Top 9 Palletizer Job Description Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for palletizer job description
In the fast-paced world of logistics and manufacturing, sourcing a comprehensive palletizer job description is crucial for companies aiming to optimize their operations. As businesses expand into international markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of palletizer roles becomes essential. This guide will delve into the various types of palletizers, their applications across different industries, and the critical skills required for success in these positions.
Moreover, we will provide insights on supplier vetting, cost considerations, and best practices for integrating palletizing solutions into existing workflows. By offering a clear framework for evaluating job descriptions and identifying the right candidates, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to enhance productivity in a manufacturing plant in Germany or streamline distribution processes in Saudi Arabia, understanding the intricacies of palletizer roles will equip you with the knowledge necessary to drive efficiency and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Embrace the opportunity to refine your operations and enhance your competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding palletizer job description Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Palletizer | Operated by workers, requires physical labor | Small to medium-sized warehouses | Pros: Low initial cost; Cons: Labor-intensive, slower throughput. |
| Automated Palletizer | Machine-operated, high-speed stacking | Large-scale production facilities | Pros: High efficiency; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
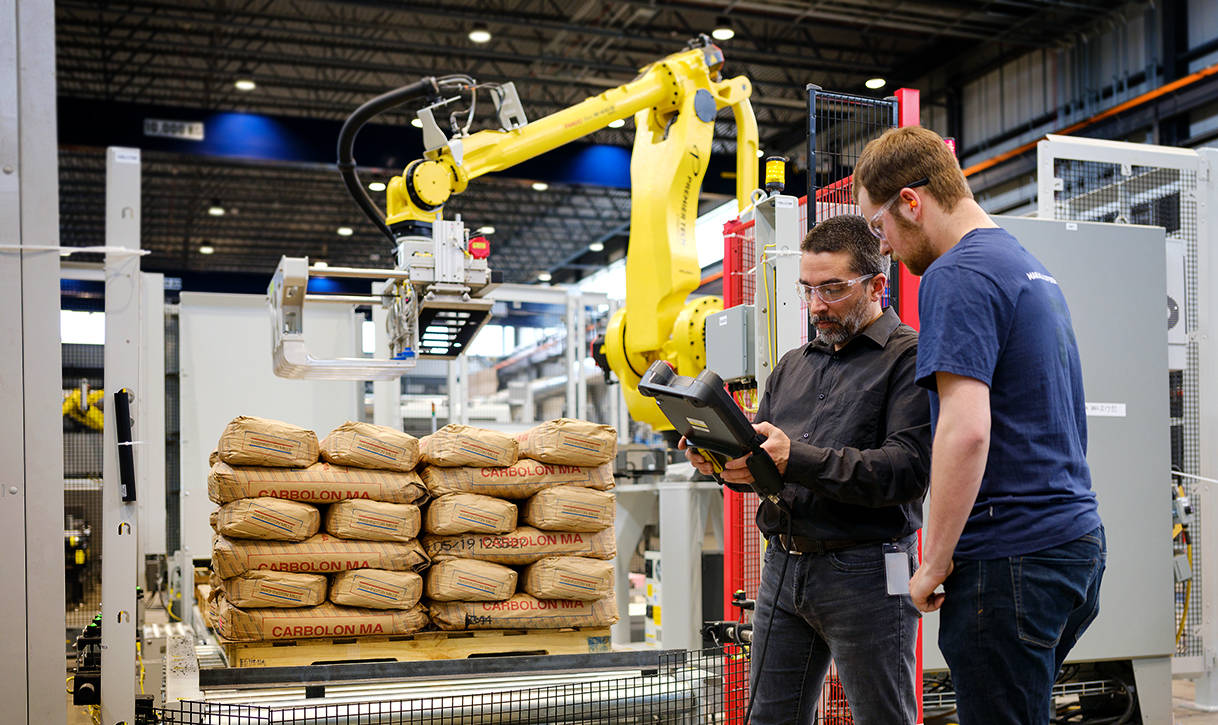
| Robotic Palletizer | Utilizes robotic arms for precision and flexibility | Industries needing customization | Pros: Versatile; Cons: Complex maintenance and programming. |
| Semi-Automated Palletizer | Combination of manual and automated processes | Transitional operations | Pros: Balanced cost and efficiency; Cons: May require skilled labor. |
| Depalletizer | Focuses on unloading products from pallets | Distribution centers | Pros: Streamlines inbound logistics; Cons: Often overlooked in planning. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of a Manual Palletizer?
Manual palletizers involve human operators physically stacking products onto pallets. This type is typically found in smaller warehouses where automation may not be financially viable. Buyers should consider the labor costs and physical demands on workers, as well as the slower throughput compared to automated systems. Manual palletizers are suitable for businesses with lower volume needs or those just starting to explore palletizing options.
How Does an Automated Palletizer Benefit Large-Scale Operations?
Automated palletizers utilize machinery to stack products quickly and efficiently, making them ideal for large-scale production environments. These systems offer high throughput and reduced labor costs, but they require a significant upfront investment. Buyers should evaluate the long-term savings on labor and increased productivity against the initial capital expenditure. Automated systems are best suited for companies with consistent high-volume production.
What Are the Advantages of Using Robotic Palletizers?
