3Rd Prong Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3rd prong
In today’s global market, sourcing reliable electrical components, particularly the third prong in plugs, poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers. As organizations expand their operations across diverse regions—such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Germany and Nigeria)—understanding the critical role of the third prong becomes essential. This grounding feature is not merely a technical specification; it is a vital safety mechanism that protects against electrical faults, ensuring the safety of devices and personnel alike.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the third prong, exploring its various types and applications, the importance of supplier vetting, and cost considerations. By examining the unique electrical standards and practices across different regions, this resource equips international buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to upgrade your electrical systems or ensure compliance with local safety regulations, understanding the nuances of three-prong plugs is crucial.
Empowered with actionable insights and expert advice, B2B buyers will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of the global market, mitigate risks, and enhance operational safety. Join us as we explore the essential aspects of the third prong, helping you ensure that your electrical sourcing strategies align with international safety standards and best practices.
Understanding 3rd prong Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Ground Prong | Round prong for grounding; typically found in North America | General appliances, power tools | Pros: Enhanced safety, prevents electrical shock; Cons: Requires compatible outlets. |
| GFCI Ground Prong | Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter; protects against shock | Wet environments, outdoor tools | Pros: High safety standard, prevents electrocution; Cons: More expensive to install. |
| Universal Ground Prong | Adaptable to various outlets; often found in international devices | Global electronics, travel adapters | Pros: Versatile, fits multiple outlet types; Cons: May compromise grounding safety in some regions. |
| Surge-Protected Prong | Built-in surge protection; often found in power strips | Sensitive electronics, data centers | Pros: Protects against surges, enhances device longevity; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Industrial Ground Prong | Heavy-duty design for high-power applications | Manufacturing, construction sites | Pros: Robust and durable, suitable for high load; Cons: Bulkier, may require specialized outlets. |
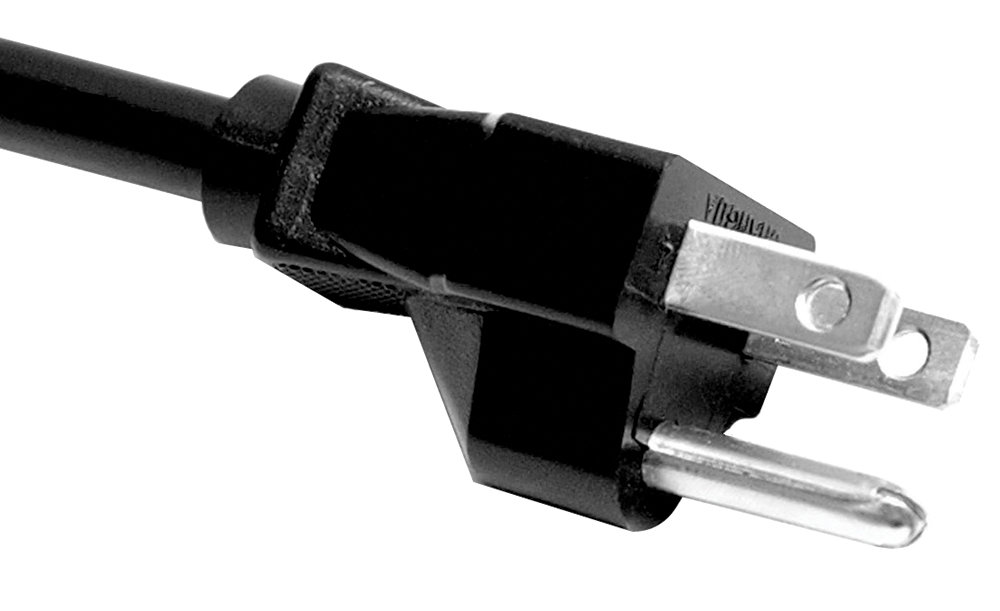
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Ground Prongs?
Standard ground prongs are characterized by their round shape, designed to connect to the grounding system of electrical outlets. Commonly used in North America, these plugs enhance safety by providing a direct path for electricity to flow in case of a malfunction. In B2B scenarios, they are essential for general appliances and power tools, ensuring that devices used in office or industrial settings are safe. Buyers should consider compatibility with existing outlets and the need for professional installation if upgrading from two-prong systems.
How Do GFCI Ground Prongs Provide Enhanced Safety?
GFCI ground prongs incorporate a ground fault circuit interrupter, which automatically cuts off electricity if it detects a ground fault. This feature is crucial in environments where moisture is present, such as kitchens and outdoor workspaces. For B2B buyers, investing in GFCI-protected devices can significantly reduce the risk of electrocution. However, the installation can be more expensive than standard outlets, so businesses should weigh the long-term safety benefits against upfront costs.
