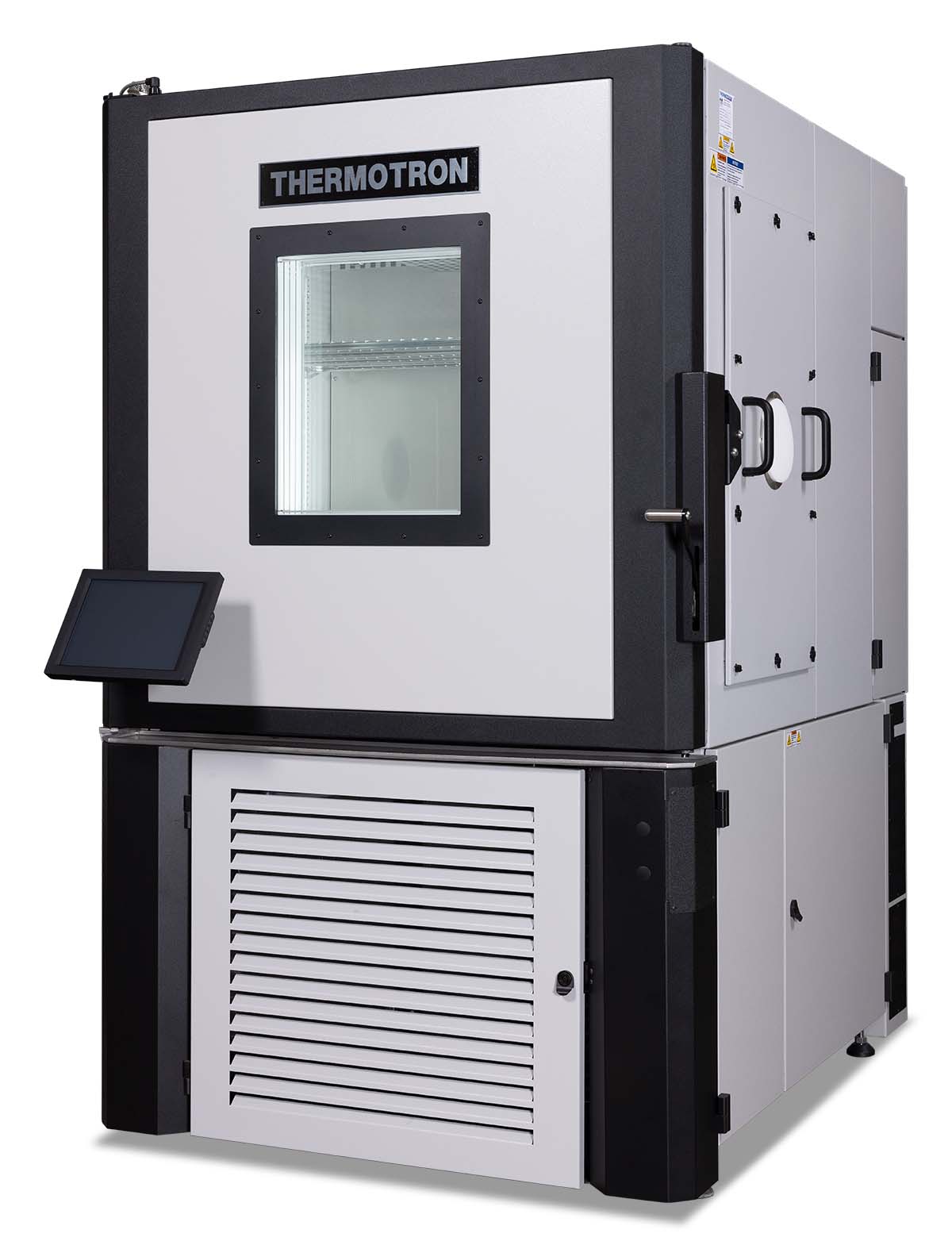
Temperature Controlled Chamber: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for temperature controlled chamber
In today’s competitive landscape, B2B buyers face the critical challenge of sourcing the right temperature-controlled chambers to meet diverse industry needs. These essential tools are pivotal for ensuring product quality, safety, and compliance across sectors such as pharmaceuticals, automotive, and electronics. This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad types of temperature-controlled chambers available, their specific applications, and the factors influencing their pricing. By equipping international buyers—particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Nigeria and Brazil—with the necessary insights, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions.
Navigating the global market for temperature-controlled chambers can be daunting, especially with varying standards and supplier capabilities. Within this guide, you will find actionable strategies for vetting suppliers, understanding the nuances of different chamber types, and recognizing the importance of features such as rapid temperature cycling and safety protocols. Furthermore, we explore the cost implications of these chambers, ensuring that you can balance quality with budgetary constraints. With these insights, you will be better positioned to enhance your operational efficiency and product development processes, ultimately driving success in your business endeavors.