Robotic palletizers offer advanced flexibility and precision in stacking products. They can handle a variety of product types and sizes, making them suitable for industries with diverse packaging needs. While they provide high efficiency, buyers must consider the complexity of programming and maintenance. Companies looking for customization and adaptability in their palletizing processes will find robotic solutions advantageous.
Why Consider a Semi-Automated Palletizer?
Semi-automated palletizers combine the strengths of manual and automated systems, allowing for flexibility in operations. They are particularly beneficial for businesses transitioning from manual processes to full automation. This type of palletizer can help balance costs and efficiency, but it may still require skilled labor for optimal operation. Buyers should assess their current workforce capabilities and future scalability needs when considering this option.
How Does a Depalletizer Fit into the Supply Chain?
Depalletizers focus on unloading products from pallets efficiently, streamlining the inbound logistics of distribution centers. While often overshadowed by palletizing equipment, they are crucial for maintaining smooth operations. Buyers should recognize the importance of integrating depalletizers into their workflow to enhance overall efficiency. This type of equipment is particularly beneficial for companies with high volumes of incoming goods that need to be processed quickly.
Key Industrial Applications of palletizer job description
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of palletizer job description | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Automated stacking of packaged goods like beverages and canned products | Increases efficiency, reduces labor costs, and enhances safety | Equipment compatibility with existing systems and local regulations |
| Pharmaceuticals | Stacking of pharmaceutical products for shipment and storage | Ensures compliance with safety standards and reduces damage risk | Need for precision and adherence to strict regulatory requirements |
| Consumer Goods | Palletizing household items such as cleaning supplies and personal care products | Streamlines distribution processes and optimizes warehouse space | Ability to handle diverse product shapes and weights |
| Construction Materials | Stacking of bags or containers of cement, sand, and aggregates | Improves loading speed and reduces workplace injuries | Durability of equipment in harsh environments and maintenance support |
| Electronics | Palletizing electronic components and devices for shipping | Minimizes damage during transport and enhances inventory accuracy | Requirements for static-free handling and precise stacking arrangements |
How Is the Palletizer Job Description Applied in Various Industries?
Food and Beverage
In the food and beverage sector, palletizers are critical for automating the stacking of packaged goods, such as beverages, canned vegetables, and snacks. This application enhances operational efficiency by enabling rapid loading and unloading, thus meeting high production demands. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing palletizing equipment that complies with local food safety regulations and can handle diverse product shapes is essential. Additionally, ensuring that the equipment is adaptable to varying production rates can significantly improve overall productivity.
Pharmaceuticals
Palletizers in the pharmaceutical industry are responsible for the secure stacking of sensitive products for distribution. This role is vital for maintaining compliance with stringent safety and quality regulations, minimizing the risk of contamination or damage during transit. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing palletizers that offer precise stacking capabilities and are equipped with features that facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance. Understanding the specific regulatory landscape in these regions is crucial to ensure that the chosen equipment meets all necessary standards.
Consumer Goods
In the consumer goods sector, palletizers are used to efficiently stack a wide range of products, from cleaning supplies to personal care items. This application helps streamline distribution processes, ensuring that products are readily available for retailers and consumers. For businesses in Africa and Europe, selecting palletizers that can accommodate various product sizes and weights is important. Furthermore, buyers should consider the equipment’s ability to integrate with existing warehouse management systems to optimize inventory handling.
Construction Materials
Palletizing construction materials such as bags of cement and aggregates is another key application. This process not only speeds up loading times but also significantly reduces the risk of workplace injuries by minimizing manual handling. Buyers should focus on sourcing robust palletizers capable of withstanding the harsh conditions typical in construction environments. Additionally, maintenance support and the availability of spare parts are critical considerations to ensure long-term operational reliability.
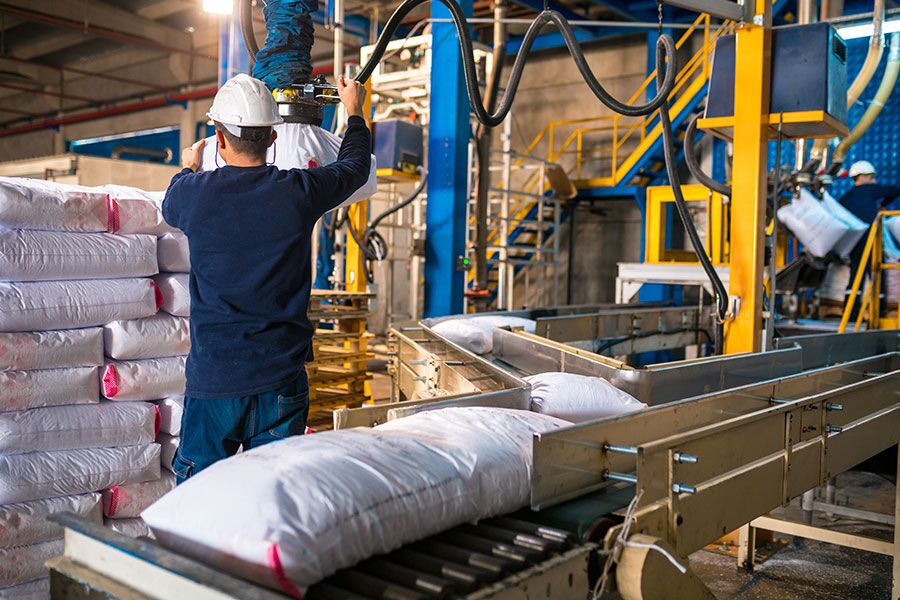

Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
Electronics
In the electronics industry, palletizers are crucial for stacking components and devices securely for shipping. This application is designed to minimize damage during transport, which is essential for maintaining product integrity. International buyers, particularly in regions with high-value electronics markets, should look for palletizers that offer static-free handling features and customizable stacking patterns. Understanding the specific requirements for electronic components, such as weight limits and stacking configurations, will help buyers select the right equipment for their needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘palletizer job description’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Finding Skilled Palletizer Operators
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in locating skilled palletizer operators who can efficiently manage automated systems. Many industries are experiencing a labor shortage, particularly for roles requiring technical skills. This shortage not only hinders production schedules but also increases operational costs due to reliance on less experienced staff. Additionally, the lack of well-defined job descriptions can lead to confusion regarding the qualifications and responsibilities necessary for the role, resulting in high turnover rates and further complications in training.
