Choosing Your Low Profile Electrical Plug: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for low profile electrical plug
In an increasingly interconnected world, the demand for low profile electrical plugs is surging as businesses seek efficient, space-saving solutions for their electrical needs. Sourcing the right low profile electrical plugs can be a complex challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. Buyers must navigate varying standards, certifications, and supplier capabilities to ensure compliance and quality.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of low profile electrical plugs, covering a range of topics including the different types available, their applications across various industries, and critical factors for supplier vetting. Furthermore, it addresses cost considerations, providing insights into pricing structures and potential cost-saving strategies. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and a clear understanding of the market landscape, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Whether you are looking to enhance product offerings, improve operational efficiency, or simply ensure compliance with local standards, this guide serves as a valuable resource. It aims to streamline your sourcing process, reduce risks associated with international procurement, and ultimately foster successful partnerships in the global market for low profile electrical plugs.
Understanding low profile electrical plug Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA 5-15P Ultra Low Profile | Angled design, UL certified, rated up to 15A 125V | Consumer electronics, appliances | Pros: Compact design, easy to install. Cons: Limited to North American standards. |
| IEC 60309 Low Profile | Splashproof, robust pin and sleeve design, multiple ratings | Industrial equipment, outdoor applications | Pros: Highly durable, suitable for harsh environments. Cons: More expensive than standard plugs. |
| GB2099 Low Profile | Heavy-duty design, CCC certified, rated up to 16A 250V | Heavy machinery, commercial appliances | Pros: High load capacity, reliable. Cons: May require adapters for non-standard sockets. |
| JIS C 8303 Low Profile | Class II design, PSE certified, compact 2-prong configuration | Consumer electronics, small appliances | Pros: Lightweight, ideal for portable devices. Cons: Limited to lower power applications. |
| CNS 10917 Low Profile | 2-pin design, BSMI certified, rated up to 15A 125V | General consumer products, electronics | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Less suitable for high-power devices. |
What are the Characteristics of NEMA 5-15P Ultra Low Profile Plugs?
The NEMA 5-15P ultra low profile plug features an angled design that minimizes space usage, making it ideal for tight setups. It is UL certified and can handle up to 15A at 125V, making it suitable for a range of consumer electronics and home appliances. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider compatibility with existing systems and the availability of custom configurations to meet specific needs.
How Does IEC 60309 Low Profile Design Stand Out?
The IEC 60309 low profile plug is designed for rugged use, featuring a splashproof pin and sleeve mechanism that ensures reliable connections in challenging environments. Rated for various amperages, it is commonly used in industrial settings and outdoor applications. Buyers should assess the specific environmental conditions and voltage requirements of their operations to ensure the right fit.
Why Choose GB2099 Low Profile Plugs for Heavy-Duty Applications?
GB2099 plugs are designed for heavy-duty applications, capable of handling up to 16A at 250V. This makes them ideal for heavy machinery and commercial appliances. B2B buyers should consider the certification standards required in their region and the need for potential adapters when integrating these plugs into existing systems.
What are the Benefits of JIS C 8303 Low Profile Plugs?
The JIS C 8303 low profile plug is a compact 2-prong configuration that is lightweight and easy to transport, making it suitable for consumer electronics and small appliances. While it offers a cost-effective solution, buyers must ensure that it meets the power requirements of the devices they plan to use it with, as it is limited to lower power applications.
How Does CNS 10917 Low Profile Plug Serve General Consumer Products?
The CNS 10917 low profile plug features a simple 2-pin design that is BSMI certified and rated for up to 15A at 125V. It is commonly used in general consumer products and electronics. When considering this option, B2B buyers should evaluate the cost-effectiveness and ease of integration into their product lines, especially for low-power devices.
Key Industrial Applications of low profile electrical plug
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of low profile electrical plug | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Power supply for compact devices like laptops and tablets | Space-saving design enhances portability and usability | Certification compliance (UL, RoHS), voltage ratings, and wire gauge options |
| Automotive | Charging stations for electric vehicles (EVs) | Efficient space management in vehicle design | Durability under varying temperatures and environments, compatibility with international standards |
| Telecommunications | Equipment powering in data centers and network installations | Improved airflow and reduced clutter in server racks | Heat resistance, electrical ratings, and custom configurations for specific setups |
| Medical Devices | Connection for portable medical equipment | Ensures safety and reliability in critical applications | Compliance with medical standards, low profile for space efficiency, and robust materials |
| Industrial Machinery | Power connections in confined spaces of manufacturing plants | Enhances safety and accessibility in tight environments | Heavy-duty construction, environmental certifications, and compatibility with various machinery |
How Are Low Profile Electrical Plugs Used in Consumer Electronics?
In the consumer electronics sector, low profile electrical plugs are essential for devices such as laptops, tablets, and portable chargers. Their compact design allows for easy integration into sleek device profiles, minimizing bulk while maximizing functionality. For international B2B buyers, ensuring that these plugs meet regional certification standards (like UL and RoHS) and understanding voltage ratings are crucial. This helps in maintaining compliance and safety across diverse markets, particularly in regions such as Africa and South America.