Understanding temperature controlled chamber Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benchtop Chambers | Compact size, stackable design, suitable for small labs | Electronics, pharmaceuticals, battery testing | Pros: Space-efficient, versatile; Cons: Limited capacity compared to larger models. |
| Walk-in Chambers | Large capacity, allows for full-scale testing | Aerospace, automotive, military applications | Pros: Accommodates large products; Cons: Higher initial investment, requires more space. |
| Temperature Cycling Chambers | Designed for rapid temperature changes, ideal for durability testing | Electronics, automotive, military testing | Pros: Identifies failure points; Cons: More complex operation, requires careful monitoring. |
| Steady-State Chambers | Maintains constant temperature for long durations | Pharmaceuticals, medical device testing | Pros: Accurate long-term stability tests; Cons: Slower results compared to cycling chambers. |
| Battery Testing Chambers | Specialized for battery performance under extreme conditions | Electric vehicles, renewable energy storage | Pros: Ensures safety and reliability; Cons: Typically more expensive due to advanced safety features. |
What Are the Characteristics of Benchtop Chambers?
Benchtop temperature chambers are designed for efficiency and compactness, making them ideal for smaller laboratories or facilities with limited space. These chambers are often stackable, allowing multiple units to be used simultaneously without occupying significant floor space. They typically cater to a range of temperatures, making them suitable for diverse applications such as electronics testing and pharmaceutical stability assessments. When considering a benchtop chamber, businesses should evaluate the specific size and temperature range needed to ensure it meets their operational requirements.
How Do Walk-in Chambers Differ from Other Types?
Walk-in temperature chambers offer expansive internal space, accommodating larger products or multiple items simultaneously. This type is particularly beneficial for industries like aerospace and automotive, where full-scale testing of components is necessary. The investment for walk-in chambers is generally higher due to their size and complexity, and they require more significant floor space. B2B buyers should consider their testing volume and the need for large-scale testing when deciding on this type of chamber.
Why Choose Temperature Cycling Chambers for Testing?
Temperature cycling chambers are engineered to expose products to rapid fluctuations in temperature, simulating extreme conditions that might occur in real-world scenarios. This capability is essential for industries such as electronics and automotive, where durability under thermal stress is critical. While they provide valuable insights into product resilience, these chambers can be more complex to operate and may require additional monitoring and control systems. Businesses should assess their testing protocols to determine if the benefits outweigh the operational challenges.
What Advantages Do Steady-State Chambers Offer?
Steady-state chambers maintain a consistent temperature over extended periods, making them ideal for stability testing in pharmaceuticals and medical devices. This type of testing ensures that products remain effective and safe throughout their intended shelf life. While they excel in providing accurate long-term data, the process may take longer compared to cycling tests. Buyers should weigh the importance of long-term stability against the need for quicker results when selecting this chamber type.
How Do Battery Testing Chambers Ensure Safety and Performance?
Battery testing chambers are specifically designed to evaluate the performance and safety of batteries under various environmental conditions. They are crucial for industries involved in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage, where battery reliability is paramount. Equipped with advanced safety features to prevent thermal runaways, these chambers can be a significant investment. Buyers should consider the specific safety standards and testing requirements their products must meet when selecting a battery testing chamber.
Key Industrial Applications of temperature controlled chamber
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of temperature controlled chamber | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Battery performance testing for electric vehicles | Ensures safety and reliability of batteries | Look for chambers with precise temperature control and fast change rates. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Stability testing of drugs and vaccines | Validates product integrity and shelf life | Consider chambers with humidity control and compliance with industry standards. |
| Aerospace | Component testing under extreme conditions | Verifies performance in real-world scenarios | Seek chambers that can simulate a wide range of temperatures and pressures. |
| Electronics | Testing electronic devices for thermal endurance | Reduces product failure rates in the market | Evaluate the need for RF shielding to avoid interference during testing. |
| Military & Defense | Equipment reliability testing in harsh environments | Meets strict military specifications | Ensure chambers can handle rapid temperature cycling and have robust safety features. |
How Are Temperature Controlled Chambers Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, temperature-controlled chambers are essential for battery performance testing in electric vehicles. These chambers simulate various thermal conditions to assess the safety and reliability of battery systems under stress. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, it’s crucial to source chambers that offer precise temperature control and rapid change rates, ensuring that battery technology meets stringent safety standards and performance expectations.
What Role Do Temperature Controlled Chambers Play in Pharmaceuticals?
Pharmaceutical companies utilize temperature-controlled chambers for stability testing of drugs and vaccines. These chambers maintain specific temperature and humidity levels to ensure that products remain effective over their intended shelf life. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it is vital to consider chambers that comply with regulatory requirements, including those set by the FDA or EMA, and that can accommodate the necessary environmental conditions for various pharmaceutical products.
How Do Temperature Controlled Chambers Benefit the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, temperature-controlled chambers are used to test components under extreme conditions, simulating the harsh environments encountered during flight. This testing ensures that materials and devices can withstand temperature fluctuations without failure. Buyers from Europe and South America should look for chambers that can replicate a wide temperature range and provide accurate readings, as these features are critical for meeting industry safety and performance standards.
What Are the Applications of Temperature Controlled Chambers in Electronics Testing?
For electronics manufacturers, temperature-controlled chambers are vital for testing devices for thermal endurance. This testing helps identify potential failure points, reducing the likelihood of product recalls and enhancing market reliability. Buyers, especially in emerging markets, should assess the need for RF shielding in their chambers to protect sensitive electronic components from interference during testing, ensuring accurate performance evaluations.
Why Are Temperature Controlled Chambers Important for Military and Defense Applications?
