A Deep Dive into Reduction Ratio Gears Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for reduction ratio gears
In the complex world of industrial machinery, sourcing reduction ratio gears can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly when balancing quality, performance, and cost-effectiveness. These essential components, often overlooked, are critical for optimizing motor performance by decreasing speed while increasing torque. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for enhanced operational efficiency, understanding the nuances of reduction ratio gears becomes paramount.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of reduction gears, including parallel shaft, worm, bevel, planetary, and strain wave gears, alongside their specific applications in sectors ranging from manufacturing to robotics. It also highlights key factors to consider when vetting suppliers, such as quality certifications, production capabilities, and support services. Additionally, the guide addresses cost considerations and emerging trends that can influence procurement strategies.
Equipped with this knowledge, international B2B buyers will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they select the right reduction ratio gears that meet their operational needs. By navigating this critical aspect of machinery procurement, businesses can enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and ultimately drive profitability in an increasingly competitive market.
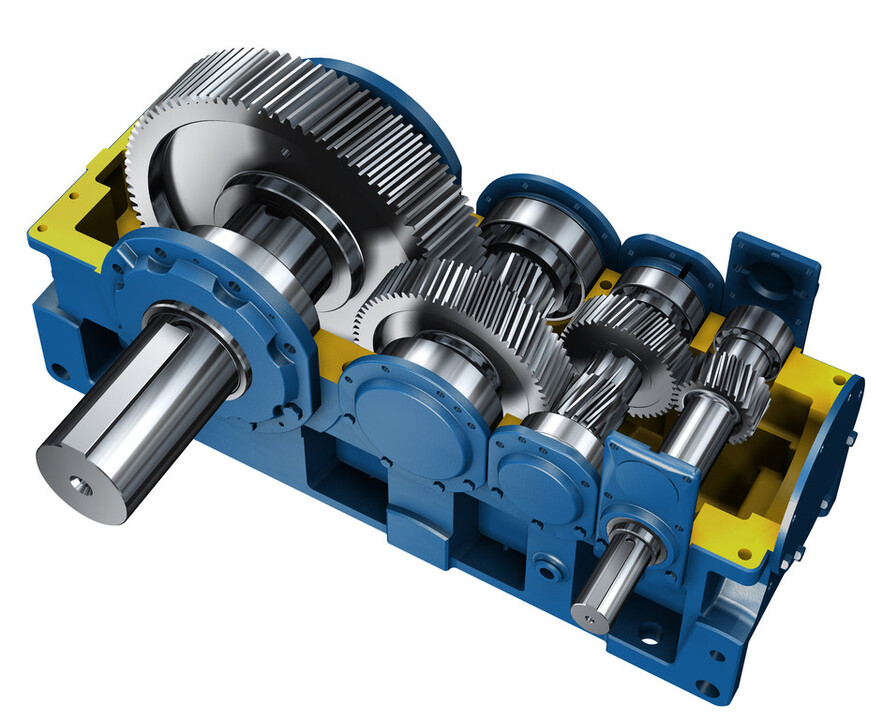
Understanding reduction ratio gears Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel Shaft Reduction Gears | Combines spur and helical gears; input and output shafts are parallel | Industrial robots, conveyor systems | Pros: High efficiency, versatile ratios. Cons: May require more space. |
| Worm Gear Reduction Gears | Uses a worm and worm wheel; high reduction in one stage | Elevators, packaging machinery | Pros: Compact design, high torque. Cons: Lower efficiency, heat generation. |
| Bevel Gear Reduction Gears | 90-degree output axis; strong teeth for heavy loads | Automotive drives, heavy machinery | Pros: High durability, efficient under load. Cons: Complexity in design. |
| Planetary Gear Reduction Gears | Sun gear with multiple planetary gears; compact and high ratios | Aerospace, robotics, automotive applications | Pros: High torque, compact size. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Strain Wave Gear Reduction Gears | Utilizes an elliptical wave generator; minimal backlash | Precision robotics, CNC machinery | Pros: Low vibration, high precision. Cons: Specialized applications may limit versatility. |
What Are the Characteristics of Parallel Shaft Reduction Gears?
Parallel shaft reduction gears are designed with both spur and helical gears, allowing for efficient power transmission while maintaining a compact form factor. The parallel alignment of input and output shafts makes them ideal for applications requiring high torque and speed reduction, such as industrial robots and conveyor systems. When considering these gears, B2B buyers should evaluate the required gear ratios and the physical space available for installation, as larger configurations may necessitate more room.

Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
Why Choose Worm Gear Reduction Gears for Your Applications?