Why Are Universal Ground Prongs Important for Global Business?
Universal ground prongs are designed to fit multiple outlet types, making them ideal for international business operations. This adaptability allows companies to use devices across different regions without the need for numerous adapters. While they offer versatility, buyers must ensure that the grounding safety standards of their local outlets are met, as compromising grounding can lead to safety hazards. Businesses should assess their international travel needs when selecting equipment with universal plugs.
What Benefits Do Surge-Protected Prongs Offer?
Surge-protected prongs are integrated into power strips and devices to shield sensitive electronics from voltage spikes. This feature is particularly valuable in data centers and environments where equipment longevity is critical. B2B buyers should prioritize these plugs for devices handling valuable or sensitive data to prevent costly damage. However, the initial investment is higher than standard plugs, so companies must consider their specific needs and budget constraints.
How Do Industrial Ground Prongs Cater to Heavy-Duty Applications?
Industrial ground prongs are designed for heavy-duty applications, featuring a robust construction that can handle high power loads. These plugs are commonly used in manufacturing and construction sites where equipment demands exceed typical household usage. B2B buyers should consider the durability and load capacity when purchasing industrial equipment. While these plugs provide enhanced performance, they may require specialized outlets, adding to installation complexity and cost.
Key Industrial Applications of 3rd prong
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 3rd prong | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Grounding of power tools and equipment | Enhances safety by preventing electric shocks and fires | Compliance with local electrical codes and standards |
| Manufacturing | Use in assembly line machinery | Reduces downtime from electrical faults and enhances safety | Availability of GFCI outlets and proper grounding systems |
| Healthcare | Grounding of medical devices and equipment | Protects patients and staff from electrical hazards | Certification and reliability of electrical equipment |
| Hospitality | Grounding of kitchen and cleaning appliances | Ensures safety in environments with moisture | Quality of grounding solutions and compliance with safety standards |
| Agriculture | Grounding of irrigation and farming equipment | Prevents equipment malfunctions and ensures operational safety | Durability of grounding solutions in outdoor conditions |
How is the 3rd Prong Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction sector, the third prong is critical for grounding power tools and heavy equipment. Grounding helps prevent electric shocks that can result from equipment malfunctions, particularly in environments where moisture is prevalent. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it’s essential to ensure that all equipment meets local electrical safety standards and that proper grounding practices are in place. This not only protects workers but also minimizes liability risks for contractors.
What Role Does the 3rd Prong Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the third prong is utilized in assembly line machinery to provide a reliable grounding mechanism. This is vital for preventing electrical faults that could lead to costly downtime or accidents. Businesses must ensure that their facilities are equipped with GFCI outlets and that proper grounding systems are installed. For buyers in Europe, particularly in Germany, adherence to stringent safety regulations is paramount, making the sourcing of compliant equipment a critical factor.
Why is the 3rd Prong Important in Healthcare?
In healthcare settings, the third prong is essential for grounding medical devices and equipment. Proper grounding safeguards both patients and healthcare staff from potential electrical hazards, which can be particularly dangerous in environments with sensitive equipment. Buyers in the healthcare sector should prioritize sourcing certified and reliable electrical devices to ensure compliance with health and safety standards, which vary significantly across regions, including the Middle East and Europe.
How Does the 3rd Prong Ensure Safety in Hospitality?
In the hospitality industry, the third prong is crucial for the grounding of kitchen appliances and cleaning equipment. Given the high moisture levels in kitchens, grounding prevents electrical shocks and potential fires, ensuring a safe working environment. Businesses should focus on sourcing high-quality grounding solutions that comply with local safety regulations. This is particularly important for international buyers, as different regions may have varying safety standards that must be adhered to.
What Benefits Does the 3rd Prong Offer in Agriculture?