The Solution: To effectively source skilled palletizer operators, it is crucial to develop a comprehensive job description that outlines specific responsibilities, required qualifications, and essential skills. This should include the ability to operate various palletizing equipment, monitor machine performance, and adhere to safety regulations. Collaborating with local vocational schools or training centers can also help create a pipeline of qualified candidates. Furthermore, leveraging online job platforms that cater to technical roles can broaden your reach. Consider implementing an internal training program that emphasizes the importance of continuous skill development, ensuring that operators stay updated with the latest technologies and safety standards.

Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality Control During Palletizing Operations
The Problem: Many companies struggle with maintaining consistent quality control during palletizing operations. When palletizer operators are not adequately trained or when job descriptions lack clarity, it can lead to errors in stacking and sorting. This not only affects product integrity during transport but also results in increased returns and customer dissatisfaction. In industries where compliance with safety and quality regulations is paramount, such inconsistencies can lead to significant operational setbacks and financial losses.
The Solution: Establish a robust quality control protocol within the job description for palletizer operators. This should include regular inspections of the palletizing process, guidelines for identifying defective products, and steps for troubleshooting equipment malfunctions. Implementing a training program that focuses on the importance of quality assurance can empower operators to take ownership of their responsibilities. Additionally, integrating technology such as sensors and automated inspection systems can help monitor product quality in real-time, reducing the reliance on manual checks and ensuring that only products meeting quality standards are dispatched.
Scenario 3: Safety Compliance Challenges in Palletizing Operations
The Problem: Safety compliance is a critical concern for companies operating palletizing systems, especially in regions with strict regulatory frameworks. B2B buyers often encounter difficulties ensuring that their palletizer operators understand and adhere to safety protocols. A lack of clear expectations outlined in the job description can lead to unsafe practices, resulting in workplace accidents, injuries, and costly fines. This situation is exacerbated in environments where multiple operators are working simultaneously, increasing the risk of safety breaches.
The Solution: To mitigate safety compliance challenges, it is essential to integrate safety responsibilities into the palletizer job description explicitly. This includes detailed instructions on operating machinery safely, recognizing hazardous situations, and reporting incidents. Conducting regular safety training sessions can reinforce these practices and ensure that operators are well-versed in compliance requirements. Additionally, creating a culture of safety within the workplace, where operators feel empowered to speak up about unsafe conditions, can significantly enhance overall safety. Investing in safety equipment and ergonomic tools can also reduce the risk of injuries, demonstrating a commitment to employee well-being and regulatory compliance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for palletizer job description
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Palletizer Job Descriptions?
When considering the materials for palletizer job descriptions, it is essential to analyze their properties, advantages, and limitations to ensure optimal performance in various operational environments. Here, we explore four common materials: steel, aluminum, plastic, and composite materials.
How Does Steel Perform in Palletizer Applications?
Steel is a widely used material in palletizers due to its high strength and durability. It has excellent temperature and pressure ratings, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel’s corrosion resistance can be enhanced with coatings, allowing it to withstand harsh environments.
Pros: Steel’s primary advantage is its robustness, which translates to a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. It is also relatively cost-effective for large-scale operations.
Cons: However, steel can be heavy, which may complicate the design of the palletizer. Additionally, it is susceptible to rust if not properly treated, which can lead to increased maintenance needs.

Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including oils and chemicals, making it versatile for various industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial. In regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia, buyers should ensure that their steel suppliers adhere to local regulations regarding material quality and safety.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in Palletizer Systems?
Aluminum is another popular choice for palletizer components due to its lightweight nature and good corrosion resistance. It is particularly effective in applications where weight reduction is essential.

Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which facilitates faster operation and easier handling. It also offers good thermal conductivity and can be anodized for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Cons: However, aluminum is generally more expensive than steel and may not provide the same level of strength for heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for environments where moisture is prevalent, as it resists corrosion effectively. However, it may not be ideal for applications involving extreme temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum in their regions and ensure that suppliers meet international quality standards, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
How Do Plastics Compare in Palletizer Applications?
