A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Glycol For Chiller Systems: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for glycol for chiller systems
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial cooling, sourcing the right glycol for chiller systems is crucial for maintaining efficiency and minimizing operational costs. With a variety of formulations available, international B2B buyers often face the challenge of identifying the most suitable glycol type for their specific applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of glycol selection, covering key aspects such as types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations. By addressing common pitfalls and best practices, this resource empowers decision-makers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Nigeria and Vietnam—to make informed purchasing choices.
Understanding the specific requirements of your chiller system is paramount, as the right glycol not only enhances heat transfer efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with corrosion and biological fouling. This guide will provide actionable insights into the importance of using inhibited glycols, the implications of mixing ratios, and the need for regular fluid management. Additionally, we will explore how to navigate local regulations and environmental considerations, ensuring compliance while optimizing system performance. With a focus on practical solutions and expert recommendations, this guide serves as an essential tool for B2B buyers aiming to enhance their cooling systems and drive operational excellence.
Understanding glycol for chiller systems Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethylene Glycol | High heat transfer efficiency; toxic to humans and animals | Industrial cooling, HVAC systems | Pros: Excellent heat transfer, widely used. Cons: Toxicity limits applications in food/beverage. |
| Propylene Glycol | Non-toxic, less efficient heat transfer; more viscous | Food and beverage processing, HVAC systems | Pros: Safe for food use, non-toxic. Cons: Lower heat transfer efficiency, higher viscosity. |
| Coolflow DTX™ | Combines thermal efficiency of ethylene glycol with non-toxicity | Food and cold storage systems | Pros: High performance, non-toxic, low viscosity. Cons: May be more expensive than traditional options. |
| Inhibited Glycol | Contains corrosion inhibitors; protects multi-metal systems | General industrial applications | Pros: Prevents corrosion, scaling, and fouling. Cons: Requires careful monitoring and maintenance. |
| Automotive Antifreeze | Not suitable for industrial chillers; contains silicates | Not recommended for chiller systems | Pros: Generally lower cost. Cons: Reduces heat transfer efficiency, risks gel formation. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Ethylene Glycol for B2B buyers?
Ethylene glycol is renowned for its superior heat transfer properties, making it a preferred choice in many industrial applications. Its high efficiency in transferring heat is particularly beneficial in large-scale cooling systems, such as those found in manufacturing and HVAC. However, its toxicity poses a significant risk in environments where human or animal contact is possible, limiting its use in the food and beverage sectors. B2B buyers should consider their operational environment and safety regulations when selecting this type of glycol.
How does Propylene Glycol meet the needs of food and beverage industries?
Propylene glycol is formulated to be non-toxic, making it an ideal choice for applications involving food and beverage processing. While it is less efficient in heat transfer compared to ethylene glycol, its safety profile allows for its use in systems where direct contact with consumables occurs. Buyers in these sectors should weigh the trade-offs between heat transfer efficiency and safety, particularly if their operations involve frequent handling of the fluid.
Why is Coolflow DTX™ a game-changer for food and cold storage applications?
Coolflow DTX™ is a high-performance fluid that merges the thermal efficiency of ethylene glycol with the non-toxic attributes of propylene glycol. This innovative formulation has gained traction in food and cold storage sectors, where both performance and safety are paramount. Buyers should consider this option for its ability to maintain optimal cooling efficiency while adhering to health and safety standards, although it may come at a higher initial cost.
What makes Inhibited Glycol crucial for maintaining industrial systems?
Inhibited glycol formulations are designed to include corrosion inhibitors that protect multi-metal systems from damage. This is particularly important in industries where equipment longevity and reliability are critical. B2B buyers must recognize the need for regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure that the inhibitors remain effective over time, as neglecting this can lead to costly repairs and downtime.
Why should automotive antifreeze be avoided in chiller systems?
Automotive antifreeze is typically not suitable for industrial chiller systems due to its formulation, which often includes silicates that can lead to reduced heat transfer efficiency and potential gel formation. For B2B buyers, using automotive antifreeze can result in increased operational costs due to frequent maintenance and system failures. It is advisable to invest in specifically formulated glycols that are designed for industrial applications to ensure optimal system performance and reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of glycol for chiller systems
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of glycol for chiller systems | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Process cooling in food manufacturing | Maintains product quality and safety by preventing microbial growth | Ensure propylene glycol is used for non-toxicity; verify compliance with food safety regulations. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Temperature control in drug manufacturing | Ensures stability and efficacy of temperature-sensitive products | Select glycol with stringent purity standards; consider local regulations on disposal. |
| HVAC Systems | Chilled water systems for commercial buildings | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces operational costs | Source inhibited glycol to prevent corrosion; analyze local water quality to determine optimal mix. |
| Data Centers | Cooling systems for server rooms and data centers | Prevents overheating, ensuring uptime and data integrity | Opt for high-performance glycol solutions; regular fluid analysis is crucial for system longevity. |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Process cooling in various manufacturing operations | Improves machinery efficiency and reduces downtime | Assess compatibility with existing systems; focus on multi-metal inhibitor formulations. |
How is Glycol Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, glycol is primarily used for process cooling, where it helps maintain optimal temperatures during production and storage. This application is critical for preserving product quality and preventing the growth of harmful microorganisms. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing propylene glycol is essential due to its non-toxic nature, which aligns with stringent food safety regulations. Buyers must ensure that the glycol formulation meets local compliance standards to avoid any health risks.
What Role Does Glycol Play in Pharmaceuticals?
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, glycol is utilized for precise temperature control, especially for products sensitive to temperature fluctuations. This application is crucial in maintaining the stability and efficacy of drugs during production and storage. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it is vital to select high-purity glycol that adheres to industry-specific regulations. Additionally, understanding local disposal regulations is essential to ensure compliance and sustainability in operations.
How Does Glycol Enhance HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, glycol serves as a heat transfer fluid in chilled water systems for commercial buildings. It plays a significant role in improving energy efficiency, which translates to reduced operational costs. For buyers in Europe and Africa, sourcing inhibited glycol is crucial to prevent internal corrosion and scaling. Analyzing local water quality helps determine the appropriate glycol-to-water mix, ensuring optimal system performance and longevity.
Why is Glycol Important for Data Centers?