In the military and defense sectors, temperature-controlled chambers are used for rigorous equipment reliability testing in harsh environments. These tests ensure that military equipment can operate effectively under extreme temperature variations. Buyers in these sectors must prioritize sourcing chambers capable of rapid temperature cycling and equipped with advanced safety features to comply with strict military specifications, ensuring operational readiness in critical situations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘temperature controlled chamber’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Temperature Control During Testing
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face the challenge of inconsistent temperature control in their temperature-controlled chambers. This inconsistency can lead to unreliable test results, which is particularly critical in industries like pharmaceuticals or electronics where even minor temperature fluctuations can compromise product integrity and safety. The anxiety of failing compliance tests or facing product recalls due to unreliable data can be overwhelming, especially when rigorous testing is part of regulatory requirements.
The Solution:
To tackle this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing temperature-controlled chambers that offer precise and reliable temperature control mechanisms. Look for chambers with a precision rating of ±0.5°C or better, as this ensures tight tolerances. Additionally, investing in systems with advanced cooling and heating technologies, such as all-electric heating systems combined with proprietary airflow designs, can enhance temperature uniformity. When specifying your requirements, consider the inclusion of features like high/low temperature control functions, which help to maintain consistent conditions. Regular calibration and maintenance of the chamber also play a crucial role in sustaining performance; establish a routine maintenance schedule with your supplier to ensure ongoing accuracy.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Associated with Temperature Chambers
The Problem:
Operational costs can be a significant pain point for B2B buyers, especially in regions with fluctuating energy prices. Many temperature-controlled chambers consume a large amount of energy, leading to rising electricity bills. This situation can be particularly burdensome for companies in developing markets, where budget constraints are a reality. The challenge intensifies when trying to balance energy efficiency with performance needs, as buyers may feel compelled to compromise on one for the other.
The Solution:
To mitigate high operational costs, buyers should seek energy-efficient temperature-controlled chambers. Look for models that feature cascade refrigeration systems or advanced insulation technologies, as these can significantly reduce energy consumption. Additionally, consider options with variable speed compressors, which adjust their operation based on the chamber’s cooling needs, thus optimizing energy use. Implementing a monitoring system to track energy consumption can also provide insights into usage patterns, enabling more strategic operational decisions. Finally, investing in a chamber with boost cooling capabilities can reduce the time required for temperature adjustments, further enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Scenario 3: Complexity in Meeting Regulatory Standards
The Problem:
Navigating regulatory standards can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly in industries such as medical devices or aerospace, where compliance is non-negotiable. Buyers often find themselves overwhelmed by the myriad of regulations that dictate testing conditions and documentation requirements. This complexity can result in delays and additional costs if not managed correctly, as the risk of non-compliance can lead to significant financial penalties and damage to reputation.
The Solution:
To streamline compliance with regulatory standards, buyers should engage with suppliers that offer temperature-controlled chambers specifically designed for regulatory testing. These chambers often come equipped with features like RF shielding for electromagnetic compatibility testing and built-in data logging systems for detailed documentation. When purchasing, ask about the chamber’s certification against specific standards (e.g., MIL-STD, ISO). Additionally, consider establishing a partnership with your supplier for ongoing training and support, ensuring that your team is well-versed in both the operation of the chamber and the regulatory landscape. Documenting all testing processes and results meticulously will not only ease compliance but also enhance the credibility of your testing protocols.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
Strategic Material Selection Guide for temperature controlled chamber
What Are the Common Materials Used in Temperature Controlled Chambers?
When selecting materials for temperature-controlled chambers, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This analysis will focus on four common materials: stainless steel, aluminum, glass, and composite materials. Each of these materials offers distinct characteristics that can influence the performance and suitability of temperature-controlled chambers for specific applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Temperature Controlled Chambers?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its high corrosion resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures, making it suitable for environments that require rigorous cleaning and maintenance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C (1472°F) and can handle high pressure.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it resists rust and degradation over time. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials and can be challenging to machine, increasing manufacturing complexity. Its weight can also be a drawback for portable applications.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for pharmaceutical and food industries where hygiene is paramount. Its compatibility with various cleaning agents ensures that it meets stringent compliance standards.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the stainless steel used complies with international standards such as ASTM A240. Understanding local corrosion factors is crucial, especially in humid climates.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Temperature Controlled Chambers?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications requiring rapid temperature changes. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°C (1112°F) and is resistant to oxidation.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication, allowing for complex designs without significant expense. However, it has lower structural integrity compared to stainless steel and is more susceptible to corrosion in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in the construction of lightweight temperature chambers for testing electronic components, where rapid thermal cycling is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local standards, such as DIN or JIS, that may dictate the specific grades of aluminum suitable for their applications. Corrosion resistance can vary based on environmental conditions, so appropriate coatings may be necessary.
How Does Glass Contribute to Temperature Controlled Chambers?
Key Properties: Glass is often used for observation windows in temperature-controlled chambers due to its transparency and ability to withstand thermal shock. It can typically handle temperatures up to 400°C (752°F).
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of glass is its ability to provide visibility into the chamber without compromising the internal environment. However, glass is fragile and can break easily, which may pose safety risks in high-pressure environments.
Impact on Application: Glass is particularly useful in laboratories where monitoring experiments visually is critical, such as in biological or chemical testing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the glass used meets safety standards for shatter resistance, especially in regions with stringent safety regulations. Compliance with ASTM standards for glass durability is also important.