Plastics are increasingly used in palletizer systems, especially for components that require flexibility and resistance to chemicals. Various types of plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are commonly employed.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight and resistant to many chemicals, making them suitable for diverse applications. They are also less expensive than metals, which can reduce overall project costs.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastics is their lower strength compared to metals, which may not be suitable for heavy loads. Additionally, they can be affected by UV exposure, leading to degradation over time.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for environments where chemical exposure is a concern, but their load-bearing capacity should be evaluated carefully.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with safety and environmental regulations in their respective countries, particularly in regions with stringent standards.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in Palletizer Systems?
Composite materials, which combine two or more constituent materials, are gaining traction in palletizer applications. They offer a unique combination of properties, including strength and lightweight characteristics.
Pros: Composites are highly durable and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for various environments. They can also be tailored to specific performance requirements.
Cons: The complexity of manufacturing composite materials can lead to higher costs. Additionally, the availability of specific composite materials may vary by region.
Impact on Application: Composites excel in applications requiring both strength and low weight, making them ideal for advanced palletizing systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that composite materials meet local standards and certifications, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where material availability may differ.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Palletizer Job Descriptions
| Material | Typical Use Case for palletizer job description | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty palletizing applications | High strength and durability | Susceptible to rust | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight palletizing systems | Low weight and good corrosion resistance | Higher cost than steel | High |
| Plastic | Chemical handling and lightweight applications | Resistant to chemicals and cost-effective | Lower load-bearing capacity | Low |
| Composite | Advanced palletizing systems | Tailored properties and durability | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for palletizer job descriptions, guiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for palletizer job description
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Palletizers?
The manufacturing process of palletizers typically involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets quality and operational standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source reliable palletizing equipment.
Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Processed?
Material preparation is the foundational step in manufacturing palletizers. This stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials, such as steel and aluminum, which are commonly used in the construction of palletizing machines. The materials undergo processes like cutting, shaping, and treatment to enhance their durability and resistance to wear and tear. Advanced techniques, such as laser cutting and CNC machining, are often employed to ensure precision in the dimensions and quality of the components.
Forming: How Are Palletizer Components Shaped and Assembled?
The forming stage involves various techniques to create the essential components of the palletizer. This may include welding, bending, and stamping operations, which shape the materials into parts like frames, conveyors, and stacking mechanisms. Automated robotic systems are frequently utilized to enhance efficiency and consistency in production. The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software during this stage allows for intricate designs that optimize space and functionality.
Assembly: What Are the Key Steps in Assembling a Palletizer?
Once the components are formed, the assembly stage brings everything together. Skilled technicians or automated systems piece together the palletizer, integrating components such as electrical systems, control panels, and safety features. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the palletizer operates smoothly and meets operational specifications. Quality checks during assembly, including alignment and functionality tests, help identify potential issues before the machine leaves the factory.
Finishing: What Processes Are Involved in the Final Touches?
The finishing stage involves painting, coating, and surface treatments to protect the palletizer from corrosion and wear. This is particularly important for machines that will operate in harsh environments. Additionally, this stage includes final inspections to ensure that all components meet quality standards and that the palletizer is ready for shipment. Proper finishing not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also extends the lifespan of the equipment.

Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Palletizers?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for palletizers. It ensures that the final product meets both international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Palletizer Manufacturing?
B2B buyers should be aware of several international standards that govern the quality and safety of palletizers. The ISO 9001 standard is particularly relevant, focusing on quality management systems and continuous improvement. Compliance with CE marking requirements is also essential for products sold in the European Union, indicating that they meet health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Buyers from regions like South America and the Middle East may also encounter local standards that must be adhered to.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is integrated at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, the completed palletizer undergoes rigorous testing to verify its performance, safety, and compliance with specifications.
These QC checkpoints help mitigate risks and ensure that the palletizers delivered to clients are of the highest quality.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
To ensure that palletizers meet the required standards, several testing methods are employed:
- Functional Testing: This involves operating the palletizer under typical working conditions to assess its performance.
- Load Testing: Palletizers are subjected to various load conditions to evaluate their structural integrity and performance under stress.
- Safety Testing: Ensuring that all safety features operate correctly is crucial, especially for equipment used in high-speed environments.
These testing methods help validate the machine’s reliability and safety, providing peace of mind to B2B buyers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential. Here are some strategies to ensure supplier reliability:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their quality assurance practices. These audits can be scheduled or surprise visits to ensure compliance.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline the QC processes, inspection results, and any certifications can help buyers assess a supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide an objective evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures, ensuring that they adhere to international standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing palletizers from international suppliers, buyers should be aware of specific quality control and certification nuances. Different regions may have varying requirements for certifications and compliance. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while buyers in the Middle East may look for compliance with local safety standards.
Additionally, understanding the cultural context of quality assurance practices is essential. In some regions, manufacturers may have differing approaches to quality control, which could affect the final product. Therefore, B2B buyers must conduct thorough research and establish clear communication with suppliers to ensure that all quality expectations are met.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for palletizers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing equipment. Ensuring compliance with international standards and verifying supplier quality control practices will lead to more successful partnerships and reliable operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘palletizer job description’
When sourcing a palletizer job description, it’s essential to ensure that the role is clearly defined to meet your operational needs. This guide provides a systematic checklist to help you create an effective job description that attracts the right candidates while aligning with your business objectives.