Data centers rely on glycol for cooling systems that prevent overheating of servers and critical equipment. The effective use of glycol ensures uptime and protects data integrity, which is vital for businesses operating in high-demand environments. For B2B buyers in regions like Nigeria and Vietnam, selecting high-performance glycol solutions is essential. Regular fluid analysis and monitoring are also recommended to extend system life and maintain cooling efficiency.
What is the Importance of Glycol in Industrial Manufacturing?
In industrial manufacturing, glycol is used for process cooling across various operations, enhancing machinery efficiency and minimizing downtime. This application is critical for maintaining optimal operating conditions, which can significantly impact production output. Buyers should assess the compatibility of glycol with existing systems and focus on formulations with multi-metal inhibitors to prevent corrosion. Understanding the specific requirements of their operations will enable buyers to make informed decisions on glycol sourcing.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘glycol for chiller systems’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Glycol Performance and Efficiency Issues
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of inconsistent performance in their chiller systems due to improper glycol selection and usage. A common scenario involves using automotive antifreeze instead of industrial-grade glycol. This leads to a significant reduction in heat transfer efficiency, as the silicate-based inhibitors in automotive products can coat metal surfaces, creating a barrier that hampers heat exchange. Additionally, these products can cause gel formation, pump seal failures, and ultimately, increased downtime, all of which lead to higher operational costs and compromised system reliability.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should source and utilize specifically formulated industrial glycols designed for chiller systems. It’s crucial to select inhibited glycol solutions that include multi-metal and multi-function inhibitors to prevent corrosion and scaling. For most industrial applications, ethylene glycol is recommended due to its superior heat transfer properties. However, for food and beverage industries, propylene glycol is a safer alternative. Buyers should ensure that the glycol mix is maintained at the correct concentration, typically around 25% v/v, to balance freeze protection and thermal efficiency. Regular analysis of glycol performance can help identify any deterioration in efficacy and allow for timely adjustments.
Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
Scenario 2: Costly Maintenance and Downtime from Poor Fluid Management
The Problem: Another prevalent pain point is the high cost of maintenance and unexpected downtime caused by inadequate fluid management in chiller systems. Over time, chiller operators may neglect the monitoring of glycol quality, leading to issues like biological fouling, corrosion, and sediment buildup. This neglect can severely impact heat transfer efficiency and increase energy consumption, resulting in exorbitant operating costs and potential system failures that disrupt production.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, businesses should implement a proactive fluid management strategy. This involves conducting regular fluid analyses to monitor the condition of the glycol and identify any contaminants or degradation. Partnering with a supplier that offers a comprehensive Fluid Monitoring Program (FMP) can streamline this process. Moreover, establishing a routine maintenance schedule that includes checking the glycol concentration and replenishing inhibitors can significantly enhance system performance and lifespan. By investing in these preventative measures, companies can reduce the frequency and severity of maintenance issues, ultimately lowering operational costs.
Scenario 3: Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Concerns
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the complexities of adhering to local environmental regulations concerning the disposal and use of glycol in chiller systems. In regions like Africa and South America, where regulations may be strict or vary widely, failure to comply can result in significant legal penalties, financial loss, and damage to reputation. Additionally, the environmental impact of improperly disposed fluids poses a serious concern, leading to heightened scrutiny from stakeholders and the public.
The Solution: To navigate these regulatory challenges, buyers should stay informed about local environmental laws and guidelines related to glycol usage and disposal. Collaborating with suppliers who are knowledgeable about regional regulations can provide critical insights and support. Buyers should also consider using biodegradable or less toxic alternatives where possible, such as certain formulations of propylene glycol, which can minimize environmental impact. Implementing a robust disposal plan that aligns with local regulations is essential. This may include partnering with certified waste disposal companies that specialize in handling industrial fluids. By prioritizing compliance and sustainability, businesses can not only avoid penalties but also enhance their brand reputation in increasingly eco-conscious markets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for glycol for chiller systems
What Are the Key Properties of Glycol Materials for Chiller Systems?
When selecting glycol for chiller systems, understanding the properties of various glycol formulations is crucial for optimizing system performance and longevity. Below, we analyze three common glycol materials: Ethylene Glycol (EG), Propylene Glycol (PG), and Coolflow DTX™. Each has its unique characteristics that can significantly impact operational efficiency and compliance with international standards.
Ethylene Glycol (EG)
Key Properties: Ethylene glycol is known for its excellent heat transfer capabilities and low freezing point, making it ideal for industrial applications. It typically operates effectively at temperatures ranging from -40°C to 150°C, with a high boiling point that supports efficient thermal management.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of EG is its superior heat transfer efficiency, which can enhance system performance and reduce energy consumption. However, its toxicity poses a significant drawback, making it unsuitable for food and beverage applications or environments with potential human contact. Additionally, EG formulations require careful handling and disposal due to environmental regulations.
Impact on Application: Ethylene glycol is compatible with various metals, but its corrosive nature necessitates the use of multi-metal inhibitors to prevent damage to the chiller system.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions such as Africa and South America should be aware of local regulations regarding the use and disposal of toxic materials. Compliance with standards like ASTM D1384 is essential for ensuring product safety and performance.
Propylene Glycol (PG)
Key Properties: Propylene glycol is a non-toxic alternative to ethylene glycol, with a lower heat transfer efficiency but greater safety for food-related applications. It operates effectively at temperatures from -30°C to 120°C.
Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of PG is its non-toxic nature, making it suitable for food and beverage processing. However, its lower thermal efficiency and higher viscosity at low temperatures can lead to increased pumping costs and reduced system performance.
Impact on Application: While PG is safe for human contact, its lower heat transfer capacity means that systems using PG may require larger volumes or more frequent maintenance to achieve desired performance levels.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must verify compliance with local food safety standards and regulations. In regions like the Middle East and Europe, certifications for food-grade materials are critical for market acceptance.
Coolflow DTX™
Key Properties: Coolflow DTX™ combines the thermal efficiency of ethylene glycol with the non-toxic benefits of propylene glycol. It operates effectively at low temperatures, providing a versatile solution for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of DTX™ is its ability to deliver high performance without the toxicity associated with traditional glycols. However, it may come at a higher cost than standard PG or EG formulations, which could be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: DTX™ is suitable for applications requiring both safety and efficiency, making it ideal for industries like food processing and cold storage.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the product’s certifications and compliance with local environmental regulations, particularly in regions with stringent safety standards like Europe.
