Top 5 Boiler System Parts Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for boiler system parts
In today’s complex and competitive landscape, sourcing reliable boiler system parts can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With varying standards, compliance requirements, and supplier capabilities across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, making informed purchasing decisions is more critical than ever. This comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for navigating the global market for boiler system parts, addressing essential aspects such as types of components, their applications, and effective supplier vetting processes.
Within these pages, you will discover detailed insights into the myriad of boiler system parts available, from liquid level gauges to heat exchangers and condensate units. Each section elucidates the unique functionalities and specifications necessary for optimal performance in diverse operational settings. Additionally, we delve into pricing structures and cost considerations, enabling buyers to strategically budget while ensuring quality and reliability.
Empowering international B2B buyers, this guide equips you with the knowledge needed to evaluate potential suppliers, understand market trends, and make confident purchasing decisions. Whether you are in Saudi Arabia seeking advanced heat exchangers or in Vietnam looking for durable gauge glass, our expert insights will help you navigate the complexities of the boiler system parts market with ease and assurance.
Understanding boiler system parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boiler Feed Pumps | Essential for maintaining water levels, typically centrifugal or reciprocating. | Power generation, manufacturing, HVAC systems. | Pros: Reliable water supply; Cons: High maintenance costs. |
| Steam Traps | Automatically discharge condensate while retaining steam. | Chemical processing, food production, and heating systems. | Pros: Energy-efficient; Cons: Risk of failure leading to steam loss. |
| Heat Exchangers | Facilitate heat transfer between two fluids without mixing. | HVAC, refrigeration, and power plants. | Pros: Improved energy efficiency; Cons: Initial installation costs. |
| Safety Relief Valves | Prevent overpressure by releasing excess steam or fluid. | Oil and gas, chemical, and utility industries. | Pros: Critical for safety; Cons: Can be costly if not regularly maintained. |
| Gauge Glasses | Provide visual indication of water levels in boilers. | All types of boiler systems. | Pros: Easy monitoring; Cons: Vulnerable to breakage. |
What Are Boiler Feed Pumps and Their Importance in B2B Operations?
Boiler feed pumps are crucial components designed to ensure a consistent supply of water to the boiler. They typically come in centrifugal or reciprocating designs, enabling them to handle varying flow rates and pressures. In B2B applications, such as power generation and manufacturing, the reliability of these pumps is paramount. Buyers should consider factors like pump efficiency, compatibility with existing systems, and maintenance requirements, as these can significantly impact operational costs.
How Do Steam Traps Enhance Efficiency in Industrial Settings?
Steam traps play a vital role in managing steam systems by allowing condensate to escape while preventing steam loss. This feature is essential in industries like chemical processing and food production, where steam is integral to operations. When purchasing steam traps, B2B buyers should evaluate the type of trap needed (e.g., thermodynamic, float), the potential for energy savings, and the likelihood of failure, which can lead to costly steam losses if not addressed.
What Are Heat Exchangers and Why Are They Beneficial for Energy Efficiency?
Heat exchangers are devices that transfer heat between two or more fluids without allowing them to mix. They are widely used in HVAC, refrigeration, and power plants to enhance energy efficiency by recovering waste heat. For B2B buyers, considerations include the type of heat exchanger (e.g., shell and tube, plate), material compatibility, and maintenance needs. While the initial investment can be high, the long-term energy savings often justify the cost.
Why Are Safety Relief Valves Critical for Industrial Boiler Systems?
Safety relief valves are essential for preventing overpressure in boiler systems by automatically releasing excess steam or fluid. This functionality is critical in industries such as oil and gas and utilities, where safety regulations are stringent. Buyers should focus on the valve’s pressure rating, response time, and maintenance requirements to ensure compliance and operational safety. While they are vital for preventing catastrophic failures, their maintenance can represent a significant ongoing expense.
What Role Do Gauge Glasses Play in Monitoring Boiler Operations?
Gauge glasses are used to provide a clear visual indication of water levels in boilers, allowing operators to monitor performance easily. They are universally applicable across various boiler systems. For B2B buyers, considerations include the material of the gauge glass, its resistance to thermal shock, and the ease of installation and maintenance. While gauge glasses offer straightforward monitoring solutions, they are also prone to breakage, which can lead to operational disruptions.
Key Industrial Applications of boiler system parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of boiler system parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Steam generation for cooking and processing | Enhanced efficiency and safety in food production | Compliance with health regulations and material safety standards |
| Oil & Gas | Heat exchangers for thermal recovery | Improved energy efficiency and reduced operational costs | Durability under extreme conditions and local sourcing options |
| Manufacturing | Steam heating for industrial processes | Increased production efficiency and reduced downtime | Compatibility with existing systems and availability of replacement parts |
| Power Generation | Boiler feedwater treatment systems | Enhanced boiler performance and longevity | Quality of materials and adherence to international standards |
| Textile | Steam supply for dyeing and finishing processes | Consistent quality and reduced cycle times | Sourcing from reliable manufacturers with proven track records |
How Are Boiler System Parts Used in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, boiler system parts play a critical role in steam generation for cooking, sterilization, and processing. High-quality steam is essential for ensuring food safety and maintaining product quality. Buyers in this industry must prioritize sourcing parts that comply with health regulations, ensuring that materials are safe for food contact. Additionally, reliability is paramount, as any downtime can lead to significant production losses.
What is the Role of Boiler System Parts in Oil & Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas industry, heat exchangers are vital components that facilitate thermal recovery processes. These systems improve energy efficiency by recovering and reusing heat generated during operations. International buyers should consider the durability of these parts, as they often operate under extreme conditions. Local sourcing options may also be beneficial to minimize lead times and ensure prompt maintenance support.
Why Are Boiler System Parts Important for Manufacturing?
Manufacturers utilize boiler systems for steam heating in various industrial processes, including molding and drying. Efficient steam generation translates to increased production efficiency and reduced downtime, which are crucial for maintaining competitive advantage. Buyers should focus on compatibility with existing systems and the availability of replacement parts to ensure seamless integration and ongoing operational reliability.
