Everything You Need to Know About Plug In Class 2 Transformer Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plug in class 2 transformer
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing reliable plug-in Class 2 transformers poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse and rapidly developing regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a myriad of suppliers and specifications available, navigating the complexities of product types, applications, and compliance standards can be daunting. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process, providing valuable insights into the various types of plug-in Class 2 transformers, their specific applications, and essential supplier vetting strategies.
Buyers will discover how to assess the quality and reliability of potential suppliers, understand cost implications, and evaluate the long-term value of their investments. The guide also addresses critical considerations such as regulatory compliance and shipping logistics, ensuring that international buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
By empowering decision-makers with actionable insights and detailed market analysis, this resource will enhance your ability to source plug-in Class 2 transformers effectively, ultimately driving efficiency and innovation within your organization. Whether you’re based in Saudi Arabia or Brazil, this guide serves as a vital tool to navigate the intricacies of the global transformer market, ensuring that your business stays competitive in an ever-evolving landscape.
Understanding plug in class 2 transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard AC Adapter | Input: 120V, Output: 18VDC, 35W; Commonly used | Consumer electronics, lighting systems | Pros: Affordable, widely available; Cons: Limited voltage options |
| Low-Voltage DC Transformer | Output: Typically 12V or 24V; Compact design | LED lighting, security systems | Pros: Efficient for low-voltage applications; Cons: May require additional converters |
| Multi-Output Transformer | Multiple output voltages; Versatile connections | Industrial automation, telecommunications | Pros: Flexibility for diverse applications; Cons: Higher cost and complexity |
| Wall-Mounted Class 2 Transformer | Space-saving design; Easy installation | Home appliances, medical devices | Pros: Convenient for tight spaces; Cons: Limited power capacity |
| Enclosed Class 2 Transformer | Enclosed design for safety; Higher wattage ratings | Heavy machinery, HVAC systems | Pros: Enhanced safety features; Cons: Bulkier and less portable |
What are the Characteristics of Standard AC Adapters?
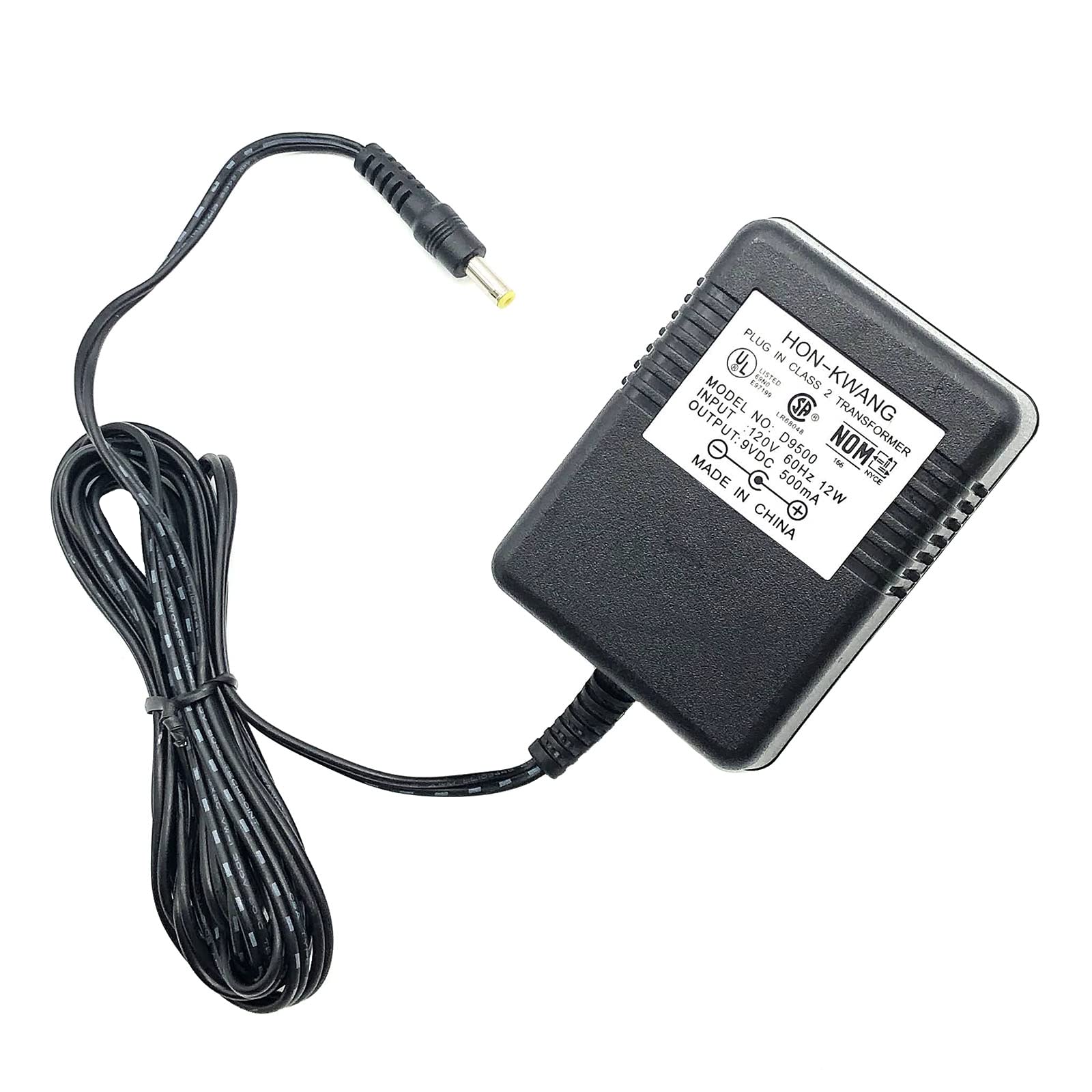
Standard AC adapters are among the most common types of plug-in Class 2 transformers, featuring an input of 120V and an output of 18VDC with a power rating of 35W. These transformers are widely utilized in consumer electronics and lighting systems, making them a staple in various industries. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider compatibility with existing equipment and ensure that the voltage and wattage meet their requirements. While they are affordable and readily available, their limited voltage options may restrict their application in more specialized scenarios.

