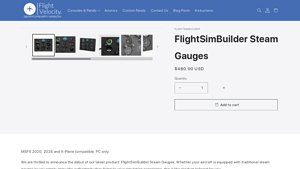
Steam Gauges: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for steam gauges
Navigating the complex landscape of sourcing steam gauges can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications across aviation, industrial, and automotive sectors, understanding the nuances of steam gauge technology is critical. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of various steam gauge types, their specific applications, and the factors influencing cost. Additionally, it offers insights on how to effectively vet suppliers to ensure quality and reliability.
As businesses expand their operations globally, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the need for informed purchasing decisions becomes paramount. This guide empowers B2B buyers by outlining key considerations such as technological advancements, compatibility with existing systems, and maintenance requirements.
By addressing these essential aspects, buyers can navigate the global market with confidence, selecting steam gauges that not only meet their operational needs but also align with their budgetary constraints. Whether you’re looking to upgrade existing equipment or invest in new technologies, this guide serves as your roadmap to making strategic purchasing decisions that drive efficiency and enhance operational performance.
Understanding steam gauges Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analog Pressure Gauge | Uses mechanical indicators, typically needle-based | Industrial boilers, HVAC systems | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited data integration, potential for mechanical failure. |
| Analog Temperature Gauge | Displays temperature through a dial or scale | Manufacturing processes, HVAC | Pros: Reliable and straightforward. Cons: Slower response to changes, less automation. |
| Bourdon Tube Gauge | Measures pressure with a curved tube mechanism | Oil & gas, chemical processing | Pros: High accuracy, robust construction. Cons: Sensitive to vibrations, requires calibration. |
| Manometer | Utilizes liquid column to measure pressure | Laboratory settings, HVAC systems | Pros: High precision, cost-effective. Cons: Fragile, limited to lower pressure ranges. |
| Differential Pressure Gauge | Compares two pressure points for measurement | Water treatment, HVAC, industrial processes | Pros: Essential for flow measurement, versatile. Cons: More complex, requires maintenance. |
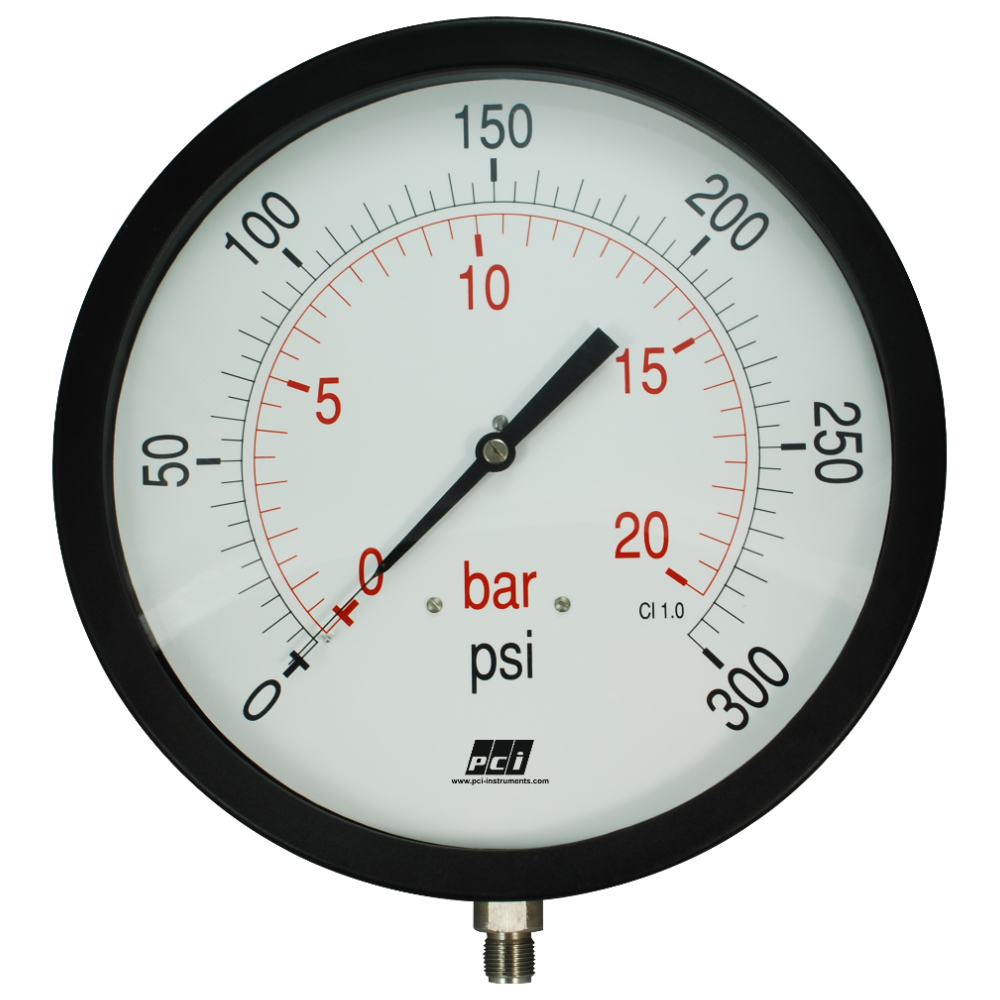
What Are the Key Characteristics of Analog Pressure Gauges?