Summary Table of Glycol Materials for Chiller Systems
| Material | Typical Use Case for glycol for chiller systems | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethylene Glycol | Industrial cooling systems | Superior heat transfer efficiency | Toxicity limits applications | Medium |
| Propylene Glycol | Food and beverage processing | Non-toxic, safe for human contact | Lower heat transfer efficiency | Medium |
| Coolflow DTX™ | Food processing and cold storage | High performance with non-toxic properties | Higher cost compared to standard glycols | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of glycol options for chiller systems. By considering the unique properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for glycol for chiller systems
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Glycol for Chiller Systems?
The manufacturing process of glycol for chiller systems typically encompasses several key stages that ensure the production of a high-quality end product.
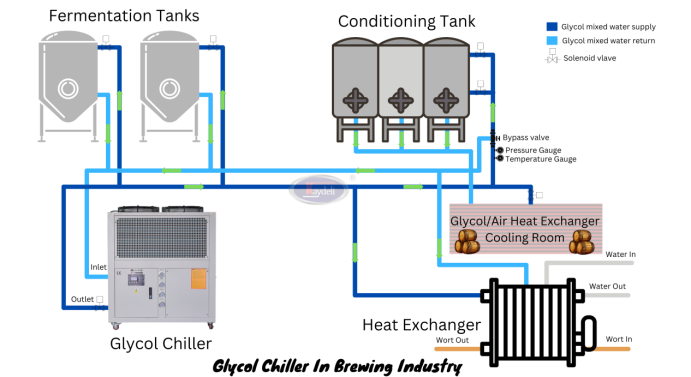
Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
Material Preparation
The first stage involves sourcing raw materials, primarily ethylene or propylene glycol, which are derived from petrochemical processes. High purity water, often deionized, is also essential for blending with glycol to create the desired formulations. Suppliers must ensure that these materials meet strict quality standards to prevent impurities that could affect the performance and stability of the final product.
Forming and Blending
Once the raw materials are prepared, they undergo a blending process where the glycol is mixed with the deionized water in precise ratios. This stage often includes the addition of corrosion inhibitors and other additives to enhance the performance of the glycol solution. Key techniques in this stage include high-shear mixing to ensure uniform distribution of additives and rigorous temperature control to prevent degradation of the glycol.
Quality Control Measures During Manufacturing
Quality control begins at the material preparation stage and continues through each step of the manufacturing process. It is crucial to monitor the blending ratios and the consistency of the mixture. Automated systems may be employed to ensure accuracy, while operators perform regular checks to confirm that the parameters are within specified limits.
Finishing Processes and Packaging
The final stage involves the filtration of the glycol solution to remove any particulate matter, followed by packaging in appropriate containers that prevent contamination. This stage also includes labeling with vital information about the product, including its composition, usage instructions, and safety data.
What International Standards Govern Glycol Manufacturing?
For B2B buyers, understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial when selecting suppliers for glycol products. Various international standards govern the manufacturing processes of glycol for chiller systems, ensuring that products meet safety and performance expectations.

Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
ISO 9001: Quality Management Systems
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers of glycol products must demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. This standard emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, making it a key consideration for B2B buyers.
CE Marking and Other Industry-Specific Standards
In the European market, products may require CE marking to indicate compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Additionally, standards from organizations like the American Petroleum Institute (API) may be relevant for specific formulations of glycol, especially those used in industrial applications. B2B buyers should inquire about compliance with these standards when assessing potential suppliers.
How Is Quality Control Implemented During Glycol Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the glycol manufacturing process, involving multiple checkpoints to ensure the final product’s integrity and performance.

Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
At the IQC stage, incoming raw materials are inspected to verify their quality and compliance with specifications. This includes testing for purity levels and checking for any contaminants that may affect the glycol’s performance. Suppliers should maintain detailed records of these inspections to provide transparency to buyers.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the blending and forming stages, IPQC measures are implemented to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, mixing speed, and blending ratios. Regular sampling and testing during this phase help ensure that the product remains within the desired specifications.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
At the FQC stage, the finished glycol product undergoes comprehensive testing before packaging. This includes evaluating its physical and chemical properties, such as viscosity, pH levels, and thermal conductivity. Additionally, performance tests may be conducted to simulate real-world conditions to verify that the glycol meets the required standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Glycol Products?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and performance of glycol products. B2B buyers should be familiar with these to assess the reliability of their suppliers.
Laboratory Analysis
Laboratory tests play a crucial role in evaluating the properties of glycol solutions. Common tests include:
- Viscosity Measurement: Determines how easily the glycol flows, which affects pump performance.
- Thermal Conductivity Tests: Assesses the heat transfer efficiency of the glycol.
- Corrosion Testing: Evaluates the effectiveness of inhibitors in preventing corrosion within chiller systems.
Field Testing
Field tests may also be conducted to assess the performance of glycol in actual operating conditions. These tests provide valuable insights into how the product will perform in the buyer’s specific application.

Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, establishing trust with suppliers is essential. Here are key strategies to verify supplier QC processes:
Supplier Audits
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Audits allow buyers to review the supplier’s QMS, production processes, and compliance with international standards. A thorough audit can reveal areas of strength and any potential risks.
Quality Reports and Certifications
Requesting quality reports and certifications from suppliers is another crucial step. These documents should detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC tests, along with any relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. These inspections can be particularly valuable for international buyers, ensuring that suppliers meet the required standards and regulations.
What Are the QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate additional complexities related to quality control and compliance when sourcing glycol products.
Regional Regulatory Compliance
Different regions may have specific regulations regarding the use and disposal of glycol products. For example, environmental regulations in Europe may differ significantly from those in Africa or South America. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local laws and regulations to avoid potential liabilities.
Language and Cultural Barriers
Language and cultural differences can pose challenges in communication, particularly when discussing quality control processes. Establishing clear lines of communication and possibly employing local representatives can help mitigate these issues.

Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for glycol products is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on supplier capabilities, compliance with international standards, and effective verification strategies, buyers can ensure they select reliable partners for their chiller system needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘glycol for chiller systems’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers seeking glycol for chiller systems. Glycol plays a critical role in maintaining optimal thermal efficiency and system longevity in cooling applications. Following this checklist will help ensure that you select the right product and supplier to meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s vital to clearly outline your technical requirements. Determine the type of glycol needed—ethylene glycol or propylene glycol—based on the specific application and safety requirements. Consider factors such as the required freeze protection level, viscosity, and compatibility with existing system materials.
