A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Wheel Worm: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for wheel worm
As international B2B buyers navigate the intricate landscape of sourcing wheel worm components, they often face significant challenges related to quality assurance, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Wheel worms, with their unique design and function in machinery, play a critical role in various applications, from automotive to industrial equipment. This guide aims to demystify the global market for wheel worms by providing essential insights into types, applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting.
Buyers will learn about the different materials used in manufacturing wheel worms, their operational advantages, and the specific lubrication requirements that ensure optimal performance. Additionally, we delve into cost considerations, helping businesses like those in Brazil and Nigeria make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Whether you are looking to enhance efficiency in your manufacturing processes or seeking reliable suppliers for high-quality components, this comprehensive resource empowers B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the wheel worm market. By equipping yourself with actionable insights and best practices, you can confidently streamline your procurement process and secure the best solutions for your business.
Understanding wheel worm Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Worm with Brass Wheel | High durability with sacrificial brass wheel | Heavy machinery, conveyors | Pros: High load capacity, easy wheel replacement. Cons: Potential corrosion issues with EP oils. |
| Steel Worm with Steel Wheel | Both components made of steel for robust applications | Industrial gearboxes, automotive | Pros: High strength, no wear from brass. Cons: Higher repair costs due to material transfer. |
| Brass Worm with Brass Wheel | Lightweight and cost-effective for low-load scenarios | Light machinery, consumer products | Pros: Flexible lubrication options. Cons: Limited load capacity, less durable. |
| Stainless Steel Worm with Plastic Wheel | Corrosion-resistant, lightweight design | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Excellent resistance to chemicals. Cons: Limited load-bearing capacity. |
| Composite Worm with Composite Wheel | Advanced materials for specialized applications | Aerospace, high-tech machinery | Pros: Lightweight, high performance. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Steel Worm with Brass Wheel?
The steel worm with a brass wheel is a popular choice in industries requiring high durability coupled with a sacrificial component. The brass wheel is designed to wear down over time, protecting the steel worm from damage. This type is particularly suitable for heavy machinery and conveyor systems where load capacity and reliability are critical. Buyers should consider the potential corrosion issues that can arise when using extreme pressure (EP) oils with brass components, which can lead to premature failure.
How Does Steel Worm with Steel Wheel Compare in Performance?
The steel worm with steel wheel configuration offers enhanced strength and durability, making it ideal for industrial gearboxes and automotive applications. This setup eliminates the risk of corrosion associated with brass wheels, providing a robust solution for high-stress environments. However, the repair costs can be significantly higher due to the material transfer that occurs during failure, which can render both components unusable. B2B buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and repair considerations.
In What Situations Is Brass Worm with Brass Wheel Suitable?
Brass worm with brass wheel systems are lightweight and cost-effective, making them suitable for low-load applications such as light machinery and consumer products. This configuration allows for flexible lubrication options, which can be an advantage for businesses looking to minimize operational costs. However, the limited load capacity and reduced durability may not meet the demands of more intensive applications, so buyers should assess their specific operational requirements before purchasing.
What Are the Advantages of Using Stainless Steel Worm with Plastic Wheel?
The stainless steel worm with a plastic wheel is designed for environments where corrosion resistance is paramount, such as in food processing and pharmaceutical industries. This combination provides a lightweight solution that maintains performance under chemical exposure. However, the load-bearing capacity is limited compared to metal components, which can restrict its use in heavier applications. B2B buyers should consider the specific industry regulations and operational conditions when evaluating this option.
Why Consider Composite Worm with Composite Wheel for Specialized Applications?
Composite worm and wheel configurations utilize advanced materials that offer lightweight and high-performance characteristics, making them suitable for aerospace and high-tech machinery applications. These materials can provide improved efficiency and durability in specialized settings. However, the higher initial investment can be a barrier for some businesses. Buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine if the performance advantages justify the investment in composite technology.
Key Industrial Applications of wheel worm
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of wheel worm | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | High torque transmission with minimal space requirements | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and load specifications |
| Automotive | Steering Mechanisms | Precise control and high reduction ratios | Evaluate materials for durability and lubrication needs |
| Agriculture | Irrigation Systems | Efficient water management with reduced energy consumption | Source high-viscosity lubricants and consider environmental factors |
| Robotics | Actuators for Robotic Arms | Enhanced precision in movement and load handling | Assess the need for custom gear designs and material properties |
| Mining and Quarrying | Equipment for Material Handling | Reliable operation under heavy loads | Consider sourcing from suppliers with expertise in high-load applications |
How is wheel worm utilized in manufacturing conveyor systems?
In manufacturing, wheel worms are integral to conveyor systems, where they facilitate the movement of materials across production lines. Their high torque transmission capabilities allow for efficient movement even in compact spaces. This is particularly valuable in industries with limited floor space, as it minimizes the number of components required. International buyers should consider the compatibility of wheel worms with existing conveyor systems and ensure the specifications meet the load requirements of their operations.