Worm gear reduction gears are characterized by their unique design, featuring a threaded worm gear that meshes with a worm wheel. This configuration allows for significant speed reduction in a single stage, making them suitable for applications like elevators and packaging machinery. However, buyers should be aware of potential heat generation and lower efficiency due to sliding motion. When selecting worm gears, consider the duty cycle and operating conditions to ensure optimal performance.
How Do Bevel Gear Reduction Gears Perform Under Load?
Bevel gear reduction gears employ a 90-degree output axis, utilizing strong teeth to handle heavy loads effectively. This type of gear is commonly found in automotive drives and heavy machinery, where durability and efficiency are paramount. Buyers should consider the complexity of the design, as it may affect installation and maintenance. Additionally, understanding the load requirements and operational environment is crucial for selecting the right bevel gear solution.
What Are the Advantages of Planetary Gear Reduction Gears?
Planetary gear reduction gears feature a central sun gear with multiple planetary gears, providing high torque and compact design. This versatility makes them ideal for applications in aerospace, robotics, and automotive sectors. However, the initial cost can be higher due to their complex design. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of high gear ratios and torque against the investment required, especially in projects where space and weight constraints are critical.
What Makes Strain Wave Gear Reduction Gears Unique?
Strain wave gear reduction gears utilize an elliptical wave generator to achieve precise motion with minimal backlash. This makes them particularly suitable for high-performance applications in precision robotics and CNC machinery. While they offer low vibration and high efficiency, their specialized nature may limit broader applications. Buyers should assess their specific needs for precision and stability when considering strain wave gears, ensuring they align with operational requirements.
Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
Key Industrial Applications of reduction ratio gears
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of reduction ratio gears | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Automation | Conveyor Systems | Enhanced efficiency and reduced operational costs | Precision and durability requirements; compatibility with existing systems |
| Renewable Energy | Wind Turbines | Improved energy conversion and reliability | Gear ratio flexibility; resistance to environmental conditions |
| Automotive | Electric Vehicles | Increased torque for better performance | Lightweight materials; thermal management solutions |
| Robotics | Industrial Robots | High precision and control in automation | Low backlash; compact design; high torque capabilities |
| Construction | Heavy Machinery | Enhanced lifting capacity and operational safety | Load ratings; environmental resistance; maintenance support |
How are reduction ratio gears utilized in manufacturing and automation?
In manufacturing and automation, reduction ratio gears are integral to conveyor systems. They help reduce the motor’s high speed while increasing torque, allowing for smooth and controlled material handling. This is crucial in high-volume production environments, where efficiency and speed are paramount. Buyers should consider precision and durability, ensuring that the gears can withstand continuous operation while fitting seamlessly into existing conveyor designs.
What role do reduction ratio gears play in renewable energy applications?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbines, reduction ratio gears are essential for converting the high-speed rotation of turbine blades into low-speed, high-torque output that can be utilized for electricity generation. This conversion process enhances energy efficiency and reliability. International buyers should prioritize gear ratios that provide flexibility and ensure that the materials used can withstand harsh environmental conditions such as moisture and dust.
How are reduction ratio gears improving performance in electric vehicles?
Reduction ratio gears are critical in electric vehicles, where they enable increased torque delivery from the electric motor to the wheels. This results in improved acceleration and overall vehicle performance. For B2B buyers in the automotive sector, sourcing lightweight materials and effective thermal management solutions is essential to optimize energy efficiency without compromising performance.

Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
Why are reduction ratio gears vital for industrial robots?
In robotics, reduction ratio gears provide the high precision and control necessary for automated tasks. They allow robots to execute movements with minimal backlash and high torque, which is vital for applications such as assembly and packaging. Buyers should focus on compact designs that can fit into limited spaces while ensuring that the gears maintain high torque capabilities for effective operation.
What benefits do reduction ratio gears offer in heavy machinery for construction?
In construction, reduction ratio gears enhance the lifting capacity and operational safety of heavy machinery. By converting high-speed motor output into high torque, these gears enable machines to handle heavier loads more efficiently. Buyers need to consider load ratings and environmental resistance when sourcing gears for construction applications, ensuring they can perform reliably in rugged conditions while minimizing maintenance needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘reduction ratio gears’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Noise Levels in Industrial Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in sectors such as manufacturing and logistics encounter significant noise issues when using standard reduction ratio gears. This can lead to a disruptive working environment, affecting employee productivity and potentially violating local noise regulations. The noise often stems from inefficient gear designs or inadequate lubrication, which can exacerbate wear and tear on the gears, leading to higher maintenance costs and reduced equipment lifespan.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing reduction ratio gears designed for quiet operation, such as those with helical or planetary gear configurations. These types of gears tend to operate more smoothly and generate less noise compared to traditional spur gears. Additionally, proper lubrication is crucial; using high-quality lubricants that are suitable for the operating environment can significantly reduce friction and noise. Regular maintenance schedules should be established to inspect and reapply lubricants, ensuring that the gears remain in optimal condition. Furthermore, implementing noise-dampening measures, such as vibration isolation mounts, can further mitigate sound levels in the workspace.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Torque Output for Heavy Loads
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently face challenges when their selected reduction ratio gears do not provide sufficient torque output for heavy-duty applications, such as in construction or heavy machinery. This can lead to underperformance, equipment failures, and the need for costly motor upgrades, resulting in operational delays and increased project costs.