How Do Boiler System Parts Enhance Power Generation?
In power generation facilities, boiler feedwater treatment systems are essential for maintaining optimal performance and extending the life of boiler equipment. These systems prevent scaling and corrosion, which can lead to significant operational issues. Buyers should ensure that sourced parts meet high-quality standards and are designed for the specific pressures and temperatures encountered in power generation environments.
What is the Significance of Boiler System Parts in the Textile Industry?
In the textile industry, boiler systems provide steam for dyeing and finishing processes, which are crucial for achieving consistent quality in fabric production. Timely and reliable steam supply reduces cycle times and enhances overall production efficiency. Buyers must prioritize sourcing from reputable manufacturers that offer parts with proven reliability and performance history to avoid production interruptions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘boiler system parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality of Replacement Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with the quality of replacement parts for boiler systems. Inconsistent quality can lead to premature failures, resulting in costly downtime and repairs. For example, a manufacturing plant in Saudi Arabia may purchase parts that do not meet the required specifications or performance standards, leading to inefficiencies and safety hazards. This not only disrupts operations but also strains relationships with clients who depend on timely production.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who provide verified high-quality parts. This includes demanding certifications and performance data for all components. It is crucial to conduct thorough research on suppliers, seeking out those with a strong track record in the industry. Additionally, leveraging platforms that aggregate user reviews can provide insights into the reliability of specific manufacturers. Buyers should also consider implementing a robust quality assurance process upon receipt of parts, including visual inspections and functional testing to confirm adherence to specifications before installation.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Finding Compatible Parts
The Problem: A common issue for B2B buyers in different regions, such as South America and Europe, is the difficulty in sourcing compatible parts for diverse boiler systems. Variations in design and specifications can create confusion, leading to the procurement of incorrect components. This not only extends lead times but can also incur additional costs for returns and reshipments. A facilities manager in Vietnam may find themselves facing delays in project timelines due to the incompatibility of parts sourced from various suppliers.
The Solution: To overcome compatibility issues, buyers should first invest time in creating a comprehensive inventory of existing boiler systems, including detailed specifications for each model. When sourcing parts, utilizing manufacturer databases and OEM catalogs can significantly improve accuracy in matching components. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in multi-brand support can provide additional assurance of compatibility. Furthermore, buyers can use digital tools and platforms that allow for cross-referencing parts based on model numbers and specifications, ensuring that the right components are sourced from the start.
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
Scenario 3: Limited Technical Support for Complex Installations
The Problem: Another pain point for B2B buyers involves the lack of technical support during the installation of complex boiler system parts. Many suppliers may provide the necessary components but fall short in offering guidance or troubleshooting assistance during critical installation phases. For instance, a company in the Middle East may encounter technical difficulties when integrating new control systems into their existing boiler infrastructure, leading to delays and potential operational disruptions.
The Solution: To enhance technical support, buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers that offer comprehensive installation services and ongoing technical assistance. This could involve negotiating service agreements that include on-site support or remote troubleshooting during critical installation phases. Additionally, investing in training for in-house maintenance teams can empower them to handle common issues independently. Suppliers that provide detailed installation manuals and video tutorials can also facilitate smoother integration processes. Establishing a clear line of communication with suppliers for real-time support during installation can further reduce the risk of costly errors and ensure efficient project completion.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for boiler system parts
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Boiler System Parts?
When selecting materials for boiler system parts, understanding the unique properties of each material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, cast iron, and copper. Each has distinct characteristics that influence their suitability for various applications.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Boiler Applications?
Carbon steel is a widely used material in boiler system parts due to its excellent strength and durability. It typically has a high-temperature rating and can withstand significant pressure, making it ideal for high-stress environments. However, carbon steel is susceptible to corrosion, especially in humid or acidic conditions, which can limit its lifespan if not properly maintained.
Pros: Carbon steel is cost-effective and relatively easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for many boiler components, including piping and structural elements.
Cons: Its susceptibility to corrosion necessitates regular maintenance and protective coatings, which can add to long-term costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for water and steam applications but may not be ideal for corrosive media without protective measures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM standards for carbon steel grades and consider local environmental conditions that may affect corrosion rates.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Boiler Parts?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, making it an excellent choice for boiler system parts exposed to moisture and aggressive chemicals. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications, including heat exchangers and valves.
Pros: The durability and longevity of stainless steel reduce the need for frequent replacements, which can be cost-effective in the long run.
Cons: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than carbon steel and can be more complex to fabricate, which may increase initial costs.
Impact on Application: Its compatibility with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, makes stainless steel a versatile option for boiler systems.
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with DIN and JIS standards for stainless steel grades, as these are commonly recognized in international markets.
Why Is Cast Iron a Traditional Choice for Boiler Components?
Cast iron has been a traditional material for boiler systems due to its excellent thermal conductivity and ability to withstand high temperatures. It is often used in boiler bodies and heat exchangers.
Pros: Cast iron is durable and provides excellent heat retention, contributing to energy efficiency.
Cons: It is brittle and can crack under stress or impact, limiting its application in high-pressure environments.
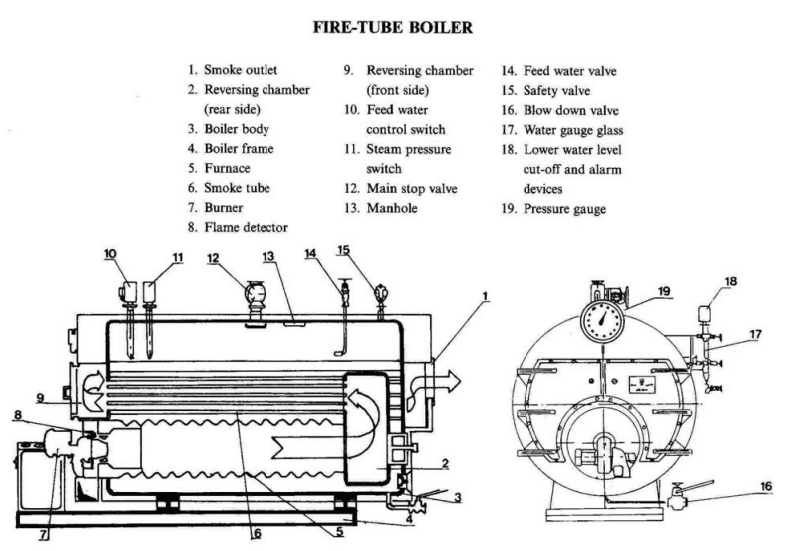
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
Impact on Application: Cast iron is best suited for low-pressure steam applications and can be used in systems where thermal efficiency is prioritized.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that cast iron components meet local standards, such as ASTM A48, to ensure quality and performance.