Step 1: Identify Key Responsibilities
Outline the primary duties of the palletizer role. This may include operating palletizing equipment, monitoring production flow, and ensuring quality control. Clearly defining these responsibilities helps potential candidates understand what is expected of them and allows for a more targeted recruitment process.
- Focus on Automation: If your operations involve automated palletizing, emphasize the need for technical skills to monitor and troubleshoot equipment.
- Include Safety Protocols: Highlight responsibilities related to adhering to safety standards and maintaining a clean work environment.
Step 2: Define Required Skills and Qualifications
Establish the necessary skills and educational background for the position. This typically includes the ability to operate heavy machinery, attention to detail, and basic math skills.
- Technical Proficiency: Candidates should be familiar with various palletizing equipment and material handling tools.
- Physical Requirements: Specify the physical demands of the job, such as the ability to lift heavy objects and stand for extended periods.
Step 3: Outline Personal Traits
Identify the personal attributes that would contribute to success in the role. This could include teamwork, reliability, and the ability to work in a fast-paced environment.

Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
- Cultural Fit: Emphasize the importance of aligning with your company’s culture and values, which can enhance team dynamics.
- Adaptability: Highlight the need for candidates to adjust to changing production schedules and priorities.
Step 4: Incorporate Quality Control Responsibilities
Detail how the palletizer will engage in quality control measures. This includes inspecting products for defects and ensuring compliance with safety and sanitation standards.
- Monitoring Procedures: Specify the methods for inspecting products and equipment to maintain high-quality output.
- Reporting Protocols: Define how issues should be communicated to supervisors or management.
Step 5: Establish Performance Metrics
Set clear expectations for performance evaluation. This may involve metrics related to efficiency, accuracy, and adherence to safety protocols.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Consider metrics such as the number of pallets processed per hour and the rate of defects found during inspections.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Outline how feedback will be provided to the palletizer to foster continuous improvement.
Step 6: Review Industry Standards and Compliance
Ensure that the job description aligns with industry standards and regulations. This is particularly important for businesses operating in regions with strict labor laws.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with local labor laws and safety regulations to avoid legal pitfalls.
- Best Practices: Research industry benchmarks for palletizer roles to ensure your job description is competitive and comprehensive.
Step 7: Solicit Input from Current Employees
Engage with existing palletizer operators or supervisors to gather insights on the role’s requirements. Their practical experience can help refine the job description.
- Gather Feedback: Conduct interviews or surveys to understand daily challenges and essential skills that may not be immediately apparent.
- Continuous Improvement: Use this feedback to update and improve the job description regularly, ensuring it remains relevant and effective.
By following this checklist, you can create a comprehensive and effective palletizer job description that not only attracts qualified candidates but also enhances your operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for palletizer job description Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing a Palletizer Job Description?
When sourcing a palletizer job description, several cost components come into play that can significantly influence your overall expenditure. Understanding these components is crucial for making informed decisions.
-
Materials: This includes the cost of any specific equipment or technology required for the palletizer role, such as automated palletizing machines, conveyors, and safety gear. The materials can vary widely in price based on their specifications and the technology level, impacting the initial investment.
-
Labor: Labor costs are often one of the most significant components. This includes salaries or wages for palletizer operators, training costs, and potential overtime. In regions such as Africa and South America, labor costs can differ greatly due to local economic conditions and labor laws.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with the production of goods, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. It is essential to factor these costs into your pricing analysis to understand the true cost of hiring palletizer operators.
-
Tooling: Depending on the complexity of the palletizing process, there may be additional tooling costs involved. These could include specialized tools for equipment maintenance or custom fixtures that enhance the efficiency of the palletizing operations.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing quality control measures to ensure the palletizing process meets safety and efficiency standards incurs costs. This includes both the personnel required for QC checks and any technology used for monitoring and maintaining quality.
-
Logistics: This involves costs related to the transportation of materials, equipment, and personnel. International buyers must consider additional logistics expenses tied to cross-border shipping, customs clearance, and local distribution.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers will include a profit margin on top of all costs. This margin can vary significantly depending on the supplier’s market position, competition, and perceived value of their services.
What Influences Pricing for Palletizer Job Descriptions?
Several factors can influence the pricing of palletizer job descriptions, which buyers should be aware of when negotiating contracts.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate pricing based on anticipated volumes, as suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized palletizer solutions may incur higher costs due to specialized equipment or specific training requirements. Buyers should assess whether customization is essential or if standard solutions suffice.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The quality of materials used in palletizing equipment and the certifications held by suppliers can significantly affect pricing. Higher quality and certified suppliers often command premium prices, but they may also provide better reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more but can offer better service and product quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international buyers. These terms dictate responsibilities for shipping costs, insurance, and liability, which can impact the total cost of ownership.
How Can Buyers Negotiate and Improve Cost-Efficiency?
