M29 Cnc Code: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for m29 cnc code
The global landscape of CNC machining is evolving, and understanding the nuances of M29 CNC code is crucial for businesses seeking to enhance their manufacturing efficiency. As B2B buyers grapple with the challenge of sourcing the right technology to ensure precise and reliable tapping operations, this guide offers a comprehensive exploration of M29 CNC code. This essential resource covers various aspects, including the types of M29 applications, supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for implementation.
International buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia—will find actionable insights tailored to their specific market conditions and operational needs. By delving into the intricacies of M29, businesses can better understand its role in enabling rigid tapping and optimizing feed rates, thereby reducing production errors and improving overall output quality.
This guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices by providing expert analysis and practical recommendations. Whether you’re looking to invest in new machinery or seeking to enhance existing capabilities, understanding M29 CNC code is pivotal in navigating the complexities of modern manufacturing. Equip your business with the knowledge to thrive in a competitive global market and enhance your operational efficiency with our in-depth insights.
Understanding m29 cnc code Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rigid Tapping | Synchronizes spindle speed with feed rate; ensures precise threading | Aerospace, automotive manufacturing | Pros: High accuracy, reduced rework. Cons: Higher initial setup costs. |
| Optional User M-Code Interface | Customizable M-code for specific machine functions | Custom machining solutions | Pros: Flexibility in programming. Cons: Requires skilled operators for setup. |
| Synchronous Feed Tapping | Allows for adjustment of feed rate based on spindle speed | High-volume production environments | Pros: Increased efficiency, minimizes downtime. Cons: Complexity in programming. |
| Repeat Synchronous Tapping | Enables multiple passes without cross-threading | Precision engineering, high-tolerance applications | Pros: Enhanced thread integrity. Cons: More time-consuming per hole. |
| Dwell Feature | Introduces a pause at the bottom of the hole before reversing | Specialized applications requiring thread quality | Pros: Improved thread quality. Cons: Slower cycle times. |
What Are the Characteristics of Rigid Tapping in M29 CNC Code?
Rigid tapping is characterized by its ability to synchronize spindle speed with feed rate, ensuring precise threading without the risk of thread damage. This method is particularly beneficial in industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where precision is critical. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the initial setup costs against the long-term benefits of accuracy and reduced rework.
How Does the Optional User M-Code Interface Enhance Flexibility?
The optional user M-code interface allows manufacturers to customize the M-code for specific functions tailored to their machining needs. This flexibility is advantageous for businesses that require bespoke machining solutions. However, it necessitates skilled operators who understand the programming intricacies, making training and expertise vital considerations for buyers.
In What Scenarios is Synchronous Feed Tapping Most Effective?
Synchronous feed tapping is designed to adjust the feed rate based on the spindle speed, making it ideal for high-volume production environments. This method enhances efficiency and minimizes downtime during operations. Buyers should weigh the increased complexity in programming against the operational benefits, particularly in fast-paced manufacturing settings.
Why Choose Repeat Synchronous Tapping for Precision Engineering?
Repeat synchronous tapping allows for multiple passes through a hole without risking cross-threading, making it essential for precision engineering and high-tolerance applications. While this method ensures enhanced thread integrity, it can lead to longer cycle times, requiring careful consideration of production timelines when making purchasing decisions.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Dwell Features?
The dwell feature introduces a pause at the bottom of the hole before reversing, which can improve thread quality in specialized applications. While this can lead to superior threading results, it also results in slower cycle times. Buyers should assess whether the quality benefits justify the potential impact on overall production efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of m29 cnc code
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of m29 cnc code | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Rigid tapping for precision components | Enhanced accuracy in thread creation, reducing rework and waste. | Compatibility with CNC machines, availability of skilled operators. |
| Automotive | Threading for engine components | Improved production efficiency and component reliability. | Quality of taps, machine specifications, and supplier certifications. |
| Electronics | Tapping for circuit board assembly | Streamlined assembly processes and reduced cycle times. | Precision of CNC programming, integration with existing systems. |
| Oil & Gas | Tapping for piping and valve components | Increased durability and performance in high-pressure environments. | Material specifications, adherence to safety and environmental standards. |
| Machinery Manufacturing | Rigid tapping in custom machinery production | Greater flexibility and customization options for varied applications. | Machine adaptability, support for different materials and sizes. |
How is M29 CNC Code Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, M29 CNC code is primarily utilized for rigid tapping in precision components, such as brackets and housings. This code allows the spindle speed to control the feed rate during the tapping process, ensuring precise thread formation without the risk of cross-threading. For international buyers, especially from regions like Europe and the Middle East, sourcing CNC machines that support M29 is critical. They must ensure that their machines are compatible and that operators are trained to utilize these advanced features effectively, minimizing the risk of production delays.

Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
What Role Does M29 CNC Code Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, the M29 code facilitates rigid tapping for critical engine components, such as cylinder heads and transmission cases. This application ensures that threads are accurately formed, which is vital for assembly integrity and performance. For buyers in South America and Africa, it’s essential to consider the availability of high-quality taps and CNC machines that can handle the specific materials used in automotive production. Additionally, understanding local supplier capabilities and lead times can help streamline the sourcing process.
How Does M29 Enhance Electronics Manufacturing Processes?
The electronics sector leverages M29 CNC code for tapping circuit boards and other assembly components. This usage helps in creating precise holes for mounting and connections, which is crucial for device reliability. Buyers in regions like Brazil and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing machines that offer high precision and adaptability to various board sizes and materials. Furthermore, ensuring that suppliers can provide technical support and training can significantly enhance operational efficiency.
What Benefits Does M29 Offer in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas industry, M29 CNC code is essential for tapping components such as valves and piping systems that must withstand high pressures. Rigid tapping ensures that threads are created with high precision, contributing to the overall durability of the components. International buyers must focus on sourcing materials that meet stringent safety and environmental standards, while also ensuring that their CNC machines are capable of handling the specific demands of the oil and gas sector.

Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
How is M29 Utilized in Machinery Manufacturing?
Machinery manufacturing benefits from M29 CNC code through its application in custom machinery production, allowing for flexible and precise threading. This capability enables manufacturers to cater to diverse client needs, facilitating the production of bespoke machinery solutions. For B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets, it’s crucial to assess the adaptability of CNC machines to various materials and sizes. Additionally, establishing relationships with suppliers who can provide ongoing support and maintenance can enhance production capabilities.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘m29 cnc code’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Confusion Over Code Functionality and Implementation
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers using M29 CNC code arises from confusion about its functionality, particularly in relation to rigid tapping cycles. Many users encounter challenges when switching between different feed rate modes (G95 and G94) and understanding how M29 interacts with these commands. This can lead to misprogramming, resulting in poor threading quality or even machine errors. Buyers, especially those in emerging markets, may not have access to comprehensive training resources, exacerbating their difficulties in effectively utilizing M29.
The Solution: To overcome this confusion, it’s crucial for buyers to invest in training and documentation specific to their CNC machinery. Engaging with vendors who provide detailed manuals and online resources can significantly improve understanding. Additionally, users should practice programming with M29 in a controlled environment, utilizing simulation software if available. This hands-on experience allows them to observe how changing spindle speeds impacts feed rates, reinforcing the relationship between M29 and G-code commands. Furthermore, forums and community discussions can be invaluable for sharing insights and solutions, fostering a network of support among users facing similar challenges.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Thread Quality and Operational Reliability
The Problem: Another significant issue faced by B2B buyers is the inconsistency in thread quality when using M29 for rigid tapping. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, including incorrect spindle speed settings or a lack of synchronization between the spindle and feed rates. Buyers in industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing, may find that these inconsistencies lead to costly rework and delays, undermining their operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
The Solution: To ensure consistent thread quality, buyers should adopt a structured approach to programming their CNC machines. First, they should confirm that their equipment is capable of utilizing M29 and that the firmware is up-to-date. It’s advisable to establish a standard operating procedure (SOP) that outlines the ideal spindle speeds and feed rates for different materials and tap sizes. Regularly calibrating machinery and conducting routine maintenance can also mitigate variability in threading quality. Collaborating with tool manufacturers to identify the right taps for specific applications can further enhance reliability, ensuring that the correct tools are employed for the intended materials.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Adapting to Machine Specifications and Limitations
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties when adapting M29 CNC code to their specific machine specifications and limitations. Each CNC machine model may have unique requirements or capabilities, leading to frustration when code that works in one environment fails in another. This challenge is particularly pronounced for companies in regions with diverse manufacturing landscapes, where varying machine types and vintage can complicate the use of standard codes like M29.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough evaluation of their CNC machines before implementing M29. This involves reviewing the machine’s technical specifications and consulting the manufacturer’s documentation to understand how M29 is implemented in their systems. Networking with other manufacturers or joining industry associations can provide insights into best practices for using M29 across different machines. Buyers should also consider investing in training programs focused on the specific machines they use, which can be beneficial for both operators and programmers. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation, companies can better navigate the complexities of M29 and improve overall operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Strategic Material Selection Guide for m29 cnc code
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials for M29 CNC Code Applications?
When selecting materials for applications involving M29 CNC code, particularly in rigid tapping operations, it is crucial to consider the specific properties that will influence performance. The following analysis covers four common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, cast iron, and titanium, focusing on their suitability for M29 CNC operations.
How Does Aluminum Perform in M29 CNC Code Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight material with excellent machinability, making it a popular choice for CNC applications. It has a high strength-to-weight ratio and good corrosion resistance, particularly in environments where moisture is present. Its thermal conductivity is also beneficial for dissipating heat during machining processes.
Pros: Aluminum is cost-effective, easy to machine, and provides good surface finishes. It is suitable for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it is not as strong as other metals like steel or titanium. It can also be prone to galling when tapped, which may affect thread quality.
Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and oils, but may not perform well in high-stress environments or with abrasive materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B211 for aluminum alloys is essential. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should also consider local sourcing for cost efficiency.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Stainless Steel for M29 CNC Code?
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments. It is often used in food processing, medical devices, and marine applications due to its hygienic properties.
Pros: The durability and resistance to rust and corrosion make stainless steel ideal for long-term applications. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, ensuring reliability in demanding conditions.
Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Cons: Stainless steel is more challenging to machine than aluminum, leading to higher manufacturing costs. The rigidity of the material can also result in tool wear if not managed properly.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including acidic and alkaline substances, making it versatile for various applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. In regions like Brazil and South Africa, sourcing local suppliers can reduce lead times and costs.
Why is Cast Iron a Preferred Material for M29 CNC Code?
Cast iron is a traditional material used in CNC machining due to its excellent wear resistance and ability to dampen vibrations. It is commonly used in heavy machinery, automotive components, and tooling.
Pros: The high durability and machinability of cast iron make it suitable for producing complex shapes. It also offers good thermal stability, which is advantageous during machining.
Cons: Cast iron is heavier than other materials, which may not be suitable for lightweight applications. It is also more brittle, making it susceptible to cracking under certain conditions.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with various media, including oils and coolants, but may not perform well in environments with high moisture content.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A48 is critical. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider the availability of specific grades to meet their application needs.
What Makes Titanium a Unique Choice for M29 CNC Code?
Titanium is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. Its high melting point and strength make it suitable for high-performance components.
Pros: Titanium is lightweight yet incredibly strong, making it ideal for applications requiring high performance. It also has excellent biocompatibility, making it suitable for medical implants.
Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Cons: The cost of titanium is significantly higher than that of other materials, and it is more difficult to machine, leading to increased production costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium is compatible with a variety of media, including seawater and aggressive chemicals, making it versatile for various applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM F136 for titanium alloys is essential. Buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and South America should be aware of the material’s availability and potential sourcing challenges.
