Everything You Need to Know About Machinery Wheels Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machinery wheels
In the dynamic landscape of international commerce, sourcing high-quality machinery wheels can present significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The need for reliable, durable wheels that can withstand heavy loads and various operating conditions is paramount. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the machinery wheels market, covering essential aspects such as types of wheels, their applications across industries, and strategies for effective supplier vetting.
Additionally, buyers will find critical insights into cost factors, ensuring that they can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. By delving into detailed descriptions of different wheel styles—including swivel, rigid, and heavy-duty options—this guide empowers international B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing machinery wheels with confidence.
Whether you are in Brazil looking for solutions for agricultural equipment or in Saudi Arabia seeking durable options for construction machinery, this resource is designed to enhance your procurement strategy. Equip yourself with the knowledge to select the most suitable machinery wheels that not only elevate operational efficiency but also offer long-term value in your business endeavors.
Understanding machinery wheels Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Duty Casters | High load capacity (up to 100,000 lbs), durable materials | Automotive manufacturing, construction | Pros: Exceptional strength; Cons: Higher cost |
| Industrial Swivel Casters | 360-degree rotation, easy maneuverability | Warehousing, AGVs, utility carts | Pros: Versatile; Cons: Can be less stable under heavy loads |
| Rigid Casters | Fixed direction, robust construction | Tool carts, maintenance carts | Pros: Stability; Cons: Limited maneuverability |
| Spring-Loaded Casters | Shock-absorbing design, reduces impact | Heavy equipment transport, sensitive items | Pros: Protects loads; Cons: More complex design |
| Stainless Steel Casters | Corrosion-resistant, suitable for wet environments | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Long-lasting; Cons: Higher price point |
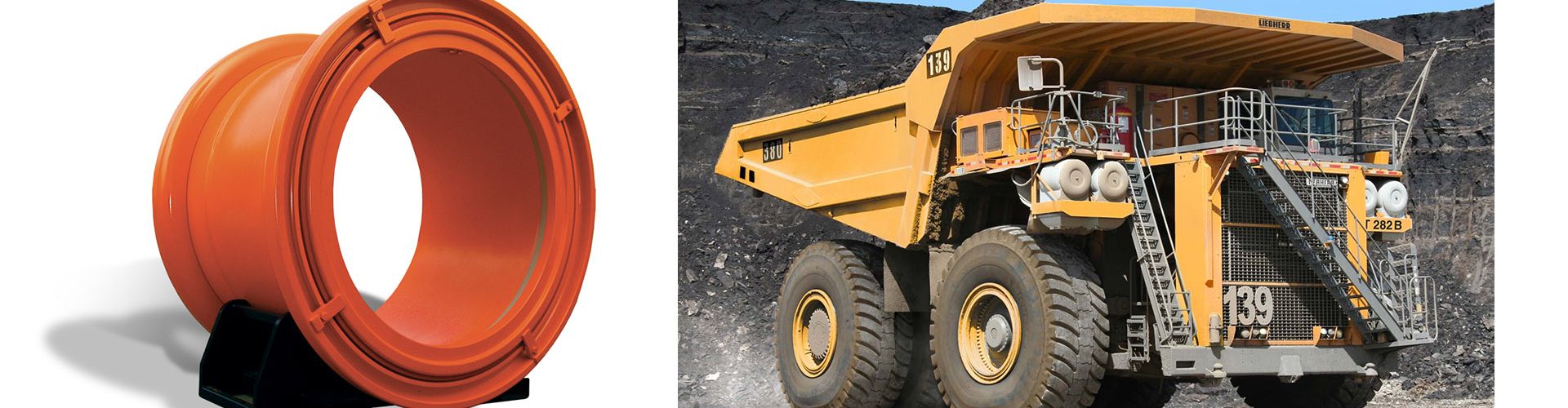
What Are Heavy Duty Casters and Their Applications?
Heavy duty casters are engineered to handle significant loads, often rated between 15,000 to 100,000 lbs. These casters are typically constructed from high-quality materials like steel or reinforced plastics, ensuring durability and longevity. B2B buyers in industries such as automotive manufacturing and construction often rely on these casters for transporting heavy equipment and materials. While their strength is a clear advantage, the higher initial investment may be a consideration for budget-conscious businesses.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
How Do Industrial Swivel Casters Enhance Maneuverability?
Industrial swivel casters offer the ability to rotate 360 degrees, allowing for easy maneuverability in tight spaces. This feature is particularly beneficial in warehousing and automated guided vehicle (AGV) applications where flexibility is critical. They often come with low rolling resistance materials, which help reduce the physical effort needed to transport goods. However, buyers should be aware that while swivel casters provide versatility, they can compromise stability when handling very heavy loads.