The Solution: To ensure that the right torque levels are achieved, buyers must first accurately calculate the torque requirements for their specific applications, taking into account factors such as load weight, speed, and operational conditions. Once these parameters are defined, selecting a reduction gear with an appropriate reduction ratio is essential. For applications requiring high torque, planetary gear systems or multi-stage reducers are often ideal, as they can provide higher torque outputs without requiring larger motors. It’s also beneficial to consult with manufacturers or suppliers who specialize in heavy-duty applications to identify gears that are specifically engineered to handle higher loads efficiently. Additionally, using gears made from durable materials can enhance performance and reliability in demanding environments.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Reliable Replacement Parts
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience frustration when sourcing reliable replacement parts for reduction ratio gears, particularly for older or specialized equipment. Delays in sourcing these parts can lead to extended downtime, negatively impacting productivity and profitability. In regions with limited access to advanced manufacturing capabilities, this issue can be even more pronounced.
The Solution: To mitigate sourcing difficulties, buyers should establish long-term relationships with multiple suppliers who specialize in reduction gears and can provide custom solutions. Creating a comprehensive inventory management system that tracks the performance and lifecycle of gears can help anticipate when replacements will be needed, allowing for timely orders. Engaging with suppliers that offer localized production or fast shipping options can further reduce lead times. Additionally, buyers should explore the possibility of standardized parts that can be easily replaced across different machines, enhancing compatibility and simplifying the sourcing process. Finally, keeping abreast of technological advancements in gear design may open up options for modern, more reliable alternatives that can extend the life of equipment.
Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
Strategic Material Selection Guide for reduction ratio gears
What Are the Key Materials Used in Reduction Ratio Gears?
When selecting materials for reduction ratio gears, it is crucial to consider their mechanical properties, durability, and suitability for specific applications. The following analysis covers four common materials used in the manufacturing of reduction ratio gears, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Reduction Ratio Gears?
Steel, particularly alloy steel, is one of the most widely used materials for reduction ratio gears due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically offers high tensile strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Steel gears can be heat-treated to enhance their hardness and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Steel gears are durable and can handle significant loads, making them ideal for industrial applications. They also have good machinability, allowing for complex designs.
Cons: Steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can be a concern in humid or corrosive environments. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, particularly for high-precision components.

Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
Impact on Application: Steel gears are compatible with various lubricants and can operate in diverse environments, but they may require protective coatings in corrosive settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential for ensuring quality. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East may prefer gears that meet stringent quality certifications.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in Reduction Ratio Gears?
Aluminum is another material often used for reduction ratio gears, particularly in applications where weight reduction is critical. Aluminum gears are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and have good thermal conductivity.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it suitable for portable equipment and applications where reducing overall weight is a priority. Additionally, aluminum gears can be anodized for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
Cons: While aluminum has good strength-to-weight ratios, it is generally less durable than steel and may not withstand heavy loads as effectively. This can limit its use in high-torque applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum gears are often used in automotive and aerospace applications where weight savings are crucial. However, they may not be suitable for environments with high mechanical stress.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific alloy grades and their compliance with international standards, especially in regions with stringent aerospace or automotive regulations.
How Does Plastic Compare as a Material for Reduction Ratio Gears?
Plastic gears, particularly those made from engineering thermoplastics like nylon or acetal, are increasingly popular due to their low weight and resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation.
Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
Pros: Plastic gears are lightweight, quieter in operation, and can be manufactured at a lower cost than metal gears. They also offer good lubrication properties, reducing the need for additional lubricants.
Cons: Plastic gears generally have lower strength and wear resistance compared to metal gears, which can limit their application in high-load scenarios. They may also deform under high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastic gears can be used in applications where noise reduction is important, such as in consumer electronics or household appliances. However, they may not be suitable for high-torque applications.

Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic material complies with relevant safety and performance standards, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Reduction Ratio Gears?
Cast iron, particularly ductile cast iron, is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb vibrations, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Cast iron gears are highly durable, have good machinability, and can withstand high loads. They are also more affordable compared to high-grade steels.