Summary Table of Material Selection for M29 CNC Code
| Material | Typical Use Case for m29 cnc code | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight components in automotive | Excellent machinability and cost | Prone to galling in tapping | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices and food processing | High corrosion resistance | Higher manufacturing costs | Med |
| Cast Iron | Heavy machinery and tooling | Excellent wear resistance | Brittle and heavy | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace and medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and difficult to machine | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of common materials used in conjunction with M29 CNC code. Understanding these factors can aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with specific application requirements.
Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for m29 cnc code
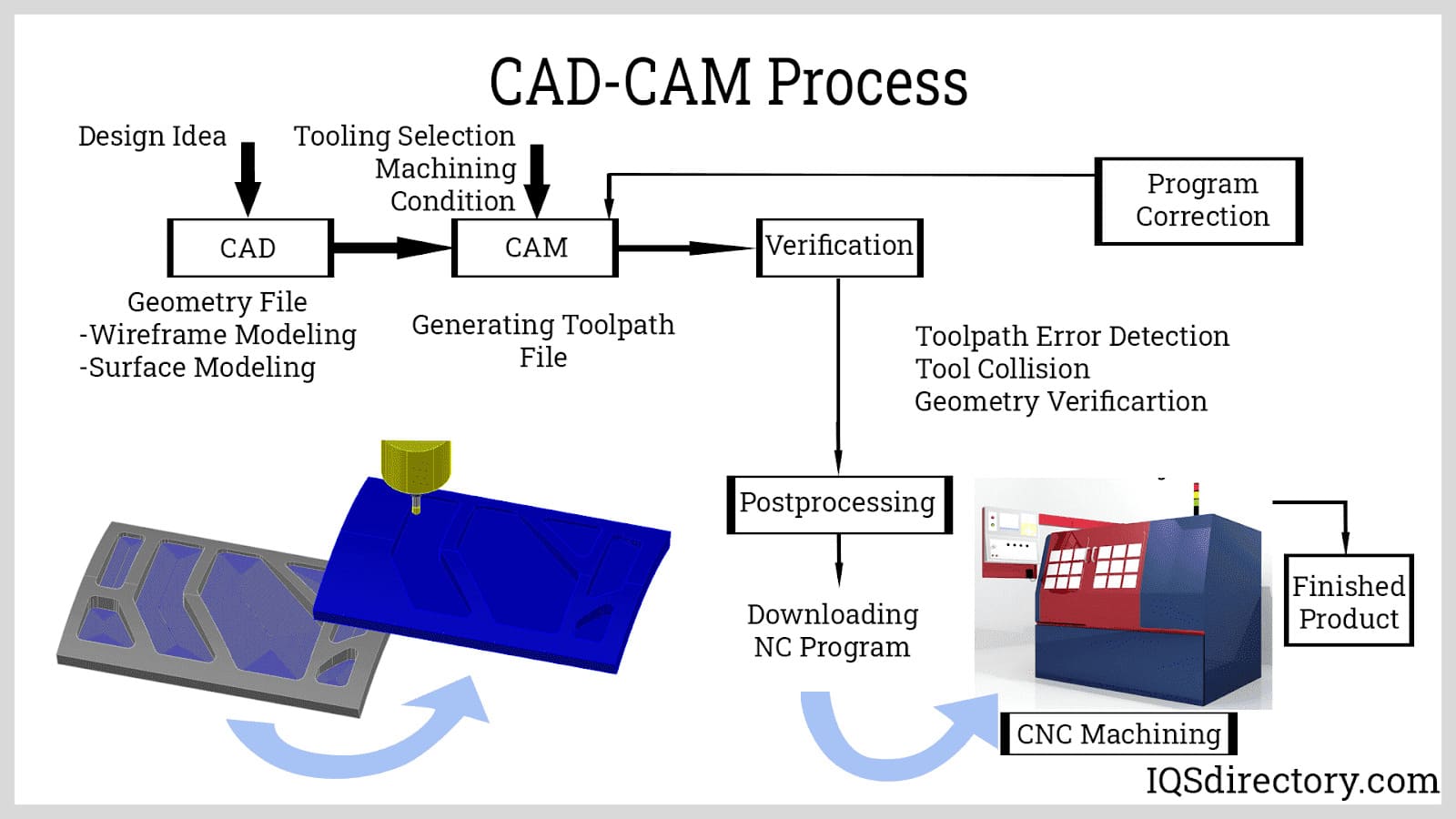
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for M29 CNC Code?
The manufacturing process for components utilizing M29 CNC code involves several critical stages, ensuring precision and reliability in operations like rigid tapping. The primary stages include:
1. Material Preparation
Material selection is crucial for any CNC operation. Common materials used in conjunction with M29 CNC code include various metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, and cast iron. The preparation stage involves sourcing high-quality raw materials that meet specific mechanical properties and standards. Suppliers should provide material certificates to verify compliance with relevant international standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO). Proper handling and storage are essential to prevent contamination and degradation.
