Everything You Need to Know About Screw Shaft Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for screw shaft
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable screw shafts can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re operating in the manufacturing sectors of Nigeria or Brazil, the need for high-quality, precision-engineered components is paramount. This guide aims to demystify the global market for screw shafts, providing insights into various types, their applications across industries, and essential considerations for supplier vetting.
With a focus on practical advice, we will explore the nuances of screw shaft specifications, including lead screw options and thread orientations that best suit your operational requirements. Additionally, we will cover critical factors such as pricing structures and the importance of understanding local and international compliance standards.
By equipping B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide serves as a comprehensive resource. It empowers organizations to navigate the complexities of sourcing screw shafts, ensuring that you not only meet but exceed your engineering and manufacturing goals. As you delve into this guide, expect actionable insights that will streamline your procurement process and enhance your operational efficiency.
Understanding screw shaft Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Screw Shafts | Trapezoidal threads, various end configurations, robust design | Machine tools, linear actuators, robotics | Pros: High precision, reliable for linear motion; Cons: Slower than ball screws. |
| Ball Screw Shafts | Rolling elements reduce friction, high efficiency | CNC machines, automation systems | Pros: High efficiency, smooth motion; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Acme Screw Shafts | Square threads, designed for power transmission | Lifts, presses, and heavy machinery | Pros: Strong and durable; Cons: Less efficient than lead screws. |
| Trapezoidal Screw Shafts | 30-degree thread angle, available in left/right-hand threads | Linear actuators, jacks, and positioning systems | Pros: Good load capacity; Cons: Limited speed capabilities. |
| Custom Screw Shafts | Tailored dimensions and specifications to meet specific needs | Specialized machinery, unique applications | Pros: Perfect fit for specific applications; Cons: Longer lead times and costs. |
What Are Lead Screw Shafts and Their Applications in B2B?
Lead screw shafts are characterized by their trapezoidal thread profiles, which facilitate linear motion. These shafts come in various configurations, including straight and stepped designs, making them versatile for applications in machine tools, robotics, and automation systems. When purchasing lead screw shafts, B2B buyers should consider factors such as load capacity, thread orientation (right or left-handed), and surface treatments for corrosion resistance. Their reliability and precision make them a preferred choice for applications requiring accurate positioning.
How Do Ball Screw Shafts Enhance Efficiency?
Ball screw shafts utilize rolling elements that minimize friction, resulting in high efficiency and smooth operation. These shafts are predominantly used in CNC machines and automation systems, where precision and speed are critical. Buyers should evaluate the load ratings, travel length, and the need for precision in their applications. Although ball screws can be more expensive initially, their long-term efficiency and reduced wear often justify the investment for businesses focused on high-performance machinery.
Why Choose Acme Screw Shafts for Heavy Machinery?
Acme screw shafts feature square threads designed for efficient power transmission, making them suitable for heavy machinery applications such as lifts and presses. Their robust construction allows them to handle significant loads, providing durability in demanding environments. B2B buyers should consider the thread pitch and material when selecting Acme screws, as these factors influence strength and performance. While they may not be as efficient as lead or ball screws, their strength and reliability make them a valuable option for heavy-duty applications.
What Are the Benefits of Trapezoidal Screw Shafts?
Trapezoidal screw shafts, with their 30-degree thread angle, are commonly used in linear actuators and jacks. They offer good load-bearing capabilities and are available in various thread orientations. When sourcing trapezoidal screws, buyers should assess the required precision, load capacity, and speed of operation. These screws are advantageous for applications where load stability is paramount, although they may have limitations in speed compared to ball screws.
How Can Custom Screw Shafts Meet Unique Business Needs?
Custom screw shafts can be engineered to meet specific dimensions and specifications, making them ideal for specialized machinery and unique applications. When opting for custom solutions, B2B buyers should communicate their exact requirements, including material, dimensions, and load specifications. While custom shafts may involve longer lead times and higher costs, the tailored fit can significantly enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness in niche markets.
Key Industrial Applications of screw shaft
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of screw shaft | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs | Quality assurance and precision engineering specifications |
| Agriculture | Seeders and planters | Enhances planting accuracy and crop yields | Durability in harsh environments and compatibility with machinery |
| Automotive | Vehicle lift systems | Improves safety and maintenance efficiency | Load capacity and material durability |
| Robotics | Linear actuators for robotic arms | Increases precision in automated tasks | Customization options and integration with existing systems |
| Medical Equipment | Surgical table adjustments | Ensures precision and patient safety | Compliance with medical standards and reliability |
How is ‘screw shaft’ used in manufacturing and what problems does it solve?
In the manufacturing sector, screw shafts are integral to automated assembly lines, facilitating precise linear movements for various components. They help streamline production processes, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should consider sourcing screw shafts that meet stringent quality assurance standards. This includes ensuring they are manufactured with high precision to minimize wear and tear, which can lead to costly downtimes.
What role does ‘screw shaft’ play in agriculture and what are the benefits?
In agriculture, screw shafts are commonly used in seeders and planters, where they enable accurate planting depth and spacing. This precision enhances crop yields and optimizes resource use, a critical advantage for farmers looking to maximize their output. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should focus on screw shafts designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring durability and reliability in their agricultural machinery.
How does ‘screw shaft’ enhance safety in the automotive sector?
