Is Your Silica Quartz Glass Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for silica quartz glass
Navigating the complex landscape of sourcing silica quartz glass presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. With its diverse applications ranging from high-performance optical components to durable laboratory equipment, understanding the nuances of silica quartz glass is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the various types of silica-based materials, including fused silica and quartz glass, while exploring their specific applications across industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, optical systems, and scientific research.
In this guide, we will address critical factors such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and market trends, tailored specifically for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Vietnam. By equipping decision-makers with actionable insights and strategic recommendations, we empower you to navigate the global market effectively and secure high-quality silica quartz glass products that meet your operational needs.
Whether you are looking to enhance your product offerings or streamline your procurement processes, this guide serves as your essential resource for understanding the intricacies of silica quartz glass. With clarity and confidence, you can tackle the challenges of sourcing and ensure your business remains competitive in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Understanding silica quartz glass Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystalline Quartz | Naturally occurring, structured atomic arrangement | Electronics (oscillators), jewelry | Pros: Natural, durable. Cons: Limited industrial applications. |
| Fused Silica | Amorphous structure, high purity, low thermal expansion | High-temperature applications, optics | Pros: Excellent thermal shock resistance. Cons: Higher cost. |
| Fused Quartz | Similar to fused silica but with natural impurities | Laboratory glassware, semiconductor manufacturing | Pros: Versatile, good chemical resistance. Cons: Impurities may affect performance. |
| Quartz Glass | General term for silica-based glass, varying purity levels | General glass applications, UV optics | Pros: Widely available, adaptable. Cons: Quality can vary. |
| Specialty Quartz | Custom formulations for specific industrial needs | Photolithography, biomedical applications | Pros: Tailored solutions. Cons: Longer lead times for production. |
What Are the Characteristics of Crystalline Quartz?
Crystalline quartz is a naturally occurring mineral characterized by its structured atomic arrangement. This crystalline form is primarily used in electronic applications, such as oscillators in watches. While it is highly durable and offers excellent wear resistance, its industrial applications are limited compared to other silica-based materials. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific purity and sourcing of the quartz, as these factors can impact performance in sensitive applications.
How Does Fused Silica Stand Out in High-Temperature Applications?
Fused silica is an amorphous form of silica known for its high purity and low thermal expansion coefficient. This unique property allows it to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without cracking, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as crucibles and trays in glass and steel manufacturing. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific thermal and optical properties required for their applications, as the higher cost of fused silica may be justified by its performance advantages.
What Are the Unique Features of Fused Quartz?
Fused quartz is produced by melting natural quartz, resulting in an amorphous material that retains some impurities. It is commonly used in laboratory glassware and semiconductor manufacturing due to its good chemical resistance and thermal stability. When considering fused quartz, buyers should assess the level of impurities and their potential impact on the intended application, especially in sensitive laboratory settings.
Why Is Quartz Glass a Popular Choice for General Applications?
Quartz glass is a broad term that encompasses various types of silica-based glass, often used interchangeably with fused silica and fused quartz. Its versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, including UV optics and general glassware. While it is widely available and adaptable, buyers should be cautious of quality variations and ensure they are sourcing from reputable suppliers to maintain performance standards.
What Are the Benefits of Specialty Quartz for Custom Applications?
Specialty quartz refers to custom formulations developed to meet specific industrial needs, such as photolithography or biomedical applications. These tailored solutions can provide significant advantages in terms of performance and compatibility with unique processes. However, buyers should be aware that such customizations may lead to longer lead times and potentially higher costs. It is essential to communicate clearly with suppliers regarding specifications to ensure the final product meets the required standards.
Key Industrial Applications of silica quartz glass
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of silica quartz glass | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor | Fabrication of photolithography masks | High precision and thermal stability for advanced microchip production | Purity levels, optical transparency, and thermal properties |
| Optical Components | Production of lenses and mirrors | Superior light transmission and resistance to thermal shock | Customization options, refractive index, and durability |
| Laboratory Equipment | Manufacturing of labware (flasks, vials) | Chemical resistance and high thermal stability for various experiments | Compliance with international standards and purity |
| Solar Energy | Construction of solar panel covers | Enhanced durability and light transmittance for energy efficiency | UV resistance, cost-effectiveness, and availability |
| Chemical Processing | Use in reaction vessels and crucibles | Excellent chemical inertness and thermal shock resistance | Specifications for high temperatures and compatibility with reactive substances |
How is Silica Quartz Glass Used in the Semiconductor Industry?
In the semiconductor industry, silica quartz glass is crucial for the fabrication of photolithography masks, which are essential for defining circuit patterns on silicon wafers. The material’s high precision and thermal stability allow for the production of advanced microchips that meet stringent performance requirements. International buyers need to consider the purity levels of the silica quartz glass, as impurities can significantly affect chip performance. Additionally, optical transparency is vital to ensure accurate pattern transfer during the manufacturing process.