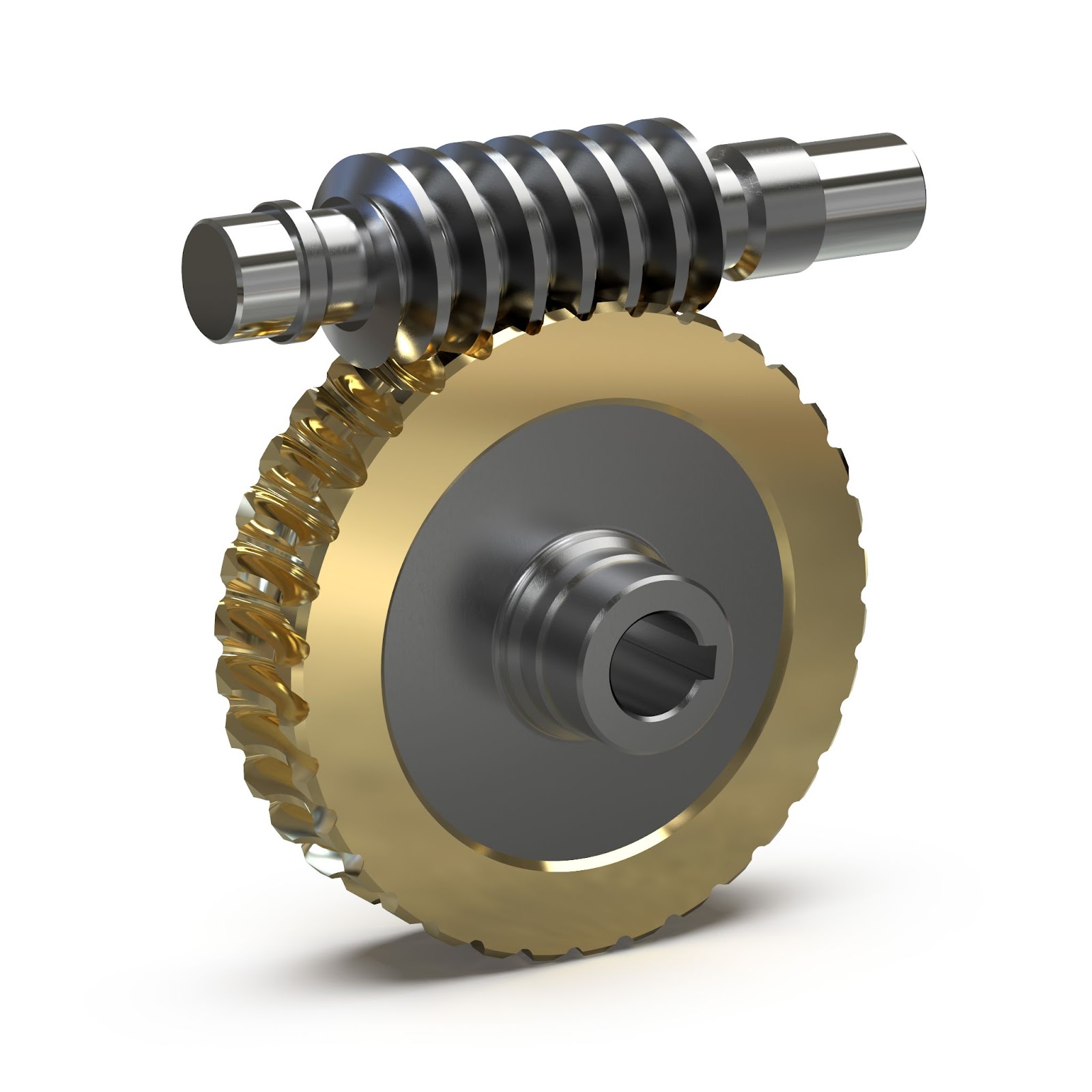
Illustrative image related to wheel worm
What role does wheel worm play in automotive steering mechanisms?
In the automotive sector, wheel worms are commonly used in steering mechanisms, providing precise control and significant reduction ratios. This allows for smoother and more responsive steering, enhancing vehicle performance. Buyers in regions like Europe and South America should assess the durability of materials used in the wheel worm system, as well as the lubrication requirements to prevent wear and ensure long-term reliability. Choosing suppliers with a strong track record in automotive components can mitigate risks.
How do wheel worms improve irrigation systems in agriculture?
Wheel worms are employed in irrigation systems to optimize water management. They facilitate the precise movement of water distribution equipment, ensuring efficient usage and reduced energy consumption. For agricultural buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing high-viscosity lubricants is crucial to maintain performance, especially in varying temperature conditions. Additionally, buyers should consider environmental factors that may affect the longevity and effectiveness of the wheel worm systems in their specific applications.
In what ways are wheel worms essential for robotic actuators?
In robotics, wheel worms are vital for actuators in robotic arms, enabling enhanced precision in movement and load handling. Their ability to provide high torque in a compact design is essential for complex tasks in automated environments. International buyers should evaluate the need for custom gear designs tailored to specific robotic applications, as well as the material properties that ensure reliability under varying operational conditions. Collaborating with suppliers experienced in robotic technologies can lead to better outcomes.
How do wheel worms contribute to equipment in mining and quarrying?
In the mining and quarrying industries, wheel worms are crucial for equipment designed for material handling. Their robust design allows for reliable operation under heavy loads, which is essential for the demanding conditions of these sectors. Buyers must consider sourcing from suppliers with expertise in high-load applications to ensure the gear’s performance meets operational demands. Additionally, understanding the lubrication needs specific to this environment will be vital for maintaining equipment longevity and efficiency.

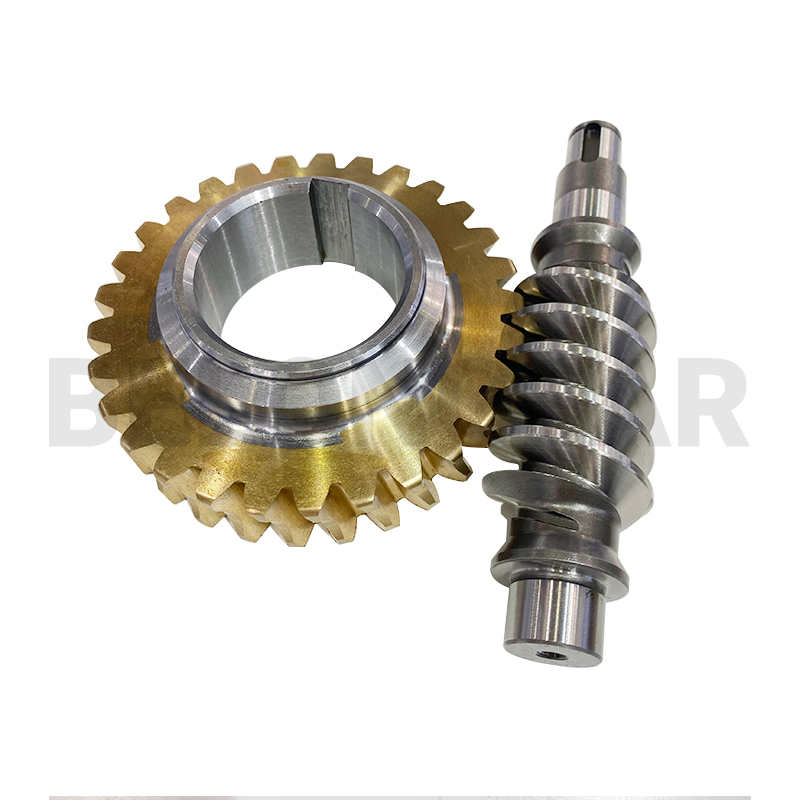
Illustrative image related to wheel worm
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘wheel worm’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Lubrication and Maintenance of Wheel Worm Gear Systems
The Problem: One of the primary challenges B2B buyers face with wheel worm gear systems is the complexity of lubrication. Due to the sliding friction inherent in worm gears, maintaining an adequate lubricant film is critical to prevent excessive wear and overheating. Many companies, particularly in industries like manufacturing and material handling, struggle with the high viscosity lubricants required for effective lubrication. The difficulty in sourcing appropriate lubricants that can withstand the sliding motion without breaking down, combined with the need for specialized pumps and filters, can lead to costly downtime and equipment failure.
