Parts Of A Simple Motor: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts of a simple motor
In the fast-evolving landscape of manufacturing and engineering, sourcing high-quality parts of a simple motor presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricate components, such as rotors, stators, and bearings, is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and product reliability. This guide delves into the diverse types of motor components, their applications across various industries, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
From the stator configurations to rotor classifications, we will explore the essential features that define motor functionality, empowering you to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we will address cost considerations and sourcing strategies tailored to the unique needs of buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil.
By equipping you with in-depth knowledge and practical insights, this guide not only simplifies the procurement process but also enhances your ability to negotiate effectively and secure optimal deals. Whether you are looking to upgrade your supply chain or ensure compliance with industry standards, understanding the parts of a simple motor is vital for maintaining a competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding parts of a simple motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squirrel-Cage Rotor | Simple design, robust, low maintenance | HVAC systems, industrial fans, pumps | Pros: Cost-effective, reliable. Cons: Limited speed control. |
| Permanent Magnet Stator | Uses permanent magnets for efficient operation | Electric vehicles, robotics, consumer electronics | Pros: High efficiency, compact design. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Brushless DC Motor | No brushes, electronic commutation | Automation, drones, electric bicycles | Pros: Longer lifespan, quieter operation. Cons: Complex control systems. |
| Induction Motor | Relies on electromagnetic induction for operation | Manufacturing, conveyor systems, compressors | Pros: Durable, versatile. Cons: Requires AC power supply. |
| Commutator Rotor | Uses a commutator to maintain current flow | Toys, small appliances, automotive applications | Pros: Simple design, easy to control. Cons: Brushes wear out, requires maintenance. |
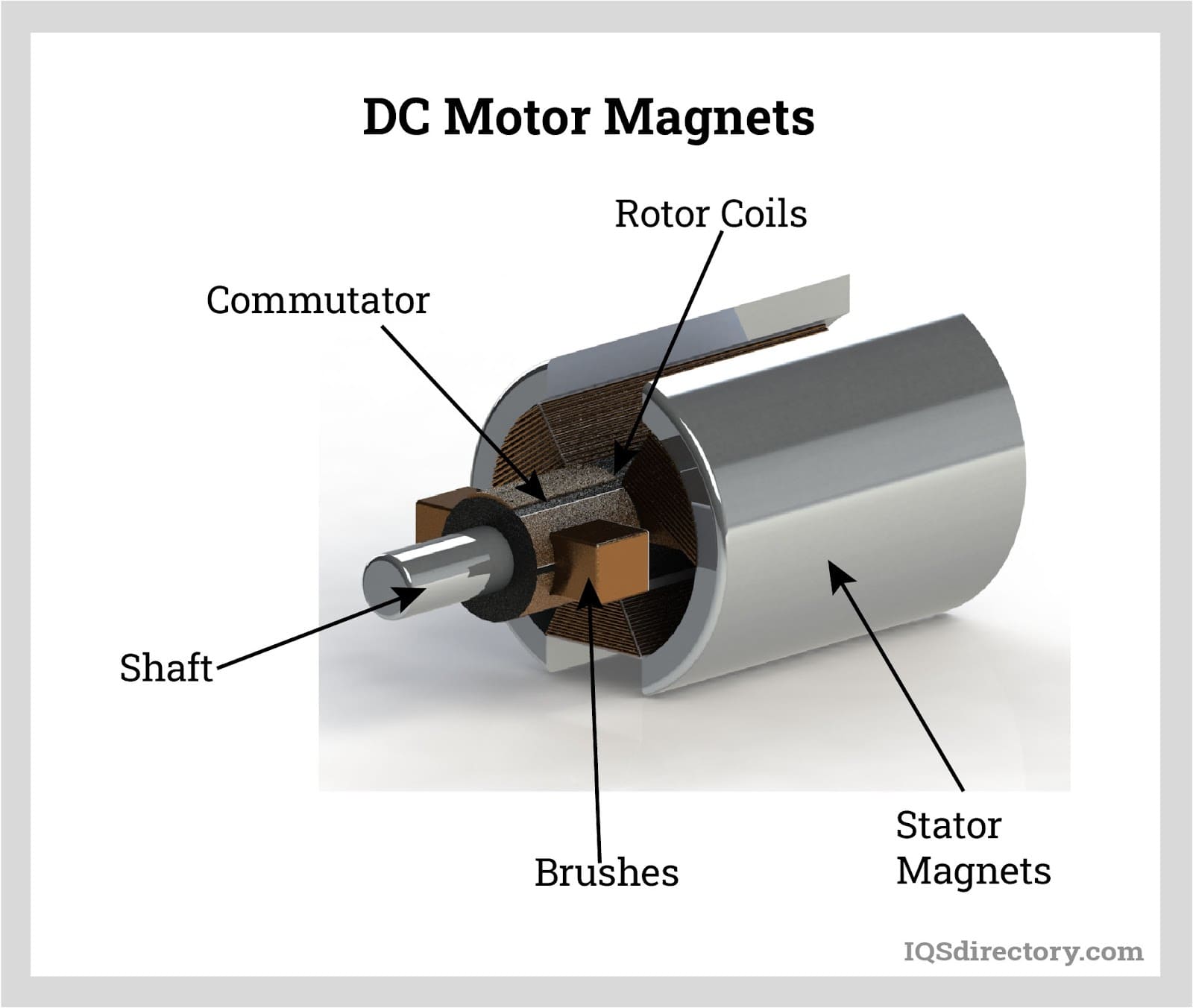
What Are the Key Characteristics of Squirrel-Cage Rotors?
Squirrel-cage rotors are characterized by their simple construction, which consists of laminated steel cores with conductive bars running parallel to the rotor axis. They are designed for robustness and low maintenance, making them ideal for applications in HVAC systems, industrial fans, and pumps. Buyers should consider the rotor’s reliability and cost-effectiveness, although it may lack advanced speed control features.
Illustrative image related to parts of a simple motor
How Do Permanent Magnet Stators Enhance Motor Efficiency?
Permanent magnet stators utilize permanent magnets to create a magnetic field, significantly enhancing efficiency, especially in compact designs. This type is commonly used in electric vehicles, robotics, and consumer electronics. B2B buyers should evaluate the higher initial costs against the long-term energy savings and performance benefits, particularly in applications requiring high efficiency.
What Advantages Do Brushless DC Motors Offer to Businesses?
Brushless DC motors are distinguished by their lack of brushes, which eliminates friction and enhances efficiency. They are widely used in automation, drones, and electric bicycles. While these motors offer a longer lifespan and quieter operation, buyers must consider the complexity of control systems and potential higher costs associated with advanced electronics.
Why Are Induction Motors a Popular Choice in Manufacturing?