Step 2: Understand Local Regulations and Standards
Familiarize yourself with local environmental regulations concerning the use and disposal of glycols. Different regions may have specific guidelines that affect your choice of glycol, especially in food or beverage applications. Ensure that your selected product meets the relevant safety and environmental standards to avoid compliance issues.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs. Request detailed company profiles, product specifications, and case studies that demonstrate their experience in your industry. Additionally, seek references from other businesses in similar sectors or regions to validate their reliability and product quality.

Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
- Supplier Certifications: Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate a commitment to quality management systems.
- Product Testing: Ensure that the supplier conducts regular testing of their glycol products for performance and safety.
Step 4: Assess Product Formulation and Inhibitors
Review the formulation of the glycol products offered by suppliers. Look for inhibited glycol solutions, which are essential for preventing internal corrosion, scaling, and biological fouling in chiller systems. The presence of multi-metal and multi-function inhibitors is critical, as these enhance the fluid’s longevity and efficiency.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your purchase, request samples of the glycol products you’re considering. Conduct performance testing under your operational conditions to assess heat transfer efficiency and system compatibility. This hands-on evaluation can reveal potential issues that may not be apparent from specifications alone.
Step 6: Establish a Maintenance and Monitoring Plan
Implement a proactive maintenance strategy that includes regular monitoring of glycol condition and system performance. Schedule periodic fluid analysis to detect any signs of degradation or contamination early. This practice not only extends the life of the glycol but also enhances the overall efficiency of your chiller system.
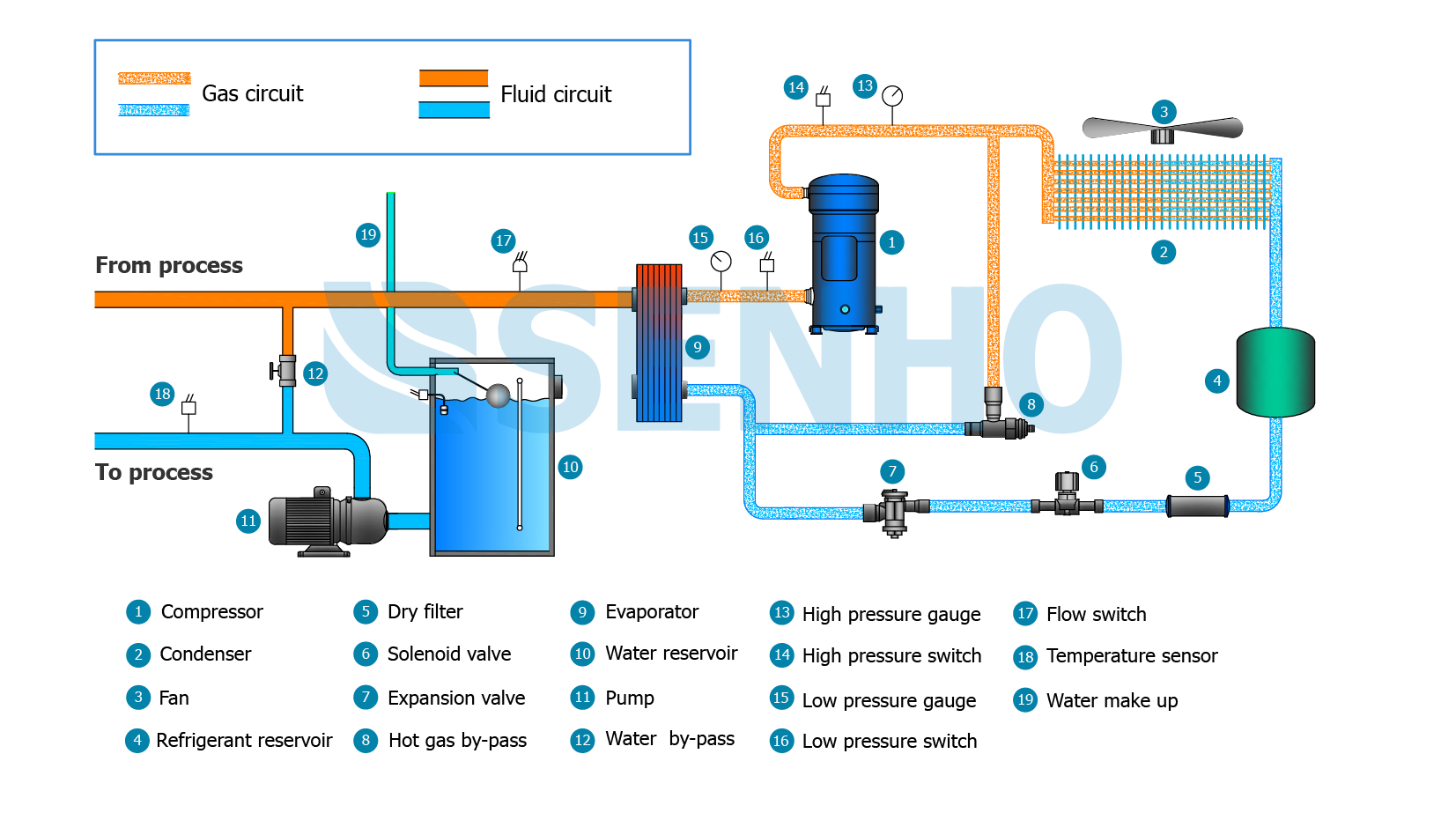
Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Finally, engage in discussions with your selected supplier to negotiate pricing, delivery terms, and support services. Ensure that you clarify warranty conditions and after-sales support, as these factors can significantly impact the long-term value of your investment in glycol for chiller systems.
By following this checklist, you can confidently navigate the procurement process for glycol, ensuring that you choose the right product and supplier to meet your business needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for glycol for chiller systems Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Glycol for Chiller Systems?
When sourcing glycol for chiller systems, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary components include:
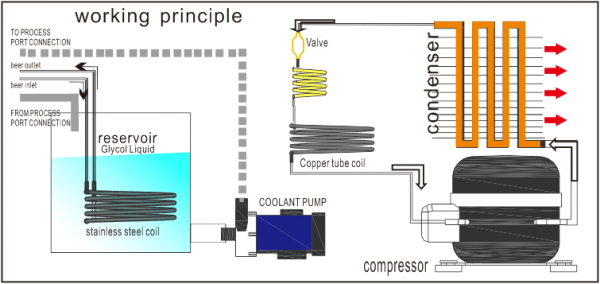
Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
-
Materials: The cost of glycol itself, whether ethylene or propylene, is a significant factor. Ethylene glycol generally offers better heat transfer properties but comes with higher toxicity concerns, while propylene glycol is more expensive due to its non-toxic nature. The purity of the glycol and any additional inhibitors or additives also affect pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both the workforce involved in manufacturing and the technicians required for installation and maintenance. Efficient labor practices can mitigate costs, but specialized skills may demand higher wages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Overhead can vary significantly based on the production scale and location of the manufacturing facility.