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
How Do Low-Voltage DC Transformers Stand Out?
Low-voltage DC transformers typically output 12V or 24V and are designed for compactness, making them ideal for applications such as LED lighting and security systems. Their efficiency in low-voltage scenarios makes them a preferred choice for energy-conscious businesses. Buyers should evaluate the specific voltage requirements of their projects and consider whether additional converters are necessary for optimal performance. Although these transformers are efficient, they may not be suitable for higher voltage needs.
What Advantages Do Multi-Output Transformers Offer?
Multi-output transformers are designed to provide various output voltages from a single unit, making them extremely versatile for applications in industrial automation and telecommunications. Their ability to accommodate different devices can streamline inventory management and reduce the need for multiple transformers. However, buyers should weigh the higher cost and complexity against the benefits of flexibility. Understanding the specific voltage requirements of connected devices is crucial for effective use.
Why Choose Wall-Mounted Class 2 Transformers?
Wall-mounted Class 2 transformers are designed for easy installation and space-saving, making them ideal for home appliances and medical devices. Their compact nature allows for use in tight spaces, which can be a significant advantage in environments where space is at a premium. Buyers should assess the power capacity to ensure it meets the demands of their applications. While convenient, these transformers may have limitations in power output, which could restrict their use in larger systems.
What Makes Enclosed Class 2 Transformers a Safe Choice?
Enclosed Class 2 transformers provide enhanced safety features, making them suitable for heavy machinery and HVAC systems. Their enclosed design protects against accidental contact, which is critical in industrial environments. When considering these transformers, B2B buyers should evaluate the wattage ratings to ensure they align with their operational needs. Though they offer superior safety, their bulkier design may impact portability, making them less suitable for applications requiring mobility.
Key Industrial Applications of plug in class 2 transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of plug in class 2 transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lighting | Used in LED lighting systems to convert AC to DC. | Ensures consistent power supply, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs. | Look for transformers with high efficiency ratings and compatibility with local voltage standards. |
| Security Systems | Powers surveillance cameras and alarm systems. | Provides reliable power, crucial for maintaining security and preventing downtime. | Consider durability, power output, and compliance with safety standards relevant to the region. |
| Consumer Electronics | Powers devices like routers and gaming consoles. | Facilitates seamless operation of devices, improving customer satisfaction and reducing returns. | Evaluate output voltage compatibility and ensure certifications meet international safety standards. |
| Medical Equipment | Powers diagnostic and monitoring devices. | Ensures patient safety and equipment reliability, which is critical in healthcare settings. | Focus on transformers with low electromagnetic interference and compliance with medical device regulations. |
| Telecommunications | Supplies power to network devices and infrastructure. | Supports uninterrupted service, enhancing communication reliability and customer trust. | Assess scalability for future expansion and compatibility with existing systems. |
How Are Plug-in Class 2 Transformers Applied in Lighting Systems?
In the lighting industry, plug-in Class 2 transformers are primarily used to power LED lighting systems. By converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), these transformers ensure a stable power supply, which is essential for optimal LED performance. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing transformers that comply with local voltage and energy efficiency standards can significantly reduce operational costs and enhance sustainability.
What Role Do Plug-in Class 2 Transformers Play in Security Systems?
Plug-in Class 2 transformers are integral to the operation of surveillance cameras and alarm systems within security frameworks. By providing a reliable power source, these transformers help prevent system failures that could compromise security. Buyers in South America and Europe should prioritize sourcing transformers that are durable and meet the safety standards specific to their regions to ensure long-term reliability.
How Are Plug-in Class 2 Transformers Beneficial for Consumer Electronics?
In the consumer electronics sector, plug-in Class 2 transformers are commonly used to power devices such as routers and gaming consoles. Their ability to provide a consistent power supply enhances device performance and customer satisfaction. For B2B buyers, particularly in Brazil and Saudi Arabia, evaluating the output voltage compatibility and ensuring that the transformers meet international safety certifications can prevent product returns and improve user experience.
What Is the Importance of Plug-in Class 2 Transformers in Medical Equipment?
In healthcare, plug-in Class 2 transformers are vital for powering diagnostic and monitoring devices. They ensure patient safety by providing a reliable power source, which is critical in medical environments. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing transformers with low electromagnetic interference and compliance with specific medical device regulations to ensure the highest standards of safety and reliability.
How Do Plug-in Class 2 Transformers Support Telecommunications?
Within the telecommunications industry, plug-in Class 2 transformers are essential for supplying power to network devices and infrastructure. Their reliability supports uninterrupted service, which is crucial for maintaining customer trust in communication services. International buyers should assess the scalability of these transformers for future expansions and ensure compatibility with existing systems to facilitate seamless integration and operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘plug in class 2 transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Power Supply Issues with Class 2 Transformers
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with the reliability of plug-in Class 2 transformers, particularly in environments where power quality is inconsistent. This can lead to equipment malfunction, damaged electronics, and ultimately, increased operational costs. Buyers in regions with unreliable power grids, such as certain areas in Africa and South America, may find that their equipment does not perform as expected, leading to dissatisfaction among end-users and potential revenue loss.