Induction motors operate based on electromagnetic induction, making them highly durable and versatile. They are commonly used in manufacturing processes, conveyor systems, and compressors. B2B buyers appreciate their robustness and reliability, but should also be mindful of the need for an AC power supply, which may limit application in certain environments.
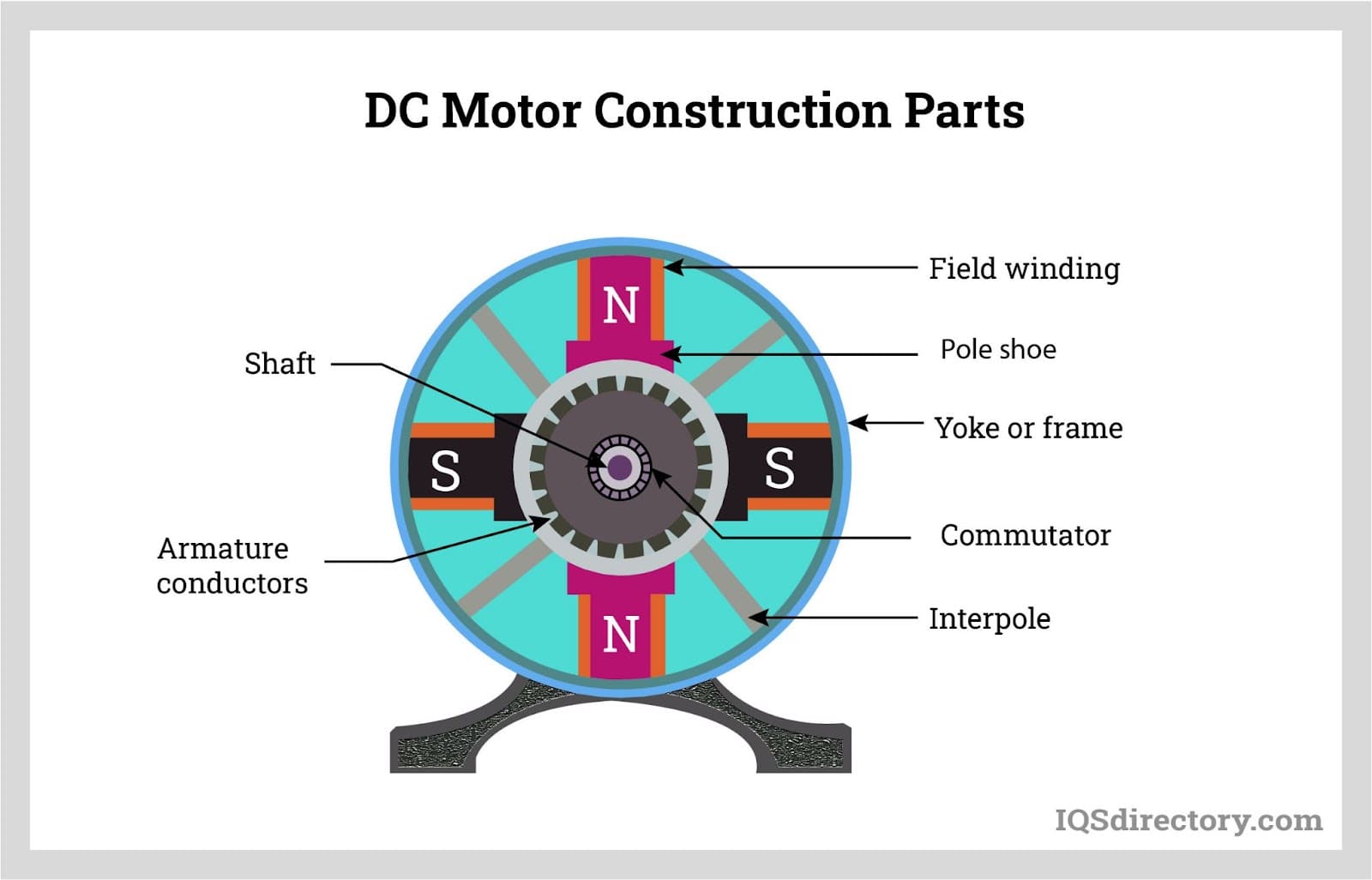
What Makes Commutator Rotors Suitable for Small Appliances?
Commutator rotors feature a simple design that allows for straightforward control of motor operation, making them suitable for toys, small appliances, and automotive applications. While they are easy to control and cost-effective, the brushes can wear out over time, necessitating regular maintenance. Buyers should weigh the initial affordability against the potential for increased maintenance costs.
Key Industrial Applications of parts of a simple motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of parts of a simple motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor systems utilizing DC motors | Enhanced production efficiency and reduced downtime | Quality of motor components, reliability, and cost-effectiveness |
| Agriculture | Electric pumps powered by AC motors | Improved irrigation efficiency and crop yield | Durability in harsh environments, energy efficiency, and maintenance support |
| Automotive | Electric power steering systems | Increased safety and improved driving experience | Compatibility with vehicle specifications, sourcing from certified manufacturers |
| HVAC | Fans and blowers in heating and cooling systems | Consistent temperature control and energy savings | Energy ratings, noise levels, and integration with existing systems |
| Robotics | Actuators in robotic arms | Precision movement and task automation | Customization options, lead times, and technical support for integration |
How Are Parts of a Simple Motor Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, parts of a simple motor, particularly DC motors, are integral to conveyor systems. These motors facilitate the smooth transport of materials along production lines, significantly enhancing efficiency and minimizing operational downtime. For international buyers, sourcing high-quality motor components is essential, as reliability directly impacts production rates. Additionally, businesses must consider the cost-effectiveness of these components to maintain profitability while ensuring consistent performance.
What Role Do Simple Motors Play in Agriculture?
Electric pumps powered by AC motors are vital in agriculture, particularly for irrigation systems. These motors allow for efficient water distribution, directly influencing crop yield and resource management. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should prioritize durable motor components that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Furthermore, energy efficiency is a crucial consideration, as it can lead to substantial cost savings over time, making the investment more appealing to farmers and agribusinesses.
How Are Simple Motors Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, simple motors are commonly found in electric power steering systems. These motors enhance vehicle safety by providing precise steering control, contributing to an improved driving experience. For B2B buyers in this sector, sourcing motors that meet specific vehicle specifications is critical. Additionally, ensuring that components come from certified manufacturers can help maintain quality and compliance with industry standards, thereby reducing the risk of recalls and enhancing brand reputation.
What Benefits Do HVAC Systems Gain from Simple Motors?
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems utilize fans and blowers powered by simple motors to maintain consistent temperature control within buildings. These motors contribute to energy savings, which is increasingly important in today’s eco-conscious market. International buyers need to consider the energy ratings and noise levels of motor components to ensure they meet local regulations and customer expectations. Furthermore, integration with existing systems should be seamless to minimize installation costs and time.
How Are Simple Motors Essential for Robotics?
