Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Difference Between A Tie Vs Bracket Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for difference between a tie vs bracket
In the competitive landscape of orthodontic supplies, understanding the difference between a tie and a bracket is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to enhance their product offerings. Sourcing the right orthodontic components not only influences treatment outcomes but also affects patient satisfaction, making it imperative to distinguish between these two essential elements. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of ties and brackets, their applications, and the implications for orthodontic practices.
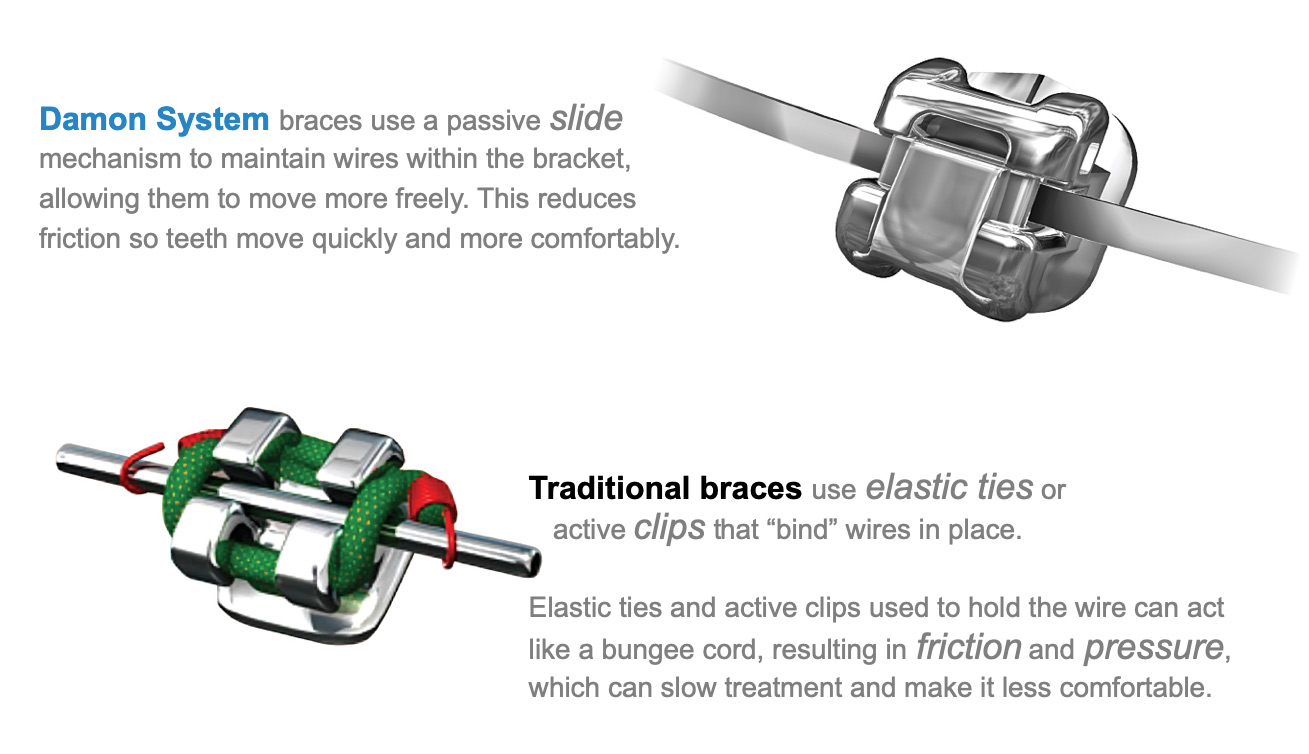
We delve into the nuances of self-ligating brackets versus traditional elastic ties, exploring their respective advantages and disadvantages in clinical settings. Additionally, we address supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and market trends that international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Nigeria and Brazil—must navigate.
By equipping buyers with actionable insights and detailed comparisons, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific needs and regional market dynamics. Whether you are looking to enhance your clinic’s inventory or seeking to understand the latest innovations in orthodontic technology, this resource is designed to streamline your decision-making process and support your business growth in the global market.