Analog pressure gauges are widely recognized for their mechanical design, employing a needle to indicate pressure levels on a dial. They are particularly suited for industrial applications, such as boilers and HVAC systems, where simplicity and reliability are paramount. B2B buyers should consider their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, but must also be aware of potential limitations in data integration and the risk of mechanical failure over time.
How Do Analog Temperature Gauges Function in B2B Settings?
Analog temperature gauges operate similarly to pressure gauges, using dials to display temperature readings. They find extensive use in manufacturing processes and HVAC systems, making them a staple in environments where straightforward, reliable temperature monitoring is crucial. Buyers should appreciate their reliability and simplicity, although it’s essential to recognize that these gauges may respond slower to temperature changes and offer limited automation capabilities.
Why Choose Bourdon Tube Gauges for Industrial Applications?
Bourdon tube gauges are renowned for their accuracy and robustness, making them ideal for demanding environments such as oil and gas and chemical processing. They utilize a curved tube that straightens under pressure, moving a needle on a dial to indicate pressure levels. For B2B buyers, the benefits include high accuracy and durability, but they should consider the need for regular calibration and the sensitivity of these gauges to vibrations, which could affect performance.
Illustrative image related to steam gauges
What Advantages Do Manometers Offer in Laboratory Settings?
Manometers are precision instruments that measure pressure using a liquid column, making them particularly useful in laboratory settings and HVAC systems. Their high precision and cost-effectiveness make them an attractive option for B2B buyers, especially in applications requiring accurate measurements at lower pressure ranges. However, buyers should be cautious of the fragility of manometers, as they can be easily damaged, limiting their use in high-traffic or harsh environments.
How Do Differential Pressure Gauges Enhance Measurement Accuracy?
Differential pressure gauges are designed to compare two pressure points, providing critical measurements for applications such as water treatment and industrial processes. Their versatility makes them indispensable for flow measurement, particularly in systems where maintaining optimal pressure is vital. B2B buyers should weigh the advantages of enhanced measurement capabilities against the more complex nature and maintenance requirements of these gauges, ensuring they align with operational needs and budget constraints.
Key Industrial Applications of steam gauges
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of steam gauges | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | Monitoring steam pressure in turbines | Ensures optimal turbine performance and safety | Accuracy, durability under high temperatures, certifications |
| Food & Beverage | Steam pressure control in sterilization processes | Guarantees product safety and compliance with health standards | Compliance with food safety regulations, ease of integration |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Monitoring steam pressure in reactors | Enhances process efficiency and safety | Material compatibility, resistance to corrosive environments |
| Aerospace | Performance monitoring in aircraft systems | Increases operational reliability and safety | Compatibility with existing systems, precision, and calibration |
| HVAC Systems | Steam pressure monitoring in heating systems | Improves energy efficiency and system reliability | Temperature range, response time, and installation requirements |
How Are Steam Gauges Used in Power Generation?
In the power generation sector, steam gauges are crucial for monitoring steam pressure in turbines. By providing real-time data on pressure levels, these gauges help operators maintain optimal performance and ensure safety protocols are followed. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing gauges that can withstand high temperatures and pressures is essential. Additionally, certifications and reliability are key factors to consider, as these gauges directly impact the efficiency of power generation processes.
What Role Do Steam Gauges Play in the Food & Beverage Industry?
Steam gauges serve a vital role in the food and beverage industry, particularly in sterilization processes where precise steam pressure control is necessary. Accurate monitoring ensures that products are safely processed and comply with health standards, preventing contamination. For B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets, it is crucial to select gauges that meet stringent food safety regulations and integrate seamlessly with existing systems. The durability and reliability of these gauges in high-stress environments are also significant considerations.
How Are Steam Gauges Utilized in Chemical Manufacturing?
In chemical manufacturing, steam gauges are instrumental for monitoring steam pressure in reactors, which is essential for maintaining safety and process efficiency. Accurate pressure readings help prevent dangerous over-pressurization and ensure optimal chemical reactions. Buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe must prioritize sourcing gauges that are compatible with various chemicals and resistant to corrosive environments. Ensuring the right material compatibility and durability is vital for the longevity and safety of operations.