What Are the Benefits of Composite Materials in Temperature Controlled Chambers?
Key Properties: Composite materials combine different substances to enhance performance, offering high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent thermal insulation properties. They can typically withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F).
Pros & Cons: Composites are lightweight and can be tailored for specific applications, providing flexibility in design. However, they can be more expensive to produce and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in aerospace applications where weight reduction is crucial, and thermal insulation is necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific composite materials used and their compliance with international standards, particularly in regions with unique environmental challenges.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Temperature Controlled Chambers
| Material | Typical Use Case for temperature controlled chamber | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Pharmaceutical and food industries | High corrosion resistance | Expensive and heavy | High |
| Aluminum | Electronic component testing | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower structural integrity | Medium |
| Glass | Laboratory observation windows | Provides visibility | Fragile and can break easily | Medium |
| Composite | Aerospace applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive and requires specialized manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on the specific requirements of their temperature-controlled chamber applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for temperature controlled chamber
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Temperature Controlled Chambers?
The manufacturing process of temperature controlled chambers involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets stringent performance and quality standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Temperature Controlled Chambers?
Material preparation is the first step in manufacturing temperature controlled chambers. High-grade materials, such as stainless steel and specialized insulation, are selected for their durability and thermal properties. Suppliers must source materials that comply with international standards, ensuring they are suitable for environmental testing. Rigorous checks are conducted on incoming materials to confirm they meet specifications. This is known as Incoming Quality Control (IQC), where suppliers may provide certificates of compliance to validate material quality.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves various techniques to shape the materials into the required components of the temperature controlled chamber. Common methods include laser cutting, CNC machining, and bending. These techniques allow for precise fabrication of parts that will fit together seamlessly during assembly. The use of automated machinery enhances consistency and reduces human error, leading to higher-quality outputs.
How Are Temperature Controlled Chambers Assembled?
Assembly is a critical phase where the individual components are brought together to create the final product. This process often involves welding, bolting, or using adhesives to secure parts. During assembly, Integrated Process Quality Control (IPQC) measures are employed to monitor the assembly line in real-time. Workers must adhere to specific guidelines to ensure that the chambers are sealed properly to maintain their thermal integrity. This stage is crucial, as any gaps or flaws can lead to performance issues later.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality Assurance?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetics and functionality of the temperature controlled chambers. These may include painting, powder coating, or polishing surfaces to prevent corrosion and improve thermal efficiency. Additionally, finishing processes often involve applying insulation materials to minimize heat loss. Before moving to quality control, a thorough inspection of the finished product is conducted to ensure compliance with design specifications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are in Place for Temperature Controlled Chambers?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of temperature controlled chambers, as it ensures that the products are reliable, safe, and effective for their intended use. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the QA processes.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look for in Temperature Controlled Chambers?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. It emphasizes a process approach to enhance customer satisfaction and ensure consistent product quality. Manufacturers should be ISO 9001 certified, as this demonstrates their commitment to quality management.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for products sold in Europe and API certifications for products used in the oil and gas sector are crucial. These certifications indicate compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards, which are particularly important for B2B buyers in sectors like pharmaceuticals and aerospace.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. The three primary checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of materials before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the assembly and forming stages, this checkpoint ensures that components are being manufactured and assembled correctly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, completed temperature controlled chambers undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specified performance criteria, including temperature accuracy and stability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the performance of temperature controlled chambers. Common methods include:
- Temperature Calibration Tests: These tests verify that the chambers can accurately reach and maintain specified temperatures.
- Thermal Cycling Tests: Simulating real-world conditions, these tests assess how well the chambers perform under alternating temperature extremes.
- Safety Tests: Ensuring that safety features function correctly, especially for chambers used in battery testing, is critical to prevent hazards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers for temperature controlled chambers. Here are several ways to verify supplier quality control:
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers can request on-site visits to observe manufacturing practices and quality management systems in action. Audits should focus on the supplier’s adherence to international standards and their internal quality control checkpoints.
How Important Are Quality Reports and Certifications?
Quality reports and certifications provide tangible evidence of a manufacturer’s commitment to quality. Buyers should request documentation such as ISO certifications, test results, and compliance reports. These documents not only verify quality claims but also provide insight into the manufacturer’s operational transparency.
Why Is Third-Party Inspection Crucial for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, third-party inspections can provide an added layer of assurance. Engaging an independent inspection agency can help verify that the products meet specified standards before shipment. This practice is especially important for buyers who may face challenges in assessing product quality remotely.
What Are the QC Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances. Different regions may have distinct regulatory requirements and standards, which can complicate the procurement process. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations in their respective markets and ensure that suppliers can meet these requirements.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences may affect communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear lines of communication and mutual understanding of quality standards is essential to ensure that both parties are aligned throughout the manufacturing process.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for temperature controlled chambers is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly processes, and stringent quality control measures, buyers can make informed decisions that ultimately lead to successful procurement and product performance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘temperature controlled chamber’
To assist international B2B buyers in sourcing temperature-controlled chambers effectively, this practical guide outlines essential steps to streamline the procurement process. By following this checklist, you can ensure that your investment aligns with your specific testing requirements and operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your technical requirements is the foundation of an effective sourcing strategy. Determine the desired temperature range, volume, and any specific features such as rapid temperature cycling or humidity control. This clarity will help you communicate your needs to potential suppliers and ensure that the chambers you consider meet your testing protocols.