In robotics, simple motors function as actuators in robotic arms, providing the necessary movement for tasks ranging from assembly to packaging. The precision offered by these motors is crucial for automation, enhancing productivity and accuracy in various applications. Buyers in the robotics sector must focus on customization options and technical support from suppliers to ensure that motors can be tailored to specific robotic functions. Lead times for sourcing these components are also important, as they can impact project timelines and budgets.
Illustrative image related to parts of a simple motor
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts of a simple motor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing Quality Components for Reliability Issues
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in sectors like manufacturing or automotive face the critical challenge of sourcing reliable motor parts. A common scenario is when they opt for low-cost components to save on initial expenses, only to discover that these parts fail prematurely. This not only leads to unexpected downtime but also incurs additional costs for replacements and repairs, disrupting production schedules and impacting customer satisfaction. Buyers often feel the pressure of balancing cost with quality, especially when operating in competitive markets where margins are tight.
The Solution: To mitigate reliability issues, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable manufacturers with a proven track record in quality control. It’s essential to conduct thorough research, including reviewing certification standards (like ISO 9001) and requesting samples for testing. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can provide better insights into the durability and performance of motor components. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in premium parts upfront, as they may save money in the long run by reducing maintenance and replacement costs. Implementing a structured vendor assessment process can also ensure consistent quality and reliability.
Scenario 2: Navigating Technical Specifications for Compatibility
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is understanding the technical specifications of motor parts, particularly when integrating new components into existing systems. For instance, a buyer may purchase a rotor that appears compatible based on size but does not align with the electrical specifications or load requirements of the motor. This oversight can lead to inefficiencies, increased energy consumption, or even system failures, causing frustration and significant operational delays.
Illustrative image related to parts of a simple motor
The Solution: To avoid compatibility issues, B2B buyers should invest time in thoroughly analyzing the technical specifications of both the existing motor and the new components. This includes reviewing parameters such as voltage ratings, torque requirements, and thermal limits. Engaging with engineering teams to create a detailed compatibility checklist can streamline this process. Furthermore, buyers should utilize simulation software to model the interaction between different motor parts before making a purchase. This proactive approach not only helps ensure compatibility but also enhances overall system efficiency.
Scenario 3: Managing Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: In today’s global market, many B2B buyers face supply chain disruptions that affect the availability of motor parts. Events such as geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or even pandemics can lead to delays in production or shipping, causing critical components to be out of stock. This situation can stall manufacturing processes and lead to missed deadlines, ultimately affecting a company’s reputation and bottom line.
The Solution: To effectively manage supply chain disruptions, B2B buyers should diversify their supplier base to include multiple vendors from different regions. This strategy reduces dependency on a single source and enhances resilience against localized disruptions. Additionally, implementing an inventory management system that forecasts demand based on historical data can help maintain optimal stock levels. Establishing strong communication channels with suppliers can provide early warnings about potential delays, allowing buyers to adjust their production schedules accordingly. Creating a contingency plan that includes alternative suppliers and expedited shipping options can further safeguard against unexpected disruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts of a simple motor
What Are the Key Materials Used in Motor Components?
When selecting materials for the various components of a simple motor, it is crucial to consider the specific properties and performance requirements of each material. Below, we analyze four common materials used in motor construction: copper, silicon steel, aluminum, and various insulating materials.
How Does Copper Perform as a Conductor in Motors?
Copper is widely used for windings and lead wires in motors due to its excellent electrical conductivity, which is essential for efficient power transfer. Key properties of copper include a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various operating environments.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity leads to lower energy losses, enhancing motor efficiency. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and shape into wires and coils.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which is higher than alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, copper is heavier, which may not be ideal for lightweight applications.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with high temperatures and its resistance to corrosion make it suitable for motors used in harsh environments, such as industrial machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and pricing fluctuations. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire may also be necessary.
What Role Does Silicon Steel Play in Motor Cores?
Silicon steel is used for the cores of both stators and rotors due to its magnetic properties, which enhance the efficiency of the motor by reducing energy losses associated with hysteresis and eddy currents. Key properties include a high permeability and low core loss at various frequencies.
Pros: Silicon steel is cost-effective and readily available, making it a popular choice for motor cores. Its magnetic properties significantly improve motor performance.
Cons: While silicon steel is durable, it can be brittle and may require careful handling during manufacturing to avoid damage.
Impact on Application: The material’s magnetic characteristics make it ideal for motors operating at different frequencies, particularly in applications requiring variable speed control.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as DIN 46231 for electrical steel is crucial. Buyers should also assess the availability of silicon steel grades that meet specific performance requirements.
Why Is Aluminum Considered for Motor Components?
Aluminum is often used in motor housings and some rotor designs due to its lightweight nature and good thermal conductivity. Key properties include a melting point of approximately 1,221°F (660°C) and natural corrosion resistance due to its oxide layer.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum can lead to reduced overall motor weight, enhancing performance in applications where weight is a concern. It is also less expensive than copper.
Cons: Aluminum has lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, which may lead to higher energy losses in windings. Additionally, it can be more challenging to work with in terms of machining and welding.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s thermal properties allow for efficient heat dissipation, making it suitable for high-speed applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local aluminum standards and certifications, such as JIS H 4000 in Japan, to ensure quality and compliance.
What Insulating Materials Are Used in Motor Construction?
Insulating materials, such as enamel, rubber, and various polymers, are critical for preventing electrical shorts and ensuring safe operation. Key properties include high dielectric strength and temperature resistance, which can vary widely depending on the specific material.
Pros: These materials are generally lightweight and can be produced in various forms, allowing for flexibility in design. They also provide good thermal insulation.
Cons: Some insulating materials may degrade over time, especially under high temperatures or in corrosive environments, necessitating regular maintenance or replacement.