Why Are Steam Gauges Important in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, steam gauges are used for performance monitoring in various aircraft systems, contributing to operational reliability and safety. They provide pilots and maintenance crews with critical data regarding pressure levels in steam systems, which can influence flight performance. International buyers, including those from Brazil and Vietnam, should consider the compatibility of these gauges with existing aircraft systems and the precision required for accurate readings. Reliability and certification to aviation standards are essential factors in sourcing.
How Do Steam Gauges Enhance HVAC Systems?
Steam gauges are key components in HVAC systems, monitoring steam pressure to improve energy efficiency and system reliability. By ensuring that steam is delivered at the correct pressure, these gauges help optimize heating processes, leading to cost savings and enhanced comfort. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it is important to select gauges that can operate within specific temperature ranges and respond quickly to changes in pressure. Installation requirements and the ability to integrate with existing systems are also critical considerations when sourcing these instruments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘steam gauges’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Compatibility Issues with Existing Systems
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges when integrating new steam gauges into existing aircraft systems or panels. Many aviation companies operate a mix of older and newer aircraft, which can complicate compatibility. Steam gauges may have specific size and mounting requirements, and if the new gauges do not match the existing dimensions, it can lead to additional costs and delays in installation. This situation is particularly prevalent among companies in regions like Africa and South America, where older aircraft models are still in service.
The Solution:
To effectively address compatibility issues, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their existing equipment before purchasing new steam gauges. This includes measuring the dimensions of the current instruments and understanding the specific mounting configurations. Buyers should consider sourcing steam gauges that are designed to match the dimensions of commonly used panels, such as those that fit seamlessly into the standard “six-pack” layout. Engaging with suppliers who offer customizable options or comprehensive installation support can also mitigate compatibility challenges. Additionally, buyers should inquire about compatibility with various aircraft models and seek gauges that offer flexible installation options, ensuring they can be adapted to different aircraft without extensive modifications.
Scenario 2: Limited Availability of Replacement Parts
The Problem:
In regions with limited access to aviation resources, buyers often struggle with the availability of replacement parts for steam gauges. This can lead to extended downtime for aircraft, negatively impacting operations and profitability. For instance, a company in the Middle East may find it challenging to source specific gauges or parts when repairs are needed, resulting in operational inefficiencies and increased maintenance costs.

Illustrative image related to steam gauges
The Solution:
To combat this issue, B2B buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers who specialize in steam gauges and their components. It’s advisable to source from manufacturers that offer comprehensive support, including a robust inventory of spare parts. Buyers can also consider investing in a small stockpile of critical replacement parts for their most commonly used steam gauges to ensure quick access during maintenance needs. Furthermore, exploring partnerships with local distributors can provide faster access to essential components, minimizing aircraft downtime and maintaining operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Training and Familiarization Challenges
The Problem:
For companies transitioning from modern glass cockpits back to steam gauges, there can be significant training and familiarization challenges for pilots and maintenance crews. This is especially true in regions where aviation technology is rapidly evolving. Pilots accustomed to digital displays may find steam gauges more difficult to interpret, leading to potential safety concerns and inefficiencies in operations.
The Solution:
To facilitate a smooth transition, companies should implement a structured training program focused on steam gauge operation and interpretation. This could involve hands-on training sessions with experienced instructors who can provide insights into the nuances of steam gauge readings. Additionally, developing training materials that compare steam gauge functionality with glass cockpit features can aid in understanding. Virtual simulations that replicate steam gauge environments can also be beneficial for practice without the need for actual flight time. Investing in ongoing training and refresher courses can ensure that pilots remain proficient in using steam gauges, ultimately enhancing safety and operational effectiveness.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for steam gauges
When selecting materials for steam gauges, it is essential to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for various applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of steam gauges, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel in Steam Gauge Manufacturing?
Stainless Steel is a popular choice for steam gauge housings and internal components due to its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. It typically withstands high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for steam applications.

Illustrative image related to steam gauges
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to rust and corrosion, ensuring a long lifespan even in harsh environments. It also has good mechanical properties, allowing it to maintain its integrity under pressure.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which is generally higher than other materials. Additionally, manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized techniques for machining and welding.
Impact on Application: Given its compatibility with steam and other fluids, stainless steel is ideal for gauges used in industrial settings, including power plants and manufacturing facilities.

Illustrative image related to steam gauges
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel grades. Different regions may have specific preferences for grades, such as 304 or 316, which offer varying levels of corrosion resistance.
How Does Brass Perform as a Material for Steam Gauges?
Brass is another commonly used material for steam gauges, particularly for fittings and connectors. It offers good thermal conductivity and is relatively easy to machine.
Pros: Brass is cost-effective compared to stainless steel and provides decent corrosion resistance. Its excellent machinability allows for intricate designs and quick production times.
