Everything You Need to Know About Molding Rubber Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for molding rubber
Navigating the complexities of sourcing high-quality molding rubber can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying material properties, manufacturing processes, and applications, understanding the nuances of rubber molding is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into the essential aspects of molding rubber, including the different types such as injection, compression, and transfer molding, as well as their respective applications across diverse industries.
Furthermore, we will explore key considerations for selecting the right rubber based on specific operational environments and performance requirements. Buyers will benefit from insights on supplier vetting processes, cost implications, and the latest industry trends, enabling them to navigate the global market with confidence. By the end of this guide, B2B purchasers will be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to source the most suitable molding rubber products for their unique needs, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry standards. With a focus on actionable insights, this comprehensive resource serves as an invaluable asset for those looking to enhance their procurement strategies in a competitive landscape.
Understanding molding rubber Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | Fast production, high precision, complex geometries | Automotive parts, consumer goods | Pros: High efficiency, minimal waste. Cons: Initial setup costs can be high. |
| Compression Molding | Simple process, suitable for large parts | Gaskets, seals, large industrial components | Pros: Lower tooling costs, good for larger volumes. Cons: Longer cycle times. |
| Transfer Molding | Versatile, allows for intricate designs | Electrical components, automotive seals | Pros: Good control over material flow. Cons: More complex than compression molding. |
| EPDM Rubber Molding | Excellent weather resistance, UV stability | Automotive weather seals, roofing membranes | Pros: Durable in outdoor applications. Cons: Limited performance at high temperatures. |
| Silicone Molding | High-temperature resistance, biocompatibility | Medical devices, food processing | Pros: Safe for sensitive applications. Cons: Higher material costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Injection Molding Rubber?
Injection molding is characterized by its ability to produce high volumes of precise parts quickly. This process involves injecting uncured rubber into a mold, where it is then heated and cured. It is ideal for complex geometries and tight tolerances, making it a preferred choice for applications in automotive and consumer goods. B2B buyers should consider factors such as mold design complexity and material selection to optimize production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
How Does Compression Molding Differ from Other Types?
Compression molding is a straightforward process where preformed rubber is placed into a heated mold. This technique is particularly suited for larger parts and simpler designs. Its lower tooling costs make it appealing for manufacturers looking to produce large volumes without the need for intricate molds. However, buyers should note that this method generally involves longer cycle times compared to injection molding, which may impact overall production schedules.
What Makes Transfer Molding a Versatile Option?
Transfer molding offers versatility by allowing manufacturers to use pre-measured amounts of uncured rubber, which are pushed into the mold cavity. This method is beneficial for producing intricate designs and is frequently used in the automotive and electrical industries. B2B buyers should evaluate the complexity of their designs and the required material properties, as transfer molding can effectively accommodate a range of specifications but may involve higher setup complexity compared to compression molding.
Why Choose EPDM Rubber for Outdoor Applications?
EPDM rubber is renowned for its exceptional resistance to weathering and UV exposure, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as automotive weather seals and roofing membranes. Its durability in various environmental conditions is a significant advantage for buyers in industries where longevity and reliability are crucial. However, it is important to consider EPDM’s performance limitations at high temperatures, which could affect its suitability for certain applications.
What Are the Benefits of Using Silicone Molding Rubber?
Silicone rubber is distinguished by its high-temperature resistance and biocompatibility, making it an excellent choice for medical devices and food processing applications. Its stability in extreme conditions ensures that it maintains performance where other materials might fail. B2B buyers should weigh the higher costs of silicone against its advantages in safety and performance, particularly in industries that prioritize compliance and reliability in sensitive applications.
Key Industrial Applications of molding rubber
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Molding Rubber | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Seals and Gaskets | Enhanced durability and resistance to extreme conditions | Quality assurance, compliance with automotive standards |
| Aerospace | Vibration Dampening Components | Improved safety and performance in critical applications | Certification of materials, lightweight properties |
| Construction | Weather Stripping and Insulation | Energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Resistance to environmental factors, customization options |
| Medical | Medical Device Components | Compliance with health regulations and patient safety | Biocompatibility, sterilization capabilities |
| Electronics | Electrical Insulation Parts | Prevention of short circuits and enhanced product lifespan | High dielectric strength, temperature stability |
How is Molding Rubber Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, molding rubber is essential for producing high-performance seals and gaskets that withstand various environmental conditions. These components prevent fluid leaks and protect sensitive parts from contaminants. Buyers must ensure that the rubber meets rigorous industry standards for durability and temperature resistance, especially in regions with extreme climates, such as the Middle East and Northern Europe. Sourcing high-quality materials that comply with automotive regulations is critical to maintaining vehicle safety and reliability.