The third prong is vital in the agricultural sector for grounding irrigation systems and farming equipment. This grounding prevents electrical malfunctions that could disrupt operations and ensures the safety of operators working in potentially hazardous conditions. Buyers should consider the durability of grounding solutions, especially in outdoor environments where equipment is exposed to the elements. Ensuring that these systems are robust can significantly reduce operational risks and enhance overall productivity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘3rd prong’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Grounding Compliance in International Markets
The Problem: As an international B2B buyer, you may find that the grounding standards for electrical installations differ significantly from one country to another. For instance, while North American appliances commonly use three-prong plugs, many regions in Africa or South America may not have the necessary grounding infrastructure in their electrical systems. This discrepancy can lead to compliance issues when importing or using electrical equipment, posing risks not only to safety but also to operational efficiency.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research on the electrical standards and grounding requirements of each target market. Partner with local electrical engineers or compliance consultants who can provide insights into local regulations and help you source appropriate adapters or converters that comply with local standards. Additionally, consider investing in equipment that features dual voltage capabilities and can accommodate different grounding configurations, ensuring safety and compatibility across various regions. Regular audits of your equipment and grounding systems can also help you stay compliant and operationally sound.

Illustrative image related to 3rd prong
Scenario 2: Overcoming Electrical Safety Concerns with Older Infrastructure
The Problem: In many regions, particularly in developing countries, the electrical infrastructure may be outdated, often lacking proper grounding. This poses a significant risk when using modern equipment that requires a three-prong plug for safety. The absence of a grounding mechanism can lead to electrical shocks or malfunctions, jeopardizing both personnel safety and equipment integrity.
The Solution: Investing in upgrading the existing electrical infrastructure should be a priority. Collaborate with local electricians to assess the current wiring and identify areas that require modernization. Installing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) can provide an additional layer of safety, particularly in environments where moisture or other hazards are present. Furthermore, when purchasing new equipment, ensure that it is designed for compatibility with older systems, or consider investing in protective devices that can safeguard against electrical faults. Training staff on the importance of grounding and the proper use of electrical equipment can also enhance safety and reduce risks.
Scenario 3: Managing Equipment Returns Due to Grounding Issues
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is dealing with the return of equipment that does not meet grounding requirements. This often arises when purchasing appliances that are supposed to function in a specific market but fail to account for local electrical standards. The resulting returns can lead to significant financial losses, strained supplier relationships, and logistical challenges.
The Solution: To address this issue proactively, implement a robust vendor qualification process that includes a thorough review of grounding compatibility before making purchases. Create a checklist of local grounding standards and ensure that suppliers can provide equipment that meets these requirements. Additionally, maintain open communication with suppliers to clarify any uncertainties regarding compatibility. Establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers who understand the nuances of international electrical standards can streamline the procurement process and minimize the risk of returns. Consider conducting pilot tests with a small batch of equipment before full-scale purchases to verify compatibility and performance in your specific environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3rd prong
What Materials Are Commonly Used for the Third Prong in Electrical Plugs?
When selecting materials for the third prong in electrical plugs, it is essential to consider various factors, including electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. The following analysis explores four common materials used in the manufacturing of the third prong, providing insights relevant to international B2B buyers.
Copper: The Most Common Choice for Electrical Conductivity
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity and is often the material of choice for the third prong.
-
Key Properties: Copper has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for high-power applications. It also exhibits good corrosion resistance when properly treated.
-
Pros & Cons: Copper’s advantages include durability and reliability in electrical connections. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials and can be susceptible to oxidation if not coated or treated.
-
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with a wide range of electrical systems and is particularly effective in environments where high conductivity is required, such as in industrial applications.
-
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and IEC, particularly in regions like Germany, where stringent regulations apply. In Africa and South America, the availability of copper may vary, impacting cost and supply chain logistics.
Brass: A Balanced Option for Strength and Conductivity
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is another common material used for the third prong.
-
Key Properties: Brass offers good electrical conductivity and is resistant to corrosion, especially in humid environments. It has a melting point of approximately 1,650°F (900°C).
-
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of brass is its strength and resistance to wear, making it suitable for high-frequency applications. However, it is less conductive than pure copper, which may limit its effectiveness in some high-power applications.
-
Impact on Application: Brass is often used in outdoor or wet area applications due to its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for plugs used in various climates.
-
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like the Middle East and Africa should be aware of local regulations regarding material properties and electrical safety standards. Brass components may also be subject to different tariffs and import duties.
Stainless Steel: A Durable Alternative for Harsh Environments
Stainless steel is increasingly being used for the third prong in applications that demand high durability and corrosion resistance.
-
Key Properties: Stainless steel has a melting point of around 2,500°F (1,370°C) and is highly resistant to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments.
-
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, especially in outdoor applications. However, it is less conductive than copper and brass, which may necessitate larger prong sizes to maintain performance.
-
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly well-suited for environments with exposure to moisture or chemicals, such as in industrial settings or coastal areas.
-
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards, such as ISO and ASTM, is crucial for stainless steel components. Buyers should also consider the higher manufacturing costs associated with stainless steel compared to copper and brass.
