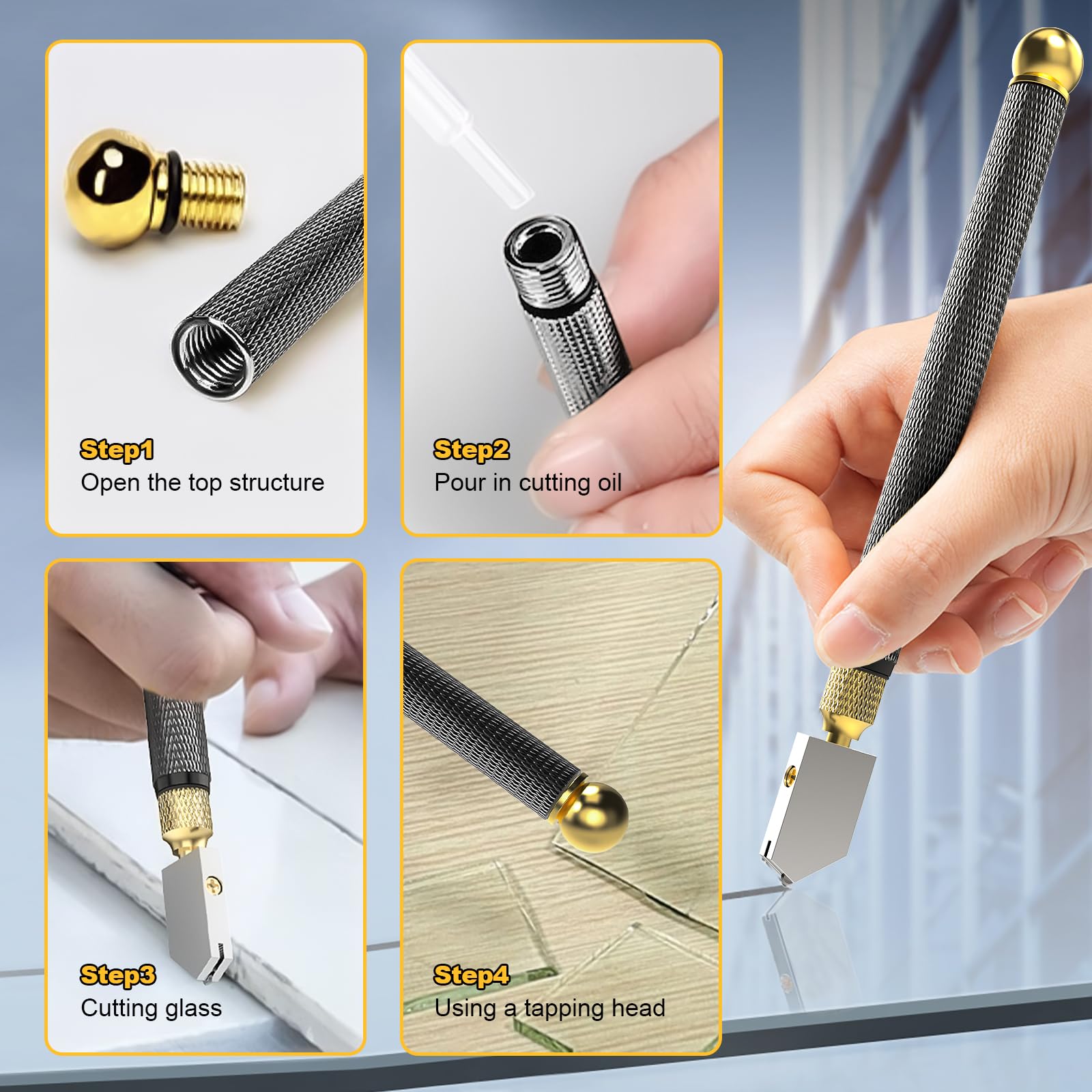
Glass Cutting Instrument: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for glass cutting instrument
In the competitive landscape of glass cutting instruments, sourcing the right tools can significantly impact operational efficiency and product quality. With the increasing demand for precision in glasswork across various sectors, international B2B buyers face the challenge of identifying reliable suppliers that offer high-quality glass cutting tools suited to their specific needs. This guide aims to streamline that process by providing a comprehensive overview of the types of glass cutting instruments available, their applications, and essential criteria for supplier vetting.
From handheld cutters and circle cutters to advanced cutting systems, understanding the diverse range of tools is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we will delve into the cost considerations and market trends that influence pricing, helping buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Vietnam and Germany—navigate their sourcing strategies effectively.
By empowering buyers with actionable insights and a structured approach to selecting glass cutting instruments, this guide serves as a vital resource for enhancing productivity, reducing waste, and ultimately achieving superior results in glass projects. Whether you’re a manufacturer, artisan, or distributor, leveraging this information will facilitate smarter investments and foster long-term partnerships in the global market.