Step 2: Identify Your Industry Requirements
Different industries have unique testing standards and regulations. For instance, the pharmaceutical sector often requires chambers that can maintain strict temperature stability for product integrity, while the automotive industry may prioritize chambers that simulate extreme conditions for battery testing. Research the specific compliance requirements relevant to your industry to ensure the chambers you procure will meet them.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it is crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with proven expertise in temperature-controlled chambers, as well as positive feedback from their clients regarding performance and support.
- Check for experience in your specific industry.
- Request testimonials or case studies that demonstrate successful deployments.
Step 4: Assess Product Quality and Features
Quality and features are paramount when selecting a temperature-controlled chamber. Evaluate the construction materials, insulation properties, and safety features. Look for options that include advanced monitoring capabilities, such as remote access and data logging, which can enhance usability and ensure compliance with testing protocols.
- Prioritize safety features like high/low temperature control and RF shielding if needed.
- Investigate warranty and support services provided by the manufacturer.
Step 5: Consider Customization Options
Depending on your testing needs, you may require custom solutions. Discuss with suppliers their ability to customize chambers according to your specifications, such as size, temperature range, and additional functionalities. Customization can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your testing processes.
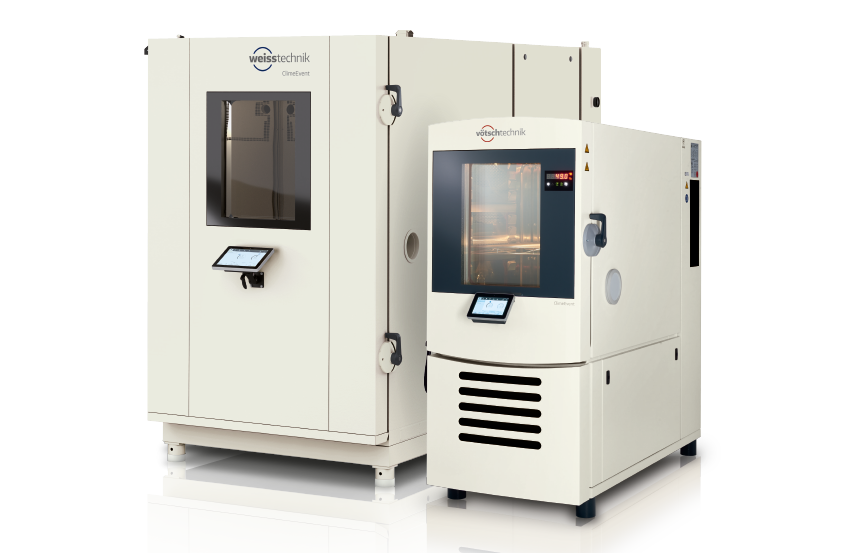

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
Step 6: Request Pricing and Compare Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline all costs, including installation and maintenance. Comparing these quotes will allow you to evaluate not only the price but also the value offered by each supplier. Look for transparency in pricing to avoid hidden costs.
Step 7: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Finally, ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and adhere to international standards. This verification is crucial for ensuring that the chambers will perform reliably and meet regulatory compliance. Certifications can include ISO standards or industry-specific qualifications that demonstrate a commitment to quality and safety.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing temperature-controlled chambers, ensuring that they select a solution that meets both their technical requirements and industry standards.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for temperature controlled chamber Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Temperature Controlled Chamber Manufacturing?
When sourcing temperature-controlled chambers, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the price. High-quality insulation, durable metals, and advanced electronic components can increase costs but enhance performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for assembly and quality assurance, which can vary by region. Labor costs may be higher in developed countries compared to emerging markets.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized chambers may be necessary and can add to the initial investment. Standard models typically have lower tooling costs.
-
Quality Control: Investment in rigorous QC processes is vital to ensure reliability and compliance with industry standards. This can influence the overall price but is crucial for long-term performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and weight of the chamber. International buyers should consider these factors when calculating total costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market demand, brand reputation, and service offerings. Buyers should assess if the price reflects value in terms of quality and support.
What Influences the Pricing of Temperature Controlled Chambers?
Several factors can influence the pricing of temperature-controlled chambers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers should consider negotiating terms based on their projected needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as enhanced cooling capabilities or specific size requirements, can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate whether these features are essential for their applications.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Chambers that meet international quality standards (ISO, CE) may have a higher price tag but offer greater reliability and compliance, especially important for industries like pharmaceuticals.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better support and warranty terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for international buyers. These terms dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, affecting the overall budget.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
To maximize value when sourcing temperature-controlled chambers, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing, especially for large orders. Suppliers may offer volume discounts or flexible payment terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime when evaluating the overall investment.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes can significantly affect the final cost. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should account for these factors in their budgets.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from various suppliers to compare prices and features. This can give you leverage in negotiations.