Aluminum: A Lightweight and Cost-Effective Option
Aluminum is often considered for the third prong due to its lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness.
-
Key Properties: Aluminum has a melting point of about 1,220°F (660°C) and offers moderate electrical conductivity. It is also resistant to corrosion when anodized.
-
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low cost and lightweight properties, making it easy to transport and install. However, it is less durable than copper and brass and can be prone to oxidation, which may affect conductivity.
-
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for low-power applications and where weight is a concern, such as in portable devices.
-
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for aluminum components across different regions. In Europe, for example, compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) is essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 3rd Prong
| Material | Typical Use Case for 3rd prong | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-power applications | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost, oxidation risk | High |
| Brass | Outdoor/wet area applications | Good strength and corrosion resistance | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environments | High durability and corrosion resistance | Lower conductivity | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, low-power devices | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable, oxidation risk | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used for the third prong in electrical plugs, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3rd prong
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for the Third Prong?
The manufacturing of the third prong in electrical plugs involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets safety and performance standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for the Third Prong?
The process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, typically copper or brass, which are chosen for their excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion. Manufacturers often source these materials in bulk, ensuring that they meet international standards for electrical components. The raw materials undergo rigorous inspection upon arrival, where they are evaluated for purity and dimensional accuracy. This initial quality check is crucial, as any defects at this stage can compromise the integrity of the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming the Third Prong?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes such as stamping or forging. Stamping involves cutting the metal into specific shapes using dies, while forging shapes the metal through compressive forces. These techniques are essential for achieving the precise dimensions required for the third prong to fit securely into electrical outlets. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines may be employed for increased accuracy and repeatability, which is vital for mass production.
How is the Assembly Process for the Third Prong Conducted?
After forming, the components proceed to the assembly stage. This typically includes attaching the third prong to the plug body. Automated assembly lines are often utilized to enhance efficiency, allowing for rapid production while maintaining quality. Each assembly line is designed to minimize human error, and workers are trained to follow strict protocols to ensure that each prong is securely attached and properly aligned.
Illustrative image related to 3rd prong
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented During Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process for the third prong. It encompasses a series of checkpoints that ensure compliance with both international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
For electrical components like the third prong, compliance with ISO 9001 is essential. This standard focuses on quality management systems and helps organizations ensure they meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and UL (Underwriters Laboratories) signify that the products meet safety and environmental standards required in various markets, particularly in Europe and North America.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint inspects raw materials for defects and verifies compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, random samples are taken for testing to ensure that the production process remains within defined parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage involves comprehensive testing of the finished products. Tests may include electrical safety tests, dimensional inspections, and durability assessments.
These checkpoints ensure that any issues are identified and addressed promptly, reducing the risk of defective products reaching the market.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for the Third Prong?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the safety and reliability of the third prong. Common tests include:
- Electrical Continuity Tests: These verify that the electrical connections are intact and functioning correctly.
- Grounding Tests: Ensuring that the grounding prong provides a proper path for electrical faults is critical for safety.
- Mechanical Stress Tests: These assess the durability and strength of the prong under various conditions, simulating real-world usage.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial to ensure product reliability.
What Audit Processes Should Be Considered?
Buyers should conduct thorough audits of potential suppliers. This can involve:
- On-Site Inspections: Visiting manufacturing facilities can provide insights into production practices, equipment quality, and overall working conditions.
- Reviewing Quality Assurance Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality management systems and any relevant certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes and product conformity.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
Different regions may have varying requirements for certifications and quality standards. For example, while CE marking is essential in Europe, UL certification is more relevant in North America. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific regulations and certifications required in their target markets to ensure compliance and marketability.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for the third prong are complex and multifaceted. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ultimately ensuring the safety and reliability of their electrical products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘3rd prong’
The objective of this guide is to equip B2B buyers with a clear, actionable checklist for sourcing third-prong electrical components, which are essential for ensuring safety and compliance in various electrical applications. As businesses increasingly prioritize safety, understanding the procurement process for these components is vital.
Step 1: Identify Your Requirements
Begin by clearly defining your technical specifications for the third-prong components you need. Consider the voltage, current ratings, and environmental conditions where the components will be used. This step is crucial because it sets the foundation for sourcing products that meet your operational standards and safety regulations.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the components can handle the required load.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider factors such as moisture, temperature, and exposure to chemicals.
Step 2: Research Reliable Suppliers
Investigate potential suppliers who specialize in electrical components, particularly those with a solid reputation in your region. This step is essential as it helps you identify partners who can provide high-quality and compliant products.