What Role Do Low Profile Electrical Plugs Play in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, low profile electrical plugs are increasingly utilized in electric vehicle (EV) charging stations. These plugs facilitate efficient power delivery while conserving space within vehicle designs. This is particularly important for manufacturers aiming to enhance the aesthetics and functionality of their EVs. Buyers should consider the durability of the plugs under varying temperatures and environmental conditions, along with ensuring compatibility with international charging standards, which is vital for markets in the Middle East and Europe.
How Are Low Profile Electrical Plugs Beneficial in Telecommunications?
Telecommunications companies leverage low profile electrical plugs for powering equipment in data centers and network installations. These plugs help streamline setups by reducing clutter and improving airflow in server racks, which is vital for cooling systems. For B2B buyers in this sector, sourcing plugs that can withstand high temperatures and meet specific electrical ratings is essential. Custom configurations may also be required to suit unique installation needs, particularly in rapidly growing markets in Africa and South America.
Why Are Low Profile Electrical Plugs Important for Medical Devices?
Low profile electrical plugs are critical in the medical devices sector, where they connect portable medical equipment like monitors and diagnostic tools. Their design ensures that devices remain compact and user-friendly, which is vital in emergency and clinical settings. Buyers in this field must prioritize compliance with medical safety standards and consider the plugs’ robustness and low profile design to enhance mobility and accessibility in various healthcare environments.
How Do Low Profile Electrical Plugs Improve Industrial Machinery Applications?
In industrial settings, low profile electrical plugs are used for power connections in confined spaces, making them ideal for manufacturing plants. These plugs contribute to enhanced safety and accessibility, allowing for efficient operation in tight environments. B2B buyers should look for heavy-duty construction and environmental certifications to ensure reliability in demanding conditions. Compatibility with various machinery and the ability to customize configurations will also be key considerations for international sourcing.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘low profile electrical plug’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Space in Equipment Design
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of integrating electrical components into equipment where space is at a premium. For manufacturers of electronic devices or appliances, using standard plugs can lead to design constraints, making it difficult to maintain a sleek aesthetic while ensuring functionality. This can particularly affect industries like consumer electronics, where product design is crucial to market competitiveness.
The Solution: To address this challenge, sourcing low profile electrical plugs is essential. These plugs are specifically designed to reduce protrusion, allowing for more compact designs without compromising electrical performance. When selecting a low profile plug, buyers should prioritize options that meet industry standards, such as NEMA or IEC certifications, ensuring safety and reliability. Furthermore, customizing the plug’s configuration can help fit specific design requirements. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers who offer OEM services can facilitate tailored solutions, enabling manufacturers to innovate while maintaining the necessary electrical standards.
Scenario 2: Compliance with International Standards
The Problem: B2B buyers operating in diverse markets often encounter regulatory compliance issues with electrical components. Different regions have varying standards for electrical safety and performance, which can complicate the sourcing process for low profile electrical plugs. For instance, a company manufacturing products for both the European and North American markets must navigate different certifications, which can lead to delays and additional costs.
The Solution: To mitigate compliance issues, buyers should work closely with suppliers who have a deep understanding of international standards such as RoHS, REACH, and UL certification. By selecting plugs that are already compliant with the necessary regulations for multiple regions, companies can streamline their supply chain and reduce the risk of non-compliance. Additionally, leveraging suppliers that provide documentation and certification can facilitate easier market entry and reassure end-users of product safety. Buyers should also consider engaging in continuous education on regulatory changes to stay ahead of potential compliance challenges.
Scenario 3: Durability in Harsh Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as manufacturing, construction, or outdoor equipment often require electrical components that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Standard plugs may not be suitable for use in environments with extreme temperatures, moisture, or exposure to dust and debris. This can lead to frequent replacements, increased maintenance costs, and potential downtime in operations.
The Solution: To ensure durability, buyers should seek low profile electrical plugs specifically designed for harsh environments. Look for products made from high-quality materials that offer flammability ratings and environmental certifications. For instance, plugs with a UL 94V-0 flammability rating or those rated for extreme temperature ranges can provide added safety and longevity. It is also beneficial to consult with suppliers who can provide insights into the best materials and designs for specific environmental challenges. Implementing a testing protocol during the selection process can help ensure that the chosen plugs will perform reliably under the expected conditions, thereby reducing long-term costs associated with replacements and maintenance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for low profile electrical plug
What Are the Key Materials for Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
When selecting materials for low profile electrical plugs, it is crucial to consider properties that impact performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of these plugs.
What Are the Key Properties of PVC in Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used material for low profile electrical plugs due to its excellent insulation properties and affordability. It has a temperature rating typically between -40°C and +75°C, making it suitable for various environments. PVC is also resistant to moisture and certain chemicals, enhancing its durability.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and easy to mold, which simplifies the manufacturing process. Its excellent electrical insulation properties make it a preferred choice for safety.

Illustrative image related to low profile electrical plug
Cons: While PVC is durable, it can degrade under prolonged exposure to UV light and certain solvents. Additionally, it may not be as robust as other materials like thermoplastic elastomers (TPE).
Impact on Application: PVC is compatible with most electrical applications but may not be suitable for extreme environments where higher temperature ratings are required.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that PVC plugs comply with local electrical standards, such as IEC or NEMA, to avoid issues related to safety and performance.