-
Effective Negotiation Strategies: Buyers should prepare for negotiations by understanding market prices and competitor offerings. Leverage existing relationships with suppliers to negotiate better terms and prices.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When assessing costs, consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import taxes, and tariffs that can affect overall costs. Local regulations and labor costs should also be considered when sourcing palletizer job descriptions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for palletizer job descriptions can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making the most cost-effective decision for their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing palletizer job description With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Palletizer Job Descriptions
In the realm of warehouse operations and logistics, the role of palletizers is crucial for efficient product handling and storage. However, businesses often face challenges in optimizing this process. Exploring alternatives to traditional palletizer job roles can provide viable solutions that enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency. Below is a comparative analysis of the palletizer job description against two alternative solutions: Automated Palletizing Systems and Manual Labor Methods.
| Comparison Aspect | Palletizer Job Description | Automated Palletizing Systems | Manual Labor Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable but can be prone to human error | High efficiency and consistent output | Varies widely based on workforce skill and training |
| Cost | Lower initial investment but higher labor costs | Higher upfront cost, lower long-term labor costs | Minimal capital investment, but higher ongoing labor costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training and adaptation | Complex setup but can be integrated with existing systems | Simple and straightforward, minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance for machines; human oversight needed | Requires specialized maintenance and monitoring | Minimal maintenance, reliant on workforce availability |
| Best Use Case | Suitable for low to moderate throughput operations | Ideal for high-volume, repetitive tasks | Effective for small-scale operations or variable workloads |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Automated Palletizing Systems?
Automated palletizing systems represent a significant advancement in warehouse operations, offering high efficiency and consistent performance. These systems can handle large volumes of products with precision and speed, reducing labor costs over time. However, the initial investment can be substantial, and the complexity of the technology may require specialized training for operators and technicians. Additionally, while automation minimizes human error, it does introduce a reliance on technology that can lead to operational disruptions if equipment malfunctions.
How Do Manual Labor Methods Compare to Palletizer Job Descriptions?
Manual labor methods involve human workers physically stacking and organizing products onto pallets. This approach can be advantageous for smaller operations or businesses with fluctuating demand, as it allows for flexibility in workforce management. The costs associated with manual labor are typically lower in terms of initial investment; however, the ongoing labor costs can add up, especially in regions with higher wage standards. The effectiveness of manual methods heavily relies on the skill and training of the workforce, which can lead to variability in performance and potential safety concerns.
Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the appropriate solution for palletizing operations, B2B buyers should consider several factors including volume of goods, budget constraints, and the specific operational environment. For high-volume operations with consistent product flows, automated palletizing systems may offer the best long-term value despite their higher upfront costs. Conversely, businesses with variable workloads or lower volumes may benefit from the flexibility of manual labor methods. Ultimately, a thorough assessment of operational needs and future growth potential will guide buyers to the most suitable palletizing solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for palletizer job description
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Palletizers?
In the realm of palletizer job descriptions, understanding the critical technical properties is essential for ensuring efficiency, safety, and compliance in operations. Here are some key specifications:
-
Load Capacity
This refers to the maximum weight a palletizer can handle at one time. It is crucial for B2B buyers to assess this specification to ensure the equipment can accommodate their specific product types and volumes. Overloading can lead to equipment failure and safety hazards, making it vital to choose a palletizer that aligns with operational needs. -
Speed of Operation
Measured in cycles per minute (CPM), the speed at which a palletizer can stack products directly affects productivity. Higher speeds can lead to increased throughput, allowing businesses to meet tight delivery schedules. Understanding the operational speed helps companies make informed decisions about their production capabilities. -
Footprint Dimensions
The physical dimensions of a palletizer (length, width, height) are important for space management within a facility. Companies must consider their warehouse layout when selecting equipment to ensure that the palletizer fits within existing workflows without causing congestion or inefficiencies. -
Energy Consumption
This property indicates the amount of power the palletizer requires to operate effectively. In regions with high energy costs, such as parts of Europe and the Middle East, energy-efficient machines can lead to significant cost savings over time. Buyers should look for machines with energy-efficient ratings to optimize operational expenses. -
Material Grade
The construction material of a palletizer affects its durability and maintenance needs. Common materials include stainless steel, which is resistant to corrosion and easier to clean, making it ideal for food and beverage applications. Understanding the material grade helps businesses evaluate long-term investment costs versus maintenance expenditures. -
Automation Level
This specification indicates whether a palletizer is manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic. Fully automated systems can significantly reduce labor costs and improve consistency in operations. Buyers must align the automation level with their workforce capabilities and production goals.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Palletizer Job Descriptions?
In addition to technical specifications, familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking for reliable sources of replacement parts or upgrades, ensuring compatibility and quality. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important for B2B buyers who want to manage inventory costs effectively. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases to avoid excess inventory or stock shortages. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specified goods or services. This process is crucial for buyers seeking competitive pricing and understanding the market. A well-crafted RFQ can lead to better deals and optimized procurement strategies. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers navigate cross-border logistics, ensuring compliance and reducing risks during shipping. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with acquiring and operating a piece of equipment over its lifespan, including purchase price, maintenance, energy costs, and disposal. Understanding TCO is essential for B2B buyers to make informed investment decisions that align with budgetary constraints. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for supply chain management, helping businesses plan their production schedules and inventory levels effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and support strategic goals in their palletizing processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the palletizer job description Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting the Palletizer Job Description Sector?