What Role Does Molding Rubber Play in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, molding rubber is used to manufacture vibration dampening components that enhance safety and performance during flight. These parts are critical for reducing noise and protecting sensitive equipment from shock and vibration. International buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing materials that meet stringent certification requirements, ensuring they can withstand high-stress environments. The lightweight nature of molded rubber components also contributes to fuel efficiency, making them a valuable asset for aircraft manufacturers.
Why is Molding Rubber Important in Construction?
Molding rubber is widely used in construction for weather stripping and insulation applications. These products help improve energy efficiency by sealing gaps that could lead to heat loss, ultimately reducing maintenance costs. Buyers should consider the rubber’s resistance to UV exposure, ozone, and varying temperatures, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions, such as Africa and South America. Customization options are also important, as specific project requirements may necessitate unique shapes or sizes.

Illustrative image related to molding rubber
How Does Molding Rubber Benefit the Medical Industry?
In the medical sector, molding rubber is crucial for creating components used in medical devices that require high levels of biocompatibility and sterilization. These parts must meet strict health regulations to ensure patient safety. International buyers need to ensure that the rubber used is not only compliant with medical standards but also capable of withstanding repeated sterilization processes. Sourcing from reputable suppliers who can provide certifications is essential for maintaining product integrity in this highly regulated market.
What Advantages Does Molding Rubber Offer in Electronics?
Molding rubber plays a significant role in the electronics industry, particularly for electrical insulation parts. These components prevent short circuits and enhance the lifespan of electronic devices. Buyers should focus on sourcing rubber with high dielectric strength and temperature stability, as these properties are vital for reliable performance. Additionally, international buyers must consider the logistics of sourcing materials that comply with varying regional electrical standards, particularly in Europe and South America, where regulations may differ significantly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘molding rubber’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing the Right Type of Rubber for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to identify the most suitable type of rubber for their specific application. With various types of rubber available, such as EPDM, Nitrile, and Silicone, selecting the appropriate material can become overwhelming. This indecision often leads to product failures, increased costs, and delays in production timelines. Buyers may also find it challenging to balance performance requirements with budget constraints, making the decision even more complex.
The Solution: To effectively source the right type of rubber, start by clearly defining the application requirements. Consider factors such as temperature ranges, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stress. Engage with suppliers who offer technical expertise, and do not hesitate to ask for samples to test under actual conditions. Establishing a collaborative relationship with manufacturers can also lead to customized solutions that meet specific needs. Create a checklist of the essential properties required for your application and use it to guide discussions with potential suppliers, ensuring you make an informed decision that balances performance and cost.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Production Inefficiencies in Rubber Molding
The Problem: Production inefficiencies can significantly impact the bottom line for B2B companies involved in rubber molding. These inefficiencies may arise from improper molding techniques, inadequate maintenance of machinery, or lack of skilled labor. Such issues can lead to increased scrap rates, longer lead times, and ultimately, a failure to meet customer demands. In competitive markets, these setbacks can jeopardize contracts and damage reputations.
The Solution: To address production inefficiencies, invest in employee training programs that focus on best practices in rubber molding techniques, including injection, compression, and transfer molding processes. Implementing a regular maintenance schedule for equipment can also prevent unexpected downtimes. Moreover, consider utilizing advanced technologies, such as automated monitoring systems, to track production metrics in real-time. This data can provide insights into potential bottlenecks and allow for proactive adjustments. Regular audits of the molding process can help identify inefficiencies and lead to continuous improvement initiatives.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Quality Control in Molded Rubber Products
The Problem: Quality control is a major concern for B2B buyers in the rubber molding industry. Inconsistent quality can result in defective products, leading to customer dissatisfaction and costly recalls. Buyers often find it challenging to maintain stringent quality assurance protocols, especially when dealing with multiple suppliers or complex manufacturing processes. This inconsistency can stem from variations in raw materials, inadequate testing procedures, or miscommunication between production teams.
The Solution: To ensure quality control, establish a comprehensive quality assurance program that includes regular testing and inspection of raw materials and finished products. Collaborate with suppliers to create standardized quality benchmarks and utilize statistical process control (SPC) techniques to monitor production quality. Implementing a traceability system can also help identify defects at any stage of production. Regular training for quality assurance personnel on the latest testing methods and industry standards is essential. By fostering a culture of quality within the organization and maintaining open communication with suppliers, B2B buyers can enhance product reliability and build stronger customer trust.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for molding rubber
What Are the Key Properties of Common Rubber Materials for Molding?
When selecting materials for molding rubber, it is essential to consider their properties, suitability for specific applications, and the implications for international buyers. Here, we analyze four common rubber materials used in molding processes: Natural Rubber, EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer), Nitrile Rubber, and Silicone Rubber. Each material has distinct characteristics that can significantly influence product performance and application.