In the automotive industry, screw shafts are utilized in vehicle lift systems, which are essential for safe maintenance and repair operations. These shafts provide reliable lifting and lowering capabilities, improving safety for technicians and reducing the risk of accidents. When sourcing screw shafts for automotive applications, businesses must prioritize load capacity and material durability to ensure long-term performance and safety compliance.
Why are ‘screw shafts’ critical for robotics applications?
For robotics, screw shafts are vital components in linear actuators, enabling robotic arms to perform precise movements. This precision is crucial for tasks such as assembly, welding, and painting, where accuracy directly impacts product quality. International B2B buyers should consider customization options when sourcing screw shafts, ensuring they can integrate seamlessly with existing robotic systems to enhance operational efficiency.
What compliance standards should be considered in medical applications of ‘screw shafts’?
In the medical equipment sector, screw shafts are used for adjusting surgical tables, ensuring precise positioning for patient safety during procedures. The reliability of these components is paramount, as any failure can have serious consequences. Buyers from Europe and other regions should ensure that the screw shafts they source comply with medical standards and certifications, focusing on quality and reliability to ensure patient safety and operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘screw shaft’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing the Right Screw Shaft for Unique Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing screw shafts that meet specific application requirements. For instance, a manufacturing plant in Brazil may need a screw shaft that not only fits a particular size but also has unique threading characteristics for a specialized machine. This can lead to delays in production and increased costs if the wrong component is sourced, or if the buyer has to go through multiple iterations to find the right fit. The complexity increases when considering factors such as material durability, corrosion resistance, and load capacity, which vary significantly across industries and applications.

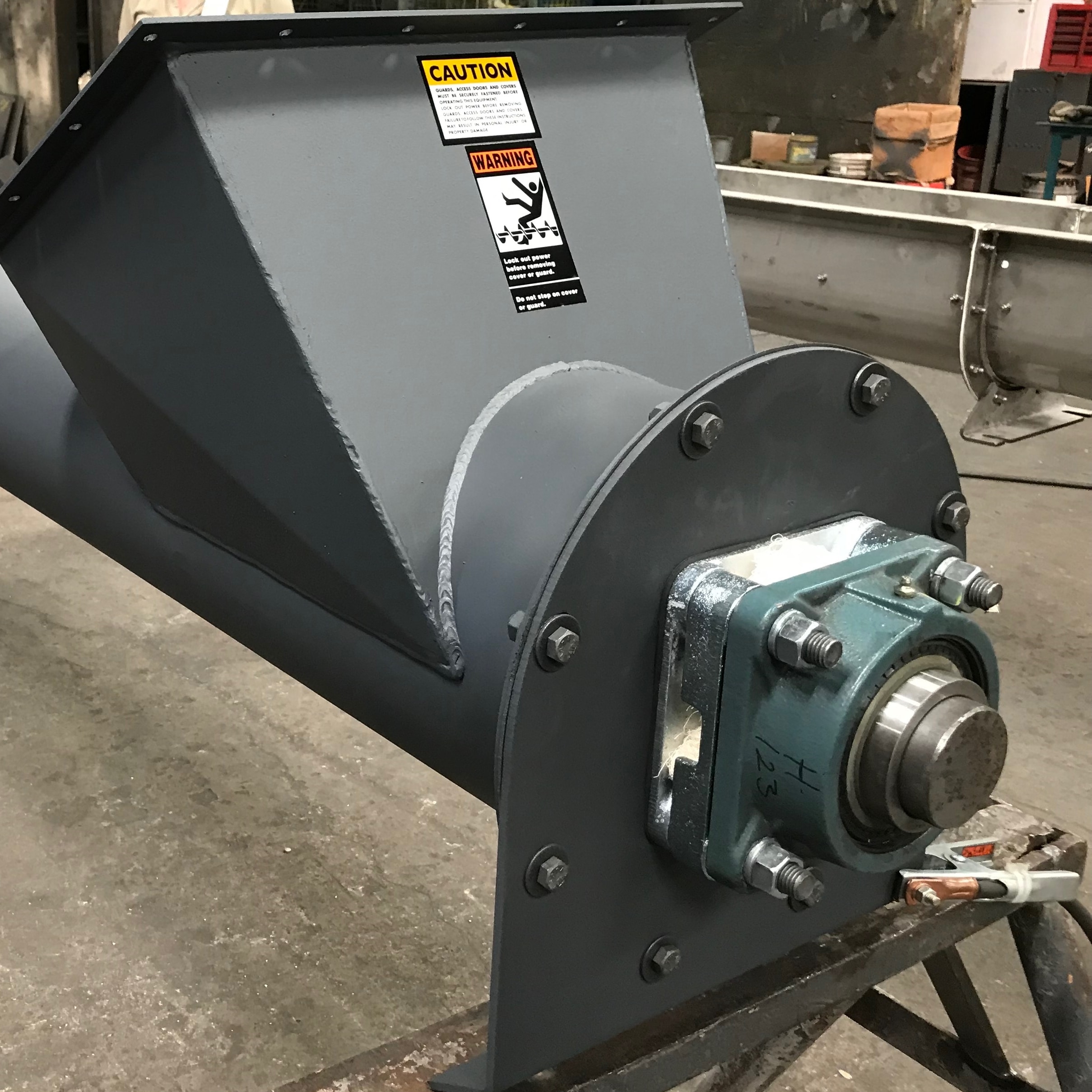
Illustrative image related to screw shaft
The Solution: To effectively address this pain point, buyers should engage with manufacturers or suppliers that offer customizable screw shafts. Look for companies that provide detailed specifications and allow for modifications based on specific application needs. When requesting quotes, buyers should provide comprehensive details about their machinery, including the type of threading required, the operating environment, and any relevant load or speed requirements. This approach ensures that the supplied screw shaft meets the precise operational demands, thereby reducing the risk of delays and additional costs. Utilizing CAD tools offered by suppliers can also help visualize the components before purchase, minimizing the chances of errors.