The Solution: To overcome lubrication challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize working with suppliers who offer tailored lubrication solutions for wheel worm applications. First, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their operating conditions to determine the right viscosity and type of lubricant. Engaging with lubricant manufacturers who specialize in high-viscosity formulations, such as mineral-based compounded gear oils or synthetic polyalphaolefin (PAO) lubricants, can provide the necessary protection against sliding wear. Furthermore, investing in proper filtration systems designed for high-viscosity lubricants will help maintain optimal lubricant quality and performance. Regular oil analysis and maintenance schedules should also be established to monitor wear metals and ensure the longevity of the gear system.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing Reliable Wheel Worm Components
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges in sourcing reliable wheel worm components, particularly in regions with limited industrial supply chains. Inconsistent quality and availability of materials can lead to performance issues, increased wear rates, and unexpected failures in machinery. This problem is exacerbated in developing markets, such as those in parts of Africa and South America, where local suppliers may lack the capability to provide high-quality worm gears or the necessary technical support.

Illustrative image related to wheel worm
The Solution: To address sourcing difficulties, businesses should establish strategic partnerships with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record in manufacturing wheel worm components. Buyers should seek out suppliers that provide comprehensive product specifications and certifications, ensuring that components meet international quality standards. Additionally, exploring online platforms that connect buyers with global manufacturers can widen sourcing options. Regular audits of suppliers can also help ensure they maintain consistent quality. Furthermore, engaging in collaborative relationships with suppliers can facilitate the development of customized solutions tailored to specific operational needs, helping to mitigate risks associated with sourcing inferior components.
Scenario 3: Inefficient Power Transmission Leading to Reduced Productivity
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience inefficiencies in power transmission when using wheel worm gears, leading to reduced productivity in their operations. This can occur due to improper gear ratios or misalignment, causing excessive energy loss and increased wear on components. Such inefficiencies can significantly impact operational costs and hinder the overall performance of machinery, especially in sectors like mining and heavy machinery where reliability is paramount.
The Solution: To enhance power transmission efficiency, buyers should start by accurately assessing their operational requirements and selecting the appropriate gear ratio for their specific applications. Utilizing simulation software can aid in visualizing the interactions between the worm and wheel, helping to identify optimal configurations. Additionally, regular alignment checks and maintenance should be implemented to ensure that all components are properly aligned and functioning effectively. Training staff on the nuances of wheel worm gear systems can also improve handling and operation, ensuring that users can recognize and address potential issues before they escalate. Investing in high-quality gears with precise engineering tolerances will further reduce energy losses and improve overall system efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for wheel worm
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Wheel Worms?
When selecting materials for wheel worms, it’s essential to consider properties such as temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and wear characteristics. The most commonly used materials include steel, brass, bronze, and polymer composites. Each material offers unique advantages and disadvantages that can significantly impact performance and application suitability.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Wheel Worms?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and excellent wear resistance. It typically operates well under high-temperature conditions, withstanding pressures that can exceed those of softer metals.
Pros & Cons: The durability of steel makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, but it can be more expensive than brass or bronze. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as steel requires precise machining to ensure proper fit and function.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including oils and greases, but it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated or lubricated.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN, as steel quality can vary significantly based on the supplier.
What Are the Benefits of Using Brass for Wheel Worms?
Key Properties: Brass offers good corrosion resistance and is relatively easy to machine. It performs well in moderate temperature applications and has a lower density than steel.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of brass is its sacrificial nature, which allows the wheel to wear instead of the worm, prolonging the lifespan of the assembly. However, brass is less durable under high load conditions and can be more susceptible to wear if exposed to extreme pressures.
Impact on Application: Brass is suitable for applications involving non-corrosive media but may require special lubricants to avoid corrosion when used with certain oils.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards is crucial, especially in regions with harsh environments, as brass can corrode if not properly maintained.
How Does Bronze Compare for Wheel Worm Applications?
Key Properties: Bronze is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and fatigue strength, making it suitable for marine and other harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: While bronze offers improved durability over brass, it is generally more expensive. Manufacturing processes are similar to brass but may require more advanced techniques due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Bronze is ideal for applications exposed to seawater or other corrosive environments, but its higher cost may be a limiting factor for some buyers.

Illustrative image related to wheel worm
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the specific grades of bronze that comply with local standards, as material specifications can vary.
Are Polymer Composites a Viable Option for Wheel Worms?
Key Properties: Polymer composites can offer good wear resistance and low friction properties, making them suitable for specific applications where metal fatigue is a concern.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of using polymers is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or loads as effectively as metals.
Impact on Application: Polymer composites are best suited for low-load applications and can be used in environments where metal corrosion is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected polymer meets relevant industry standards, as performance can vary significantly based on the formulation.

Illustrative image related to wheel worm
Summary Table of Material Selection for Wheel Worms
| Material | Typical Use Case for wheel worm | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty machinery | High tensile strength and wear resistance | Higher cost and moderate manufacturing complexity | High |
| Brass | General-purpose applications | Sacrificial wear prolongs lifespan | Less durable under high loads | Medium |
| Bronze | Marine and corrosive environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to brass | High |
| Polymer Composites | Low-load, corrosion-sensitive applications | Lightweight and low friction | Limited temperature and load resistance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key materials used for wheel worms, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for wheel worm
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Wheel Worms?
The manufacturing process of wheel worms involves several critical stages, ensuring that the final product meets the high standards expected in various industrial applications. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Wheel Worm Production?
The process begins with material selection, often involving high-quality steel for the worm and brass for the wheel. The choice of materials is crucial as it impacts the durability and performance of the gear system. Once selected, the materials undergo cutting and shaping to meet specified dimensions. This preparation might involve machining techniques like turning and milling, which ensure precise dimensions and surface finishes.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Wheel Worm Manufacturing?
The next stage is forming, where the prepared materials are shaped into the desired components. For the worm, this typically involves the creation of a helical thread through processes such as hobbing or grinding. Hobbing is particularly effective for producing the worm’s intricate spiral design, while grinding ensures a smooth surface finish, crucial for reducing friction during operation. For the wheel, the teeth are cut into the brass material, often using gear shaping or broaching techniques to achieve the required tooth profile and spacing.