Understanding difference between a tie vs bracket Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Ligating Brackets | Utilize a door mechanism to secure archwires | Orthodontic clinics, dental suppliers | Pros: Less frequent adjustments; easier cleaning. Cons: Higher cost; may require specialized training. |
| Elastic Ligatures | Colorful rubber bands that hold archwires in place | Orthodontic supplies distributors | Pros: Customizable colors; good grip in detailing. Cons: More plaque accumulation; requires frequent adjustments. |
| Metal Ligatures | Steel wires tied around brackets for archwire stability | Orthodontic practices, dental labs | Pros: Strong hold; faster tooth movement. Cons: Can be uncomfortable; potential for poking. |
| Ceramic Brackets | Aesthetic, tooth-colored brackets | Cosmetic dentistry, orthodontic clinics | Pros: Discreet appearance; suitable for adults. Cons: More fragile; higher cost than metal options. |
| Power Chains | Continuous elastic bands connecting multiple teeth | Orthodontic suppliers, dental clinics | Pros: Effective for closing gaps; versatile application. Cons: Can be uncomfortable; requires precise application. |
What Are Self-Ligating Brackets and Their Key Benefits for B2B Buyers?
Self-ligating brackets feature an innovative design that uses a built-in mechanism to secure the archwire without the need for elastic ligatures. This technology allows for easier cleaning and reduces the frequency of patient visits, making it an appealing choice for busy orthodontic practices. For B2B buyers, investing in self-ligating brackets can enhance patient satisfaction and streamline operations, though they may come at a higher initial cost and require staff training to implement effectively.
How Do Elastic Ligatures Enhance Patient Experience?
Elastic ligatures, often available in various colors, allow patients to personalize their orthodontic experience. These rubber bands are used to secure archwires to brackets, providing a fun and engaging aspect of treatment. For B2B buyers, elastic ligatures offer a low-cost option that appeals to younger demographics, although they do require more frequent adjustments and can lead to hygiene challenges, necessitating careful consideration in procurement decisions.
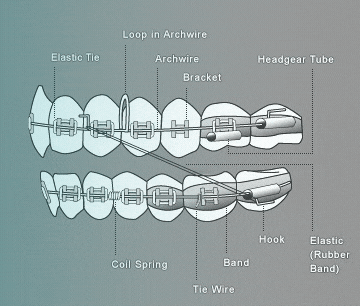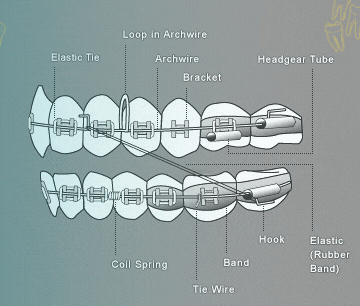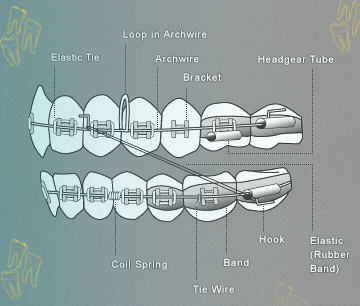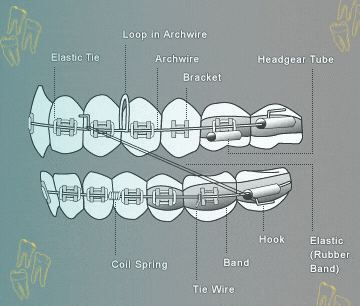
Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Why Choose Metal Ligatures Over Other Options?
Metal ligatures involve tying steel wires around the brackets to ensure archwire stability. This method is particularly beneficial for rapid tooth movement and is often used in complex cases. B2B buyers in orthodontic practices should consider metal ligatures for their effectiveness, although they may present comfort issues for patients and the potential for irritation. The ability to achieve faster results can be a strong selling point when discussing options with clients.
What Makes Ceramic Brackets a Popular Choice for Aesthetic Concerns?