- Supplier Reviews: Look for testimonials or case studies from other businesses in your industry.
- Industry Certifications: Verify that the suppliers have relevant certifications, such as ISO or IEC standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Compliance with Safety Standards
Safety is paramount when sourcing third-prong components. Ensure that the suppliers adhere to international safety standards, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne) markings. This ensures that the products you source are safe to use and reduce the risk of electrical hazards.
- Documentation Review: Request compliance documentation to confirm adherence to safety regulations.
- Third-party Testing: Inquire if the products have undergone independent testing for safety and performance.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the third-prong components to assess their quality. This step is vital as it allows you to evaluate the physical attributes and performance of the components before committing to a bulk purchase.
- Testing Procedures: Implement your testing protocols to ensure the components meet your specifications.
- Fit and Compatibility: Check if the samples fit your existing equipment and systems.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you are satisfied with the samples, negotiate the terms of purchase, including pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. This step is crucial for ensuring a mutually beneficial agreement that aligns with your budget and project timelines.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing for larger orders to optimize your budget.
- Delivery Schedules: Establish clear timelines for delivery to avoid operational delays.
Step 6: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication with your supplier is essential throughout the sourcing process. Establishing a communication plan ensures that both parties are aligned on expectations and can address any issues that arise promptly.
- Point of Contact: Designate a contact person from your team and the supplier’s side for efficient communication.
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your order and address any concerns.
Step 7: Review and Assess Post-Purchase
After the procurement process is complete, review the performance of the sourced components and the supplier’s service. This step is important for future sourcing decisions and helps you build a reliable network of suppliers.
- Performance Metrics: Assess the components’ functionality and durability in real-world applications.
- Supplier Evaluation: Provide feedback to the supplier based on your experience, which can help improve future transactions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively source third-prong electrical components, ensuring both safety and compliance while optimizing their procurement process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3rd prong Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing for 3rd Prong Electrical Plugs?
When sourcing three-prong electrical plugs, understanding the cost structure is vital for effective budgeting and pricing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. High-quality metals for prongs, durable plastics for insulation, and reliable grounding components are essential. Sourcing materials locally may reduce costs, but international suppliers can sometimes offer better pricing for bulk orders.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, impacting the final price. Countries with lower labor costs can provide competitive advantages, but quality assurance must not be compromised. Skilled labor is necessary for the assembly of plugs to ensure safety standards are met.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help lower overhead costs, making the final product more competitive.
-
Tooling: The investment in tooling is significant, especially for custom designs. The initial tooling costs can be high, but they are amortized over production runs. Understanding the tooling requirements upfront can save costs in the long term.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes is critical, especially for electrical components that must meet safety regulations. While this adds to costs, it is essential for maintaining product reliability and avoiding costly recalls.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly based on the destination, shipping method, and volume. Understanding the logistics landscape is crucial, as it can significantly impact the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a margin that reflects their operational costs and desired profit. Buyers should be aware of the average margins in the industry to negotiate effectively.
What Influences Pricing for Three-Prong Plugs?
Several factors influence the pricing of three-prong plugs:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often benefit from reduced per-unit pricing. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers plan their purchases to maximize savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized plugs or those with specific certifications can incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential savings from standard products.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like UL or CE) increase costs but are often necessary for compliance and safety. Buyers should assess the importance of these factors against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance and support.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) affect the overall cost of sourcing. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better deals and manage risks associated with international shipments.
What Are the Best Tips for Buyers Sourcing Three-Prong Plugs?
To navigate the complexities of sourcing three-prong plugs effectively, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in negotiations to explore pricing flexibility, especially for large orders or long-term contracts. Building strong relationships can lead to better terms and pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront cost. Consider factors like warranty, maintenance, and potential failures when assessing value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand the regional market dynamics. For example, buyers from Africa and South America may face different import duties or tariffs compared to those in Europe. This knowledge can inform better pricing strategies.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly review industry trends and market conditions, as these can affect material costs and supplier availability. Staying informed can lead to better timing in purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices and cost structures mentioned herein are indicative and can vary based on multiple factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough research and consult with suppliers for the most accurate and tailored pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 3rd prong With Other Solutions
When considering electrical safety solutions, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to evaluate the effectiveness of the three-prong plug against other viable alternatives. The third prong serves as a grounding mechanism, significantly enhancing user safety by redirecting fault currents. Below, we compare the three-prong plug with two alternative solutions: the two-prong plug and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs).