Impact on Application: The choice of insulating material affects the motor’s operational lifespan and reliability, particularly in extreme conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards, such as IEC 60085 for thermal insulation, is essential. Buyers should also consider the local climate and environmental factors that may impact material performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Motor Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for parts of a simple motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings, lead wires | Excellent electrical conductivity | Higher cost compared to aluminum | High |
| Silicon Steel | Stator and rotor cores | Cost-effective with good magnetic properties | Brittle and requires careful handling | Medium |
| Aluminum | Motor housings, some rotor designs | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Insulating Materials | Insulation for windings and components | Good dielectric strength | Potential degradation over time | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance requirements, cost considerations, and compliance with relevant standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts of a simple motor
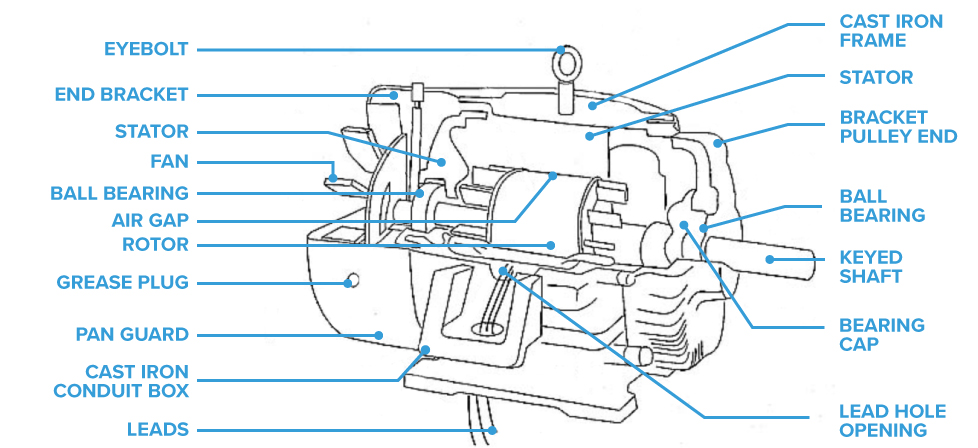
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Motor Components?
The manufacturing process for motor components involves several critical stages, each of which plays a vital role in ensuring the final product’s performance and reliability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Motor Parts Manufacturing?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials, such as copper for windings, silicon steel for cores, and various polymers for insulation. Suppliers should provide certificates of analysis (CoA) to verify material properties. This stage also involves cutting and processing materials to meet specific dimensions and tolerances required for the motor components. For instance, copper wires are drawn to precise gauges, while steel sheets are cut to shape for stator and rotor cores.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
Forming techniques for motor components vary depending on the part being produced. Common methods include:
- Stamping and Die-Cutting: Used for creating the stator and rotor laminations from steel sheets, ensuring they are thin to reduce eddy current losses.
- Winding: Magnet wire is wound around the stator and rotor cores. Precision in winding is crucial for generating the required electromagnetic fields.
- Casting and Molding: Some components, such as housings and end plates, may be produced using aluminum die-casting or injection molding techniques, allowing for complex shapes and lightweight structures.
These techniques must ensure dimensional accuracy and consistency, as any discrepancies can lead to performance issues.
How Are Motor Components Assembled?
Assembly is a critical phase that requires meticulous attention to detail. Components such as the stator, rotor, bearings, and brackets are brought together in a clean environment to prevent contamination. During assembly, the following practices are essential:
- Alignment: Ensuring that the rotor is correctly aligned within the stator to minimize friction and wear.
- Fastening: Using screws, bolts, or adhesives to securely attach components while maintaining the integrity of the assembly.
- Integration of Electrical Components: Lead wires must be connected accurately to ensure proper electrical flow. This includes soldering and crimping techniques that need to be performed under strict quality control.
What Finishing Processes Are Required for Motor Parts?
Finishing processes enhance the performance and durability of motor components. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: This may involve coating, painting, or anodizing to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Balancing: Rotors may undergo dynamic balancing to ensure smooth operation and minimize vibration during use.
- Inspection: Post-assembly inspections verify that all components meet design specifications and function correctly.
What Quality Control Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of motor components. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring consistency and reliability in production. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets or API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications may be relevant depending on the motor’s intended use.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. These checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials upon arrival, ensuring they meet specifications before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing stages, including dimensional checks and functional tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the completed motor components to ensure they meet all performance and safety standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verifying supplier quality control processes. Key strategies include:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to assess manufacturing practices, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
- Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline testing results, defect rates, and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate products before shipment, ensuring adherence to specifications and quality standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware of Regarding Quality Control?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control nuances:
Illustrative image related to parts of a simple motor
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations can help in negotiating and establishing effective partnerships.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have specific regulations that must be adhered to. Familiarity with these regulations is essential for avoiding compliance issues.
- Logistical Challenges: Buyers should account for potential delays in shipping and customs clearance, which can impact the timely delivery of quality components.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can better assess suppliers, ensuring they receive high-quality motor components that meet their operational needs. This thorough understanding not only enhances procurement strategies but also fosters stronger supplier relationships, ultimately leading to improved business outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts of a simple motor’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to source components of a simple motor. Understanding each part and its specifications is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in your applications. Follow these steps to streamline your sourcing process and make informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for each motor component you need. This includes dimensions, materials, and performance characteristics such as torque ratings and voltage specifications. Having precise specifications helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and reduces the likelihood of errors in the procurement process.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers that specialize in motor components and have a proven track record in your target market. Pay attention to their production capabilities, quality control processes, and customer reviews, particularly from businesses in regions similar to yours.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Verify that your selected suppliers hold necessary certifications and comply with international standards, such as ISO 9001. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality and consistency in production. Additionally, ensure that they meet regional compliance standards relevant to your industry, which can help avoid legal and operational issues later on.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Before finalizing any order, request samples of the motor components you intend to purchase. Assess the quality of materials, craftsmanship, and adherence to your specifications. This hands-on evaluation can help you identify any potential issues and allows you to make adjustments to your order if needed.
Step 5: Inquire About Warranty and Support Services
Discuss warranty terms and after-sales support with your suppliers. Understanding the warranty coverage can protect your investment and provide peace of mind in case of defects or failures. Additionally, inquire about the availability of technical support and replacement parts, as reliable support can be crucial for maintenance and operational efficiency.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations to secure favorable pricing and payment terms. Be transparent about your budget and expected order volume, as this can often lead to discounts or better terms. Consider long-term partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate flexibility and a willingness to support your business needs.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Plan
Set up a communication plan with your suppliers to ensure ongoing dialogue throughout the procurement process. Regular updates on order status, shipment tracking, and any potential delays can help manage expectations and foster a strong working relationship. Effective communication is key to addressing any issues promptly and efficiently.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing parts for a simple motor, ensuring that they select the right components for their applications while building strong relationships with reliable suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts of a simple motor Sourcing
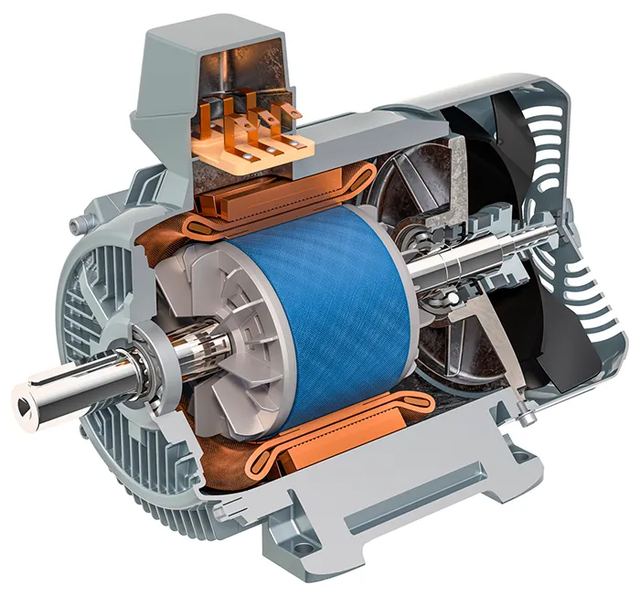
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Parts for a Simple Motor?