What Role Does Silica Quartz Glass Play in Optical Components?
Silica quartz glass is extensively used in the production of optical components such as lenses and mirrors. Its superior light transmission and resistance to thermal shock make it ideal for applications ranging from high-performance cameras to scientific instruments. Businesses in this sector should focus on sourcing silica quartz glass that offers customization options, including specific refractive indices and durability characteristics, to meet the unique demands of their optical designs.
How is Silica Quartz Glass Essential for Laboratory Equipment?
In laboratory settings, silica quartz glass is favored for manufacturing labware like flasks and vials due to its excellent chemical resistance and high thermal stability. This allows researchers to conduct a wide range of experiments without the risk of contamination or breakage under varying temperature conditions. B2B buyers from international markets must ensure that the sourced labware complies with international standards and possesses the required purity levels to maintain the integrity of their research.
Why is Silica Quartz Glass Important in Solar Energy Applications?
Silica quartz glass plays a vital role in the construction of solar panel covers, enhancing the durability and light transmittance necessary for energy efficiency. Its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions while allowing maximum light penetration contributes to the overall performance of solar panels. Buyers should consider factors such as UV resistance and cost-effectiveness when sourcing silica quartz glass for solar applications, as these attributes directly impact the longevity and efficiency of solar installations.
How Does Silica Quartz Glass Benefit Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, silica quartz glass is used in reaction vessels and crucibles due to its excellent chemical inertness and resistance to thermal shock. This ensures safe handling of reactive substances at high temperatures. For B2B buyers, it is crucial to specify the thermal and chemical compatibility of the silica quartz glass with the substances being processed, ensuring the material can withstand the operational demands of their specific applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘silica quartz glass’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Differences Between Silica Quartz Glass Variants
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face confusion regarding the various types of silica quartz glass, such as fused silica and fused quartz. This lack of clarity can lead to improper sourcing decisions, resulting in suboptimal product performance or incompatibility in applications. For example, a semiconductor manufacturer might mistakenly order standard quartz instead of the high-purity fused silica required for photolithography, causing delays and potential financial losses.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific properties and applications of each variant. Conduct thorough research on the differences between fused silica, fused quartz, and other silica-based materials. When engaging suppliers, ask pointed questions about the purity levels, thermal properties, and chemical resistances of the materials. Additionally, consider requesting technical datasheets that clearly outline these specifications. Establishing a solid relationship with suppliers who can provide expertise and insights into the suitable type for specific applications will ensure you make informed decisions.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Consistent Quality and Supply Chain Reliability
The Problem: One significant pain point for buyers is ensuring the consistent quality of silica quartz glass, especially when sourcing from different regions or suppliers. Variability in quality can lead to defects in critical applications like optics or semiconductor manufacturing, where precision is paramount. For instance, fluctuations in material purity or mechanical strength can result in product failures, affecting production timelines and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To tackle this challenge, B2B buyers should implement a rigorous supplier evaluation and quality assurance process. This includes establishing clear quality standards and conducting regular audits of suppliers to ensure adherence to these benchmarks. Moreover, buyers should consider leveraging partnerships with suppliers who can offer traceability for their products, including batch testing and certifications. Utilizing third-party testing services for quality assurance can provide an additional layer of reliability. Lastly, maintaining a diversified supplier base can help mitigate risks associated with single-source dependency, ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality materials.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost Efficiency and Budget Constraints
The Problem: Cost is a critical concern for B2B buyers, particularly in industries where margins are tight, such as electronics or manufacturing. Buyers often struggle with balancing the need for high-quality silica quartz glass against budget constraints. This dilemma can lead to decisions that favor lower-priced materials, ultimately compromising performance and longevity, which may incur higher replacement costs in the long run.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should conduct a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis rather than focusing solely on upfront prices. This analysis should consider factors such as longevity, maintenance costs, and performance efficiency over time. Engaging in discussions with suppliers about bulk purchasing or long-term contracts can also yield cost savings. Additionally, consider working with suppliers who offer customized solutions tailored to your specific needs. This approach can optimize material usage and reduce waste, leading to more cost-effective operations. Finally, investing in training for your procurement team on material selection strategies will empower them to make decisions that align with both quality and budgetary goals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for silica quartz glass
What Are the Key Properties of Fused Quartz for B2B Applications?
Fused quartz, also known as fused silica, is an amorphous solid primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Its key properties include a high melting point (approximately 1,700°C), low thermal expansion, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Fused quartz is also highly transparent to a wide range of wavelengths, from ultraviolet to infrared, which enhances its utility in optical applications. Its low coefficient of thermal expansion allows it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it suitable for environments with thermal shock.