Illustrative image related to low profile electrical plug
How Does Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Compare for Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer a flexible alternative to traditional materials. They have excellent temperature resistance, typically ranging from -40°C to +100°C, and are highly resistant to abrasion and chemicals.
Pros: TPE provides superior flexibility and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent movement. It is also recyclable, which appeals to environmentally conscious buyers.
Cons: TPE can be more expensive than PVC and may require more complex manufacturing processes, which can lead to higher production costs.
Impact on Application: TPE is particularly suitable for environments where flexibility and resilience are paramount, such as in portable devices or outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and South America should verify that TPE materials meet relevant environmental regulations, such as RoHS and REACH compliance.

Illustrative image related to low profile electrical plug
What Advantages Do Nickel-Coated Brass Blades Offer in Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
Nickel-coated brass is commonly used for the blades of low profile electrical plugs due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. This material is capable of withstanding high temperatures and mechanical stress.
Pros: The conductivity of nickel-coated brass ensures efficient power transmission, while its corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of the plug.
Cons: Nickel-coated brass can be more expensive than other materials and may require additional processing steps to achieve the desired finish.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly effective in high-load applications where reliability is critical, such as in industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that nickel-coated brass components meet international standards such as ASTM or DIN to guarantee quality and safety.
How Does Polycarbonate Perform as a Material for Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
Polycarbonate is known for its high impact resistance and transparency, making it suitable for applications where visibility of internal components is beneficial. It can operate effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to +120°C.
Pros: The high impact resistance of polycarbonate makes it an excellent choice for environments where plugs may be subject to physical stress.
Cons: Polycarbonate can be more expensive than PVC and may not offer the same level of flexibility as TPE.
Impact on Application: This material is ideal for applications requiring durability and visibility, such as in consumer electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards and certifications is essential, especially in regions with stringent electrical regulations, such as Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Low Profile Electrical Plugs
| Material | Typical Use Case for low profile electrical plug | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | General electrical applications | Cost-effective and good insulation | Degrades under UV exposure | Low |
| TPE | Flexible and portable devices | Superior flexibility and durability | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Med |
| Nickel-Coated Brass | High-load industrial applications | Excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and additional processing needed | High |
| Polycarbonate | Consumer electronics with visibility needs | High impact resistance | Higher cost and limited flexibility | Med |
Selecting the right material for low profile electrical plugs involves balancing performance, cost, and compliance with international standards. Understanding the properties and applications of each material can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and market requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for low profile electrical plug
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
The manufacturing process of low profile electrical plugs involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets high-quality standards and performance requirements. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to low profile electrical plug
-
Material Preparation: The initial step involves sourcing high-quality raw materials. For low profile plugs, this typically includes PVC for the outer mold and nickel-coated brass for the blades. Suppliers often ensure that materials comply with environmental regulations such as RoHS and REACH. Each batch of material undergoes inspection to verify specifications before entering production.
-
Forming: This stage involves shaping the materials into the desired plug components. For example, the blades are stamped or molded into their specific profiles. Precision is crucial here, as the dimensions affect electrical conductivity and safety. Technologies like injection molding are commonly employed to create the outer casing, which must also adhere to flammability ratings such as UL 94V-0.
-
Assembly: Once the components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This process may be automated or manual, depending on the manufacturer. Key aspects include ensuring proper alignment of the blades and secure connections for electrical components. Quality checks occur at this stage to verify the integrity of the assembly.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes surface treatments and additional inspections. This can involve applying protective coatings or conducting tests to ensure the plug meets aesthetic and functional standards. Final products are often packaged in compliance with international shipping regulations to facilitate global distribution.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Low Profile Electrical Plug Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of low profile electrical plugs, ensuring that they meet both international standards and specific industry requirements.
-
Relevant International Standards: Manufacturers typically adhere to standards like ISO 9001 for quality management systems, which ensures consistency in quality and operational efficiency. Additionally, compliance with CE marking for European markets and UL certification for North American markets is essential for regulatory acceptance.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the target market, other certifications such as the API (American Petroleum Institute) may be relevant, particularly for plugs used in industrial applications. For B2B buyers, understanding these certifications can help gauge the reliability and safety of products.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Key checkpoints in the QC process include:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during production focus on detecting defects early and ensuring that processes are followed correctly.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, finished plugs undergo comprehensive testing, including electrical safety tests (e.g., Hi-Pot testing), dimensional checks, and continuity tests to verify performance.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
Testing methods are crucial to validate the quality and safety of low profile electrical plugs. Common methods include:
- Hi-Pot Testing: This tests the dielectric strength of the plug, ensuring that it can handle high voltages without breaking down.
- Continuity Testing: Ensures that electrical pathways are intact and functioning as intended.
