and fibers | General automotive applications, older vehicles | Pros: Affordable, versatile. Cons: Limited durability, not suitable for high-performance use. |
| Elastomeric | Steel core with elastomeric beads for sealing | Light-duty engines, some automotive applications | Pros: Effective sealing, good for lower pressures. Cons: Limited lifespan, not suited for high-performance scenarios. |
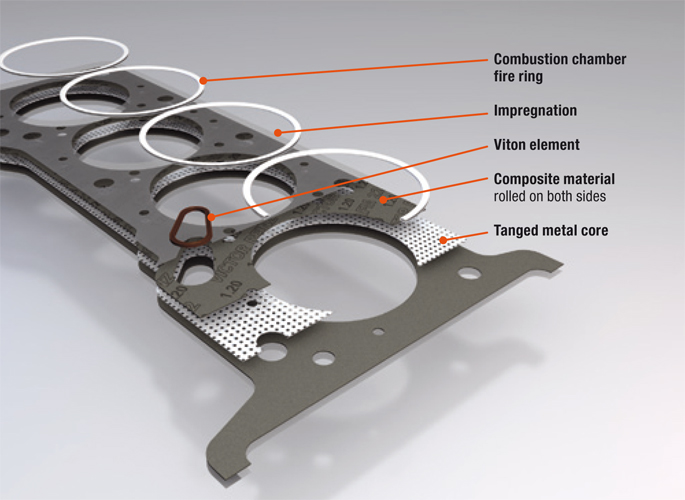
What are the Characteristics of Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) Head Gaskets?
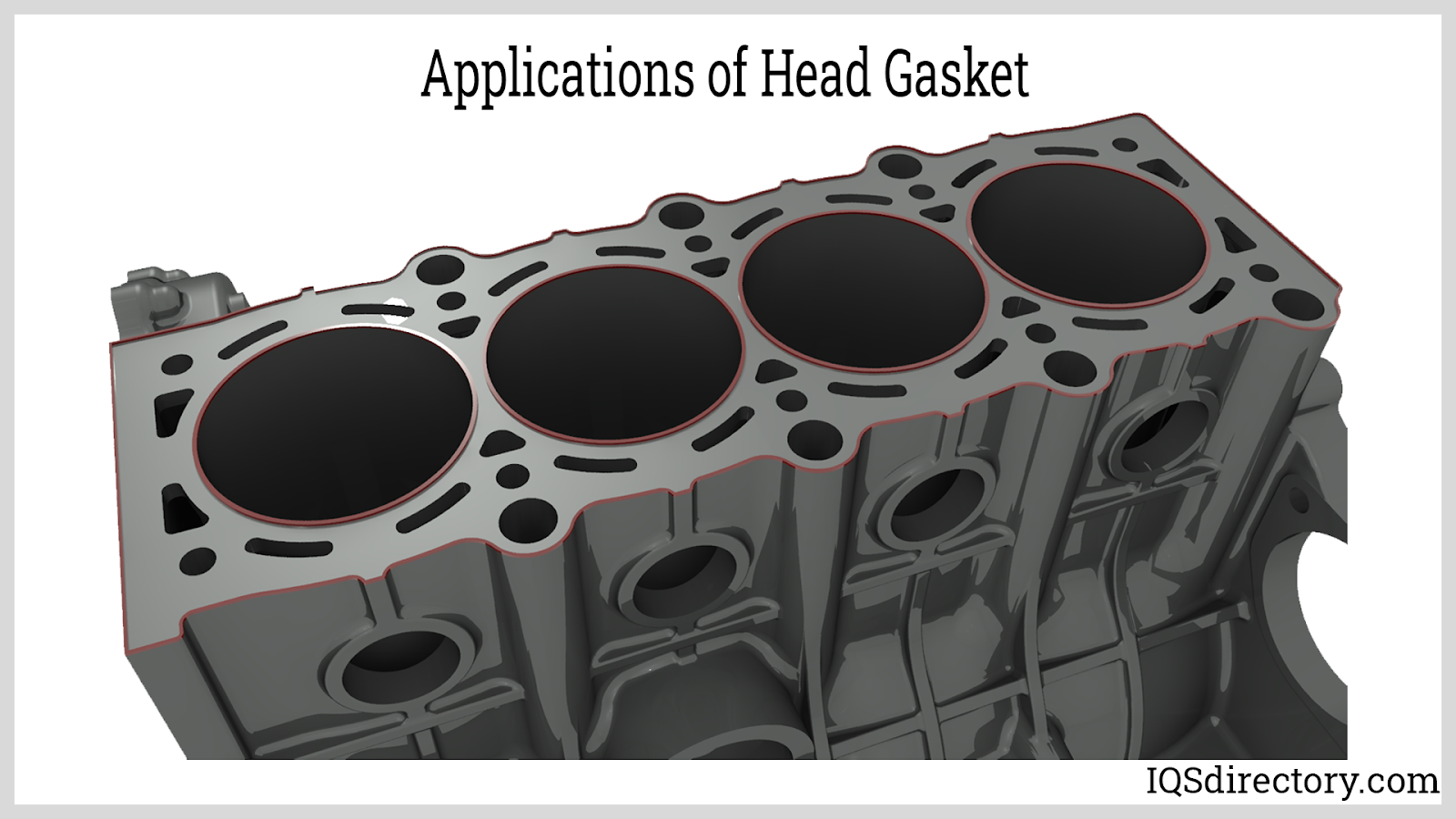
Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets are engineered with multiple layers of stainless steel, often ranging from two to five layers. This design allows them to maintain a tight seal even under extreme pressure and temperature fluctuations. They are particularly suitable for high-performance engines, making them a preferred choice in modern automotive applications. B2B buyers should consider the installation precision required, as improper fitting can lead to sealing failures, which may incur significant repair costs.
How Does Graphite Head Gasket Material Perform?
Graphite head gaskets are known for their flexibility, which enables them to adapt to minor surface irregularities. This characteristic makes them suitable for older engine models where the sealing surfaces may not be perfectly flat. While they offer good heat resistance and are cost-effective, buyers should be cautious about their longevity, especially in high-stress environments. It is essential for B2B buyers to assess the specific engine conditions to determine if graphite gaskets are the right fit.