Illustrative image related to silica quartz glass
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Fused Quartz in Industrial Settings?
The advantages of fused quartz include its durability and chemical inertness, which make it suitable for use in harsh environments, such as semiconductor manufacturing and laboratory applications. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, while it offers high performance, the initial investment can be significant compared to other materials. Therefore, businesses must weigh the long-term benefits against the upfront costs when considering fused quartz for their applications.
How Does Fused Silica Impact Specific Applications?
Fused silica is particularly effective in applications requiring high thermal stability and optical clarity. For instance, it is widely used in photolithography for semiconductor devices, where precise light transmission is critical. Its compatibility with various media, including corrosive chemicals, makes it a preferred choice in laboratory settings. However, buyers should be aware of its limitations in applications involving hydrofluoric acid, which can etch the material.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Sourcing Silica Quartz Glass?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider compliance with local and international standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS. Understanding these standards ensures that the materials sourced meet the necessary quality and safety requirements. Additionally, preferences for specific grades of silica quartz glass may vary by region, necessitating a thorough market analysis to align product offerings with local demands.
Summary of Material Options for Silica Quartz Glass
| Material | Typical Use Case for silica quartz glass | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz | Semiconductor manufacturing | High thermal stability and optical clarity | High manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
| Fused Silica | Laboratory glassware | Excellent chemical resistance | Limited compatibility with hydrofluoric acid | Medium |
| Quartz Glass | Optical lenses and mirrors | Wide spectrum light transmission | Lower thermal shock resistance than fused quartz | Medium |
| Synthetic Quartz | Electronic components | Consistent quality and purity | Higher cost of production compared to natural quartz | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key materials related to silica quartz glass, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers. Understanding these factors will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions aligned with their specific application needs.

Illustrative image related to silica quartz glass
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for silica quartz glass
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Silica Quartz Glass?
Manufacturing silica quartz glass involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the high purity and performance characteristics required for industrial applications. The process typically includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Silica Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of raw silica. This involves sourcing high-purity silica sand or quartz crystal, which is then subjected to several treatments to remove impurities. These treatments may include washing, magnetic separation, and chemical cleaning to achieve the desired purity levels, often exceeding 99.9% SiO₂. The quality of raw materials is paramount, as impurities can significantly affect the optical and thermal properties of the final product.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Silica Quartz Glass?
Once the raw material is prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves melting the purified silica in high-temperature furnaces, where it reaches temperatures exceeding 1,700°C. The molten silica is then shaped using various techniques, including:
- Casting: Pouring the molten silica into molds to create specific shapes.
- Blowing: Using air to form hollow glassware or tubing.
- Pressing: Applying mechanical pressure to form flat glass sheets or other geometrical shapes.
Each technique has its advantages, depending on the intended application, such as optical components, laboratory glassware, or industrial vessels.
Assembly: How Are Different Components Joined Together?
In applications where multiple components are required, assembly becomes crucial. This stage often employs techniques such as:
- Fusing: Heating components to a temperature where they can bond without melting completely.
- Sealing: Utilizing specialized adhesives or thermal methods to create airtight connections.
Proper assembly ensures that the final product maintains structural integrity and performance under operational conditions.
Finishing: What Processes Enhance the Final Product Quality?
The finishing stage includes polishing, grinding, and coating to achieve the desired surface quality and optical clarity. Techniques such as diamond grinding and chemical etching are commonly used. Additionally, optical coatings may be applied to enhance light transmission and reduce glare, particularly for lenses and mirrors.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Silica Quartz Glass?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of silica quartz glass manufacturing, ensuring that products meet stringent international and industry-specific standards.

Illustrative image related to silica quartz glass
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in quality management systems for manufacturers. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer follows rigorous processes for quality control, documentation, and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (European Conformity) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be relevant, depending on the application of the glass.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product quality. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assessing raw materials for purity and compliance with specifications before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring parameters during production, such as temperature and viscosity, to ensure consistency.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive tests on finished products, including dimensional checks, thermal resistance, and optical quality.
These checkpoints help identify defects early and ensure that only products meeting quality standards proceed to the market.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are utilized to verify the quality of silica quartz glass. Common techniques include:
- Spectrophotometry: Assessing the optical clarity and transmission of light through the glass.
- Thermal Shock Testing: Evaluating the material’s resistance to rapid temperature changes.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Determining how the glass reacts to various chemicals, particularly in industrial applications.
These tests provide crucial data on the performance characteristics of the glass, ensuring it meets the specific needs of B2B buyers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential. Here are actionable steps to ensure supplier compliance with quality standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This can help identify potential issues before they affect your supply chain.