Scenario 2: Dealing with Lead Time and Inventory Challenges
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant lead time challenges when ordering screw shafts, particularly when working with international suppliers. For instance, a distributor in Nigeria may require screw shafts urgently for a local assembly line but finds that the lead times from overseas manufacturers are prohibitive. This situation can lead to production halts, unsatisfied clients, and lost revenue, particularly in industries where time-to-market is critical.
The Solution: To mitigate lead time issues, buyers should consider establishing relationships with local or regional suppliers who maintain an inventory of screw shafts. These suppliers can offer quicker delivery times and more flexible ordering processes. Additionally, buyers can implement a just-in-time (JIT) inventory strategy that aligns closely with production schedules, ensuring that the required components are available when needed without overstocking. Regular communication with suppliers regarding anticipated demand and potential changes in production can also help in securing priority processing of orders.
Scenario 3: Addressing Quality Control and Performance Reliability
The Problem: Quality control is a pressing concern for buyers of screw shafts, especially in high-stakes environments such as aerospace or automotive manufacturing. A buyer in South America may experience issues with screw shafts that do not meet quality standards, leading to equipment failures and safety risks. These quality discrepancies can arise from variations in manufacturing processes, material defects, or inadequate testing protocols, ultimately affecting the reliability of the final product.
The Solution: To ensure high-quality screw shafts, buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers with established quality assurance processes. Look for suppliers that provide certifications and test reports for their products, demonstrating compliance with relevant industry standards. Additionally, buyers can request samples or prototypes before placing larger orders to assess quality firsthand. Establishing a robust feedback loop with suppliers helps to address any quality concerns promptly and encourages continuous improvement in the manufacturing process. Furthermore, leveraging third-party inspection services for critical components can provide an extra layer of assurance, enhancing product reliability and performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for screw shaft
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Screw Shafts?
When selecting materials for screw shafts, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly affect the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the screw shaft in various applications.
Steel: A Versatile Choice for Screw Shafts
Steel is one of the most commonly used materials for screw shafts due to its excellent strength and durability. It typically offers high tensile strength, making it suitable for applications requiring significant load-bearing capacity. Steel also has good machinability, which allows for precise manufacturing of screw threads.
Pros: Steel’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials, making it a popular choice among manufacturers.
Cons: Steel is susceptible to corrosion, especially in humid or chemically aggressive environments. This limitation necessitates additional treatments such as galvanization or coating, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Steel screw shafts are compatible with a wide range of media, including water and oils. However, they may not be suitable for environments with high corrosion risk without protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or ISO. Additionally, the availability of corrosion-resistant options may vary by region.
Stainless Steel: Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel is an alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments. It maintains its strength at elevated temperatures and is often used in food processing and medical applications.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, which extends the lifespan of screw shafts in challenging conditions. It also requires minimal maintenance.
Cons: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than standard steel, which can impact budget considerations. Its lower machinability compared to carbon steel may also lead to higher manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel screw shafts are ideal for applications in wet or corrosive environments, such as food and beverage processing or marine applications. However, they may not be the best choice for high-load applications due to their lower tensile strength compared to carbon steel.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA regulations) is crucial for buyers in the food industry. Buyers in Europe should also be aware of EU regulations regarding material safety.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Aluminum screw shafts are increasingly popular due to their lightweight nature and good corrosion resistance. This material is often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight properties reduce the overall weight of machinery, enhancing energy efficiency. It is also less expensive than many high-grade steels, making it an attractive option for cost-sensitive projects.
Cons: While aluminum has good strength, it is generally not as strong as steel, which limits its use in high-load applications. Additionally, its lower melting point can be a concern in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum screw shafts are suitable for applications involving low to moderate loads and are compatible with various media, including water and some chemicals. However, they may not be suitable for high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local standards such as ASTM and JIS. The availability of aluminum alloys may vary, impacting the selection process.
Plastic: A Lightweight Alternative for Specific Applications
Plastic screw shafts, often made from materials like nylon or PVC, offer unique advantages in specific applications, particularly where chemical resistance and low friction are required.
Pros: Plastic screw shafts are lightweight, non-corrosive, and can be manufactured with low friction properties, making them ideal for applications in chemical processing and food handling.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastic is its lower strength compared to metals, which restricts its use in high-load applications. Additionally, plastics can degrade under UV exposure and high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastic screw shafts are excellent for applications involving corrosive chemicals or where electrical insulation is necessary. However, they may not be suitable for heavy-duty mechanical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant safety and environmental standards, particularly in industries like food processing. The availability of specific plastic materials may also vary by region.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Screw Shafts
| Material | Typical Use Case for screw shaft | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy machinery, automotive applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, lower machinability | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower strength, not suitable for high loads | Medium |
| Plastic | Chemical processing, food handling | Non-corrosive, low friction properties | Lower strength, UV sensitivity | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for screw shafts, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for screw shaft
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Screw Shafts?