- Polarity Testing: Verifies that the plug’s wiring is configured correctly, preventing potential electrical hazards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain robust quality control processes:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess manufacturing practices, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. This firsthand observation can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s operational integrity.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for documented evidence of quality control measures, including certificates of compliance and testing results. These documents should detail the methodologies used and the outcomes of various tests.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These agencies can conduct random checks on production batches and provide detailed reports on compliance and quality.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing low profile electrical plugs from international suppliers, B2B buyers must navigate various certification and quality control nuances:
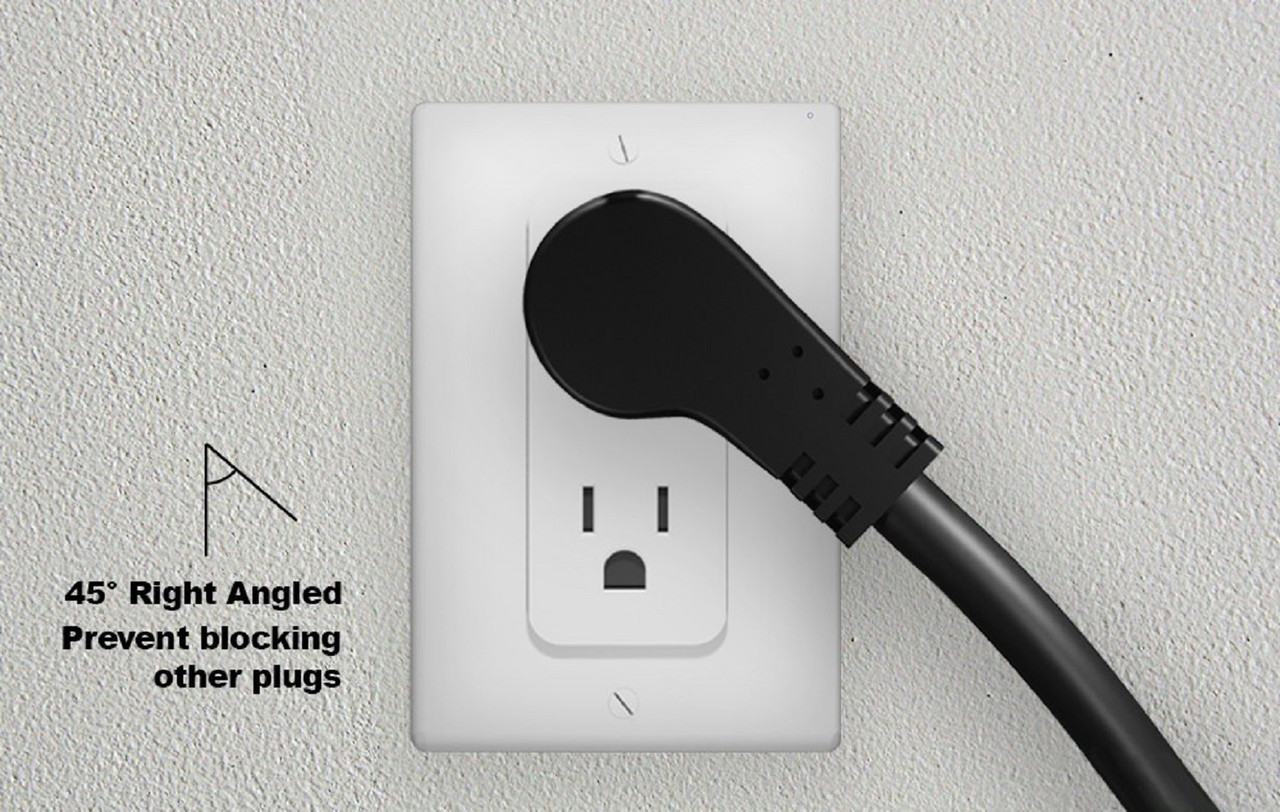

Illustrative image related to low profile electrical plug
-
Regional Compliance: Different regions have specific certification requirements. For example, plugs intended for the European market must meet CE standards, while those for North America require UL certification. Understanding these differences is essential for avoiding compliance issues.
-
Cultural and Regulatory Variations: In regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, local regulations may differ significantly. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure that products meet local safety and quality standards.
-
Language Barriers: Documentation and communication may be complicated by language differences. It is advisable to work with suppliers who provide documentation in the buyer’s preferred language to ensure clarity regarding quality standards and testing results.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for low profile electrical plugs is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance supply chain reliability and product safety.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘low profile electrical plug’
Introduction
This guide provides a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure low profile electrical plugs. Sourcing these components requires careful consideration of technical specifications, supplier reliability, and compliance with international standards, particularly for businesses operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Following this checklist will help ensure you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific technical requirements for the low profile electrical plugs you need. Consider factors such as voltage rating, current capacity, and the type of connectors required.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Common specifications include 15A at 125V, but verify if your application demands different ratings.
- Connector Types: Identify if you need NEMA standards, IEC configurations, or other specific connectors based on your equipment.
Step 2: Research Compliance and Certification Standards
Ensure that the plugs you are considering meet relevant international and regional compliance standards. This is vital for ensuring safety and reliability.
- Certifications: Look for certifications like UL, RoHS, and REACH, which indicate adherence to safety and environmental regulations.
- Country-Specific Requirements: Be aware that different regions may have distinct compliance requirements, so tailor your sourcing approach accordingly.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations to ensure they can meet your needs.
- Company Profiles: Request detailed company profiles, including history, expertise, and case studies.