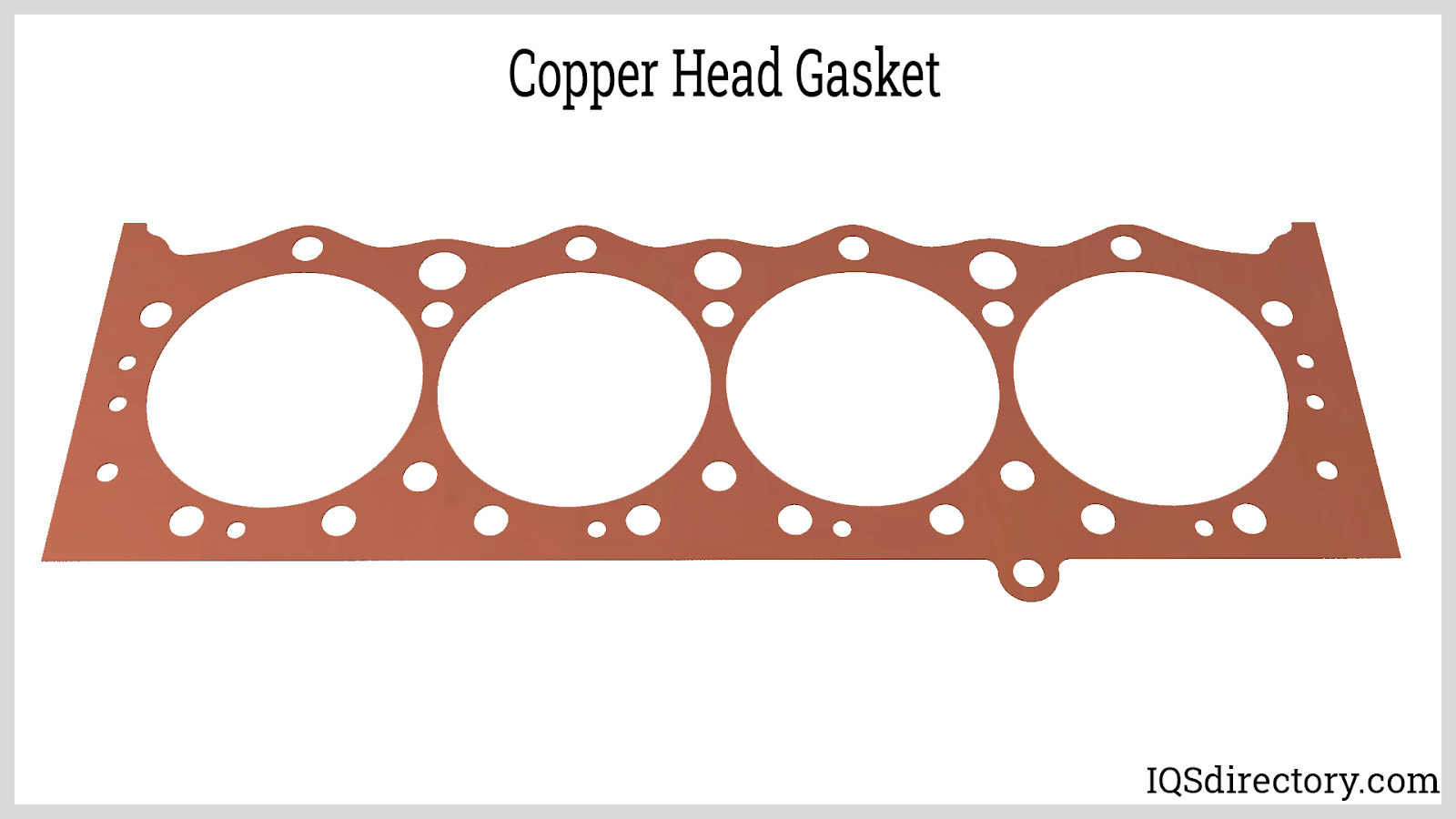
What Advantages Do Copper Head Gaskets Offer?
Copper head gaskets are made of solid copper, providing exceptional strength and thermal conductivity. They are ideal for racing applications or high-compression engines where heat management is critical. However, their installation requires specialized machinery, making them less accessible for standard automotive repairs. B2B buyers must weigh the benefits of superior performance against the complexity and cost of installation when considering copper gaskets.
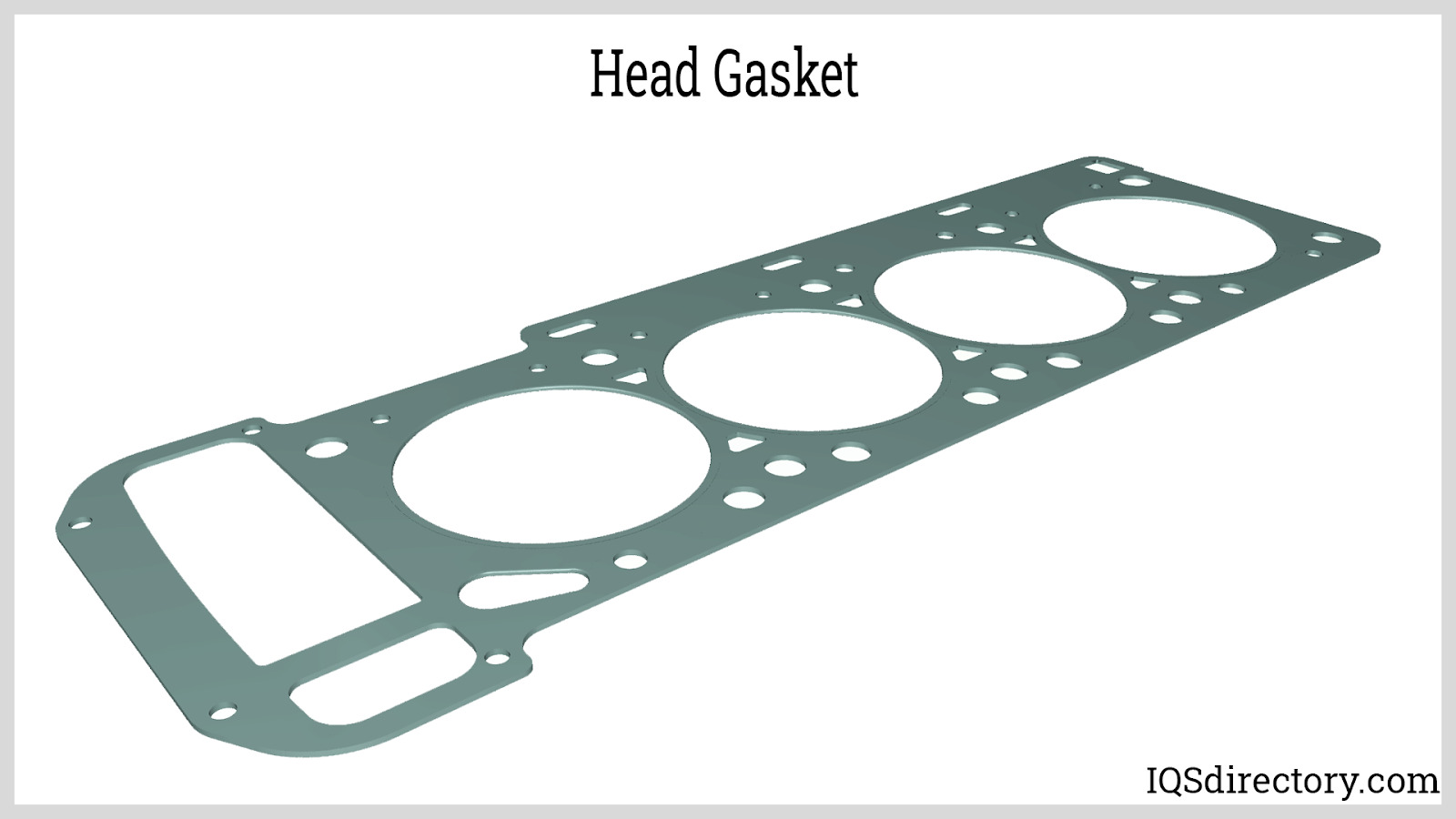
Illustrative image related to head gasket material
Why Consider Composite Head Gaskets for Older Vehicles?