How Does Natural Rubber Perform in Molding Applications?
Natural rubber is derived from the latex of rubber trees and is renowned for its excellent elasticity and resilience. It typically operates well within a temperature range of -50°F to 275°F (-46°C to 135°C). Its high tensile strength and abrasion resistance make it suitable for applications requiring durability, such as automotive parts and seals.
Pros and Cons: Natural rubber is cost-effective and offers superior performance in terms of flexibility and elasticity. However, it has limited resistance to UV radiation and ozone, which can lead to degradation over time. For international buyers, compliance with ASTM standards is crucial, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
What Advantages Does EPDM Offer for Molding Rubber?
EPDM is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent weather resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -20°F to 350°F (-29°C to 177°C) and is resistant to UV rays, ozone, and various chemicals.
Pros and Cons: The key advantage of EPDM is its durability in harsh environmental conditions, making it suitable for gaskets, seals, and roofing membranes. However, it is generally more expensive than natural rubber. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should ensure that EPDM products meet local compliance standards, such as DIN or JIS.
Why Choose Nitrile Rubber for Specific Applications?
Nitrile rubber, or NBR, is particularly valued for its oil and solvent resistance, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. It operates effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°F to 226°F (-40°C to 108°C).

Illustrative image related to molding rubber
Pros and Cons: Nitrile rubber offers excellent abrasion resistance and low-temperature flexibility, making it suitable for gaskets and seals. However, it can be more expensive than natural rubber and may not perform as well in extreme temperatures. B2B buyers should consider the specific chemical compatibility of nitrile rubber with the media it will encounter in their applications.
What Makes Silicone Rubber a Preferred Choice?
Silicone rubber is recognized for its stability and resistance to extreme temperatures, ranging from -150°F to 480°F (-100°C to 250°C). It is non-reactive and suitable for medical and food-grade applications due to its biocompatibility.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of silicone rubber is its versatility and ability to withstand extreme conditions without degrading. However, it tends to be more costly than other rubber types, which may impact budget considerations for buyers. In regions like Africa and South America, where food safety regulations are stringent, ensuring that silicone products meet local standards is vital.
Summary of Material Selection for Molding Rubber
| Material | Typical Use Case for molding rubber | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Automotive parts, seals | Excellent elasticity and cost-effective | Limited UV and ozone resistance | Low |
| EPDM | Gaskets, seals, roofing membranes | Superior weather and chemical resistance | Generally higher cost | Medium |
| Nitrile Rubber | Gaskets, seals, automotive parts | Excellent oil and solvent resistance | More expensive; limited extreme temperature performance | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber | Medical devices, food-grade products | Versatile, stable across extreme temperatures | Higher cost | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common rubber materials used in molding applications, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for molding rubber
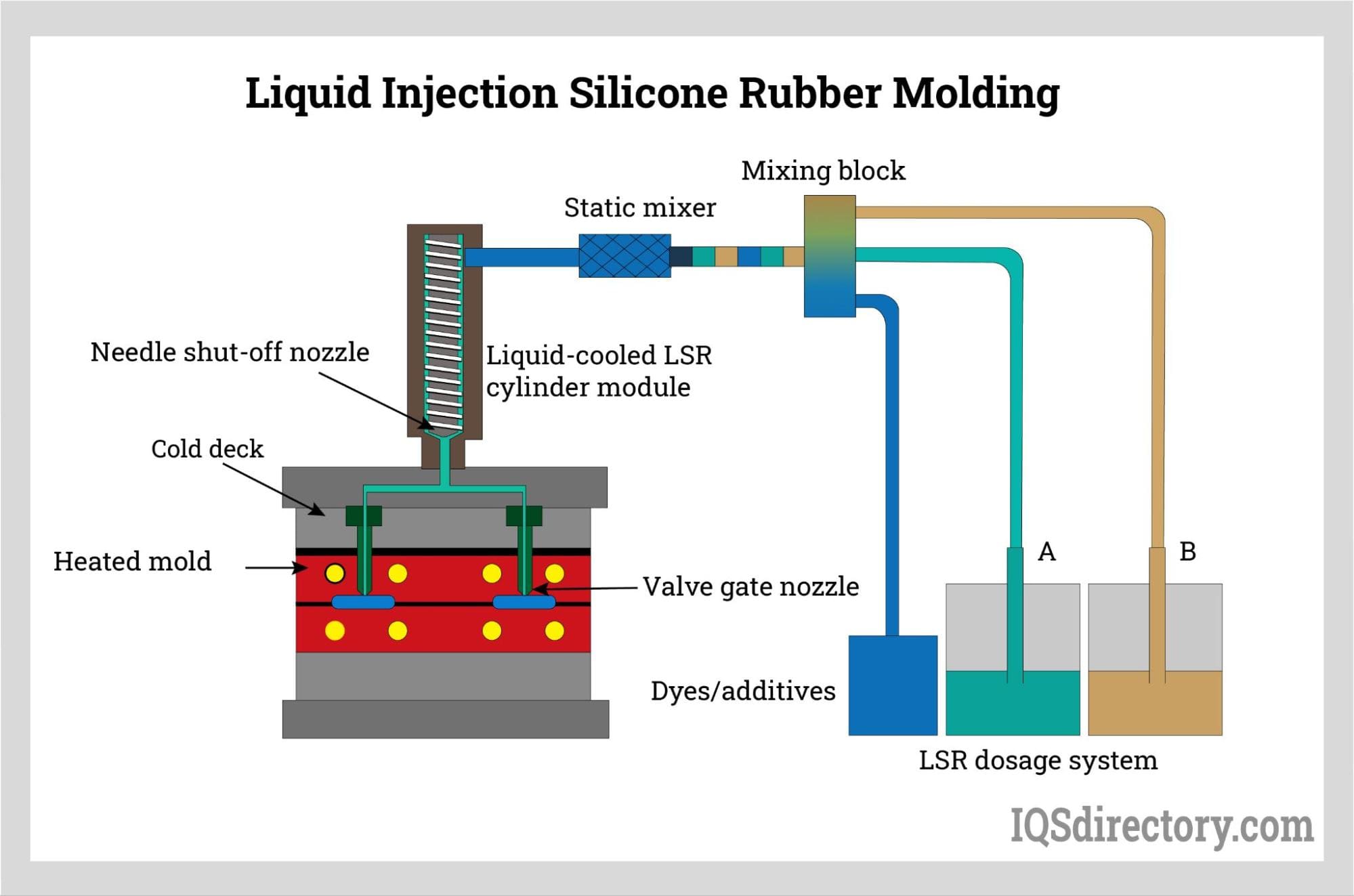
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Molding Rubber?
The manufacturing process for molding rubber typically involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the final product meets the specific requirements of its intended application.