Why Choose Rigid Casters for Stability?
Rigid casters are designed to move in a straight line, providing enhanced stability for heavy loads. They are commonly used in tool carts and maintenance applications where directional control is essential. The robust construction of rigid casters allows them to withstand high impact and frequent use. However, their limited maneuverability may pose challenges in dynamic environments, making it crucial for buyers to assess their specific mobility needs before purchase.
What Are the Benefits of Spring-Loaded Casters?
Spring-loaded casters feature a shock-absorbing design that minimizes the impact on both the caster and the load being transported. This makes them ideal for applications involving heavy equipment or sensitive items that require extra care during transport. While they offer significant advantages in protecting loads, the complexity of their design may lead to higher maintenance requirements, which buyers should factor into their purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
When to Consider Stainless Steel Casters?
Stainless steel casters are specifically designed for environments where corrosion and rust are concerns, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. Their resilience to harsh conditions ensures a longer lifespan, making them a worthwhile investment for B2B buyers in these sectors. However, the initial cost is typically higher than standard casters, so businesses must weigh the long-term benefits against the upfront expense.
Key Industrial Applications of machinery wheels
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Machinery Wheels | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Assembly line carts | Enhanced mobility for heavy parts and tools | Load capacity, wheel material, and maintenance needs |
| Food Processing | Mobile food processing equipment | Efficient transport and hygiene compliance | Non-marking, easy to clean materials, and durability |
| Construction | Heavy-duty scaffolding equipment | Safe and efficient movement of heavy materials | Weight capacity, wheel size, and terrain compatibility |
| Warehousing and Logistics | Pallet jacks and carts | Streamlined operations and reduced labor costs | Ergonomics, low rolling resistance, and durability |
| Agriculture | Agricultural machinery transport | Increased productivity and reduced manual handling | Resistance to debris, weatherproof materials, and load ratings |
How Are Machinery Wheels Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, machinery wheels are integral to the operation of assembly line carts, which transport heavy parts and tools across the production floor. These wheels facilitate smooth mobility, reducing the physical strain on workers and increasing productivity. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing wheels with high load capacities and materials that withstand the rigors of industrial environments, ensuring longevity and reliability.
What Role Do Machinery Wheels Play in Food Processing?
Machinery wheels are crucial in mobile food processing equipment, allowing for the efficient transport of ingredients and finished products. The use of non-marking and easy-to-clean materials is essential to maintain hygiene standards in food facilities. Buyers from this sector need to prioritize sourcing wheels that provide durability and comply with food safety regulations, especially in regions with stringent health standards.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
Why Are Machinery Wheels Important in Construction?
In construction, machinery wheels are employed in heavy-duty scaffolding equipment, enabling the safe and efficient movement of materials on job sites. The ability to handle substantial loads while ensuring stability is paramount. Buyers should consider the weight capacity, wheel size, and compatibility with various terrains when sourcing these wheels, especially in regions with diverse construction environments.
How Do Machinery Wheels Enhance Warehousing and Logistics Operations?
Machinery wheels are vital for pallet jacks and carts used in warehousing and logistics, streamlining operations by facilitating the quick movement of goods. This mobility reduces labor costs and enhances operational efficiency. Buyers should seek wheels with ergonomic designs and low rolling resistance to minimize worker fatigue and ensure smooth transport of heavy items, particularly in high-volume distribution centers.
What Benefits Do Machinery Wheels Offer in Agriculture?
In agriculture, machinery wheels are used for transporting equipment and produce across fields, significantly increasing productivity while reducing manual handling. The wheels must be resistant to debris and weather conditions to maintain functionality in varied environments. Buyers should focus on sourcing wheels with high load ratings and robust materials to withstand the demands of agricultural applications, particularly in regions with challenging terrains.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machinery wheels’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Heavy Load Capacity Challenges in Manufacturing
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in manufacturing sectors frequently encounter difficulties when transporting heavy loads, often exceeding the standard capacities of available machinery wheels. For instance, a factory might require moving equipment or materials weighing up to 30,000 lbs. Using standard casters can lead to wheel failure, safety hazards, and potential downtime, significantly impacting productivity and increasing operational costs. Buyers often struggle to find wheels that not only meet the load capacity but also offer durability and reliability under constant use in harsh environments.
The Solution: To address these challenges, it’s crucial to opt for extra heavy-duty casters designed specifically for high-load applications. B2B buyers should look for wheels with a load capacity rating between 15,000 lbs to 34,999 lbs. When sourcing these wheels, consider factors such as the wheel material—steel or reinforced polyurethane can provide added durability and resistance to wear. It’s also advisable to explore customizable solutions that can be tailored to specific operational needs. Collaborating with suppliers who offer engineering support can help in selecting the right wheel type, ensuring it fits seamlessly with existing equipment and meets safety standards. Conducting regular maintenance checks can further prolong the lifespan of these wheels, allowing for consistent performance without compromising safety.