Ceramic brackets are designed to blend in with the natural color of teeth, making them a preferred option for adults seeking a more discreet orthodontic solution. They provide the same functional benefits as traditional metal brackets but with enhanced aesthetics. B2B buyers should weigh the advantages of ceramic brackets against their higher cost and fragility, particularly when targeting clients who prioritize appearance over cost.
How Do Power Chains Work in Orthodontic Treatment?
Power chains are a series of connected elastic bands that can be used to close gaps between teeth or move teeth more effectively. They are versatile and can be adapted for various orthodontic treatments. For B2B buyers, power chains represent a cost-effective solution that can enhance treatment outcomes; however, they require precise application and may cause discomfort for patients. Understanding their use and benefits can help orthodontic suppliers better serve their clients.

Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Key Industrial Applications of difference between a tie vs bracket
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of difference between a tie vs bracket | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orthodontics | Use of self-ligating brackets vs. traditional ties in braces | Reduced treatment time and improved patient comfort | Quality of materials, ease of installation, and patient acceptance |
| Construction | Securing structural elements using brackets versus ties | Enhanced stability and load distribution | Durability, resistance to environmental factors, and compliance with local regulations |
| Automotive | Application of brackets for mounting components versus using ties | Improved safety and reliability of vehicle parts | Weight, strength, and compatibility with various vehicle models |
| Aerospace | Use of brackets for securing instruments vs. ties for temporary fixes | Increased safety and performance in flight | Lightweight materials, aerodynamics, and compliance with aviation standards |
| Electrical Engineering | Differentiating between ties and brackets for cable management solutions | Better organization and reduced risk of damage | Material conductivity, insulation properties, and ease of installation |
How Do Orthodontists Benefit from the Difference Between Ties and Brackets?
In orthodontics, the choice between self-ligating brackets and traditional ties directly impacts treatment efficiency and patient experience. Self-ligating brackets, which require no elastic ties, streamline the adjustment process, reducing the frequency of patient visits. This is particularly advantageous in regions with limited access to orthodontic care, such as parts of Africa and South America. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing high-quality self-ligating systems that ensure patient comfort and effectiveness in treatment.
How Does the Construction Industry Utilize Brackets Over Ties?
In construction, brackets are essential for securing structural components, providing superior stability compared to traditional ties. Brackets distribute loads more evenly, which is crucial for safety in building designs, especially in seismic-prone regions. When sourcing these components, businesses must consider the material’s durability and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring compliance with local building codes, which can vary significantly across regions such as Europe and the Middle East.
What Are the Advantages of Brackets in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, brackets are used to securely mount various components, enhancing the safety and reliability of vehicles. Unlike ties, which may not provide the same level of strength, brackets ensure that critical parts remain securely in place, reducing the risk of mechanical failure. For international buyers, especially in markets like Brazil, sourcing brackets that meet specific weight and strength requirements is vital for maintaining vehicle performance and safety standards.
How Do Brackets Enhance Safety in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace applications, brackets are preferred over ties for securing instruments and components, as they offer increased safety and performance. The lightweight materials used in brackets are essential for maintaining aerodynamics while ensuring that instruments remain secure during flight. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing brackets that meet stringent aviation standards, considering factors such as material integrity and compliance with international aviation regulations.