Cons: Cast iron is relatively heavy, which may not be suitable for applications where weight is a concern. Additionally, it can be brittle, leading to potential failures under sudden impacts.
Impact on Application: Cast iron gears are commonly used in industrial machinery and automotive applications where durability is prioritized over weight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with industry standards is crucial, particularly in regions like Germany, where engineering precision is highly valued.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Reduction Ratio Gears
| Material | Typical Use Case for reduction ratio gears | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High durability and load capacity | Prone to corrosion, complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics and appliances | Low weight, quieter operation | Lower strength and wear resistance | Low |
| Cast Iron | Industrial machinery and automotive | Excellent durability and wear resistance | Heavy and brittle under impact | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on the specific requirements of their applications and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for reduction ratio gears
What Are the Main Stages in Manufacturing Reduction Ratio Gears?
The manufacturing process of reduction ratio gears involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision, performance, and durability. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from diverse global markets.
How Is Material Prepared for Reduction Ratio Gears?
Material selection is the first step in the manufacturing process. Common materials include high-carbon steels, alloy steels, and sometimes polymers, depending on the application requirements. The selected materials undergo a rigorous preparation process, which includes:
- Material Inspection: Each batch of raw material is inspected for quality, ensuring it meets the required specifications and standards.
- Cutting: The raw material is cut to size using techniques like saw cutting or laser cutting. Precision in this stage is crucial as it sets the foundation for subsequent processes.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Gear Production?
Forming is the next stage, where the prepared material is shaped into gear components. Several techniques are employed, including:
- Forging: This process involves shaping the material using compressive forces. Forging enhances the mechanical properties of the material, making it more durable.
- Machining: After forging, components undergo machining processes such as turning, milling, and grinding. These methods ensure precise dimensions and surface finishes, which are vital for gear performance.
- Heat Treatment: To improve hardness and strength, components often undergo heat treatment. This process can include quenching and tempering, which refine the material’s properties for optimal performance.
How Are Reduction Ratio Gears Assembled?
Assembly is a critical phase in manufacturing reduction ratio gears. It involves:
- Component Assembly: Individual parts, such as gears, shafts, and bearings, are assembled. Precise alignment is essential to minimize backlash and ensure smooth operation.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is applied to reduce friction and wear during operation, which is crucial for longevity and efficiency.
- Final Adjustments: This includes checks for alignment, backlash, and torque transmission efficiency. Any adjustments made at this stage can significantly affect the gear’s performance.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality Gear Production?
Finishing processes enhance the surface quality and performance of the gears. Key finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as shot peening, coating, or polishing are applied to improve wear resistance and reduce friction.
- Quality Inspection: After finishing, each gear undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets the specified tolerances and quality standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Reduction Ratio Gears?
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing of reduction ratio gears. B2B buyers should be aware of various international and industry-specific standards that govern quality assurance processes.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is essential for ensuring consistent quality across manufacturing processes.
- ISO 14001: For companies focused on environmental management, ISO 14001 ensures that the manufacturing processes comply with environmental standards.
What Industry-Specific Certifications Are Important?
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: For gears used in the oil and gas industry, API standards ensure that products meet specific performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Gear Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are vital in maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. B2B buyers should understand the various checkpoints involved:

Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the manufacturing process. Ensuring that materials meet specifications is crucial for the overall quality of the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various inspections occur at different stages. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes, ensuring that any deviations are caught early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection assesses the completed gears against the specifications. It includes performance tests to verify that the gears operate efficiently under expected loads and conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure the quality control processes of their suppliers are robust:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers allows buyers to verify compliance with quality standards and assess manufacturing practices firsthand.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC processes and any issues encountered during production.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Assurance for International Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider specific nuances in quality assurance:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations to avoid potential legal issues.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and manufacturing can help buyers navigate supplier relationships more effectively.
-
Logistical Considerations: International shipping can pose challenges, such as customs inspections and delays. Buyers should factor in these logistical elements when planning procurement.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for reduction ratio gears is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing, relevant standards, quality control checkpoints, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘reduction ratio gears’
When sourcing reduction ratio gears, it’s vital to follow a structured approach that ensures you find the best fit for your specific application needs. This checklist will guide you through the essential steps to make informed purchasing decisions, ultimately enhancing the performance and efficiency of your machinery.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline the technical requirements for your reduction ratio gears. Consider factors such as the desired torque output, speed reduction ratio, size constraints, and operating environment.
– Key Considerations: Identify the type of gear mechanism (e.g., planetary, worm, or bevel) that best suits your application needs.