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with inconsistent power supply, it is essential to source high-quality Class 2 transformers designed for variable input conditions. Look for transformers with built-in surge protection and voltage regulation features. When specifying transformers, ensure they meet the local voltage requirements while also having a slightly higher tolerance to fluctuations. Additionally, working with reputable suppliers who offer warranties and customer support can provide peace of mind. Regular maintenance and testing of transformers in the operational environment can also help identify issues before they affect performance.
Scenario 2: Compatibility Challenges with Diverse Equipment
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the compatibility of plug-in Class 2 transformers with various devices. Different manufacturers may have unique specifications for input and output voltages, which can complicate sourcing decisions. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe often deal with a wide range of equipment, from LED lighting systems to low-voltage electronics, making it challenging to find a transformer that meets all requirements.

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
The Solution: To overcome compatibility issues, buyers should start by clearly identifying the voltage and current requirements of each device that will be powered by the Class 2 transformer. A comprehensive compatibility checklist can be created to ensure that the chosen transformer meets the specifications of all connected devices. It is also beneficial to choose transformers that come with adjustable output settings or those that are modular in design, allowing for future upgrades without needing to replace the entire unit. Partnering with suppliers who provide detailed product specifications and expert advice can further streamline the selection process.
Scenario 3: Shipping and Delivery Delays for International Orders
The Problem: International B2B buyers often encounter delays in shipping and delivery when ordering plug-in Class 2 transformers, which can disrupt project timelines and lead to increased costs. Buyers in regions such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia may face logistical challenges, including customs clearance and extended lead times, which can impact their ability to meet client deadlines.
The Solution: To address shipping and delivery concerns, buyers should establish relationships with suppliers that offer reliable international shipping options and have experience navigating customs regulations. It is advisable to discuss shipping timelines upfront and consider suppliers who can provide expedited shipping services. Additionally, placing bulk orders can sometimes mitigate shipping costs and delays. Buyers should also explore local distributors or manufacturers in their region to reduce shipping times and costs while ensuring they maintain the quality and compliance standards required for Class 2 transformers. Investing time in building strong supplier relationships can lead to better communication and more reliable delivery schedules.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plug in class 2 transformer
What Are the Key Materials Used in Plug-in Class 2 Transformers?
When selecting materials for plug-in class 2 transformers, several factors must be considered, including electrical performance, thermal management, and environmental resistance. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these transformers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
How Does Copper Influence Performance in Plug-in Class 2 Transformers?
Key Properties: Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, low resistivity, and thermal conductivity. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances the transformer’s efficiency. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to alternatives like aluminum, and it is prone to corrosion if not properly coated or insulated. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, requiring specialized processes for winding and insulation.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for high-performance applications where efficiency is critical, such as in sensitive electronic devices. It is compatible with various media and can handle significant electrical loads.

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that their suppliers adhere to these standards to guarantee quality and reliability.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Plug-in Class 2 Transformers?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good electrical conductivity, though not as high as copper. It is resistant to corrosion due to the formation of a protective oxide layer.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and lighter weight, which can reduce shipping expenses. However, its lower conductivity can lead to increased energy losses, and it may require larger cross-sectional areas compared to copper. Manufacturing processes for aluminum are generally less complex.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight and cost are significant factors, such as portable devices. However, its lower conductivity may limit its use in high-load applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of aluminum used, as they must comply with standards such as ASTM B221. In regions like Africa and South America, ensuring proper sourcing can mitigate issues related to material quality.
How Do Plastics Enhance Durability in Plug-in Class 2 Transformers?
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics, offer excellent insulation properties and resistance to moisture and chemicals. They can withstand a range of temperatures, depending on the type used.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastics is their versatility and cost-effectiveness. They are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, enhancing design flexibility. However, plastics may not be as durable under extreme conditions, and some types can degrade over time when exposed to UV light or high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are often used for housings and insulation in transformers, providing necessary electrical isolation. They are suitable for indoor applications but may require additional protection for outdoor use.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as UL 94 for flammability is crucial. Buyers in regions with strict environmental regulations, such as Europe, should ensure that the plastics used are RoHS compliant.
Why Is Steel Important in the Construction of Plug-in Class 2 Transformers?
Key Properties: Steel is used primarily for the transformer core due to its magnetic properties, which enhance efficiency. It can endure high temperatures and is available in various grades.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s primary advantage is its ability to efficiently channel magnetic fields, which improves transformer performance. However, it is heavier than other materials and can be more expensive, depending on the grade. Manufacturing complexity is high due to the need for precise machining.
Impact on Application: Steel is essential in applications requiring high magnetic efficiency, such as in power distribution transformers. Its compatibility with high-frequency applications is also noteworthy.

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is vital. Buyers from the Middle East and Africa should consider local sourcing to reduce costs and ensure compliance with regional standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Plug-in Class 2 Transformers
| Material | Typical Use Case for Plug-in Class 2 Transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-performance transformers | Superior conductivity | High cost and corrosion potential | High |
| Aluminum | Cost-sensitive and lightweight applications | Lower cost and weight | Lower conductivity and potential energy loss | Medium |
| Plastics | Insulation and housing | Versatile and cost-effective | Durability issues under extreme conditions | Low |
| Steel | Transformer core for magnetic efficiency | High magnetic performance | Heavier and more expensive | Medium |
This material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in diverse international markets, ensuring informed decisions that align with performance requirements and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plug in class 2 transformer
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
The manufacturing of plug-in Class 2 transformers is a multifaceted process that involves several critical stages, each ensuring the final product meets safety and performance standards. Understanding these stages can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Class 2 Transformers?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, where high-quality raw materials are sourced. Common materials include silicon steel for the core, copper for windings, and durable plastics for casing. The selection of materials is crucial, as they directly influence the transformer’s efficiency, thermal performance, and longevity. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that utilize materials compliant with international standards, ensuring the transformers can perform reliably in various environments.