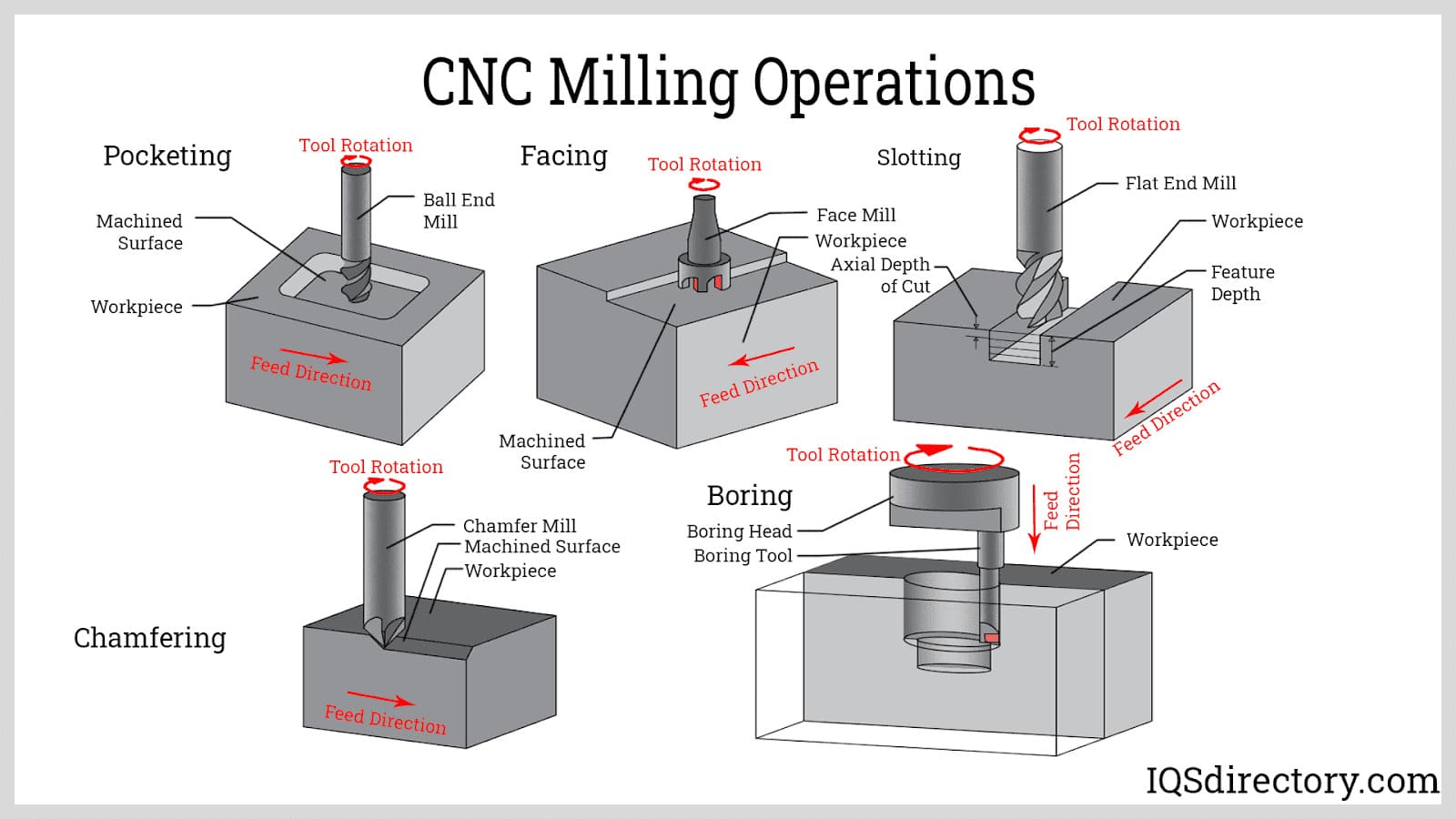
2. Forming
The forming stage encompasses various machining operations, including drilling, tapping, and threading. For M29 CNC code, rigid tapping is a significant focus, where the spindle speed is synchronized with the feed rate, allowing for precise thread creation without the risk of cross-threading. CNC machines equipped with M29 capabilities can adjust feed rates dynamically based on spindle speed, enhancing efficiency. It is essential to program the CNC correctly, using G-code commands effectively to control the tapping cycle, ensuring the correct pitch and depth are achieved.
3. Assembly
In cases where multiple components are involved, assembly becomes a vital process. This stage may involve the integration of tapped components into larger assemblies. It is essential that assembly techniques adhere to stringent quality standards to ensure that final products meet customer specifications. Proper documentation and traceability during assembly are necessary to maintain quality assurance.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes, such as deburring, coating, or surface treatment, are crucial to enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of the final product. Techniques like anodizing or powder coating may be applied depending on the material and application. The finishing stage also ensures that the components meet the required surface roughness and other specifications.
Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing of M29 CNC Code?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process for components utilizing M29 CNC code. The goal is to ensure that every product meets international quality standards and customer expectations.
Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance
For B2B buyers, it is essential to ensure that suppliers comply with recognized international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system (QMS), emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Other industry-specific certifications may also apply, such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas components.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are embedded at various stages of the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Verification of material certificates, dimensional checks, and visual inspections ensure that the materials meet specified standards before processing begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During machining operations, continuous monitoring is essential. Operators should perform regular checks on dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes to ensure conformity. Utilizing statistical process control (SPC) techniques can help identify variances early in the production process.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, final inspections are conducted. This may include functional testing, dimensional verification, and surface quality assessments. Documentation of these inspections is crucial for traceability and accountability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods can be employed to ensure the quality of components produced using M29 CNC code:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Tools such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) are used to verify that components meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
-
Functional Testing: This involves testing the components under actual working conditions to ensure they perform as intended. For tapped holes, this might include verifying thread integrity and fit with mating parts.
-
Surface Roughness Testing: Instruments like surface roughness testers assess the texture of the finished surface, ensuring it meets specified standards for application.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes, quality management systems, and adherence to standards. This includes reviewing documentation, observing processes, and assessing the overall quality culture.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that include inspection results, non-conformance reports, and corrective actions taken. This transparency builds trust and ensures accountability.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly important for international transactions where direct oversight may be challenging.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital.
-
Regional Standards Compliance: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards applicable in their regions. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while Middle Eastern buyers may look for specific certifications related to local regulations.
-
Cultural Considerations in Quality Assurance: Different regions may have varying practices and expectations regarding quality assurance. Understanding these cultural nuances can enhance communication and collaboration with suppliers.
-
Logistical Considerations: International shipping and logistics can impact the quality of products. Ensuring that suppliers follow best practices in packaging and transportation can mitigate risks of damage or degradation during transit.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers who deliver high-quality components that meet their specifications and industry standards.

Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘m29 cnc code’
In the competitive landscape of CNC machining, understanding and effectively utilizing M29 CNC code is critical for achieving optimal results, particularly in rigid tapping operations. This guide provides a structured checklist for B2B buyers to navigate the procurement process of M29 CNC code, ensuring they make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency.
Step 1: Identify Your Operational Needs
Begin by assessing your specific machining requirements. Understanding the type of materials you will be working with and the complexity of the components you need to produce will help you determine how M29 can enhance your tapping processes. Consider factors such as material type, hole sizes, and threading requirements to inform your selection.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications that your CNC machines must meet to effectively implement M29 code. This includes evaluating machine compatibility, software requirements, and any necessary hardware upgrades. Ensuring that your equipment is capable of handling rigid tapping with M29 will directly impact your productivity and quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to thoroughly vet potential suppliers of M29 CNC code. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other clients, especially those in similar industries or regions. This step is crucial to ensure that the supplier has a proven track record of delivering reliable and effective CNC solutions.
- Check for Industry Experience: Look for suppliers with extensive experience in CNC machining and a focus on tapping applications.
- Seek Customer Feedback: Ask for testimonials or case studies that demonstrate the supplier’s capabilities and customer satisfaction.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering comply with relevant industry standards and possess necessary certifications. This could include ISO certifications or other quality assurance certifications pertinent to CNC machining. Compliance not only assures you of quality but also reduces the risk of operational disruptions.

Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Trials
Where possible, request demonstrations or trial periods to test the M29 code in action. Observing the code’s performance in real-time will provide insights into its effectiveness and compatibility with your existing systems. This hands-on approach can help identify potential issues before making a larger commitment.
Step 6: Assess Technical Support and Training Services
Evaluate the level of technical support and training services offered by the supplier. Effective implementation of M29 CNC code may require additional training for your operators and programmers. A supplier that provides robust support can help ensure a smoother transition and ongoing operational success.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Finally, once you’ve identified a preferred supplier, negotiate favorable terms and conditions. This includes pricing, delivery schedules, warranty terms, and service agreements. Clear contractual agreements will protect your interests and ensure that you receive the support necessary for successful implementation.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source M29 CNC code, ensuring it aligns with their operational needs and contributes to improved machining efficiency.

Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for m29 cnc code Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for M29 CNC Code Sourcing?
When sourcing M29 CNC code, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of materials for CNC machining varies significantly based on the type of metal or composite used. For example, sourcing aluminum or stainless steel will yield different pricing due to market fluctuations and material availability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor costs can fluctuate based on regional wage standards. In regions like Africa and South America, labor may be more affordable, which can lower overall costs. However, this must be balanced against the availability of skilled technicians familiar with M29 programming.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Overhead can vary based on the efficiency of the manufacturing process and the technology used in CNC machining.
-
Tooling: The cost of tools specifically designed for M29 operations must be factored in. High-quality tooling may require a higher initial investment but can lead to better precision and lower overall machining costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing a robust QC process to ensure that M29 operations meet specifications can add to the cost but is essential for maintaining quality and reducing defects.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can significantly impact overall costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on competition and market demand.
What Influences the Pricing of M29 CNC Code?
Several factors influence the pricing of M29 CNC code, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders generally result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider negotiating MOQs that align with their production needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized M29 code that requires additional engineering or programming expertise may incur higher costs. Providing clear specifications upfront can help streamline the sourcing process.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects cost but also impacts machining time and tool wear. Buyers should evaluate the total cost implications of different material choices.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers that offer certified products or adhere to industry standards (such as ISO certifications) may charge a premium. However, investing in higher-quality sources can lead to long-term savings by reducing defects and rework.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can significantly affect pricing. Suppliers with a strong track record may command higher prices but can offer better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipment (such as FOB, CIF, etc.) can help buyers assess total landed costs. This is particularly important for international transactions where additional fees may apply.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs in M29 CNC Code Sourcing?
B2B buyers can leverage several strategies to optimize costs when sourcing M29 CNC code:
-
Negotiation: Engaging in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures and potential discounts for bulk orders can lead to significant savings.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyzing the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just upfront costs can provide a more accurate picture of value. This includes considering maintenance, operational efficiencies, and potential downtime.
-
International Pricing Nuances: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of currency fluctuations and trade tariffs that can influence pricing. Building relationships with local suppliers can also yield favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Requesting quotes from multiple suppliers allows buyers to compare prices, quality, and lead times. This competitive analysis can drive better deals.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for M29 CNC code can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Buyers should conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions. Always consider market conditions, supplier reliability, and the overall value proposition when evaluating costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing m29 cnc code With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions in CNC Tapping
In the realm of CNC machining, particularly for tapping operations, understanding the various coding options available is crucial for optimizing performance and efficiency. The M29 CNC code stands out for its ability to facilitate rigid tapping, but it is essential to explore alternative methods that can offer comparable or enhanced capabilities. This analysis compares M29 with two prevalent alternatives—G84 and G95 codes—highlighting their respective advantages and limitations.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | M29 CNC Code | G84 Code | G95 Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for rigid tapping; ensures synchronization of feed and spindle speed | Good for general tapping; less control over feed synchronization | Effective for thread cutting; requires manual RPM feed calculation |
| Cost | Often included in advanced CNC systems; minimal additional costs | Standard feature in most CNC machines; no extra costs | Typically free to implement; no additional hardware needed |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific machine compatibility; setup may be complex | Straightforward implementation; widely supported | Easy to program; intuitive for experienced operators |
| Maintenance | Minimal; dependent on machine capabilities | Low; routine checks are sufficient | Low; requires operator knowledge for optimal use |
| Best Use Case | High-precision applications requiring tight tolerances | General machining tasks with standard threading | Applications needing flexibility in feed rate adjustments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
G84 Code
The G84 code is a conventional tapping cycle used in CNC programming. It is widely supported across various CNC machines, making it an accessible option for many manufacturers. One of its key advantages is its straightforward implementation, which allows operators to quickly set up tapping operations without extensive training. However, G84 lacks the sophisticated synchronization capabilities of M29, which can lead to inconsistencies in feed rates if spindle speeds are adjusted during operation. It is best suited for general machining tasks where precision is not as critical.