How Are Wheel Worm Components Assembled?
Following the forming stage, the assembly of the wheel worm components is performed. This involves aligning the worm with the wheel to ensure proper meshing and functionality. Careful attention is paid to tolerances during this phase to prevent premature wear and ensure efficient power transmission. Any necessary pre-lubrication is applied at this stage to enhance performance and longevity.
What Finishing Processes Enhance Wheel Worm Quality?
The finishing stage is vital for enhancing the performance and durability of wheel worms. Processes such as heat treatment may be applied to increase hardness and wear resistance. Additionally, surface treatments like coating or polishing can reduce friction and improve corrosion resistance. These finishing touches not only extend the lifespan of the wheel worm but also ensure it operates smoothly under varying loads and conditions.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Wheel Worm Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of wheel worms to ensure they meet international standards and customer expectations. Various QA measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process, adhering to relevant international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For wheel worm manufacturers, compliance with ISO 9001 is essential as it outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). This standard ensures that products consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets or API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications may also apply. B2B buyers should inquire about these certifications to ensure the manufacturer adheres to recognized quality standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Wheel Worm Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to monitor quality and ensure adherence to specifications. These checkpoints typically include:
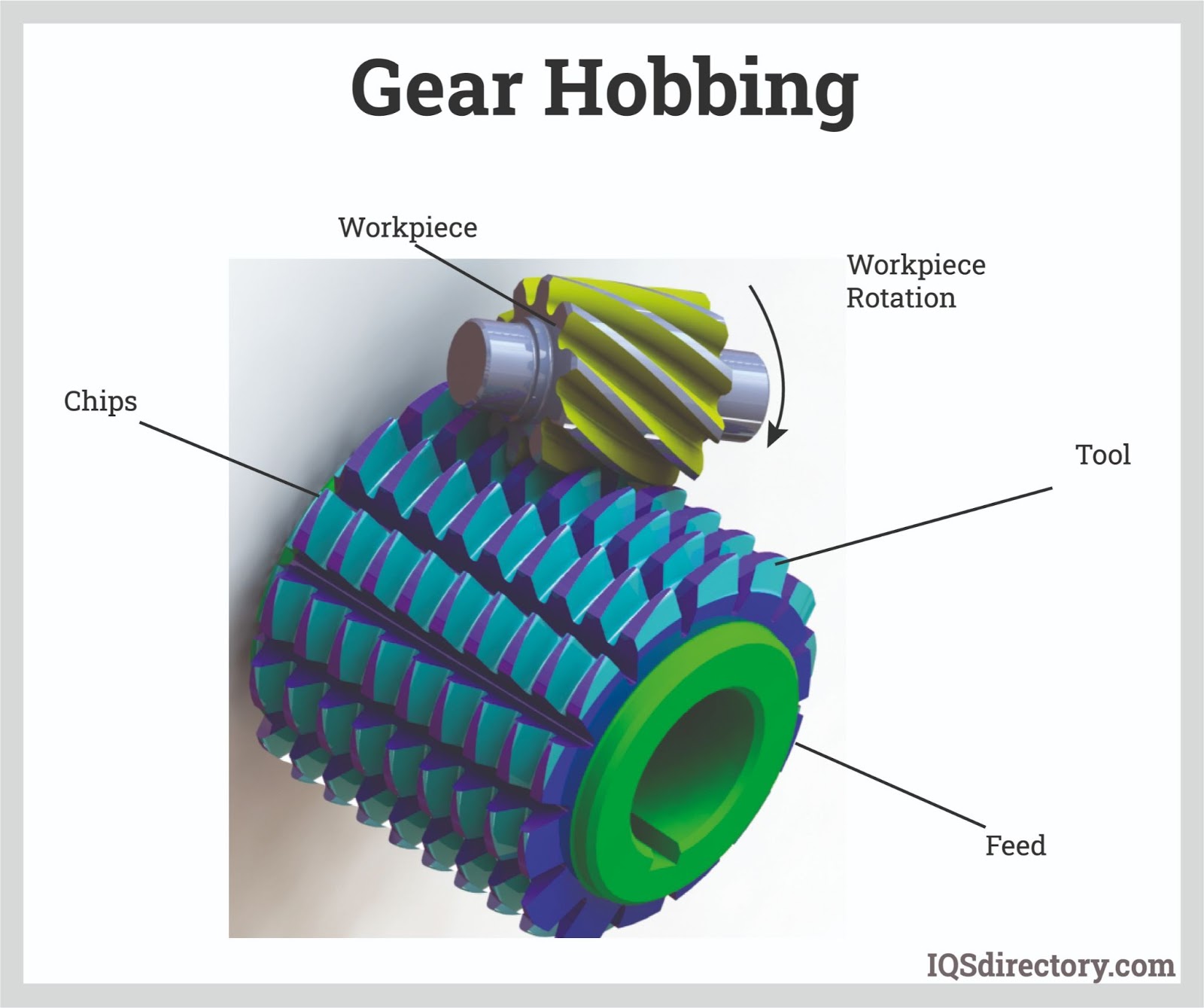
Illustrative image related to wheel worm
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with quality standards before they enter the production process. This is crucial for identifying potential issues early and ensuring that only suitable materials are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor key parameters such as dimensions, surface finish, and assembly integrity. This helps identify any deviations from specifications in real-time, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the wheel worms are fully assembled, a comprehensive inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing, dimensional checks, and performance evaluations to ensure that the products meet all specified standards before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are some effective strategies:
What Audit and Reporting Practices Should Buyers Consider?
Conducting supplier audits is an excellent way for buyers to assess the quality management systems in place. This can involve on-site inspections of the manufacturing facilities, reviewing quality documentation, and evaluating the implementation of QA practices. Buyers should also request quality reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC, to gain insight into the supplier’s performance and consistency in producing high-quality wheel worms.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections for B2B Buyers?
Third-party inspections can provide an additional layer of assurance regarding the quality of wheel worms. Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the manufacturing process and final products can help verify that the supplier meets industry standards and specifications. This is particularly important for buyers in regions such as Africa and South America, where access to reliable local suppliers may vary.
What Unique Quality Control Considerations Exist for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific quality control nuances. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and standards that must be met. For instance, buyers in Europe may require CE certification, while those in the Middle East might prioritize compliance with local standards.