- References: Seek references from other businesses within your industry or region that have sourced similar products.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Before placing a bulk order, always request samples of the low profile electrical plugs. This allows you to assess quality directly.
- Material and Build Quality: Inspect the materials used, such as nickel-coated brass for blades and PVC for insulation.
- Functional Testing: Conduct tests for electrical performance, durability, and safety features to ensure they meet your specifications.
Step 5: Verify Shipping and Logistics Capabilities
Assess the supplier’s ability to handle shipping and logistics effectively, especially if you are sourcing internationally.
- Shipping Options: Ensure they offer reliable shipping methods that align with your timeline and budget.
- Customs and Duties: Clarify who is responsible for customs clearance and duties, particularly for international orders.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have selected a potential supplier, negotiate the terms of the contract, focusing on pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for bulk orders, as many suppliers offer discounts for larger purchases.
- Payment Terms: Establish clear payment terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring supplier confidence.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Develop a clear communication strategy with your chosen supplier to ensure ongoing collaboration.
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to discuss order status, quality concerns, and future needs.
- Feedback Mechanism: Create a channel for providing feedback on product performance and service quality, which can help strengthen the business relationship.
Following this checklist will help ensure that you source low profile electrical plugs that meet your operational requirements while minimizing risks associated with supplier selection and product quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for low profile electrical plug Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Low Profile Electrical Plug Sourcing?
When sourcing low profile electrical plugs, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is essential for informed decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials significantly influence the overall cost. For instance, nickel-coated brass for blades, high-grade PVC for outer molds, and compliance with environmental standards like RoHS and REACH can elevate costs but also enhance product durability and safety.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are affected by local wage standards. In regions like Africa or South America, labor may be less expensive, but this can also reflect on the skill level and quality of workmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for molds and specific configurations can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. Buyers should factor in these costs when evaluating overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product reliability and compliance with international standards, which can add to the cost but is crucial for market acceptance.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, especially for international orders, can vary significantly. Factors such as distance, method of transport, and customs duties play a crucial role in determining total logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better rates.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Low Profile Electrical Plug Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of low profile electrical plugs:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers are typically more willing to offer discounts for larger orders, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom configurations, such as specific voltage ratings or unique designs, can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess whether the customization is necessary or if standard products would suffice.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., UL, CE) come at a premium but can result in better performance and compliance with safety regulations, which is particularly important for international markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but they often provide better warranties and customer support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact overall costs.
What Tips Can Buyers Utilize for Effective Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency?
B2B buyers should consider several strategies to optimize costs when sourcing low profile electrical plugs:

Illustrative image related to low profile electrical plug
-
Negotiate with Suppliers: Engage in open discussions about pricing and explore options for bulk discounts. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better terms over time.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, energy efficiency, and replacement costs. Investing in higher-quality plugs may reduce long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to be aware of local regulations and import duties that can affect pricing. Custom duties can vary widely, so consulting with local experts can provide clarity.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of trends in material costs, labor rates, and technological advancements can provide leverage during negotiations.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost and pricing landscape for low profile electrical plugs requires a comprehensive understanding of various cost components and price influencers. By employing strategic negotiation tactics and considering the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remember that indicative prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so continuous engagement with suppliers is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing low profile electrical plug With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Low Profile Electrical Plugs
In the realm of electrical connectivity, low profile electrical plugs offer a sleek and efficient solution for various applications. However, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider alternative solutions that may also meet their operational needs. This analysis compares low profile electrical plugs with two viable alternatives: standard electrical plugs and modular power distribution systems. Each solution presents its own advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial to evaluate them based on specific business requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Low Profile Electrical Plug | Standard Electrical Plug | Modular Power Distribution System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High; ergonomic design reduces space usage | Moderate; bulkier design can obstruct other connections | High; flexible configuration for multiple outputs |
| Cost | Moderate; competitive pricing based on design | Low; widely available and inexpensive | High; initial investment can be significant |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; often requires minimal tools | Very simple; standard fittings and widespread compatibility | Moderate; may require professional installation for optimal setup |
| Maintenance | Low; durable materials with low failure rates | Low; simple design with few components | Moderate; may require periodic checks and updates |
| Best Use Case | Tight spaces where aesthetics and functionality are critical | General use in home and office settings | Environments needing flexible power solutions, like data centers |
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
Standard Electrical Plug
Standard electrical plugs are ubiquitous in both commercial and residential settings. Their low cost and universal compatibility make them a go-to option for many applications. However, their bulkier design can hinder space efficiency and restrict access to adjacent outlets. While installation is straightforward, the performance may not match that of low profile options, particularly in settings where space is at a premium.
Modular Power Distribution System
Modular power distribution systems provide a highly flexible solution for environments requiring multiple power outputs. They can be customized to fit a variety of configurations, making them ideal for data centers or industrial applications. However, the initial investment can be significant, and professional installation is often required, which may not be suitable for all buyers. Maintenance can also be more involved, requiring regular checks to ensure optimal performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
Selecting the right electrical plug solution hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your operation. For businesses operating in tight spaces or requiring a sleek design, low profile electrical plugs present an excellent choice. Conversely, if cost is the primary concern and the application is standard, traditional plugs may suffice. For organizations that demand flexibility and scalability, investing in modular power distribution systems could prove beneficial despite the higher upfront costs.