G95 Code
G95 is a feed-per-revolution code that allows operators to specify the feed rate based on the spindle speed. This method can provide greater flexibility in adjusting feed rates without recalculating the parameters, making it a preferred choice for experienced machinists who require quick adaptations during production. The simplicity of programming G95 makes it a favorite for many CNC users. However, it does not inherently provide the same level of precision as M29 for rigid tapping, especially in high-tolerance applications, and requires a thorough understanding of feed rates to maximize its effectiveness.
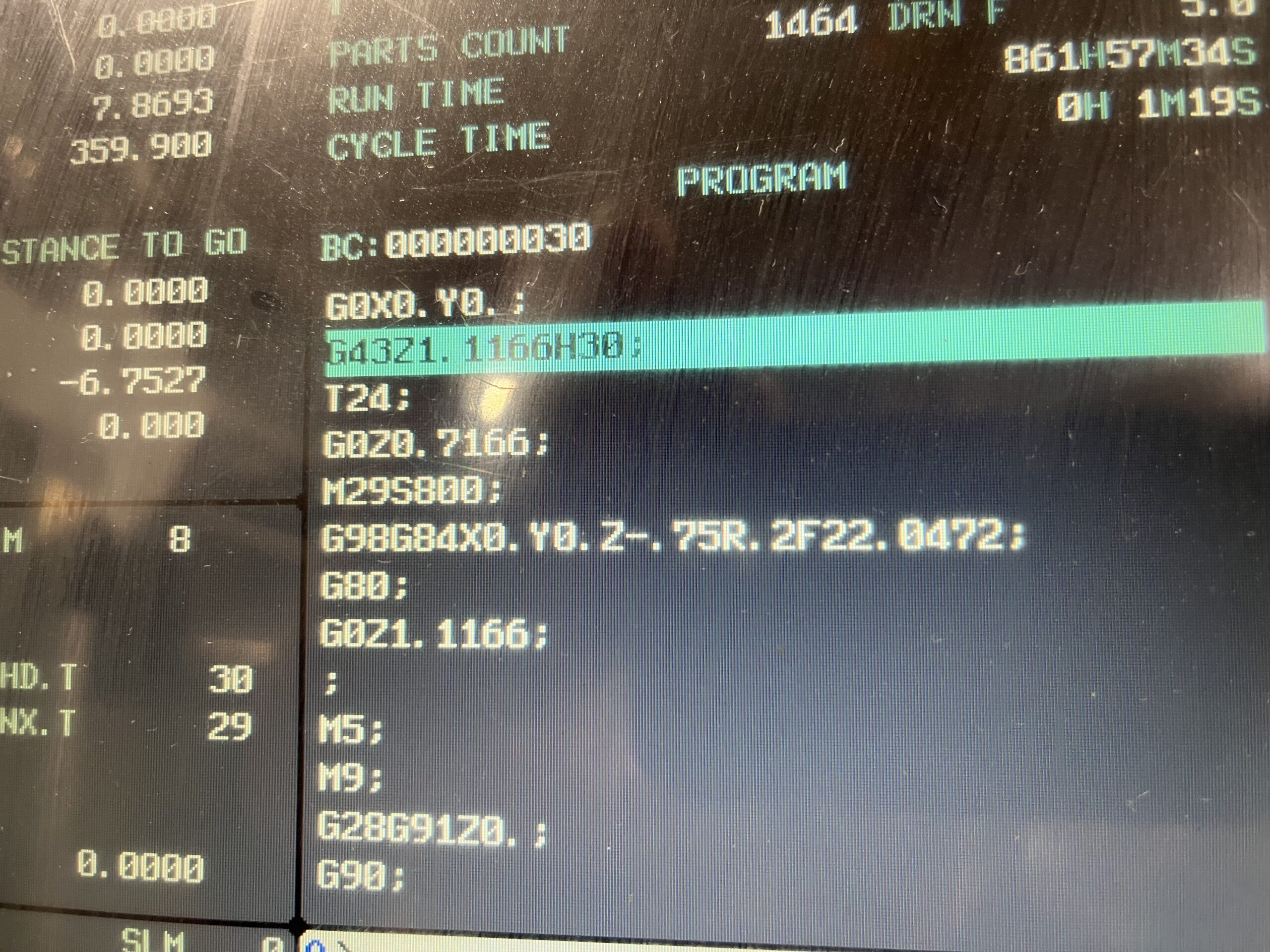
Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your CNC Tapping Needs
When selecting a CNC tapping solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, including the precision needed, ease of implementation, and the types of materials being processed. M29 offers a robust option for those prioritizing synchronization and precision in tapping operations, particularly in high-stakes environments. Conversely, G84 and G95 provide valuable alternatives for general machining and flexibility, respectively. Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational goals and technical capabilities of the buyer’s machining setup, ensuring optimal productivity and quality in their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for m29 cnc code
What Are the Key Technical Properties of M29 CNC Code?