What Role Does Copper Play in Boiler Systems?
Copper is less commonly used for large boiler components but is often found in smaller parts, such as tubing and fittings, due to its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: Copper’s thermal efficiency can lead to reduced energy costs and improved system performance.
Cons: It is more expensive than other materials and can be susceptible to erosion corrosion in certain conditions.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for hot water systems and applications where rapid heat transfer is essential.
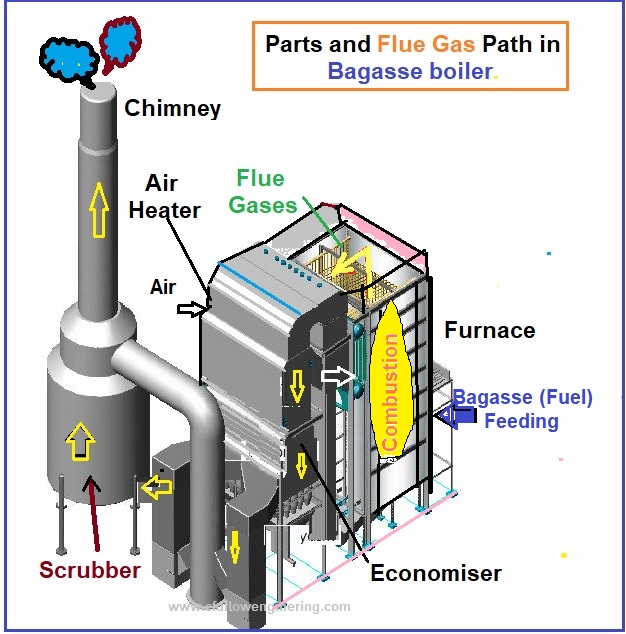
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards for copper alloys, such as ASTM B75, is essential, especially for buyers in regions with specific regulatory requirements.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Boiler System Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for boiler system parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Piping and structural components | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Heat exchangers and valves | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher initial cost | High |
| Cast Iron | Boiler bodies and heat exchangers | Good thermal conductivity | Brittle and can crack | Med |
| Copper | Tubing and fittings | Superior thermal conductivity | Expensive and erosion susceptible | High |
This guide provides insights into the strategic selection of materials for boiler system parts, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for boiler system parts
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Boiler System Parts?
The manufacturing of boiler system parts involves several critical stages that ensure the final products meet industry standards and customer specifications. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials such as steel, copper, and specialized alloys. Suppliers often conduct tests to verify material properties, including tensile strength and corrosion resistance. The materials are then cut and shaped into manageable sizes, ready for the next phase.
-
Forming: In this stage, various techniques such as stamping, casting, and machining are employed to create the desired shapes of components. For instance, boiler tubes may be produced through extrusion or rolling processes, while valves might be machined from solid blocks of metal. The choice of technique depends on the specific part being manufactured and its functional requirements.
-
Assembly: Once individual components are formed, they are assembled into larger subassemblies or complete units. This may involve welding, bolting, or using adhesives, depending on the type of part and its intended use. Precision is vital here, as any misalignment can lead to failures in performance or safety.
-
Finishing: The final stage of manufacturing includes surface treatments such as painting, coating, or polishing to enhance durability and aesthetics. This stage may also involve heat treatment to improve mechanical properties. Effective finishing processes are essential to ensure that components can withstand the harsh conditions typically found in boiler systems.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing of Boiler Parts?
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that all parts meet both international standards and customer expectations. The QA process typically follows a series of checkpoints, including Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers must provide certificates of conformity, and materials are checked for compliance with specifications. Any non-conforming materials are rejected or returned.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor adherence to quality standards. This can include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and tests for specific properties, ensuring that any issues are identified early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the assembly is complete, the final inspection ensures that the product meets all specifications before shipment. This may include functional testing, pressure testing, and safety checks. Any defective parts are reworked or discarded.
What International Standards and Industry-Specific Certifications Are Relevant for Boiler Parts?
International standards play a vital role in ensuring the quality and safety of boiler parts. Key standards include ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems, and industry-specific certifications such as CE marking and API standards.
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management principles, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Manufacturers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to quality processes.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates that products comply with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is particularly important for components used in boiler systems operating in EU countries.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) has developed standards for various components used in oil and gas applications, including boiler systems. Compliance with API standards assures buyers of the quality and reliability of the parts.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in the Quality Assurance of Boiler Parts?
Testing methods used in the quality assurance of boiler parts can vary widely depending on the component and its intended use. Common methods include:
-
Hydrostatic Testing: This test checks for leaks and structural integrity by filling the component with water under pressure. It’s critical for safety-critical parts like pressure vessels.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and radiographic testing are employed to detect internal and surface defects without damaging the part.
-
Functional Testing: This involves testing components under operational conditions to ensure they perform as expected. For instance, valves may be tested for their response to pressure changes.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some effective methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This firsthand evaluation can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Quality Control Reports: Requesting documentation on quality control processes, including inspection reports and certifications, helps buyers understand the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s operations and compliance with relevant standards. This can be particularly useful for buyers unfamiliar with local suppliers.
What Are the QC/Certifications Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, B2B buyers must navigate various certifications and compliance requirements that can differ by region. For example, while CE marking is essential for products sold in Europe, other regions may have different standards, such as the ASME certification for North America or local standards applicable in African and South American markets.
