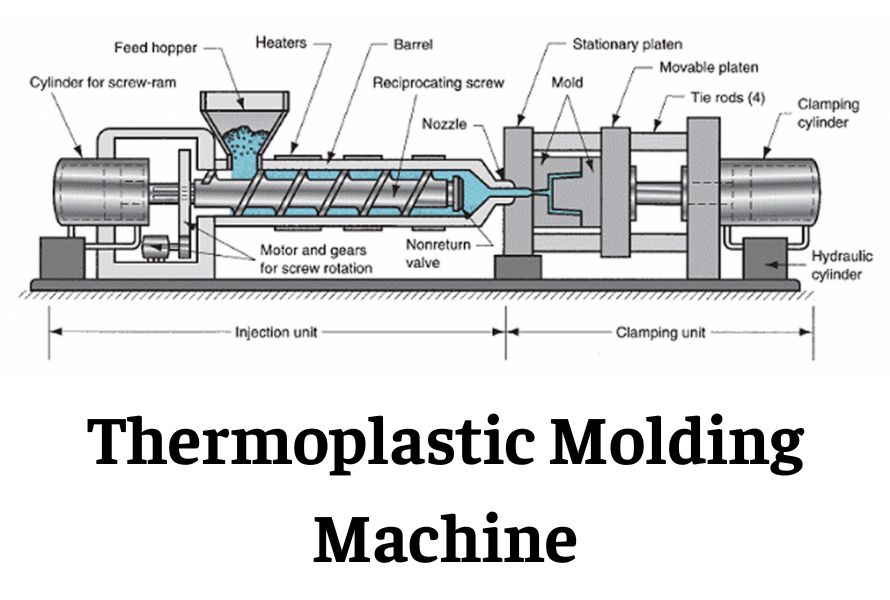
A Deep Dive into Thermoplastic Mold Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thermoplastic mold
In the quest for high-quality thermoplastic molds, international B2B buyers often face the daunting challenge of ensuring both reliability and cost-effectiveness in their sourcing decisions. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of the thermoplastic mold market, offering insights into various types, applications, and the critical factors influencing supplier selection. By understanding the nuances of thermoplastic molding processes—such as injection molding, blow molding, and overmolding—buyers can better navigate their options to meet specific industrial needs.
Our comprehensive resource goes beyond basic knowledge, addressing vital aspects such as material selection, manufacturing techniques, and cost considerations. We delve into the intricacies of sourcing, equipping decision-makers with the necessary tools to evaluate potential suppliers effectively. With a focus on the unique market dynamics in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil—this guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals.
By providing actionable insights and strategic recommendations, this guide serves as a crucial asset for businesses looking to optimize their supply chains and enhance production capabilities. Whether you are a seasoned procurement professional or new to the industry, understanding the global landscape of thermoplastic molds will enable you to forge strong partnerships and drive successful outcomes in your projects.
Understanding thermoplastic mold Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Injection Molding | High precision, complex shapes, and mass production | Automotive, consumer goods | Pros: Cost-effective for large volumes; Cons: High initial setup cost. |
| Blow Molding | Produces hollow parts, uses air pressure | Bottles, containers | Pros: Ideal for lightweight products; Cons: Limited to hollow shapes. |
| Compression Molding | Uses heat and pressure to shape thermoplastics | Electrical components, automotive | Pros: Lower cost for small runs; Cons: Slower cycle times. |
| Rotational Molding | Creates seamless, hollow parts through rotation | Tanks, playground equipment | Pros: Excellent for large, complex shapes; Cons: Longer production times. |
| Overmolding | Combines two materials for enhanced functionality | Ergonomic grips, automotive parts | Pros: Improved durability and aesthetics; Cons: More complex tooling. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is characterized by its ability to produce high-precision parts in large volumes. This method involves injecting molten thermoplastic into a precisely engineered mold, allowing for intricate designs that cater to various industries, particularly automotive and consumer goods. B2B buyers should consider the initial setup costs against the long-term benefits of mass production and material efficiency. Selecting the right thermoplastic material is crucial for achieving the desired mechanical properties and aesthetic finishes.
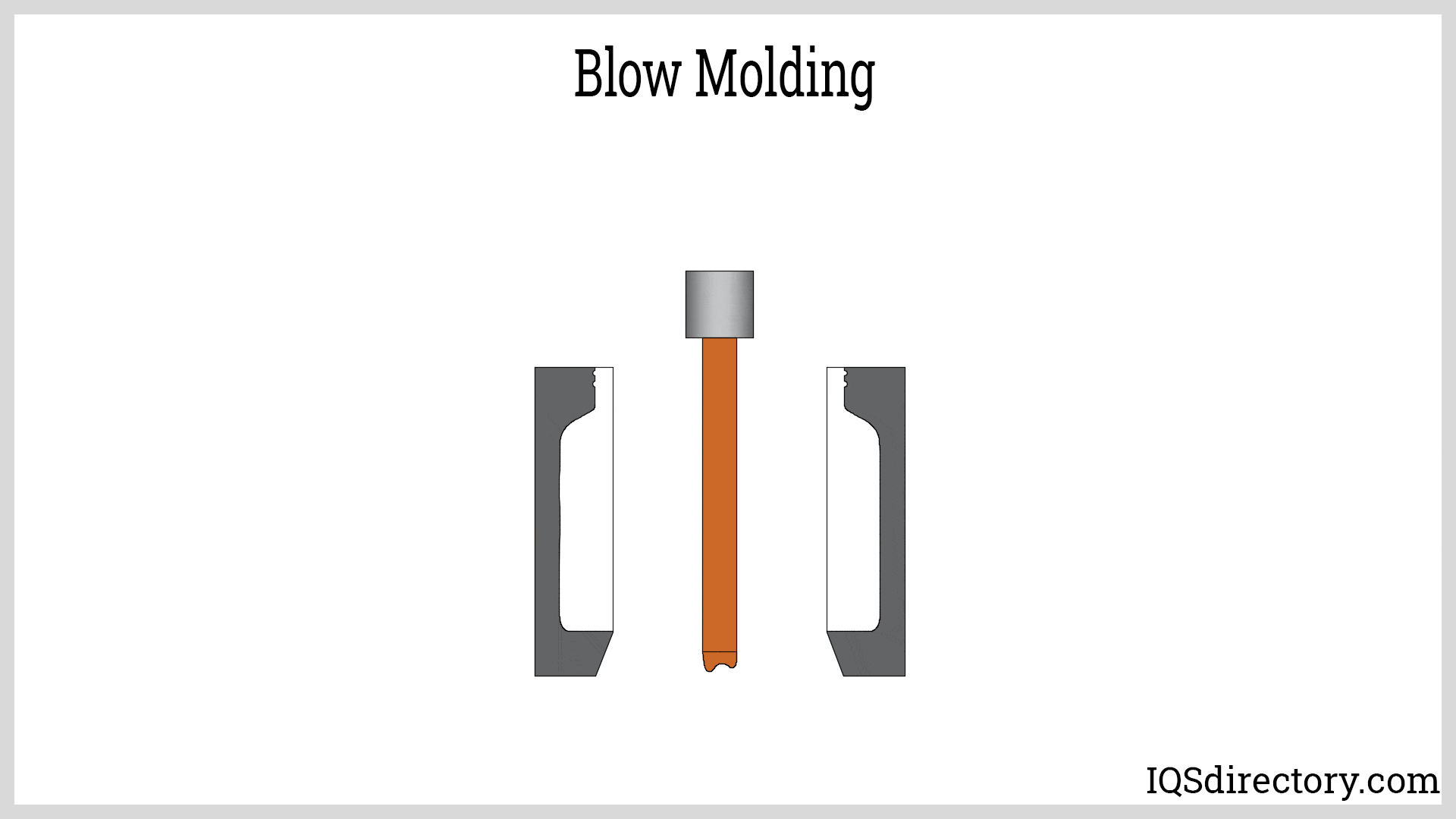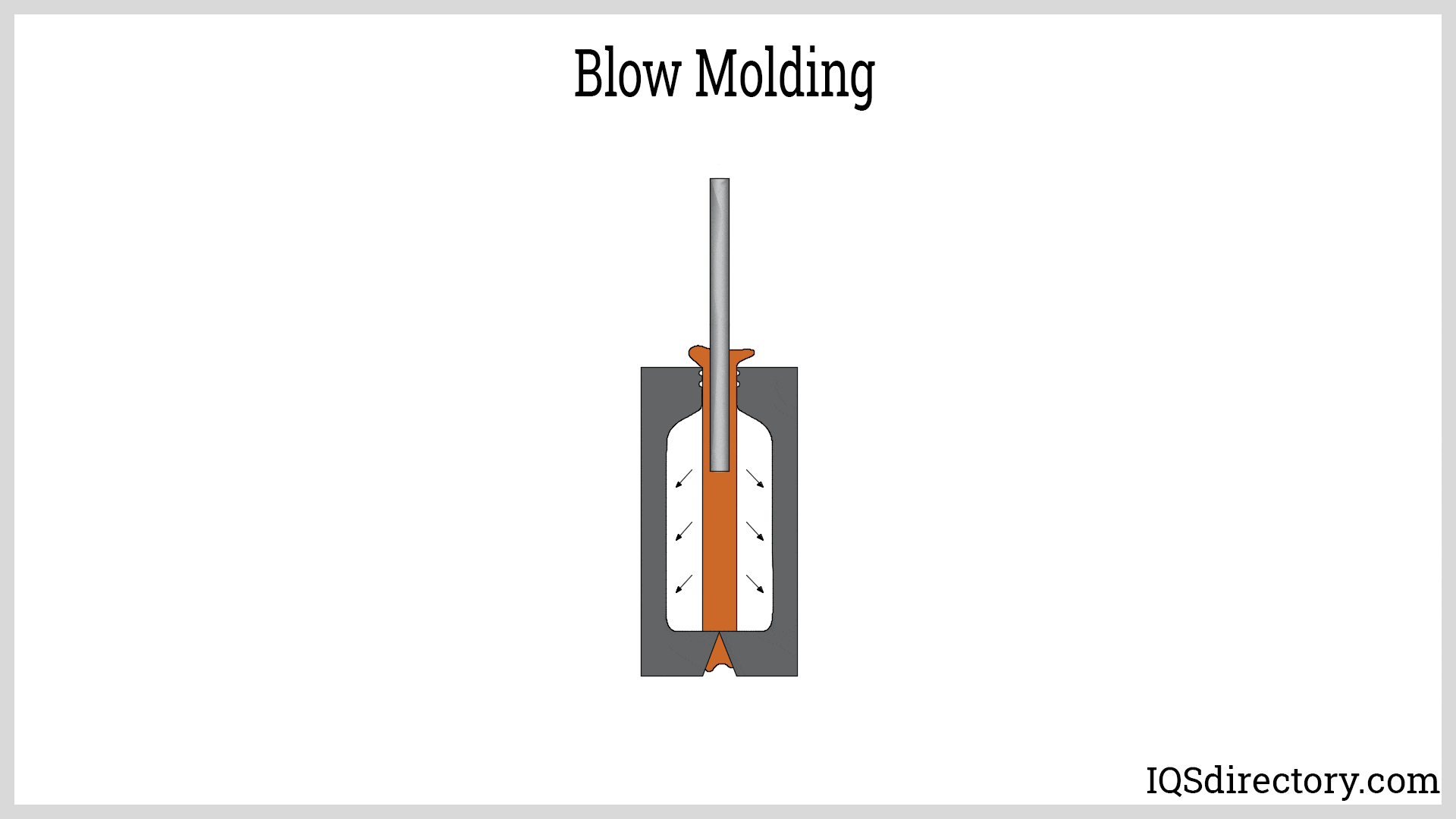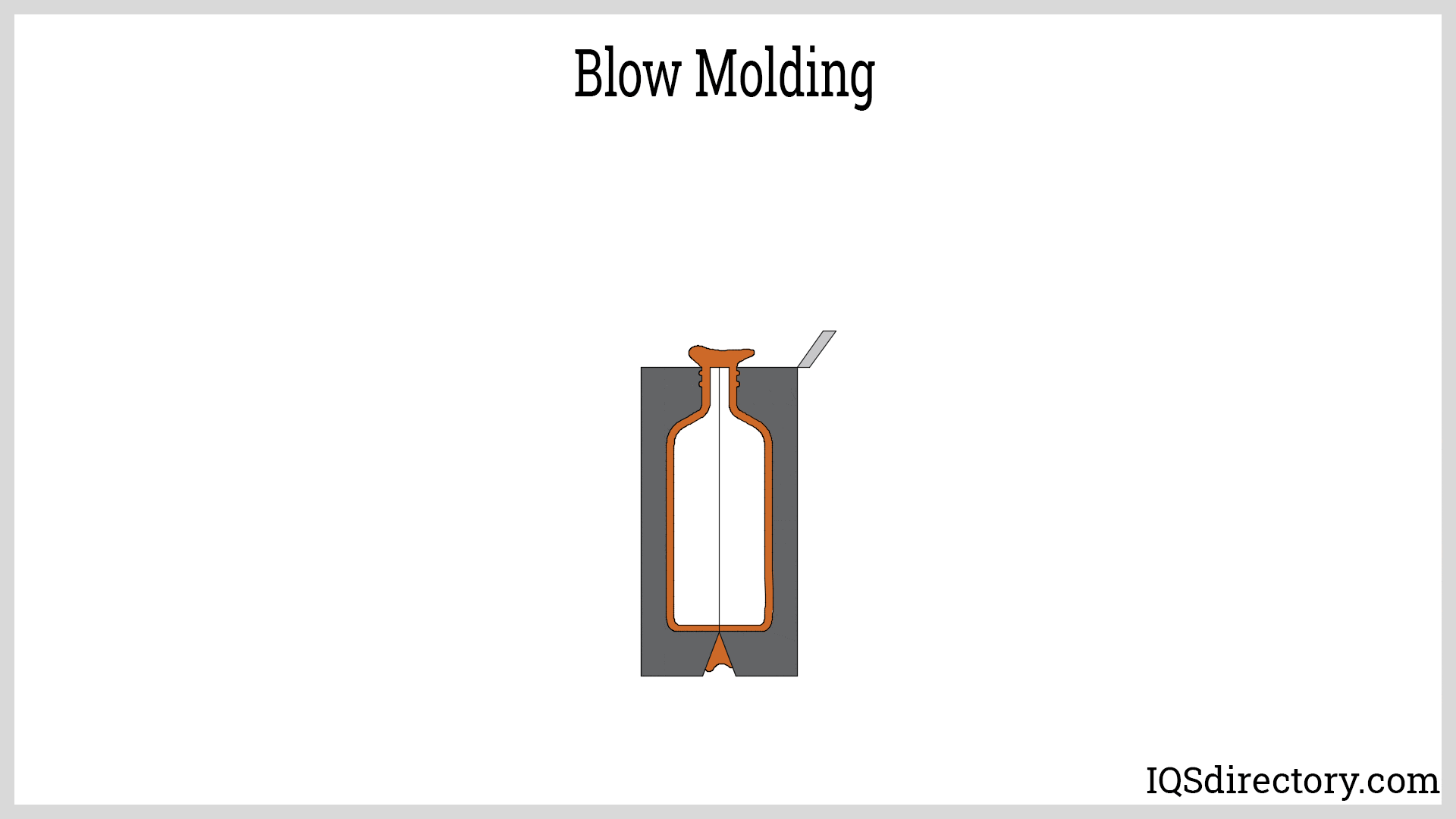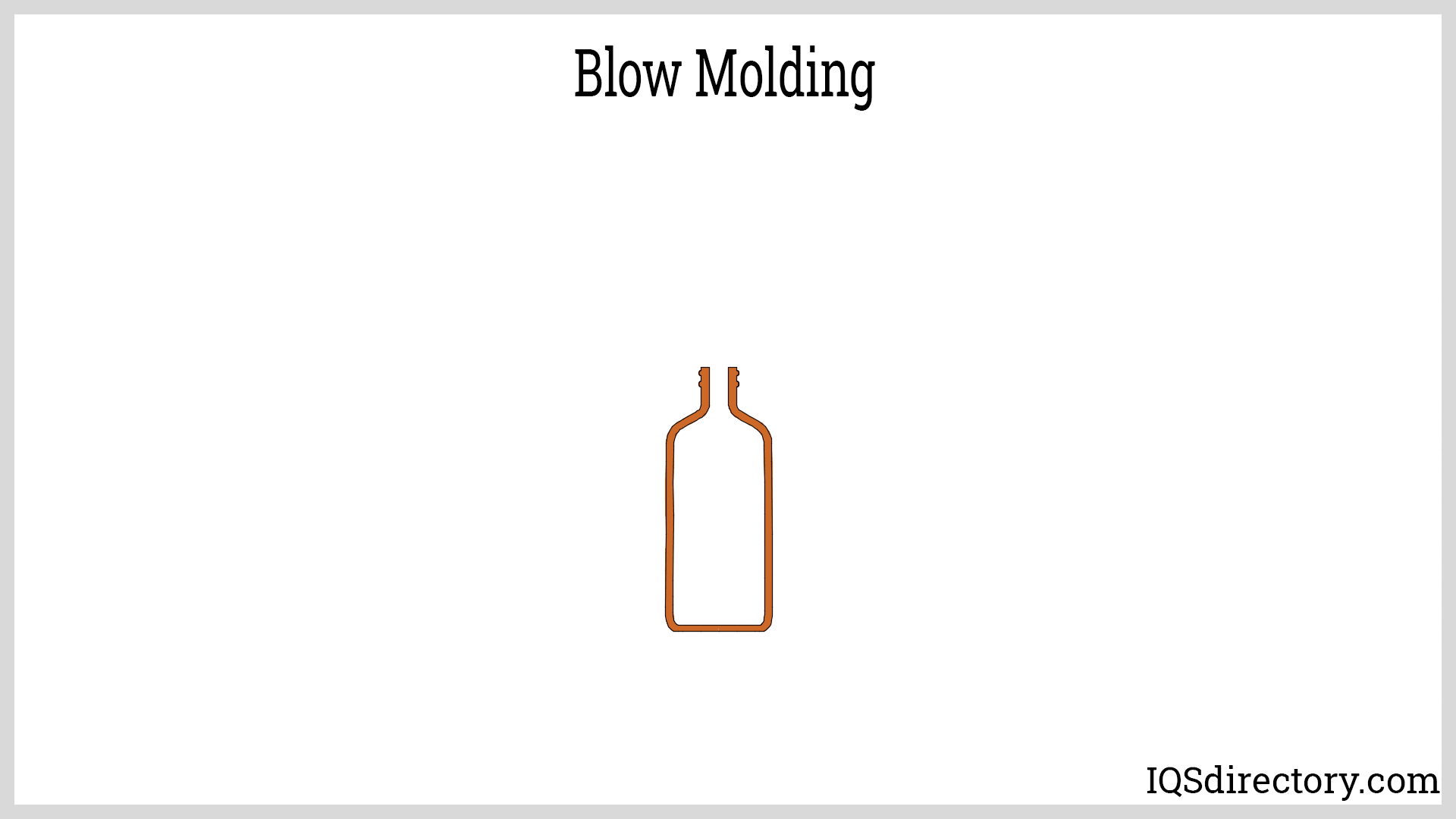