Illustrative image related to molding rubber
How Is Material Prepared for Rubber Molding?
Material preparation is the first stage in the rubber molding process. It involves selecting the appropriate type of rubber—either natural or synthetic—based on the desired properties such as elasticity, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. The rubber is then compounded with additives like accelerators, fillers, and stabilizers to enhance its performance characteristics.
Once the formulation is complete, the rubber is processed into a workable form, often as sheets or preformed shapes, depending on the molding technique to be used. This preparation may also include pre-curing the rubber to optimize its flow characteristics during the molding process.
What Are the Key Techniques Used in Rubber Molding?
The primary techniques for molding rubber include:
-
Injection Molding: In this method, uncured rubber is injected into a heated mold under high pressure. The rubber fills the mold cavity and is held there until it vulcanizes into its final shape. This technique is highly efficient for producing complex shapes and high-volume production.
-
Compression Molding: This technique involves placing a pre-measured amount of uncured rubber into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed using hydraulic pressure, allowing the rubber to take shape. Compression molding is often used for larger parts and is more cost-effective for lower production volumes.
-
Transfer Molding: Similar to injection molding, transfer molding starts with uncured rubber placed in a transfer pot. A ram pushes the rubber through a runner system into the mold cavity, where it cures. This method is ideal for producing intricate parts with varying wall thicknesses.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Rubber Molding?
Quality assurance in rubber molding is crucial to ensure that products meet international standards and customer specifications. Key quality assurance measures include adherence to relevant international standards, establishing checkpoints throughout the production process, and implementing rigorous testing protocols.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are pivotal for manufacturers in the rubber molding industry. ISO 9001 focuses on quality management systems and emphasizes customer satisfaction, process efficiency, and continual improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE for European markets and API for oil and gas applications enhance credibility and compliance for products intended for specialized sectors.
What Are the QC Checkpoints in the Rubber Molding Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product quality. Common checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to molding rubber
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial phase involves inspecting raw materials for conformity to specifications before production begins. It ensures that the right type and quality of rubber are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring of parameters such as temperature, pressure, and curing time is conducted. This step helps identify any deviations from the set processes that could affect the final product quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After molding, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify their performance characteristics. This may include dimensional checks, physical property tests, and visual inspections to detect defects.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality in Rubber Products?
Common testing methods for rubber products include:
-
Tensile Strength Testing: Measures the maximum amount of tensile stress a rubber material can withstand before failure, providing insights into its durability and elasticity.