| Comparison Aspect | 3rd Prong | Two-Prong Plug | Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High – provides a reliable grounding path, reducing shock risk. | Moderate – lacks grounding, increasing shock risk in case of faults. | High – detects ground faults and cuts off power rapidly. |
| Cost | Moderate – slightly more expensive due to design and materials. | Low – generally cheaper and widely available. | Moderate to High – costs vary based on installation and device. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires compatible outlets; installation may need professional help. | Easy – can be plugged into standard outlets without modification. | Requires installation by a qualified electrician for safety compliance. |
| Maintenance | Low – minimal upkeep once installed properly. | Low – generally requires no maintenance. | Moderate – requires regular testing to ensure functionality. |
| Best Use Case | Best for high-risk environments (wet areas, outdoor use) where shock protection is critical. | Suitable for low-risk devices and indoor use where grounding is not critical. | Ideal for wet locations (bathrooms, kitchens) where electrical safety is paramount. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using a Two-Prong Plug?
Two-prong plugs are common in many regions and are generally less expensive than their three-prong counterparts. They are easy to use and can fit into standard outlets without the need for any special installations. However, the lack of a grounding mechanism can expose users to higher risks of electrical shock, especially in environments where devices may be exposed to moisture or electrical faults. For low-power devices in dry areas, they may suffice, but for safety-critical applications, they are not recommended.
How Do Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) Compare?
GFCIs are advanced safety devices designed to protect against ground faults by quickly cutting off electrical supply when an imbalance is detected. They are particularly effective in high-risk environments such as bathrooms and kitchens. While they offer superior safety compared to two-prong plugs, they can be more costly and require professional installation. Additionally, regular testing is essential to ensure they function correctly, adding a layer of maintenance that may not be necessary with a three-prong plug.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting an electrical safety solution, B2B buyers must consider the specific context of their operations. The three-prong plug is the best choice for environments where user safety is paramount, particularly in wet areas or with high-power devices. Alternatively, two-prong plugs may be sufficient for low-risk applications, while GFCIs provide excellent protection in critical zones but require more investment and maintenance. By evaluating the unique needs of their operations, buyers can make informed decisions that balance safety, cost, and practicality, ensuring a secure electrical infrastructure that meets international safety standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3rd prong
What Are the Key Technical Properties of the 3rd Prong?
Understanding the technical properties of the third prong in electrical plugs is essential for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing electrical appliances and equipment. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The third prong is typically made from conductive metals such as brass, copper, or aluminum. The choice of material affects both conductivity and corrosion resistance. High-grade materials ensure longevity and reliability, minimizing the risk of electrical failures, which is crucial in industrial applications. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the allowable variations in dimensions and specifications. For the third prong, precise tolerances are vital to ensure a snug fit in outlets, which enhances safety by preventing loose connections. In B2B contexts, ensuring that products meet specific tolerances is essential for compliance with safety standards and regulations. -
Electrical Rating (Amperage and Voltage)
The third prong must be rated to handle specific electrical loads, typically aligned with the device’s requirements. For example, plugs designed for heavy machinery may need higher amperage ratings. Understanding these ratings helps buyers select appropriate products that can handle operational demands without risk of overheating or failure. -
Grounding Resistance
Grounding resistance is the measure of how effectively the third prong can divert electrical faults to the ground. Lower resistance values indicate better safety performance. For businesses, investing in products with optimal grounding properties is crucial to preventing electrical hazards and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. -
Durability and Weather Resistance
For applications in outdoor or industrial environments, the durability of the third prong against moisture, dust, and other environmental factors is essential. Buyers should consider products that are rated for weather resistance, as these will perform better in challenging conditions, reducing maintenance costs over time. -
Compatibility Standards
The third prong must comply with international standards such as IEC, UL, or CE certifications, which ensure safety and interoperability across different regions. For international buyers, understanding these compatibility standards is key to ensuring that products can be used without legal or operational issues.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to the 3rd Prong?
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and decision-making in B2B transactions. Here are several essential terms:

Illustrative image related to 3rd prong
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for specific components, such as plugs with a third prong, to ensure they source high-quality and compatible parts. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for budgeting and inventory management, as it helps businesses plan their purchases according to demand without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, submitting RFQs for electrical components, including those with third prongs, can facilitate competitive pricing and better negotiation outcomes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B transactions, as they clarify shipping costs, insurance, and risk, ensuring all parties are aligned on logistics related to the delivery of electrical components. -
GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter)
A GFCI is a device designed to protect against electrical shock by shutting off the power if it detects an imbalance in the electrical current. For buyers, understanding GFCI requirements is critical when sourcing equipment that will be used in wet or outdoor environments. -
Certification Standards
These refer to the various safety and quality standards that electrical products must meet. Certifications such as UL, CE, and IEC are essential for ensuring that products, including those with a third prong, are safe for use and compliant with local regulations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their electrical equipment meets safety standards and operational needs effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 3rd prong Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the 3rd Prong Sector?