How Does Blow Molding Differ from Other Processes?
Blow molding is distinct in its ability to create hollow products using air pressure, making it ideal for items such as bottles and containers. This process begins with heating a plastic tube (parison) and then inflating it within a mold. Buyers in industries requiring lightweight and durable packaging solutions should weigh the advantages of cost-effectiveness and the limitations of shape, as blow molding is confined to hollow designs.
What are the Advantages of Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a versatile technique that utilizes heat and pressure to shape thermoplastic materials. This method is particularly suitable for producing electrical components and automotive parts where lower production runs are needed. B2B buyers can benefit from lower costs and simpler tooling compared to injection molding; however, they must consider the trade-off of slower cycle times, which can impact overall production efficiency.
Why Choose Rotational Molding for Complex Designs?
Rotational molding stands out for its capability to produce seamless, hollow parts through a unique rotation process. This technique is particularly beneficial for large items such as storage tanks and playground equipment. B2B purchasers should note the advantages of design flexibility and material efficiency, but should also be prepared for longer production times, which may affect project timelines.
What is the Value of Overmolding in Product Development?
Overmolding is a specialized process that combines two different materials to enhance product functionality and aesthetics. This is commonly used in ergonomic grips and automotive components where durability and comfort are essential. For B2B buyers, the primary consideration should be the complexity of the tooling and the potential for increased costs, balanced against the enhanced product performance and marketability achieved through this innovative technique.
Key Industrial Applications of thermoplastic mold
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of thermoplastic mold | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of interior and exterior components | Lightweight, durable parts that improve fuel efficiency and performance | Material compatibility, regulatory compliance, and local production capabilities |
| Consumer Electronics | Manufacturing of housings and enclosures | Enhanced design flexibility and aesthetic appeal | Supplier reliability, lead times, and post-processing services |
| Medical Devices | Creation of precision components and casings | High-quality, sterile parts that meet strict safety standards | Certifications, material properties, and production scalability |
| Packaging | Development of custom containers and closures | Improved shelf life and product protection | Customization options, sustainability practices, and cost-effectiveness |
| Industrial Equipment | Production of gears and mechanical components | Increased efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Technical support, material selection, and tooling capabilities |