Cons: While brass performs well in many environments, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications as it can weaken under extreme heat. Additionally, it may corrode in certain acidic or alkaline conditions.
Impact on Application: Brass is often used in steam gauges that operate at lower pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for residential or light industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific brass alloy standards (like ASTM B36) and check for local regulations regarding lead content, as some regions have strict limits on lead in brass components.
What are the Advantages of Using Plastic in Steam Gauge Components?
Plastic materials, such as polycarbonate or nylon, are sometimes used in steam gauges, particularly for non-pressure components or as protective covers.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion. They can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Cons: The main limitation is their lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals, which can restrict their application in high-stress environments. Additionally, plastics may degrade over time when exposed to UV light or certain chemicals.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are suitable for steam gauges in less demanding environments or where weight savings are crucial, such as in portable equipment.

Illustrative image related to steam gauges
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic complies with relevant standards (like ASTM D638 for tensile properties) and is suitable for the specific media being measured.
How Does Glass Contribute to the Functionality of Steam Gauges?
Glass is often used for the gauge face or viewing window, providing clarity and durability.
Pros: Glass is resistant to scratching and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for steam applications. It also allows for easy visibility of the gauge readings.
Cons: Glass can be brittle and may shatter under impact, which poses a risk in certain environments. Additionally, its manufacturing can be more complex and costly.
Impact on Application: Glass is ideal for applications where visibility and readability are essential, such as in laboratory settings or high-precision industrial environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with safety standards for glass, especially in regions with specific regulations regarding shatterproof materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Steam Gauges
| Material | Typical Use Case for steam gauges | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Industrial steam applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Brass | Residential/light industrial gauges | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Plastic | Non-pressure components/protective covers | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower temperature/pressure ratings | Low |
| Glass | Gauge face/viewing window | High visibility and scratch resistance | Brittle and potential shattering risk | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions about material selection for steam gauges, ensuring compliance with regional standards and compatibility with specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for steam gauges
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Steam Gauges?
The manufacturing of steam gauges involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets performance and quality standards. Each stage is critical, from material preparation to finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Steam Gauge Manufacturing?
The first step in manufacturing steam gauges is the careful selection and preparation of materials. Typically, manufacturers use high-grade metals such as brass or stainless steel for the gauge casing and internal components due to their durability and resistance to corrosion.
-
Material Selection: The choice of materials is essential, considering factors like thermal expansion and pressure tolerance. For instance, components exposed to high temperatures must have high thermal resistance.
-
Cutting and Machining: Once materials are selected, they are cut and machined to precise dimensions. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed for their accuracy, ensuring that each component fits perfectly during assembly.
-
Surface Treatment: After machining, surfaces may undergo treatments such as polishing or anodizing to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal. This step is particularly important for components that will be visible to end-users.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the components of the steam gauge.
-
Stamping and Bending: Metal sheets are stamped and bent to create the gauge’s housing and dial. This process requires precision tooling to maintain consistent quality across batches.
-
Casting: For certain components, casting techniques may be used. This process allows for complex shapes and can reduce material waste, thus lowering production costs.
-
Welding and Joining: Parts are then welded or joined using methods such as soldering or adhesive bonding. Each joint must be thoroughly inspected to ensure integrity, especially since these gauges often operate under high pressure.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for Steam Gauges?
Assembly is where all individual components come together to create the final product.
-
Component Assembly: Skilled technicians assemble the various parts, including the dial, needle, and internal mechanisms. Each component must fit precisely to ensure accurate readings.
-
Calibration: Once assembled, the gauges undergo calibration to ensure they provide accurate pressure readings. This process involves applying known pressures and adjusting the gauge accordingly.
-
Final Assembly: After calibration, the gauges are fully assembled, including the installation of protective glass and any electronic components if applicable.
What Are the Key Finishing Steps for Steam Gauges?
The finishing stage is crucial for both functionality and aesthetics.
-
Quality Checks: Before moving to the next stage, gauges undergo initial quality checks to identify any defects. This might include visual inspections and basic functional tests.
-
Coating: A protective coating may be applied to enhance resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and dust. This step is vital for ensuring longevity, especially in industrial applications.
-
Packaging: Finally, the gauges are carefully packaged to prevent damage during transportation. Packaging materials are chosen to provide adequate protection while being environmentally friendly.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Steam Gauge Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of steam gauge manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system. It ensures that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for equipment used in the oil and gas industry, including pressure gauges. Compliance with these standards can be a significant factor for buyers in those sectors.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that defects are caught early.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, periodic checks are conducted to monitor the quality of components as they are being made. This might include measuring dimensions and checking for defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the assembly and finishing stages, a final quality control inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing of the gauges to confirm accuracy and reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence to ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures.
-
Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers should request access to audit reports and findings.