The palletizer job description sector is evolving rapidly, driven by globalization, technological advancements, and a growing demand for efficiency in supply chains. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Germany and Saudi Arabia) seek to optimize their operations, the focus is shifting towards automation and smart technologies. Automated palletizers are becoming increasingly prevalent, allowing companies to enhance productivity while minimizing labor costs. This trend is complemented by the rise of Industry 4.0, where data analytics, IoT, and machine learning are integrated into logistics and manufacturing processes, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of palletizing equipment.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a critical factor in sourcing decisions. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices, such as using recyclable materials and energy-efficient machinery. This shift not only meets consumer demand for sustainability but also aligns with regulatory requirements in various regions, particularly in Europe, where stringent environmental policies are in place.
Additionally, the current geopolitical landscape and economic fluctuations are influencing sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly looking for local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global supply chains, such as shipping delays and tariff implications. Understanding these dynamics is essential for international buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing palletizer roles effectively.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Palletizer Job Description Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount in the palletizer job description sector, reflecting a broader shift in global business practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing and logistics is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt greener practices. For palletizer operations, this means investing in energy-efficient machines and exploring alternative materials that reduce waste and carbon footprints.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers to ensure they adhere to labor laws and fair trade practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming essential criteria for suppliers in the palletizing industry. This not only enhances a company’s brand reputation but also fosters trust among consumers and stakeholders.
As the demand for “green” certifications grows, buyers should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability through certifications and transparent reporting. This approach not only contributes to environmental goals but also positions companies favorably in a competitive market increasingly influenced by consumer preferences for ethical practices.
What Is the Evolution of the Palletizer Job Description Sector?
The palletizer job description sector has undergone significant evolution over the past few decades, transitioning from manual processes to highly automated systems. Initially, palletizing was a labor-intensive task, with workers manually stacking products onto pallets. However, the introduction of automated palletizing machines revolutionized the industry, drastically improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.

Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
In recent years, the integration of advanced technologies such as robotics and artificial intelligence has further transformed palletizing operations. Modern palletizers can now adapt to various product types and sizes, optimize stacking patterns in real-time, and even communicate with other equipment within the supply chain. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards automation and smart manufacturing, enabling companies to streamline their operations and respond more agilely to market demands.
As the sector continues to evolve, understanding these historical shifts is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to invest in palletizing solutions that enhance productivity while aligning with sustainability goals and ethical sourcing practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of palletizer job description
-
How do I ensure the palletizer job description meets my operational needs?
To tailor a palletizer job description to your operational needs, start by analyzing your workflow requirements and production volume. Define specific responsibilities such as machine operation, quality control, and safety compliance. Additionally, consider the skill set required, including experience with automated systems and physical capabilities for handling heavy loads. Collaborate with your HR team or a recruitment specialist to ensure the job description attracts candidates who align with your business goals and culture. -
What is the best way to evaluate potential palletizer candidates?
When evaluating candidates for a palletizer position, focus on both technical skills and soft skills. Assess their experience with palletizing equipment and their ability to perform quality control checks. Use practical assessments to gauge their proficiency in machine operation and troubleshooting. Additionally, consider their teamwork and communication skills, as these are vital for maintaining a safe and efficient work environment. Structured interviews and reference checks can also provide insights into their reliability and past performance. -
What are the key components of a comprehensive palletizer job description?
A comprehensive palletizer job description should include the job title, purpose, key responsibilities, required skills, qualifications, and working conditions. Highlight essential duties such as operating palletizing equipment, conducting quality checks, and maintaining safety standards. Specify educational requirements, like a high school diploma or equivalent, and mention any necessary certifications or training in material handling. Including information about the work environment, such as physical demands and shift patterns, can also help attract suitable candidates. -
How can I customize a palletizer job description for different regions?
To customize a palletizer job description for different regions, consider local labor laws, cultural expectations, and market conditions. Research the specific skills and qualifications that are prevalent in each region, as these may vary significantly. For instance, in Europe, certifications related to machinery operation may be essential, whereas in Africa or South America, experience with manual processes might be more relevant. Tailor the language and benefits offered to align with regional preferences to attract the right candidates. -
What factors should I consider when setting minimum order quantities (MOQ) for palletizers?
When setting MOQs for palletizers, consider factors like production capacity, storage space, and the financial implications of bulk purchases. Assess your operational needs and forecast demand to determine an appropriate MOQ that ensures efficiency without overcommitting resources. Additionally, evaluate supplier capabilities and their willingness to accommodate smaller orders, especially if you are exploring new suppliers or entering a new market. Balancing cost efficiency with flexibility is key to optimizing your procurement strategy. -
How do payment terms affect my procurement of palletizers?
Payment terms can significantly impact your cash flow and overall procurement strategy for palletizers. Common terms include advance payments, net 30, or net 60 days. Assess your financial situation and negotiate terms that allow for adequate cash flow while minimizing financial risk. Opt for terms that align with your operational cycle, ensuring you can meet payments without straining your budget. Additionally, consider the supplier’s reliability and reputation, as favorable terms often come with established, trustworthy partners. -
What quality assurance practices should I implement when sourcing palletizers?