The manufacturing process of screw shafts involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Typically Used for Screw Shafts?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Screw shafts are primarily made from metals like stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel due to their strength and durability. These materials are selected based on the intended application and environmental conditions. For example, stainless steel is often preferred for applications requiring corrosion resistance, while carbon steel is suitable for high-strength requirements.
During this phase, raw materials are inspected for quality, and specifications are verified. This preliminary quality control (QC) step is essential for ensuring that the materials used will perform as expected in the final product.
How Is the Forming Process of Screw Shafts Executed?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming. This process involves shaping the raw material into the desired screw shaft geometry through various techniques such as:
- Turning: A lathe machine rotates the material, and cutting tools shape it into the precise dimensions required for screw threads.
- Milling: This technique is used to create complex shapes and features that may be needed on the screw shaft.
- Thread Rolling: This method forms threads by deforming the material rather than cutting it, which enhances strength and surface finish.
Each of these techniques has its advantages, and the choice often depends on the desired precision, volume, and cost-effectiveness of the production.
What Steps Are Involved in the Assembly and Finishing of Screw Shafts?
Once the screw shafts are formed, they undergo assembly and finishing processes. Assembly may involve attaching additional components, such as nuts or bearings, which are critical for the screw shaft’s functionality in its intended application.
Finishing processes include:
- Heat Treatment: This improves the mechanical properties of the screw shafts, such as hardness and tensile strength.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as plating, anodizing, or applying a black oxide coating enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetics.
- Precision Machining: Further machining operations may be required to ensure that the screw threads meet tight tolerances and surface finish requirements.
This comprehensive approach to assembly and finishing is crucial for ensuring that the screw shafts perform reliably in their applications.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Screw Shaft Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the screw shafts meet international and industry-specific standards. Buyers must understand these QA practices to ensure they are sourcing high-quality products.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
International standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems, are essential for manufacturers of screw shafts. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that the manufacturing process is consistently monitored and improved, leading to high-quality products.
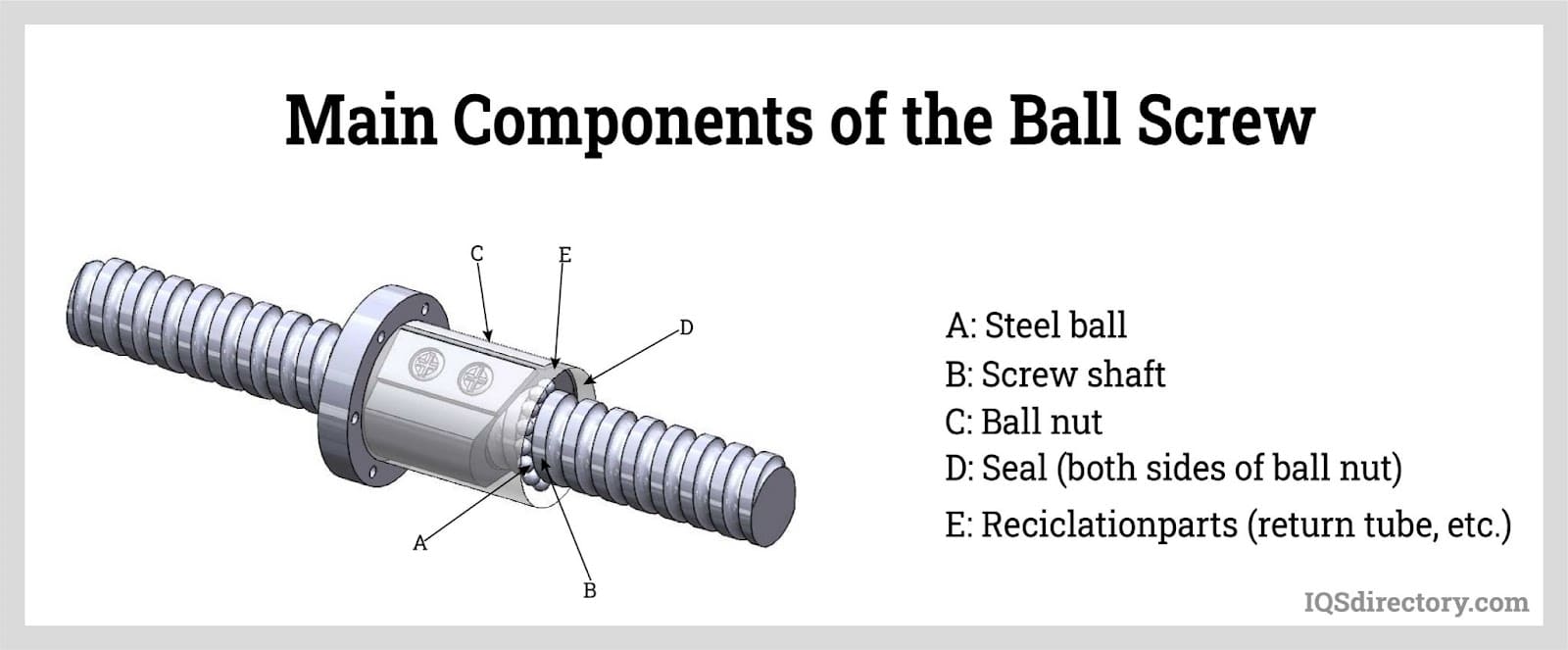
Illustrative image related to screw shaft
Additionally, industry-specific certifications may be relevant, depending on the application of the screw shafts. For instance:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for screw shafts used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet strict performance and safety criteria.