When sourcing parts for a simple motor, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
Illustrative image related to parts of a simple motor
-
Materials: The core materials, such as copper for windings and silicon steel for cores, often represent a significant portion of the total cost. Prices fluctuate based on global demand and supply chain dynamics, so buyers should stay informed about market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing processes. In countries with lower labor costs, such as some in Africa and South America, the overall pricing may be more competitive.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and indirect labor costs associated with production. Efficient manufacturers often have lower overhead costs, which can translate into better pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized equipment can be substantial, particularly for custom parts. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs and whether these are amortized over production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet specific standards often requires investment in quality control processes. This can include testing and certification, which may add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly depending on the distance and mode of transport. It’s essential to consider these costs, especially for international shipments, where tariffs and customs duties can apply.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin, which can vary based on competition and market conditions. Understanding the margins can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions for Motor Parts?
Several factors influence the pricing of motor components that buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to balance inventory costs with potential savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts or specific design requirements may lead to higher costs. Buyers should evaluate whether standard parts can meet their needs to minimize expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. High-quality materials may lead to higher initial costs but can result in better performance and lower maintenance over time.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts that meet international quality standards may come at a premium. However, investing in certified components can reduce the risk of failures and enhance the longevity of the motor.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better guarantees and service, while newer suppliers might be less expensive but come with higher risk.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can influence shipping costs and responsibilities. Buyers should understand the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) versus CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight).
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate with Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. It’s advisable to request quotes and compare them to identify the most cost-effective options.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than solely concentrating on the upfront cost, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtimes. This holistic view can lead to better long-term savings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing strategies influenced by local market conditions, tariffs, and currency fluctuations. Being aware of these factors can aid in making informed sourcing decisions.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Long-term partnerships often yield mutual benefits, such as favorable payment terms or priority service.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Regularly monitoring industry news and market reports can help buyers anticipate price changes and make timely purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is essential to note that the prices of motor parts can vary significantly based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific order requirements. Therefore, the prices mentioned in discussions should be considered indicative and not definitive. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts of a simple motor With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Motor Components
In the evolving landscape of industrial machinery, businesses are often presented with multiple solutions to achieve similar outcomes. When it comes to the components of a simple motor—such as the rotor, stator, and other integral parts—it’s essential to evaluate alternative technologies that may offer enhanced performance, cost-effectiveness, or ease of use. This analysis will compare the traditional parts of a simple motor with two viable alternatives: stepper motors and linear actuators.
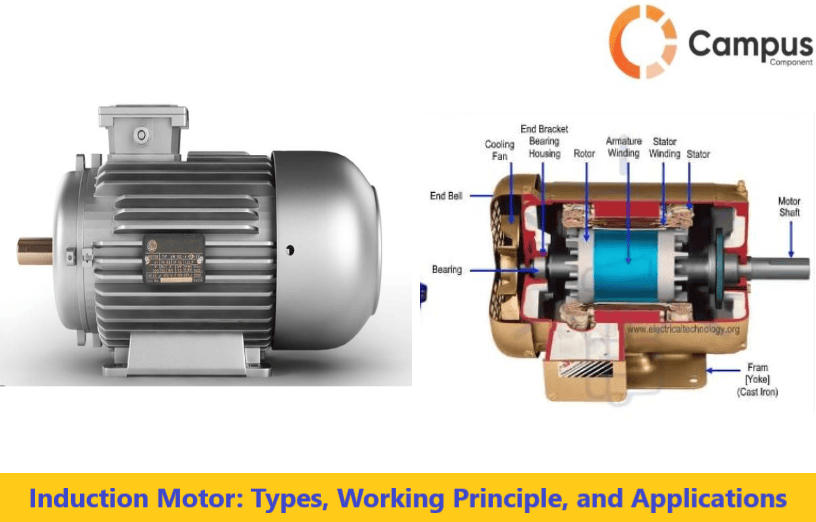
Illustrative image related to parts of a simple motor
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Parts Of A Simple Motor | Stepper Motor | Linear Actuator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, suitable for continuous rotation tasks | Excellent for precise positioning and control | Ideal for linear movement with high force |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower long-term costs | Higher initial cost; economical for high-volume applications | Variable costs; often higher due to complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward installation | Requires precise control systems | Installation can be complex, often needing additional components |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; robust design | Moderate; may require calibration | Low to moderate; depends on usage frequency |
| Best Use Case | General applications needing rotational motion | Robotics, CNC machines, and applications requiring precision | Automated systems, machinery requiring linear motion |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Stepper Motor: When Is It the Right Choice?
Stepper motors are designed for precise control and positioning, making them an excellent alternative for applications requiring exact movement. They operate by dividing a full rotation into a series of steps, allowing for high accuracy in positioning. However, the initial investment can be higher compared to traditional motor components, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, while they offer moderate maintenance needs, the requirement for calibration can add complexity. Businesses in robotics or CNC applications will find stepper motors particularly beneficial due to their precision.
Linear Actuator: What Makes It Stand Out?
Linear actuators convert rotational motion into linear movement, making them ideal for applications that require pushing or pulling actions. Their ability to deliver high force makes them suitable for heavy-duty tasks, such as in automated systems and manufacturing equipment. However, they tend to be more expensive due to their intricate design and the need for additional control systems. Installation can also be more complex, requiring careful planning and integration with existing systems. Companies looking to automate processes that involve linear motion will find that linear actuators provide the necessary strength and precision.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between traditional motor components and alternative technologies, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and the desired outcome. Factors such as the application’s complexity, precision needs, and maintenance capabilities will significantly influence the decision. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option, businesses can make informed choices that align with their strategic goals, ensuring they invest in the most effective solution for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts of a simple motor
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Motor Parts?
When sourcing parts for a simple motor, understanding critical technical properties is essential for ensuring compatibility, performance, and longevity. Here are some of the most important specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific composition and quality of materials used in motor components, such as copper wire or silicon steel cores. For instance, copper is commonly used for windings due to its excellent conductivity. Selecting the right material grade can significantly impact the motor’s efficiency and durability, making it crucial for B2B buyers to consider when evaluating suppliers.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension or measurement. In motor components, precise tolerances are vital for ensuring that parts fit together seamlessly and function correctly. For example, if the rotor and stator do not align properly due to excessive tolerance, it can lead to performance issues or mechanical failure. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide components with tight tolerances to enhance reliability.