Composite head gaskets consist of a mixture of materials, including graphite and aramid fibers. They were commonly used in vehicles from the 1980s and earlier. While they offer affordability and versatility, their durability is limited compared to modern alternatives, making them less suitable for high-performance engines. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific needs of older vehicle models and consider composite gaskets as a cost-effective option, albeit with a shorter lifespan.
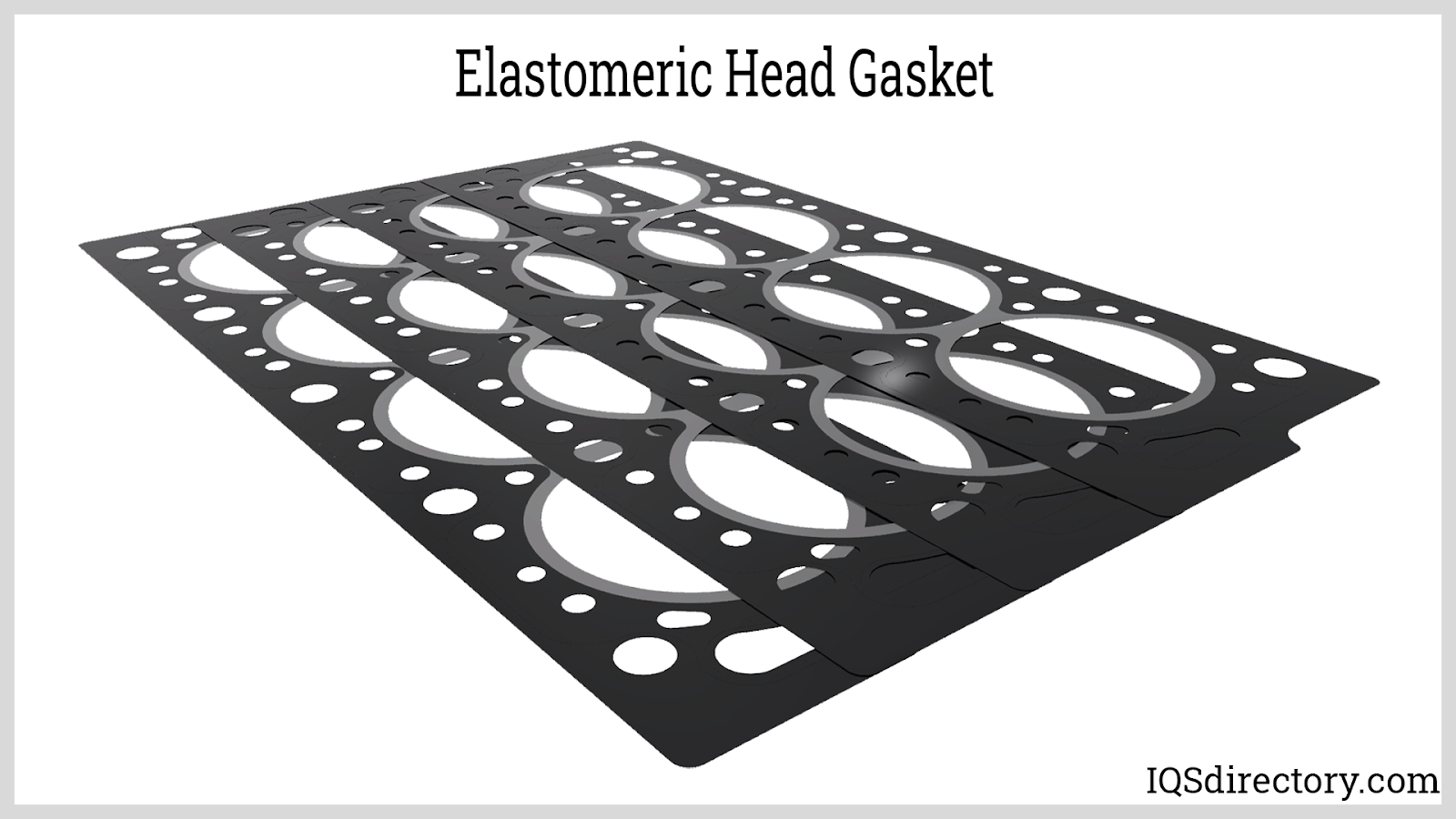
What are the Key Features of Elastomeric Head Gaskets?
Elastomeric head gaskets combine a steel core with elastomeric beads, providing effective sealing for light-duty engines. They are designed to handle lower pressures, making them suitable for everyday automotive applications. However, their lifespan may be limited under high-performance conditions. B2B buyers should consider the operational requirements of their engines and the expected performance levels to determine if elastomeric gaskets meet their needs effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of head gasket material
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of head gasket material | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Engine assembly in vehicles | Ensures reliable engine performance and longevity | Material compatibility, thermal resistance, and pressure ratings |
| Heavy Machinery | Gaskets for industrial engines | Prevents coolant and oil leaks, enhancing machinery uptime | Durability under extreme conditions, customization options |
| Marine Engineering | Head gaskets in marine engines | Maintains engine efficiency and reduces maintenance costs | Corrosion resistance, ability to withstand saltwater exposure |
| Aerospace | Sealing components in aircraft engines | Critical for safety and operational efficiency | Lightweight materials, high-temperature performance |
| Power Generation | Gaskets in generators and turbines | Optimizes energy output and reduces operational failures | Compliance with industry standards, sourcing from certified suppliers |
How is Head Gasket Material Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, head gasket materials are crucial for engine assembly. They create a seal between the engine block and cylinder head, preventing leaks of coolant and oil that could lead to catastrophic engine failure. For international B2B buyers, especially those in emerging markets like Nigeria and South America, sourcing durable materials that can withstand high pressures and temperatures is essential. Buyers should consider the specific engine requirements, including the type of fuel used and the expected operating conditions, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What Role Does Head Gasket Material Play in Heavy Machinery?
Heavy machinery relies on robust head gasket materials to maintain engine integrity and performance. These gaskets prevent leaks that can compromise machinery uptime and lead to costly repairs. In regions like the Middle East, where machinery often operates under extreme conditions, sourcing head gaskets made from materials that can withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress is vital. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide customized solutions tailored to the unique demands of their machinery, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
How is Head Gasket Material Applied in Marine Engineering?
In marine engineering, head gaskets are essential for sealing engines that operate in harsh environments. They help maintain engine efficiency while preventing leaks that can lead to serious mechanical issues. For businesses in Europe and the Middle East, where marine activities are prevalent, sourcing corrosion-resistant head gasket materials is critical. Buyers must also ensure that the materials meet the specific requirements of marine engines, including resistance to saltwater and high humidity, to avoid premature failure and ensure safety.