Understanding these standards helps buyers assess the reliability and quality of potential suppliers.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Screw Shaft Manufacturing?
Throughout the manufacturing process, several quality control checkpoints are crucial for maintaining product integrity:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is essential to detect any deviations from quality standards. This includes regular measurements and visual inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is completed, the final products undergo rigorous testing to verify that they meet all specifications and performance criteria.
Implementing these QC checkpoints ensures that any issues are identified and addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of defective products reaching the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:

Illustrative image related to screw shaft
What Auditing Methods Can Buyers Use?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a manufacturer’s quality assurance processes. Buyers can either perform audits themselves or hire third-party inspection services to evaluate the supplier’s facilities, processes, and adherence to quality standards.
During an audit, buyers should focus on:
- Documentation: Review quality management system documentation, including quality manuals, process maps, and records of previous audits.
- Physical Inspections: Examine production processes, machinery, and working conditions to ensure compliance with safety and quality standards.
- Employee Training: Assess the qualifications and training of employees involved in the manufacturing and quality control processes.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Screw Shafts?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and performance of screw shafts, including:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of the material.
- Hardness Testing: Determines the hardness of the screw shaft, which correlates with its wear resistance.
- Dimensional Inspection: Verifies that the screw shafts meet the specified dimensions and tolerances using tools like calipers and gauges.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing are used to detect internal defects without damaging the product.
By understanding these testing methods, B2B buyers can better evaluate the quality assurance practices of their suppliers.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face specific challenges when sourcing screw shafts. Key considerations include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international regulations, as failure to meet these can lead to delays and increased costs.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can enhance communication and collaboration, facilitating better quality assurance.
- Logistics and Shipping: Assess the supplier’s logistics capabilities to ensure that products can be delivered on time and in compliance with quality standards.
By keeping these factors in mind, international B2B buyers can mitigate risks and establish successful partnerships with their suppliers.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for screw shafts is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and rigorous quality control, businesses can ensure they are sourcing reliable and high-quality products for their applications.

Illustrative image related to screw shaft
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘screw shaft’
To assist B2B buyers in sourcing screw shafts effectively, this guide outlines a practical step-by-step checklist. Following these steps will ensure that you procure high-quality components that meet your specific requirements while minimizing risks.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications of the screw shafts you need. Consider parameters such as material type, thread orientation (right-hand or left-hand), diameter, length, and any specific coatings required for corrosion resistance. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers who specialize in screw shafts. Look for companies with a solid track record in your industry and geographical region. Utilize online platforms, trade shows, and industry forums to gather information about potential suppliers and their product offerings.
- Key Considerations:
- Supplier experience in producing screw shafts for your specific application.
- Customer reviews and testimonials to gauge reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a commitment, verify the certifications and quality standards of your shortlisted suppliers. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and operational excellence. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to relevant regulations is essential for maintaining product integrity.
- What to Check:
- Validity of certifications and any recent audits.
- Compliance with international standards, especially if importing from different regions.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Always request samples or prototypes of the screw shafts before placing a bulk order. This step allows you to assess the quality, dimensions, and performance of the product firsthand. Testing samples can help identify any potential issues early on and ensure that the product meets your specifications.
- Testing Criteria:
- Dimensional accuracy and tolerances.
- Material properties and resistance to wear.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, compare their pricing structures and payment terms. While it may be tempting to go with the lowest price, consider the overall value, including quality, delivery timelines, and after-sales support. Transparency in pricing is crucial to avoid hidden costs.
- Factors to Consider:
- Bulk order discounts and payment flexibility.
- Shipping costs and lead times.
Step 6: Negotiate Contracts and Terms
Engage in negotiations to finalize the contract terms with your chosen supplier. Ensure that all aspects, including delivery schedules, payment terms, warranties, and return policies, are clearly defined in the contract. A well-structured agreement can protect both parties and foster a strong business relationship.
- Key Aspects to Include:
- Penalties for late delivery or non-compliance with specifications.
- Conditions for warranty claims and product returns.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Once the contract is in place, set up a communication plan with your supplier. Regular updates on production status, shipping timelines, and any potential issues will help maintain transparency and ensure that both parties are aligned throughout the sourcing process.
- Effective Communication Tips:
- Schedule regular check-ins and updates.
- Utilize project management tools to track progress.
Following this checklist will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing screw shafts, ensuring that they acquire high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for screw shaft Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Screw Shaft Manufacturing?
When analyzing the costs associated with screw shaft sourcing, several critical components contribute to the overall price. These include:

Illustrative image related to screw shaft
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. Common materials for screw shafts include steel, stainless steel, and various alloys. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand and availability, which is vital for buyers to monitor.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in the manufacturing process. This can vary based on geographic location and labor market conditions, particularly in regions such as Africa and South America, where labor costs may be lower than in Europe.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs include expenses related to factory operations, utilities, maintenance, and administrative functions. These costs are typically absorbed into the product price and can vary based on the efficiency of the manufacturing facility.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling is significant, particularly for customized screw shafts. Tooling costs can vary based on the complexity and precision required for the product, impacting the overall pricing structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that screw shafts meet specifications involves rigorous quality control processes. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the level of certification required (e.g., ISO standards), which is increasingly important for international buyers.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can add a considerable amount to the total price, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and shipping regulations will influence these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in the final price. Understanding the typical margins in different regions can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Volume and Customization Affect Screw Shaft Pricing?