– Performance Metrics: Specify load capacity and operational temperature ranges to ensure compatibility with your machinery.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough market research to compile a list of potential suppliers. Focus on companies that specialize in reduction ratio gears and have a proven track record in your industry.
– Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies that highlight their reliability and product quality.
– Geographic Considerations: Given your target regions, prioritize suppliers with a solid distribution network in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before proceeding with a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. This step is crucial to ensure that the gears meet quality and safety regulations.
– Certification Types: Check for ISO certifications, CE markings, or other relevant industry standards that confirm product quality.
– Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the supplier adheres to local regulations regarding manufacturing and environmental standards, especially if you are sourcing from diverse regions.
Step 4: Request Technical Documentation and Samples
Engage with shortlisted suppliers to request technical documentation, including product specifications, installation guidelines, and performance test results. Additionally, ask for samples to evaluate their products firsthand.
– Documentation Importance: Technical documents help you understand the gear’s capabilities and limitations, allowing for better integration into your systems.
– Sample Evaluation: Testing samples can reveal potential issues and help you assess the quality and performance of the gears in real-world conditions.

Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have identified suitable suppliers, request detailed quotations that include pricing, lead times, and payment terms. Transparent pricing will enable you to make a cost-effective decision without compromising on quality.
– Cost Analysis: Compare the total cost of ownership, including shipping, taxes, and potential maintenance costs, rather than just the upfront price.
– Payment Flexibility: Look for suppliers offering favorable payment terms that align with your financial planning.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Agreement
After evaluating the quotes and terms, enter negotiations with your preferred supplier. Aim for a mutually beneficial agreement that covers pricing, delivery schedules, warranty conditions, and after-sales support.
– Contract Clarity: Ensure that all terms are clearly documented to avoid misunderstandings later on.
– Support Services: Discuss the availability of technical support and service agreements that can assist you post-purchase.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Maintenance
Finally, develop a plan for the installation and maintenance of the reduction ratio gears. Proper installation is critical for optimal performance, and ongoing maintenance will extend the lifespan of the equipment.
– Installation Guidelines: Collaborate with the supplier to follow best practices during installation to minimize downtime and ensure functionality.
– Maintenance Schedule: Establish a routine maintenance plan, including lubrication and inspections, to keep the gears operating efficiently.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing reduction ratio gears effectively, ensuring they invest in solutions that enhance their operational efficiency and reliability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for reduction ratio gears Sourcing
Reduction ratio gears are vital components across various industries, influencing both the performance and cost-effectiveness of machinery. Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, as well as established regions like Europe and the Middle East.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Reduction Ratio Gears?
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost of reduction ratio gears. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys. High-strength materials may incur additional costs but offer enhanced durability and performance, particularly in high-torque applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Skilled labor is often required for precision machining and assembly, which can elevate costs, particularly in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead, impacting the overall pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the creation and maintenance of molds, dies, and fixtures necessary for production. Custom tooling for specialized gear designs can significantly increase initial costs but may be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that reduction ratio gears meet specific quality standards often requires rigorous QC processes. This can involve testing for precision, durability, and performance, adding to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, especially for international shipments, can impact pricing. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties play a critical role in the final cost to the buyer.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a profit margin based on their operational costs and market positioning. Understanding supplier margins can provide insight into pricing flexibility during negotiations.
What Influences Pricing for Reduction Ratio Gears?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Pricing often benefits from economies of scale. Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs, making it essential for buyers to assess their purchasing needs and potential for bulk orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions tailored to specific applications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against the standard options available in the market.
-
Material Selection: The type of material chosen for reduction gears can significantly affect costs. High-performance materials that offer better wear resistance may lead to a higher upfront investment but can reduce long-term maintenance costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Gears that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) often come at a premium. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more, but they often offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Choosing favorable terms can help manage costs effectively.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Reducing Costs?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leveraging multiple quotes can create competition and lead to better pricing.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, operational costs, and maintenance. A lower upfront cost may not always translate to lower TCO if the product requires frequent replacements or extensive servicing.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can affect final pricing. Staying informed about these factors can help in budgeting effectively.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and increased flexibility in negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that pricing for reduction ratio gears can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to gain a comprehensive understanding of current pricing trends and ensure the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing reduction ratio gears With Other Solutions
In the realm of mechanical engineering, especially in applications that require precise control of speed and torque, reduction ratio gears are a popular choice. However, businesses may also consider several alternative technologies that can achieve similar outcomes. This section explores these alternatives, providing a comparative analysis to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Reduction Ratio Gears | Servo Motors | Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque output with precise control | Excellent speed control with high responsiveness | Smooth speed variation, less torque at low speeds |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, long-term savings due to durability | Higher upfront costs, but longer lifespan | Variable costs, can be economical for larger systems |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific installation and alignment | Straightforward installation, requires programming | Moderate complexity, needs configuration and setup |
| Maintenance | Generally low, periodic lubrication needed | Low, but may require software updates | Moderate, occasional recalibration may be needed |
| Best Use Case | Applications needing high torque at low speeds | Robotics and automation requiring precise positioning | HVAC systems and conveyor belts needing variable speed control |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Servo Motors Compared to Reduction Ratio Gears?