-
Tooling: For customized glycol solutions, tooling costs can be substantial. This includes the initial setup for production lines tailored to specific formulations or packaging requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the glycol meets industry standards is crucial, especially for applications in sensitive environments like food processing. QC processes add to the overall cost but are necessary to prevent system failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly based on the distance and method of transport. For international buyers, understanding local tariffs and customs regulations is essential to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a markup to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on competition and market demand.
What Price Influencers Should International Buyers Consider?
Several factors can influence the price of glycol for chiller systems:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to significant discounts, so understanding minimum order quantities (MOQs) can lead to better pricing strategies. Larger quantities reduce per-unit costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom formulations or specific quality certifications may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of these customizations against their budget constraints.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications (like FDA approval for food-grade applications) will generally command higher prices. Buyers should assess their operational requirements to determine the necessary quality level.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their perceived reliability and service quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of sale is critical for international transactions. Different Incoterms (like FOB or CIF) can affect the overall cost structure, including shipping responsibility and risk.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Better Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance negotiation outcomes:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the long-term costs associated with glycol use, including maintenance and operational efficiencies. A cheaper upfront price may lead to higher long-term costs if the product is of inferior quality.
-
Negotiate for Volume Discounts: If your business can commit to larger orders, use this leverage to negotiate better terms. Suppliers often have more flexibility on pricing for bulk orders.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Currency fluctuations can impact pricing, particularly for international transactions. Buyers should consider hedging options or negotiating contracts that account for potential currency risks.
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the local market dynamics can provide insights into fair pricing. Compare quotes from multiple suppliers to gauge competitive pricing.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a reliable partnership with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service terms over time. Loyalty can often yield additional benefits, such as priority support or exclusive offers.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for glycol can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing glycol for chiller systems With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives for Glycol in Chiller Systems
In the realm of cooling technology, glycol has long been a staple for chiller systems, offering effective heat transfer and freeze protection. However, as industries evolve and environmental considerations grow, the search for alternative solutions has gained traction. This section explores viable alternatives to glycol, comparing their performance, costs, maintenance requirements, and best-use cases to help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Glycol For Chiller Systems | Alternative 1: Ammonia Refrigeration | Alternative 2: CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent heat transfer and freeze protection; suitable for various applications | High efficiency, particularly in large-scale systems; excellent heat absorption | Good performance in low-temperature applications; environmentally friendly |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; potential for high long-term maintenance costs | Lower operational costs but high initial investment | Moderate initial investment; low operational costs due to efficiency |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward; requires knowledge of fluid management | Complex installation; requires specialized training and safety measures | Requires technical expertise; installation can be challenging |
| Maintenance | Regular monitoring needed; requires fluid analysis and potential refills | Minimal maintenance but requires regular system checks | Requires regular maintenance; less frequent than glycol but still essential |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for industrial applications where low toxicity is not a concern | Best for large-scale industrial refrigeration needs, like food processing | Suitable for commercial applications focused on sustainability |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Ammonia Refrigeration: What Are the Pros and Cons?
Ammonia (NH3) refrigeration systems are known for their exceptional efficiency and performance, especially in large industrial applications. The primary advantage of ammonia is its low operational cost, which can lead to significant savings over time. However, the initial setup cost is notably higher, and the system requires trained personnel for both installation and maintenance due to ammonia’s toxicity and flammability. This makes ammonia refrigeration a viable option primarily for large-scale operations that can invest in the necessary infrastructure and expertise.
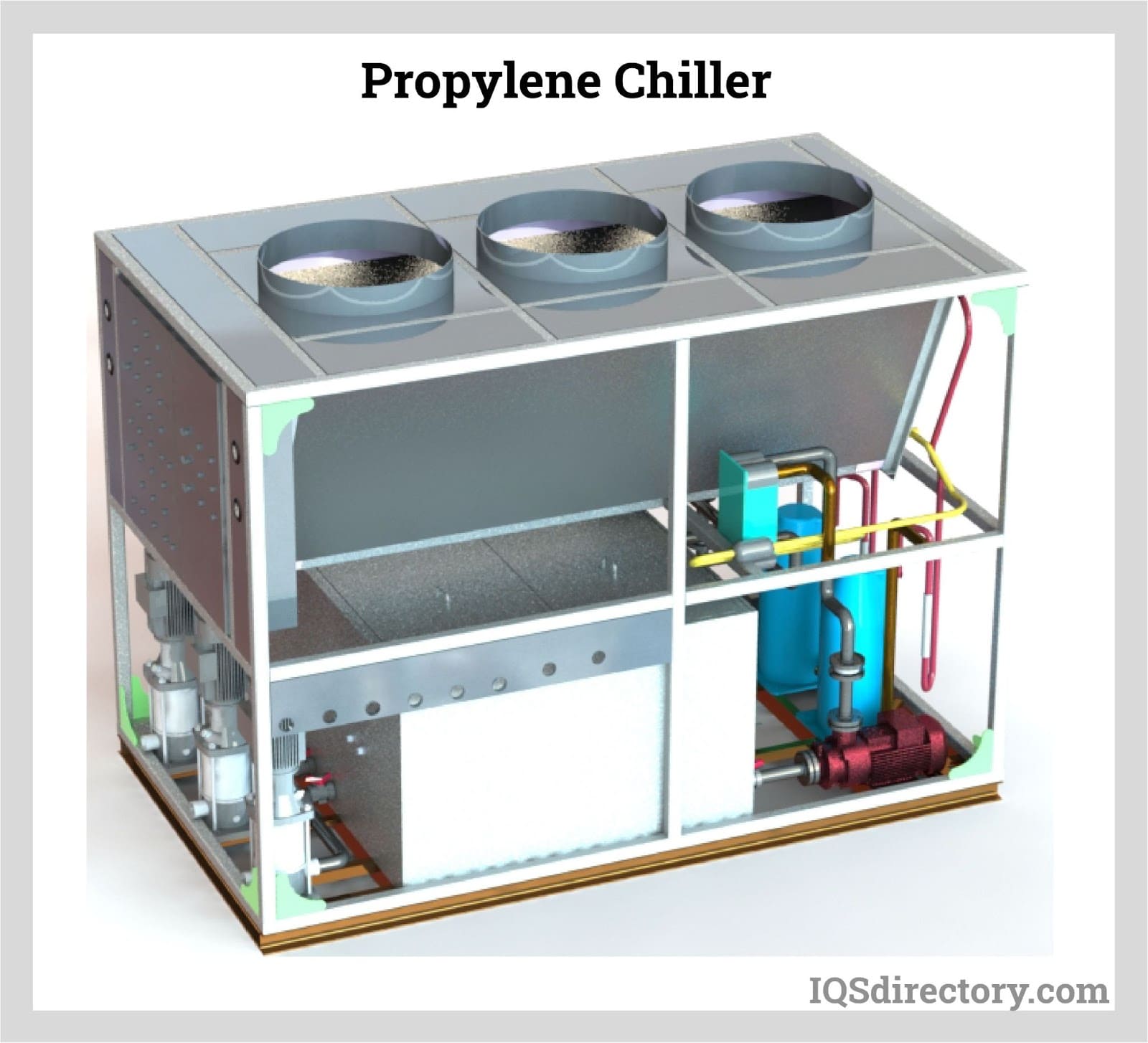
Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) Systems: What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks?