In conclusion, B2B buyers should weigh the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and specific use cases when evaluating these alternatives. A thorough assessment of operational needs will guide the decision-making process, ensuring that the chosen solution aligns perfectly with the business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for low profile electrical plug
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
Understanding the essential technical properties of low profile electrical plugs is crucial for B2B buyers. These specifications not only ensure product compatibility but also influence performance, safety, and regulatory compliance.
1. Connector Standard
The connector standard defines the design and functionality of the plug, such as the NEMA 5-15P standard commonly used in North America. This standardization is vital for ensuring that the plugs can interface correctly with sockets and electrical systems in different regions. Buyers should prioritize products that adhere to relevant standards to avoid compatibility issues.
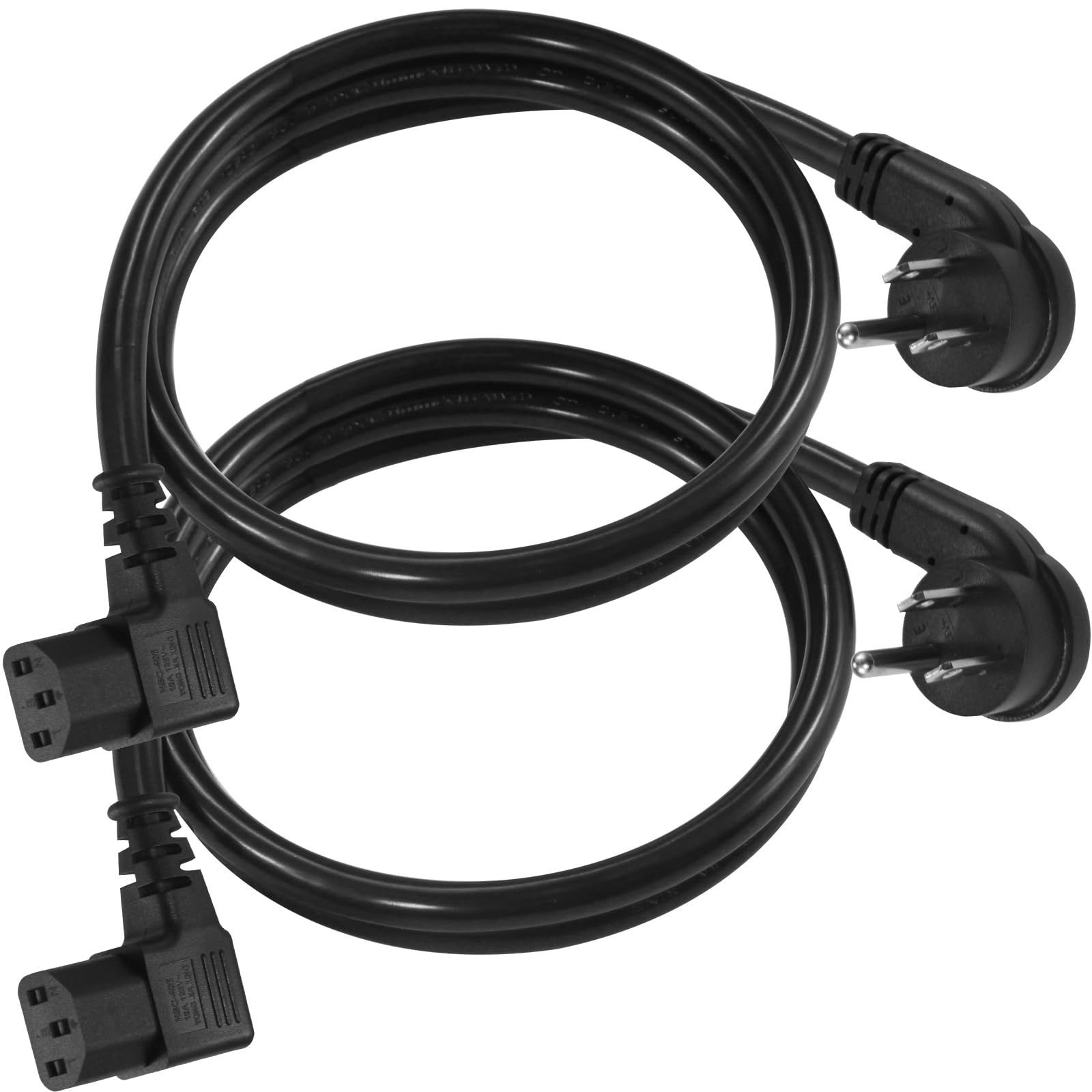

Illustrative image related to low profile electrical plug
2. Maximum Current Rating
This specification indicates the maximum amount of electrical current the plug can handle, typically measured in Amperes (A). For instance, a rating of 15A signifies that the plug can safely carry that current without overheating. Understanding current ratings is essential for selecting plugs that match the electrical load requirements of specific applications, thereby ensuring operational safety.