-
Hardness Testing: Determines the hardness of rubber using durometers, which is critical for applications where material flexibility is required.
-
Aging and Environmental Testing: Evaluates the material’s resistance to aging, ozone, and UV exposure to ensure longevity in various environmental conditions.
-
Compression Set Testing: Assesses the material’s ability to return to its original shape after being compressed, which is vital for applications requiring resilience.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential for ensuring product reliability and compliance with international standards. Here are several strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their manufacturing processes, quality systems, and adherence to standards. This practice can uncover potential risks and ensure alignment with buyer expectations.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation regarding their quality control processes, including inspection reports and test results. This transparency builds trust and confidence in their operations.
-
Engage Third-party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of product quality and adherence to specifications. This approach is particularly beneficial for international buyers to mitigate risks associated with overseas sourcing.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various certification requirements. Understanding regional differences in quality standards and certifications is crucial. For instance:
-
European Union: Products sold within the EU must comply with CE marking requirements, ensuring they meet safety and performance standards.
-
Middle East: Buyers should be aware of local regulations and certifications, such as the Gulf Conformity Mark, which may be necessary for products entering GCC markets.
-
Africa and South America: Regional standards may vary significantly, and buyers should ensure that suppliers are familiar with local compliance requirements to avoid costly delays or rejections at customs.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of the rubber molding manufacturing process and quality assurance practices is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the right materials, manufacturing techniques, and rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality rubber products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘molding rubber’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in effectively procuring molding rubber. By following this step-by-step checklist, buyers can ensure they select the right materials and suppliers, ultimately leading to successful production processes and product quality.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the rubber products you need. This includes understanding the type of molding process (injection, compression, or transfer molding) and the specific rubber material (natural or synthetic) that fits your application. Consider factors like elasticity, durability, temperature resistance, and environmental exposure to ensure your specifications align with your operational needs.
Step 2: Research the Market
Conduct thorough market research to identify potential suppliers. Look for companies that specialize in the type of rubber and molding processes relevant to your needs. Utilize online directories, industry trade shows, and networking platforms to gather information on various suppliers, comparing their offerings and market reputation.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to assess their capabilities. Check for references from buyers in similar industries or regions to validate their reliability and quality of service.
- Key considerations:
- Look for suppliers with experience in your specific application.
- Assess their production capacity to ensure they can meet your demand.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your potential suppliers adhere to relevant industry standards and certifications. This may include ISO certifications, REACH compliance, or other regional regulations. Compliance not only guarantees product quality but also mitigates risks related to legal liabilities and market acceptance.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the rubber materials you intend to purchase. Conduct rigorous testing to evaluate the samples against your defined specifications. This step is critical for assessing the material’s performance under real-world conditions and ensuring it meets your quality standards.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in negotiations with your selected suppliers to establish favorable pricing and terms. Consider factors such as order volume, payment terms, and delivery schedules. A clear agreement can lead to better long-term relationships and potential discounts for future orders.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a quality control process for incoming materials from your suppliers. This includes defining inspection criteria and testing methods to ensure the rubber meets your specifications upon delivery. Establishing this process not only guarantees consistent quality but also strengthens your supplier relationships through open communication about quality expectations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for molding rubber, ensuring they select the right materials and suppliers to meet their production needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for molding rubber Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Molding Rubber Production?
When sourcing molded rubber products, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant portion of the total expense. Natural rubber tends to be less expensive than synthetic alternatives, but the choice depends on application requirements. Prices fluctuate based on market demand, availability, and quality specifications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly by region. In areas with higher wage standards, such as parts of Europe, labor costs may elevate overall pricing. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs can be advantageous but may come with trade-offs in quality or communication.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Custom molds and tooling represent a fixed cost that can be substantial, especially for specialized applications. Investing in high-quality tooling can lead to better production efficiency and product quality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. However, it adds to the overall costs. Buyers should evaluate the balance between cost and quality assurance.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely depending on the location of the supplier and the buyer. Factors such as shipping distance, method (air, sea, road), and Incoterms can significantly impact the total logistics cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the standard markup in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
What Influences Pricing in Rubber Molding?
Several factors affect the pricing of molded rubber products, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can influence pricing. Larger orders typically lead to bulk discounts, whereas smaller orders might incur higher per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or unique specifications generally lead to higher prices due to increased production complexity and tooling costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: The choice between natural and synthetic rubber impacts pricing. Specialty materials designed for specific applications can also elevate costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet stringent quality standards or certifications (like ISO) often come with a higher price tag. Buyers should assess whether the added costs align with their application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and service level can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is critical, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can impact overall costs.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs in Molding Rubber Sourcing?