When navigating the complexities of M29 CNC code, understanding its technical properties is crucial for optimizing machining processes. Here are several critical specifications that define its utility and importance in a B2B context:
-
Feed Rate Control
M29 enables synchronous feed tapping, which allows the spindle speed to dictate the feed rate automatically. This ensures that the feed rate remains consistent with the spindle’s RPM, reducing the risk of thread damage. For international buyers, maintaining accurate feed rates is vital for quality assurance and operational efficiency, especially in high-volume production settings. -
Compatibility with CNC Systems
Not all CNC machines support M29; it is typically found in more advanced models. Understanding the compatibility of M29 with specific machines is essential for B2B buyers, as it influences equipment selection and integration into existing manufacturing setups. Buyers must verify if their machines are equipped for rigid tapping, as this can directly affect production capabilities. -
Precision Tapping
M29 facilitates rigid tapping, which locks the spindle during the tapping process, ensuring precise thread formation. This precision is particularly important in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where tolerances are critical. B2B buyers must prioritize machines that support this feature to ensure high-quality output and reduce rework costs. -
Dwell Time Adjustment
The M29 command allows for dwell time settings during the tapping process. Dwell time is the pause at the bottom of the hole, which can help in ensuring complete thread formation. Understanding how to adjust this parameter can improve thread integrity and longevity, making it a valuable aspect for buyers focused on quality and performance. -
Material Compatibility
The effectiveness of M29 can vary based on the material being machined. For instance, tapping into softer materials like aluminum may yield different results compared to harder materials like stainless steel. B2B buyers must consider the material specifications when selecting machines and tooling to ensure optimal performance. -
Operational Efficiency
By automating feed rate adjustments, M29 contributes to overall operational efficiency. This is particularly beneficial in high-production environments, where time and resource management are crucial. Buyers should assess how M29 can fit into their productivity goals and streamline their machining processes.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to M29 CNC Code?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and decision-making for B2B buyers. Here are some essential trade terms related to M29 CNC code:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to the company that manufactures the original machine or component. Understanding OEM specifications is vital for buyers to ensure compatibility and support for M29 functionality in their CNC machines. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. In the context of CNC machining tools and parts, knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategies effectively, especially when sourcing specialized components for M29 applications. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting price quotations from suppliers. It is essential for B2B buyers to issue RFQs when sourcing CNC machines or components that utilize M29, ensuring competitive pricing and informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions involving CNC machinery and components, as they dictate shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities. -
TPI (Threads Per Inch)
TPI is a measurement of thread density, indicating how many threads exist within one inch. This metric is vital for programming M29, as it affects feed calculations and thread formation quality. -
G-Code
G-Code is the programming language used to control CNC machines. Understanding G-Code commands, including those related to M29, is essential for effective programming and machine operation.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their machining capabilities and support their operational objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the m29 cnc code Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the M29 CNC Code Sector?
The global CNC machining industry is witnessing rapid evolution, influenced by technological advancements and changing market demands. Key drivers include the increasing need for precision in manufacturing processes and the rise of automation in production lines. The M29 CNC code, particularly in the context of rigid tapping, represents a significant trend as manufacturers seek to enhance efficiency and accuracy in threading operations. The adoption of M29 is gaining traction among international buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where manufacturing capabilities are expanding.
Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0, IoT integration, and advanced CNC systems are reshaping sourcing strategies. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that offer machines compatible with M29 and other advanced programming codes, as these features allow for real-time adjustments to feed rates based on spindle speeds. This flexibility is particularly crucial in high-volume production settings, where efficiency and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
Furthermore, the demand for skilled operators who can effectively utilize these advanced programming codes is rising. This trend is particularly evident in emerging markets where workforce development is essential for maintaining competitiveness. As such, B2B buyers must not only focus on the machinery but also consider the training and support services offered by suppliers to ensure successful implementation of M29 and related technologies.
How are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Integrated into the M29 CNC Code Supply Chain?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the CNC machining sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny as companies strive to meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations for greener practices. The M29 CNC code, while enhancing operational efficiency, can also contribute to sustainability goals by minimizing material waste during the tapping process.

Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Ethical sourcing is increasingly important, particularly for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where supply chain transparency can significantly influence purchasing decisions. Buyers are seeking suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management are becoming essential indicators of a supplier’s credibility.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials and sustainable manufacturing practices is gaining traction. Suppliers that utilize eco-friendly lubricants and cutting fluids in conjunction with M29 programming can position themselves as leaders in sustainability. By integrating these practices into their operations, B2B buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute to a more sustainable future in the CNC machining sector.
How Has the M29 CNC Code Evolved Over Time?
The M29 CNC code has evolved significantly since its inception, driven by the need for more efficient and precise machining operations. Originally introduced to facilitate rigid tapping, M29 has become synonymous with advanced manufacturing techniques that allow for synchronous feed control. This evolution reflects broader trends in CNC technology, where precision and adaptability are paramount.
As manufacturers began to recognize the limitations of traditional tapping methods, the need for codes like M29 became apparent. This code allows for real-time adjustments to feed rates based on spindle speeds, enhancing the accuracy of threaded holes. The introduction of M29 has thus not only streamlined the tapping process but also reduced the risk of defects in threaded components, addressing a critical pain point in machining operations.
Today, as CNC technology continues to advance, the M29 code is being integrated into more sophisticated machining centers, further broadening its applicability across various industries. As a result, international B2B buyers must stay informed about the latest developments in M29 technology to leverage its full potential in their manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of m29 cnc code
-
How do I solve issues with M29 CNC code during tapping operations?
To address problems with M29 CNC code, ensure that your machine is compatible with this command, as it is used for rigid tapping. Verify the spindle speed and feed rate settings, as incorrect configurations can lead to misalignment or damaged threads. Additionally, consult your CNC machine’s manual for specific instructions on using M29, and consider reaching out to technical support if persistent issues arise. Proper training for operators on the nuances of M29 can also minimize errors during tapping operations. -
What is the best CNC machine for using M29 code in tapping applications?
The optimal CNC machines for utilizing M29 code are those equipped with rigid tapping capabilities, such as newer models from manufacturers like Haas, Fanuc, and Nakamura. These machines allow for precise control over the spindle speed and feed rate, ensuring accurate thread formation. When selecting a machine, consider factors like the material you’ll be working with, the complexity of your tapping operations, and the required cycle time. Always consult with your supplier for recommendations based on your specific needs. -
How can I verify the quality of M29 CNC code from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of M29 CNC code from suppliers, request samples of their code and run them on your CNC machine. This will help you gauge compatibility and performance. Additionally, check for certifications and industry standards compliance, such as ISO 9001. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers about their programming practices and quality assurance processes can provide further insights into their reliability and expertise. -
What customization options are available for M29 CNC code?