Pricing for screw shafts is heavily influenced by order volume and customization requirements.
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer tiered pricing based on the quantity ordered. Higher volumes usually result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. International buyers should consider negotiating Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized screw shafts, such as those with unique dimensions or thread types, can incur additional costs. Buyers must be clear about their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Quality and Certification Factors Should Buyers Consider?
Quality and certification are crucial factors that can influence pricing and sourcing decisions.
-
Materials and Quality: Higher quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques typically lead to higher costs but can improve longevity and performance. Buyers should weigh the benefits of higher initial costs against potential savings in maintenance and replacement.
-
Certifications: Certifications, such as ISO or industry-specific standards, can add to the cost but also provide assurance of quality. Buyers should assess the importance of these certifications based on their application and industry requirements.
What Supplier Factors Should Buyers Keep in Mind?
The choice of supplier can significantly affect pricing and sourcing efficiency.
-
Supplier Reputation: Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their reputation for quality and reliability. However, this can translate to lower total costs in the long run due to reduced failure rates and warranty claims.
-
Location: The geographic location of the supplier can impact both pricing and logistics. Suppliers closer to the buyer may offer better shipping rates and faster turnaround times, while those in regions with lower manufacturing costs might provide more competitive pricing.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Prices?
Effective negotiation is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize costs.
-
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider the TCO, which includes not only the purchase price but also costs related to installation, maintenance, and potential downtime. This broader view can strengthen a buyer’s negotiating position.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Factors such as currency fluctuations, customs duties, and import taxes can affect pricing. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of these nuances and factor them into their budget.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for screw shafts can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers should request quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing screw shaft With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Screw Shafts in Industrial Applications
When evaluating mechanical solutions for linear motion or power transmission, it’s essential to consider various alternatives to screw shafts. Each option may offer unique advantages depending on specific application requirements, such as performance, cost-effectiveness, and ease of maintenance. Here, we compare screw shafts with two viable alternatives: linear actuators and belt drives.
| Comparison Aspect | Screw Shaft | Linear Actuator | Belt Drive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and load capacity | Moderate precision, variable load capacity | High speed, moderate load capacity |
| Cost | Generally moderate | Higher initial investment | Lower initial costs, but potential maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple integration with existing systems | Requires careful installation and alignment | Straightforward installation, but requires space |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable | Moderate maintenance required | Regular maintenance needed for belts |
| Best Use Case | Precision applications in machinery | Automation in robotics, medical devices | High-speed conveyor systems, automotive applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Linear Actuators?
Linear actuators are devices that create motion in a straight line and are often used in automation systems. They provide moderate precision and can handle varying load capacities. While they offer the advantage of automation and integration into robotic systems, the initial investment can be significantly higher than that of screw shafts. Additionally, proper alignment during installation is crucial to ensure optimal performance, which may require more specialized knowledge. Maintenance is moderate, as wear and tear on the actuator’s internal components can affect performance over time.
How Do Belt Drives Compare to Screw Shafts?
Belt drives are another alternative that can achieve linear motion and power transmission. They excel in applications requiring high speed, such as conveyor systems, making them ideal for manufacturing and assembly lines. The initial costs of belt drives are often lower compared to screw shafts; however, they can incur higher ongoing maintenance costs due to wear on the belts. The installation process is generally straightforward, but it does require adequate space for the belts to operate effectively. While they are versatile, belt drives may not provide the same precision as screw shafts, making them less suitable for applications where accuracy is paramount.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate solution for linear motion or power transmission, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs. Factors such as the required precision, load capacity, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities should guide the decision-making process. For applications demanding high precision and durability, screw shafts may be the optimal choice. However, for projects focused on speed and automation, linear actuators or belt drives could prove more beneficial. Ultimately, understanding the unique requirements of each application will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Illustrative image related to screw shaft
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for screw shaft
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Screw Shafts?
When evaluating screw shafts for industrial applications, several critical specifications should be considered to ensure compatibility and efficiency. Understanding these properties can significantly impact the performance and longevity of machinery.
-
Material Grade: The material used in screw shafts typically includes stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel. Each material offers different strengths, corrosion resistance, and thermal properties. For instance, stainless steel is ideal for environments prone to moisture, while carbon steel is often chosen for its strength and cost-effectiveness. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for meeting application-specific demands, especially in sectors like automotive and manufacturing.
-
Tolerance: Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in the dimensions of screw shafts. Precision in tolerance is crucial for ensuring proper fit and function in assemblies, as it affects the shaft’s ability to transmit motion effectively. Tight tolerances are particularly important in applications requiring high accuracy, such as CNC machinery. A misunderstanding of tolerance specifications can lead to operational inefficiencies or increased wear.