The 3rd prong sector, primarily involving electrical safety and grounding solutions, is witnessing significant market dynamics driven by technological advancements and regulatory changes. Globally, the demand for safe electrical systems is increasing, with a growing emphasis on protecting both consumers and devices from electrical faults. This demand is particularly acute in regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure development is ongoing and safety standards are being prioritized. In Europe, especially in countries like Germany, there is a strong push for compliance with rigorous safety regulations, creating opportunities for suppliers of three-prong solutions.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the integration of smart technology in grounding systems, which enhances monitoring and safety through real-time data analytics. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms for sourcing electrical components is reshaping traditional procurement processes, allowing buyers to access a broader range of products and suppliers. Sustainability is also becoming a critical factor; buyers are increasingly looking for products that not only meet safety standards but are also manufactured using environmentally friendly practices.
For international B2B buyers, understanding local market conditions is vital. In the Middle East, for instance, expanding urbanization is driving the need for reliable electrical solutions in construction projects. Buyers must adapt their sourcing strategies to align with regional demands while leveraging global suppliers that can meet both quality and compliance standards.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Enhance the 3rd Prong Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are integral to the 3rd prong sector, especially as environmental concerns gain prominence worldwide. The production of electrical components, including three-prong plugs and grounding systems, can have significant environmental impacts if not managed responsibly. Ethical sourcing involves ensuring that materials are obtained through processes that are not only environmentally friendly but also socially responsible.
International buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or reducing carbon footprints in their manufacturing processes. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of green materials are becoming essential criteria in the sourcing decision-making process. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also ensure compliance with evolving regulations aimed at reducing environmental harm.
Moreover, ethical sourcing can foster stronger supplier relationships and enhance brand loyalty among consumers who are increasingly conscious of the environmental and social implications of their purchases. By choosing suppliers committed to sustainability, B2B buyers can position themselves as leaders in responsible procurement, gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
What is the Historical Context of the 3rd Prong in Electrical Safety?
The evolution of the 3rd prong in electrical safety can be traced back to the early 20th century when the need for enhanced electrical safety became apparent. Initially, electrical systems primarily utilized two-prong plugs, which posed significant risks, particularly in environments where moisture was present. The introduction of the grounding prong was a response to increasing incidents of electrical shocks and fires, particularly as electrical devices became more prevalent in households and industries.
In the mid-20th century, with the establishment of safety standards and regulations, the three-prong plug became a standard in many countries, including the United States and parts of Europe. This evolution was accompanied by the development of Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs), which further enhanced safety by preventing electrical shocks in wet locations. As global awareness of electrical safety has grown, so too has the emphasis on the importance of grounding systems in both residential and commercial applications.
This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as it underscores the importance of investing in reliable and compliant electrical solutions. Understanding the evolution of safety standards can inform purchasing decisions and highlight the necessity for ongoing innovation in the 3rd prong sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3rd prong
-
How do I ensure the safety of electrical devices using three-prong plugs?
To ensure the safety of devices with three-prong plugs, verify that your outlets are properly grounded. Conduct regular inspections to ensure that the grounding circuits are intact and functioning. For devices used in outdoor or wet conditions, it’s crucial to use GFCI outlets to prevent electrical shocks. Additionally, consider investing in surge protection devices to safeguard against power surges that may damage your equipment. -
What should I look for when sourcing three-prong plugs from suppliers?
When sourcing three-prong plugs, prioritize suppliers who comply with international safety standards. Verify their certifications and quality assurance processes to ensure that products are reliable and safe for use in your region. Request samples to assess the durability and functionality of the plugs before making bulk orders. Additionally, inquire about their production capabilities and lead times to align with your project timelines. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for three-prong plugs?
MOQs for three-prong plugs can vary significantly between suppliers. Typically, MOQs range from 500 to 5,000 units, depending on the manufacturer’s capacity and the complexity of the product. It’s advisable to negotiate with suppliers if your initial order is below their MOQ, especially if you are looking to establish a long-term partnership. Discussing potential future orders can also lead to more favorable terms. -
What payment terms are standard for international purchases of electrical components?