Servo motors are a popular alternative that offers precise control over speed and position. They excel in applications where rapid and accurate movements are essential, such as in robotics and CNC machinery. The main advantage of servo motors is their ability to provide high responsiveness and adaptability, making them ideal for dynamic operations. However, they often come with higher upfront costs and may require sophisticated programming and integration into existing systems, which could be a barrier for some businesses.
How Do Variable Frequency Drives Offer a Different Approach to Speed Control?
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are another alternative, primarily used to control the speed of electric motors by varying the frequency of the electrical supply. VFDs are especially effective in applications that require variable speed control, such as HVAC systems and conveyor belts. The advantages of VFDs include their ability to provide smooth acceleration and deceleration, which enhances energy efficiency. However, they may not deliver the same level of torque at low speeds as reduction ratio gears, which can limit their effectiveness in high-torque applications.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between reduction ratio gears and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications. Factors such as the necessary torque, budget constraints, ease of implementation, and maintenance capabilities should guide their decision. For applications that demand high torque and precise speed control, reduction ratio gears may be the best choice. Conversely, for systems requiring flexible speed variations and rapid adjustments, servo motors or VFDs might be more suitable. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and long-term goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for reduction ratio gears
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Reduction Ratio Gears?
Understanding the technical specifications of reduction ratio gears is essential for B2B buyers to ensure the right fit for their applications. Here are several critical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material used in reduction gears significantly impacts their durability and performance. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys. Carbon steel offers high strength and toughness, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance, which is crucial in harsh environments. Selecting the right material ensures the longevity and reliability of the gears, reducing maintenance costs over time. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the gear components. Tight tolerances are critical for high-precision applications, especially in sectors like robotics and aerospace. Precise tolerances reduce backlash and enhance the efficiency of power transmission, which can lead to improved performance and reduced wear. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance specifications is essential to ensure compatibility with other machine components. -
Reduction Ratio
The reduction ratio indicates the relationship between the input speed and output speed of the gear system. It is expressed as a ratio (e.g., 10:1), which shows how many times the output speed is reduced compared to the input. A higher reduction ratio can result in increased torque but may also lead to greater complexity in the gear system. Buyers must consider the required torque and speed for their specific applications to select the appropriate reduction ratio. -
Backlash
Backlash is the amount of play or movement between the teeth of gears when they are engaged. Low backlash is crucial in applications requiring high precision, as excessive backlash can lead to inaccuracies and reduced performance. Understanding the acceptable backlash levels for specific applications helps buyers make informed decisions, especially in sectors such as robotics and automation. -
Lubrication Type
The type of lubrication used in reduction gears affects their efficiency and lifespan. Common lubrication methods include grease and oil, each with its advantages. Grease is typically used for lower-speed applications, while oil is preferred for high-speed operations. Proper lubrication ensures smooth operation, reduces friction, and minimizes heat generation, which is vital for maintaining performance and durability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Reduction Ratio Gears?
Familiarity with industry terminology can enhance communication and negotiations between buyers and suppliers. Here are several essential trade terms:

Illustrative image related to reduction ratio gears
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of reduction gears, buyers may seek OEMs for customized solutions tailored to their specific machinery requirements. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers secure reliable products designed to fit seamlessly into their systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers as it affects purchasing decisions and inventory management. Understanding MOQ helps businesses plan their orders effectively and avoid excess stock or shortages, especially when sourcing reduction gears in bulk. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing, terms, and conditions for specific products. For reduction ratio gears, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to gather competitive pricing and evaluate supplier capabilities. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline the procurement process and foster better supplier relationships. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions involving reduction gears, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost allocation. This knowledge helps buyers avoid misunderstandings and disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. It is an important consideration for B2B buyers, particularly when project timelines are tight. Understanding lead times can aid in effective planning and inventory management, ensuring that projects proceed smoothly without delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing reduction ratio gears, ultimately optimizing their operations and enhancing productivity.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the reduction ratio gears Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends: What Are the Current Dynamics in the Reduction Ratio Gears Sector?