-
Leverage Industry Connections: Use industry contacts to gain insights into fair pricing and reliable suppliers. Networking can uncover hidden costs or better deals.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is essential to note that indicative prices for temperature-controlled chambers can vary widely based on specifications, supplier practices, and market conditions. The base prices for standard chambers typically range from $15,000 to $20,000, but customization and additional features can significantly increase this range. Always consult with suppliers for accurate quotes tailored to specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing temperature controlled chamber With Other Solutions
When evaluating environmental testing solutions, businesses often encounter a variety of options that can serve similar purposes as temperature-controlled chambers. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for making informed decisions that align with specific testing requirements, budget constraints, and operational capacities. Below, we compare temperature-controlled chambers against two viable alternatives: thermal shock testers and environmental simulation chambers.
| Comparison Aspect | Temperature Controlled Chamber | Thermal Shock Tester | Environmental Simulation Chamber |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides precise temperature control over a wide range, allowing for steady-state and cycling tests. | Rapidly alternates between extreme temperatures to identify failure points quickly. | Simulates a variety of environmental conditions (e.g., humidity, temperature) in one chamber. |
| Cost | Typically ranges from $15,000 to $100,000+ depending on size and features. | Generally less expensive, starting around $10,000, but limited in scope. | Can be more costly due to multi-functionality, often exceeding $50,000. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires a dedicated space and proper installation for optimal performance. | Easier to set up, often requiring less space than a full chamber. | More complex installation, especially if integrating multiple environmental factors. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for calibration and safety features; can be complex depending on model. | Lower maintenance requirements, but limited testing scope may necessitate additional equipment. | May require extensive maintenance due to its multifaceted capabilities and complexity. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for industries needing precise temperature testing (e.g., pharmaceuticals, electronics). | Best for rapid testing scenarios where quick identification of defects is crucial. | Suitable for industries requiring a comprehensive simulation of varied environmental conditions (e.g., automotive, aerospace). |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Thermal Shock Testers?
Thermal shock testers provide a rapid evaluation of a product’s durability under extreme temperature fluctuations. The primary advantage of this method is its speed; it allows engineers to quickly identify critical failure points without the need for prolonged testing cycles. However, the limitation lies in its scope: thermal shock testers typically focus solely on temperature extremes, lacking the comprehensive environmental control that temperature-controlled chambers offer.
How Do Environmental Simulation Chambers Compare?
Environmental simulation chambers are versatile solutions that combine temperature control with other environmental factors such as humidity and pressure. This multi-functionality makes them suitable for industries that require a broader testing framework, such as aerospace and automotive. The downside is that these chambers can be significantly more expensive and complex to maintain, often requiring specialized training for operators.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
In choosing the right solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific testing requirements, including the types of products being tested, budget constraints, and the necessary precision of results. For businesses focused solely on temperature testing, a temperature-controlled chamber may provide the best performance and reliability. Conversely, companies needing quick defect identification may benefit from thermal shock testers, while those looking for comprehensive environmental simulations should consider environmental simulation chambers despite their higher costs and complexity. By aligning the choice of testing solution with operational needs, companies can enhance product development processes and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for temperature controlled chamber
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Temperature Controlled Chambers?
When evaluating temperature controlled chambers, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications that significantly impact performance and suitability for various applications:
1. Temperature Range
The temperature range defines the minimum and maximum temperatures the chamber can maintain. Common ranges include -70°C to +180°C. For B2B buyers, this specification is critical because it determines whether the chamber can handle the specific thermal conditions required for testing products, such as pharmaceuticals or electronics.
2. Temperature Tolerance
Temperature tolerance, often expressed as ± degrees Celsius, indicates how closely the chamber can maintain the set temperature. A tolerance of ±0.5°C is standard for high-precision testing. For businesses, this specification ensures reliability in test results, essential for compliance with industry standards and product safety.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
3. Ramp Rates
Ramp rates refer to the speed at which a chamber can change temperatures, typically measured in degrees per minute. Faster ramp rates (e.g., 3.9°C/minute to 9°C/minute) are vital for applications requiring quick temperature transitions, such as thermal cycling tests. Understanding ramp rates helps buyers assess whether a chamber can meet their testing timelines and efficiency needs.
4. Volume Capacity
Volume capacity indicates the internal space available for testing products, measured in cubic feet. Options range from small benchtop models (2-8 cu ft) to large walk-in units. For B2B buyers, selecting the right volume is essential to accommodate the size and number of products being tested without compromising test integrity.
5. Cooling and Heating Systems
The type of cooling and heating systems influences both performance and maintenance costs. Chambers may use air or water cooling systems, with water systems generally offering faster cooling rates. Buyers should consider operational costs and installation complexity when choosing between these systems.
6. Safety Features
Safety features, such as high/low temperature controls and emergency shut-off mechanisms, are crucial for protecting both products and personnel. Chambers designed for battery testing often include advanced safety protocols to prevent thermal runaways. For buyers, these features provide peace of mind and compliance with safety regulations.
Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Temperature Controlled Chambers?
Familiarity with industry terminology can enhance communication and negotiation processes. Here are some common trade terms that every B2B buyer should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of temperature controlled chambers, buyers often seek OEMs for customized solutions that meet specific testing requirements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, as it can affect overall purchasing costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. For temperature controlled chambers, an RFQ allows businesses to compare pricing, specifications, and delivery options, facilitating better purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade, clarifying the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping logistics and costs when importing temperature controlled chambers from global suppliers.
5. Calibration
Calibration refers to the process of adjusting the accuracy of a chamber’s temperature settings. Regular calibration ensures that the chamber operates within its specified tolerance, maintaining the integrity of testing. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer calibration services to ensure consistent performance.