Scenario 2: Maneuverability Issues in Tight Spaces
The Problem: In industrial environments where space is often limited, maneuverability becomes a significant concern for B2B buyers. For example, warehouses or manufacturing plants may require moving carts and equipment through narrow aisles or around tight corners. Using rigid casters can make it cumbersome to navigate these areas, leading to increased strain on workers and a higher risk of accidents or equipment damage.
The Solution: Implementing swivel casters can significantly enhance maneuverability in confined spaces. B2B buyers should consider selecting industrial swivel casters with features like locking mechanisms to provide stability when stationary. It’s important to choose wheels with a smaller diameter, which can facilitate easier turns without compromising load capacity. When purchasing, ensure the casters have low rolling resistance to minimize the effort required for pushing or pulling. Additionally, investing in ergonomic designs can help reduce strain on workers, promoting a safer working environment. Training staff on how to best utilize these casters for optimal movement can also enhance overall efficiency.
Scenario 3: Debris Accumulation and Maintenance Concerns
The Problem: In many industrial settings, debris such as metal shavings, wood chips, and dust can accumulate around machinery wheels, leading to performance degradation. B2B buyers often report that debris can cause wheels to jam, increasing rolling resistance and making equipment difficult to move. This not only slows down operations but can also lead to increased maintenance costs and reduced operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
The Solution: To combat debris accumulation, it’s essential to select wheels that feature non-marking and debris-repellent materials, such as high-quality polyurethane or nylon. These materials help to minimize debris retention and maintain smooth operation. Buyers should also consider wheels with a design that allows for easy cleaning or maintenance access. Regularly scheduled maintenance, including cleaning the wheels and inspecting for wear and tear, can prevent issues before they escalate. Additionally, implementing a routine inspection protocol can ensure that any potential problems are identified early, thus extending the life of the wheels and enhancing operational efficiency. Collaboration with suppliers who can provide maintenance-free options may also be beneficial for reducing long-term upkeep costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machinery wheels
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Machinery Wheels?
When selecting materials for machinery wheels, it’s essential to consider their specific properties, as these directly influence performance, durability, and application suitability. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of machinery wheels: rubber, polyurethane, steel, and cast iron.
How Does Rubber Perform in Machinery Wheel Applications?
Rubber is a widely used material for machinery wheels due to its excellent shock absorption and noise-dampening properties. It typically has a good temperature resistance, functioning effectively in environments ranging from -40°F to 180°F (-40°C to 82°C). However, rubber is less resistant to chemicals and UV exposure, which can lead to degradation over time.
Pros: Rubber wheels are durable and provide a smooth ride, making them suitable for applications where noise reduction is critical. They are also relatively inexpensive to manufacture.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
Cons: Rubber can wear out faster in abrasive environments and may not support heavy loads as effectively as harder materials.
Impact on Application: Rubber wheels are ideal for indoor applications, such as hospital equipment or light-duty carts, where noise and floor protection are priorities.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards for materials, especially in food processing or medical applications, is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe may require adherence to specific safety and environmental regulations.
What Advantages Does Polyurethane Offer for Machinery Wheels?
Polyurethane is another popular choice for machinery wheels, known for its superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity. It performs well in a wide temperature range, typically from -30°F to 180°F (-34°C to 82°C), and offers excellent chemical resistance compared to rubber.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
Pros: Polyurethane wheels are durable and can handle heavier loads, making them suitable for industrial applications. They also have low rolling resistance, which enhances maneuverability.
Cons: The manufacturing process for polyurethane can be more complex and costly than rubber, impacting overall pricing.
Impact on Application: These wheels are well-suited for environments with high wear, such as warehouses and manufacturing facilities, where heavy loads and debris are common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Polyurethane wheels often comply with various international standards, making them versatile for global applications. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers provide material certifications.
Why Choose Steel for Heavy-Duty Machinery Wheels?
Steel wheels are renowned for their strength and durability, making them the go-to choice for heavy-duty applications. They can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for rigorous industrial environments. Steel is also highly resistant to damage from impacts.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
Pros: Steel wheels offer exceptional load capacity and longevity, making them ideal for heavy machinery and industrial carts.
Cons: The primary drawback is their weight, which can hinder maneuverability. Additionally, steel is prone to rust and corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel wheels are best used in outdoor or heavy-duty applications, such as construction sites or heavy machinery transport.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider corrosion resistance in humid or coastal regions. Compliance with safety standards like ASTM or DIN is also essential for ensuring quality and reliability.
What Are the Benefits of Cast Iron in Machinery Wheels?