To maximize cost efficiency, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume commitments and long-term relationships to negotiate better prices. Understanding market conditions can provide leverage during discussions.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront costs but also long-term operational expenses. Factors like durability, maintenance, and replacement frequency can influence the overall value.
-
Research Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional pricing variations and potential tariffs or duties that could affect total costs.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide insights into competitive pricing and help identify the best value.
-
Build Strong Supplier Relationships: Establishing a reliable partnership with suppliers can lead to better pricing, service, and product quality over time.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While the information provided aims to give a comprehensive understanding of cost structures and pricing influences, it is essential to note that actual prices can vary based on numerous dynamic factors. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain updated quotes to inform their purchasing decisions accurately.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing molding rubber With Other Solutions
When considering manufacturing solutions, businesses often seek alternatives that can meet their specific needs effectively. Molding rubber is a widely used process in various industries, but it’s essential to evaluate other methods that might offer similar benefits or address particular requirements more efficiently. This section analyzes molding rubber against alternative solutions such as 3D printing and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE).
| Comparison Aspect | Molding Rubber | 3D Printing | Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High elasticity, durability, and resistance to temperature and chemicals | Varies by material; generally lower mechanical properties than rubber | Good elasticity and flexibility; resistant to wear and tear |
| Cost | Moderate initial costs; lower in high-volume production | Potentially higher for small runs due to material and machine costs | Generally lower than molding rubber; varies by type |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized molds and equipment | Requires software and design skills; setup can be complex | Easier to process than rubber; uses standard injection molding techniques |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance of molds; durable final products | Minimal maintenance on printers; material changes can require recalibration | Low maintenance; TPEs are less prone to degradation |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of complex shapes and durable parts | Prototyping, low-volume production, and custom designs | Applications needing flexibility and ease of processing, such as consumer goods |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing Compared to Molding Rubber?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, offers significant flexibility in design and rapid prototyping capabilities. It allows for the creation of complex geometries without the need for molds, making it ideal for custom applications or small production runs. However, the mechanical properties of printed parts may not match those produced through molding rubber, especially in high-stress environments. The cost can also be higher for small batches, which may deter some B2B buyers looking for cost-effective solutions.
What Are the Key Benefits and Drawbacks of Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)?
Thermoplastic elastomers combine the properties of rubber with the ease of processing typical of plastics. They are versatile, easily molded, and can be recycled, making them an attractive alternative for many applications. TPEs provide good flexibility and durability but may not offer the same level of heat and chemical resistance as traditional molding rubber. Their processing is straightforward, which can lead to reduced production times and costs, making them suitable for various consumer products.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the most suitable manufacturing solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, including performance characteristics, production volume, and cost constraints. Molding rubber excels in high-volume applications requiring durability and resistance, while 3D printing is ideal for customization and prototyping. Thermoplastic elastomers serve as a practical middle ground, providing flexibility and ease of use. By carefully evaluating these aspects, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for molding rubber
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Molding Rubber?
When selecting rubber for molding applications, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring product performance and durability. Here are several key specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of rubber based on its chemical composition and physical properties. Different grades are tailored for various applications, influencing factors such as temperature resistance, elasticity, and chemical resistance. Choosing the right material grade is vital for applications that require specific characteristics, ensuring that the final product meets performance standards.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in a dimension, which is critical in molding processes. For rubber components, maintaining tight tolerances is essential to ensure proper fit and function within assemblies. Inconsistent tolerances can lead to product failures, increased waste, and higher production costs, making it a key consideration for B2B buyers.
3. Shore Hardness
Shore hardness measures the hardness of rubber on a scale from A (soft) to D (hard). This property affects the flexibility and resilience of the rubber, which can influence its application in various industries. For example, softer rubbers are often used in seals and gaskets, while harder rubbers may be employed in industrial applications. Understanding the appropriate hardness level is crucial for product performance.

Illustrative image related to molding rubber
4. Temperature Resistance
Temperature resistance defines the range of temperatures at which rubber can maintain its properties without degrading. Different rubber types exhibit varying levels of heat and cold resistance. For applications exposed to extreme environments, selecting rubber with appropriate temperature resistance is essential to prevent failure and ensure longevity.
5. Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance indicates the rubber’s ability to withstand exposure to various chemicals without losing integrity. This property is particularly important in industries such as automotive and manufacturing, where components may encounter oils, fuels, or other harsh substances. Understanding the chemical compatibility of rubber materials helps in selecting the right type for specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Rubber Molding Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the rubber molding sector. Here are several commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for B2B buyers as it often indicates the quality and specifications of components used in larger assemblies.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it can impact inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to plan their purchases effectively, particularly for specialized rubber components.