-
Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline testing results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken in case of defects.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent inspectors can verify compliance with international standards and the supplier’s internal quality measures.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements that must be met. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to avoid compliance issues.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother communication and negotiation regarding quality expectations.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping can introduce risks, such as damage during transit. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and handling procedures in place to mitigate these risks.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for steam gauges, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source reliable and high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘steam gauges’
To ensure a successful procurement process for steam gauges, follow this detailed checklist designed specifically for B2B buyers. Each step is critical in securing high-quality products that meet operational needs and compliance standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for your steam gauges is the foundation of your sourcing process. Consider factors such as compatibility with existing systems, dimensions, and the type of aircraft or machinery they will be used in. Detailing these specifications will help streamline your search and ensure you receive products that fit your operational environment.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers specializing in steam gauges. Look for companies with a proven track record in the industry, positive customer reviews, and robust product offerings. Utilize resources such as trade shows, industry publications, and online directories to compile a list of potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications and compliance with international standards. This may include ISO certifications or specific aviation regulations relevant to your region. Ensuring these certifications can safeguard against potential quality issues and enhance reliability in your procurement.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Obtaining samples of the steam gauges you are considering is essential for assessing quality and compatibility. Review the materials, design, and functionality to ensure they meet your defined specifications. Additionally, testing the samples in real-world applications can provide insights into performance and durability.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather detailed pricing information from your shortlisted suppliers to evaluate overall costs. Look beyond the initial price; consider factors like bulk discounts, shipping costs, and payment terms. A clear understanding of the total cost of ownership will help you make informed financial decisions.
Step 6: Inquire About After-Sales Support
Evaluate the level of customer support and after-sales services offered by potential suppliers. Reliable support can be crucial for installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of steam gauges. Ask about warranty terms, availability of technical assistance, and any training programs for your team.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts with Clear Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that the contract outlines all agreed-upon terms clearly. This should include delivery timelines, payment schedules, and any penalties for non-compliance. A well-defined contract protects both parties and minimizes the risk of disputes down the line.
Illustrative image related to steam gauges
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategy for steam gauges, ensuring they select the best products and suppliers to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for steam gauges Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Steam Gauge Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of steam gauges is essential for B2B buyers looking to source these instruments effectively. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in steam gauges significantly affect pricing. Common materials include metal for casing and glass for the gauge face. Higher-grade materials can lead to increased durability and performance, but they also escalate costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for assembly and calibration, especially for high-precision gauges. Labor costs can vary significantly by region, impacting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, thus reducing the final price for buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized gauges. Buyers should consider this when negotiating prices, as suppliers may need to recoup these costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that steam gauges meet industry standards requires a robust QC process. This involves testing and certification, which can add to the overall cost but is crucial for safety and reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the destination, with international shipping often incurring additional tariffs and fees. Understanding these logistics is vital for calculating total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Steam Gauge Costs?
Several factors can influence the price of steam gauges, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs with suppliers to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can drive up costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and recognized certifications (e.g., ISO) can justify premium pricing. Buyers should assess the value of these certifications against their specific needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their quality assurance processes, while newer entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly impact pricing and responsibilities between buyer and seller. Clear communication regarding Incoterms helps avoid misunderstandings and unexpected costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for B2B Buyers of Steam Gauges?
Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms for steam gauge purchases. Here are some strategies:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct market research to understand prevailing prices and supplier capabilities. Use this information to inform your negotiations.
-
Long-Term Relationships: Building relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing over time. Consider establishing partnerships that allow for bulk purchasing or exclusive agreements.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and potential downtime. This holistic approach can justify a higher initial investment if long-term savings are evident.
-
Flexibility in Orders: Be open to negotiating MOQs or payment terms, which can lead to better pricing. Suppliers may be more willing to adjust terms for committed buyers.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: When dealing with international suppliers, understanding cultural nuances can aid in negotiations. Respect for local practices and customs can foster goodwill and potentially better terms.
What Should International Buyers Consider in Pricing Nuances?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate unique pricing challenges:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of currency exchange rates, as they can impact the final cost. Consider locking in rates when negotiating large contracts.
-
Tariffs and Duties: Import tariffs can significantly affect the total cost. Research local regulations and factor these into your pricing calculations.
-
Shipping Delays: International logistics can introduce delays. Ensure that timelines are clearly defined in contracts to avoid penalties or additional costs.
-
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying standards for safety and quality. Ensure that sourced steam gauges comply with local regulations to prevent costly issues down the line.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for steam gauges can vary widely based on numerous factors, including those outlined above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing and value for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing steam gauges With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Steam Gauges?