Understanding glass cutting instrument Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld Glass Cutters | Simple, portable, and easy to use; manual scoring | Small-scale glass fabrication, DIY projects | Pros: Affordable, versatile. Cons: Limited precision for large projects. |
| Circle Cutters | Designed to cut circular shapes; adjustable radius | Stained glass art, custom glass designs | Pros: Accurate circles, reduces waste. Cons: Requires practice for best results. |
| Breaking Pliers | Used to snap glass along scored lines; ergonomic design | Glass installation and repair | Pros: Clean breaks, reduces chipping. Cons: Not suitable for thick glass. |
| Cutting Systems | Integrated systems with multiple functions; often automated | Large-scale production, architectural applications | Pros: High efficiency, consistent quality. Cons: Higher upfront investment, requires training. |
| Specialty Glass Cutters | Tailored for specific applications (e.g., thin glass, mosaics) | Niche markets, artistic glasswork | Pros: Enhanced precision for specific tasks. Cons: May not be versatile for general use. |
What Are the Characteristics of Handheld Glass Cutters?
Handheld glass cutters are the most common tools used in glass cutting, ideal for small-scale projects. They typically feature a simple design with a cutting wheel that scores the glass surface. These tools are portable and easy to handle, making them perfect for DIY enthusiasts and small workshops. When purchasing, buyers should consider the cutter’s wheel material and replaceability, as well as ergonomic design for comfort during extended use.
How Do Circle Cutters Enhance Glass Design?
Circle cutters are specialized tools that allow users to cut perfect circles in glass with adjustable diameters. They are essential for stained glass artists and those looking to create custom shapes. The precision of circle cutters minimizes waste and improves the quality of finished pieces. B2B buyers should focus on the cutter’s build quality and ease of adjustment, as well as the availability of replacement parts to ensure longevity in production.
What Role Do Breaking Pliers Play in Glass Cutting?
Breaking pliers are essential for snapping glass along scored lines, allowing for clean breaks without chipping. Their ergonomic design provides better leverage and control, making them a favorite among professionals in glass installation and repair. When choosing breaking pliers, buyers should look for features such as grip comfort and durability, as well as compatibility with the thickness of the glass being used.
Why Invest in Cutting Systems for Large-Scale Production?
Cutting systems are advanced tools that integrate multiple functions, often automating the cutting process for high-volume production. These systems are suited for architectural applications and manufacturers needing consistent quality. While they require a higher initial investment and training, the efficiency gained can significantly reduce labor costs and increase output. Buyers should consider the system’s compatibility with different glass types and the technical support available.
How Do Specialty Glass Cutters Serve Niche Markets?
Specialty glass cutters are designed for specific tasks, such as cutting thin glass or for use in mosaic projects. They provide enhanced precision and can cater to niche markets where standard tools may not suffice. Buyers in these segments should evaluate the cutter’s specific capabilities and whether it aligns with their production needs, as well as the availability of specialized training or resources for optimal use.
Key Industrial Applications of glass cutting instrument
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of glass cutting instrument | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Window and Door Frame Fabrication | Enhanced precision and reduced material waste | Quality and durability of cutting tools |
| Automotive | Glass Installation in Vehicles | Improved safety and aesthetics | Compliance with safety standards and regulations |
| Art and Craft | Stained Glass Art and Mosaics | Unique designs and artistic expression | Versatility and range of cutting tools available |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Glass Panels for Displays and Screens | High-quality finishes and reduced defects | Precision in cutting and availability of sizes |
| Furniture Design | Glass Tabletops and Shelving | Customization options and enhanced aesthetics | Supplier reliability and material sourcing |
How is Glass Cutting Instrument Used in Construction, and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the construction industry, glass cutting instruments are essential for fabricating window and door frames. These tools enable precise scoring and breaking of glass, which is crucial for minimizing waste and ensuring that pieces fit seamlessly into architectural designs. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality cutting tools that withstand varying environmental conditions is vital. Additionally, suppliers should be evaluated based on their ability to provide tools that adhere to local building codes and standards.
What Role Do Glass Cutting Instruments Play in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive sector, glass cutting instruments are used to install windshields and windows in vehicles. The precision offered by these tools ensures that glass panels are cut to the exact specifications required for safety and aesthetics. This is particularly important in markets like Europe and the Middle East, where stringent safety regulations exist. Buyers must consider the compliance of cutting tools with industry standards and the availability of replacement parts to maintain operational efficiency.
How Do Artisans Utilize Glass Cutting Tools in Artistic Applications?
Artisans in the art and craft industry utilize glass cutting instruments for creating stained glass art and intricate mosaics. These tools allow for creative freedom, enabling artists to achieve unique designs and finishes. In regions with rich artistic traditions, such as Europe, the availability of diverse cutting tools is essential for artisans looking to differentiate their work. Buyers should seek suppliers that offer a range of specialized tools, ensuring they can meet various artistic needs while maintaining quality.