Illustrative image related to molding rubber
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process wherein a company solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ is a critical step in sourcing and procurement, allowing for comparison of prices and terms across multiple suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping goods. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for costs, risks, and logistics at various stages of the delivery process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In rubber molding, lead times can vary based on material availability, production schedules, and shipping. Awareness of lead times is essential for B2B buyers to ensure timely delivery and project planning.

Illustrative image related to molding rubber
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing rubber products for their specific applications, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the molding rubber Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Molding Rubber Sector?
The molding rubber market is experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. The increasing demand for high-performance materials across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods is one of the primary drivers. This demand is fueled by the need for durable, flexible, and weather-resistant components that can perform under extreme conditions. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as 3D printing and automation, are revolutionizing the rubber molding process, allowing for more efficient production and customization of products.
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is essential. Emerging trends include a shift towards synthetic rubber due to its superior properties and the growing preference for injection molding techniques, which offer faster production times and reduced material waste. International buyers are also increasingly leveraging digital platforms for sourcing, which enhances transparency and reduces lead times.
Moreover, the competitive landscape is evolving with the entry of new players and increased consolidation among established firms. This presents both opportunities and challenges for international buyers who must navigate varying quality standards and regulatory requirements across markets. Adapting to these trends will be crucial for B2B buyers to maintain a competitive edge.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Molding Rubber Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone in the molding rubber sector, driven by environmental concerns and consumer demand for eco-friendly products. The production of traditional rubber can have significant environmental impacts, including deforestation and high energy consumption. As a response, manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as sourcing natural rubber from certified plantations and utilizing recycled materials in their products.

Illustrative image related to molding rubber
For B2B buyers, the importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers that prioritize sustainability and can provide certifications that demonstrate their commitment to environmentally friendly practices. Certifications like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for natural rubber and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are critical indicators of a supplier’s dedication to sustainability.
Additionally, the use of bio-based materials and innovative rubber formulations that minimize environmental impact is on the rise. These ‘green’ materials not only appeal to eco-conscious consumers but also help businesses meet regulatory requirements and corporate social responsibility goals. For international buyers, aligning with suppliers who embrace sustainability can enhance brand reputation and open doors to new markets.
What Is the Evolution of the Molding Rubber Sector and Its Implications for B2B Buyers?
The molding rubber sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially dominated by natural rubber sourced from tropical regions, the industry saw a shift towards synthetic alternatives in response to rising demand and supply chain challenges. This transition was accelerated during World War II when synthetic rubber became essential for military applications.
Over the decades, advancements in polymer science have led to the development of specialized rubber compounds that cater to diverse applications, from automotive seals to medical devices. This evolution has not only enhanced product performance but also diversified sourcing options for B2B buyers.
Today, buyers must navigate a complex landscape characterized by a mix of traditional and innovative materials. Understanding the historical context of rubber molding enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions about material selection and supplier partnerships. As the industry continues to adapt to technological advancements and sustainability demands, staying informed about these trends will be vital for maintaining a competitive advantage in the global marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of molding rubber
-
1. How do I choose the right type of molding rubber for my application?
Selecting the appropriate type of molding rubber involves understanding your specific application needs. Consider the operating temperature range, environmental stresses (like exposure to chemicals or UV light), and the physical forces the product will encounter. For instance, if your application requires high durability and chemical resistance, synthetic rubbers like Nitrile or Viton may be suitable. Engaging with suppliers who can provide technical support and material data sheets will help ensure you make an informed choice. -
2. What is the best rubber molding process for high-volume production?
For high-volume production, rubber injection molding is often the most efficient process. This method allows for quick cycle times and consistent part quality, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing. Compression molding can also be effective but may not match the speed or precision of injection molding. Consider your production volume, budget, and desired quality standards when selecting a molding process, and consult with manufacturers to evaluate the best fit for your needs. -
3. What are the key factors to consider when vetting a rubber supplier?
When vetting a rubber supplier, assess their industry experience, certifications (like ISO), and production capabilities. Look for testimonials or case studies from previous clients to gauge reliability and quality. Additionally, inquire about their material sourcing, customization options, and ability to meet your specific requirements. A supplier with robust quality assurance processes and excellent customer service will be better equipped to address any issues that arise during production. -
4. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for molding rubber products?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Generally, MOQs for molded rubber products can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production requirements. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for new clients or smaller projects, so it’s worth exploring options. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing molding rubber internationally?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers and regions. Common terms include full payment upfront, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon shipment. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. It’s essential to clarify terms before finalizing agreements and ensure they are documented in your purchase order to avoid misunderstandings. -