-
Thread Type and Orientation: Screw shafts can come with various thread types, including trapezoidal, square, or acme threads, and may feature right-hand or left-hand orientations. The choice of thread impacts the load capacity and speed of linear motion transfer. For example, trapezoidal threads are commonly used for lead screws due to their efficiency in converting rotary motion into linear motion. Correctly specifying thread types is essential for ensuring the compatibility of components in a mechanical system.
-
Shaft Shape: Screw shafts may be straight, stepped, or double-stepped, depending on their intended application. Stepped shafts, which feature varying diameters along their length, can accommodate different components and support structures. The shape of the shaft must align with the specific requirements of the assembly to ensure optimal performance.
-
Surface Treatment: Surface treatments, such as black oxide coatings, enhance the screw shaft’s resistance to corrosion and wear. This is particularly important in environments where exposure to moisture or chemicals is a concern. Selecting the right surface treatment can extend the lifespan of the component and reduce maintenance costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Screw Shafts?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions involving screw shafts. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of screw shafts, OEMs are crucial as they often provide specialized components that meet the specific needs of original machinery designs.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ represents the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to determine their purchasing strategy, especially when sourcing custom or specialized screw shafts.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a formal process in which buyers invite suppliers to provide pricing and terms for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ for screw shafts allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals based on detailed specifications.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Incoterms determine who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and the risk of loss during transit, which is particularly important when dealing with cross-border procurement of screw shafts.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the time taken from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and inventory management, especially for businesses that rely on just-in-time manufacturing processes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, streamline procurement processes, and enhance operational efficiency in their respective industries.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the screw shaft Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Screw Shaft Market?
The screw shaft market is experiencing significant transformation driven by several global factors. The rise of automation and Industry 4.0 is pushing the demand for precision components, including screw shafts, particularly in manufacturing and robotics. As industries increasingly adopt advanced technologies, such as CNC machining and additive manufacturing, the need for high-quality, customizable screw shafts is becoming paramount. Additionally, the growth of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy sectors is fostering new applications for screw shafts, necessitating innovations in materials and design.

Illustrative image related to screw shaft
In regions like Africa and South America, burgeoning industrialization is creating new opportunities for suppliers. As manufacturers in these regions aim to modernize their production capabilities, sourcing high-quality screw shafts has become crucial. Meanwhile, in Europe and the Middle East, stringent regulations on manufacturing processes and materials are prompting buyers to seek suppliers who can meet these standards while ensuring quality and efficiency.
Emerging trends also include the increasing use of digital platforms for sourcing and procurement. B2B buyers are leveraging online marketplaces to discover suppliers, compare products, and facilitate transactions with greater ease, making it essential for businesses to maintain a robust online presence.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Screw Shaft Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become vital considerations for B2B buyers in the screw shaft market. With growing concerns over environmental impact, companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes the use of recycled materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and responsible waste management strategies.
Furthermore, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Buyers are more inclined to partner with manufacturers who can provide these certifications, as they reflect a dedication to minimizing environmental footprints.

Illustrative image related to screw shaft
In addition to regulatory compliance, ethical sourcing practices that promote fair labor standards and responsible sourcing of raw materials are gaining traction. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where local communities are often impacted by industrial activities. By choosing suppliers who uphold ethical practices, businesses can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute to the socioeconomic development of the regions from which they source.
What Has Been the Evolution of the Screw Shaft Industry?
The screw shaft industry has undergone significant evolution since its inception, adapting to technological advancements and changing market demands. Initially, screw shafts were rudimentary, primarily serving basic fastening functions. However, as machinery and manufacturing processes became more complex, the design and functionality of screw shafts evolved.
The introduction of CNC technology in the late 20th century marked a turning point, allowing for more precise manufacturing of screw shafts, which, in turn, facilitated their use in sophisticated applications such as robotics and aerospace. Today, screw shafts are available in various designs and materials, including options that cater to specific applications, such as corrosion-resistant coatings for use in harsh environments.

Illustrative image related to screw shaft
This evolution reflects the industry’s responsiveness to the needs of modern manufacturing, emphasizing the importance of quality, precision, and sustainability. As industries continue to innovate, the screw shaft market is likely to witness further advancements, driven by the demand for high-performance components that align with global sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of screw shaft
-
How do I ensure the quality of screw shafts from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, consider implementing a multi-step vetting process for suppliers. Start by checking certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request samples to evaluate material quality and performance under operational conditions. Additionally, leverage third-party inspection services to conduct quality checks before shipment. Establish clear quality assurance protocols in your contract, including specific tolerances and testing requirements, to safeguard against receiving subpar products. -
What is the best screw shaft type for linear motion applications?
For linear motion applications, trapezoidal lead screw shafts are highly recommended due to their effective load-bearing capacity and ability to convert rotational motion into linear motion efficiently. Look for shafts with a stepped design for better alignment and integration with other components. Additionally, consider the thread orientation—right-hand threads are common, but left-hand options are available for specific applications. Evaluate the load requirements and speed to select the most suitable screw shaft configuration for your project. -
What factors should I consider when customizing screw shafts?
Customization of screw shafts should take into account the specific application requirements, such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and desired operational speed. Consider the material type—stainless steel offers corrosion resistance, while carbon steel is cost-effective for non-corrosive environments. Decide on thread type and shaft length based on the mechanical design. Collaborate closely with the manufacturer to ensure that the customizations align with your operational needs and quality standards. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for screw shafts?