Customization options for M29 CNC code can include adjustments to feed rates, spindle speeds, and dwell times based on your specific machining requirements. Suppliers may offer tailored solutions based on the materials you are working with and the desired thread specifications. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers and inquire about their ability to provide customized code that aligns with your production processes. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for sourcing M29 CNC code?
Minimum order quantities for M29 CNC code can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may offer flexible MOQs, especially for custom programming services, while others may require larger orders for standard code sets. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly to potential suppliers and negotiate terms that align with your production capacity and budget. Requesting a trial order can also help establish a working relationship without committing to large quantities upfront. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing M29 CNC code internationally?
When sourcing M29 CNC code internationally, payment terms typically range from upfront payments to net 30 or net 60 days, depending on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation outcomes. Common payment methods include bank transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal. It’s important to clarify payment terms in advance to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier may also lead to more favorable payment terms over time. -
How do I assess the logistics for sourcing M29 CNC code from international suppliers?
Assessing logistics involves evaluating shipping methods, delivery times, and costs associated with importing M29 CNC code. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide reliable shipping options, including express and standard freight services. Additionally, consider customs regulations and any potential tariffs that may apply to your shipments. Collaborating with a logistics partner can streamline the process and help manage any challenges that arise. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement for M29 CNC code?
Implementing quality assurance measures for M29 CNC code involves regular testing and validation of the code on your machines to ensure it meets performance standards. Establish a protocol for reviewing code before it is executed, including checks for syntax errors and compatibility with machine specifications. Training your operators to identify and report issues can also enhance quality control. Regular audits of supplier performance can further ensure that the code provided consistently meets your quality expectations.
Top 8 M29 Cnc Code Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Practical Machinist – Rigid Tapping with M29
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Rigid tapping with M29 is a method used in CNC machining that allows for precise threading by synchronizing the spindle speed with the feed rate. Key details include:
– G-code commands: G84 for tapping cycle, G95 for feed per revolution, G94 for feed per minute, and M29 as an optional user M Code interface.
– The program example for tapping cast aluminum with a 3/4-16 tap includes: S200 M3 G98 G…
2. IQS Directory – M-Code Commands Guide
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: M-Code Commands: M00 (Program stop), M01 (Optional program stop), M02 (End of program), M03 (Spindle start forward CW), M04 (Spindle start backward CCW), M05 (Spindle stop), M08 (Coolant on), M09 (Coolant off), M29 (Rigid tap mode), M30 (End of program reset), M40 (Spindle gear at middle), M41 (Low Gear Select), M42 (High Gear Select), M68 (Hydraulic chuck close), M69 (Hydraulic chuck open), M78 (…
3. Haas CNC – M-Code Command List
Domain: haascnc.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: M-Code List for CNC Machines includes commands such as: M00 (Stop Program), M01 (Optional Program Stop), M02 (Program End), M03 (Spindle Forward Command), M04 (Spindle Reverse Command), M05 (Spindle Stop Command), M06 (Tool Change), M07 (Shower Coolant On), M08/M09 (Coolant On/Off), M10/M11 (Engage/Release 4th Axis Brake), M12/M13 (Engage/Release 5th Axis Brake), M19 (Orient Spindle), M30 (Program…
4. CNC Cookbook – G84 & G74 Tapping Solutions
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: G84 G Code: Tapping of right hand threads with M3 spindle rotation. G74 G Code: Tapping of left hand threads with M4 spindle rotation. Rigid Tapping requires synchronization of feed motion with spindle speed, typically an extra-cost option. Example code for G84: M03 M8 S400 F20 Z1.0 G00 X0.0 Y0.0 G01 M29 G84 Z-0.5 R0.2. For machines lacking Rigid Tapping, use a Tapping Head or Tension-Compression …
5. eMastercam – M29 Code for Rigid Tapping
Domain: emastercam.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: M29 code for Fanuc controls activates rigid tapping before the G84 tapping cycle. It synchronizes the feed rate during tapping with the spindle speed, allowing for the use of various chucks instead of a tapping holder. The feed rate is calculated as F = Rotating speed x pitch.
6. HAAS – Rigid Tapping Solutions
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Rigid tapping on HAAS mills allows for tapping operations to be performed without the need for a floating tap holder. The discussion mentions the use of G84 canned tapping cycle, which is standard for tapping, and the importance of ensuring that rigid tapping is enabled in the machine parameters. There is a mention of G95 (feed per revolution mode) causing alarms on older HAAS controls, while G94 …
7. CNC Training Centre – Rigid Tapping G84 Canned Cycle
Domain: cnctrainingcentre.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Rigid Tapping G84 Canned Cycle is a CNC machining technique that allows the tap to remain rigid throughout the tapping cycle, held in a chuck similar to an endmill or drill. Advantages include: no need for expensive tension and compression tapping heads, accurate control of thread depth, ability to re-tap holes, quicker set-up times, and the feed rate being the same as the tap pitch. It is commonl…
8. Facebook – Rigid Tapping Parameter
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Rigid Tapping Parameter, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for m29 cnc code
In the realm of CNC machining, the M29 code plays a critical role in enhancing the efficiency and precision of rigid tapping operations. By enabling synchronous feed adjustments based on spindle speed, M29 allows manufacturers to streamline their processes, reduce the risk of errors, and improve overall productivity. This capability is especially valuable for B2B buyers who seek to optimize their machining workflows and maintain high-quality standards in their production lines.
Strategic sourcing of CNC equipment and technology that supports M29 functionality can yield significant competitive advantages. Buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who offer advanced machining solutions that incorporate M29 and similar codes. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters innovation and adaptability in a rapidly evolving industry.
As global markets continue to expand, now is the time to invest in technologies that elevate your manufacturing capabilities. Explore suppliers that provide comprehensive training and support for M29 and other CNC codes, ensuring your team is well-equipped to leverage these advancements. Embrace this opportunity to future-proof your operations and drive sustainable growth in your business.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to m29 cnc code
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.