Buyers should ensure that suppliers are not only certified but also compliant with the specific regulations and standards of the markets they serve. This includes understanding the nuances of local regulations regarding safety, environmental impact, and manufacturing practices.
By being informed about the manufacturing processes, quality assurance practices, and relevant standards, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing boiler system parts, ultimately leading to better operational efficiency and safety in their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘boiler system parts’
The following practical sourcing guide is designed for B2B buyers looking to procure boiler system parts effectively. It offers a step-by-step checklist to help streamline the process, ensuring you make informed decisions while sourcing components for your boiler systems.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline the technical specifications required for the boiler parts. This includes details such as size, material type, and performance standards. Accurate specifications help in avoiding compatibility issues and ensure that the parts meet your operational requirements.
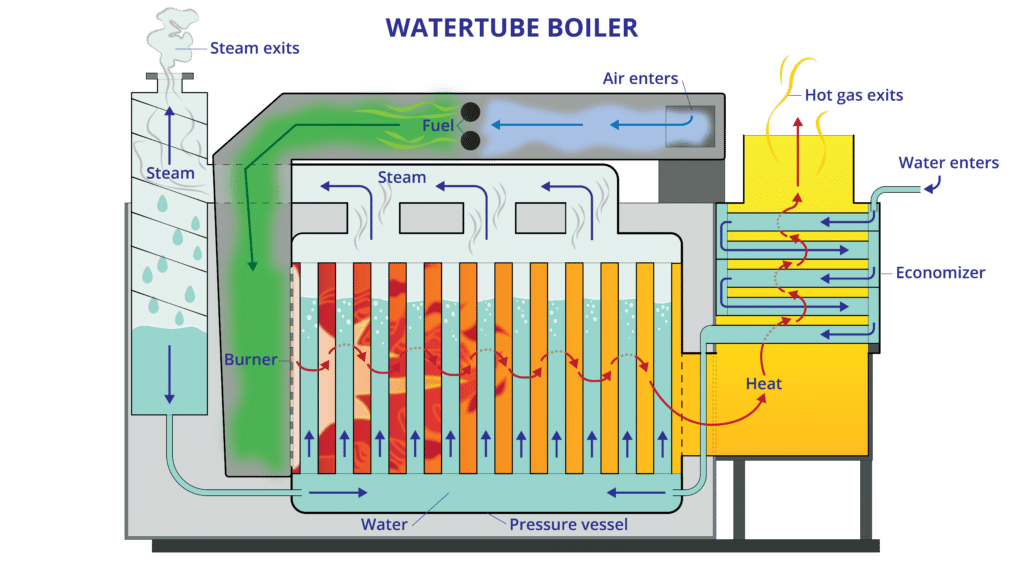
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in boiler system parts. Utilize online marketplaces, industry directories, and trade shows to compile a list of potential vendors. Focus on suppliers with experience in your specific industry and geographical region, as they are more likely to understand your unique needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers that have a proven track record of reliability and quality in their products.
- Check Reviews: Seek out customer reviews and ratings to gauge supplier reliability.
- Ask for Certifications: Verify whether they hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, ASME) that ensure quality standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Product Specifications
Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, request samples or detailed product specifications. This step is essential to verify the quality and compatibility of the parts with your existing systems.
- Assess Material Quality: Ensure that the materials used meet industry standards and are suitable for your operational environment.
- Review Compliance: Confirm that the products comply with local regulations and safety standards.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in negotiations to secure the best pricing and terms for your boiler parts. Consider factors such as bulk order discounts, payment terms, and delivery schedules. A well-structured negotiation can lead to significant cost savings and better service levels.
- Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the purchase price, but also shipping, handling, and potential tariffs.
- Discuss Warranty and Support: Ensure that warranty terms are clear and that the supplier offers adequate support in case of issues.
Step 6: Finalize Contracts and Place Orders
After agreeing on terms, finalize contracts with your selected supplier. Ensure that all aspects of the agreement are documented, including delivery timelines and payment schedules.
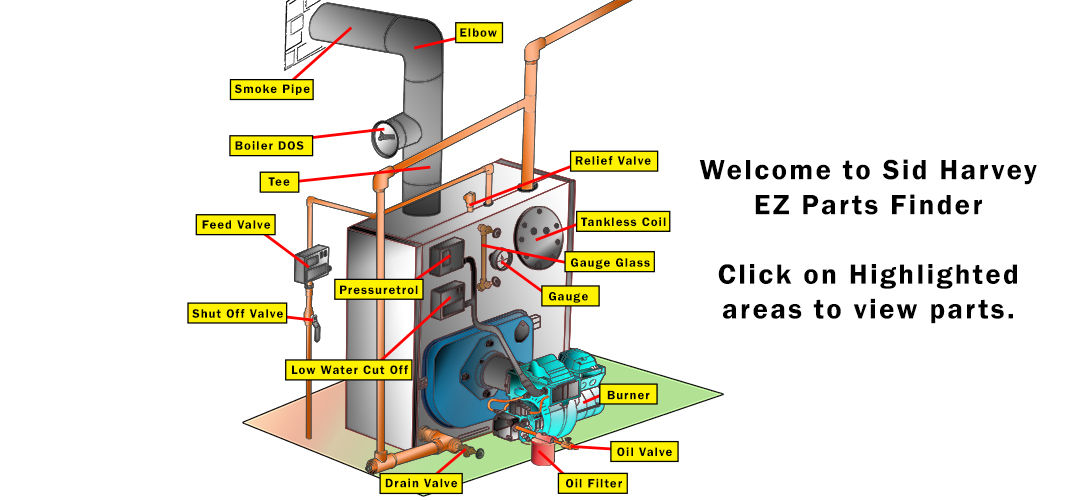
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
- Include Performance Clauses: Add clauses that outline penalties for non-compliance or late deliveries.
- Establish Clear Communication Channels: Define points of contact to facilitate smooth communication throughout the order process.