When it comes to aviation instrumentation, steam gauges have long been a staple for pilots. However, as technology advances, numerous alternatives have emerged that offer unique benefits and challenges. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions about their avionics systems. This comparison will examine steam gauges against two prominent alternatives: glass cockpits and digital instrumentation.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Steam Gauges | Glass Cockpit | Digital Instrumentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable but limited data | High information density | Customizable and intuitive |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial investment | Varies; often mid-range |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward setup | Complex installation required | Easy integration with software |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks | Self-monitoring features | Minimal upkeep, software updates |
| Best Use Case | Simple aircraft, training | Advanced aircraft, IFR flying | Versatile; can be tailored |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Glass Cockpit
Glass cockpits represent the cutting edge of avionics technology, integrating multiple functions into a single digital display. They offer pilots a wealth of information at a glance, including navigation, system status, and performance metrics. While they significantly enhance situational awareness, glass cockpits are typically more expensive than traditional steam gauges, both in terms of initial purchase and installation. Additionally, transitioning from steam gauges to glass cockpits can be challenging for pilots, as it requires a different skill set and understanding of the integrated systems. However, for complex flights requiring advanced navigation and real-time data, glass cockpits are unmatched.
Illustrative image related to steam gauges
Digital Instrumentation
Digital instrumentation offers a modern approach to aircraft monitoring by utilizing electronic displays that can be customized to a pilot’s specific needs. This flexibility allows for tailored layouts that can prioritize the most critical information. In terms of cost, digital instruments can vary widely depending on the specific technology and features chosen, often falling between steam gauges and glass cockpits. They are typically easy to implement, especially with existing software solutions that integrate seamlessly into the aircraft’s systems. Maintenance is often minimal, as digital displays require less physical upkeep than mechanical gauges. However, the reliance on software means that regular updates and cybersecurity measures are necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Choosing the right avionics solution depends on various factors, including budget, aircraft type, and operational requirements. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the specific needs of their operations is paramount. Steam gauges remain a cost-effective and reliable choice for simple aircraft and training environments, while glass cockpits and digital instrumentation cater to advanced aviation needs. Ultimately, the decision should align with both immediate operational goals and long-term strategic plans, ensuring that the selected technology enhances safety, efficiency, and pilot performance.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for steam gauges
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Steam Gauges?
Understanding the essential technical properties of steam gauges is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to ensuring compatibility, reliability, and performance in various applications. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in steam gauge construction often include high-grade aluminum, stainless steel, or specialized plastics. The choice of material impacts durability, resistance to corrosion, and overall weight. For instance, stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments, while aluminum is lighter and often used in aviation applications. Selecting the right material can significantly affect the lifespan and maintenance costs of the gauges. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in manufacturing. In steam gauges, precision is vital for accurate readings. A typical tolerance might be ±0.5% of full scale. High tolerance levels ensure that gauges provide reliable data, which is essential in industries such as aviation and manufacturing, where safety and performance depend on precise measurements. -
Operating Pressure Range
This specification defines the range of pressures that the steam gauge can accurately measure. Common ranges might be from 0 to 300 psi (pounds per square inch). Understanding the operating pressure range is critical for buyers to ensure that the gauges meet the requirements of their specific applications, such as steam boilers or hydraulic systems. -
Response Time
Response time indicates how quickly a gauge reacts to changes in pressure or temperature. A rapid response time (e.g., less than 1 second) is crucial in dynamic environments where conditions can change rapidly. This property is particularly important in processes that require real-time monitoring and adjustments, ensuring operational efficiency and safety. -
Environmental Ratings
Environmental ratings denote the conditions under which the steam gauge can operate effectively. Ratings such as IP (Ingress Protection) levels indicate resistance to dust and moisture. For B2B buyers, selecting gauges with appropriate environmental ratings ensures that instruments function reliably in various conditions, from humid factories to dusty construction sites. -
Calibration Standards
Calibration standards define how gauges are tested for accuracy. Common standards include ISO 9001 or ANSI/NCSL Z540.1. Ensuring that steam gauges meet recognized calibration standards is essential for maintaining quality assurance and compliance, particularly in regulated industries.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Steam Gauges?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can streamline the purchasing process and enhance communication among B2B stakeholders. Here are several key terms that are frequently used in the steam gauge market:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components that are used in the manufacturing of larger systems or products. In the context of steam gauges, OEMs may provide the original gauges for industrial machinery or aircraft. Understanding whether a product is OEM can assure buyers of its quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ signifies the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This is critical for B2B buyers to consider, as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their purchases based on demand and budget constraints. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. This process allows companies to compare costs and negotiate terms. A well-structured RFQ can lead to better pricing and more favorable contract conditions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers navigate logistics and clarify who bears the cost and risk at different stages of transportation. -
Calibration Certification
This term refers to documentation proving that a steam gauge has been calibrated according to specific standards. Buyers should ensure that gauges come with calibration certification to guarantee accuracy and reliability, especially in regulated industries. -
Lead Time
Lead time indicates the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for inventory planning and meeting production schedules, particularly in industries where timing is critical.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the steam gauges Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Steam Gauges Sector?