Minimum order quantities for screw shafts can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the customization. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to several hundred units. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you require a smaller quantity for testing or initial production runs. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for new customers or bulk orders, so be prepared to explore multiple sourcing options. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing screw shafts internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include advance payments, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., 30 or 60 days after shipment). For first-time orders, suppliers may require a partial upfront payment to mitigate risk. Ensure to clarify payment methods accepted (wire transfer, PayPal, etc.) and any associated fees. Establishing clear payment terms in your contract can help prevent disputes and facilitate smoother transactions. -
How can I manage shipping and logistics for screw shafts?
Managing shipping and logistics requires careful planning. First, select a reliable freight forwarder experienced in international shipments. Discuss shipping options, including air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Ensure proper documentation, including customs declarations and invoices, is prepared to avoid delays. Consider insurance to protect your investment during transit. Finally, maintain communication with your supplier and logistics provider to stay updated on shipment status and any potential issues. -
What certifications should I look for in screw shaft suppliers?
When sourcing screw shafts, look for suppliers with relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and industry-specific certifications like AS9100 for aerospace applications. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality and adherence to international standards. Additionally, inquire about material certifications, especially if the shafts are to be used in critical applications, ensuring they meet the required mechanical and chemical properties. -
How do I handle disputes or quality issues with suppliers?
In the event of a dispute or quality issue, first, communicate directly with the supplier to address the problem. Document the specifics of the issue, including photos and reports, to provide clear evidence. Refer to your contract to understand the terms regarding returns, refunds, or replacements. If resolution is not achieved, consider involving a third-party mediator or legal counsel, particularly if the supplier is overseas. Establishing clear communication channels and expectations upfront can help mitigate disputes before they arise.
Top 6 Screw Shaft Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. McMaster – Screw Shafts & Lead Screws
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Screw Shafts & Lead Screws, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. MISUMI – Lead Screw Shafts
Domain: us.misumi-ec.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Lead Screw Shafts are thirty-degree trapezoidal lead screws with screw threads angled at 30 degrees and trapezoidal cross-sections. They are used for linear movement in mechanical components like screw jacks, rather than for fastening. Available shapes include straight, stepped at one end, double-stepped at one end, and double-stepped at both ends. Thread orientations include right-hand, left-hand…
3. ION – #10-32 Shaft End Screws
Domain: revrobotics.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: {“name”:”#10-32 Shaft End Screws”,”MSRP”:”$12.00 – $16.00″,”SKU”:”Various”,”brand”:”ION”,”types”:[{“name”:”#10-32 Shaft End Screw V1 – 0.5in – 10 Pack”,”SKU”:”REV-21-2056-PK10″},{“name”:”#10-32 Shaft End Screw V2 – 0.5in – 25 Pack”,”SKU”:”REV-21-2805-PK25″},{“name”:”#10-32 Shaft End Screw V2 – 1.25in – 25 Pack”,”SKU”:”REV-21-3738-PK25″},{“name”:”#10-32 Shaft End Screw V2 – 1.75in – 25 Pack”,”SKU”:…
4. Steinmeyer – Screw Shafts for Rolled Ball Screws
Domain: steinmeyer.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Screw Shafts for Rolled Ball Screws from Steinmeyer are available for model series 2446, 3446, 8436, 8446, 8132, and 8142. The maximum available length of screw shafts is up to 3m for nominal diameters of 20mm or below, and up to 6m for diameters of 25mm and above. The standard accuracy class is T7, with tolerance classes T5, T9, and T10 available upon request. Length tolerance is specified as 3m …
5. Trick Drums – Drive Shaft Center Section Screw
Domain: trickdrums.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Drive Shaft Center Section Screw”, “price”: “$4.99”, “description”: “Replacement Drive Shaft Center Section Screw, used on the center section of all current P1V6 Drive Shafts, including Retrofit models. This screw is also used for female Drive Shaft pedal connections on Retrofit Drive Shafts only (Drive Shaft for Trick Pedals uses BP-022).”, “SKU”: “753382556220”, “weight”: “45 g”, “dime…
6. TDL Mould – Screw Shaft Solutions
Domain: tdlmould.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: The screw shaft is a cylindrical metal rod with threads used to hold machine parts together, primarily in automotive and aerospace engineering, as well as in building and construction. Key components include: 1. Threads – Spiral dies machined on the screw shaft for fastening. 2. Shaft Material – Common materials include aluminum, iron alloys, and stainless steel, affecting application and durabili…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for screw shaft
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing and engineering, strategic sourcing of screw shafts is not merely a procurement tactic; it is a vital component of operational excellence. By prioritizing quality, customization, and supplier reliability, international B2B buyers can significantly enhance their production capabilities. The diverse applications of screw shafts—from linear motion systems to precision instruments—underscore the need for tailored solutions that meet specific operational demands.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to grow, buyers must leverage strategic sourcing to navigate complexities in supply chains and ensure they remain competitive. Engaging with suppliers who offer robust product ranges, like those with various thread orientations and materials, allows businesses to optimize their assembly processes and reduce downtime.
Looking ahead, the importance of sustainable sourcing practices will only increase. Buyers should consider suppliers committed to eco-friendly production methods and materials to align with global sustainability goals. By proactively seeking out innovative solutions and building strong supplier partnerships, international buyers can position themselves for success in a dynamic marketplace. Now is the time to explore strategic sourcing opportunities that will drive growth and efficiency in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.