Implementing robust quality assurance practices when sourcing palletizers involves conducting thorough supplier audits and requiring certifications related to safety and machinery standards. Establish a clear set of quality metrics to evaluate the performance of the palletizers upon delivery. Consider requesting samples or conducting site visits to assess the equipment’s performance in a real-world setting. Regular communication with your supplier about quality expectations and continuous monitoring can help ensure consistent product quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing palletizers?
When importing palletizers, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who understands the complexities of international shipping and can navigate customs efficiently. Consider the total landed cost, which includes shipping, duties, and handling fees. Additionally, plan for storage and installation at your facility, ensuring that your supply chain can accommodate the arrival of the equipment without disrupting operations. Proper logistics planning can minimize delays and reduce costs associated with importation.
Top 9 Palletizer Job Description Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Palletizer Operator – Job Overview
Domain: dot-job-descriptions.careerplanner.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Job Title: PALLETIZER OPERATOR I
Job Description: Operates console that controls automatic palletizing equipment to sort, transfer, and stack on pallets containers of finished products, such as sugar, canned vegetables, citrus juice, and cigarettes. Responsibilities include reading production and delivery schedules, observing packages on conveyor, controlling stacking arrangement, supplying loadin…
2. HiringPeople – Palletizer Job Overview
Domain: hiringpeople.io
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Palletizer job involves loading products onto pallets for storage and transport. Responsibilities include operating palletizing equipment, ensuring proper stacking of products, adhering to safety regulations, inspecting product boxes for defects, and maintaining a clean work environment. Skills required are attention to detail, ability to lift up to 50 lbs, and operating material handling equipmen…
3. Robopac USA – Palletizer Machines
Domain: robopacusa.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Robopac USA offers palletizer machines designed to optimize secondary packaging workflows. These machines automate the palletizing process, allowing for efficient movement and stacking of products. Key roles of a palletizer operator include monitoring machine operation, assisting with quality control, adhering to safety requirements, and performing machine changeovers to ensure smooth workflow and…
4. Siouxland Chamber – Palletizer Position
Domain: directory.siouxlandchamber.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Position: Palletizer
Posted: 08/17/2025
Responsibilities: Operate box conveyors, accumulation, palletizing, stretch wrap, pallet accumulation, pallet labeling, and reject area. Maintain machinery and ensure packaging material availability. Oversee product from the plant via conveyor system, maintain product regulation, and ensure pallet accuracy for freezer. Correct palletizer malfunctions and mai…
5. Owens Corning – Manual Labor Positions
Domain: careers.owenscorning.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Owens Corning – Manual Labor Positions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Palletizer – Automated Equipment Operator
Domain: qwikresume.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Palletizer is a machine operator responsible for controlling automated palletizing equipment that sorts and stacks pallet containers on finished products. Key duties include reading production schedules, identifying defective packaging, supplying loading equipment with empty pallets, operating depalletizing equipment, clearing jams, and observing packages on conveyors. Skills required are knowledg…
7. Palletizer/Operator – Sustainable Packaging
Domain: jobs.ball.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: Palletizer/Operator position at Ball Corporation in Milton Keynes, UK. The role involves supporting the production of sustainable aluminium packaging products, including recyclable aluminium cans, cups, and aerosol bottles. Starting salary is £32,500 per annum, increasing to £35,000 and then £37,500 upon skill matrix completion. The position requires shift work (12-hour shifts) and emphasizes safe…
8. Seneca Foods – Packaged Fruits and Vegetables
Domain: careers.senecafoods.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Seneca Foods is a leading provider of packaged fruits and vegetables in North America, sourcing products from over 1,400 American farms. The company holds the largest share of the retail private label, food service, and export canned vegetable markets, distributing to over 90 countries. Products are sold under various brands including Libby’s®, Aunt Nellie’s®, READ®, Seneca Farms®, Green Valley®, …
9. Simmons Pet Food – Palletizer Operator
Domain: accessdubuquejobs.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Job Title: Palletizer Operator
Shift: Day Shift – A Shift (Mon-Wed 6a-6p; Thur 6a-12p)
Company: Simmons Pet Food
Location: Dubuque, IA
Positions Available: 1
Job Overview: Responsible for producing pallets of properly stacked product, ensuring quality and efficiency in the palletizing process.
Essential Responsibilities:
– Operate and troubleshoot palletizing machines.
– Ensure quality of finishe…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for palletizer job description
As businesses navigate the complexities of logistics and supply chain management, understanding the pivotal role of palletizers becomes increasingly critical. Effective palletizer job descriptions should highlight the importance of operational efficiency, safety compliance, and quality control. By strategically sourcing skilled palletizer operators, companies can enhance their productivity and ensure that their products are securely packaged for transport.
Investing in trained personnel not only improves workflow but also mitigates risks associated with equipment malfunction and product damage. The ability to adapt to automated systems while maintaining high standards of operational excellence is essential in today’s competitive landscape.
Looking ahead, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize the strategic sourcing of palletizer roles as part of their logistics strategy. By aligning workforce capabilities with advanced technology, businesses can foster a resilient supply chain. Seize the opportunity to enhance your operational effectiveness today—review your sourcing strategies and ensure your workforce is equipped to meet the demands of tomorrow’s marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to palletizer job description
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.