The steam gauges market is witnessing a notable shift driven by global technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. As industries increasingly prioritize automation and smart technologies, the demand for steam gauges—traditional yet reliable instruments—continues to hold strong, particularly in sectors like aviation, automotive, and manufacturing. International B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly interested in sourcing steam gauges that offer compatibility with modern systems while maintaining the robustness of classic designs.
A significant trend is the gradual transition from analog steam gauges to digital equivalents in certain applications. However, many pilots and operators still prefer the tactile feedback and straightforward readability of steam gauges for training purposes and in less complex aircraft. This preference is often rooted in the reliability and ease of use that steam gauges provide, making them a staple in pilot training programs. Furthermore, the integration of steam gauges with digital platforms, such as flight simulation software, is becoming more commonplace, allowing for a hybrid approach that meets diverse user needs.
Emerging markets are also playing a pivotal role in shaping sourcing trends. Countries like Brazil and Vietnam are expanding their aviation sectors, leading to increased demand for both new and refurbished steam gauges. This growth is fostering competitive pricing and innovation among suppliers, compelling international buyers to stay informed about the latest offerings and technological enhancements in the steam gauges sector.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Purchases of Steam Gauges?
The environmental impact of manufacturing steam gauges has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers. As sustainability gains traction, companies are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains to ensure ethical sourcing practices. This involves selecting suppliers who prioritize environmentally friendly materials and processes. For instance, manufacturers are now exploring the use of recycled metals and sustainable materials in the production of steam gauges, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with their lifecycle.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations are becoming benchmarks for ethical sourcing. Buyers should seek suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with these standards, ensuring that their products are not only high-quality but also responsibly produced. Moreover, as consumers and regulatory bodies alike push for greater transparency in manufacturing, businesses that prioritize sustainability in their sourcing strategies can enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
In addition, the adoption of green technologies in the production of steam gauges, such as energy-efficient manufacturing processes and waste reduction initiatives, can lead to cost savings in the long run. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who are committed to sustainability, as this not only contributes to environmental stewardship but can also offer competitive advantages in a market that increasingly values corporate social responsibility.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Steam Gauges in the B2B Context?
The evolution of steam gauges can be traced back to the early days of aviation and engineering, where they were developed as essential instruments for measuring various parameters such as pressure, temperature, and speed. Initially, steam gauges were purely mechanical devices, relying on analog technology to provide real-time data to pilots and operators. Their simplicity and reliability made them a preferred choice in aviation and other industries.

Illustrative image related to steam gauges
Over time, advancements in technology led to the integration of electronic components, enhancing the accuracy and functionality of steam gauges. Despite the rise of digital displays and glass cockpit technology, steam gauges have maintained their relevance due to their intuitive design and ease of use. They continue to be favored for pilot training and in certain aircraft, where straightforward data interpretation is paramount.
Today, steam gauges are undergoing a renaissance, as manufacturers adapt them for compatibility with modern systems, including flight simulators and digital interfaces. This evolution reflects a broader trend in the industry, where traditional technologies are being reimagined to meet contemporary demands, ensuring that steam gauges remain a valuable asset for B2B buyers across various sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of steam gauges
-
How do I select the right steam gauge for my application?
Choosing the right steam gauge involves understanding your specific requirements, including the type of machinery or equipment it will be used with, the operating environment, and the accuracy needed. Assess the gauge’s compatibility with your systems and whether it offers features like easy readability and durability. Additionally, consult with suppliers to obtain technical specifications and recommendations based on your industry, whether it’s aviation, manufacturing, or another sector. -
What are the benefits of using steam gauges over digital displays?
Steam gauges provide several advantages, such as simplicity and reliability. Many pilots and operators prefer the analog representation for its straightforward readability, allowing for quick interpretation of critical information at a glance. They also tend to be less susceptible to electronic failures, which can be crucial in environments where reliability is paramount. Furthermore, steam gauges often come at a lower cost compared to digital alternatives, making them a budget-friendly option for many businesses. -
What is the typical lead time for steam gauge orders?
Lead times for steam gauge orders can vary significantly based on factors such as the supplier’s inventory, customization requirements, and shipping logistics. Generally, standard orders may take anywhere from 2 to 6 weeks for delivery, while customized gauges could extend this timeline to 8 weeks or more. To ensure timely delivery, it’s advisable to communicate your requirements early and confirm lead times with your supplier. -
How can I vet suppliers of steam gauges effectively?
Vetting suppliers is crucial to ensure quality and reliability. Start by researching their industry reputation, looking for reviews or testimonials from previous clients. Verify their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001. Request samples of their products to assess quality firsthand and inquire about their manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider their experience in your specific industry and their ability to provide after-sales support. -
What customization options are available for steam gauges?