What Is the Importance of Glass Cutting Instruments in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, glass cutting instruments are critical for producing glass panels used in displays and screens. The precision and quality of cuts directly affect the functionality and appearance of electronic devices. Buyers in this sector, especially from technologically advanced regions like Germany, must prioritize sourcing tools that deliver high-quality finishes and reduce defects. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements for glass thickness and type is crucial for ensuring compatibility with manufacturing processes.
How Are Glass Cutting Instruments Used in Furniture Design?
In furniture design, glass cutting instruments are pivotal for creating custom tabletops and shelving solutions. These tools enable designers to craft unique pieces that enhance the aesthetic appeal of furniture while offering durability. For buyers in emerging markets, reliability in sourcing quality cutting tools is essential to meet customer demands for bespoke designs. Furthermore, suppliers should be evaluated based on their ability to provide a wide range of glass types and cutting solutions tailored to furniture applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘glass cutting instrument’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Cutting Quality Leading to Wasted Resources
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of inconsistent cutting quality when using glass cutting instruments. This can be particularly detrimental in large-scale production environments, such as glass manufacturing or construction projects. When the tools used fail to produce clean, precise cuts, it not only leads to wasted glass but also extends project timelines and increases costs. Buyers may struggle to identify the right tools that provide the accuracy needed for high-quality outputs, resulting in frustration and financial losses.
The Solution: To overcome issues with inconsistent cutting quality, buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality, specialized glass cutting tools. Invest in professional-grade glass cutters that feature precision-engineered blades, such as carbide-tipped or diamond-tipped options, which are known for their durability and clean scoring capabilities. Additionally, incorporating cutting fluids can significantly enhance the cutting process by reducing friction and prolonging the life of the blade. Training staff on proper cutting techniques—such as applying consistent pressure and maintaining the right angle—will also help improve accuracy. Finally, consider establishing a regular maintenance schedule for tools to ensure they remain in optimal condition, thus preventing the degradation of cutting quality over time.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Achieving Complex Cuts
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter significant challenges when attempting to achieve intricate or complex cuts in glass. Whether it’s for custom architectural designs or artistic glass installations, the inability to accurately execute these cuts can lead to delays and unsatisfactory results. This is often compounded by a lack of access to the right tools or techniques, leaving buyers feeling overwhelmed and underprepared to meet client expectations.
The Solution: To facilitate complex glass cutting tasks, buyers should consider investing in advanced cutting systems that are designed for intricate work. Tools like circle cutters and specialized grozing pliers can significantly enhance precision when making detailed cuts. Additionally, utilizing templates or guides can help ensure accuracy in complex designs. Providing staff with specialized training in advanced glass cutting techniques—such as scoring and breaking methods—will also empower them to execute difficult cuts confidently. Collaborating with experienced glass artists or technicians for initial projects can provide valuable insights and techniques that can be applied in future work, further enhancing skill levels within the team.
Scenario 3: Safety Concerns During Glass Cutting Operations
The Problem: Safety is a major concern for B2B buyers in industries that involve glass cutting. The risk of injury from sharp glass edges or improper handling of cutting tools can lead to serious workplace accidents, which not only affect employee well-being but can also result in costly legal and insurance issues. Buyers may struggle to implement effective safety measures, leaving them vulnerable to these risks.
The Solution: To mitigate safety concerns, buyers should prioritize the procurement of ergonomic and safety-focused glass cutting tools. Look for instruments designed with safety features, such as protective grips and blade guards, to minimize the risk of accidents. Additionally, establishing comprehensive safety protocols is essential; this includes providing personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and cut-resistant clothing. Regular safety training sessions should be conducted to ensure all employees are aware of best practices when handling glass and cutting tools. Creating a culture of safety, where employees feel empowered to report unsafe conditions and practices, will further enhance workplace safety and reduce the likelihood of accidents occurring.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for glass cutting instrument
When selecting materials for glass cutting instruments, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations to ensure optimal performance and suitability for specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in glass cutting tools, focusing on their relevance to international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Tungsten Carbide in Glass Cutting Instruments?
Tungsten carbide is a popular choice for glass cutting blades and wheels due to its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. This material can withstand high-pressure applications and maintains its cutting edge even at elevated temperatures. Additionally, tungsten carbide exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of tungsten carbide is its durability, which leads to a longer lifespan for cutting tools. However, its high cost can be a drawback for some buyers. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as tungsten carbide requires specialized equipment for shaping and finishing.
Impact on Application: Tungsten carbide is particularly effective for cutting toughened or laminated glass, which requires precise scoring to achieve clean breaks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM and DIN, is crucial for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should also consider local sourcing options to minimize shipping costs and delays.
How Does High-Speed Steel Perform in Glass Cutting Tools?
High-speed steel (HSS) is another widely used material in glass cutting instruments, known for its ability to retain hardness at high temperatures. HSS offers good toughness and is relatively easy to sharpen, making it a popular choice for hand-held glass cutters.
Pros and Cons: The key advantage of HSS is its balance between cost and performance. It is less expensive than tungsten carbide while still providing decent durability. However, it is not as wear-resistant as tungsten carbide, which may lead to more frequent replacements.