Step 7: Monitor Delivery and Quality Control
Once your order is placed, monitor the delivery process closely. Upon receipt, conduct a thorough inspection of the parts to confirm they meet your specifications. Implement quality control measures to ensure all components function as intended within your boiler systems.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a more efficient and effective sourcing process for boiler system parts, leading to improved operational reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for boiler system parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Boiler System Parts Sourcing?
When sourcing boiler system parts, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. Key cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials used in manufacturing boiler parts can significantly influence costs. Common materials include steel, brass, and specialized alloys, with prices varying based on market demand and availability. For example, fluctuations in steel prices can lead to increased costs for components like heat exchangers and valves.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality control. Labor rates can vary by region, with higher costs typically found in developed countries compared to emerging markets. This disparity can impact total costs for international buyers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment necessary for production. Manufacturers often factor these costs into the pricing of parts, which can vary based on operational efficiency and the scale of production.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specialized parts, which adds to the initial investment. Buyers should consider whether they need standard parts or customized solutions, as tooling costs can be substantial for bespoke items.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet industry standards involves rigorous testing and inspection, contributing to overall costs. Certifications such as ASME or ISO can add value but may increase pricing due to compliance processes.
-
Logistics: Shipping, handling, and storage costs must also be accounted for, especially when sourcing internationally. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can greatly affect the final price.
-
Margin: Manufacturers and suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary widely based on market competition and perceived value.
What Influences Pricing for Boiler System Parts?
Numerous factors can influence the pricing of boiler system parts, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating for better pricing based on volume can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts designed to meet specific operational needs often carry higher prices than standard components. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of customization versus the cost implications.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certified components usually come at a premium. Buyers must assess the balance between cost and the longevity or efficiency gains from investing in higher-grade materials.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer better service and assurance of quality.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade (Incoterms) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Boiler Parts Pricing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic negotiation and cost management are vital:
-
Conduct a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis: Look beyond the initial purchase price to consider long-term costs, including maintenance, energy efficiency, and potential downtime. This can provide a clearer picture of the true value of parts.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Regular communication and feedback can foster trust and enhance negotiation outcomes.
-
Research and Benchmark: Understanding market rates and competitor pricing can empower buyers during negotiations. Conducting thorough research on similar products can provide leverage in discussions.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be conscious of currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and local regulations that may affect pricing. Staying informed about geopolitical factors can also play a role in cost management.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of cost and pricing in boiler system parts sourcing requires a detailed understanding of various components and influencers. By employing strategic negotiation tactics and conducting comprehensive analyses, B2B buyers can optimize their purchasing decisions and achieve better financial outcomes. Always remember that the prices provided are indicative and can vary based on market conditions and individual supplier circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing boiler system parts With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Boiler System Parts: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of industrial heating solutions, boiler system parts play a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and maintenance of boiler systems. However, various alternatives exist that can fulfill similar functions, offering different benefits and considerations. This section compares traditional boiler system parts with two viable alternative solutions: electric heating systems and thermal fluid heaters.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Boiler System Parts | Electric Heating Systems | Thermal Fluid Heaters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency for steam and hot water generation | Quick heating, lower response time | Excellent heat transfer efficiency |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Higher upfront costs; lower operational costs | Moderate to high initial costs; longer payback |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor for installation and maintenance | Easier installation; less skilled labor needed | Complex installation; requires specific design |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance | Minimal maintenance; typically more reliable | Regular checks required; specialized technicians needed |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large-scale industrial applications | Suitable for smaller operations or facilities with lower heat demands | Best for processes requiring stable and high-temperature heating |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Heating Systems
Electric heating systems utilize electrical energy to produce heat, making them a popular choice for facilities that require a quick and efficient heating solution. The primary advantage of electric heating is its lower operational costs due to minimal maintenance requirements and higher reliability. They are particularly effective in smaller operations where quick heat-up times are essential. However, the initial investment can be higher compared to traditional boiler systems, and they may not be suitable for high-demand applications where large volumes of steam or hot water are necessary.
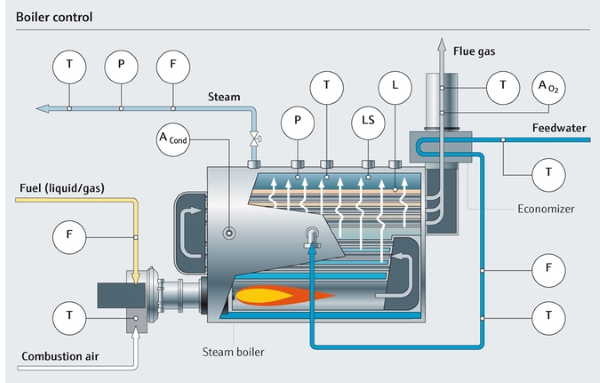
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
Thermal Fluid Heaters
Thermal fluid heaters operate using a heat transfer fluid, which allows for high-temperature heating without the need for high pressure. These systems excel in applications where consistent and stable heating is critical, such as in chemical processing or food manufacturing. They offer excellent heat transfer efficiency, which can lead to energy savings in the long run. However, their installation can be complex and requires specialized knowledge, resulting in higher upfront costs and the need for skilled technicians for maintenance. Their best use case is in industries where process stability and temperature control are paramount.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Heating Solution for Your Business Needs
When evaluating heating solutions, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Boiler system parts may provide the best performance for large-scale operations, while electric heating systems could be more advantageous for smaller facilities seeking efficiency and reliability. Thermal fluid heaters, on the other hand, serve industries with specific heating demands that prioritize temperature stability. By weighing the pros and cons of each option against their operational needs, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their heating systems’ efficiency and reliability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for boiler system parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Boiler System Parts?
Understanding the essential technical properties of boiler system parts is crucial for B2B buyers, as these specifications directly impact performance, safety, and longevity. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the quality and type of materials used in manufacturing boiler components, typically including metals like stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloys.
– B2B Importance: Material grade affects the durability and corrosion resistance of parts. For instance, higher-grade stainless steel is preferable in corrosive environments, ensuring longer service life and reduced replacement costs. -
Tolerance Levels
– Definition: Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension, such as diameter or thickness of a component.