Why is Head Gasket Material Important in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, head gasket materials are vital for sealing components in aircraft engines. The integrity of these gaskets is critical for safety and operational efficiency, as any failure can lead to catastrophic outcomes. International B2B buyers in this sector need to focus on lightweight materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. Sourcing from certified suppliers who comply with stringent aerospace standards is essential to ensure reliability and performance in flight.
How Does Head Gasket Material Benefit Power Generation?
In the power generation sector, head gaskets are used in generators and turbines to optimize energy output and prevent operational failures. Reliable sealing is essential to maintain efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. For buyers in regions like Africa, where power generation is often challenged by environmental factors, sourcing high-quality head gasket materials that comply with industry standards is crucial. Buyers should consider the specific operating conditions and ensure that the materials are capable of withstanding the demands of continuous operation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘head gasket material’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Quality and Reliability in Gasket Selection
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the challenge of selecting the right head gasket material that ensures long-term reliability in various engine applications. In regions with diverse climatic conditions, such as Africa and South America, the risk of gasket failure can escalate due to extreme temperatures and humidity. This inconsistency can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased maintenance costs, especially when sourcing from multiple suppliers who may not guarantee quality. Furthermore, the pressure to meet stringent local regulations adds another layer of complexity.
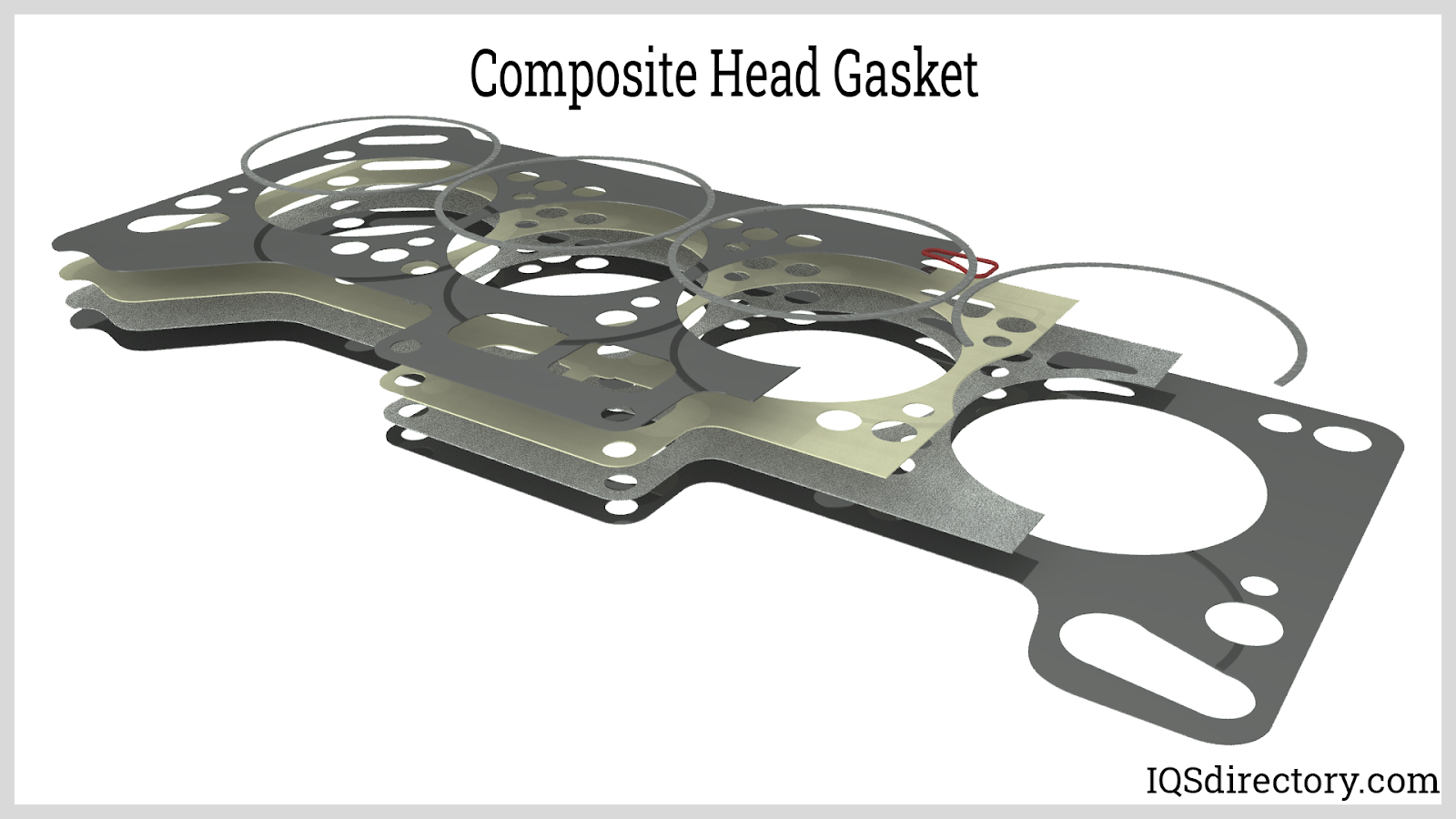
Illustrative image related to head gasket material
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should establish partnerships with reputable manufacturers known for their rigorous quality control processes. It is essential to request detailed specifications, including material certifications and testing standards, to ensure the chosen head gasket material can withstand specific operational conditions. A proactive approach involves conducting thorough research on the supplier’s history and client testimonials. Additionally, consider investing in multi-layer steel (MLS) gaskets due to their superior strength and reliability under pressure. By prioritizing quality and performance, buyers can significantly reduce the likelihood of gasket failure and associated costs.
Scenario 2: Navigating the Challenges of Diverse Engine Requirements
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face difficulties in sourcing head gasket materials that cater to a wide variety of engine specifications and applications. This challenge is particularly pronounced in the automotive aftermarket, where engines vary significantly in design and performance across different brands and models. The risk of selecting an incompatible gasket material can lead to severe engine damage, loss of performance, and costly repairs, ultimately impacting customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
The Solution: A strategic approach to address this issue is to develop a comprehensive catalog of available head gasket materials that aligns with specific engine types. Collaboration with manufacturers that offer customization options can greatly enhance the ability to meet diverse engine requirements. Buyers should also invest in training for their technical teams to better understand the nuances of different gasket materials, such as the benefits of composite versus copper gaskets. Utilizing software tools that assist in selecting the correct gasket based on engine specifications can streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that the right product is selected every time.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost-Effectiveness in Gasket Procurement
The Problem: Cost management is a persistent pain point for B2B buyers when procuring head gasket materials. As economic conditions fluctuate, especially in emerging markets, buyers must balance the need for high-quality materials with budget constraints. This often results in the temptation to choose cheaper alternatives that may not provide the necessary durability or performance, ultimately leading to higher long-term costs due to frequent replacements and repairs.