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
Forming: How Are Transformer Components Shaped and Assembled?
The next stage involves forming the components of the transformer. This includes cutting and shaping the core and winding the copper wire to create the primary and secondary coils. Advanced techniques such as precision CNC machining and automated winding machines are often employed to ensure accuracy and reduce labor costs. B2B buyers should inquire about the machinery and technology used in the forming process, as this can affect the consistency and quality of the end product.
Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
Once the components are formed, they are assembled in a controlled environment. This stage includes placing the core, winding the coils, and connecting them to the terminals. Quality assurance during assembly is critical, as improper connections can lead to performance issues or safety hazards. Suppliers should demonstrate robust assembly procedures, including the use of jigs and fixtures to maintain accuracy.
Finishing: What Are the Final Touches Applied to Transformers?
The finishing stage encompasses the application of protective coatings, insulation, and labeling. Transformers are often tested for electrical safety and environmental resistance at this stage. B2B buyers should ensure that the suppliers adhere to finishing standards that enhance durability and reduce the risk of failure, especially in challenging climates prevalent in regions like Africa and South America.
How Do Quality Assurance Practices Ensure the Reliability of Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of plug-in Class 2 transformers. Effective QA processes not only ensure compliance with safety standards but also enhance customer trust and satisfaction.
What International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers often comply with international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. This certification indicates that a manufacturer has established a systematic approach to managing processes and ensuring quality. Other relevant standards include CE marking for compliance with European safety directives and UL certification, particularly important for buyers in North America.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints should be established at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, periodic checks are conducted to monitor the quality of components and assembly processes.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): At this stage, finished transformers undergo comprehensive testing, including electrical performance tests, thermal imaging, and safety evaluations.
B2B buyers should request detailed reports on these QC processes to assess the reliability of their suppliers.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Product Quality?
Several testing methods are employed to validate the performance and safety of plug-in Class 2 transformers:
- Electrical Testing: Measures voltage, current, and insulation resistance to ensure compliance with specifications.
- Thermal Testing: Assesses the transformer’s ability to operate under various temperature conditions.
- Load Testing: Evaluates the transformer’s performance under maximum load conditions.
Buyers should consider suppliers that provide comprehensive testing documentation as part of their quality assurance practices.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for international B2B buyers. Here are some actionable strategies:
What Should Buyers Look for During Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits can provide insights into a manufacturer’s quality assurance practices. During these audits, buyers should evaluate the following:
- Compliance with international and industry-specific standards.
- Documentation of quality control processes and results.
- Employee training programs and safety protocols.
How Can Buyers Leverage Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help buyers assess the consistency of manufacturing practices. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control systems. This is particularly important for buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe, where compliance with stringent regulations is critical.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of regional standards and regulations that may differ from local practices. For instance, transformers sold in Europe must comply with the EU’s Low Voltage Directive (LVD), while products distributed in the Middle East may require specific certifications based on local regulations. Understanding these nuances can help buyers avoid potential compliance issues and ensure the transformers meet their operational requirements.
Conclusion: Why Is a Robust Manufacturing and Quality Assurance Process Essential for B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, especially those sourcing plug-in Class 2 transformers from diverse regions, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing and quality assurance processes is crucial. By focusing on the key stages of production, relevant international standards, and effective quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions that lead to successful partnerships and high-quality products. Investing time in supplier evaluation and verification not only mitigates risks but also fosters long-term relationships built on trust and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘plug in class 2 transformer’
To assist B2B buyers in successfully sourcing plug-in Class 2 transformers, this guide provides a structured checklist designed to streamline the procurement process. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they select the right products and suppliers, optimizing their investment and operational efficiency.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical for ensuring the transformer meets your project’s requirements. Consider factors such as voltage, wattage, and current ratings. For instance, if your application requires an 18V output with a capacity of 35W, make this a key criterion when evaluating options.
2. Research Market Options
Conduct thorough market research to identify available products that fit your specifications. Utilize online platforms, trade shows, and industry publications to gather information on different brands and models. Pay attention to product reviews and ratings to gauge reliability and performance.

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in your industry. This step helps you verify the supplier’s credibility and their experience in delivering quality transformers.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure that the suppliers have the necessary certifications (e.g., UL, CE) to guarantee compliance with international safety standards.
- Assess Delivery Capabilities: Confirm that the supplier can meet your delivery timelines, particularly if you have tight project schedules.
4. Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare their pricing structures and payment terms. Look beyond the initial price to consider total cost implications, including shipping fees and taxes. Favor suppliers that offer flexible payment options, which can help manage your cash flow effectively.
5. Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the transformers you are considering. This allows you to evaluate the product’s performance in your specific application. Testing for reliability and compatibility with your existing systems is crucial to prevent future operational issues.
6. Review After-Sales Support and Warranty
Understand the after-sales support and warranty policies of the suppliers. A solid warranty can provide peace of mind, protecting your investment against potential defects. Additionally, inquire about the availability of technical support for troubleshooting and maintenance.

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
7. Finalize Contractual Agreements
After selecting a supplier, ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in a formal contract. This should include delivery schedules, pricing agreements, and warranty details. Clear contractual obligations can help mitigate risks associated with misunderstandings or disputes.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing plug-in Class 2 transformers more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plug in class 2 transformer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
When sourcing plug-in Class 2 transformers, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used directly affects the cost. High-quality components, such as copper wire and durable plastic housing, typically increase the price but enhance reliability.