Standard payment terms for international purchases of electrical components, such as three-prong plugs, often include options like a letter of credit, advance payment, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may request a deposit of 30% upfront, with the remaining balance due before shipping. Ensure to clarify payment terms in your contract and consider using escrow services for added security in transactions. -
How do I assess the quality assurance processes of a three-prong plug supplier?
To assess the quality assurance processes of a supplier, request documentation of their quality control measures, including ISO certifications. Inquire about their testing procedures for electrical safety, durability, and compliance with relevant regulations. Visiting the supplier’s facility or arranging third-party audits can also provide insights into their manufacturing practices and commitment to quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing three-prong plugs?
When importing three-prong plugs, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Air freight may be faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation for customs clearance. Collaborate with a logistics provider familiar with your target market to navigate any challenges related to delivery timelines and compliance. -
What customization options are typically available for three-prong plugs?
Customization options for three-prong plugs can include variations in color, size, and material used in the plug housing. Some suppliers may offer custom branding or labeling to align with your business identity. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to determine their capabilities and any additional costs associated with customized orders. -
How can I ensure compliance with local regulations when importing three-prong plugs?
To ensure compliance with local regulations when importing three-prong plugs, familiarize yourself with the electrical safety standards applicable in your country or region. This may include certifications required by local authorities, such as CE marking in Europe or SABS approval in South Africa. Collaborate with your supplier to obtain the necessary documentation proving compliance and consider engaging a local compliance consultant to assist with the process.
Top 5 3Rd Prong Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. US Electric – Three-Prong Plug Safety
Domain: us-electric.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: The third prong in a plug is a grounding safety feature that protects from malfunctions and prevents electric shock. It is crucial for devices used in outdoor or wet areas, as it helps prevent hazardous malfunctions and electrical fires. The article discusses the importance of three-prong plugs, the risks of using adapters with two-prong outlets, and the need for professional electricians to upgra…
2. Reddit – Electrical Safety Essentials
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The necessity of a third prong on power plugs for tools and appliances is determined by the need for electrical grounding and the safety of the device’s construction. Devices can either have a third prong for grounding or be double insulated, where all parts that can be touched are non-conductive. If a device has metal parts that can be touched, it must be grounded to prevent electric shock in cas…
3. Wadsworth City – Three-Prong Plug Safety
Domain: wadsworthcity.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The three-prong plug features a third prong that provides a path to ground for stray or leaking electricity, enhancing safety by protecting equipment and preventing electric shock. It is advised not to remove or bend the third prong to fit a two-slot outlet; instead, use an adapter only if the grounding wire is connected to an electrical ground or install a proper three-slot outlet.
4. HowStuffWorks – Understanding Plug Types
Domain: electronics.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Two-pronged plugs have two vertical slots: one for neutral (left) and one for hot (right), while three-pronged plugs add a ground slot below. Three-prong plugs provide safety by grounding appliances with metal cases, preventing electric shock if a wire comes loose. Existing two-prong outlets are legal and can be replaced if no ground connection exists. Cutting off the third prong disables safety f…
5. Woodpecker – 3-Prong Adapter
Domain: woodpecker.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: The “3-Prong Adapter” is a simple and inexpensive device essential for performing musicians using amplification. It addresses the common problem of noticeable hum or buzz in speakers when plugging in an amplifier or PA system, often caused by wiring interactions in various venues. Despite warnings from experts and authorities against its use, many musicians rely on it to avoid performance disrupti…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3rd prong
In conclusion, understanding the importance of the third prong in electrical plugs is crucial for international B2B buyers who prioritize safety and reliability in their operations. The third prong serves as a grounding mechanism, mitigating risks associated with electrical faults and enhancing the overall safety of electrical devices. This insight is particularly relevant for businesses operating in sectors where equipment is frequently used in challenging environments, such as construction, manufacturing, and technology.
Strategic sourcing of electrical equipment and components that include this safety feature is not just a matter of compliance; it can significantly reduce liability and improve operational efficiency. As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate complex supply chains, the emphasis on quality and safety can set them apart in a competitive marketplace.
Looking forward, it is essential for B2B buyers to leverage partnerships with suppliers who prioritize safety standards and offer products that are designed to withstand diverse conditions. By making informed decisions about sourcing, companies can not only ensure compliance with local regulations but also foster trust with their customers. Engage with trusted suppliers and invest in high-quality, compliant electrical solutions that will empower your business for sustainable growth.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.