The Solution: To achieve cost-effectiveness without compromising quality, buyers should adopt a value-based procurement strategy. This includes evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Engage with suppliers to negotiate bulk purchasing agreements that can lower costs while ensuring consistent quality. Additionally, consider implementing a rigorous vendor evaluation process that assesses not only price but also reliability, delivery timelines, and support services. Establishing a long-term relationship with a trusted supplier can lead to better pricing and product innovations that enhance performance, ultimately creating a win-win scenario for both parties.

Illustrative image related to head gasket material
Strategic Material Selection Guide for head gasket material
What are the Key Properties of Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) Head Gaskets?
Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets are composed of multiple layers of stainless steel, typically ranging from three to five layers. This structure provides exceptional durability, allowing them to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for high-performance engines. MLS gaskets also exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, which is crucial in environments where coolant and oil may be present.
Pros: The primary advantages of MLS head gaskets include their robustness and reliability, which contribute to long-term engine performance. They are less prone to failure under extreme conditions compared to other materials.
Cons: However, the manufacturing complexity of MLS gaskets can lead to higher production costs. Additionally, their installation requires precise machining and surface preparation, which may complicate the manufacturing process for some suppliers.
Impact on Application: MLS gaskets are particularly well-suited for modern engines that operate under high stress, making them a preferred choice for automotive manufacturers in regions with demanding driving conditions.
Illustrative image related to head gasket material
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local automotive standards, such as ASTM or DIN, to guarantee quality and performance.
How Does Graphite Compare as a Head Gasket Material?
Graphite head gaskets are known for their flexibility and excellent thermal conductivity. They can conform to irregularities in the sealing surfaces, which enhances their sealing capability. Graphite gaskets can handle moderate temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for various engine types.
Pros: The flexibility of graphite allows for effective sealing, and its resistance to thermal cycling is beneficial in engines that experience frequent temperature fluctuations.
Cons: On the downside, graphite gaskets may not provide the same level of durability as MLS gaskets under extreme conditions. They are also less effective in preventing leaks compared to more advanced materials, which can lead to higher maintenance costs.
Illustrative image related to head gasket material
Impact on Application: Graphite gaskets are often used in older engine models or in applications where moderate performance is acceptable.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the potential for variations in quality and ensure that the graphite gaskets meet international standards for automotive components.
What Advantages Do Composite Head Gaskets Offer?
Composite head gaskets are made from a blend of materials, including graphite and aramid fibers. They provide a balance between sealing ability and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for a wide range of engine applications.
Pros: The primary advantage of composite gaskets is their affordability, making them accessible for manufacturers and repair shops operating on tight budgets. They also offer decent sealing capabilities for standard engines.
Cons: However, composite gaskets may not withstand high temperatures and pressures as effectively as MLS or copper gaskets, leading to a higher likelihood of failure in demanding applications.
Impact on Application: Composite gaskets are often used in standard passenger vehicles, but they may not be suitable for high-performance or heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the specific performance requirements of their engines and consider the longevity of composite gaskets when making purchasing decisions.
What are the Unique Features of Copper Head Gaskets?
Copper head gaskets are known for their exceptional thermal conductivity and strength. They are often used in high-performance applications where extreme conditions are expected.
Pros: The primary advantage of copper gaskets is their ability to handle high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for racing or modified engines.
Cons: However, copper gaskets require precise installation techniques, including the use of o-rings, which can complicate the manufacturing process. They are also generally more expensive than other materials.
Impact on Application: Copper gaskets are well-suited for specialized applications, such as racing or high-performance vehicles, where reliability under extreme conditions is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific installation requirements and ensure that their suppliers can meet the necessary manufacturing standards.
Summary Table of Head Gasket Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for head gasket material | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Layer Steel | High-performance engines | Exceptional durability and pressure resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
| Graphite | Older engine models | Flexibility and good thermal cycling resistance | Less durable under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Composite | Standard passenger vehicles | Cost-effective and decent sealing capability | Not suitable for high-performance applications | Low |
| Copper | Racing and high-performance applications | Superior thermal conductivity and strength | Requires precise installation and is expensive | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for head gasket material
What Are the Main Stages in Manufacturing Head Gasket Materials?
The manufacturing process for head gasket materials involves several critical stages that ensure high-quality products capable of withstanding the rigors of engine operation. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Head Gasket Production?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Depending on the chosen type of head gasket, various raw materials are sourced, including multi-layer steel, graphite, copper, and composites. Each material requires specific handling and treatment. For instance, steel layers may undergo processes such as annealing to improve ductility and strength, while graphite might be treated to enhance its thermal properties. Quality sourcing of raw materials is crucial; suppliers should provide certification to ensure compliance with international standards.
What Forming Techniques Are Utilized in Head Gasket Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming, which involves shaping them into the required dimensions. Techniques such as stamping and laser cutting are commonly employed to achieve precise shapes. For multi-layer steel gaskets, the layers are assembled and bonded using advanced adhesives or elastomers, which enhance their sealing properties. The forming stage must ensure that tolerances are maintained to avoid future sealing failures, as even minor deviations can lead to catastrophic engine damage.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for Head Gaskets?
The assembly stage is where the individual components are brought together. For multi-layer steel gaskets, this involves stacking the layers and applying pressure to bond them effectively. In the case of composite gaskets, layers of different materials may be fused together to create the final product. The assembly process must be conducted in a clean environment to prevent contamination, which can compromise the gasket’s performance.
What Finishing Techniques Are Important for Head Gasket Quality?
After assembly, finishing techniques come into play. This stage often involves surface treatment, such as coating with specialized materials to enhance resistance to heat and chemicals. Surface smoothness is critical; any imperfections can lead to sealing failures. Techniques like grinding or polishing are employed to achieve the necessary surface finish. Finally, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that the gaskets meet the required specifications.
How Does Quality Control Ensure the Integrity of Head Gasket Materials?
Quality control (QC) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for head gaskets, ensuring that each product meets international and industry-specific standards. Compliance with ISO 9001 is common, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking and API standards may apply, depending on the market and application.
Illustrative image related to head gasket material
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Head Gasket Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are critical throughout the manufacturing process. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) assesses raw materials upon arrival, ensuring they meet specified standards. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) takes place during manufacturing, where operators regularly check dimensions and material properties. Finally, Final Quality Control (FQC) involves comprehensive testing of finished products before they are shipped. This may include pressure testing, thermal cycling tests, and dimensional inspections to confirm that the gaskets meet or exceed performance expectations.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Validate Head Gasket Quality?
To ensure that head gaskets will perform reliably in engine applications, various testing methods are employed. These can include:
- Pressure Testing: Verifying that the gasket can withstand the pressure exerted during engine operation.
- Thermal Cycling Tests: Assessing the gasket’s performance under extreme temperature variations to simulate engine conditions.
- Leak Testing: Checking for any potential leaks that could compromise engine integrity.
These tests help identify any weaknesses in the gasket design or manufacturing process, allowing for corrective measures before the product reaches the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential. Buyers should consider the following approaches:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. These audits can be performed in-house or by third-party organizations.