Impact on Application: HSS tools are suitable for general glass cutting applications, including stained glass and craft projects, where precision is important but extreme durability is not critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that HSS tools meet local quality standards and consider the availability of replacement parts in their region.
What Are the Benefits of Ceramic Materials in Glass Cutting Instruments?
Ceramic materials, particularly those reinforced with zirconia, are increasingly being used in glass cutting tools due to their hardness and low friction properties. Ceramics can withstand high temperatures and are generally resistant to corrosion.
Illustrative image related to glass cutting instrument
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of ceramic tools is their ability to maintain sharpness longer than metal counterparts, reducing the need for frequent replacements. However, ceramics can be brittle, making them susceptible to chipping or breaking under impact.
Impact on Application: Ceramic cutting tools are ideal for precision applications where a clean cut is essential, such as in artistic glasswork or intricate designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers in Africa and South America, it is essential to evaluate the availability of ceramic tools and their compatibility with local glass types.

Illustrative image related to glass cutting instrument
How Does Plastic Reinforced with Fiberglass Compare in Glass Cutting Instruments?
Plastic materials reinforced with fiberglass offer a lightweight and cost-effective alternative for certain components of glass cutting tools, such as handles and supports. These materials provide good strength-to-weight ratios and are resistant to chemicals.
Pros and Cons: The key advantage of fiberglass-reinforced plastics is their affordability and ease of manufacturing. However, they lack the hardness of metal or ceramic cutting edges, which can limit their effectiveness in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: These materials are suitable for non-critical applications, such as hobbyist tools or educational settings where cost is a primary concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the durability of plastic components in their specific environments, especially in regions with extreme temperatures or humidity.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Glass Cutting Instruments
| Material | Typical Use Case for glass cutting instrument | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Carbide | Cutting toughened or laminated glass | Exceptional durability and wear resistance | High cost | High |
| High-Speed Steel | General glass cutting applications | Good balance of cost and performance | Less wear-resistant than carbide | Medium |
| Ceramic | Precision artistic glasswork | Maintains sharpness longer | Brittle and susceptible to chipping | Medium |
| Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic | Hobbyist tools and educational settings | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lacks hardness for cutting edges | Low |
This analysis provides insights into the various materials used in glass cutting instruments, emphasizing their unique properties and considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors can guide buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for glass cutting instrument
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Glass Cutting Instruments?
The manufacturing process of glass cutting instruments typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding each stage can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation
The first stage focuses on sourcing high-quality materials, which are crucial for producing durable and effective glass cutting tools. Common materials include high-carbon steel for cutter blades and various alloys for handles. Suppliers often prioritize materials that offer resistance to wear and corrosion, ensuring longevity and performance. Rigorous testing of raw materials is essential to confirm that they meet the necessary specifications before proceeding to the next stage.

Illustrative image related to glass cutting instrument
Forming Techniques
In the forming stage, manufacturers utilize various techniques to shape the glass cutting tools. These may include forging, machining, and precision casting. For instance, high-quality glass cutters often undergo a forging process that enhances the strength of the blades. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are widely used for precise machining of components, ensuring that each part meets exact specifications. This level of precision is critical for the performance of the tool, as even minor deviations can affect cutting accuracy.
Assembly Process
The assembly process is where different components of the glass cutting instruments come together. This stage may involve fitting blades into handles, attaching grips, and ensuring that any cutting mechanisms function smoothly. During assembly, manufacturers often employ automated systems to enhance consistency and reduce human error. A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that all parts fit correctly and operate as intended.
Finishing Touches
The final stage, finishing, includes surface treatments such as polishing, coating, and applying protective layers. These finishing processes not only improve the aesthetic appeal of the tools but also enhance their durability and resistance to corrosion. For instance, some manufacturers apply anti-rust coatings to prolong the life of steel components. Final quality checks are conducted during this stage to ensure that each tool meets the desired standards before packaging and shipping.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Glass Cutting Instruments?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component in the manufacturing of glass cutting instruments, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. Understanding the QA process can help B2B buyers assess supplier reliability.
Relevant International Standards
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets and API standards for specific applications can provide further assurance of product quality.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This step is crucial for preventing defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Inspections during the manufacturing process help identify any issues early on, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each product undergoes rigorous testing and inspection to verify that it meets all quality specifications before being packaged for shipment.
Common Testing Methods Used in Quality Assurance
Several testing methods are employed to evaluate the performance and durability of glass cutting instruments:
-
Functional Testing: Ensures that the cutting mechanism operates smoothly and effectively.
-
Durability Testing: Assesses the wear resistance of blades and handles through simulated usage scenarios.
-
Safety Testing: Evaluates the safety features of the tools, ensuring they are safe for end-users.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers need to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards through effective verification methods. Here are several strategies for assessing supplier QC processes:
Conducting Audits and Inspections
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control practices. Buyers should consider scheduling on-site visits to evaluate the production environment, QC procedures, and overall compliance with international standards. A comprehensive audit will help identify any potential risks and ensure that suppliers adhere to best practices.