How is Thermoplastic Mold Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, thermoplastic molds are crucial for producing lightweight interior and exterior components, such as dashboards, bumpers, and panels. These parts not only reduce vehicle weight, enhancing fuel efficiency but also improve overall performance. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, understanding material compatibility and regulatory compliance is essential to ensure that sourced components meet local standards and performance expectations.
What Role Does Thermoplastic Mold Play in Consumer Electronics?
Thermoplastic molding is extensively used in the consumer electronics industry for creating housings and enclosures for devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. This process allows for intricate designs and high aesthetic value, essential for consumer appeal. Buyers should consider supplier reliability and lead times, as well as the availability of post-processing services like painting or texturing to enhance the final product’s look and feel.
How Are Thermoplastic Molds Essential for Medical Devices?
In the medical device sector, thermoplastic molds are employed to manufacture precision components and casings that require strict adherence to safety standards. The use of high-quality materials ensures that products are both durable and sterile, which is critical for patient safety. International buyers must prioritize sourcing from manufacturers with the necessary certifications and material properties to guarantee compliance with health regulations and production scalability.
What Are the Benefits of Thermoplastic Mold in Packaging?
Thermoplastic molds are utilized in packaging for developing custom containers and closures that offer improved shelf life and product protection. These molds can create intricate designs that enhance functionality while ensuring products remain secure during transport. When sourcing, businesses should focus on customization options and sustainability practices, as environmentally friendly packaging solutions are increasingly in demand in global markets.
How is Thermoplastic Mold Applied in Industrial Equipment Manufacturing?
In the industrial equipment sector, thermoplastic molds are vital for producing gears and other mechanical components that enhance efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. These components can be tailored to specific operational requirements, ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Buyers should seek suppliers that provide technical support and expertise in material selection, as well as tooling capabilities to ensure high-quality production outcomes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘thermoplastic mold’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Thermoplastic Material for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with selecting the appropriate thermoplastic material for their projects. This decision is critical, as the wrong choice can lead to product failure, increased costs, and production delays. Buyers often face confusion due to the vast array of thermoplastic options available—each with different properties, such as strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance. For instance, a company looking to produce automotive components may inadvertently select a material that cannot withstand high temperatures, resulting in structural failures and safety concerns.