3. Insulation Class
The insulation class indicates the maximum temperature that motor components can withstand without degrading. Motors are classified into different insulation classes (like Class B, F, or H), each with a specific temperature range. Understanding insulation class is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects the motor’s performance in various environmental conditions and its lifespan.
4. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings, such as those defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), indicate how effectively a motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Higher efficiency ratings mean lower energy costs and reduced heat generation, which can extend the lifespan of the motor. Buyers should look for suppliers offering high-efficiency components, especially in energy-conscious markets.
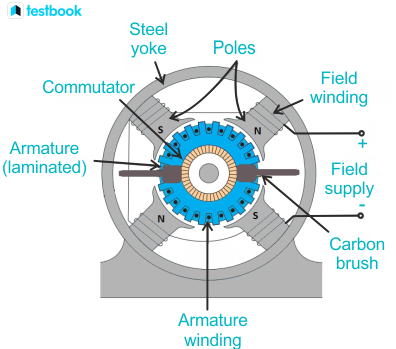
Illustrative image related to parts of a simple motor
5. Torque Rating
Torque rating measures the rotational force produced by the motor. This specification is critical for applications requiring specific power outputs. Understanding torque ratings helps buyers select motors that meet their operational needs without overloading or underutilizing their systems.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Motor Parts Industry?
Navigating the B2B landscape requires familiarity with industry jargon. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the motor industry, purchasing from OEMs can ensure that the parts are designed to meet specific standards and compatibility requirements, which is vital for maintaining product integrity.
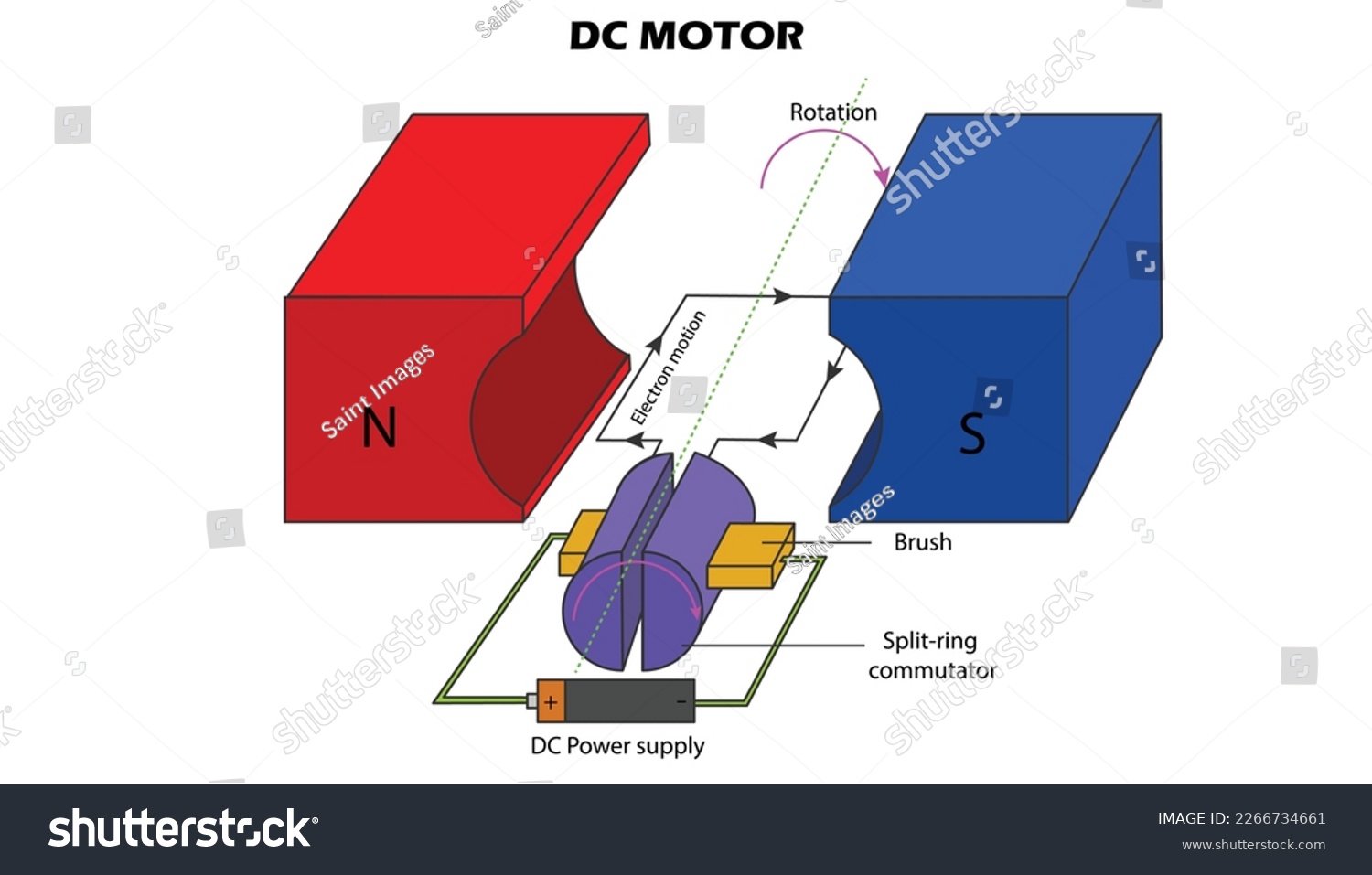
Illustrative image related to parts of a simple motor
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules and inventory needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. Providing clear RFQs can help ensure that suppliers understand the buyer’s needs, leading to more accurate pricing and timely responses.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B transactions, as it clarifies liability and helps avoid disputes related to the delivery of motor parts.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management, especially for businesses that rely on just-in-time manufacturing processes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing motor parts, ensuring they select the right components for their applications while optimizing costs and supply chain efficiency.
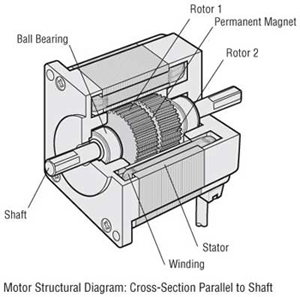
Illustrative image related to parts of a simple motor
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts of a simple motor Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Impacting the Parts of a Simple Motor Sector?
The global market for motor components is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs), automation in manufacturing, and advancements in renewable energy. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil, are witnessing a surge in the adoption of electric motors due to government initiatives promoting sustainable energy solutions. The shift toward electric mobility has led to a heightened focus on sourcing high-quality rotor and stator components, particularly those that enhance efficiency and performance.
Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0 and IoT are transforming how motor components are manufactured and sourced. Smart manufacturing processes are improving production efficiencies, while real-time data analytics is enabling suppliers to optimize inventory management and reduce lead times. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that can offer not only high-quality parts but also innovative solutions that integrate seamlessly into automated systems.