Cast iron wheels are celebrated for their robustness and ability to handle heavy loads. They are particularly effective in high-temperature applications and provide excellent wear resistance. However, cast iron is brittle, which can lead to cracking under extreme stress.
Pros: Cast iron wheels are highly durable and can support substantial weight, making them suitable for industrial settings.
Cons: The brittleness of cast iron can be a significant disadvantage in applications where shock loads are common. They are also heavy, which can complicate maneuverability.
Impact on Application: Ideal for stationary equipment or heavy machinery that requires stability, cast iron wheels are commonly used in manufacturing and heavy transport.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that cast iron wheels meet local regulatory standards for safety and performance, particularly in regions with strict industrial regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Machinery Wheels
| Material | Typical Use Case for machinery wheels | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Hospital equipment, light-duty carts | Excellent shock absorption | Less durable in abrasive environments | Low |
| Polyurethane | Warehouses, manufacturing facilities | Superior abrasion resistance | Higher manufacturing cost | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy machinery, industrial carts | Exceptional load capacity | Prone to rust without treatment | High |
| Cast Iron | Manufacturing, heavy transport | Highly durable and stable | Brittle, can crack under stress | Medium |
This comprehensive guide to material selection for machinery wheels provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machinery wheels
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Machinery Wheels?
The manufacturing process of machinery wheels is intricate and requires precision at each stage to ensure high performance and reliability. The main stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
How Is Material Prepared for Machinery Wheels?
Material selection is crucial for durability and performance. Common materials used in machinery wheels include various grades of steel, polyurethane, and nylon. The preparation phase involves cutting raw materials to specific dimensions and conducting initial quality checks to ensure they meet the required standards. For instance, steel components may undergo processes such as heat treatment to enhance strength and wear resistance.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Process?
The forming stage is where raw materials are shaped into their final design. This can involve techniques such as casting, forging, and machining.
- Casting: This technique involves pouring molten metal into a mold. It is effective for producing complex shapes and allows for high-volume production.
- Forging: Often used for steel wheels, forging enhances the material’s strength through deformation. This process is particularly valuable for heavy-duty applications where load-bearing capacity is critical.
- Machining: This involves removing material to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining ensures high precision and repeatability, which is essential for components that require tight tolerances.
How Are Machinery Wheels Assembled?
After forming, the next step is assembly. This phase can include integrating various components, such as wheels, axles, and bearings.
- Welding: For certain wheel types, welding may be employed to join parts securely. It is essential to ensure that welds are done correctly to maintain structural integrity.
- Press Fitting: This method is often used to fit bearings into wheel hubs, ensuring a snug fit that minimizes play and enhances performance.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Machinery Wheels?
Finishing processes are critical for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and durability of machinery wheels. Common finishing techniques include:
- Coating: Wheels may be coated with paint, powder, or galvanizing to protect against corrosion and wear. This is particularly important in industrial environments where exposure to harsh conditions is common.
- Polishing: This step improves the surface finish, reducing friction and enhancing the visual appeal of the wheels.
What International Standards and Quality Assurance Practices Are Relevant for Machinery Wheels?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of machinery wheels, particularly for B2B buyers who demand reliability and safety. International standards such as ISO 9001 set the framework for effective quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) can be crucial, depending on the application of the wheels.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This involves continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) may be employed to detect variations that could affect quality.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection ensures that the finished products meet all specifications before they are shipped. This may include load testing, dimensional checks, and visual inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are several strategies:
What Methods Can Be Used to Verify Quality Control?
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality management systems, and compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC practices, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and product reliability.
What Are the Specific QC/CERT Nuances for International Buyers?
Different regions may have specific requirements regarding certifications and quality standards. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE marking for compliance with EU regulations, while buyers in the Middle East might focus on local standards. Understanding these nuances can help buyers make informed decisions when sourcing machinery wheels.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for machinery wheels are vital for ensuring that these components meet the rigorous demands of various industries. By understanding the stages of production and the importance of quality control, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Ensuring compliance with international standards and conducting thorough evaluations of potential partners will significantly enhance the reliability and performance of machinery wheels in their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machinery wheels’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of machinery wheels can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. This step-by-step checklist is designed to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and industry standards.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before exploring suppliers, outline the specific technical requirements of the machinery wheels you need. Consider factors such as load capacity, wheel diameter, material composition, and tread type. This clarity helps you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensures that you select products that meet your operational demands.
- Load Capacity: Assess the maximum weight the wheels will need to support.
- Material: Choose between options like polyurethane, nylon, or metal based on environmental conditions and application requirements.
Step 2: Research Available Options
Conduct thorough research on the types of machinery wheels available in the market. Look into various designs, such as swivel, rigid, and locking casters. Understanding the options will help you identify which types best suit your applications and operational needs.