Reviewing Quality Assurance Reports
Requesting quality assurance reports from suppliers can offer additional transparency. These reports should detail the results of quality inspections, testing outcomes, and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues. A supplier committed to quality will readily provide these documents and demonstrate a proactive approach to quality management.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance the verification process. Independent inspectors can evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing practices, quality control measures, and compliance with relevant standards. This unbiased assessment can provide B2B buyers with confidence in their supplier’s ability to deliver high-quality products.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing glass cutting instruments from international suppliers, B2B buyers must be aware of several quality control nuances that can impact their purchasing decisions.
Understanding Regional Standards
Different regions may have varying quality standards and regulations. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while those in the Middle East might focus on compliance with Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the relevant standards in their target markets to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
Cultural and Communication Considerations
Cultural differences can influence how quality control processes are perceived and implemented. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers is essential to address any quality concerns promptly. Buyers should ensure that they have a mutual understanding of quality expectations and that suppliers are equipped to meet them.

Illustrative image related to glass cutting instrument
Navigating Supply Chain Challenges
International shipping and logistics can introduce additional challenges related to quality assurance. B2B buyers should work closely with suppliers to establish robust supply chain management practices that minimize the risk of damage during transit. Implementing quality checks at various points along the supply chain can help ensure that products arrive in optimal condition.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with glass cutting instruments, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships with suppliers. This knowledge is essential for ensuring that they procure high-quality tools that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘glass cutting instrument’
This guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a clear and actionable checklist for sourcing glass cutting instruments. Whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, the following steps will help you make informed decisions while procuring these essential tools.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by identifying the specific requirements for your glass cutting instruments. Consider factors like the type of glass you will be cutting (e.g., stained, tempered, or laminated), the thickness of the glass, and the complexity of your cutting tasks. Clearly defined specifications will help you narrow down the options and ensure that the tools you select are suitable for your intended applications.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to find suppliers that specialize in glass cutting instruments. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, positive customer reviews, and a proven track record of reliability. Utilize online platforms, industry forums, and trade shows to gather information about potential suppliers and compare their offerings.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Standards
Before making a purchase, verify that your chosen suppliers meet relevant industry certifications and standards. This includes checking for compliance with ISO standards, safety certifications, and any local regulatory requirements. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to these standards not only guarantees product quality but also protects your business from potential liabilities.
Step 4: Request Samples or Demonstrations
Whenever possible, request samples or demonstrations of the glass cutting instruments you are considering. This step allows you to assess the quality, ease of use, and performance of the tools firsthand. Pay attention to details such as the sharpness of the cutting edges, ergonomic design, and overall build quality, as these factors can significantly impact productivity and user satisfaction.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms of Sale
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, compare pricing and terms of sale from different suppliers. Look beyond just the initial cost; consider factors such as shipping fees, payment terms, and volume discounts. Understanding the total cost of ownership will help you make a more informed decision that aligns with your budget and financial goals.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty Options
Inquire about after-sales support, warranty options, and return policies offered by suppliers. Reliable support can be crucial, especially if you encounter issues with the tools post-purchase. A strong warranty can also indicate the manufacturer’s confidence in their product quality, providing you with peace of mind.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Establish Long-Term Relationships
After completing your evaluations, finalize your order with the selected supplier. Consider establishing a long-term relationship, as this can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products in the future. Regular communication and feedback can enhance your partnership, ensuring that your glass cutting needs are consistently met.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for glass cutting instruments, ensuring they select the right tools to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for glass cutting instrument Sourcing
When sourcing glass cutting instruments, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The total cost comprises several components, each contributing to the final pricing of the tools.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Glass Cutting Instruments?
-
Materials: The primary materials used in glass cutting tools include high-carbon steel for blades, carbide for cutting edges, and various plastics for handles. The quality and source of these materials significantly influence pricing. Higher-quality materials may come at a premium but can enhance tool durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region of manufacturing. Countries with lower labor costs, such as some in Southeast Asia, may offer competitive pricing. However, if high-quality craftsmanship is required, it may be worth considering suppliers in regions like Germany, known for their engineering excellence, despite potentially higher labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive prices.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling for manufacturing specific designs can add to initial costs. Buyers should inquire about tooling charges, especially for customized or unique designs, as these can vary widely among suppliers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the products meet international standards, which is particularly important for buyers in regions with strict import regulations. While this may increase costs, it mitigates the risk of returns and enhances customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs play a significant role in the overall expense. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and packaging requirements can influence logistics costs. For instance, bulk orders may benefit from economies of scale, leading to reduced per-unit shipping costs.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s positioning strategy.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Glass Cutting Instruments?
Several factors can influence the pricing of glass cutting tools:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer discounts for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized tools or specific specifications may lead to increased costs due to additional design and manufacturing processes. Buyers should assess whether the benefits of customization justify the additional expense.