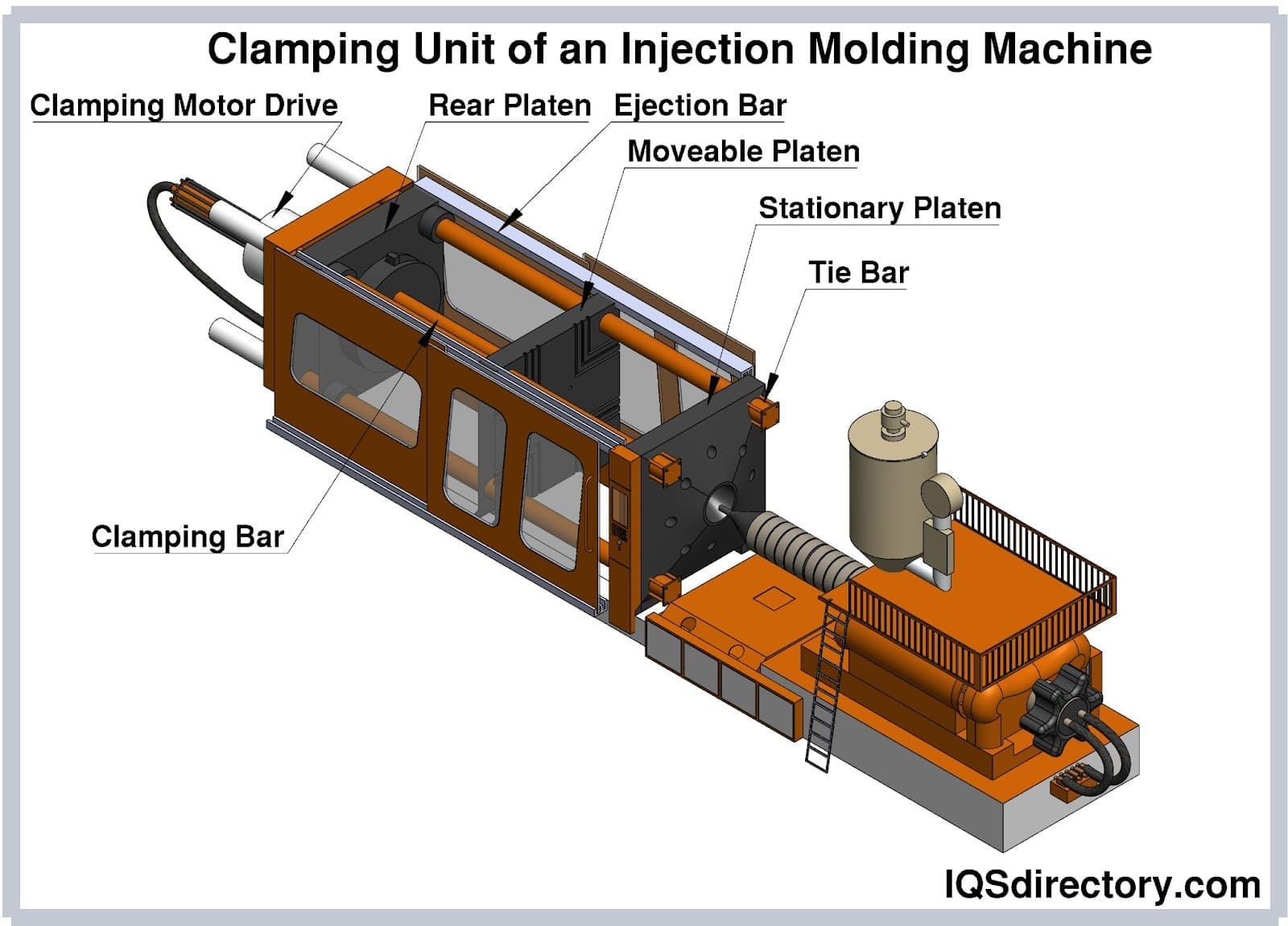
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic mold
The Solution: To address this challenge, it’s essential to conduct a thorough material analysis before making a selection. Buyers should engage with material suppliers who can provide detailed technical data sheets for various thermoplastics, highlighting their mechanical properties, thermal stability, and suitability for specific applications. Additionally, consider utilizing prototyping services that allow for testing different materials under real-world conditions. By collaborating with suppliers and leveraging their expertise, companies can make informed choices that align with their product specifications and performance requirements, ultimately reducing the risk of costly errors.
Scenario 2: Inefficiencies in the Thermoplastic Injection Molding Process
The Problem: Inefficiencies in the thermoplastic injection molding process can lead to increased cycle times, higher operational costs, and reduced output quality. B2B buyers often encounter issues such as inadequate mold design, improper temperature settings, or insufficient cooling time. These problems can result in defects like warping or incomplete fills, which not only compromise product integrity but also necessitate additional rework and wasted materials.
The Solution: To enhance the efficiency of the injection molding process, buyers should focus on optimizing each stage of production. First, invest in advanced simulation software to analyze mold flow and thermal dynamics before production begins. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues in mold design and allows for adjustments that can minimize defects. Additionally, regular training for machine operators on best practices for temperature control and cycle optimization is crucial. Implementing a structured maintenance schedule for molding machines can also prevent breakdowns and ensure consistent performance. By adopting these strategies, companies can significantly improve productivity and reduce costs associated with inefficiencies.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Quality Control and Product Consistency
The Problem: Maintaining consistent quality in thermoplastic molded products can be a significant pain point for B2B buyers, especially when scaling production. Variability in raw materials, mold wear and tear, or fluctuations in processing parameters can lead to inconsistencies in the final product. This can affect client satisfaction and result in costly returns or recalls. Buyers often find it challenging to implement robust quality control measures that can adapt to these variables while still meeting production demands.
The Solution: To tackle quality control challenges, establish a comprehensive quality management system that incorporates real-time monitoring and feedback loops throughout the manufacturing process. Invest in sensors and automated systems that track critical parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and cycle times, allowing for immediate adjustments if deviations occur. Additionally, implementing a rigorous inspection protocol for incoming raw materials can help ensure that only high-quality inputs are used in production. Regular training sessions for quality assurance teams on industry best practices can further enhance product consistency. By fostering a culture of quality and leveraging technology, companies can achieve higher levels of reliability and customer satisfaction in their thermoplastic products.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thermoplastic mold
What Are the Key Properties of Common Thermoplastic Mold Materials?
When selecting materials for thermoplastic molds, it’s essential to consider the specific properties that will impact product performance. Here, we analyze four common thermoplastic materials: Polypropylene (PP), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Polycarbonate (PC), and Nylon (PA).
How Does Polypropylene (PP) Perform as a Thermoplastic Mold Material?
Polypropylene is known for its excellent chemical resistance, low density, and good fatigue resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of around 100°C and is suitable for applications requiring moderate strength and flexibility.
Pros: Polypropylene is lightweight and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for mass production. Its resistance to moisture and various chemicals enhances its durability in diverse environments.
Cons: However, PP has lower heat resistance compared to other thermoplastics, which may limit its application in high-temperature environments. Its surface finish may also not be as aesthetically pleasing as other materials.
Impact on Application: PP is often used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods, where chemical exposure is common.
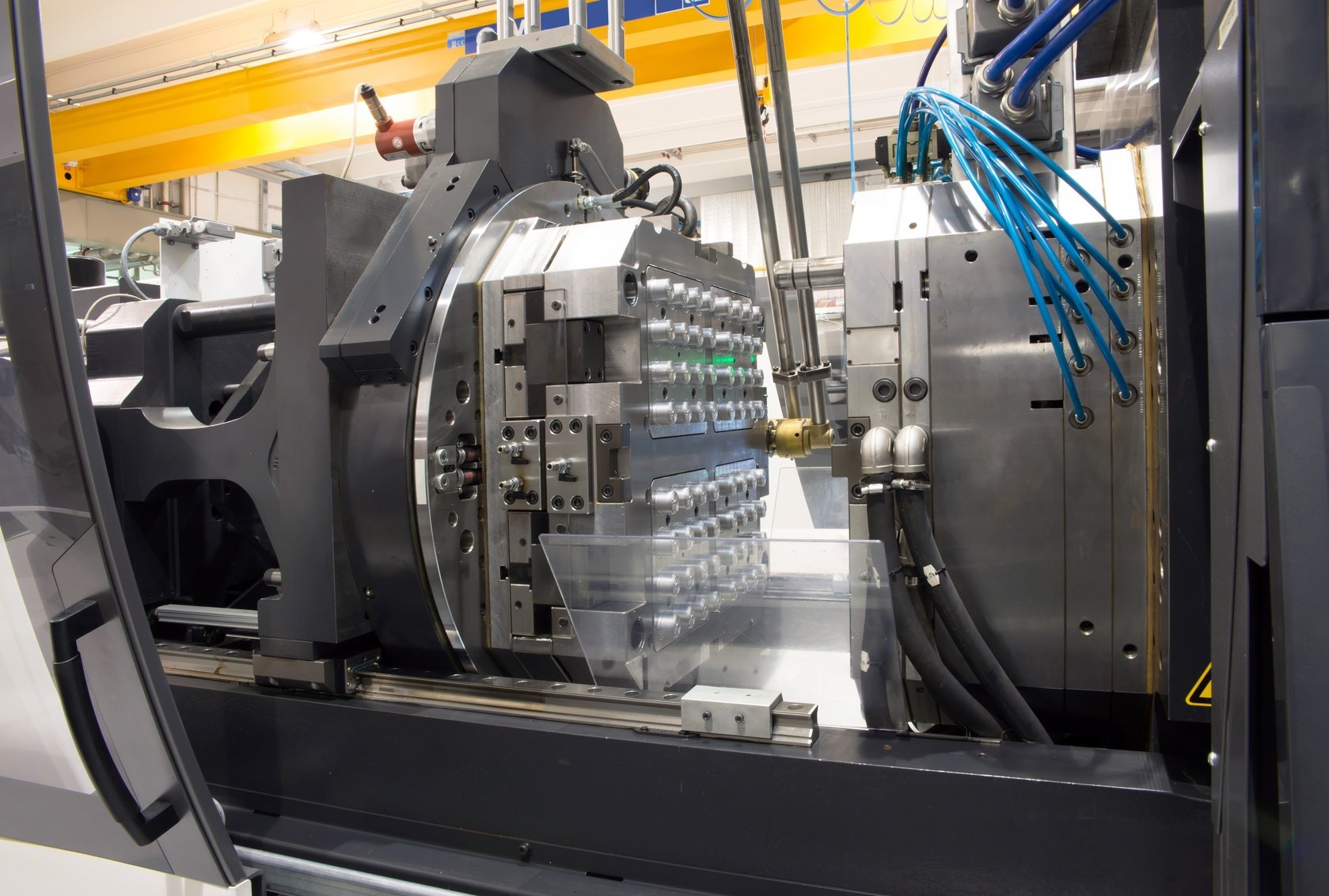
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic mold
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM and JIS, especially in regulated industries. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing reliable suppliers is crucial due to varying quality standards.