As the market evolves, buyers must navigate fluctuations in raw material costs and supply chain disruptions, particularly as geopolitical tensions and trade policies impact sourcing strategies. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Changing the Parts of a Simple Motor Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the motor parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning energy consumption and waste generation, has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt ‘green’ certifications, utilize recyclable materials, and implement energy-efficient production methods.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses recognize the need for transparent supply chains that ensure fair labor practices and minimize environmental degradation. Motor components, especially those made from metals and plastics, can have significant ecological footprints. Therefore, B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers that demonstrate commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainability through certifications like ISO 14001 or adherence to the Responsible Minerals Initiative.
The integration of renewable materials in the production of motor components is gaining traction. For instance, the use of bio-based plastics and eco-friendly insulation materials can reduce the carbon footprint associated with traditional manufacturing processes. As a result, B2B buyers can enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles while meeting the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
What Is the Historical Context of the Parts of a Simple Motor Sector?
The development of motor components has evolved significantly since the advent of electricity. Early electric motors relied on simple design principles, using basic materials to create efficient systems. Over time, technological advancements led to the introduction of sophisticated components such as brushless motors, which have increased reliability and efficiency.
The industrial revolution marked a turning point, as electric motors became integral to mechanized production. The introduction of standardized components allowed for mass production, significantly lowering costs and improving accessibility. With the rise of automation in the late 20th century, the demand for specialized motor parts surged, prompting innovations in materials and manufacturing techniques.
Today, the sector continues to evolve, with a focus on sustainability and efficiency. As electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions gain prominence, the parts of a simple motor sector is poised for further transformation, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay abreast of emerging trends and technological advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts of a simple motor
-
How do I choose the right rotor type for my application?
Selecting the appropriate rotor type depends on your specific application requirements, including speed, torque, and efficiency. Consider factors such as the operational environment (e.g., temperature, humidity), the power supply (AC or DC), and the desired performance characteristics. Common rotor types include squirrel-cage, permanent magnet, and salient-pole rotors. Collaborate with your supplier to understand the advantages and limitations of each type, ensuring that the rotor aligns with your motor’s intended use. -
What are the key components I should consider when sourcing motor parts?
When sourcing motor parts, focus on critical components such as the rotor, stator, bearings, and lead wires. Each component plays a vital role in the motor’s performance and longevity. Additionally, consider the materials used (e.g., copper for windings, silicon steel for cores) and the quality of insulation. Ensure that your suppliers adhere to industry standards and provide certifications to guarantee the reliability and efficiency of the components you are purchasing. -
What is the importance of quality assurance (QA) in sourcing motor parts?
Quality assurance is crucial in the procurement of motor parts, as it directly impacts performance, safety, and durability. Implementing rigorous QA processes helps identify defects early, minimizing costly operational disruptions. Work with suppliers that have established QA protocols, including material testing, dimensional verification, and performance assessments. Request certifications and compliance documentation to ensure that the parts meet international quality standards, particularly if you are importing from different regions. -
How can I ensure timely delivery of motor parts across international borders?
To ensure timely delivery of motor parts, establish clear communication with your suppliers regarding lead times and shipping methods. Utilize reliable logistics partners experienced in international trade to navigate customs and regulatory requirements. Consider using a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory approach to minimize delays, but also maintain a buffer stock for critical components. Regularly track shipments and stay informed about any potential disruptions in the supply chain. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for motor parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly based on the type of motor part and the supplier. Generally, manufacturers set MOQs to offset production costs and ensure efficiency. When sourcing motor parts, inquire about the MOQ during your initial discussions and explore negotiation options, especially if you are a smaller buyer. Some suppliers may offer flexibility or discounts for larger orders, so it’s beneficial to assess your needs and budget before committing. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing motor parts internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can range from upfront payments to net terms, depending on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common payment methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, and payment platforms like PayPal. It’s essential to clarify payment terms before finalizing the order, including any advance deposits required. Understanding the currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees can also help you manage your budget effectively. -