- Swivel vs. Rigid: Swivel wheels provide maneuverability, while rigid wheels offer stability.
- Special Features: Consider features like low rolling resistance or debris-repelling capabilities that enhance performance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request information about their company history, product range, and customer feedback. This step is crucial to ensure that you partner with a reliable source that understands your industry.
- References: Ask for testimonials or case studies from businesses in your region or industry.
- Certifications: Verify any relevant industry certifications that demonstrate compliance with quality standards.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of the machinery wheels. Testing samples in your operational environment can provide valuable insights into performance, durability, and suitability for your specific applications.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate how the wheels perform under load and in your typical working conditions.
- Durability Assessment: Check for wear and tear after a designated test period to gauge longevity.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions with your chosen supplier to negotiate pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Clear communication at this stage can prevent misunderstandings later on and secure the best deal for your organization.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about pricing tiers based on order quantities.
- Lead Times: Clarify production and shipping timelines to align with your project schedules.
Step 6: Finalize Your Order and Monitor Delivery
After finalizing the terms, place your order, and keep track of the shipment. Ensure that you have a clear point of contact for any potential issues during the delivery process.
- Order Confirmation: Get a written confirmation detailing the specifications and expected delivery dates.
- Delivery Tracking: Use tracking systems provided by the supplier to monitor the shipment’s progress.
Step 7: Conduct Post-Purchase Evaluation
After receiving your machinery wheels, perform a post-purchase evaluation to assess their performance and overall satisfaction. This feedback can inform future purchases and strengthen your relationship with the supplier.
- Performance Review: Assess how well the wheels meet your operational needs.
- Supplier Feedback: Share your experience with the supplier to help improve their offerings.
By following this checklist, you can effectively navigate the procurement process for machinery wheels, ensuring that your operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machinery wheels Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing of machinery wheels is essential for international B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The sourcing of these components involves several cost components and influences that can significantly impact overall expenses.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machinery Wheels Sourcing?
-
Materials: The choice of materials—such as polyurethane, steel, or nylon—directly influences the cost of machinery wheels. High-quality materials can enhance durability and performance but typically come at a premium. Additionally, the cost of raw materials can fluctuate based on market demand and availability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this may compromise quality. Skilled labor is often necessary for producing high-quality machinery wheels, especially for customization and precision engineering.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive prices.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are particularly relevant for custom designs. Specialized molds and machinery can require significant investment. Buyers should consider whether they need standard products or customized solutions, as this will affect tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that machinery wheels meet industry standards involves quality control processes, which can add to the overall cost. Certifications such as ISO can also contribute to higher pricing but provide assurance of quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary based on the distance, weight, and size of the order, as well as the chosen Incoterms. International shipping may incur additional customs duties and taxes, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary depending on the competitive landscape and market conditions.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Machinery Wheels Pricing?
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders often lead to bulk discounts, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their needs and purchasing power.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can raise costs due to additional labor and tooling requirements. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against the potential cost savings of standard products.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality standards and certifications often command a premium price. However, investing in quality can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer lifespans, enhancing overall value.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service level can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their proven track record and support services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Different terms can lead to varying cost implications.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Machinery Wheels Prices?
-
Negotiate Based on Volume: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating better pricing based on order volume. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts for larger commitments.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Evaluate the long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential downtime, which can significantly impact overall expenditure.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Understand that pricing may vary based on geographic location, currency fluctuations, and local economic conditions. Buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia should stay informed about local market trends.
-
Request Quotes from Multiple Suppliers: Compare pricing and terms from various suppliers to ensure you are getting a competitive deal. This can also provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Clarify Incoterms: Ensure that both parties understand the agreed-upon Incoterms to avoid unexpected costs during shipping and delivery.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for machinery wheels can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they make informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machinery wheels With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Machinery Wheels
In the quest for efficient material handling and mobility solutions, machinery wheels are often a preferred choice for many industries. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider alternative solutions that may better suit their specific operational needs. This analysis explores two viable alternatives to machinery wheels—industrial casters and automated guided vehicles (AGVs)—to help buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, implementation ease, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Machinery Wheels | Industrial Casters | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load capacity; versatile in use | Medium to heavy duty; ergonomic design | Efficient for automated transport |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; durable | Cost-effective; varies by type | Higher upfront cost; ROI through efficiency |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to install on existing setups | Simple installation; versatile options | Requires significant planning and setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional inspections | Low maintenance; some types are maintenance-free | Regular maintenance for optimal operation |
| Best Use Case | Heavy machinery and equipment transport | Carts, AGVs, and various industrial applications | Automated transport of materials in warehouses |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Industrial Casters?