-
Request Quality Reports: Ask for documentation that outlines the results of quality control tests, including certificates of compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to evaluate the supplier’s products and processes. This independent verification can provide additional assurance of quality.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of the nuances in quality certification, which can vary by region and industry. For instance, while ISO certifications are widely recognized, additional certifications may be required for specific applications, such as API certifications for oil and gas applications. Buyers should also consider the regulatory environment in their home countries, as certain standards may be mandated for imported goods.
Furthermore, language barriers and differences in documentation practices can pose challenges. Buyers should ensure that all quality documentation is available in a language they understand and that it includes detailed information about the testing methods and compliance standards.

Illustrative image related to silica quartz glass
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for silica quartz glass is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of production and the importance of rigorous quality control, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Ensuring compliance with international standards and conducting thorough verification processes will help mitigate risks and foster successful business relationships in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘silica quartz glass’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure silica quartz glass. The process of sourcing this specialized material involves understanding its unique properties, identifying reliable suppliers, and ensuring compliance with industry standards. By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process and make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements for silica quartz glass. This includes specifications such as purity levels, dimensions, thermal resistance, and any relevant industry standards.
– Why it’s important: Precise specifications help suppliers understand your needs, reducing the risk of receiving unsuitable products.
– What to look for: Identify the specific applications, such as UV optics or high-temperature environments, to guide your specifications.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in silica quartz glass. Utilize online resources, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of potential candidates.
– Why it’s important: Not all suppliers have the same expertise or product quality; understanding their capabilities is crucial.
– What to look for: Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry and those who are transparent about their sourcing and manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to silica quartz glass
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO standards or other industry-specific accreditations.
– Why it’s important: Certifications ensure that the supplier adheres to quality control and safety standards, which is critical for high-performance applications.
– What to look for: Request documentation that proves their compliance and check for any customer feedback regarding their certification processes.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Before making a large order, request samples of silica quartz glass to evaluate its quality and suitability for your applications.
– Why it’s important: Physical samples allow you to assess the product’s performance in real-world conditions, ensuring it meets your requirements.
– What to look for: Examine the clarity, purity, and thermal properties of the samples to ensure they align with your specifications.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Analyze the pricing structures offered by your shortlisted suppliers, considering factors such as bulk discounts and payment terms.
– Why it’s important: Understanding the total cost of ownership, including shipping and handling, helps you budget effectively.
– What to look for: Compare not just prices but also value-added services like technical support or warranty options.

Illustrative image related to silica quartz glass
Step 6: Review Delivery and Logistics Options
Discuss delivery timelines and logistics with potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your project deadlines.
– Why it’s important: Delays in receiving materials can disrupt production schedules, impacting your bottom line.
– What to look for: Confirm their shipping capabilities and ask about tracking options to stay informed about your order status.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Set up a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier to facilitate ongoing dialogue regarding orders, changes, and technical support.
– Why it’s important: Effective communication can prevent misunderstandings and ensure quick resolutions to any issues that arise.
– What to look for: Identify key contacts within the supplier’s organization who will handle your account and establish regular check-ins.
By following these steps, you can effectively source high-quality silica quartz glass that meets your business needs while fostering strong relationships with reliable suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for silica quartz glass Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Silica Quartz Glass?
When sourcing silica quartz glass, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:

Illustrative image related to silica quartz glass
-
Materials: The raw material cost is influenced by the quality and purity of silica used. High-purity fused silica typically commands a premium price due to its superior thermal and optical properties.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and the complexity of the glass fabrication process. Skilled labor is essential for tasks such as cutting, grinding, and polishing quartz glass, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Overhead can vary significantly based on the manufacturer’s operational efficiency and technology.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and machinery for producing high-precision quartz glass products can be capital-intensive. These costs are often amortized over production runs, affecting pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality assurance processes are crucial to ensure product consistency and compliance with industry standards. Investments in QC can increase costs but are necessary to avoid defects and ensure customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs can be substantial, particularly for international shipments. The weight and fragility of quartz glass necessitate careful handling, which can further influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the typical margin in your market can help in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Silica Quartz Glass?
Several factors can influence the pricing of silica quartz glass:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders can lead to volume discounts, making it advantageous to consolidate purchases when possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products often incur additional costs due to the need for specialized manufacturing processes. Clearly defining specifications upfront can prevent unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-grade materials with certifications (e.g., for semiconductor applications) are priced higher. Buyers should assess whether the quality meets their application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and service levels of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly affect the final cost. Understanding terms such as FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost Insurance Freight) is crucial for budgeting logistics costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Silica Quartz Glass Prices?