3. Maximum Voltage
The maximum voltage rating, such as 125V for many low profile plugs, is the highest voltage that the device can safely accommodate. Choosing plugs with the correct voltage rating is critical to prevent electrical failures or hazards, especially in regions with varying voltage standards.
4. Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of low profile plugs, such as nickel-coated brass for blades and PVC for the outer mold, impact durability and safety. High-quality materials enhance the plug’s resistance to wear, environmental factors, and heat. Buyers should look for plugs that are RoHS and REACH compliant to ensure environmental safety and regulatory adherence.
5. Temperature Rating
Temperature ratings indicate the operating range within which the plug can function safely, often expressed in degrees Celsius (°C). A rating from -40°C to +75°C, for example, ensures that the plug can withstand extreme temperatures, making it suitable for various environments. This feature is particularly important for international buyers operating in diverse climates.
6. Flammability Rating
The flammability rating, often indicated as UL 94V-0, assesses the plug’s resistance to ignition and its ability to self-extinguish. A higher flammability rating signifies a safer product, which is a critical consideration for industries where electrical safety is paramount.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Low Profile Electrical Plug Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can greatly enhance communication and negotiation processes for B2B buyers. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electrical plugs, OEMs often create custom solutions tailored to specific buyer requirements. Understanding OEM relationships can help businesses leverage partnerships for exclusive products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is crucial for buyers to understand, as it affects inventory management and procurement strategies. Negotiating MOQs can lead to cost savings and better alignment with business needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from suppliers. This process is vital for buyers looking to compare offers from multiple vendors, ensuring they secure the best deal based on their technical specifications and budget constraints.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Familiarity with these terms is essential for international transactions, as they clarify who bears the costs and risks associated with transport, customs clearance, and insurance.
5. Certification Compliance
Certification compliance refers to the adherence to international safety and quality standards, such as UL, CE, or RoHS. For B2B buyers, ensuring that products meet these certifications is crucial for compliance with local regulations and for maintaining safety and quality assurance.
6. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for effective supply chain management and can impact project timelines and operational efficiency. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers to establish realistic lead times that align with their production schedules.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure safety, compliance, and compatibility in their electrical systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the low profile electrical plug Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Low Profile Electrical Plug Sector?
The low profile electrical plug market is experiencing significant growth driven by global trends toward compact and efficient electrical solutions. Increasing demand for space-saving designs in consumer electronics and industrial applications is a key driver. Regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in infrastructure development, leading to higher consumption of electrical components, including low profile plugs. Moreover, the rise of smart devices and IoT applications is fueling the need for versatile and adaptable power solutions, making low profile plugs an attractive option for B2B buyers.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the integration of smart technology within electrical plugs, such as built-in surge protection and energy monitoring features. These innovations appeal to international buyers looking for enhanced safety and efficiency. Additionally, the trend towards customization is gaining traction, with suppliers offering tailored solutions to meet specific regulatory and operational requirements across different markets. For instance, plugs that conform to various international standards like NEMA and IEC are increasingly in demand, facilitating cross-border trade.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in the sourcing of low profile electrical plugs. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and product lifecycle management is under increasing scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies alike. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that adopt sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste in production. This shift is especially relevant for markets in Africa and South America, where environmental regulations are evolving rapidly.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance. Buyers are more inclined to partner with manufacturers who can demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and adherence to labor laws. Certifications such as RoHS and REACH not only ensure compliance with environmental standards but also serve as a mark of quality and ethical responsibility. By sourcing low profile electrical plugs from certified suppliers, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
The evolution of low profile electrical plugs can be traced back to the need for more ergonomic and space-efficient designs in the electrical component market. Initially developed for consumer electronics, these plugs have expanded into various applications, including industrial and automotive sectors. The introduction of international standards such as NEMA and IEC has facilitated the proliferation of low profile plugs across global markets.
In recent years, technological advancements have further transformed these products, leading to enhanced safety features and energy efficiency. As businesses continue to seek compact solutions that do not compromise on performance, the low profile electrical plug sector is poised for sustained growth. This evolution underscores the importance of staying updated with market trends and sourcing practices to remain competitive in an increasingly globalized economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of low profile electrical plug
-
How do I solve compatibility issues with low profile electrical plugs?
Compatibility issues with low profile electrical plugs often arise from differing regional standards. To address this, first identify the plug type required in your region, such as NEMA for the USA or IEC standards for Europe and other regions. Ensure that the plug you are sourcing meets these specifications, including voltage and amperage ratings. Collaborate with suppliers who can provide detailed product specifications and certifications to guarantee compatibility with your equipment. Consider investing in universal adapters if multi-region usage is anticipated. -
What is the best low profile electrical plug for my equipment?
The best low profile electrical plug for your equipment depends on the specific power requirements and design of your devices. Look for plugs with certifications that match your equipment’s voltage and current ratings, such as NEMA 5-15P for North America or IEC C13 for Europe. Additionally, consider ergonomic designs that facilitate space-saving installations. Consult with your manufacturer or supplier to ensure that the plug you choose aligns with the operational and safety standards necessary for your applications. -
What customization options are available for low profile electrical plugs?