CO2 refrigeration systems are gaining popularity due to their low environmental impact and excellent performance in low-temperature applications. These systems are particularly suitable for commercial settings, such as supermarkets and food storage facilities. While the initial investment is moderate, the operational efficiency can lead to lower energy costs over time. However, CO2 systems can be complex to install and maintain, requiring specialized knowledge. Additionally, they may not be as effective in all scenarios compared to glycol solutions, particularly in applications requiring freeze protection.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the optimal cooling solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the scale of operations, environmental regulations, and long-term cost implications. Glycol remains a strong contender for many industrial applications, particularly where low toxicity is not a concern. However, ammonia and CO2 systems offer compelling alternatives, especially for businesses focused on sustainability and energy efficiency. Evaluating each option’s performance, cost, and maintenance needs can help decision-makers identify the best fit for their specific requirements, ensuring optimal system efficiency and compliance with local regulations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for glycol for chiller systems
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Glycol for Chiller Systems?
Understanding the technical specifications of glycol is essential for optimizing chiller system performance. Here are some critical properties that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures a fluid’s ability to transfer heat. Higher thermal conductivity in glycol formulations means more efficient heat transfer, leading to reduced energy consumption and improved system performance. For industrial applications, selecting a glycol with optimal thermal conductivity can significantly impact overall operational efficiency. -
Freezing Point Depression
Glycol solutions are often used to prevent freezing in chiller systems. The freezing point depression is determined by the concentration of glycol in the solution; for example, a 25% v/v ethylene glycol solution typically offers freeze protection to about -10°C. Understanding this property helps in selecting the right glycol concentration based on the local climate and operational conditions. -
Viscosity
Viscosity indicates a fluid’s resistance to flow. Glycol’s viscosity changes with temperature, affecting pump performance and energy consumption. Low-viscosity glycols are easier to pump and circulate, reducing the risk of system strain and energy losses. Buyers should select a glycol that balances viscosity with thermal efficiency for optimal performance. -
Corrosion Inhibition
Many glycol formulations include multi-metal inhibitors to prevent corrosion within the chiller system. Corrosion can lead to costly repairs and downtime, making corrosion inhibition a crucial property. Buyers should ensure that the glycol used complies with industry standards, such as ASTM D1384, to guarantee protection against corrosion. -
Biological Stability
Biological fouling can occur in chiller systems due to the growth of microorganisms. Glycol solutions should contain inhibitors that prevent biological growth, ensuring system reliability and efficiency. Regular monitoring for biological stability is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent system failures.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Glycol for Chiller Systems?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline communication and negotiations between buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of glycol, knowing the OEM of your chiller system can help you source the appropriate glycol formulations that meet specific system requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, especially for international buyers who may need to purchase larger quantities to meet shipping and cost efficiencies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for glycol can ensure competitive pricing and help establish clear expectations regarding delivery timelines and product specifications. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping agreements. Understanding these terms is vital for international transactions involving glycol, as they dictate who bears the risks and costs associated with transportation. -
TDS (Technical Data Sheet)
A TDS provides detailed information about a product’s specifications, applications, and handling instructions. For glycol products, a TDS is essential for ensuring compatibility with chiller systems and understanding the properties that affect performance. -
Compatibility
Compatibility refers to the ability of a glycol formulation to work effectively with the materials used in a chiller system, including metals and seals. Ensuring compatibility is critical to prevent system failures and maintain efficiency.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting glycol for chiller systems, optimizing performance while minimizing risks and costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the glycol for chiller systems Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Impacting Glycol for Chiller Systems?
The global glycol market for chiller systems is witnessing significant transformation driven by increasing demand for efficient cooling solutions across various sectors, including manufacturing, food and beverage, and HVAC. One of the primary drivers is the rising focus on energy efficiency and the need for reliable temperature control in industrial applications. As businesses become more aware of the operational costs associated with inefficient cooling systems, the preference for high-performance glycol formulations, such as inhibited ethylene and propylene glycol, is growing.
Emerging trends in technology, such as the integration of IoT and data analytics in monitoring cooling systems, are also shaping the market landscape. These advancements allow for real-time analysis and management of glycol systems, enabling operators to optimize fluid management and reduce downtime. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics, including regional regulations and environmental considerations, is essential. For instance, in countries like Nigeria and Vietnam, the local regulatory landscape may dictate specific requirements for fluid disposal, influencing sourcing decisions.