– B2B Importance: Tight tolerances are crucial for the proper fit and function of boiler parts. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to inefficiencies, increased wear, and potential safety hazards, making it essential for buyers to specify and verify tolerances in their orders. -
Pressure Rating
– Definition: This specification indicates the maximum pressure that a boiler part can safely withstand during operation, often expressed in pounds per square inch (PSI).
– B2B Importance: Understanding the pressure rating is vital for ensuring that components can handle the operational demands of the system. Selecting parts with appropriate ratings can prevent failures, ensuring operational efficiency and safety. -
Temperature Resistance
– Definition: This property defines the maximum temperature that a boiler component can tolerate without degrading.
– B2B Importance: High-temperature resistance is crucial in steam boilers where components are subject to extreme conditions. Ensuring the selected parts can withstand these temperatures helps in maintaining system integrity and reducing maintenance costs. -
Weldability
– Definition: Weldability refers to the ease with which a material can be welded without compromising its mechanical properties.
– B2B Importance: For custom installations or repairs, understanding the weldability of materials ensures that modifications or replacements can be carried out effectively, minimizing downtime and ensuring reliable operation. -
Flow Coefficient (Cv)
– Definition: The flow coefficient quantifies the flow capacity of a valve or fitting, indicating how much fluid can pass through it at a given pressure drop.
– B2B Importance: A higher Cv value means better flow efficiency, which is essential for optimizing system performance. Buyers should consider Cv values when selecting valves and fittings to ensure they meet the operational needs of their boiler systems.
Which Trade Terms Are Commonly Used in Boiler Parts Procurement?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the boiler parts market. Here are some commonly used trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding whether a part is OEM or aftermarket helps buyers assess quality, compatibility, and warranty options, impacting overall system performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively. It can also affect pricing negotiations and overall project costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Importance: Submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, enabling informed purchasing decisions and better cost management. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers for the delivery of goods.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms helps in clarifying shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs, which is vital for smooth international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time is the time between the initiation of an order and its completion.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time is critical for project planning and ensuring that parts are available when needed, thereby preventing delays in operations. -
Warranty
– Definition: A warranty is a guarantee provided by a manufacturer regarding the condition of its product, typically covering repairs or replacements for a specified period.
– Importance: Understanding warranty terms is essential for assessing the risk associated with a purchase and can influence the total cost of ownership for boiler components.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and safeguard their investments in boiler systems.
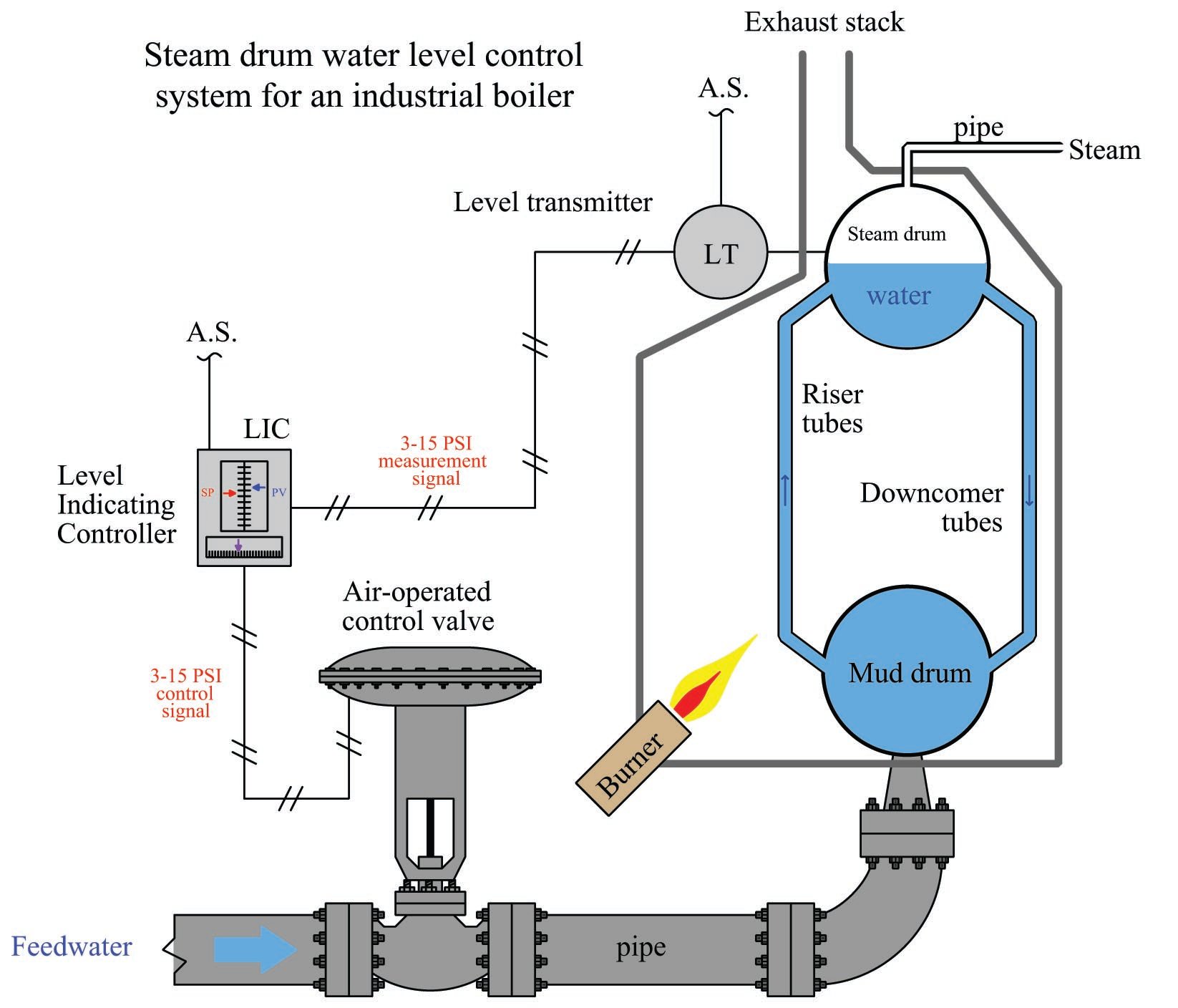
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the boiler system parts Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting the Boiler System Parts Sector?