- Certification Review: Buyers should request and review copies of relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, CE, or API. These documents serve as evidence of compliance with quality standards.
- Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can occur at various stages of production, offering peace of mind to buyers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must also be aware of specific nuances related to quality control. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that could impact the performance of head gaskets. For example, gaskets sold in Europe may need to comply with stricter environmental regulations compared to those in other regions. Understanding these differences is crucial for avoiding legal and operational issues.
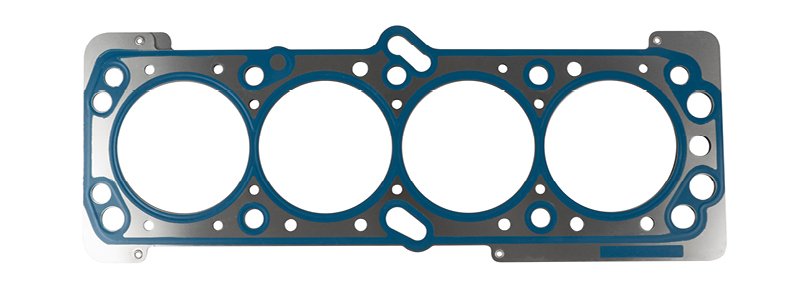
Illustrative image related to head gasket material
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can complicate communication regarding quality standards. Buyers should establish clear lines of communication with suppliers and consider employing translators or local representatives who can facilitate understanding.
Conclusion: Why Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance Matter for B2B Buyers
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for head gasket materials are vital for ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ultimately safeguarding their operations against costly failures. Investing time in verifying quality control measures will pay dividends in the long run, leading to enhanced engine performance and customer satisfaction.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘head gasket material’
In the competitive landscape of automotive components, selecting the right head gasket material is crucial for ensuring engine integrity and performance. This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers aiming to procure high-quality head gasket materials suitable for various applications. Follow these steps to make informed decisions and enhance your sourcing process.

Illustrative image related to head gasket material
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for your engine is the first step in sourcing head gasket materials. Consider factors such as operating temperatures, pressure levels, and compatibility with engine fluids. This clarity will help in narrowing down the material options, ensuring they meet the demands of your application.
- Consider engine type: Is it a high-performance engine or a standard one?
- Assess environmental conditions: Will the gaskets be exposed to extreme temperatures or corrosive substances?
Step 2: Research Material Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of head gasket materials available in the market. Common options include Multi-Layer Steel (MLS), copper, graphite, and composite materials. Each type has distinct advantages depending on the application and performance needs.
- MLS: Known for durability and high-pressure resistance, ideal for modern engines.
- Copper: Offers excellent sealing but may require specialized installation techniques.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to verify their certifications and industry standards compliance. This ensures that the materials meet quality and safety benchmarks, minimizing the risk of failures.
- ISO Certifications: Look for suppliers with ISO 9001 or equivalent certifications.
- Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about their testing protocols for material integrity.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples before making bulk purchases. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the material’s performance in real-world conditions, ensuring it meets your specifications.
- Conduct stress tests: Assess how the material holds up under pressure and temperature variations.
- Check compatibility: Verify that the material works well with the engine fluids it will encounter.
Step 5: Assess Supplier Reliability and Support
A reliable supplier not only provides quality materials but also offers robust customer support. Evaluate their track record in delivering on time and their responsiveness to inquiries.
- Request references: Speak to other clients about their experiences with the supplier.
- Evaluate communication: Ensure they have a dedicated support team that can assist with technical queries.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. A well-structured agreement can lead to better pricing and flexibility.
- Consider bulk purchasing discounts: Many suppliers offer reduced rates for larger orders.
- Discuss warranty options: Understand the terms of warranty in case of material failure.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract and Place Orders
After thorough evaluation and negotiation, finalize the contract with your chosen supplier. Ensure all specifications, terms, and conditions are clearly outlined to avoid future disputes.
- Review all details: Double-check quantities, delivery timelines, and pricing.
- Maintain open communication: Keep a line of communication open with the supplier for any follow-up questions or adjustments.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for head gasket materials, ensuring they choose options that enhance engine performance and longevity.

Illustrative image related to head gasket material
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for head gasket material Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Head Gasket Material Sourcing?
When sourcing head gasket materials, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) gaskets, for instance, are more expensive than composite or graphite options due to their durability and performance. The price can also vary based on the quality and source of the raw materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to skilled technicians involved in the manufacturing process. Complex gaskets, such as those requiring precise engineering, may incur higher labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running the manufacturing facility, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. High-quality production often requires advanced machinery, which can elevate overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for producing specific gasket types can be substantial. Custom designs or unique specifications may require specialized tools, contributing to higher costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that head gaskets meet stringent quality standards involves rigorous testing and inspection processes, which can add to overall costs. Certifications for quality assurance also influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs can vary based on the distance from the manufacturing site to the buyer’s location. Buyers should factor in shipping fees, customs duties, and potential tariffs, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their expenses and generate profit. This margin can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Head Gasket Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of head gasket materials:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers are more willing to negotiate prices for bulk purchases, making it advantageous for buyers to plan ahead.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements can lead to increased costs. Standard gaskets may be more economical, so buyers should assess their needs carefully.
-
Materials: The choice of material directly affects pricing. For example, MLS gaskets, while more expensive, offer superior performance, potentially justifying their higher cost in applications where reliability is crucial.
-
Quality and Certifications: Gaskets that meet specific industry standards or certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in high-quality materials.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Local suppliers may offer lower shipping costs, while international suppliers might provide competitive rates but could introduce complexities in logistics.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms agreed upon in the contract is vital. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, impacting overall pricing.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Head Gasket Procurement?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic approaches can enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume purchases to negotiate better pricing. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to favorable terms and discounts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront cost but the total cost associated with the product over its lifecycle. Investing in higher-quality gaskets may reduce maintenance and replacement costs in the long run.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and shipping times when sourcing internationally. These factors can significantly impact the final cost and delivery timeline.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Compare quotes, check references, and assess their production capabilities to ensure you are getting the best value for your investment.
Conclusion
The cost and pricing dynamics of head gasket materials are complex, driven by various components and influencers. By understanding these factors and employing strategic procurement practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always consider these insights as indicative, and conduct detailed assessments tailored to your specific circumstances before finalizing any agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing head gasket material With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Traditional Head Gasket Material
In the world of automotive engineering, the head gasket plays a critical role in maintaining engine integrity by sealing the combustion chamber and preventing oil and coolant leaks. While traditional head gasket materials like Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) are widely used, there are several alternative solutions that can also achieve effective sealing. This section examines these alternatives, providing valuable insights for B2B buyers in international markets.