-
Labor: Manufacturing labor costs can vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as those in Southeast Asia, the overall production cost may be reduced, impacting the final price offered to buyers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers with optimized production processes can offer better pricing due to lower overhead.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific transformer designs can be a significant upfront investment. This cost is often amortized over large production runs, affecting pricing per unit.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes ensure product reliability. However, they also add to the overall cost. Buyers should consider whether the additional QC costs are justified by the expected performance and lifespan of the transformer.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the origin of the products and the destination market. Buyers must account for these expenses when evaluating the total cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin that can vary based on competition and market demand. Understanding the margin can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
Several factors influence the pricing of plug-in Class 2 transformers, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize their costs while ensuring adequate stock levels.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as different voltage outputs or specific certifications, can significantly impact pricing. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against the potential cost increases.
-
Materials Used: The choice of materials can affect both the performance and price. Higher-quality materials, while more expensive, can provide better longevity and reliability.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international safety standards or possess certifications may carry a premium price. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their markets.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and production capacity can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for international buyers. Different Incoterms can affect the total landed cost, including duties and taxes, which may not be included in the initial quote.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Optimize Costs and Pricing?
To navigate the complexities of pricing for plug-in Class 2 transformers, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Engage suppliers in discussions to explore volume discounts or flexible payment terms. Building long-term relationships can also yield better pricing over time.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with installation, maintenance, and potential failures. A lower upfront price may not always result in lower TCO.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions that can affect final costs.
-
Conduct Market Research: Compare prices from multiple suppliers and understand the competitive landscape. This research can help in negotiations and decision-making.
-
Evaluate Supplier Capabilities: Assess suppliers not only based on price but also on their ability to meet delivery timelines, quality standards, and customer service expectations. A reliable supplier can mitigate risks associated with delays and defects.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the cost components, price influencers, and strategic negotiation techniques will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing plug-in Class 2 transformers. Keep in mind that prices can vary widely based on specific requirements and market conditions, so always seek indicative pricing tailored to your needs.
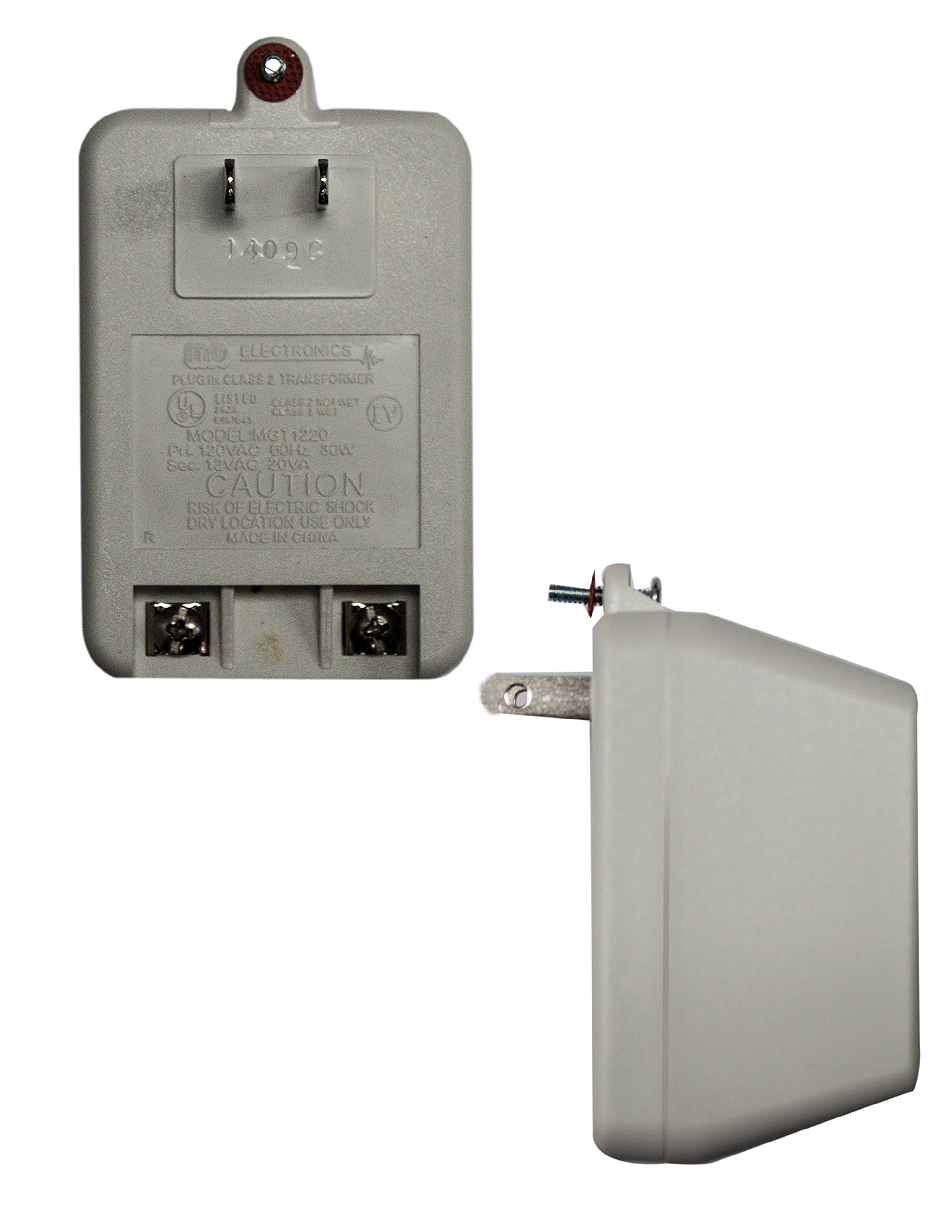

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing plug in class 2 transformer With Other Solutions
In the quest for efficient power supply solutions, businesses often find themselves evaluating various options to meet their specific needs. This section explores alternatives to the plug-in Class 2 transformer, analyzing how they stack up in terms of performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases. By understanding these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Plug In Class 2 Transformer | Switching Power Supply | Linear Power Supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Stable output voltage, limited to 35W | High efficiency, variable output | Low efficiency, high heat generation |
| Cost | Affordable (~$13.50) | Moderate ($20 – $100) | Higher ($50 – $200) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple plug-and-play design | Requires more technical setup | Requires technical setup |
| Maintenance | Low, minimal wear and tear | Moderate, may need cooling | High, frequent replacements due to heat |
| Best Use Case | Low-power applications (e.g., LED lighting) | High-efficiency applications (e.g., computers) | Audio equipment needing low noise |
What Are the Pros and Cons of a Switching Power Supply?