The boiler system parts sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, is a primary driver. Countries like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam are investing heavily in industrialization and infrastructure, leading to a surge in boiler installations. This growth is further accelerated by stringent regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions, pushing manufacturers to innovate and supply more efficient components.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends as well. The adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) for predictive maintenance is gaining traction, allowing businesses to minimize downtime and optimize operations. B2B buyers are increasingly turning to digital platforms for sourcing, facilitating quicker decision-making and access to a wider range of suppliers. Moreover, the integration of AI in inventory management is helping companies better predict demand and streamline procurement processes.
Another notable trend is the shift towards local sourcing. International buyers are looking for suppliers closer to their operational bases to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions. As a result, partnerships with regional manufacturers are becoming more prevalent, offering buyers not only cost advantages but also shorter lead times.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Boiler Parts Market?
Sustainability has emerged as a crucial factor in the procurement of boiler system parts. The environmental impact of production processes and the lifecycle of materials used in manufacturing are now under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and utilizing eco-friendly materials.
Ethical sourcing is equally significant, with many organizations now requiring suppliers to adhere to social responsibility standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management are becoming prerequisites for suppliers looking to engage with international buyers. Additionally, using ‘green’ materials, such as recycled metals and biodegradable insulation, can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious clients.
By focusing on sustainability, businesses not only comply with regulatory requirements but also contribute positively to their brand image. This commitment can lead to increased customer loyalty and a competitive edge in a market that is progressively valuing ethical practices.
What Is the Historical Context of the Boiler Parts Industry?
The boiler system parts industry has evolved considerably over the last century. Initially dominated by simple steam boilers, the sector has transitioned to highly sophisticated systems that integrate advanced technologies. The early 20th century saw the introduction of safety features and automation, significantly improving operational efficiency and safety.
Post-World War II, the global demand for energy surged, leading to innovations in boiler design and materials. The oil crises of the 1970s further catalyzed the shift towards energy efficiency, prompting manufacturers to develop more advanced heat exchange systems and controls.
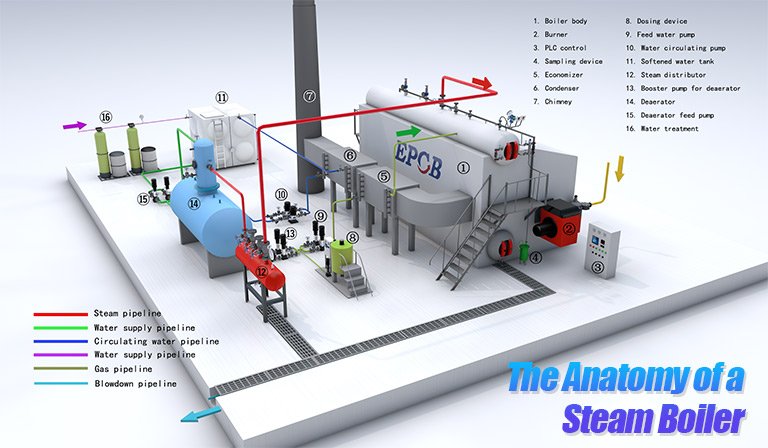
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and digitalization, reflecting broader societal trends. As international regulations tighten around emissions and energy efficiency, the boiler parts sector is poised for continued evolution, adapting to meet the needs of a changing world while maintaining a commitment to quality and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of boiler system parts
-
How do I solve issues with boiler system parts compatibility?
To address compatibility issues, start by identifying the specific model and make of your boiler system. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications or documentation to determine the required part numbers. Engage with suppliers who can provide detailed product information and compatibility charts. If possible, opt for OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts to ensure a perfect fit. For custom solutions, communicate your requirements clearly to suppliers, as they may offer tailored options that meet your needs. -
What is the best type of boiler part for high-efficiency systems?
For high-efficiency systems, focus on components designed to optimize energy use, such as advanced heat exchangers, variable speed pumps, and programmable controls. Look for parts that are certified for efficiency standards, such as those from ASME or ISO. Additionally, consider integrating smart controls that can adjust performance based on real-time data. Collaborate with suppliers who specialize in high-efficiency technologies to ensure you select the best parts for your system’s specific requirements. -
How can I vet potential suppliers of boiler system parts?
To effectively vet suppliers, begin by checking their industry reputation through online reviews and testimonials. Verify their certifications and compliance with international standards relevant to boiler systems, such as ASME or ISO. Request references from other clients, especially those in your region, to assess their reliability and service quality. Additionally, consider conducting site visits or audits to evaluate their facilities and inventory management practices. -
What are the typical payment terms in international B2B transactions for boiler parts?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier and region, but common practices include upfront deposits (20-30%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms (30-60 days) for established relationships. It’s crucial to clarify terms before finalizing any agreements. Consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks, especially when dealing with new suppliers or large orders. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for boiler system parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for boiler parts can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific parts required. Some suppliers may have MOQs as low as one unit for standard items, while others may require larger quantities for custom or specialized parts. Always inquire about MOQs before placing an order, as they can affect pricing and lead times. If your needs are small, consider negotiating or exploring suppliers who cater to smaller orders. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing boiler parts internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications, including material certifications and performance standards. Many reputable suppliers will provide quality control documentation and inspection reports. If possible, visit the supplier’s facility to observe their quality control processes. Additionally, consider third-party inspection services before shipment to verify compliance with your specifications and standards, especially for critical components. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing boiler parts?