What Advantages Does Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Offer?
ABS is renowned for its toughness and impact resistance, with a temperature rating typically around 80-100°C. It provides a good balance of rigidity and flexibility.
Pros: ABS is easy to machine and can be painted or glued, enhancing its versatility. Its impact resistance makes it suitable for applications requiring durability.
Cons: The primary drawback of ABS is its susceptibility to UV degradation, which can limit its outdoor applications unless treated. Additionally, it can be more expensive than PP.
Impact on Application: ABS is widely used in automotive interiors, consumer electronics, and toys, where appearance and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the potential need for UV stabilization in regions with high sun exposure. Compliance with safety standards is also critical, especially in the toy industry.
Why Is Polycarbonate (PC) a Preferred Choice for Certain Applications?
Polycarbonate is highly regarded for its exceptional strength and impact resistance, with a temperature rating of approximately 120°C. It also offers excellent optical clarity.
Pros: The high durability and heat resistance of PC make it ideal for applications requiring transparency and strength, such as safety glasses and automotive components.
Cons: However, PC can be more expensive and may require special handling due to its susceptibility to scratching without proper coatings.
Impact on Application: PC is commonly used in applications like eyewear, light covers, and protective equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the cost implications and ensure suppliers can provide UV-resistant grades for outdoor applications. Compliance with international safety standards is also essential.
What Makes Nylon (PA) Stand Out in Thermoplastic Molding?
Nylon is known for its excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and temperature resistance, typically rated up to 120°C. It also has good wear resistance.
Pros: Nylon’s durability and flexibility make it suitable for applications requiring high-performance materials, such as gears and bearings.
Cons: Its moisture absorption can lead to dimensional changes, which may affect precision in certain applications. Additionally, it can be more expensive compared to other thermoplastics.
Impact on Application: Nylon is extensively used in automotive, industrial, and consumer products where strength and wear resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for moisture control in storage and processing. Understanding local material standards and certifications is also vital for compliance.
Summary Table of Thermoplastic Mold Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for thermoplastic mold | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Packaging, automotive parts | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower heat resistance | Low |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Automotive interiors, consumer electronics | Toughness and impact resistance | Susceptible to UV degradation | Medium |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Eyewear, light covers | Exceptional strength and clarity | More expensive, scratches easily | High |
| Nylon (PA) | Gears, bearings | High tensile strength and wear resistance | Moisture absorption can affect precision | Medium |
This guide should assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding material selection for thermoplastic molds, ensuring they choose the right material for their specific applications and compliance needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thermoplastic mold
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Thermoplastic Molds?
The manufacturing of thermoplastic molds involves a series of critical stages that ensure high-quality production. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers appreciate the complexity and precision needed in the mold-making process.
Material Preparation: How Are Thermoplastic Materials Processed?
The first step in manufacturing thermoplastic molds is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate thermoplastic polymer based on the desired properties of the final product, such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to heat or chemicals. Commonly used materials include polyethylene, polycarbonate, and polypropylene.
Once the material is selected, it typically comes in the form of pellets that require proper drying to eliminate moisture. Moisture can negatively impact the melting process and the quality of the final molded part. The dried pellets are then loaded into the injection molding machine, ready for melting.
How Does the Forming Process Work in Thermoplastic Mold Manufacturing?
The forming stage is where the actual molding occurs. This is predominantly done through injection molding, where the prepared thermoplastic material is heated until it reaches a molten state. The molten plastic is then injected into a meticulously designed mold cavity under high pressure. This pressure is crucial as it ensures the plastic fills the entire mold, capturing all intricate details and features.
Once the material is injected, it is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold. Cooling time can vary based on the thickness of the part and the thermal properties of the material used. Efficient cooling not only speeds up production cycles but also ensures dimensional accuracy and surface finish quality.
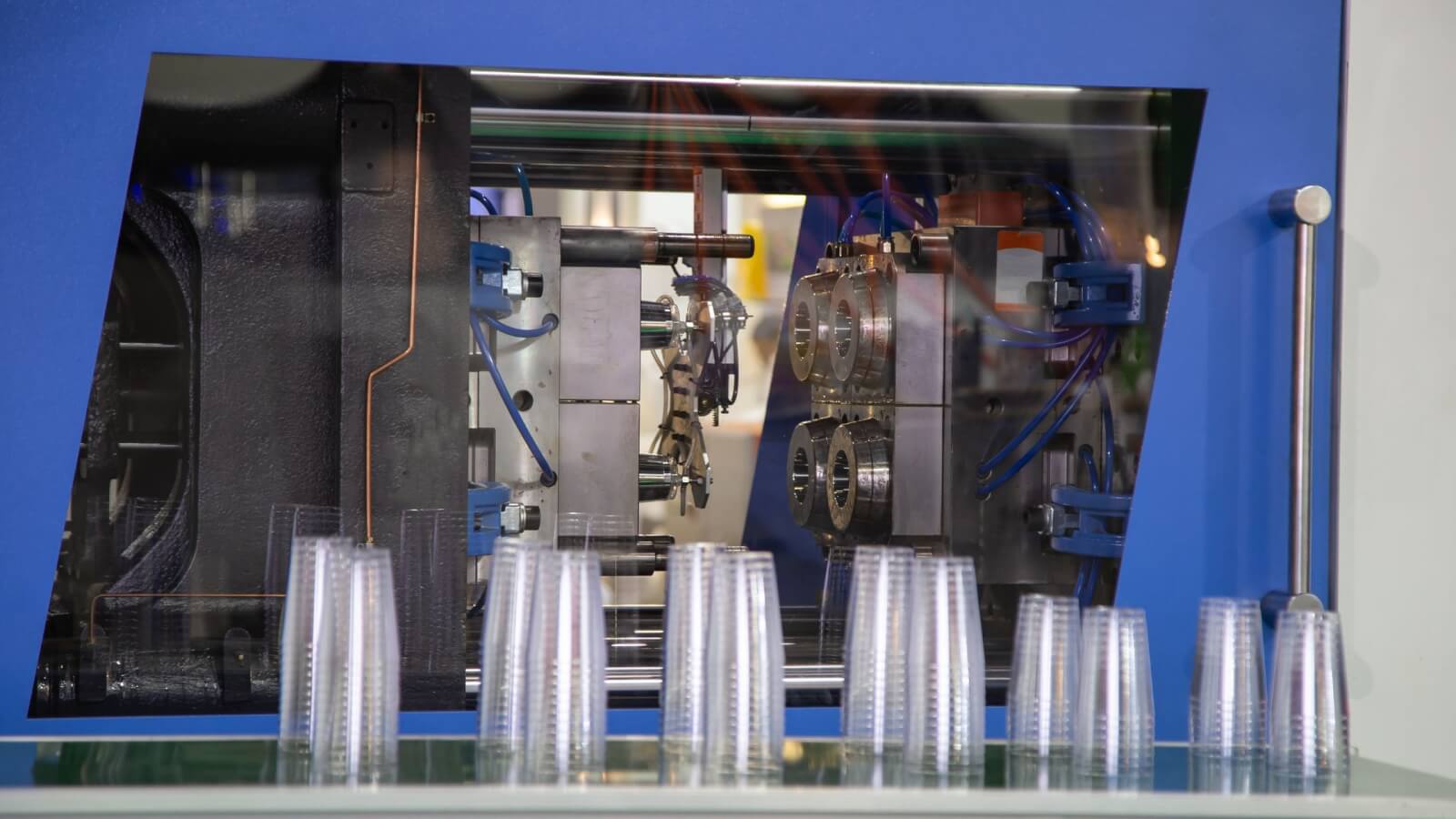
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic mold
What Are the Steps Involved in Assembly and Finishing of Thermoplastic Molds?