Many suppliers offer customization options for low profile electrical plugs, including variations in wire length, gauge, plug color, and connector types. Customization can also extend to the manufacturing materials, allowing for specific environmental compliance such as RoHS and REACH. If you have unique requirements, reach out to potential suppliers to discuss your needs. They can provide insights into feasible modifications that can enhance performance or meet specific industry standards. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for low profile electrical plugs?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for low profile electrical plugs can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units for standard products, while customized plugs may have higher MOQs due to the setup costs involved in manufacturing. When sourcing, clarify the MOQ with your supplier upfront to ensure it aligns with your purchasing capabilities and project timelines. In some cases, suppliers may offer flexibility for trial orders or bulk discounts. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing low profile electrical plugs?
Payment terms for sourcing low profile electrical plugs can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include full payment upfront, a deposit followed by the balance upon shipment, or net terms extending 30 to 90 days post-delivery. It’s essential to negotiate payment terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring supplier trust and reliability. Be aware of international payment methods and currency considerations, especially when dealing with suppliers from different regions. -
How can I ensure the quality of low profile electrical plugs from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of low profile electrical plugs, request samples before committing to a bulk order. Look for certifications such as UL, CE, or ISO to validate product safety and performance standards. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer warranties or guarantees on their products. Establishing a strong communication channel for quality assurance checks and regular audits can help maintain product integrity throughout the supply chain. -
What shipping options are available for low profile electrical plugs?
Shipping options for low profile electrical plugs typically include air freight, sea freight, and express courier services, depending on urgency and cost considerations. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is economical for larger orders. Discuss with your supplier about their preferred logistics partners and options for tracking shipments. Ensure that you understand customs regulations in your region to avoid delays or unexpected fees upon arrival. -
How do I vet suppliers for low profile electrical plugs effectively?
Vetting suppliers for low profile electrical plugs involves assessing their manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and customer reviews. Start by checking their compliance with international safety standards. Request references from other customers to gauge reliability and quality. Conduct site visits if possible, or utilize third-party inspection services to verify production processes. Online platforms can also provide insights into supplier ratings and performance history, aiding in your decision-making process.
Top 5 Low Profile Electrical Plug Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Electriduct – Flat Plug Power Extension Cords
Domain: electriduct.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Flat Plug Power Extension Cords, UL Listed, 125V, 16/3, 3 Prong, 16AWG Copper, 13Amp, 1625W, Flat Plug approximately 0.58″ thick, available in 4pc Multi-Pack (1.5ft, 3ft, 5ft, 10ft) and 5pc Multi-Pack (1.5ft, 3ft, 5ft, 10ft, 15ft), priced at $9.99.
2. Hug-A-Plug – Right Angle Plug Solution
Domain: cabletiesandmore.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This company, Hug-A-Plug – Right Angle Plug Solution, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Cable Matters – 2-Pack Low Profile Flat Plug Extension Cord
Domain: cablematters.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “2-Pack Low Profile Flat Plug Extension Cord (NEMA 5-15P to NEMA 5-15R)”, “Product ID”: “400021”, “Price”: “”, “Product Rating”: “0”, “Amazon Rating”: “1392”, “Available Sizes (ft)”: [1, 3, 6, 10, 15], “Features”: [“Low profile design”, “Flat plug for space-saving”, “NEMA 5-15P to NEMA 5-15R compatibility”], “Related Products”: [“2-Pack Braided Low Profile Power Extension Cord”, “…
4. Electrical Box Solutions – Low Profile Options
Domain: diy.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Low profile/depth electrical boxes for power outlets; options include: 1.5″ deep standard 4×4 metal box, 1-gang box at 1-1/4″ deep, Carlon box at 1.25″ deep. GFCI protection recommended, especially in shallow boxes.
5. Lee Valley – Hug-A-Plug Low-Profile Plug Adapter
Domain: leevalley.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Hug-A-Plug Low-Profile Plug Adapter”, “colors”: [“White”, “Black”], “dimensions”: “1 5/8 inch thick”, “features”: [“Splits power from the outlet into two sockets”, “Allows cords to plug in parallel to the wall”, “Reduces risk of fires from kinked or damaged cords”], “socket_rating”: “15 amps, 120 volts”, “certifications”: [“UL listed”, “cUL listed”], “usage”: “Indoor use”, “made_in”: “US…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for low profile electrical plug
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement of Low Profile Electrical Plugs?
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of low profile electrical plugs is essential for optimizing supply chains and ensuring product quality. By leveraging comprehensive market insights and evaluating suppliers based on certifications such as UL, RoHS, and REACH, B2B buyers can secure reliable products that meet international standards. This approach not only mitigates risks associated with compliance and safety but also enhances operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Investing in low profile electrical plugs that feature ergonomic designs and robust materials—such as nickel-coated brass and flame-retardant PVC—can significantly reduce failure rates and enhance customer satisfaction. As the demand for compact, versatile electrical solutions grows across diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, staying ahead of trends will be crucial.
For international buyers, the call to action is clear: prioritize strategic sourcing to navigate the complexities of the electrical component market effectively. Engage with suppliers who can offer tailored solutions and robust support, ensuring your operations remain competitive in an evolving landscape. Embrace innovation in your procurement strategies today to secure a sustainable and successful future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.