Switching power supplies are a popular alternative due to their high efficiency and compact design. They convert power using high-frequency switching, resulting in less heat generation compared to traditional transformers. However, the complexity of their design means that they may require more technical expertise to implement and troubleshoot. They also tend to be more costly than plug-in Class 2 transformers, making them less ideal for low-power applications where budget constraints are a concern.
How Does a Linear Power Supply Compare?
Linear power supplies are known for their simplicity and ability to provide a clean output voltage with minimal noise, making them a favored choice for sensitive audio equipment and laboratory applications. However, they are less efficient than switching supplies and can generate considerable heat, necessitating additional cooling solutions. Their higher cost and maintenance needs can be a barrier for businesses focused on budget management and operational efficiency.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Power Supply Solution?
When selecting a power supply solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and available technical expertise. The plug-in Class 2 transformer is an excellent choice for low-power applications due to its affordability and ease of use. However, for applications that demand higher efficiency or lower noise, switching or linear power supplies may be more suitable. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of each option, buyers can align their choice with both operational needs and financial considerations, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their power supply solutions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plug in class 2 transformer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
Understanding the technical specifications of plug-in Class 2 transformers is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
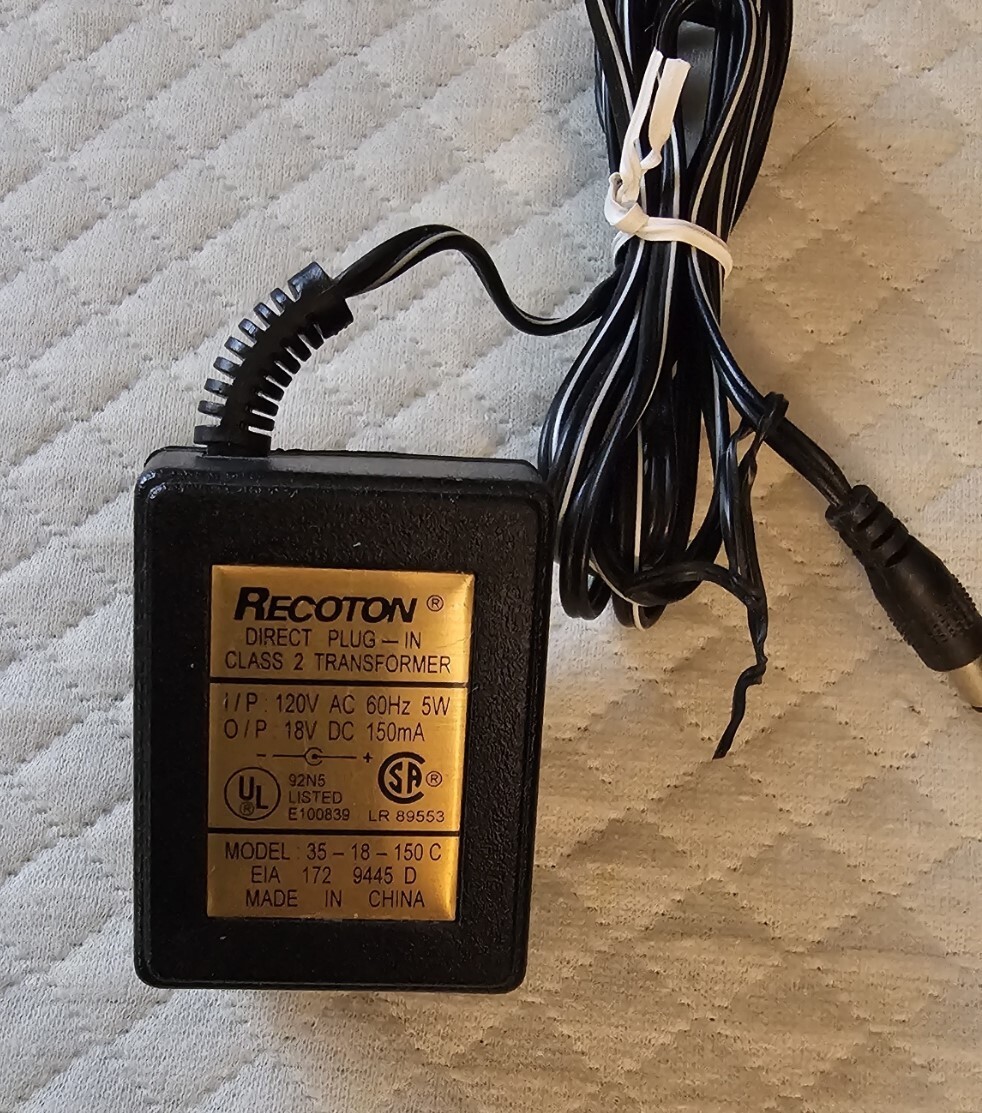

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
-
Voltage and Amperage Ratings
Voltage ratings indicate the electrical potential difference across the transformer, while amperage ratings denote the maximum current the transformer can handle. For instance, a typical Class 2 transformer may have an input voltage of 120V and an output voltage of 18V, with an amperage rating of 0.8A. These specifications are critical for ensuring compatibility with your electrical systems and preventing overloads. -
Power Output (Watts)
The power output, measured in watts, signifies the total amount of electrical power the transformer can deliver. For example, a 35W transformer can efficiently power devices requiring up to that amount. Selecting a transformer with the appropriate wattage is vital to ensure that your devices operate effectively without risking damage from under or over-voltage conditions. -
Lead/Terminal Type
The lead or terminal type refers to how the transformer connects to the electrical system or device. Common types include plug-in cords or terminal blocks. Understanding the lead type is essential for installation compatibility with existing systems and ensuring a secure connection. -
Frequency
Frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), indicates the number of cycles per second in an alternating current (AC). Most plug-in Class 2 transformers operate at 60Hz in North America or 50Hz in other regions. It’s important to match the frequency with your local electrical standards to avoid malfunction. -
Material and Build Quality
The materials used in transformers, such as plastic casings or copper windings, can affect durability and heat dissipation. A transformer with high-quality materials will typically have a longer lifespan and better performance. This is particularly important for businesses in regions with extreme climates or frequent power fluctuations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Plug-In Class 2 Transformers?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms relevant to plug-in Class 2 transformers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of transformers, an OEM may supply components for various electrical devices, ensuring quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest number of units a buyer must purchase in a single order. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for businesses looking to scale their operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific products. For plug-in Class 2 transformers, an RFQ can help businesses compare prices and terms from different manufacturers, ensuring the best value. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Knowing Incoterms is critical for understanding shipping costs, risk management, and delivery timelines when sourcing transformers from global suppliers. -
CE Marking
The CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area. For B2B buyers in Europe, ensuring that transformers are CE marked is essential for compliance and marketability. -
UL Certification