After cooling, the molded part is ejected from the mold using ejector pins. This process must be carefully managed to prevent damage to the part. Once ejected, the part may undergo various finishing processes, which could include trimming excess material, surface polishing, and applying coatings or paints for aesthetic or functional purposes.
The assembly stage may involve integrating multiple molded components or adding additional features such as inserts or electronics. Each step in this stage is critical to the overall quality and performance of the final product.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Thermoplastic Mold Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of thermoplastic mold manufacturing, ensuring that the final products meet both industry standards and customer specifications. For international B2B buyers, understanding the QA processes can help in selecting reliable suppliers.
What International Standards and Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
One of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems is ISO 9001. This certification indicates that a manufacturer adheres to rigorous quality management principles, including strong customer focus, the involvement of top management, and a process-based approach.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications may be relevant. For example, products intended for the European market may require CE marking, while those in the oil and gas sector might need API certification. Buyers should verify that suppliers hold the necessary certifications that align with their industry requirements.
How Are QC Checkpoints Structured During the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control in thermoplastic mold manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production process. It ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cycle times are monitored. This real-time inspection helps identify defects early, reducing waste and rework.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the parts are completed, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the finished products. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional testing to ensure they meet specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Product Quality?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality of thermoplastic molds:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers to ensure that parts conform to specified dimensions.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and hardness to ensure the material performs as expected.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, color consistency, and overall aesthetics.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To establish confidence in a supplier’s quality control practices, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits to assess the manufacturing process and quality control measures directly. This provides insight into the supplier’s operational practices and adherence to quality standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes. These documents should provide transparency regarding defect rates and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspection: Engaging independent third-party inspectors to evaluate the supplier’s facilities and processes can add an extra layer of assurance. These inspectors can provide unbiased assessments of the supplier’s capabilities and compliance with industry standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and industry standards that must be adhered to.
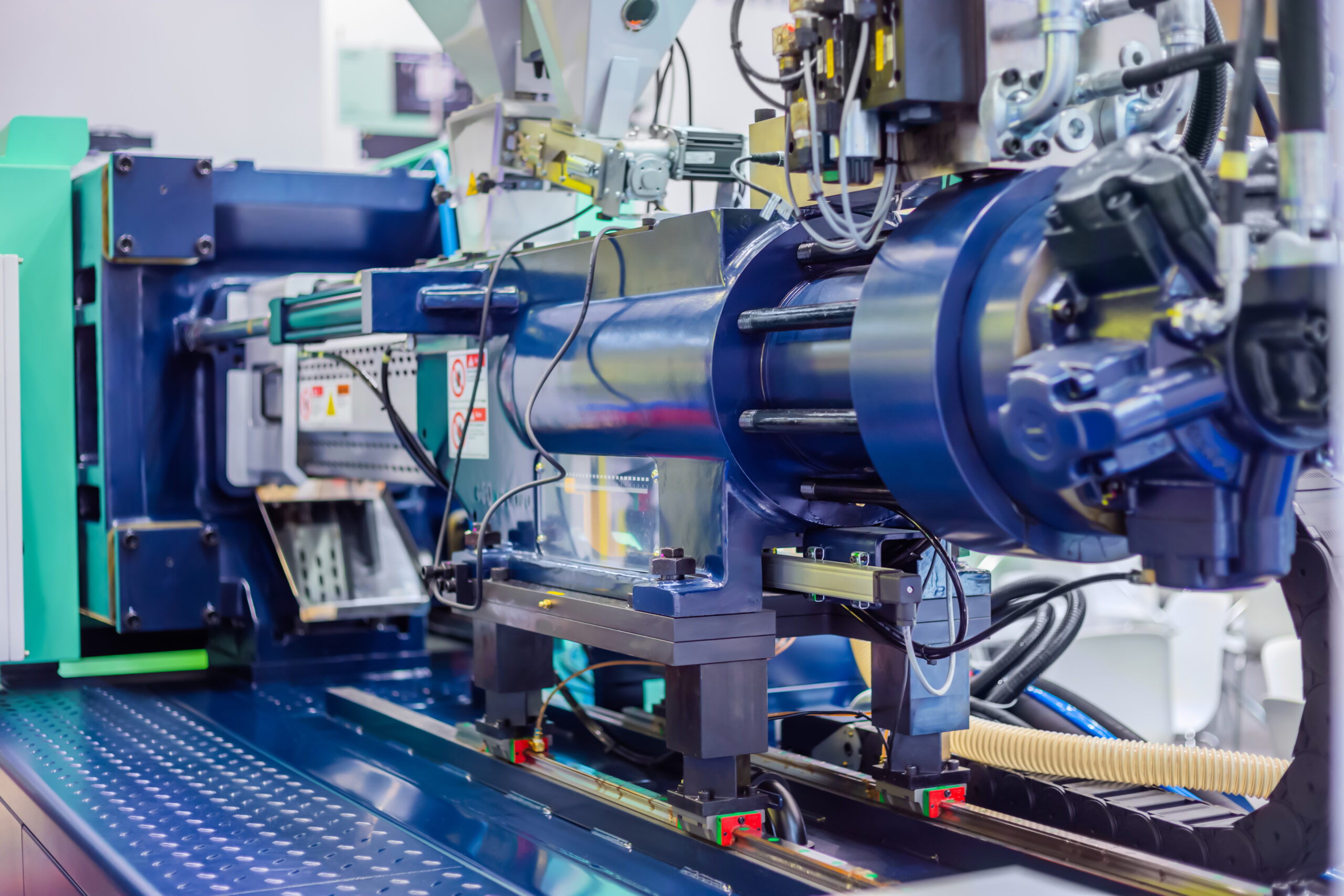
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic mold
Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are not only compliant with local standards but are also knowledgeable about international requirements. This may involve additional certifications or documentation that can facilitate smoother trade across borders.
By understanding the intricacies of the manufacturing processes and the importance of quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for thermoplastic molds. This knowledge not only enhances the potential for successful partnerships but also helps ensure the reliability and quality of the products they procure.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘thermoplastic mold’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of thermoplastic molds requires a structured approach to ensure you receive high-quality products that meet your specific needs. This step-by-step checklist is designed to guide international B2B buyers through the essential stages of sourcing thermoplastic molds, enabling you to make informed decisions and build successful supplier relationships.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the thermoplastic molds you need. This includes dimensions, tolerances, material types, and any specific performance characteristics relevant to your application.
– Considerations: Identify the end-use of the molded parts, as this will influence material selection and design features.
– Documentation: Create detailed specifications documents to share with potential suppliers, ensuring clarity in your expectations.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers specializing in thermoplastic molds. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of candidates.
– Due Diligence: Look for suppliers with a strong track record in your industry and positive customer reviews.
– Geographic Considerations: Evaluate suppliers based on their location, as this can impact shipping costs and lead times.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the manufacturing capabilities of each potential supplier to ensure they can meet your production needs. This involves examining their equipment, technology, and workforce expertise.
– Key Questions: Inquire about their production processes, quality control measures, and capacity for scaling production.
– Visit Facilities: If possible, arrange site visits to gain insight into their operations and quality assurance practices.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing a supplier, request samples or prototypes of their molds. This will allow you to evaluate the quality and precision of their work firsthand.
– Testing: Use the samples in practical applications to assess their performance under real-world conditions.
– Feedback Loop: Provide detailed feedback to the supplier, which can help refine the mold design before full-scale production.
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic mold
Step 5: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers possess relevant certifications and comply with industry standards. This is crucial for maintaining quality and safety in your products.
– Common Certifications: Look for ISO certifications, compliance with ASTM standards, or any specific certifications relevant to your industry.
– Documentation Review: Request documentation that verifies these certifications and ensure they are up-to-date.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in discussions with your shortlisted suppliers to negotiate favorable terms and pricing. This includes not only the cost of the molds but also payment terms, lead times, and warranty policies.
– Value Beyond Price: Consider the overall value offered, including quality guarantees and after-sales support.