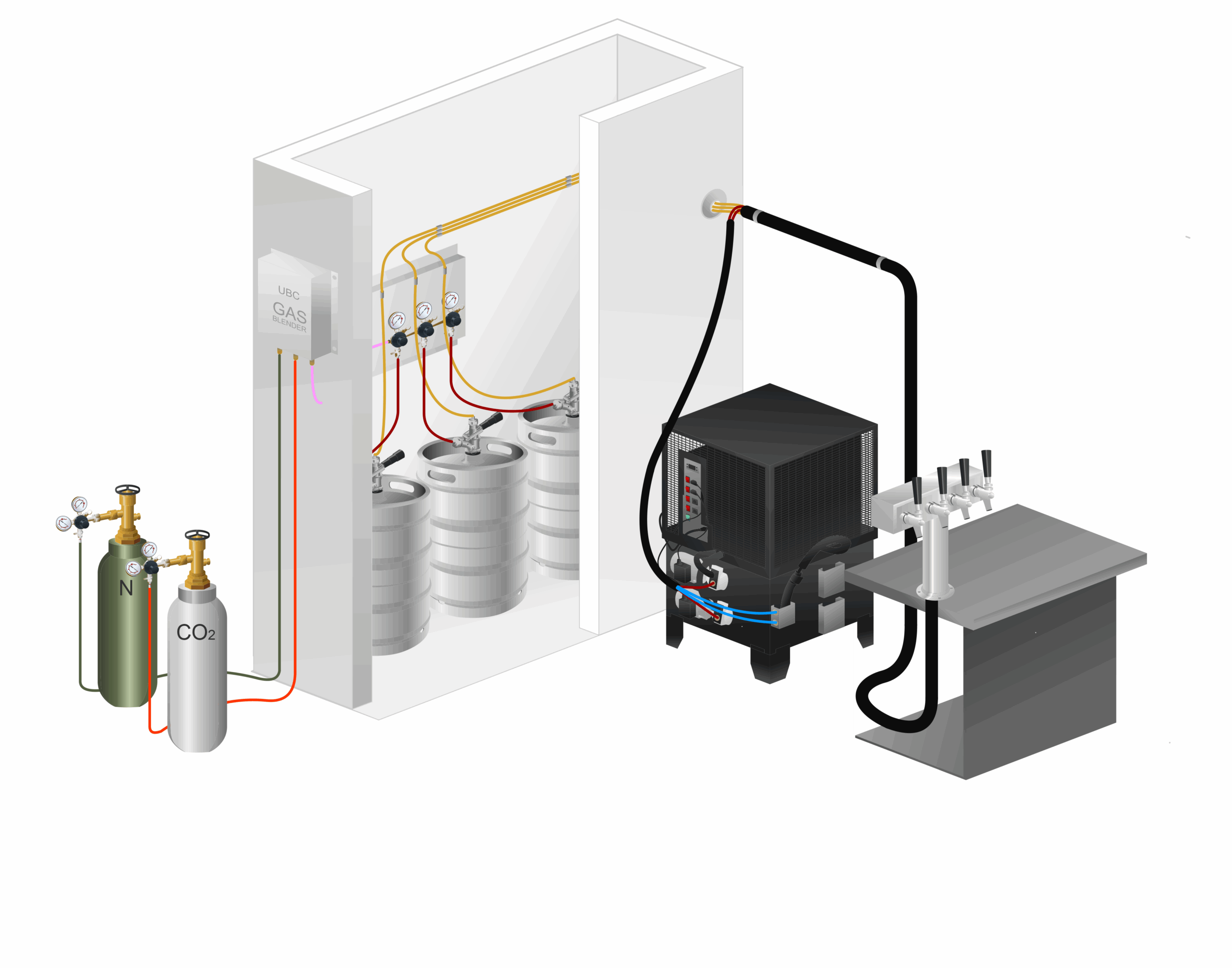
Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
Additionally, there is an increasing trend towards sourcing from suppliers who offer comprehensive support services, including regular fluid analysis and system management, which can significantly enhance system longevity and efficiency. Buyers are now seeking partnerships with suppliers who not only provide high-quality products but also demonstrate a commitment to customer service and technical support.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Glycol Sourcing Decisions in B2B?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the glycol market for chiller systems. As environmental concerns continue to rise, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. The production and disposal of glycol can have significant environmental impacts, particularly if the fluids are not handled responsibly. This has led to a growing demand for “green” certifications and materials, which not only ensure compliance with local regulations but also align with corporate sustainability goals.
In regions like Europe, stringent regulations regarding chemical usage and disposal are pushing companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Suppliers who offer bio-based glycols or those certified for low toxicity are becoming more appealing to buyers focused on minimizing their ecological footprint. For example, propylene glycol is often favored in food and beverage applications due to its lower toxicity compared to ethylene glycol, making it a more ethical choice for industries where human contact is likely.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now looking for transparency in sourcing, which includes understanding the origin of materials and the manufacturing processes involved. Suppliers that can provide detailed information about their sustainability practices and certifications will likely gain a competitive edge in the market.

Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
What Is the Historical Context of Glycol in Chiller Systems?
The use of glycol in chiller systems dates back several decades, evolving significantly as technology and industry standards have progressed. Initially, ethylene glycol was the primary choice due to its superior heat transfer properties. However, concerns over its toxicity have led to increased adoption of propylene glycol, particularly in applications where safety is paramount, such as food and beverage processing.
As the industrial landscape grew more complex, the formulations of glycol began to incorporate various inhibitors to address issues such as corrosion and biological fouling. This evolution has been crucial in enhancing the performance and longevity of cooling systems. Today, the market is characterized by a diverse range of glycol products tailored to meet specific operational needs and regulatory requirements, reflecting the dynamic interplay between technology, safety, and environmental considerations in the industry.
Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers as it highlights the importance of selecting the right glycol formulation for their specific applications, ensuring both optimal performance and compliance with evolving industry standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of glycol for chiller systems
-
How do I solve issues with glycol freeze-up in my chiller system?
To prevent glycol freeze-up, ensure you are using the correct concentration of glycol for your specific climate and application. Typically, a 25% v/v inhibited glycol mix offers freeze protection down to -10°C. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the glycol solution are essential to avoid dilution and maintain the necessary concentration. Additionally, perform periodic analysis of the heat transfer fluid to identify any potential issues before they escalate, and adjust your glycol mix accordingly for optimal protection. -
What is the best glycol for industrial chiller systems?
For most industrial applications, ethylene glycol is preferred due to its superior heat transfer capabilities. However, if toxicity is a concern, especially in food processing, propylene glycol is a safer alternative, albeit with lower heat transfer efficiency. It’s crucial to assess your specific needs, local regulations, and potential exposure risks when selecting the appropriate glycol. Consulting with suppliers can provide insights into the best formulations for your application. -
How can I ensure the quality of glycol products from suppliers?