Illustrative image related to wheel worm
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Therefore, establishing clear communication channels and documentation practices is essential to ensure that both parties understand the required quality standards and specifications.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for wheel worms is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships with manufacturers, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘wheel worm’
The following practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure wheel worms. This guide outlines essential steps to ensure informed decision-making and successful procurement.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your requirements is crucial. Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications for the wheel worm you need. This includes dimensions, load capacity, material composition (such as steel or brass), and the required gear ratio.
- Consider your application: Different industries may have specific needs, such as high torque or low-speed operations.
- Document your specifications: This will serve as a reference point during discussions with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Identifying reputable suppliers is key to successful sourcing. Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers that specialize in wheel worms.

Illustrative image related to wheel worm
- Look for experience and expertise: Suppliers with a proven track record in manufacturing wheel worms are more likely to meet quality standards.
- Review their product range: Ensure they offer the specific types of wheel worms that match your technical requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verifying supplier certifications can mitigate risks. It’s essential to check if suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management systems are in place.
- Ask for documentation: Request copies of certifications and any industry-specific compliance standards.
- Consider regional regulations: Ensure that the supplier complies with regulations relevant to your geographic area, especially if you are sourcing internationally.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Testing samples can validate quality claims. Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, request samples of their wheel worms for evaluation.
- Conduct performance tests: Assess the samples for durability, efficiency, and how well they meet your specifications.
- Evaluate lubrication requirements: Pay attention to how well the samples perform under different lubrication conditions, as this can significantly impact longevity.
Step 5: Analyze Pricing and Terms
Understanding pricing structures and terms is essential for budgeting. Request detailed quotes from your shortlisted suppliers, ensuring they include all costs associated with the procurement process.
- Look for transparency: Ensure that the quotes provide a breakdown of costs, including shipping, taxes, and any potential tariffs.
- Negotiate terms: Discuss payment terms, delivery schedules, and after-sales support to find the most favorable arrangement.
Step 6: Check Customer References and Reviews
Customer feedback can provide valuable insights. Before finalizing your supplier choice, request references from other clients who have sourced wheel worms from them.
- Reach out to references: Inquire about their experiences regarding product quality, delivery timeliness, and customer service.
- Look for online reviews: Search for independent reviews or testimonials to gather a broader perspective on supplier reliability.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Securing a formal agreement protects both parties. Once you have selected a supplier, draft a purchase agreement that outlines all terms and conditions, including warranty and return policies.
- Ensure clarity: Make sure all specifications, pricing, and timelines are clearly stated in the agreement.
- Include performance metrics: Consider including quality and performance metrics to hold the supplier accountable for their product.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a streamlined and effective procurement process for wheel worms, ultimately leading to successful operational outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for wheel worm Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Wheel Worm Sourcing?
When sourcing wheel worms, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The most significant cost typically stems from the materials used in manufacturing wheel worms. Commonly, a combination of steel for the worm and brass for the wheel is preferred due to their properties. The choice of materials directly impacts both performance and pricing, as high-quality materials can elevate costs but may offer better durability and efficiency.

Illustrative image related to wheel worm
Labor: Skilled labor is often required for the precise machining and assembly of wheel worms. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, buyers might encounter higher pricing compared to regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa or South America.
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with running manufacturing facilities, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can help reduce overhead, but these costs are often passed on to the buyer.
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the expense of specialized equipment needed for production. Custom tooling for unique specifications can be a significant investment, and these costs may be amortized over the production run, influencing the per-unit price.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the wheel worms meet specific quality standards is crucial, especially for applications requiring precision. The costs associated with QC processes can vary, with rigorous testing leading to higher prices. Certifications and compliance with international standards can also add to the overall cost.
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can be substantial, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms play a critical role in determining logistics expenses.
Margin: Lastly, suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s positioning within the industry.
What Influences the Pricing of Wheel Worms?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of wheel worms in the B2B market.
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger order volumes often lead to better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their orders.
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized manufacturing processes. While customization can meet unique operational needs, it is essential to weigh the benefits against the potential price increases.
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials can greatly affect pricing. Higher-grade materials or those with specific certifications for quality will generally cost more. Buyers should evaluate whether the additional expense aligns with their operational requirements.
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and geographic location can all affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices, while newer or less reputable suppliers might offer lower rates but could compromise on quality.
Incoterms: The terms of shipment can also influence pricing. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they dictate who bears the costs and risks during transportation. This can impact the total landed cost of the wheel worms.
What Are the Essential Tips for Buyers to Negotiate Pricing Effectively?
Negotiation plays a vital role in achieving cost efficiency in wheel worm sourcing. Here are some actionable tips for B2B buyers:

Illustrative image related to wheel worm
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than focusing solely on the upfront price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, downtime, and replacement costs. A higher initial investment may result in lower long-term expenses if the quality is superior.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Gathering quotes from multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. Understanding market rates and supplier capabilities will help in making informed decisions.
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to discuss payment terms, delivery schedules, and other contractual aspects that can influence overall costs. Flexible payment terms can ease cash flow challenges.
-
Be Open to Bulk Purchases: If feasible, consider consolidating orders to meet MOQs for better pricing. This strategy can lead to significant savings over time.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Understanding the market dynamics and price fluctuations can aid in timing your purchases effectively. Monitoring trends can provide insights into when to negotiate or lock in prices.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is essential to note that the prices for wheel worms can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. As such, the provided insights should be viewed as indicative rather than definitive. Buyers should always conduct thorough research and engage in direct negotiations with suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing wheel worm With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Wheel Worm Technology
When evaluating solutions for mechanical power transmission, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider various alternatives to the wheel worm system. Each option presents unique advantages and disadvantages that can impact operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall performance. The following analysis highlights key alternatives, helping international buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Wheel Worm | Gearbox (Spur Gear) | Rack and Pinion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High reduction ratio, compact | Moderate reduction, efficient | Direct linear motion, reliable |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized lubrication | Generally lower, standard parts | Moderate, depending on size |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate, requires specific setup | Easy, standard design | Straightforward, requires alignment |
| Maintenance | High, specialized lubricants needed | Low, standard maintenance | Moderate, periodic checks |
| Best Use Case | Heavy torque applications | General machinery, low loads | Linear motion applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Gearbox (Spur Gear)
Spur gears are one of the most common alternatives to wheel worm systems. They provide a moderate reduction ratio and are generally more efficient in power transmission. The simplicity of spur gears means they are easier and cheaper to implement and maintain, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, they do not offer the same high torque capabilities as wheel worms and require careful alignment to avoid backlash, which can lead to operational inefficiencies.