To secure the best pricing and value when sourcing silica quartz glass, consider the following strategies:
-
Effective Negotiation: Approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your requirements and the supplier’s cost structure. Use data and market insights to justify your pricing expectations.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and potential downtime costs associated with lower-quality materials.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local market dynamics, tariffs, and shipping costs. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct thorough market research to understand regional pricing trends.
-
Consider Long-Term Relationships: Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into market trends. Long-term partnerships often yield more favorable terms.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing?
While indicative prices for silica quartz glass can vary widely based on the factors discussed, it is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and leverage negotiation strategies to secure the best deals. By understanding the cost components and price influencers, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing silica quartz glass With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Silica Quartz Glass
When considering materials for high-performance applications, silica quartz glass is often a leading choice due to its unique properties. However, buyers should also evaluate viable alternatives that may better suit their specific needs. This analysis compares silica quartz glass with two notable alternatives: borosilicate glass and aluminosilicate glass. Each material has distinct characteristics that influence performance, cost, and application suitability.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Silica Quartz Glass | Borosilicate Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal stability, low thermal expansion, excellent optical clarity | Good thermal resistance, moderate expansion, decent optical properties | High thermal and chemical resistance, enhanced mechanical strength |
| Cost | Higher due to purity and processing | Moderate, generally more affordable | Moderate to high, depending on formulation |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling and processing | Easy to handle and fabricate | Specialized manufacturing may be needed |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, chemically inert | Low maintenance, resistant to thermal shock | Requires careful handling due to brittleness |
| Best Use Case | Semiconductor manufacturing, optical applications | Laboratory glassware, kitchenware | High-performance electronics, aerospace components |
Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is well-known for its excellent thermal resistance and durability. It is commonly used in laboratory glassware and kitchen items due to its ability to withstand sudden temperature changes. The moderate cost and ease of fabrication make it a popular choice for many applications. However, borosilicate glass does not offer the same level of thermal stability or optical clarity as silica quartz glass, which may limit its use in high-performance optical applications.
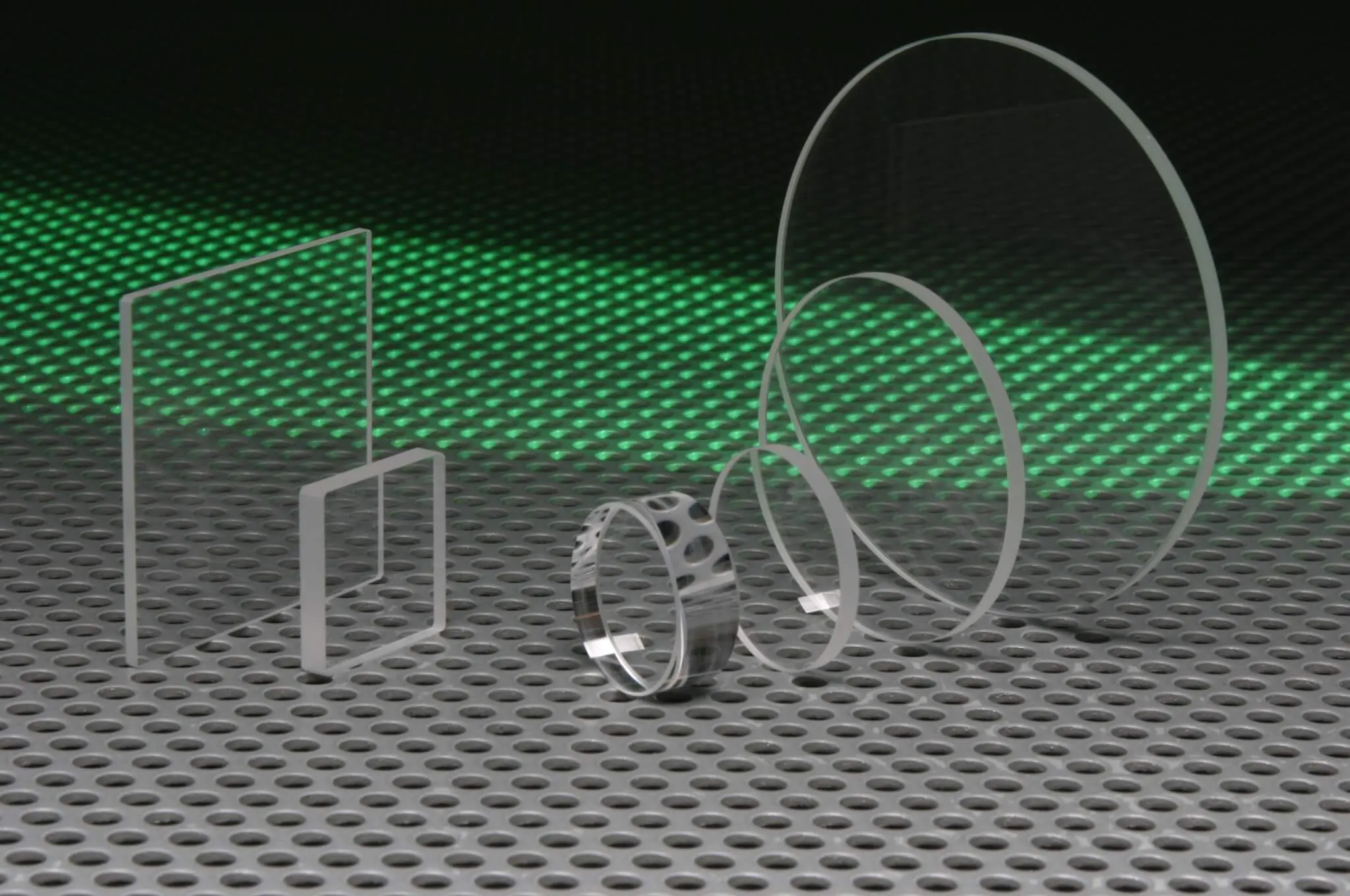
Illustrative image related to silica quartz glass
How Does Aluminosilicate Glass Compare?