Industrial casters serve as a flexible alternative to machinery wheels, especially in environments that require frequent movement of carts and equipment. They come in various designs—swivel, rigid, and locking—allowing for tailored solutions to meet specific needs. The ergonomic design of industrial casters reduces physical strain on workers, making them ideal for industries that prioritize safety. However, while they are generally cost-effective, the need to select the right type based on load capacity and application can complicate the purchasing process.
How Do Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) Enhance Material Handling Efficiency?
AGVs represent a modern approach to material handling, utilizing technology to automate the transportation of goods. They excel in environments that demand high efficiency and can significantly reduce labor costs over time. AGVs can navigate complex warehouse layouts and optimize routes, enhancing productivity. However, the initial investment and setup complexity can be a barrier for some organizations. Additionally, AGVs require regular maintenance and software updates to ensure smooth operation, which could impact long-term operational costs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate solution for material handling hinges on understanding specific operational requirements and constraints. Machinery wheels offer robust performance for heavy loads and are easy to implement, making them suitable for traditional setups. In contrast, industrial casters provide ergonomic benefits and versatility for various applications, while AGVs offer advanced automation capabilities for high-efficiency environments. B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their unique contexts, including budget, workload, and desired operational efficiency, to determine the best option for their business. Each solution has distinct advantages and potential drawbacks, making it crucial to align the choice with long-term strategic goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machinery wheels
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machinery Wheels?
When selecting machinery wheels for industrial applications, understanding their technical properties is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Below are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Load Capacity
Load capacity refers to the maximum weight that a wheel can support. This specification is crucial as it directly impacts the safety and efficiency of operations. Wheels with inadequate load capacity may fail under pressure, leading to equipment damage or workplace accidents. It’s essential to match the wheel’s capacity with the specific requirements of the machinery and materials being transported.
2. Material Composition
The material of the wheel significantly affects its durability, resistance to wear, and suitability for various environments. Common materials include polyurethane, nylon, and cast iron. For instance, polyurethane wheels are known for their shock-absorbing properties and are ideal for environments with debris, while cast iron offers higher load capacities but may not be suitable for all floor types due to potential floor damage.
3. Wheel Diameter
The diameter of the wheel influences both maneuverability and load distribution. Larger wheels can roll over obstacles more easily and reduce rolling resistance, which is particularly advantageous in heavy-duty applications. Conversely, smaller wheels may be more suitable for tight spaces but can lead to increased effort required for movement.
4. Tread Design
The tread design of a wheel affects its traction, stability, and floor protection. Tread patterns can be smooth, ribbed, or textured, each serving different purposes. For example, smooth treads reduce rolling resistance but may offer less grip, while textured treads enhance traction but can increase wear on flooring. Selecting the appropriate tread design is vital for ensuring optimal performance in specific operational conditions.
5. Bearing Type
The type of bearing used in machinery wheels can influence their efficiency and maintenance needs. Common bearing types include ball bearings, roller bearings, and plain bearings. Ball bearings generally offer lower rolling resistance and smoother operation, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Understanding the bearing type helps in selecting wheels that require minimal maintenance and provide reliable performance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Machinery Wheels?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the machinery wheels market. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of machinery wheels, an OEM may supply wheels that are integrated into larger machinery systems. Buyers often seek OEM products for their guaranteed compatibility and quality assurance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for inventory management, as it can affect purchasing decisions and overall project costs. Buyers should consider their needs and negotiate MOQs that align with their operational requirements.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products or services. In the context of machinery wheels, an RFQ helps buyers obtain competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping, insurance, and the transfer of risk. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border procurement of machinery wheels to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the products. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management, particularly in industries where machinery wheels are critical to operational continuity.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing machinery wheels, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and safety.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machinery wheels Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Machinery Wheels Market?
The machinery wheels market is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by various global factors. Increased industrialization and urbanization in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are propelling demand for machinery wheels across diverse sectors, including construction, manufacturing, and logistics. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as automation and robotics, are influencing the design and functionality of machinery wheels. For instance, the integration of low rolling resistance materials is enhancing the performance of industrial casters, making them essential for automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and other material handling equipment.
International buyers are also increasingly focused on sourcing high-capacity machinery wheels, particularly in heavy-duty applications, where load-bearing capabilities can reach up to 100,000 lbs. The trend towards customization is emerging, with businesses seeking tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements. Additionally, digital platforms are transforming procurement processes, allowing for better comparison of product specifications, pricing, and supplier reliability, thereby streamlining the sourcing of machinery wheels.
Another noteworthy trend is the growing emphasis on ergonomic design in machinery wheels, which aims to reduce physical strain on workers and improve overall workplace safety. This is particularly relevant for regions experiencing a labor shortage, where efficiency and worker well-being are paramount.
Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Trends for Machinery Wheels?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the sourcing of machinery wheels. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their purchasing decisions, seeking suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials, such as high-quality polyurethane and recycled metals, which minimize the carbon footprint associated with production.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining traction, as businesses strive to ensure transparency and fairness in their sourcing practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other ‘green’ credentials are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract conscientious buyers. Moreover, the focus on reducing waste through circular economy principles is influencing product design and manufacturing processes, promoting longer-lasting and more easily recyclable machinery wheels.
Investing in sustainable products not only enhances a company’s corporate social responsibility profile but can also lead to cost savings over time through reduced maintenance and replacement needs. As global markets continue to prioritize sustainability, international buyers must consider these factors when sourcing machinery wheels.
What Is the Historical Evolution of Machinery Wheels in the B2B Context?
The evolution of machinery wheels can be traced back to the industrial revolution, where the need for efficient transport of heavy materials led to the development of rudimentary wheel designs. Early wheels were often made from wood and metal, with limited load-bearing capabilities. As industries evolved, so did the materials and technology used in wheel manufacturing. The introduction of rubber and polyurethane revolutionized the industry, offering better durability, shock absorption, and traction.
In the late 20th century, advancements in engineering and manufacturing processes led to the production of specialized wheels designed for specific applications, such as heavy-duty industrial casters and ergonomic designs. Today, the machinery wheels market is characterized by a diverse range of products that cater to various sectors, driven by technological innovation and a growing emphasis on sustainability. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of selecting suppliers that not only understand the evolution of machinery wheels but also are poised to meet future demands through innovative and sustainable practices.

Illustrative image related to machinery wheels
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machinery wheels
-
How do I choose the right machinery wheels for my application?
Selecting the right machinery wheels depends on several factors including load capacity, wheel material, and the specific conditions of use. Consider the weight of the equipment, the type of flooring, and whether the wheels will be subjected to outdoor conditions. For heavy-duty applications, look for wheels made from durable materials like polyurethane or steel that offer high load ratings. Additionally, assess if you need swivel or rigid wheels for better maneuverability based on your operational needs. -
What is the best material for machinery wheels in industrial settings?
The best material for machinery wheels largely depends on the operational environment and load requirements. Polyurethane wheels are favored for their versatility, providing excellent shock absorption and durability on various surfaces, while steel wheels are ideal for heavy-duty applications due to their strength. For environments exposed to moisture or chemicals, stainless steel wheels are recommended to prevent corrosion. Always evaluate the specific demands of your application before making a choice. -
What are the common load capacities for industrial machinery wheels?
Industrial machinery wheels come in a wide range of load capacities, typically from 1,000 lbs to over 100,000 lbs. For lighter applications, such as utility carts, capacities around 1,000 to 5,000 lbs are sufficient. In contrast, heavy-duty applications, such as those found in manufacturing or shipping, may require wheels capable of supporting loads of 15,000 lbs and above. It’s crucial to match the wheel capacity with the maximum load it will encounter to ensure safety and efficiency. -
How can I ensure the quality of machinery wheels from suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by vetting suppliers with a proven track record in the machinery wheel industry. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Request samples to evaluate the materials and construction firsthand. Additionally, ask about their quality assurance processes, including testing methods for load capacity and durability. Checking customer reviews and case studies can also provide insights into the supplier’s reliability. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for machinery wheels?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of machinery wheels you need. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 10-50 units for standard wheels to several hundred for specialized or customized options. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify MOQs upfront and explore the possibility of lower quantities for trial orders, especially if you are testing new products or entering new markets. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing machinery wheels internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of machinery wheels typically range from 30% to 50% upfront, with the remainder due upon delivery or after inspection. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms based on your credit history and relationship. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and to consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to protect both parties during the transaction. -
How do logistics and shipping affect the procurement of machinery wheels?
Logistics and shipping play a crucial role in the timely procurement of machinery wheels. Factors such as shipping method, lead time, and customs clearance can significantly impact delivery schedules. When sourcing internationally, work with suppliers who have reliable logistics partners and can provide tracking information. Be aware of potential delays due to customs and factor in additional costs such as tariffs and taxes that may apply when importing goods into your country. -
Can I customize machinery wheels to fit specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for machinery wheels. Customization can include variations in size, material, load capacity, and design features like tread patterns or mounting styles. When considering customization, communicate your specific requirements clearly and inquire about the design process, lead times, and any additional costs involved. Custom wheels can enhance performance and efficiency in specialized applications, making them a worthwhile investment.
Top 7 Machinery Wheels Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Caster Concepts – Extra Heavy Duty Casters
Domain: casterconcepts.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Extra Heavy Duty Casters – Built for the Toughest Loads (15,000lbs. to 34,999lbs.)