6. How can I ensure quality assurance during the rubber molding process?
To ensure quality assurance, establish clear quality criteria and inspection processes with your supplier. Request regular updates during production and consider third-party inspections if needed. It’s also beneficial to review the supplier’s quality management system and certifications, as this will indicate their commitment to maintaining high standards. Building a strong relationship with your supplier will facilitate better communication and adherence to quality expectations. -
7. What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing molding rubber?
When importing molding rubber, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Assess whether air freight or sea freight is more cost-effective based on your delivery timeline. Familiarize yourself with import tariffs and compliance requirements in your country. Working with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can streamline the process, ensuring timely delivery while navigating any potential challenges. -
8. Can I customize rubber formulations for my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for rubber formulations to meet specific application requirements. Customization can include altering the rubber’s hardness, color, or adding specific additives for enhanced properties like UV resistance or improved flexibility. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and requirements to your supplier. Collaborating closely during the development phase will help ensure the final product aligns with your expectations.
Top 6 Molding Rubber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Alumilite – Amazing Mold Rubber
Domain: alumilite.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Amazing Mold Rubber is a fast-curing, tin-cure silicone designed for mold making. It offers exceptional detail reproduction and fast curing, with a low-viscosity formula that requires no degassing. The product is available in multiple sizes: 9.25 oz for $24.99, 5 lb for $129.99, 10 lb for $259.98, and 50 lb for $737.86. Features include long-lasting durability, versatility for various applications…
2. Lake Erie Rubber – Rubber Molding Solutions
Domain: lakeerierubber.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Rubber molding is a manufacturing process that transforms uncured rubber into usable products using heating and reshaping in a metal cavity. The three main types of rubber molding are: 1. Injection Molding: Involves injecting uncured rubber into a mold where it vulcanizes into its final shape. 2. Compression Molding: Preformed shapes of uncured rubber are placed into heated mold cavities and close…
3. Smooth-On – Mold Star™ Series Silicone Mold Rubber
Domain: smooth-on.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Mold Star™ Series, Easy to Use Silicone Mold Rubber. Cures to soft, strong rubbers that are tear resistant with very low long term shrinkage. Suitable for casting wax, gypsum, resins, and other materials. Heat resistant up to 450°F (232°C). One to One Mix Ratio (1A:1B by volume, no weighing scale necessary). No vacuum degassing required for most applications due to low viscosity. Translucent Serie…
4. Contenti – Spin Casting Mold Rubber
Domain: contenti.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Spin Casting Mold Rubber from Contenti includes various options such as silicone and organic black mold rubber for vulcanizing and casting. The product line features multiple diameters and types, including: Lower Silicone Mold Making Putty (1.2 lbs. – $32.50), RTV (Room Temperature Vulcanizing) Silicone Rubber (starting at $34.70), Nicem® White Lower Cost Silicone Mold Rubber (starting at $32.35),…
5. RISD Museum – Dragon Skin Silicone Rubber
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: – Project Title: Making a One-part Rubber Mold and Casting an Object
– Author: risdmuseum
– Institution: RISD Museum
– Exhibition Connection: Arlene Shechet’s exhibition Meissen Recast
– Key Materials Used:
– Dragon Skin, Medium Set (silicone rubber)
– Smooth-Cast 300 (casting material)
– Key Steps in the Process:
1. Create a mold sized to your object (using cardboard or acrylic).
2. Tap…
6. Etiroltec – Polyisoprene
Domain: etiroltec.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: {‘Polyisoprene’: {‘description’: ‘Produced through the polymerization of synthetic isoprene, shares properties with natural rubber.’, ‘properties’: ‘High tensile strength, tear resistance, high purity.’, ‘applications’: [‘Bearings’, ‘Springs’, ‘Pipe gaskets’, ‘Motor mounts’, ‘Hoses and tubing’, ‘Seals’]}, ‘Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)’: {‘description’: ‘General-purpose synthetic rubber made from…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for molding rubber
How Can Strategic Sourcing Transform Your Molding Rubber Procurement?
In the competitive landscape of molding rubber, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital tool for international B2B buyers. By understanding the nuances of rubber molding processes—such as injection, compression, and transfer molding—buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs. Prioritizing the right rubber type based on properties like temperature resistance, durability, and environmental stress can lead to enhanced product performance and longevity.

Illustrative image related to molding rubber
Furthermore, sourcing from reliable suppliers who adhere to quality standards is crucial for minimizing risks associated with subpar materials. As global markets evolve, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must embrace a proactive approach to procurement, leveraging data and supplier relationships to optimize costs and efficiency.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality, specialized rubber products is set to grow. By investing in strategic sourcing now, you position your business to capitalize on emerging trends and innovations in the molding rubber industry. Engage with suppliers who are committed to sustainability and technological advancements to stay ahead of the curve. Your proactive sourcing strategy today will ensure your competitive edge tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to molding rubber