Rack and Pinion
The rack and pinion system is another viable alternative, particularly for applications requiring linear motion. This system converts rotational motion into linear motion efficiently, making it ideal for machinery like conveyor systems and automated manufacturing equipment. While the initial setup is straightforward, it requires precise alignment to maintain performance. The maintenance is moderate, but the system is generally robust and reliable for various industrial applications. However, it lacks the high reduction ratios offered by wheel worms, which can be a limiting factor in high-torque applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
In selecting the appropriate mechanical power transmission solution, B2B buyers must carefully evaluate their specific operational requirements, including load capacity, space constraints, and maintenance capabilities. The wheel worm system excels in applications demanding high torque and compact design, while alternatives like spur gears and rack and pinion systems may offer better cost efficiency and lower maintenance needs for less demanding tasks. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each option, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and operational demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for wheel worm
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Wheel Worms?
When evaluating wheel worms for industrial applications, several technical properties are critical to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability. Understanding these specifications can significantly influence procurement decisions.
1. Material Composition
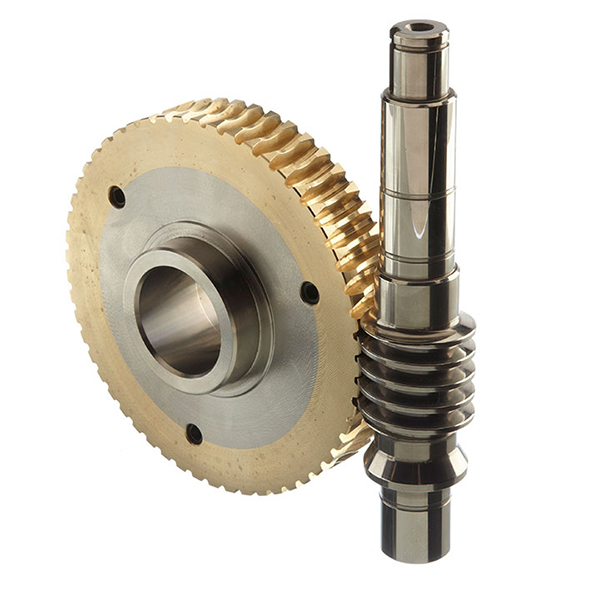
The most common materials used for wheel worms include steel and brass. The steel worm is typically paired with a brass wheel, offering a balance of durability and wear resistance. Steel provides strength and load-bearing capability, while brass acts as a sacrificial material, minimizing wear on the worm itself. Choosing the right material is vital as it affects not only the gear’s lifespan but also its operational efficiency.
2. Gear Ratio
Gear ratio defines the relationship between the rotational input of the worm and the output of the wheel. A higher gear ratio signifies greater torque output and reduced speed, making it ideal for applications requiring significant force with minimal movement. Understanding gear ratios is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure that the wheel worm meets the specific operational needs of their machinery.
3. Viscosity Grade of Lubricants
Worm gears require specialized lubricants with high viscosity to mitigate sliding friction during operation. Common viscosity grades include ISO 460 and ISO 680. Selecting the appropriate lubricant is essential to prevent excessive wear, overheating, and potential failure of the gear system. Buyers must consider the operational conditions, such as temperature and load, when choosing lubricant viscosity.
4. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in the manufacturing process. High tolerance levels ensure precise engagement between the worm and the wheel, reducing backlash and enhancing operational efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility with existing systems and minimizing maintenance issues.
5. Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum load a wheel worm can handle without failure. This property is essential for determining the suitability of a worm gear for specific applications. Buyers should assess the expected loads in their operations and select a wheel worm that can safely accommodate these requirements to avoid costly breakdowns.
6. Surface Finish
The surface finish of the worm and wheel affects friction, wear resistance, and overall performance. A smoother finish can reduce friction and improve efficiency, while a rougher finish may increase wear. Buyers should inquire about the surface finish specifications to ensure optimal performance in their specific application.
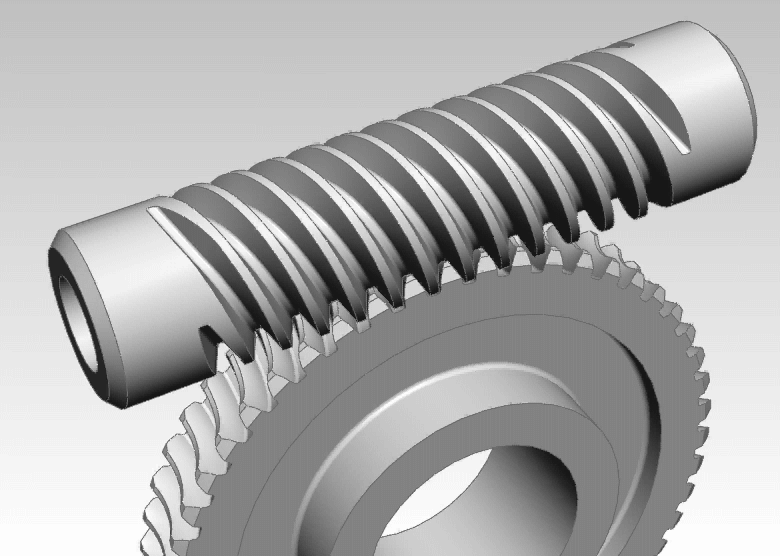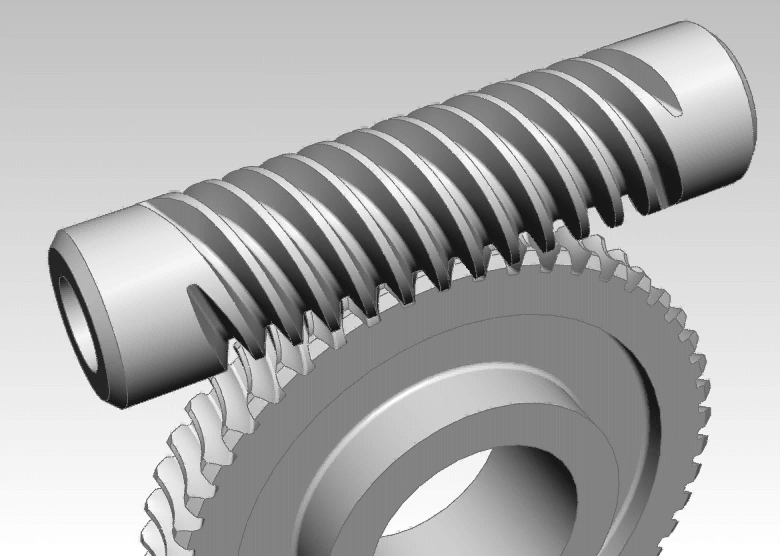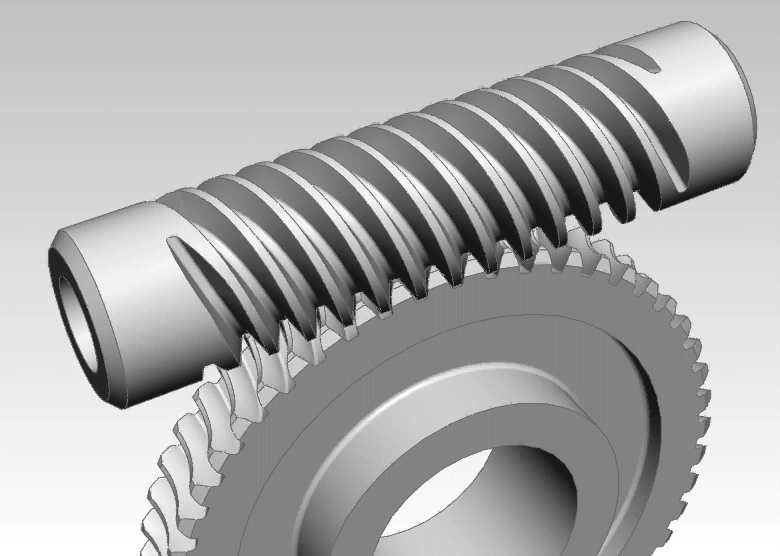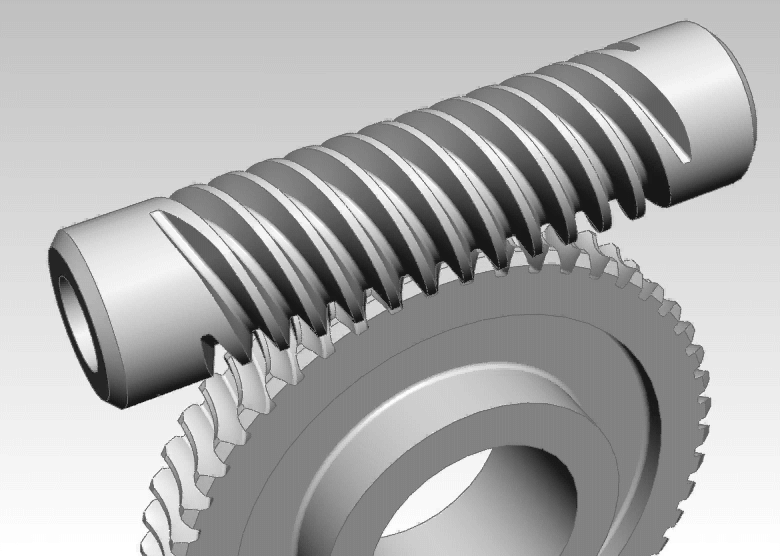
Illustrative image related to wheel worm
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Wheel Worms?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms frequently encountered in the context of wheel worms.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of wheel worms, OEMs provide original components that meet the specific requirements of machinery manufacturers. Buyers should ensure that they are sourcing from reputable OEMs to guarantee quality and compatibility.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for procurement planning, especially for businesses with limited storage capacity or those looking to minimize upfront investment.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. In the wheel worm market, an RFQ helps buyers obtain competitive pricing and terms, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations, ensuring a smoother procurement process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the wheel worm supply chain, lead time can vary based on manufacturing capabilities and shipping methods. Buyers should factor in lead times when planning their operations to avoid disruptions.
6. Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration for which the supplier guarantees the performance of the wheel worm against defects. Understanding warranty terms is essential for buyers to protect their investments and ensure they have recourse in case of product failure.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding wheel worms, ultimately leading to more efficient operations and reduced costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the wheel worm Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Wheel Worm Sector?
The wheel worm sector is witnessing transformative growth driven by advancements in automation, increasing demand for precision engineering, and the need for efficient power transmission solutions. Globally, industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and renewable energy are increasingly adopting worm gears due to their high reduction ratios and compact designs. This shift is particularly pronounced in emerging markets like Brazil and Nigeria, where industrial growth is accelerating.
One of the significant trends is the integration of smart technologies into gear manufacturing. Industry 4.0 is reshaping how businesses approach sourcing, with an emphasis on data-driven decision-making and predictive maintenance. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide not just products but also insights into performance analytics and lifecycle management. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is making it easier for international buyers to source components directly from manufacturers, bypassing traditional distribution channels.
Another key trend is the growing focus on customized solutions. As industries evolve, the need for tailored gear solutions that fit specific operational requirements is becoming more pronounced. Suppliers that offer flexibility in manufacturing and quick turnaround times are likely to gain a competitive edge in this dynamic market.
How Can B2B Buyers Address Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Wheel Worm Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the wheel worm sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the sourcing of materials are under increasing scrutiny. Buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who implement sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing waste.
Furthermore, ethical sourcing is essential in ensuring that the supply chains are free from exploitative labor practices. Buyers should look for suppliers who adhere to recognized ethical standards and certifications. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can provide assurance that suppliers are committed to sustainable and ethical practices.
The use of “green” materials is also gaining traction. For instance, the adoption of bio-based lubricants and materials that reduce friction can enhance the performance of wheel worm systems while minimizing environmental harm. By aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals, B2B buyers can contribute to a more responsible supply chain.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Wheel Worm Technology in B2B Context?
The history of wheel worm technology dates back to ancient civilizations, where simple mechanical devices were used for various applications. The modern iteration, characterized by its high reduction ratio and compact design, emerged in the 19th century as industries began to demand more efficient machinery.
Over the decades, advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes have significantly enhanced the performance and durability of worm gears. Initially made from bronze and iron, today’s worm gears utilize advanced materials like brass and high-strength steel, which improve reliability and reduce maintenance needs.
The evolution of wheel worm technology reflects broader trends in engineering and manufacturing, where precision and efficiency are paramount. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it underscores the importance of innovation and adaptability in sourcing decisions. Understanding the technological advancements can help buyers make informed choices about the products that best meet their operational needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of wheel worm
-
How do I choose the right wheel worm for my application?
Choosing the right wheel worm involves assessing your specific application requirements, including load capacity, speed reduction ratio, and environmental conditions. Consider the material of both the worm and the wheel; for example, a brass wheel paired with a steel worm is common for its sacrificial properties. Additionally, evaluate lubrication needs, as high-viscosity lubricants are often required for optimal performance. Consulting with manufacturers about your operational parameters can help in selecting the most suitable wheel worm for your needs. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing wheel worms internationally?