– Long-term Relationships: Aim for agreements that foster long-term partnerships, which can lead to better pricing and reliability in future orders.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Plan
Once a supplier is selected, set up a communication plan to ensure ongoing collaboration throughout the production process. This includes regular updates on production status, quality checks, and any potential issues.
– Point of Contact: Designate a primary contact person on both sides to streamline communication.
– Feedback Mechanism: Implement a system for providing feedback and addressing concerns promptly to ensure smooth operations.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively source thermoplastic molds that meet their requirements while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thermoplastic mold Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Thermoplastic Mold Sourcing?
When sourcing thermoplastic molds, understanding the cost structure is critical for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of thermoplastic material significantly impacts the cost. Common materials like polyethylene, polycarbonate, and nylon vary in price based on their properties and market demand. Specialty materials with enhanced characteristics (like heat resistance or flexibility) can lead to higher costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in both the design and manufacturing processes. Skilled labor for mold design and machine operation can vary widely between regions, influencing overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, maintenance, and depreciation of machinery. Efficient operations can lower overhead costs, but these expenses must be factored into the total price of the molds.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom molds. The complexity of the mold design and the type of manufacturing process (e.g., injection molding vs. blow molding) will dictate tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous testing and inspection adds to the cost but is essential for maintaining standards and certifications. This is particularly crucial for industries with stringent regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs should not be overlooked. Factors such as the distance from the supplier, the mode of transport, and import duties can significantly affect the final pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and risks. Understanding market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Thermoplastic Mold Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of thermoplastic molds:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider whether they can meet MOQs to take advantage of these savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized molds or those requiring advanced features tend to be more expensive. Clearly defining specifications can help mitigate costs.
-
Materials: As previously mentioned, the choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Buyers should evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of different materials based on their application needs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality molds with necessary certifications (like ISO or ASTM) may come at a premium. It’s crucial to balance quality needs with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products due to perceived quality or service reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs and risks. This knowledge can help in negotiating better terms and avoiding unexpected expenses.
What Tips Can Buyers Utilize to Optimize Costs in Thermoplastic Mold Sourcing?
International B2B buyers can employ several strategies to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures. Being transparent about your budget and requirements can lead to mutually beneficial agreements.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the entire lifecycle cost of the molds, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential waste. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and regional manufacturing capabilities when sourcing from different countries. For example, sourcing from Vietnam may offer competitive pricing due to lower labor costs compared to Europe.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and improved negotiation leverage for future orders.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for thermoplastic molds can fluctuate based on various market conditions, material availability, and global economic factors. It’s advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing thermoplastic mold With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Thermoplastic Molding
In the manufacturing landscape, thermoplastic molding stands out for its versatility and efficiency in producing plastic components. However, several alternative solutions may also fit specific needs or applications. Understanding these alternatives helps B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational goals, budget constraints, and product requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Thermoplastic Mold | Blow Molding | Compression Molding | Reaction Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and detail | Ideal for hollow parts | Good for large, thick parts | Excellent for complex shapes |
| Cost | Moderate upfront investment | Lower cost for mass production | Lower material waste | Higher material costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized machinery | Easier setup for large runs | Simple tooling | Complex setup and equipment |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance needs | Lower maintenance requirements | Higher maintenance due to wear | Moderate maintenance |
| Best Use Case | High volume, intricate designs | Bottles, containers | Automotive parts, large items | Complex, multi-material parts |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Blow Molding
Blow molding is a process primarily used to create hollow plastic products. It operates by inflating a heated plastic tube (parison) within a mold, forming items like bottles and containers. This method is cost-effective for high-volume production and offers faster cycle times than thermoplastic molding. However, it is limited to hollow shapes and may not provide the same level of precision for detailed components. Companies focused on producing large quantities of simple, hollow items may find blow molding to be a suitable alternative.
Compression Molding
Compression molding is a technique where preheated material is placed into a heated mold, which is then closed to form the product. This method is advantageous for producing large and thick parts with minimal material waste. It’s particularly effective for items like automotive components and industrial parts. However, the setup can be more complicated, and the maintenance demands can be higher due to mold wear. Buyers looking for durable, large components might consider this method, especially if they can tolerate longer cycle times.
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic mold
Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)
Reaction injection molding involves mixing two reactive chemical components that are injected into a mold, where they chemically react to form a solid part. This method excels in creating complex shapes and allows for the incorporation of multiple materials, including flexible and rigid components. While it offers high design flexibility, the initial setup costs and material prices can be higher compared to thermoplastic molding. RIM is ideal for applications requiring innovative designs and material combinations, making it suitable for specialized industries such as automotive and consumer goods.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the most appropriate molding solution hinges on several factors, including product requirements, production volume, and budget constraints. Thermoplastic molding is highly effective for intricate designs and high-volume production, while alternatives like blow molding and compression molding offer unique advantages depending on the application. Buyers should assess their specific needs, including performance requirements and cost considerations, to determine the best fit for their manufacturing processes. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method, businesses can optimize their production capabilities and drive efficiency in their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thermoplastic mold
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Thermoplastic Molds?
Understanding the technical specifications of thermoplastic molds is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when selecting materials and processes that align with product requirements. Here are several critical properties that should be considered:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of thermoplastic resin used in the molding process, such as ABS, polycarbonate, or polypropylene. Each material possesses distinct mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties, making it crucial to select the right grade for the intended application. For instance, polycarbonate is known for its high impact resistance, making it suitable for automotive components, while ABS offers excellent toughness for consumer goods.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension, which is critical in ensuring that molded parts fit together correctly. In B2B transactions, tight tolerances can significantly affect the functionality and quality of the final product, especially in industries like aerospace or medical devices, where precision is paramount. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers assess whether a supplier can meet their quality standards.
3. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time taken to complete one cycle of the injection molding process, from material loading to part ejection. A shorter cycle time can lead to increased production efficiency and lower costs, making it a vital consideration for businesses aiming to optimize their manufacturing processes. Buyers should inquire about cycle times when negotiating with suppliers to ensure they can meet production schedules.
4. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and appearance of the molded part’s surface. It can significantly influence the aesthetics and functionality of the product, especially in consumer-facing applications. Different molding techniques can achieve various surface finishes, such as glossy, matte, or textured. Buyers must specify their surface finish requirements to ensure that suppliers can deliver the desired quality.
5. Heat Resistance
Heat resistance is the ability of a thermoplastic material to withstand elevated temperatures without deforming or degrading. This property is crucial in applications that involve exposure to heat, such as automotive and electronic components. Buyers should evaluate the heat resistance of materials to ensure that the final products will perform effectively under their intended operating conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Thermoplastic Molding Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential trade terms:

Illustrative image related to thermoplastic mold
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of thermoplastic molding, OEMs often rely on specialized molders to produce components that meet their specifications. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers seeking partnerships in product development.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units that a supplier is willing to produce or sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs with suppliers to align production volumes with market demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services. In thermoplastic molding, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs, lead times, and specifications from multiple suppliers, aiding in informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as delivery points, risk transfer, and cost allocation. For buyers sourcing thermoplastic molds globally, understanding Incoterms helps mitigate risks and ensures clarity in logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from when an order is placed until it is fulfilled. In the context of thermoplastic molding, lead time can impact production schedules and inventory levels. Buyers should inquire about lead times during negotiations to ensure timely delivery of their products.
Illustrative image related to thermoplastic mold
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, streamline procurement processes, and foster successful supplier relationships in the thermoplastic molding industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the thermoplastic mold Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Thermoplastic Mold Sector?
The thermoplastic mold sector is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. As industries increasingly adopt automation and smart manufacturing practices, the demand for precision-engineered plastic components is surging. This trend is particularly evident in sectors such as automotive, consumer goods, and electronics, where lightweight and durable thermoplastic materials are preferred for their performance and design flexibility. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are also witnessing increased investments in manufacturing capabilities, leading to a growing demand for thermoplastic molds.
Key sourcing trends include the rise of digital procurement platforms that streamline the sourcing process for B2B buyers. These platforms enable buyers to access a wider range of suppliers, compare prices, and ensure quality standards more efficiently. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on supply chain transparency, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who can provide detailed information about their manufacturing processes and material sourcing. This trend is particularly pertinent for international buyers from regions like Europe, Vietnam, and Brazil, where regulatory requirements are stringent and product quality expectations are high.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Thermoplastic Mold Market?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration in the thermoplastic mold sector, with increasing awareness of environmental impacts prompting companies to adopt more eco-friendly practices. The production of thermoplastics can have significant environmental repercussions, from resource extraction to waste generation. Therefore, many B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers who incorporate sustainable practices in their operations, such as using recycled materials or adopting energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are increasingly aware of the social implications of their supply chains. Ensuring fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials not only enhances brand reputation but also complies with emerging regulatory frameworks in various regions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and materials with recognized ‘green’ certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By aligning with suppliers who prioritize these values, businesses can mitigate risks and enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles.