To ensure quality, vet suppliers by checking their certifications, product testing methods, and adherence to industry standards, such as ASTM D1384. Request product data sheets and safety data sheets (SDS) to understand the composition and performance characteristics. Additionally, look for suppliers who offer regular fluid analysis services to monitor the condition of the glycol and its effectiveness over time, ensuring long-term system performance. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing glycol for chiller systems?
When importing glycol, consider the shipping regulations and customs requirements specific to your region. Ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation, including compliance certificates and safety data sheets. Assess the supplier’s ability to handle logistics, including transportation and storage conditions, to maintain product integrity. It’s also wise to factor in lead times for international shipping, which can impact your operations. -
What customization options are available for glycol formulations?
Many suppliers offer customizable glycol formulations to meet specific operational needs. This may include adjusting the concentration of glycol, selecting specific inhibitor packages, or tailoring the product for unique environmental conditions. Engage with potential suppliers to discuss your requirements, as they may also provide technical support to help optimize the formulation for your chiller system’s performance. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for glycol purchases?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely between suppliers based on their production capabilities and distribution strategies. It’s common for industrial suppliers to have MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness. When negotiating, inquire about flexibility in MOQs, especially if you’re testing a new product or have fluctuating demand. Some suppliers may also offer bulk discounts, which can reduce overall costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing glycol internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers and regions. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or net 30/60 days after delivery. It’s crucial to clarify payment expectations upfront and consider factors such as currency fluctuations and transfer fees. Ensure that you have a clear agreement that protects both parties, especially when dealing with international transactions. -
How often should I analyze glycol fluid for quality assurance?
Regular analysis of glycol fluid is essential for maintaining optimal chiller system performance. It is recommended to conduct fluid testing at least every six months to monitor for corrosion, biological fouling, and concentration levels. Implementing a routine analysis helps identify issues early, allowing for timely corrective actions, thus extending the life of both the glycol and the chiller system. Engaging with suppliers who provide fluid monitoring programs can further enhance your maintenance strategy.
Top 9 Glycol For Chiller Systems Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tower Water – Glycol Solutions
Domain: towerwater.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Glycol is an organic compound used in cooling systems, primarily in two forms: ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. Ethylene glycol offers superior heat transfer efficiency and freeze protection at a lower cost, suitable for closed-loop systems with limited human contact, but is toxic and requires careful handling. Propylene glycol is non-toxic, FDA recognized as safe, and often required by build…
2. AmChiller – Glycol Chillers for Various Applications
Domain: amchiller.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Glycol applications include Brewery Glycol Chillers, Cold Plunge Chillers, Dry Cleaning Chillers, Food & Beverage Chillers, Ice Cream & Yogurt Machine Chillers, Medical Chillers, Plastics Process Chillers, and Winery Glycol Chillers. Recommended glycol type is Inhibited Propylene Glycol, which contains corrosion inhibitors and pipe lubricants. It is non-hazardous and food grade. A 40% propylene gl…
3. MoreBeer – Propylene Glycol Chiller
Domain: morebeer.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, MoreBeer – Propylene Glycol Chiller, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. KegWorks – Glycol Cooling Systems
Domain: kegworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Glycol Cooling Systems are designed to keep draft beer cooled consistently from keg to tap. They are ideal for long-draw systems, requiring the chiller to be at least 75 feet away from the dispensing point. The systems include Glycol Power Packs that accommodate trunk lines ranging from 75 to 450 feet. Trunk lines are sold separately and come in three diameter options: 1/4″, 3/8″, and can hold up …
5. Reddit – Glycol Solutions for Chiller Systems
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Glycol is used in chiller systems to prevent freezing and maintain efficient heat exchange. A typical recommendation is a 3:1 food-grade glycol/water mix, especially if temperatures drop below freezing. For temperatures between 50–70°F, some users consider using just water with a corrosion inhibitor, but many experts advise following manufacturer specifications to avoid potential issues with freez…
6. Drake Chillers – Glycol Chillers
Domain: blog.drakechillers.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: A glycol chiller is an industrial process chiller that uses a glycol-water mixture as a coolant, typically at a 60/40 ratio for optimal antifreeze properties. It can use either ethylene glycol (toxic, not suitable for food applications) or propylene glycol (non-toxic, safe for food and beverage applications). Glycol chillers provide consistent cooling temperatures, protect food from spoilage, acco…
7. Chardon Labs – Glycol Solutions
Domain: chardonlabs.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Glycol is a viscous, colorless, and odorless synthetic liquid used as an antifreeze in mechanical cooling systems and automotive engines. It can absorb and release large amounts of heat while maintaining a consistent temperature, making it suitable for beverage chillers and industrial refrigeration applications. There are two main types of glycol: Ethylene glycol, primarily used in industrial appl…
8. IQS Directory – Glycol Chillers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Glycol chillers are industrial cooling devices that use a blend of glycol (ethylene or propylene) and water to achieve low temperatures. The typical mixture is 60% glycol and 40% water. They are essential for maintaining temperature precision in various industrial processes, preventing overheating, and ensuring equipment reliability. There are two main types: Ethylene Glycol Chillers, known for th…
9. Geson Chiller – Glycol Cooling Solutions
Domain: gesonchiller.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Glycol chiller is a cooling system using glycol-based coolant, suitable for closed and open loop systems. It circulates glycol through coils to absorb heat, ideal for industrial applications like food processing and HVAC systems. Glycol lowers freezing point, has high boiling point, and is non-toxic and biodegradable. Glycol chillers use refrigerants like Freon to transfer heat, are efficient for …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for glycol for chiller systems
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of glycol for chiller systems is vital for ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity of cooling operations. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of selecting the right formulation, such as inhibited ethylene or propylene glycol, to prevent corrosion and maintain heat transfer efficiency. Buyers should prioritize sourcing products that meet local environmental regulations and consider the specific requirements of their operational environments, particularly in regions with varied water quality and climatic conditions.
As the demand for sustainable and efficient cooling solutions continues to grow, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the focus on high-quality glycol formulations will only intensify. International buyers are encouraged to engage with reputable suppliers who can provide comprehensive fluid management services and technical support. By investing in the right glycol solutions today, businesses can significantly reduce maintenance costs, enhance system reliability, and ensure compliance with environmental standards, paving the way for future success in their cooling operations.
Take action now to optimize your chiller systems and secure a competitive edge in your market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to glycol for chiller systems
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.