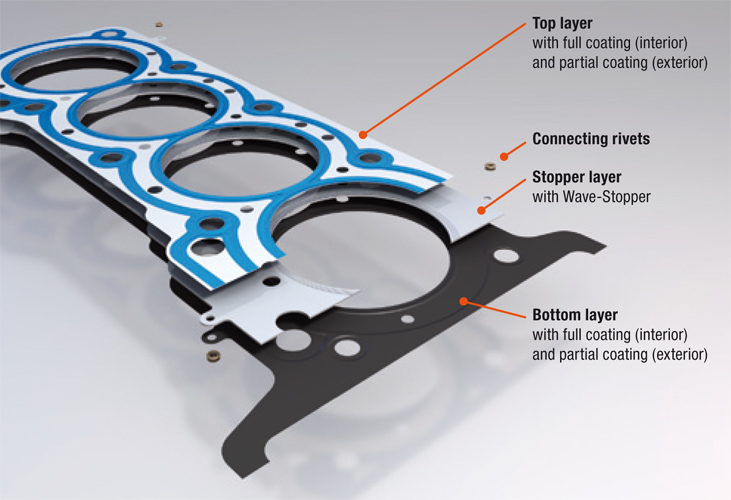
Illustrative image related to head gasket material
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Head Gasket Material | Alternative 1: Copper Gaskets | Alternative 2: Composite Gaskets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent sealing under high pressure and temperature; durable for high-performance engines. | Superior thermal conductivity and strength; effective for high-stress applications. | Good sealing capability but less effective in extreme conditions; may require frequent replacements. |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost, especially for high-performance MLS gaskets. | Moderate cost; installation requires special tools, adding to overall expenses. | Typically lower cost, making them attractive for budget-conscious applications. |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation; can be used in most modern engines. | Requires specialized installation techniques, including o-ringing. | Easy to install; compatible with older engine designs. |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance required; designed for longevity. | May require regular checks for tightness; potential for corrosion over time. | Requires more frequent monitoring and replacement due to wear. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for modern, high-performance engines requiring reliable sealing. | Best for racing applications or high-performance builds needing superior heat management. | Suitable for older vehicles or budget-sensitive applications where high performance is not critical. |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Copper Gaskets
Copper gaskets are known for their excellent thermal conductivity and strength, making them suitable for high-performance engines that experience significant temperature fluctuations. They provide a robust seal and are effective in preventing leakage. However, their installation is more complex, requiring special tools and techniques such as o-ringing, which can increase labor costs. Additionally, copper gaskets may be prone to corrosion over time, necessitating more frequent checks and maintenance.
Composite Gaskets
Composite gaskets are often a cost-effective solution, especially for older vehicle models. Made from a mix of materials, including graphite, they offer decent sealing capabilities and are easier to install than copper options. However, they may not perform as well under extreme temperatures and pressures, leading to a higher likelihood of failure compared to MLS and copper gaskets. This can result in more frequent replacements, which could offset their initial cost advantage in the long run.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When selecting a head gasket material or an alternative solution, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider their specific application requirements, including engine type, performance expectations, and budget constraints. For high-performance applications, Multi-Layer Steel gaskets remain the gold standard due to their durability and reliability. Conversely, for older or less demanding engines, copper or composite gaskets may present viable options that balance cost and performance. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each material will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for head gasket material
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Head Gasket Material?
When selecting head gasket material, several critical technical specifications must be understood to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of an engine. Here are the essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the head gasket material, which can significantly affect its performance. Common grades include Multi-Layer Steel (MLS), copper, and composite materials. The choice of material grade impacts factors such as thermal conductivity, pressure resistance, and corrosion resistance, all of which are vital for maintaining engine integrity under varying operational conditions. -
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio is a crucial specification that indicates the degree to which the head gasket can compress under engine pressure. A higher compression ratio typically means better performance but also demands a more robust head gasket. Understanding this ratio is essential for buyers to ensure compatibility with specific engine designs and performance expectations. -
Thickness Tolerance
Thickness tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the thickness of the head gasket material. This property is significant as it affects the sealing performance and the fit between the cylinder head and engine block. Precise thickness is crucial for achieving the right compression and preventing leaks, which can lead to catastrophic engine failure. -
Temperature Resistance
Temperature resistance denotes the ability of the head gasket material to withstand extreme heat without degrading. This property is vital for engines operating under high-performance conditions or in extreme climates. Selecting a gasket with suitable temperature resistance ensures longevity and reliability, reducing the risk of failure due to overheating. -
Sealing Capability
Sealing capability measures how effectively the head gasket can prevent leaks between the engine components. This property is influenced by the material composition and design of the gasket. High sealing capability is essential to maintain the separation of oil, coolant, and combustion gases, which is critical for engine performance and durability. -
Durability and Lifespan
Durability refers to the ability of the head gasket to withstand mechanical stress and environmental factors over time. A durable gasket minimizes the need for replacements and repairs, offering cost savings for B2B buyers. Understanding the expected lifespan of different materials helps in making informed purchasing decisions.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Head Gasket Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms used in the head gasket sector:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to components that are produced by the original manufacturer of the vehicle. In the context of head gaskets, OEM parts are often preferred for their guaranteed compatibility and performance. Buyers should consider OEM gaskets for maintaining warranty coverage and ensuring the reliability of repairs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers looking to manage inventory effectively or negotiate pricing. Suppliers may offer better pricing for larger orders, making it beneficial to understand their MOQ policies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request made by buyers to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for a specific product. In the head gasket market, submitting an RFQ can help businesses compare offers from multiple suppliers and negotiate better deals. -
Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are standardized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping, insurance, and liability, ensuring smooth logistics and reducing potential disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes for an order to be processed and shipped. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their procurement schedules and manage inventory levels effectively, especially in industries where timing is critical. -
Aftermarket
The aftermarket refers to the market for parts and accessories that are not sourced from the original manufacturer. Many buyers consider aftermarket head gaskets for cost-effectiveness and availability. However, it is vital to assess the quality and compatibility of aftermarket parts to ensure they meet required performance standards.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the most suitable head gasket materials for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the head gasket material Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Impacting the Head Gasket Material Market?
The head gasket material market is currently influenced by several global drivers, including the rapid evolution of automotive technologies, heightened focus on performance and efficiency, and the ongoing transition towards electric vehicles (EVs). As manufacturers strive to meet stringent emissions regulations and consumer demand for high-performance vehicles, the choice of head gasket material becomes increasingly critical. Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) gaskets, for instance, are gaining popularity due to their superior sealing capabilities and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for both traditional combustion engines and emerging hybrid technologies.
B2B tech trends are also shaping sourcing strategies, with digital platforms facilitating real-time inventory management and procurement processes. International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (e.g., Saudi Arabia and Nigeria) are increasingly leveraging these technologies to streamline their supply chains and improve cost-efficiency. Moreover, the rise of additive manufacturing (3D printing) is opening up new avenues for producing custom gaskets, allowing for greater flexibility in material choice and design specifications. This trend is particularly beneficial for manufacturers looking to cater to niche markets or specialized applications.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Head Gasket Material Sector?
The environmental impact of head gasket materials is an important consideration for B2B buyers, as the automotive industry increasingly prioritizes sustainability. Traditional materials, such as asbestos and certain metals, pose significant environmental and health risks, leading to a shift towards safer, greener alternatives. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who utilize sustainable materials, such as composites made from recycled resources or bio-based polymers, which can significantly reduce their carbon footprint.