Many manufacturers offer customization options, including size, scale, and design features tailored to your specific needs. You can often request specific measurement ranges, dial colors, and mounting styles. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand what customization is feasible and any associated costs. Customization may take additional time, so factor this into your project timeline. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for steam gauges?
Minimum order quantities can vary by supplier and are often influenced by the gauge type and customization level. Standard steam gauges may have an MOQ of 10 to 50 units, while custom gauges could require larger orders to justify production costs. Always confirm MOQs with your suppliers before placing an order, as some may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or bulk purchases. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing steam gauges?
Payment terms for steam gauges can differ significantly among suppliers. Common practices include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or before shipping. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms, allowing for payment within a specified period after delivery. Ensure you clarify payment terms before finalizing your order to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How is quality assurance handled for steam gauges?
Quality assurance processes for steam gauges typically involve multiple stages, including raw material inspection, in-process quality checks, and final product testing. Reputable manufacturers adhere to strict quality standards, often certified by international organizations. Request documentation of their QA processes and any relevant certifications to ensure the gauges meet your operational standards and compliance requirements.
Top 8 Steam Gauges Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Forums – Steam Gauges Overview
Domain: forums.flightsimulator.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Steam gauges refer to classic, analog cockpit instrumentation used in aviation, characterized by their needle and dial displays. They are often contrasted with modern glass cockpit displays, which provide digital readouts and additional information. The term ‘steam gauges’ is a light-hearted reference to early steam-powered machinery that utilized similar pressure and temperature gauges. Many pilo…
2. Flightsim Builder – Steam Gauge Setup
Domain: flightsimbuilder.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: This company, Flightsim Builder – Steam Gauge Setup, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. McMaster – Steam Gauges
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Steam Gauges, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Airplane Academy – Glass Cockpit Solutions
Domain: airplaneacademy.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Glass cockpits integrate traditional instruments into dynamic displays, offering advantages such as reduced mechanical errors, more redundancy, and integrated systems information compared to traditional steam gauges. Steam gauges are often easier for new pilots to interpret quickly, especially in simpler aircraft. Transitioning from glass to steam can be challenging for pilots accustomed to the ad…
5. Flight Velocity – Steam Gauge Setup
Domain: flightvelocity.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: This company, Flight Velocity – Steam Gauge Setup, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Aviation – Steam Gauges
Domain: aviation.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: The term ‘steam cockpit’ is actually a misnomer; the correct term is ‘steam gauges.’ These gauges resemble traditional steam pressure gauges found in steam engines and turbines, featuring round dials, calibrated scales, and needles that indicate current values. No aircraft instruments operate on steam due to safety concerns. The term ‘steam gauge’ has become common, especially in contrast to moder…
7. Antique Star Brass Mfg. Co. – Steam Pressure Altitude Gauge
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Steam Gauge for sale on eBay includes various antique and vintage steam gauges. Key products listed are: 1. Antique Star Brass Mfg. Co. Steam Pressure Altitude Gauge (7 1/4″, Pre-Owned, $100.00, $18.40 shipping) 2. Ashcroft 11″ Steam Gauge (Pre-Owned, $375.00, $62.93 shipping) 3. Antique BURROUGHS Tractor Engine Boiler Steam Gauge (7.5″, Pre-Owned, $120.00, $15.00 shipping) 4. Standard 7″ Steam pu…
8. Vans Air Force – Steam Gauges
Domain: vansairforce.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Steam gauges are presented as an economical and reliable alternative to glass panels for aircraft, particularly for VFR flying. Key points include: 1. Parts availability: Replacement gauges are often readily available, reducing downtime. 2. User preference: Many pilots find analog gauges easier to read at a glance compared to digital displays. 3. Backup systems: Some pilots express concern about t…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for steam gauges
As the aviation industry continues to evolve, the relevance of steam gauges remains significant, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. International B2B buyers must recognize that strategic sourcing of steam gauges can lead to enhanced operational efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and improved pilot training experiences. The ability to integrate these traditional instruments into modern aircraft systems provides a unique advantage, catering to a diverse range of pilot preferences and budget considerations.
Investing in quality steam gauges not only ensures reliability but also facilitates a smoother transition for pilots moving from complex glass cockpits to more straightforward instrumentation. By prioritizing suppliers who offer compatibility with existing systems and a clear understanding of regional aviation needs, buyers can maximize their procurement strategies.
Looking ahead, the demand for steam gauges is likely to persist, driven by a blend of nostalgia and practicality in aviation training and operations. We encourage B2B buyers to explore partnerships that prioritize innovation, quality, and responsiveness to the unique challenges of their markets. Embrace the future of aviation instrumentation with confidence—source strategically and equip your operations for success.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.