6. Thermal Cycling
Thermal cycling is a testing method that involves subjecting products to repeated temperature changes to assess durability and performance. Understanding this term is crucial for buyers looking to validate their products under real-world conditions, ensuring reliability and compliance with industry standards.
By grasping these essential properties and terminology, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when selecting temperature controlled chambers tailored to their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the temperature controlled chamber Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Temperature Controlled Chamber Sector?
The temperature controlled chamber market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand for environmental testing across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As global supply chains become more complex, international B2B buyers are prioritizing precision and reliability in environmental testing equipment. Regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are seeing heightened investment in temperature chambers to support local manufacturing and R&D initiatives.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT-enabled remote monitoring systems, are transforming how temperature chambers are utilized. These advancements allow for real-time data analysis and improved operational efficiency, making them attractive for businesses aiming to enhance their testing capabilities. Additionally, the rise of battery technology—particularly in electric vehicles—has spurred demand for specialized chambers capable of simulating extreme thermal conditions.
Cost remains a critical factor for buyers, with price variations influenced by chamber size, performance specifications, and customization options. As a result, manufacturers are focusing on offering flexible solutions tailored to specific industry needs. For international buyers, understanding these market dynamics is essential for making informed sourcing decisions that align with both budgetary constraints and technological advancements.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence the Temperature Controlled Chamber Market?
Sustainability is becoming a focal point in the temperature controlled chamber sector, as both manufacturers and buyers recognize the environmental impact of production processes. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using energy-efficient technologies and recyclable materials. This shift is particularly relevant for industries under pressure to meet stringent environmental regulations, especially in Europe and North America.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies aim to ensure that their supply chains are free from labor abuses and environmentally harmful practices. Buyers are encouraged to verify that their suppliers adhere to ethical standards and possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management.
Moreover, the adoption of “green” certifications and materials in the manufacturing of temperature chambers is gaining traction. This includes using non-toxic refrigerants and energy-efficient components that reduce carbon footprints. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can not only comply with regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What Is the Historical Context of Temperature Controlled Chambers in B2B?
The evolution of temperature controlled chambers can be traced back to the early 20th century when the need for controlled environments in laboratories became apparent. Initially designed for basic temperature regulation, these chambers have undergone significant technological advancements, leading to the sophisticated systems available today.
The introduction of digital controls and automated systems in the late 20th century marked a pivotal moment, allowing for precise temperature management and data logging. As industries grew more reliant on environmental testing, the demand for custom solutions surged, prompting manufacturers to innovate further.
Today, temperature controlled chambers are integral to product development across multiple sectors, reflecting a broader trend towards scientific rigor in product testing. This historical context underscores the importance of selecting reliable, high-quality temperature chambers that can adapt to evolving industry standards and technological advancements, ensuring that B2B buyers remain competitive in their respective markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of temperature controlled chamber
1. How do I choose the right temperature-controlled chamber for my testing needs?
Selecting the appropriate temperature-controlled chamber involves assessing your specific testing requirements, including the temperature range, volume, and type of tests you intend to conduct. Consider factors like the size of the items being tested and the maximum and minimum temperatures required. Additionally, explore whether you need features like rapid temperature cycling or humidity control. Collaborating with a manufacturer can help tailor a solution that meets your unique criteria, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in your tests.
2. What are the key features to look for in a temperature-controlled chamber?
When evaluating temperature-controlled chambers, prioritize features such as precise temperature control, rapid change rates, and safety mechanisms. Look for chambers with advanced cooling and heating systems, reliable air circulation for uniform temperature distribution, and customizable options to fit specific testing protocols. Additional features like remote monitoring, energy efficiency, and compliance with international safety standards are also critical for ensuring the reliability and longevity of your investment.
3. What is the typical price range for temperature-controlled chambers?
The price of temperature-controlled chambers varies widely based on size, capabilities, and customizations. Standard models typically start around $15,000 to $20,000, but specialized features such as enhanced cooling systems or larger volumes can significantly increase costs. It’s advisable to request quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and features. Additionally, consider long-term operational costs, including energy consumption and maintenance, when evaluating your budget.
4. How do I ensure the quality and reliability of a temperature-controlled chamber?
To ensure quality and reliability, choose manufacturers with a proven track record in the industry. Look for certifications such as ISO or compliance with international testing standards. Request detailed product specifications and inquire about the testing procedures used during manufacturing. Additionally, ask for customer testimonials and case studies to understand how the chambers have performed in real-world applications. Regular maintenance and support options should also be part of your evaluation process.
Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
5. What customization options are available for temperature-controlled chambers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific testing needs, including temperature ranges, chamber sizes, and additional features such as humidity control or RF shielding. You may also request specialized fixtures for battery testing or modifications to accommodate unique products. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options and ensure the chamber is tailored to your operational needs.
6. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for temperature-controlled chambers?
Minimum order quantities for temperature-controlled chambers can vary by manufacturer and may depend on the complexity of the customization requested. While some suppliers may accept single-unit orders, others might have higher MOQs, particularly for custom models. It’s essential to communicate your needs upfront and inquire about MOQs during the negotiation process to align your purchasing strategy with the supplier’s capabilities.
7. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a temperature-controlled chamber?