Ethical supply chains are equally vital in today’s B2B landscape. Sourcing materials from suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards not only enhances brand reputation but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the Global Recycle Standard (GRS) can serve as benchmarks for buyers looking to ensure the sustainability of their sourcing practices. By prioritizing suppliers with such certifications, companies can align their procurement strategies with broader corporate social responsibility goals.
What Has Been the Evolution of Head Gasket Materials Over Time?
Historically, head gaskets were primarily made from materials like asbestos and copper, which offered adequate sealing but posed significant health risks and limitations in high-performance applications. The advent of composite materials in the late 20th century marked a significant shift, allowing for improved flexibility and durability. However, the real game-changer has been the development of Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) gaskets, which combine multiple layers of steel to provide unmatched sealing capabilities under extreme conditions.
As automotive technology advances, the focus on innovative materials continues to evolve, with manufacturers increasingly exploring advanced composites and synthetic materials. This evolution not only reflects the demands for enhanced performance but also aligns with the industry’s commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing. B2B buyers can leverage this historical context to make informed decisions about the materials they choose for their applications, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly changing market.

Illustrative image related to head gasket material
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of head gasket material
-
How do I choose the right head gasket material for my engine?
Selecting the appropriate head gasket material involves considering factors like engine type, operating conditions, and performance requirements. Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) gaskets are ideal for high-performance applications due to their durability and resistance to high pressures and temperatures. Conversely, if your engine experiences significant thermal cycling, a graphite gasket may be more suitable due to its flexibility. Always consult with your supplier to ensure compatibility with your specific engine model and requirements. -
What are the common types of head gasket materials used in automotive applications?
The most common head gasket materials include Multi-Layer Steel (MLS), copper, composite, and elastomeric. MLS gaskets are favored for their strength and sealing capabilities, while copper gaskets provide excellent thermal conductivity but require careful installation. Composite gaskets, made from materials like graphite, offer flexibility but are less common in modern engines. Elastomeric gaskets feature a steel core with rubber coatings, providing good sealing for a range of applications. Understanding these types will help you make informed sourcing decisions. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for head gasket materials?
When evaluating suppliers, consider their manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and experience in the industry. Request samples to assess the quality of their products and inquire about their production processes to ensure they adhere to industry standards. Additionally, check for customer reviews and references, especially from clients in your region, to gauge reliability and service levels. Communication is key; a responsive supplier can significantly enhance your sourcing experience. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for head gasket materials?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely based on the supplier and the specific material required. Generally, MOQs may range from a few dozen to several thousand units, particularly for customized orders. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your business requirements. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for first-time buyers or bulk orders, so don’t hesitate to ask. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing head gasket materials internationally?
Payment terms vary by supplier and can include options such as upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. Common methods include bank transfers, letters of credit, or payment through escrow services for added security. It’s advisable to clarify payment terms before finalizing any agreements to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for head gasket materials?
To maintain high-quality standards, request documentation of the supplier’s QA processes, including certifications like ISO 9001. Ask for test reports or certificates of compliance for the materials used, and inquire about their inspection methods during production. Many reputable suppliers will offer warranties or guarantees on their products, providing additional assurance of quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing head gasket materials?
Logistics play a crucial role in international sourcing. Consider factors such as shipping methods, transit times, customs clearance, and local regulations in your country. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure compliance with documentation and tariffs. Additionally, partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can help streamline the import process, minimizing delays and unexpected costs. -
How can I customize head gasket materials for specific engine applications?
Customization options often depend on the supplier’s capabilities. Discuss your specific requirements, such as dimensions, material composition, and performance specifications, with potential suppliers. Many manufacturers can create bespoke solutions tailored to your engine’s needs, whether you require unique shapes, thicknesses, or material blends. Be prepared to provide detailed technical specifications to ensure the final product meets your expectations.
Top 5 Head Gasket Material Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. ALL ABOUT RUBBER – Reinforced Graphite Composite Cylinder Head Gasket Sheet
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Reinforced Graphite Composite Cylinder Head Gasket Sheet”, “dimensions”: “3/32 x 12 x 12 inches”, “price”: “$47.49”, “original_price”: “$49.99”, “discount”: “5% off”, “shipping”: “Free”, “seller”: “ALL ABOUT RUBBER”, “seller_feedback”: “99.8% positive feedback”, “payment_options”: “4 interest-free payments of $11.87 available with Klarna”, “estimated_delivery”: “Sat, Sep 13 – Wed…
2. Homeshop Machinist – Gasket Material
Domain: bbs.homeshopmachinist.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1. Original gasket material: Black, approximately .031″ thick, sheet size 8″ x 9.5″, easily cut with scissors, heat resistant, no metallic insert. 2. Replacement material: Fel-Pro #3157, 1/32″ thick, claims resistance to oil, water, gasoline, rubber/fiber construction, doubts about heat resistance. 3. New order: McMaster Carr High Temperature Carbon Buna-N Gasket Material #13015k51, 15″ square, 1/…
3. Haynes – Multi-Layer Steel Head Gaskets
Domain: us.haynes.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Haynes – Multi-Layer Steel Head Gaskets, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Practical Machinist – Engine Head Gasket Materials
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Suitable materials for small engine head gaskets include: 1. Soft aluminum (3003, 0.050 or 1/16″ thickness) – compresses well to fill irregularities. 2. Fully annealed thin copper sheet (max 1/16″) – recommended for durability. 3. Automotive gasket material – can be used with high-tack adhesive. 4. Steel core gasket material with paper/rubber layers – available at NAPA (P.N. JV222). 5. Household s…
5. On All Cylinders – High-Performance Gaskets
Domain: onallcylinders.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Carbon Gaskets: Superior sealing, withstand high temperatures, ideal for nitrous/turbo applications. Composite Gaskets: Resist coolant, gasoline, alcohol, oil; easy to trim; maintain torque retention. Copper Gaskets: Durable, distribute heat evenly, conform to rough surfaces, embossed edges for tight seal. Cork Gaskets: Positive seal, compressible, withstand high-vacuum/temperature, extra-thick op…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for head gasket material
As international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing head gasket materials, understanding the critical role that material selection plays in engine performance is essential. Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) gaskets stand out for their durability and ability to withstand extreme conditions, making them a preferred choice for high-performance applications. Buyers should also consider the specific requirements of their engines, as alternatives like copper, composite, and elastomeric gaskets each have unique benefits and limitations.
Strategic sourcing of head gasket materials not only mitigates the risk of engine failure but also enhances operational efficiency and reduces long-term costs associated with repairs. By partnering with reliable manufacturers who offer tailored solutions, buyers can ensure they acquire the right materials that align with their operational needs.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced head gasket solutions is likely to increase, driven by evolving engine technologies and environmental regulations. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to explore innovative materials and suppliers that can support their growth. Investing in quality head gasket materials today will pave the way for sustained performance and reliability in the future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.