When sourcing wheel worms internationally, key factors include the supplier’s reputation, manufacturing standards, and compliance with international quality certifications. Assessing the supplier’s experience in your industry can also provide insights into their capability. Additionally, consider logistics, including shipping times and costs, as well as any tariffs or trade regulations that may apply in your region. Engaging with suppliers who have a transparent communication process can facilitate smoother transactions. -
What are common customization options available for wheel worms?
Customization options for wheel worms can include variations in size, material composition, and design features tailored to specific operational requirements. Some manufacturers offer bespoke solutions, allowing for unique specifications such as different gear ratios or enhanced corrosion resistance. When discussing customization, provide detailed requirements to ensure the supplier can meet your expectations. Always request samples or prototypes to evaluate the customizations before placing larger orders. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for wheel worms?
Minimum order quantities for wheel worms can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the product. Generally, MOQs range from a few dozen units to several hundred. It’s crucial to discuss MOQs upfront during negotiations, especially for international orders, as this can impact your procurement strategy. Some suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time buyers or bulk orders, so it’s worth exploring these options. -
What payment terms are typically offered by suppliers of wheel worms?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common arrangements include advance payment, net 30, net 60, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, suppliers may also require a letter of credit or escrow service to mitigate risk. It’s advisable to clarify payment methods, potential discounts for early payments, and any fees associated with currency conversion or international wire transfers. Establishing clear terms can help prevent misunderstandings later in the transaction. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing wheel worms?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing wheel worms, request documentation such as material certifications, inspection reports, and compliance with relevant industry standards. Many reputable suppliers will have a quality management system in place and will be able to provide details on their testing procedures. Conducting a factory audit or visiting the supplier’s facility can also provide insights into their manufacturing practices and quality controls, ensuring that the products meet your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing wheel worms?
Logistics considerations for importing wheel worms include shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance processes. Choose a reliable shipping partner familiar with international trade regulations specific to your region, as this can help avoid delays. Additionally, account for potential tariffs and import duties, which can affect overall costs. It’s also wise to track shipments and maintain open communication with your logistics provider to ensure timely delivery. -
What are the common applications for wheel worms in industrial settings?
Wheel worms are widely used in various industrial applications, including conveyor systems, robotics, and material handling equipment due to their high torque and compact design. They are ideal for situations requiring significant speed reduction and high load capacities. Industries such as automotive, manufacturing, and mining frequently employ wheel worms for their durability and efficiency. Understanding the specific operational environment can help in selecting the right configuration for optimal performance.
Top 6 Wheel Worm Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Machinery Lubrication – Worm Gears
Domain: machinerylubrication.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Worm gears consist of a shaft with a spiral thread that engages with a toothed wheel, typically made of steel (worm) and brass (wheel). They change rotational movement by 90 degrees and provide a high reduction ratio with fewer moving parts. Worm gears are difficult to lubricate due to sliding friction, requiring high viscosity lubricants (ISO 320 and greater). Common lubricant types include miner…
2. KHK Gears – Worm Gears
Domain: khkgears.net
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Worm Gears are a type of staggered shaft gear that transmits motion between non-intersecting and non-parallel shafts. They provide a large speed reduction in a compact design. A worm gear consists of a thread cut into a round bar (the worm) and a worm wheel that meshes with it at a 90-degree angle. There are two types of worm gears: cylindrical worm gears and drum-shaped (throated) worm gears. The…
3. Gear Solutions – Worm Gear Pairs
Domain: gearsolutions.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Worm gear pairs consist of two components: the worm and the worm wheel. The worm is a cylindrical piece with gear teeth resembling a screw, produced either as an integral part of a shaft or with a bore for fixing to a shaft. The worm wheel is similar to a helical gear but has a concave tooth surface to improve contact area with the worm. Key parameters for calculating geometry include module, pres…
4. WMBerg – Worm Gear Drives
Domain: wmberg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Worm gear drives are shaft gear assemblies that transmit power between non-intersecting drive (input) and driven (output) shafts, typically at 90° angles. Components include a worm (driving shaft) and a worm gear (driven shaft) with angled teeth for optimal performance. Worm gears reduce speed and increase torque, making them suitable for applications requiring significant torque output, such as c…
5. Maedler – Bronze Gear 16:1
Domain: maedlernorthamerica.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: {“Part Number (SKU)”: “30100500”, “Material”: “Bronze”, “Surface”: “Blank”, “Module”: “1.5”, “No. of Teeth”: “16”, “Ratio”: “16 : 1”, “Outer Diameter (d_a)”: “28.4 mm”, “Bore (B_H7)”: “8 mm”, “Max Torque (M_D)”: “1.33 Nm”, “Weight”: “60 g”, “Price”: “$48.90”, “Availability”: “3 in stock (backorders ship within 1-2 weeks)”, “Pressure Angle”: “20°”, “Efficiency”: “approx. 0.49”, “Self-Locking”: “Not…
6. Kelston Actuation – Worm Drives
Domain: kelstonactuation.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Worm drives are right angled drives used in screw jacks where the input shaft is at right angles to the lifting screw. They provide a compact means of decreasing speed while increasing torque, ideal for lifting equipment with high gear ratios driven by small motors. A worm drive consists of a worm wheel (similar to a spur gear) and a worm gear (screw) with a flank angle of 20°. Gear ratios typical…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for wheel worm
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Sourcing Wheel Worms?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of wheel worms is vital for businesses aiming to optimize their operations through efficient power transmission solutions. Understanding the unique advantages of worm gears—such as their high reduction ratios and resistance to reverse motion—can help buyers make informed decisions. However, it’s essential to be aware of the lubrication challenges and material compatibility issues that may arise, particularly when dealing with brass and steel combinations.
How Can International Buyers Leverage Strategic Sourcing for Competitive Advantage?
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the emphasis should be on building strong supplier relationships that prioritize quality, reliability, and tailored solutions. By sourcing from reputable manufacturers who understand local market needs, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs.
What’s Next for Businesses in the Wheel Worm Market?
As the demand for advanced gear solutions continues to grow, buyers should remain proactive in exploring innovative technologies and materials that can further improve performance and durability. Engage with suppliers, attend industry conferences, and keep abreast of emerging trends to ensure your sourcing strategy remains competitive. Investing in high-quality wheel worms today will pave the way for robust operational capabilities tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.