Payment terms can differ significantly among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial deposits, or payment upon delivery. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger purchases. Always clarify payment terms, including any applicable taxes or shipping costs, before finalizing your order to avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process.
8. How does international shipping and logistics work for temperature-controlled chambers?
Shipping temperature-controlled chambers internationally requires careful planning due to their size and sensitivity. Discuss logistics with your supplier, including shipping methods, costs, and estimated delivery times. Ensure that the manufacturer provides necessary export documentation and adheres to international trade regulations. It’s also advisable to work with experienced logistics partners who can handle customs clearance and ensure safe transport to your facility.
Top 9 Temperature Controlled Chamber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fisher Scientific – Environmental Chambers
Domain: fishersci.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Environmental chambers are enclosures that allow control of light, humidity, air pressure, and gas. They are available in multiple capacities, suitable for drug stability studies, shelf-life testing, controlled temperature storage, and biological research applications. Key specifications include:
– **Capacity (Metric)**: Ranges from 102 L to 940 L, with various models available.
– **Voltage Optio…
2. Humidity Control – Environmental Chambers
Domain: humiditycontrol.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Environmental Chambers: Temperature & Humidity Controlled Chambers
Key Product Details:
1. **Product Types:**
– Stability Chambers
– Reach-In Stability Chambers
– Environmental Test Chambers
– Battery Test Chambers
– Drying and Heating Chambers
– Laboratory Growth Incubators
– Cold Storage
– Walk-In Stability Rooms
– Humidity Control Rooms
– Cold Rooms and Freezers
…
3. Zwick Roell – Temperature Chambers
Domain: zwickroell.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Temperature Chambers -80 °C to +360 °C
– Temperature range: -80°C to +250°C, -80°C to +360°C, -50°C to +180°C
– Load range: Up to 250 kN (for larger chambers), Up to 2.5 kN (for smaller chamber)
– Advantages: Precise temperatures, flexible extensometer integration, flexible in use, can be retrofitted
– Applications: Testing for standard and engineering plastics (ISO 527-1, ASTM D638), elastomers a…
4. CorePoint Scientific – Temperature and Humidity Test Chambers
Domain: corepointscientific.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Temperature Test Chambers: Utilize heat pumps or refrigeration systems to create different temperature environments; focus solely on temperature; used for testing products not affected by humidity. Humidity Chambers: Also known as humidity stability chambers; focus on both temperature and humidity; use steam generators and/or air dryers to create varying conditions; test for structural integrity, …
5. Thermotron – Environmental Chambers
Domain: thermotron.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Thermotron temperature chambers come in a variety of sizes and performance configurations, including optional humidity capabilities. Key product lines include: SE-Series Environmental Chamber (most fully-featured), Walk-In Chambers (for large components and assemblies), S/SM-Series Chamber (for prototyping and durability testing), and Benchtop Chambers (for a wide range of applications).
6. Labrepco – Environmental Testing Chambers
Domain: labrepco.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Environmental Testing Chambers from Memmert, BINDER, and PHCbi. Features include climate testing capabilities, humidity testing, and stability testing. Options available for reach-in chambers, battery test chambers, BOD incubators, and environmental walk-in rooms. Suitable for various laboratory applications including controlled temperature and humidity environments.
7. Weiss – Temperature Chambers
Domain: weiss-na.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Temperature chambers, also known as environmental or climatic chambers, are specialized testing environments designed to simulate a wide range of temperatures, from -70°C to +150°C (-94°F to +302°F) or higher. They are equipped with advanced heating and cooling systems, precise temperature control mechanisms, and can accommodate various sizes, from small benchtop units to large walk-in and drive-i…
8. TotalTemp Technologies – Key Products
Domain: totaltemptech.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: TotalTemp Technologies offers a range of temperature test chambers and environmental chambers designed for various testing purposes. Key products include: 1. **Model C460**: Benchtop chamber with dimensions 16″ x 19.5″ x 12.5″. Features left and right 3.8″ cabling feed-throughs. 2. **Model C230**: Benchtop temperature chamber made to order, dimensions not specified. Offers even heating and cooling…
9. Reddit – Climate Incubator Solutions
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Temperature controlled chamber, ON/OFF controller, fan heater, polystyrene insulation, cooling methods (ice packs, water, dry ice), fast thermal sensor (thermocouple), PID controller, low-wattage heat source, bidirectional Peltier element, H-bridge, dual output PWM controller, climate incubator.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for temperature controlled chamber
In navigating the complexities of sourcing temperature-controlled chambers, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to understand the diverse applications and specifications that meet their industry needs. From pharmaceuticals to aerospace, these chambers are integral for ensuring product reliability, safety, and compliance with international standards. Strategic sourcing not only helps in identifying the right technology but also aligns procurement with long-term operational goals, ensuring that investments yield maximum returns.

Illustrative image related to temperature controlled chamber
As industries evolve, the demand for advanced temperature-controlled solutions is expected to grow, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who offer tailored solutions, robust support, and innovative features such as remote monitoring and safety compliance.
Looking ahead, the landscape of temperature-controlled chambers will be shaped by advancements in technology and increasing regulatory pressures. This presents an opportunity for businesses to enhance their testing capabilities and ensure product integrity. Engage with reputable suppliers to secure the best solutions that not only meet current needs but also prepare your operations for future challenges. Embrace the journey of strategic sourcing to propel your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.