– Load Rating: 15,000 lbs. to 34,999 lbs. per caster
– Applications: Material handling challenges
– Customization: Available for specific needs or off-the-shelf options
– Series: Various series available including Series 30, 51, 52, 54, 55, 57, 61, 62, 66, 25, 33, 40, 50, 103, 112, 134, 138, 140, 154
– Brands: Caste…
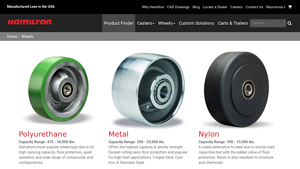
2. Hamilton Caster – Polyurethane & Metal Casters
Domain: hamiltoncaster.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Polyurethane”:{“Capacity Range”:”475 – 34,000 lbs.”,”Features”:”High carrying capacity, floor protection, quiet operation, wide range of compounds and configurations.”},”Metal”:{“Capacity Range”:”250 – 23,000 lbs.”,”Features”:”Highest capacity & tensile strength, easiest rolling sans floor protection, popular for high heat applications.”},”Nylon”:{“Capacity Range”:”350 – 10,000 lbs.”,”Features”:…
3. Industrial Caster & Wheel – Wide Range of Casters and Wheels
Domain: industrialcasterandwheel.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Industrial Caster & Wheel offers a wide range of casters and wheels including:
– Caster Types:
– Furniture Casters
– Light Duty Casters
– General Duty Casters
– Light Medium Duty Casters
– Medium Heavy Duty Casters
– Heavy Duty Casters
– Extra Heavy Duty Casters
– Business Machine Casters
– Specialty Casters
– Wheel Types:
– Rubber
– Polyurethane
– Metal
…
4. Toolwell – JUWAthan K Wheel
Domain: toolwell.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: [{‘MPN’: ‘Roller K JUWAthan K Wheel (Yellow) – Full-size’, ‘Diameter’: ‘3.3in’, ‘Width’: ‘3.3in’, ‘Fits’: ‘JUNG AB3-12 T6-12 XY14’, ‘Price’: ‘$108.00’}, {‘MPN’: ‘Roller K JUWAthan K Wheel (Yellow) – Half-size’, ‘Diameter’: ‘3.3in’, ‘Width’: ‘1.7in’, ‘Fits’: ‘JUNG D3-5 and R1-8’, ‘Price’: ‘$87.00’}, {‘MPN’: ‘Roller R JUWAmid R Wheel (black)’, ‘Diameter’: ‘3.3in’, ‘Width’: ‘1.7in’, ‘Fits’: ‘JUNG R2-…
5. Titan International – Agriculture Wheels
Domain: titan-intl.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Titan International offers a range of agriculture wheels designed for modern agricultural equipment, including tractors, combines, grain carts, and sprayers. Key features include: 1. Collaboration with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to develop innovative wheel solutions. 2. Durable construction with powder-coated components, high-quality welds, and robust steel for long service life. 3. C…
6. GMI Wheels – EM / EV Series
Domain: gmiwheels.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: GMI Wheels offers construction wheels compatible with all equipment makes and models, including haulers, loaders, skid steers, dozers, and graders from brands like CAT, Deere, Komatsu, and Volvo. Key product lines include:
1. **EM / EV Series (5-Piece)**:
– Sizes: 24″ to 49″
– Features: Fully machined surfaces, class-leading tire fitment and air seal, customizable bolt patterns and offse…
7. ServiceCaster – Caster Wheels and Heavy Duty Wheels
Domain: shop.servicecaster.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Caster Wheels and Heavy Duty Wheels for Equipment. Most Orders Placed by 3 pm EST Ship Same Day! Available payment options: Credit Card, Amazon Pay, Paypal Express. Contact: 1-800-215-8220. Product categories include: Chair and Furniture Casters, Grip Ring Stem, Grip Neck Stem, Threaded Stem, Ball Casters, Pacer, Pilot, Series 05, Softech, Spherical Ball Casters, Ultima, Metric Stems, Large & Heav…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machinery wheels
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing of machinery wheels is pivotal for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. By prioritizing factors such as load capacity, material durability, and ergonomic design, businesses can select the right products that meet their unique operational demands. Leveraging suppliers who offer customized solutions and robust after-sales support can further streamline procurement processes and ensure long-term reliability.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality, heavy-duty machinery wheels will only increase. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who understand the local landscape and can provide tailored solutions that align with regional requirements.
The future of machinery wheels is bright, with innovations in materials and design enhancing performance and sustainability. As you explore your sourcing options, consider the long-term benefits of investing in superior machinery wheels that can withstand the rigors of industrial applications. Start a conversation with trusted suppliers today and position your business for success in a competitive global market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.