Aluminosilicate glass combines aluminum oxide with silica, resulting in a material that boasts superior thermal and chemical resistance. This makes it ideal for use in high-performance applications such as electronics and aerospace components. While it offers enhanced mechanical strength compared to other glasses, aluminosilicate can be more brittle, requiring careful handling during manufacturing and use. The costs can also be higher depending on the specific formulation, which may deter some budget-conscious buyers.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate material depends heavily on the specific requirements of the application. For industries that prioritize thermal stability and optical performance, silica quartz glass remains an excellent choice, particularly in semiconductor and optical fields. However, for applications that require good thermal resistance and lower costs, borosilicate glass may be more suitable. If the focus is on high mechanical strength and chemical resistance, aluminosilicate glass could be the best option.
Ultimately, B2B buyers should assess their unique needs—considering factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and the specific environment in which the material will be used—to make an informed decision. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of each alternative, businesses can ensure they select the most effective solution for their applications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for silica quartz glass
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Silica Quartz Glass?
Understanding the essential technical properties of silica quartz glass is crucial for B2B buyers involved in various industries, including electronics, optics, and materials engineering. Here are some key specifications that influence purchasing decisions:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the purity and composition of the silica quartz glass. High-grade silica typically contains over 99.9% SiO₂, which is vital for applications requiring minimal impurities, such as semiconductor manufacturing and laboratory equipment. Choosing the right material grade can directly impact the performance and reliability of the final product. -
Thermal Expansion Coefficient
This property measures how much the material expands or contracts with temperature changes. Silica quartz glass has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), making it resistant to thermal shock. This is particularly important in applications where rapid temperature changes occur, such as in glassware used in laboratories or in high-heat industrial processes. Selecting materials with an appropriate CTE ensures durability and longevity. -
Chemical Resistance
Silica quartz glass exhibits excellent resistance to most acids and solvents, except for hydrofluoric acid. This characteristic is crucial for industries like pharmaceuticals and chemicals, where equipment must withstand aggressive environments without degradation. Buyers should prioritize chemical resistance when sourcing materials for applications that involve harsh chemicals. -
Optical Transparency
The optical properties of silica quartz glass allow it to transmit a wide range of wavelengths, including ultraviolet and infrared light. This makes it indispensable in optical applications such as lenses, mirrors, and fiber optics. Understanding the optical transparency of the glass is essential for buyers in the optical and telecommunications sectors to ensure compatibility with their systems. -
Mechanical Strength
Mechanical strength indicates the material’s ability to withstand stress without fracturing. Silica quartz glass is known for its high mechanical strength, which is critical in applications where structural integrity is paramount, such as in high-performance laboratory equipment and protective devices. Buyers must assess the mechanical strength to avoid potential failures in demanding applications. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension or property of the glass. For precision applications, like those in the aerospace or semiconductor industries, tight tolerances are essential. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can meet specific tolerance requirements to maintain quality and functionality in their end products.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Silica Quartz Glass Industry?