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification signifies that a product has been tested and meets specific safety standards. For electrical components like Class 2 transformers, UL certification is crucial for ensuring safety and reliability, especially in commercial applications.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing plug-in Class 2 transformers, ensuring they select the right products for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the plug in class 2 transformer Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Impacting Plug-In Class 2 Transformer Sourcing?
The global market for plug-in class 2 transformers is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for efficient power solutions across various sectors, including telecommunications, lighting, and industrial applications. This surge is particularly evident in emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where infrastructural development and urbanization are accelerating the need for reliable electrical components. In Europe, the emphasis on energy efficiency and regulatory compliance is shaping the landscape, with buyers increasingly seeking transformers that meet stringent standards.
Current sourcing trends indicate a shift towards suppliers that offer not only competitive pricing but also high-quality products that adhere to international safety and performance standards. International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for procurement, allowing for greater transparency and efficiency in the sourcing process. Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 is prompting manufacturers to integrate smart technologies into transformers, enhancing their functionality and appeal to tech-savvy buyers.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence the Plug-In Class 2 Transformer Market?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the plug-in class 2 transformer sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of electrical components are under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek suppliers committed to reducing their carbon footprint. Ethical sourcing practices are equally important, as buyers prioritize suppliers who maintain transparent supply chains and adhere to fair labor practices.
The demand for ‘green’ certifications is on the rise, with many buyers looking for transformers made from recyclable materials or those that meet eco-friendly standards. Certifications such as Energy Star and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) not only demonstrate a commitment to sustainability but also enhance a company’s reputation in the marketplace. By aligning procurement strategies with sustainable practices, B2B buyers can not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also appeal to environmentally-conscious customers.

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
What is the Evolution of Plug-In Class 2 Transformers in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of plug-in class 2 transformers can be traced back to the increasing reliance on electronic devices and the need for reliable power sources. Initially, these transformers were primarily utilized in low-voltage applications, serving as essential components in consumer electronics. Over the decades, advancements in technology have led to improved efficiency and versatility, enabling their use in more demanding applications such as industrial automation and smart home systems.
As industries have evolved, so too have the specifications and features of plug-in class 2 transformers. Today, they are designed not only for efficiency but also to integrate seamlessly with modern electronic systems, reflecting the growing trend towards connectivity and smart technology. This evolution highlights the importance of staying abreast of technological advancements and market demands, ensuring that procurement strategies align with the current and future needs of the industry.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics and trends within the plug-in class 2 transformer market is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on sustainable practices, ethical sourcing, and staying informed about technological advancements, companies can enhance their procurement strategies and position themselves favorably in a competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plug in class 2 transformer
-
1. How do I solve compatibility issues with plug-in Class 2 transformers?
To address compatibility issues, start by confirming the voltage and current specifications of your devices. Ensure the transformer’s output matches the required input of your equipment. Additionally, verify the connector type; many devices use different plug sizes. If issues persist, consider consulting with the manufacturer or a technical expert to ensure your transformer meets the necessary standards for your application. -
2. What is the best plug-in Class 2 transformer for low-power applications?
For low-power applications, a transformer with a lower wattage rating, such as 12W to 35W, is typically adequate. Look for models that provide the necessary voltage output, such as 12V or 24V, while ensuring they comply with safety standards. It’s also important to consider the transformer’s size and weight if space is a constraint. Always check for certifications like UL or CE, which indicate compliance with international safety standards. -