-
Quality Certifications: Tools that meet specific international quality standards (ISO, CE) may be priced higher due to the associated testing and certification costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their project requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established brands may charge a premium, but they often provide assurances of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total landed cost of the products.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage in discussions with suppliers to explore potential discounts, especially for bulk orders. Building a long-term relationship can also facilitate better terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchase price, consider maintenance, replacement, and operational costs when evaluating suppliers. High-quality tools may have a higher upfront cost but could lead to savings in the long run due to durability and reduced waste.
-
Research Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Pricing can vary greatly between regions. For instance, suppliers in Europe may offer high-quality tools with certifications, while those in Africa or South America might provide more cost-effective options. Understanding these regional differences can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Request Price Quotes from Multiple Suppliers: Comparing quotes from various suppliers can provide insights into market pricing trends and help identify the best value for the desired quality.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for glass cutting instruments can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and exchange rates. It is advisable for buyers to conduct due diligence and seek updated quotations tailored to their specific sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing glass cutting instrument With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives for Glass Cutting Solutions
When it comes to glass cutting, businesses often seek the most effective and efficient tools to ensure precision and quality. While glass cutting instruments are widely used, there are alternative methods and technologies available that can achieve similar results. This section explores various options, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and operational contexts.
| Comparison Aspect | Glass Cutting Instrument | Laser Cutting Technology | Water Jet Cutting System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for intricate designs | Exceptional accuracy and speed | Excellent for thick materials and complex shapes |
| Cost | Low to moderate (typically $5 – $50) | High initial investment (typically $10,000+) | Moderate to high (typically $50,000+) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple, requires minimal training | Requires specialized training | Requires skilled operators and setup |
| Maintenance | Low, mainly blade replacement | Moderate, needs regular calibration | High, requires maintenance of pumps and jets |
| Best Use Case | Small-scale projects, artistic glassworks | Mass production, industrial applications | Heavy-duty cutting, intricate designs on thick materials |
Laser Cutting Technology: Pros and Cons
Laser cutting technology utilizes focused light beams to slice through glass. Its primary advantage lies in its ability to produce clean, precise cuts with minimal material wastage. The speed of operation is another significant benefit, making it ideal for large-scale production runs. However, the high initial costs and the need for specialized training to operate the machinery can be a barrier for smaller businesses. Additionally, laser cutting may not be suitable for all types of glass, particularly thicker materials that may require more robust cutting methods.
Water Jet Cutting System: Advantages and Disadvantages
Water jet cutting is a method that uses high-pressure water, often mixed with abrasives, to cut through various materials, including glass. This method excels in cutting thick glass and allows for complex shapes and designs without inducing thermal stress. Its versatility makes it suitable for various industries, from construction to art. However, the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs can be substantial. Moreover, it requires skilled operators to ensure efficiency and accuracy, which may not be feasible for smaller operations or those with limited budgets.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Glass Cutting Solution
Choosing the right glass cutting solution depends on various factors, including project scale, budget, and desired precision. For small-scale, intricate projects, traditional glass cutting instruments may be the most cost-effective and user-friendly option. Conversely, for large-scale operations where speed and precision are paramount, investing in laser cutting technology or water jet systems may yield greater long-term benefits despite the higher upfront costs. B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific needs, workforce capabilities, and financial resources to select the most suitable glass cutting solution.

Illustrative image related to glass cutting instrument
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for glass cutting instrument
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Glass Cutting Instruments?
When sourcing glass cutting instruments for B2B purposes, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The quality of the materials used in glass cutting tools can significantly impact performance. Common materials include tungsten carbide and high-speed steel. Tools made from these materials exhibit higher durability and sharper cutting edges, which translates to cleaner cuts and reduced breakage, essential for minimizing waste during production. -
Cutting Angle
The cutting angle is the degree at which the cutting wheel meets the glass surface. Standard angles typically range from 120 to 140 degrees. A sharper angle allows for finer scoring, which is critical for precision in intricate designs. Understanding the optimal cutting angle for specific glass types can enhance productivity and reduce the likelihood of errors. -
Wheel Size and Type
The size and type of the cutting wheel affect the versatility and effectiveness of the tool. For instance, larger wheels may be suited for thicker glass, while smaller wheels are ideal for detailed work. Additionally, different wheel materials (e.g., diamond or carbide) provide varying levels of sharpness and longevity, directly influencing operational costs and efficiency. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions during the cutting process. High tolerance levels indicate a tool’s capability to produce precise cuts that adhere closely to specified dimensions. This is particularly important for manufacturers who require strict adherence to design specifications to ensure product compatibility and quality. -
Ergonomics and Design
The ergonomics of glass cutting instruments, including grip and weight distribution, play a vital role in user comfort and efficiency. Tools designed with ergonomic considerations can reduce fatigue during prolonged use, enhancing productivity. For businesses, investing in ergonomic tools can lead to lower injury rates and higher employee satisfaction.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Glass Cutting Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of glass cutting tools, OEM products are often used to ensure quality and compatibility with existing machinery. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, as it directly affects purchasing costs and stock levels. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their operational needs while ensuring cost-effectiveness. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. It is a vital part of the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. Crafting a clear RFQ can streamline sourcing and facilitate better supplier relationships. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is essential for managing logistics, costs, and risks associated with shipping glass cutting instruments across borders. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers negotiate favorable shipping terms. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the glass cutting industry, understanding lead times is critical for production planning and inventory management. Buyers should factor lead times into their procurement strategy to avoid delays in project timelines. -
Warranty and Service Agreements
These terms refer to the guarantees provided by manufacturers regarding product performance and the support offered post-purchase. A clear understanding of warranty terms can protect buyers from potential defects and ensure they receive necessary support, thereby enhancing overall satisfaction with their purchase.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the glass cutting instrument market with greater confidence, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the glass cutting instrument Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Glass Cutting Instrument Sector?