When importing boiler parts, consider shipping times, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that could affect your total costs. Ensure that the supplier can provide all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including bills of lading and certificates of origin. Collaborate with a reliable freight forwarder who understands the specific requirements for boiler parts to facilitate smooth logistics. Additionally, account for storage and handling upon arrival to ensure proper treatment of sensitive components. -
How can I customize boiler parts to meet specific operational needs?
Customization of boiler parts typically involves collaboration with suppliers who specialize in engineering solutions. Clearly define your operational requirements and any specific performance metrics you need to meet. Many manufacturers offer design services that allow for modifications to existing parts or the creation of entirely new components. Discuss lead times and costs associated with custom orders upfront to avoid surprises. Additionally, ensure that prototypes or samples are tested before full-scale production to validate performance.
Top 5 Boiler System Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
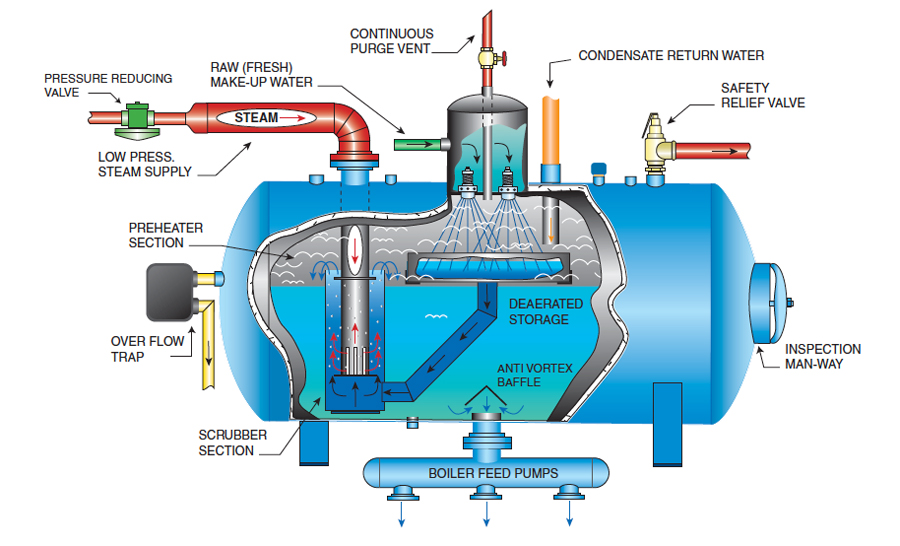
1. Ware Inc – Boiler Parts & Supplies
Domain: wareinc.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Boiler Parts & Supplies: More than 40,000 parts in stock, extensive boiler parts inventory. Key products include: Air Pressure Switches, Blowdown Valves, Boiler Gaskets, Boiler Sight Glass and Valves, Flame Safeguard, Fuel Oil Valves, Gas Pressure Switches, Gas Regulators, Gas Valves, Gauges and Thermometers, Ignitors and Ignition Transformer, Modulating Motors, Modulating Feedwater Valves, Boiler…
2. BoilerWAREhouse – Boiler Parts and Supplies
Domain: boilerwarehouse.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: BoilerWAREhouse offers a wide range of boiler parts and supplies, including:
– Air Pressure Switches
– Blowdown Valves
– Burner Diffusers
– Flame Safeguard Controls
– Fuel Oil Valves and Actuators
– Gas Pressure Switches
– Gas Regulators
– Gas Valves and Actuators
– Gaskets and Gasket Kits
– Gauges
– Hand Hole and Manway Plates
– Hot Water Boilers
– Ignition Transformers
– Ignitors and Accessories…
3. Chardon Labs – Steam Boiler Parts
Domain: chardonlabs.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The main steam boiler parts and their functions include: 1. Burner – Creates combustion based on thermostat alerts and adjusts fuel burning according to heat requirements. 2. Tubes – Heat water to produce steam, available in water-tube or fire-tube designs. 3. Pressure Vessel – Holds high temperature and high-pressure gases. 4. Combustion Chamber – Where fuel burning occurs, transferring heat to t…
4. Ferguson – Boilers & Replacement Parts
Domain: ferguson.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, Ferguson – Boilers & Replacement Parts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Oswald Supply – Boiler Parts and Accessories
Domain: oswaldsupply.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Top-Quality Sections and Assembly Boiler Parts available at Oswald Supply. Categories include Handhole/Manhole Gaskets, Trash Chute Doors/Parts, Boilers/Heating Supplies, Radiators, and Mini Split Systems. Products include Handhole Plates, Manhole Plates, Complete Assemblies, Gaskets, Burner Tubes, Ceramic Fire Blankets, Tankless Coils, and various Boiler Repair Parts. Major manufacturers include …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for boiler system parts
In the competitive landscape of boiler system parts, strategic sourcing emerges as a cornerstone for operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By fostering relationships with reliable suppliers, businesses can secure high-quality components that meet stringent compliance and performance standards. This not only enhances the longevity and reliability of boiler systems but also streamlines maintenance processes, ultimately leading to reduced downtime and improved productivity.
For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing is crucial. Engaging with diverse suppliers allows companies to leverage regional strengths, tap into innovative technologies, and adapt to varying market demands.
Looking ahead, the emphasis on sustainability and technological advancements in boiler systems will drive the evolution of sourcing strategies. Buyers are encouraged to actively seek out partnerships that prioritize not only quality but also environmental responsibility. By doing so, they can position themselves as leaders in their industries while contributing to a more sustainable future. Embrace strategic sourcing today to unlock the potential for growth and resilience in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
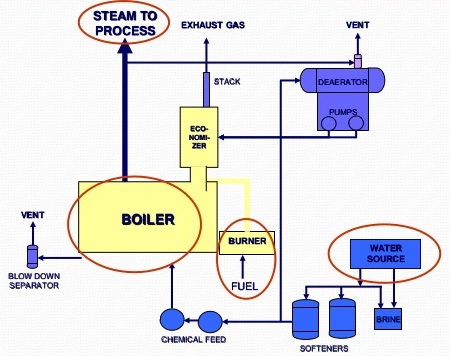
Illustrative image related to boiler system parts
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.