The global reduction ratio gears market is poised for substantial growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation in manufacturing and industrial processes across various sectors. Key trends include a shift towards advanced gear technologies such as planetary and strain wave gears, which offer higher efficiency and performance in compact designs. As industries like robotics, automotive, and renewable energy ramp up production, the need for precision and reliability in gear systems has never been more critical.
International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly influenced by the demand for cost-effective and high-quality solutions. The integration of IoT and AI technologies into manufacturing processes is also shaping sourcing trends, as companies seek gears that can seamlessly integrate with smart systems for enhanced performance monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in sourcing decisions. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to environmentally friendly practices and materials. This is especially relevant in regions where regulatory frameworks around sustainability are tightening, such as the European Union, prompting companies to look for compliant and innovative gear solutions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B: How Important Are Environmental Considerations for Reduction Ratio Gears?
As the world shifts towards sustainable practices, the reduction ratio gears sector is not exempt from this trend. The environmental impact of gear production, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers that utilize eco-friendly manufacturing processes and materials, such as recycled metals and low-emission production techniques.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies are increasingly held accountable for their sourcing decisions, and aligning with suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices is essential. Certification programs, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety, are valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Investing in reduction ratio gears that come with ‘green’ certifications not only enhances a company’s brand image but also ensures compliance with international standards and regulations. This can lead to better market positioning, particularly in environmentally conscious markets like Europe, where consumers and businesses alike are advocating for sustainable solutions.
Brief Evolution/History of Reduction Ratio Gears: How Have They Developed Over Time?
The evolution of reduction ratio gears has been marked by significant technological advancements since their inception in the early industrial age. Initially, simple gear arrangements were used to reduce speed and increase torque, primarily in steam engines and early machinery. Over time, innovations led to the development of various gear types, including worm, bevel, and planetary gears, each offering unique advantages in terms of efficiency and application versatility.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards precision engineering and miniaturization, driven by the demands of modern automation and robotics. The introduction of strain wave gearing has revolutionized the market, allowing for high torque in compact designs with minimal backlash. This historical progression highlights the importance of ongoing research and development in the sector, ensuring that reduction ratio gears continue to meet the evolving needs of industries worldwide.
As B2B buyers navigate this landscape, understanding the historical context can inform better sourcing decisions and foster partnerships with manufacturers that are at the forefront of innovation in gear technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of reduction ratio gears
-
How do I choose the right reduction ratio gear for my application?
Selecting the appropriate reduction ratio gear involves understanding your specific operational requirements, such as the desired output speed, torque, and load conditions. Start by assessing the motor specifications and the application’s demands. It’s essential to consider the gear type, as different designs (e.g., worm, planetary) offer unique advantages in terms of torque capacity, efficiency, and space constraints. Collaborating with suppliers who provide detailed product specifications and application support can help ensure you choose the right gear for optimal performance. -
What is the best type of reduction gear for high torque applications?
For high torque applications, planetary gear reduction systems are often the best choice due to their ability to handle large loads while maintaining a compact size. They distribute the load across multiple gears, enhancing durability and efficiency. Worm gears can also provide high torque but may generate more heat and have lower efficiency. Evaluating factors such as installation space, required torque, and efficiency will guide you in selecting the most suitable gear type for your needs. -
What are the key quality assurance measures to consider when sourcing reduction gears?
When sourcing reduction gears, it’s vital to ensure that suppliers adhere to strict quality assurance protocols. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate a commitment to quality management systems. Request documentation on testing procedures, including load testing and performance evaluations. It’s also beneficial to inquire about the materials used in gear construction, as high-quality materials can significantly impact durability and performance. Regular audits and quality checks during production can further assure the reliability of the products. -
How can I verify the reliability of a supplier for reduction gears?
To verify a supplier’s reliability, start by checking their reputation through industry references and customer reviews. Assess their experience in manufacturing reduction gears and their compliance with international standards. Engage in direct communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to provide technical support. Additionally, consider requesting samples or visiting the manufacturing facility to observe their production processes firsthand. A transparent supplier with a proven track record in your industry is crucial for establishing a successful partnership. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for reduction ratio gears?
The minimum order quantity for reduction ratio gears can vary significantly between suppliers and may depend on factors such as production capabilities and the type of gear required. Generally, MOQs can range from a few pieces for standard items to larger quantities for custom or specialized gears. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your project requirements and budget constraints. -
What payment terms are typically offered by international suppliers of reduction gears?
Payment terms can vary widely among international suppliers, often influenced by factors such as order size and buyer-supplier relationships. Common terms include payment in advance, net 30/60/90 days, or a letter of credit for larger transactions. To facilitate smoother transactions, consider negotiating flexible payment options that suit your cash flow needs. It’s also essential to clarify the currency of payment and any additional fees related to international transactions to avoid unexpected costs. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing reduction gears?