The glass cutting instrument market is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing demand across various industries, including construction, automotive, and art. As urbanization accelerates in regions like Africa and South America, there is a heightened need for efficient and precise cutting tools that can cater to both commercial and residential projects. In Europe, particularly in Germany, innovations in glass technology are pushing the boundaries of design, necessitating advanced cutting instruments that ensure accuracy and minimize waste.
Emerging technologies such as automated cutting systems and smart glass cutting tools are transforming the sourcing landscape. These innovations enhance productivity and reduce labor costs, making them attractive to B2B buyers. Additionally, the integration of digital platforms for sourcing has streamlined procurement processes, enabling international buyers to connect with suppliers more efficiently. This digital shift is particularly crucial for businesses in regions like Vietnam, where rapid industrialization is creating a surge in demand for high-quality glass cutting instruments.
Moreover, the market is experiencing a trend towards specialization, with tools designed for specific applications such as stained glass, glass art, or industrial uses. This specialization allows manufacturers to cater to niche markets, enhancing their competitive edge. As buyers become more discerning, the emphasis on quality over price is likely to grow, prompting suppliers to focus on delivering superior products that meet stringent performance standards.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions for Glass Cutting Instruments?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing strategies of B2B buyers in the glass cutting instrument sector. As companies face increasing scrutiny regarding their environmental impact, there is a growing demand for sustainable materials and ethical supply chains. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and who utilize eco-friendly materials in their products.

Illustrative image related to glass cutting instrument
The introduction of “green” certifications and standards is influencing purchasing decisions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems provide buyers with the assurance that their suppliers adhere to sustainable practices. Additionally, the use of recycled materials in the production of glass cutting tools is gaining traction, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
Moreover, the focus on sustainability extends beyond the products themselves to encompass the entire supply chain. B2B buyers are increasingly evaluating suppliers based on their sourcing practices, waste management strategies, and overall commitment to corporate social responsibility (CSR). This shift not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with consumer expectations for sustainability, making it a vital consideration for businesses aiming to thrive in a competitive market.
How Has the Glass Cutting Instrument Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of glass cutting instruments can be traced back to the early days of glassmaking, where rudimentary tools were used to shape and cut glass. Over the centuries, advancements in technology have significantly transformed the industry. The introduction of diamond-tipped cutters and carbide tools in the 20th century revolutionized the precision and efficiency of glass cutting, enabling artisans and manufacturers to create intricate designs and high-quality products.
In recent decades, the rise of computer numerical control (CNC) technology has further enhanced the capabilities of glass cutting instruments. CNC machines allow for intricate cuts and patterns, catering to the demands of modern architecture and design. As the industry continues to innovate, the integration of smart technology is paving the way for automated cutting processes, minimizing human error and maximizing output. This historical context underscores the importance of staying abreast of technological advancements, ensuring that B2B buyers can source the most effective and innovative glass cutting tools available.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of glass cutting instrument
-
How do I choose the right glass cutting instrument for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate glass cutting instrument depends on your specific applications. Consider factors such as the type of glass you will be cutting (e.g., stained, tempered, or laminated), the thickness, and the precision required. Handheld cutters are versatile for small projects, while automated cutting systems are ideal for larger, industrial applications. It’s advisable to consult with suppliers about the best tools suited for your specific requirements and to review product specifications and user feedback. -
What are the key features to look for in a glass cutting tool?
When sourcing glass cutting tools, prioritize features such as blade material, cutting precision, ergonomic design, and ease of maintenance. High-quality blades made from carbide or diamond offer durability and clean cuts. Ergonomic handles can enhance user comfort, especially during prolonged use. Additionally, tools with adjustable settings allow for flexibility in cutting various glass thicknesses, improving overall efficiency. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for glass cutting instruments?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs ranging from 50 to several hundred units, depending on production capabilities and inventory levels. It’s essential to communicate directly with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your business needs, especially if you are a smaller enterprise or are testing a new product line. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing glass cutting tools internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common practices include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Be sure to clarify acceptable payment methods, such as wire transfers, letters of credit, or online payment platforms. Understanding the payment terms is crucial for cash flow management, especially when dealing with international transactions that may involve currency exchange risks. -
How do I ensure the quality of glass cutting instruments before purchasing?