Navigating the world of silica quartz glass requires familiarity with industry-specific terminology. Understanding these terms can enhance communication and streamline purchasing processes:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the silica quartz glass sector, buyers often collaborate with OEMs to create custom components tailored to their specific applications. Knowing OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers for specialized products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to consider when budgeting for materials and planning inventory. Understanding MOQs helps in negotiating better terms with suppliers and ensuring that orders align with production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. This is an essential step in the procurement process, as it allows buyers to compare offers and make informed purchasing decisions. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline negotiations and enhance supplier relationships. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, delivery responsibilities, and risk management, which is particularly important when sourcing silica quartz glass from international suppliers. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. This metric is critical for production planning and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about lead times to ensure timely project execution and avoid delays. -
Custom Fabrication
This term refers to the process of creating customized glass products based on specific customer requirements. Many suppliers offer custom fabrication services, which can be vital for applications that demand unique shapes, sizes, or properties. Understanding this service can help buyers get tailored solutions that meet their unique needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the silica quartz glass Sector
What Are the Key Trends and Market Dynamics in the Silica Quartz Glass Sector?
The silica quartz glass market is witnessing robust growth driven by several global factors. Increasing demand for high-performance materials in industries such as electronics, telecommunications, and healthcare is reshaping the landscape. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Germany and Vietnam), the expansion of the semiconductor industry and the growing emphasis on renewable energy technologies are significant contributors to this trend. For international B2B buyers, understanding the regional demand patterns is crucial for strategic sourcing.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced optical fibers and photolithography, are creating new opportunities for silica quartz glass applications. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer customized solutions tailored to specific industry requirements. This trend is bolstered by the rapid evolution of manufacturing processes, including automation and digitalization, which enhance production efficiency and reduce lead times. Furthermore, with the rise of e-commerce platforms, B2B buyers now have easier access to a wider range of suppliers and product specifications, facilitating better decision-making.
How Can B2B Buyers Address Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Silica Quartz Glass?
The environmental impact of silica quartz glass production is an essential consideration for B2B buyers. As industries globally shift towards sustainability, there is a growing need for materials that minimize ecological footprints. Ethically sourced silica quartz glass not only reduces environmental harm but also enhances brand reputation among increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) can be indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, many manufacturers are exploring ‘green’ silica alternatives, which are produced with lower energy consumption and fewer emissions, appealing to buyers looking for environmentally friendly options.

Illustrative image related to silica quartz glass
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Silica Quartz Glass in the B2B Context?
Silica quartz glass has a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations, where natural quartz was utilized for various applications. However, the modern evolution began in the late 19th century with advancements in glass-making technologies. The introduction of fused silica in the mid-20th century marked a significant milestone, as it offered superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to traditional glass.
In the B2B context, the rise of the semiconductor and telecommunications industries in the latter half of the 20th century propelled the demand for high-purity silica quartz glass. Today, it serves as a critical component in a variety of applications, from laboratory equipment to optical systems. Understanding this historical evolution provides B2B buyers with valuable insights into the material’s increasing importance in contemporary industrial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of silica quartz glass
-
How do I choose the right type of silica quartz glass for my application?
Selecting the appropriate silica quartz glass depends on your specific application requirements. Consider factors such as thermal resistance, chemical inertness, and optical properties. For high-temperature applications, fused silica is ideal due to its low thermal expansion and ability to withstand rapid temperature changes. If your application involves exposure to UV light, opt for high-purity fused silica, which offers excellent transparency across a broad spectrum. Collaborate with suppliers who can provide technical data sheets and samples to ensure the chosen material meets your needs. -
What are the key differences between fused silica and quartz glass?
Fused silica is an amorphous solid made by melting pure silica, while quartz glass is crystalline and contains natural impurities. Fused silica is known for its superior thermal shock resistance, low thermal expansion, and high optical clarity, making it suitable for demanding applications like optics and semiconductor manufacturing. Quartz glass, on the other hand, is typically used in applications requiring lower thermal stress. Understanding these differences will help you select the right material for your project. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for silica quartz glass?
Minimum order quantities for silica quartz glass can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product type. Generally, MOQs can range from a few kilograms for standard products to several tons for custom fabrications. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly to potential suppliers. Many manufacturers may offer flexibility in MOQs for first-time buyers or long-term partnerships, so it’s worth discussing your requirements directly. -
How can I ensure quality and consistency in silica quartz glass products?
To ensure quality, work with reputable suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Request product specifications, test reports, and certifications that validate the purity and performance of the silica quartz glass. It’s also beneficial to inquire about their quality assurance processes, including inspections and testing methods. Establishing a clear communication line regarding quality expectations will help maintain consistency in your orders. -
What payment terms are typically offered for silica quartz glass purchases?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and the size of the order. Common arrangements include upfront payment, a deposit with the balance due upon delivery, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). International buyers should also consider currency exchange rates and transaction fees. It’s advisable to discuss payment options early in negotiations and consider using letters of credit or escrow services for larger transactions to protect both parties. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing silica quartz glass?
When importing silica quartz glass, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and the potential for damage during transit. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling fragile materials. Ensure that your supplier provides proper packaging and documentation to facilitate a smooth customs clearance process. Additionally, be aware of import duties and taxes specific to your region, as these can significantly affect the overall cost. -
How do I vet suppliers of silica quartz glass for international trade?