3. How can I vet suppliers of plug-in Class 2 transformers for international sourcing?
To vet suppliers, start by reviewing their company history, certifications, and product reviews. Request samples to assess product quality and compliance with specifications. Additionally, check their responsiveness and willingness to provide information on manufacturing processes and materials used. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources to compare ratings and feedback from other buyers. Engaging with suppliers directly through video calls can also help gauge their reliability and professionalism. -
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for plug-in Class 2 transformers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from 100 to 1,000 units. Factors influencing MOQs include the supplier’s production capacity, product type, and customization requirements. If you need smaller quantities, consider sourcing from distributors or wholesalers who may offer more flexible purchasing options. Always negotiate MOQs with suppliers, especially if you’re a new buyer or require a trial order. -
5. What payment terms are common when purchasing plug-in Class 2 transformers internationally?
Common payment terms include upfront payment, a 30% deposit with the balance due upon shipment, or net 30/60 days after delivery. Ensure clarity on payment methods accepted, such as wire transfers, letters of credit, or online payment platforms. It’s advisable to use secure payment methods that offer buyer protection. Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to more favorable payment terms in future transactions. -
6. How do I ensure the quality of plug-in Class 2 transformers?
To ensure quality, request certifications that verify compliance with international standards, such as ISO, UL, or CE. Conduct factory audits if feasible, or hire third-party quality assurance services to inspect products before shipment. It’s also beneficial to establish clear quality control criteria in your purchase agreement, detailing specifications, testing procedures, and acceptable defect rates. Regular communication with the supplier throughout the production process can help mitigate potential quality issues. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing plug-in Class 2 transformers?
When importing transformers, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and duties applicable in your country. Select a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling electronic components to navigate shipping logistics. Ensure your shipment is properly labeled and documented to comply with customs requirements. Familiarize yourself with import tariffs and potential delays to avoid unexpected costs or disruptions in your supply chain. -
8. Can plug-in Class 2 transformers be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for plug-in Class 2 transformers, including voltage, wattage, and connector types. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and application requirements to the supplier. Be prepared for potential minimum order quantities for customized products and inquire about lead times. Custom transformers may also involve additional costs, so ensure that these are factored into your budget.
Top 6 Plug In Class 2 Transformer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Various Brands – Class 2 Transformer
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Class 2 Transformer, Input Voltage: 120V AC, Frequency: 60Hz, Various Output Voltages available (3V, 4.5V, 5V, 6V, 7.5V, 9V, 12V, 13.5V, 15V, 16V, 18V, 20V, 24V), Type: AC/DC Adapter, AC/AC Adapter, Multi-Tip Adapter, Battery Charger, Power Cord, Transformer, Condition: New, Pre-Owned, Various Brands available.
2. Reddit – Class 2 Transformer
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Class 2 transformer, typically used for low voltage applications such as doorbells or security systems. It was found connected to an outlet in a house, and upon disconnection, no immediate issues were observed with lights or AC. Potential uses mentioned include powering alarm systems or other devices like motion detectors.
3. JustAnswer – Universal Plug-In Class 2 Transformer
Domain: justanswer.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Universal Plug-In Class 2 Transformer; Input: 120VAC 60Hz 48W; Output: 16.5VAC 40VA; Connection terminals: 3 (not labeled); Wires: green (ground), yellow (ground), red, black; Connection guidance: black to AC, red to AC, green & yellow together to ‘earth’; Voltage requirement for alarm: 16.5VAC; Class 2 designation; Associated with home security control panel.
4. Hammond – BPD2G Class 2 Transformer Plug-In
Domain: be-electronics.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Hammond BPD2G Class 2 Transformer Plug-In”, “output_voltage”: “24VAC”, “output_current”: “833mA”, “power_rating”: “20VA”}
5. WAC Lighting – 120V/24V 60W Plug-In Electronic Transformer
Domain: citylightssf.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 120V/24V 60W Plug-In Electronic Transformer Class 2 Power Supply by WAC Lighting. Regular price: $101.95. Free shipping available. In stock. Drop shipped directly from the manufacturer’s warehouse.
6. Unbranded – AC DC Adaptor Class 2 Transformer
Domain: electronicsflip.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“Title”:”AC DC Adaptor Direct Plug In Class 2 Transformer Model 35A-D05-140″,”Voltage”:”AC120V”,”Frequency”:”60Hz”,”Power”:”2W”,”UPC”:”371671695568″,”Type”:”Electronics”,”Condition”:”Used: Very Good”,”Notes”:”Very Good Condition”,”Brand”:”Unbranded”,”Output Voltage”:”5 V”,”Color”:”Black”,”Country/Region of Manufacture”:”Unknown”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plug in class 2 transformer
As the demand for reliable power solutions continues to rise across diverse industries, the strategic sourcing of plug-in Class 2 transformers emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. These transformers not only offer versatility and safety but also ensure compliance with regulatory standards, making them essential for applications ranging from lighting to electronic devices. By prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers known for quality and reliability, businesses can mitigate risks associated with power supply failures and enhance operational efficiency.
Investing in strategic sourcing means leveraging competitive pricing and superior product quality while also considering logistical factors such as shipping costs and lead times. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively engage with suppliers that align with their specific needs and operational capabilities. This proactive approach not only fosters long-term relationships but also ensures access to innovative technologies that can drive business growth.
Looking ahead, the landscape for plug-in Class 2 transformers is set to evolve with advancements in energy efficiency and smart technologies. Now is the opportune time for international B2B buyers to reassess their sourcing strategies and explore new opportunities that can enhance their competitive edge in the global market. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure a sustainable future for your power supply needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to plug in class 2 transformer
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.