Can I customize motor parts to meet my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for motor parts to cater to specific application requirements. Customization can include alterations in size, material selection, or unique design features. When seeking customized parts, provide detailed specifications and collaborate closely with your supplier to ensure feasibility. Keep in mind that custom orders may involve longer lead times and higher costs, so plan accordingly to align with your project timelines. -
What factors should I consider when vetting motor parts suppliers?
When vetting suppliers for motor parts, evaluate their experience, reputation, and certifications. Check for industry-specific certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) that indicate a commitment to quality. Request references from previous clients and assess their ability to meet your quality, delivery, and service expectations. Additionally, consider their geographical location, as local suppliers may offer faster delivery times and easier communication. Establishing a solid relationship with a reliable supplier can significantly enhance your procurement process.
Top 8 Parts Of A Simple Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Byju’s – Electric Motor Components
Domain: byjus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: An electric motor is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Key components include: 1. Power Supply: Mostly DC for a simple motor. 2. Field Magnet: Can be a permanent magnet or an electromagnet. 3. Armature or Rotor: Helps the motor to run. 4. Commutator: Rotating interface of the armature coil with a stationary circuit. 5. Brushes: Conduct current between stationary wires and m…
2. Nidec – Motor Components
Domain: nidec.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
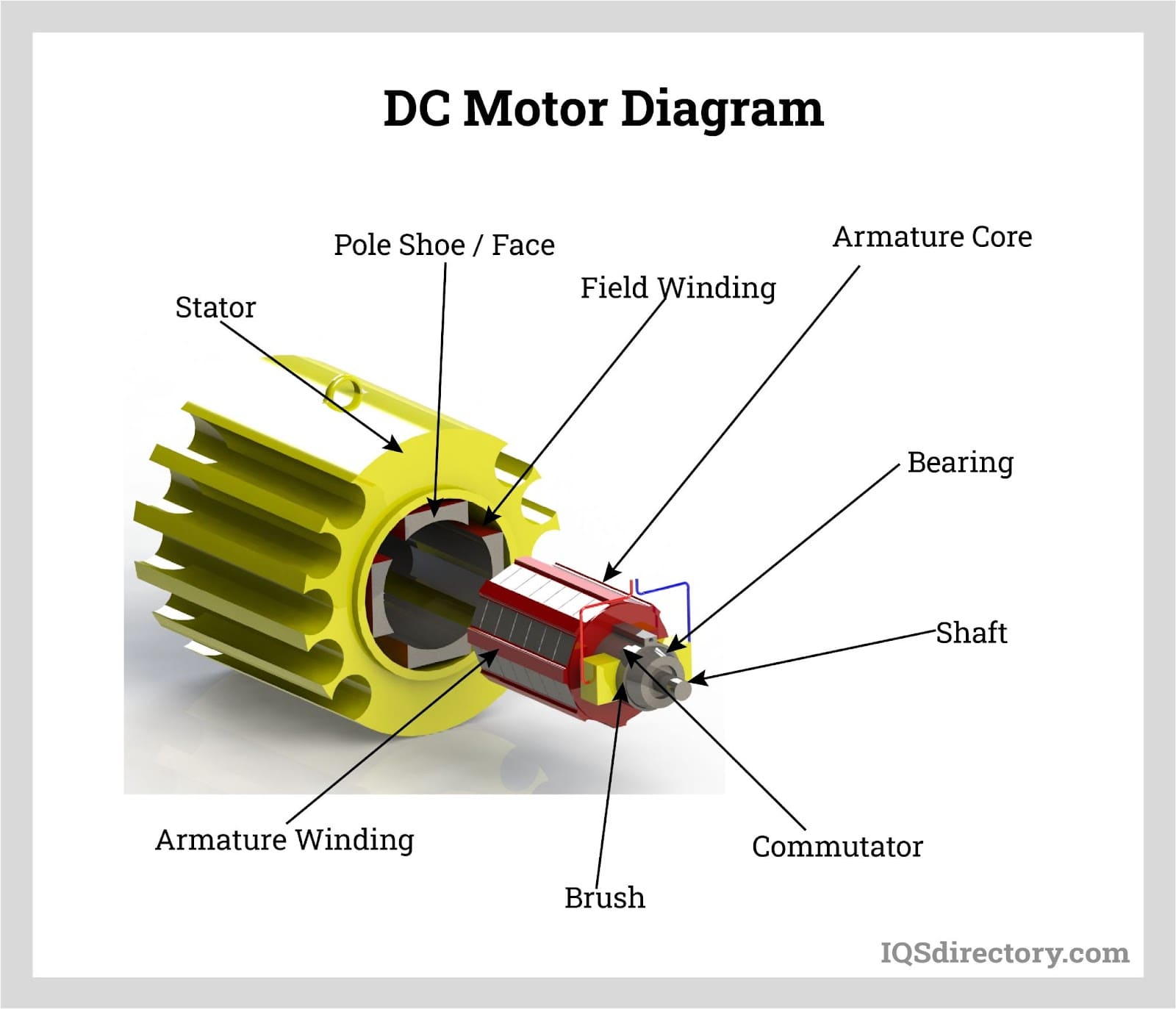
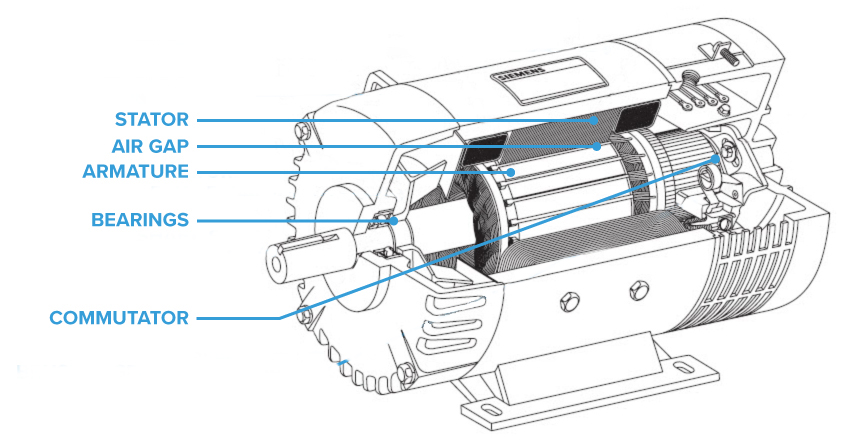
Introduction: Motor components are classified into five main portions: (1) Rotor – the rotating part; (2) Bearing – supports the rotating shaft of the rotor; (3) Stator – generates force to rotate the rotor; (4) Bracket or end plate – supports the bearing integral for the stator; (5) Lead wire – connects to the drive circuit supplying power to the motor. Typical stator structures include: A) Stator of distribut…
3. Kurz – Electric Motors
Domain: kurz.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Electric motors play a large role in industrial operations, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy for shaft rotation. Key parts include: 1. Rotor: Responsible for turning the shaft and delivering mechanical power, containing conductors that interact with the magnetic field of the stator. 2. Stator and Stator Core: Fixed part of the motor, made of permanent magnets or windings, with a…
4. MiniScience – Simple Electric Motor Kit
Domain: miniscience.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Make a Simple Electric Motor Kit
– Educational activity for school or science projects
– Teaches conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy
– Cost: Approximately $8.00
– Main components:
1. Battery Holder
2. Ceramic Disk Magnet
3. Magnet Wire
4. Safety Pins
5. Screws
6. Wood Block
– Suitable for classroom presentations and science fairs
– Available in single pack and c…
5. HowStuffWorks – Electric Motor
Domain: electronics.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: The electric motor features a steel can body, an axle, a nylon end cap, and two battery leads. The nylon end cap is secured by two tabs on the steel can. Inside the end cap are brushes that transfer power from the battery to the commutator. The axle holds the armature, which consists of three electromagnets made of thin metal plates with copper wire coiled around each pole. Each wire is soldered t…
6. LN Electric – Electric Motors
Domain: lnelectric.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: The electric motor consists of three basic parts: a stator, a commutator, and a rotor. The stator remains stationary and typically contains a row of magnets housed in a drum-like casing. The rotor, which is inserted into the stator, is made of copper wire coiled around a spinning axle. The commutator, a metal ring at the end of the coil, reverses the current between the rotor and the battery to ma…
7. The Engineering Mindset – DC Motors Explained
Domain: theengineeringmindset.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: DC motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. They consist of several key components: a metal protective casing (stator), a shaft for transferring mechanical energy, a rotor made of laminated discs with T-shaped arms, coil windings that carry electrical current, a commutator with segmented plates, and brushes that complete the circuit. The motor operates using permanent magnets to cr…
8. Fine Art Storehouse – Simple Electric Motor Components
Domain: fineartstorehouse.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Main Components of a Simple Electric Motor
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts of a simple motor
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Motor Component Procurement?
In the ever-evolving landscape of motor components, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal approach for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricate relationships between key motor parts—such as rotors, stators, bearings, and lead wires—enables businesses to make informed procurement decisions. By leveraging insights into component specifications and market trends, buyers can identify reliable suppliers that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Moreover, effective sourcing strategies can lead to improved supply chain resilience, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market dynamics can vary significantly. By fostering partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize quality and innovation, businesses can enhance their product offerings and remain competitive in their respective markets.
Looking ahead, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay abreast of technological advancements and material innovations within the motor industry. As electric motors become more integral to various applications, engaging with suppliers who are committed to sustainability and efficiency will be crucial. Embrace the opportunity to refine your sourcing strategies today—collaborate with knowledgeable partners and drive your business forward in this dynamic sector.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.