Illustrative image related to thermoplastic mold
What Is the Historical Context of Thermoplastic Molding in B2B Applications?
The evolution of thermoplastic molding dates back to the early 20th century, with significant milestones that have shaped its current state. The development of Bakelite by Leo Baekeland in the 1900s marked the first synthetic plastic, paving the way for the advanced thermoplastic materials we utilize today. Over the decades, innovations in molding processes such as injection molding, blow molding, and rotational molding have expanded the applications of thermoplastics across various industries.
Initially, thermoplastic molds were primarily used for simple components. However, advancements in technology have enabled the production of complex geometries and high-precision parts. This evolution not only reflects the advancements in material science but also the changing demands of industries looking for efficient, scalable, and cost-effective manufacturing solutions. As a result, thermoplastic molding has become integral to modern manufacturing, catering to diverse markets and setting the stage for continued growth in the B2B landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thermoplastic mold
-
How do I choose the right thermoplastic mold supplier for my business?
Selecting a reliable thermoplastic mold supplier involves assessing several critical factors. Start by evaluating their industry experience and track record in delivering quality molds that meet your specifications. Request samples of their previous work to gauge the quality and precision of their products. Additionally, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards, particularly if you’re sourcing from different regions. Engaging in direct communication can also provide insights into their responsiveness and customer service, which are vital for long-term collaboration. -
What are the key considerations for customizing thermoplastic molds?
When customizing thermoplastic molds, consider the specific requirements of your project, including the material type, part complexity, and production volume. Discuss the design and functionality with your supplier to ensure they can accommodate your needs. It’s also essential to evaluate the lead time for customization and any associated costs. Collaborate closely on design iterations to prevent issues during production, and ensure that the supplier has the necessary technology and expertise to execute the customizations accurately. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for thermoplastic molds?
The minimum order quantity for thermoplastic molds can vary significantly depending on the supplier, the complexity of the mold, and the production process. Generally, MOQs can range from a few pieces for simple designs to hundreds or thousands for more intricate molds. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to find a mutually agreeable MOQ. Some suppliers may also offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially if you are willing to pay a premium or commit to a longer-term partnership. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing thermoplastic molds internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of thermoplastic molds can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common options include upfront payments, partial payments before production, and the balance upon delivery. Letters of credit and escrow services are often used for larger transactions to protect both parties. It’s crucial to clarify payment terms in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. Consider the implications of currency exchange rates and transaction fees when budgeting for your purchase. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for thermoplastic molds?
To ensure quality assurance for thermoplastic molds, establish clear quality criteria and standards with your supplier upfront. Request documentation of their QA processes, including material testing, mold inspections, and compliance with international standards. Implement regular communication and updates during the production phase to address any potential issues. Additionally, consider third-party inspections or certifications to verify that the molds meet your specifications before shipment, thereby reducing the risk of defects. -
What logistics considerations should I take into account when importing thermoplastic molds?
When importing thermoplastic molds, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Work closely with your supplier to determine the best shipping options that align with your timeline and budget. Ensure you understand the customs duties and taxes applicable in your country to avoid unexpected costs. It’s also prudent to have a reliable freight forwarder who can navigate the complexities of international shipping, ensuring timely delivery and compliance with all regulations. -
What types of thermoplastic materials are best suited for injection molding?
The choice of thermoplastic materials for injection molding depends on the intended application and required properties. Common materials include polyethylene (PE) for its versatility, polycarbonate (PC) for high-impact resistance, and polypropylene (PP) for its lightweight and chemical resistance. Each material has unique characteristics, such as tensile strength, heat resistance, and flexibility. Discussing your specific needs with your supplier can help identify the most suitable material to optimize the performance and durability of your molded parts. -
How does the thermoplastic injection molding process work?
The thermoplastic injection molding process involves several key stages: material preparation, melting, injection, cooling, and ejection. First, plastic pellets are dried and loaded into the injection machine. They are then heated until molten and injected into a mold under high pressure. Once the plastic fills the mold, it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. Finally, the molded part is ejected from the mold. Each stage is crucial for ensuring the quality and precision of the final product, so understanding this process helps buyers make informed decisions.
Top 7 Thermoplastic Mold Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Thermoplastic Molding Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Thermoplastic molding involves forming plastic parts by injecting molten resin into a mold. Key aspects include:
– **Types of Thermoplastic Molding**: Rapid injection molding for prototypes, production injection molding for full-scale manufacturing.
– **Materials**: Thermoplastics, which can be reheated and reshaped, allowing for recycling with a limit of 30% recycled content.
– **Applications*…
2. Forged Acrylics – Thermoplastic Molding Solutions
Domain: forgedacrylics.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Thermoplastic molding is a versatile manufacturing process used to produce various plastic products. Key techniques include injection molding, blow molding, compression molding, and extrusion molding. Essential tools for thermoplastic molding projects include an injection molding machine, CAD software for design, mold release agents, a drill press, aluminum mold frames, water baths for temperature…
3. Toray – Carbon Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic
Domain: cf-composites.toray
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: {“Thermoplastic Molding Materials”: {“Short Fiber Pellet”: {“Description”: “Carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic (CFRTP) designed for injection molding.”, “Properties”: [“Light weight”, “Excellent strength”, “Stiffness”, “Dimensional accuracy”, “Sliding properties”], “Base Resins”: [“PP”, “PC”, “ABS”, “Nylon 6”, “Nylon 66”, “Nylon 610”, “PBT”, “PPS”], “Applications”: [“Automotive”, “Electric home…
4. Core Molding Technologies – Advanced Molding Solutions
Domain: coremt.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Core Molding Technologies specializes in various molding processes including Thermoset and Thermoplastic Compression Molding, Injection Molding, DLFT, Structural Foam Molding, Structural Web Molding, DCPD Reaction Injection Molding, SMC, Resin Transfer Molding, Hand Lay-Up, and Spray-Up. They cater to multiple industries such as Automotive, Building Products, Construction/Agriculture, Consumer, Fo…
5. Aline Components – Custom Injection Molding Services
Domain: alinecomponents.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Thermoplastic Injection Molding Process at Aline Components includes custom injection molding services since 1965. Key features include: High Quality Thermoplastic Materials, Custom Manufactured Molds made from high quality steel or aluminum, and Advanced Injection Molding Machines. The process involves heating thermoplastic materials (pellets or granules) until melted, injecting the melt into a m…
6. DimcoGray – Custom Thermoplastic Molding
Domain: dimcogray.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: DimcoGray offers custom thermoplastic molding services with expertise in thermomolding plastics since 1924. They provide custom molded components for OEMs across various industries, utilizing reduced weight and high structural strength techniques. Their design process includes engineering support for structural integrity, rapid prototyping using 3D printing, and Fused Deposition Molding (FDM). Pro…
7. Witmold – Custom Plastic Injection Molds
Domain: witmold.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Custom Plastic Injection Molds, High Precision Molds, Unscrewing Molds, Two Shot Injection Molds, High Cavitation Molds, Gas Assist Molds, Structural Foam Molds, Collapse Core Molds, Thermoset Molds, Compression Tooling, Thermoset Injection Molds, Thermoset Transfer Molding, BMC Mold Inserted Molding Tools, Die Casting Tools.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thermoplastic mold
In the rapidly evolving landscape of thermoplastic mold manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital strategy for international B2B buyers. By leveraging the versatility of thermoplastic materials, businesses can enhance product design, reduce manufacturing costs, and improve time-to-market. Understanding the various molding processes—such as injection, overmolding, and blow molding—allows buyers to select the most suitable techniques that align with their specific product requirements.
Sourcing from reliable suppliers not only ensures quality but also fosters innovation, enabling companies to stay competitive in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability, the recyclability of thermoplastics presents an additional advantage, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and stakeholders alike.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality thermoplastic components will continue to grow, driven by advancements in technology and shifts in consumer preferences. Now is the time for international buyers to forge strong partnerships with leading manufacturers and suppliers in the thermoplastic industry. Embrace strategic sourcing today to secure a competitive edge in tomorrow’s market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.