Logistics is a critical aspect of sourcing reduction gears internationally. Ensure that your supplier has robust shipping capabilities, including experience with customs clearance and handling international regulations. Assess the shipping methods available, such as air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, and consider lead times for production and delivery. Additionally, discuss the packaging standards to prevent damage during transit and inquire about tracking options to monitor your shipment’s progress. -
Can reduction gears be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for reduction gears to meet specific application requirements. Customization can include variations in gear ratios, sizes, materials, and configurations to accommodate unique operational demands. When seeking custom solutions, provide detailed specifications and performance criteria to your supplier. Collaborating closely during the design and testing phases can help ensure that the final product meets your expectations and integrates seamlessly into your equipment.
Top 7 Reduction Ratio Gears Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Orbray – Reduction Gears
Domain: orbray.com
Introduction: Reduction gears, also known as speed reducers, are essential components used in products powered by motors, such as industrial robots and machine tools. They reduce the number of rotations of a power source while increasing torque, allowing for appropriate rotational speed and torque for various applications. Key types of reduction gears include: 1. Parallel shaft reduction gears – combine spur an…
2. Groschopp – Gear Reduction Solutions
Domain: groschopp.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Gear Reduction refers to the process of reducing the output speed and increasing the torque of a rotary machine, such as an electric motor, through the use of gears. It is achieved by using gear ratios greater than 1:1, where a smaller gear drives a larger gear. Common types of gear reducers include parallel shaft, planetary, and right-angle worm gearboxes. For example, a 13-tooth pinion gear driv…
3. KHK Gears – Gear Reducers
Domain: khkgears.net
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Types of Gear Reducers: 1. Gear Reducers with Parallel Axes: – Use spur gears, helical gears, or herringbone gears. – Reduction ratios: 1/1 – 1/7 (one-stage), 1/10 – 1/30 (two-stage), 1/5 – 1/200 (more than three-stage). – High precision with transmission efficiency of 95-98%. – Commonly used in machines with high rotation. – Applications: steel facilities, ships, cranes, elevators, conveyors. 2. …
4. igus – Gear Reduction Solutions
Domain: toolbox.igus.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Gear reduction is a mechanical process that reduces speed and increases torque through a set of gears (gear train). It is achieved by using a smaller gear with fewer teeth to drive a larger gear. The gear ratio, defined as the ratio of the number of teeth on the driven gear to the driving gear, determines the reduction amount. A higher gear ratio results in higher torque and lower speed, while a l…
5. LinkedIn – Gear Reduction Solutions
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Gear reduction is a mechanical concept that changes the speed and torque of a system using gears. Key benefits include increased torque, speed control, efficiency, and size savings. Applications span various industries such as automotive, industrial machinery, robotics, aerospace, and construction. Types of gear reduction include: 1. Spur Gear Reduction – simple and efficient for speed reduction a…
6. Reddit – Gear Ratio Calculations
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Gear Ratio Calculations, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Omni Calculator – Gear Ratio Calculator
Domain: omnicalculator.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: The Gear Ratio Calculator determines the mechanical advantage of a two-gear setup in a machine. It calculates the gear ratio, which indicates how much an output gear is sped up or slowed down, and how much torque is lost or gained. The calculator uses the gear ratio equation and gear reduction equation for quick calculations. A gear is a toothed wheel that changes the direction, torque, and speed …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for reduction ratio gears
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing for Reduction Ratio Gears?
In the competitive landscape of reduction ratio gears, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal approach for international B2B buyers. By leveraging strategic partnerships with reputable manufacturers, companies can secure high-quality components that ensure optimal performance and reliability. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Additionally, understanding the diverse types of reduction gears—such as planetary, worm, and bevel gears—enables buyers to select the most suitable solutions tailored to their specific applications.
How Can Buyers Prepare for Future Trends in Reduction Ratio Gears?
As the demand for precision and efficiency continues to rise across various sectors, including robotics and automation, the outlook for reduction ratio gears remains promising. Buyers should stay informed about technological advancements and market trends, including the integration of smart technologies in gear systems. This proactive approach will facilitate informed purchasing decisions and foster long-term partnerships that drive innovation.
What Action Should International Buyers Take?
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to assess your sourcing strategies. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize quality, innovation, and sustainability can lead to significant competitive advantages. By embracing strategic sourcing, you can ensure that your operations remain agile and well-equipped to meet the evolving demands of the market. Reach out to trusted manufacturers today to explore how reduction ratio gears can optimize your machinery and enhance your operational capabilities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.