Vetting suppliers involves assessing their credibility, production capabilities, and compliance with international standards. Start by checking their business licenses, certifications, and customer references. Look for reviews or testimonials from previous clients. Additionally, consider visiting their facility if possible, or request virtual tours to evaluate their production processes. Engaging in trade shows or industry events can also provide valuable insights into potential suppliers. -
What customization options are available for silica quartz glass products?
Many suppliers offer customization options such as specific dimensions, shapes, and surface finishes for silica quartz glass. You can request features like ground edges, polished surfaces, or custom fabrications to meet your application needs. When approaching suppliers, provide detailed specifications and discuss your requirements to explore the available options. Customization may affect lead times and costs, so clarify these aspects during the negotiation process.
Top 6 Silica Quartz Glass Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AZOM – Fused Silica Solutions
Domain: azom.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Fused silica is nominally pure silica (SiO2) that has been melted and cooled to form a glassy, amorphous solid, while fused quartz is an amorphous solid formed by melting naturally occurring quartz, containing impurities based on its geological origin. Fused silica has high-performance applications due to its distinct electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties, including high working temperatu…
2. Tydex Optics – Fused Quartz and Fused Silica Solutions
Domain: tydexoptics.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Fused Quartz and Fused Silica are types of Quartz Glass containing primarily silica in amorphous form. Fused Quartz is made by melting high purity naturally occurring quartz crystals at around 2000°C using either an electrically heated furnace or a gas/oxygen-fuelled furnace. Fused Quartz is normally transparent. Fused Silica is produced using high purity silica sand and is normally melted using a…
3. RP Photonics – Fused Silica
Domain: rp-photonics.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Fused silica is amorphous silicon dioxide, also known as fused quartz, quartz glass, silica glass, or vitreous silica. It is a key optical material used in various applications, particularly in optics and fiber optics. Key properties include: high mechanical strength, low thermal expansion coefficient (~0.5 · 10−6 K−1), high thermal shock resistance, wide transparency range (0.18 μm to 3 μm), and …
4. Torr Scientific – Fused Silica & Z-Cut Quartz
Domain: torrscientific.co.uk
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Fused silica and natural z-cut quartz are optical materials that are both colorless and transparent to visible light, chemically identical as silicon dioxide (SiO2). Fused silica is a glass with a disordered molecular structure, while natural z-cut quartz is crystalline with an orderly structure. Fused silica has a softening point around 1600°C and can withstand working temperatures up to 1000°C, …
5. Xometry – Silica Glass
Domain: xometry.pro
Introduction: {“Alternative Designations”: “SiO2”, “Price Range”: “€ € € €€”, “Colors”: “Highly clear / See through”, “Description”: “Silica glass is an isotropic material commonly seen as the glassy form of quartz. It is tough, hard, and expands slowly. Vitreous silica is the generic term that describes all forms of silica glass. The two major types of silica glass are fused quartz and fused silica. Both mater…
6. Accuratus – Fused Silica
Domain: accuratus.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Fused Silica”, “Chemical Composition”: “SiO2”, “Properties”: {“Thermal Expansion”: “Near zero thermal expansion”, “Thermal Shock Resistance”: “Exceptionally good thermal shock resistance”, “Chemical Inertness”: “Very good chemical inertness”, “Finish”: “Can be lapped and polished to fine finishes”, “Dielectric Constant”: “Low dielectric constant”, “Dielectric Loss”: “Low dielectr…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for silica quartz glass
Why is Strategic Sourcing Crucial for Silica Quartz Glass?
In today’s competitive landscape, effective strategic sourcing of silica quartz glass is essential for international B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances between quartz, fused silica, and their applications can lead to informed purchasing decisions that enhance product quality and operational efficiency. Prioritizing suppliers who offer high-purity materials and advanced manufacturing capabilities ensures access to innovative solutions tailored to specific industry needs, whether in semiconductor, laboratory, or optical applications.
How Can Buyers Prepare for Future Trends in Silica Quartz Glass?
As demand for advanced materials continues to rise across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, staying ahead of market trends will be vital. Buyers should explore partnerships with reliable manufacturers who can provide customized solutions, ensuring adaptability to evolving technological requirements. By fostering strong supplier relationships, businesses can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and leverage new opportunities for growth.
What Steps Should International Buyers Take Next?
Now is the time for international B2B buyers to assess their sourcing strategies and engage with suppliers that align with their operational goals. Embrace the potential of silica quartz glass by investing in quality materials and innovative applications. Reach out to industry experts and suppliers to explore how strategic sourcing can elevate your business and meet the challenges of tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.