To ensure quality, request samples from suppliers and conduct thorough inspections. Look for certifications that indicate adherence to international quality standards, such as ISO or CE markings. Additionally, reading reviews and testimonials from other businesses can provide insights into product reliability and performance. Establishing a clear quality assurance process with your supplier can also help mitigate risks. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing glass cutting tools?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, import duties, and transit times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who can navigate customs regulations in your region. Be aware of any tariffs or taxes that may apply to your imports. Additionally, consider the packaging and handling requirements for glass products to prevent damage during transit. Planning your logistics effectively can reduce costs and ensure timely delivery. -
Can I customize glass cutting tools to meet specific operational needs?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for glass cutting tools, allowing you to tailor features such as blade size, handle design, and additional accessories to suit your operational requirements. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers and inquire about their customization capabilities. Custom tools may have longer lead times and higher costs, but they can significantly enhance efficiency and productivity in your operations. -
How do I vet suppliers for glass cutting instruments in international markets?
Vetting suppliers involves researching their reputation, experience, and customer feedback. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the glass cutting industry and check for certifications that demonstrate quality standards. Request references from previous clients and verify their business legitimacy through trade associations or local chambers of commerce. Conducting thorough due diligence can help you establish trustworthy partnerships and ensure a reliable supply chain.
Top 6 Glass Cutting Instrument Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fletcher – 3000 Wall-Mounted Glass Cutter
Domain: thegrumble.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Recommended glass cutter for occasional use: oil-filled glass cutter with a tungsten carbide wheel, suitable for cutting glass sizes up to 24 X 36. Suggested brands include Fletcher (specifically the Fletcher 3000 wall-mounted cutter) and diamond-headed cutters for better pressure control. A glass cutting straight edge with a grippy back is also recommended. Ideal working surface includes a thick …
2. Rainbow Art Glass – CJ’s Glass Cutting Oil 8oz.
Domain: shoprainbowartglass.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Glass Cutters & Tools – Stained Glass Supplies – Rainbow Art Glass
Key Products:
1. CJ’s Glass Cutting Oil 8oz. – $7.95
2. Value Pistol Grip Glass Cutter Oil Fed Carbide Wheel – $8.88 (Currently Unavailable)
3. Toyo Pistol Grip Glass Cutter w/ CJ’s Cutting Oil – $36.95
4. Toyo Pistol Grip Supercutter w/ TAP Wheel – $35.88
5. Fletcher Pistol Grip Cutter – $56.68
6. Gryphon Studio Pistol Glass Cutt…
3. Everything Stained Glass – Key Products
Domain: everythingstainedglass.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Key products mentioned include: 1. Taurus 3 Ring Saw – recommended for cutting stained glass, with strengths and weaknesses compared to other saw types. 2. Various types of stained glass saws – Ring Saws, Band Saws, and Wire Saws. 3. Circle Cutter – designed for cutting perfect circles in glass. 4. Grozer and Running Pliers – specialized pliers for stained glass work. 5. Cutter’s Mate – a tool for…
4. Weisser Glass – Quality Cutting Tools
Domain: shopweisserglass.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: This company, Weisser Glass – Quality Cutting Tools, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Warmglass – Top Glass Cutters
Domain: warmglass.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 1. Bohle Silberschnitt Cutter – Preferred by some users for its easy grip design. 2. MacInnes Glass Cutter – Features special carbide wheels, allows for different wheels for various glass types, highly recommended by experienced users. 3. Toyo Pistol Grip Cutter – Used by multiple users for its reliability and ease of use, suitable for various glass thicknesses. 4. Toyo Custom Grip Tap Wheel Cutte…
6. Fine Woodworking – Essential Tools and Supplies
Domain: finewoodworking.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Glass cutter, tungsten edge, kerosene lubricant, carbide drill bit, diamond plate, Klingspor belts for sanding, safety goggles, leather gloves, wooden straight edge, spring clamps, mirror glass cutter.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for glass cutting instrument
In the competitive landscape of glass cutting instruments, strategic sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chain and enhance operational efficiency. By focusing on quality and precision, businesses can significantly reduce material waste and improve the overall craftsmanship of their glass products. Selecting reliable suppliers that provide high-quality tools—such as handheld cutters, breaking pliers, and cutting systems—can lead to better production outcomes and increased profitability.
Moreover, understanding regional market dynamics in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe is crucial. Tailoring sourcing strategies to local preferences and regulatory requirements can create a competitive advantage. As the demand for glass products continues to rise, investing in superior glass cutting tools will be pivotal for businesses looking to innovate and expand their offerings.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage technology and data analytics in their sourcing decisions, ensuring they stay ahead of market trends. By prioritizing partnerships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers, businesses can not only enhance their product quality but also secure their position in the global marketplace. Embrace the future of glass cutting—invest wisely in your sourcing strategy today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.