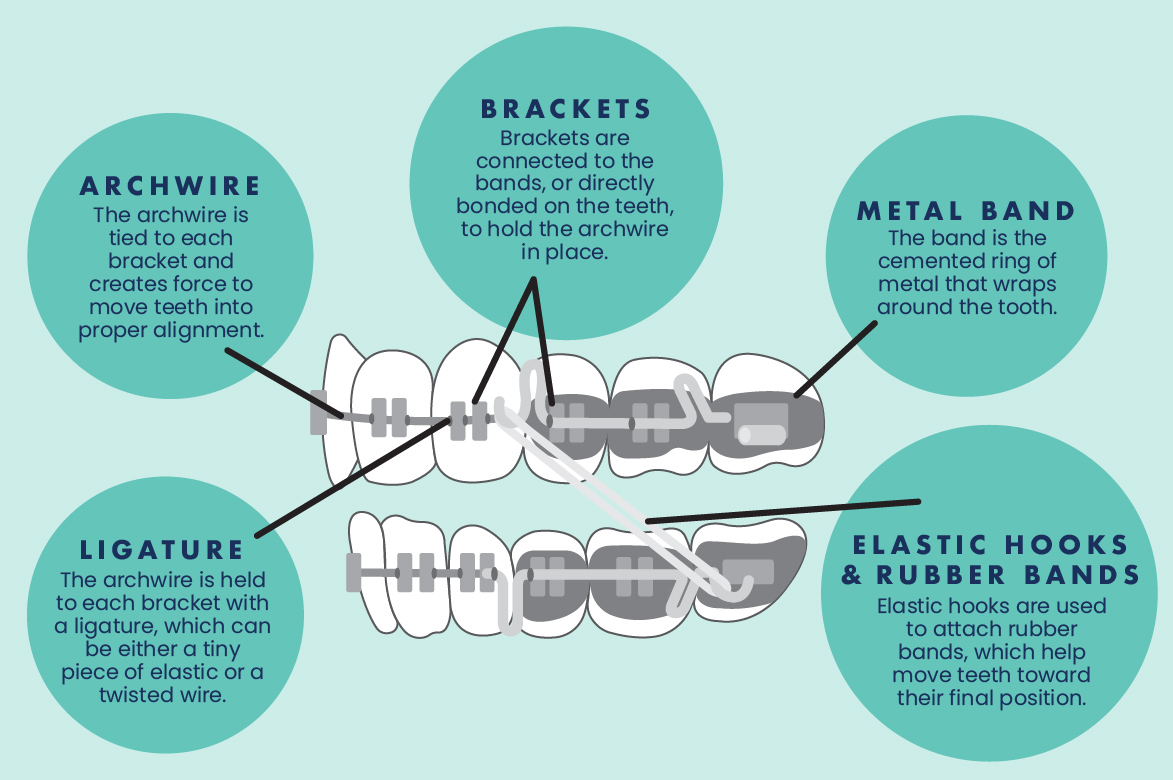
Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
What Role Do Brackets Play in Electrical Engineering Solutions?
In electrical engineering, the distinction between ties and brackets is crucial for effective cable management. Brackets provide a more organized and secure method for routing cables, significantly reducing the risk of damage. For businesses sourcing these components, it is important to consider the materials used, especially regarding conductivity and insulation properties, to ensure long-term reliability and safety in electrical installations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘difference between a tie vs bracket’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Impact of Ligature Types on Treatment Outcomes
The Problem: International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, often struggle with selecting the appropriate ligation method for orthodontic treatments. Many buyers may not fully understand the differences between elastic ties and self-ligating brackets, leading to potential mismatches between patient needs and treatment effectiveness. This confusion can result in longer treatment times, increased costs, and dissatisfaction among both orthodontists and patients, ultimately affecting business relationships and patient retention.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, it’s essential for B2B buyers to invest time in educating themselves and their staff about the nuances of ligation methods. Start by organizing training sessions or workshops with orthodontic specialists who can explain the clinical implications of each ligation type. Buyers should also create comparison charts that highlight the benefits and drawbacks of elastic ties versus self-ligating brackets in terms of treatment efficiency, maintenance, and patient comfort. By fostering a deeper understanding, orthodontic suppliers can make informed decisions that align with their clients’ needs, thereby enhancing service delivery and improving patient outcomes.
Scenario 2: Managing Inventory and Supply Chain Challenges
The Problem: Distributors in the orthodontic field often face difficulties in maintaining inventory levels for various ligation types, particularly when demand fluctuates. For instance, a sudden increase in demand for self-ligating brackets may lead to stock shortages, while an overstock of elastic ligatures can result in wasted resources. This imbalance not only disrupts treatment continuity for practitioners but also strains supplier relationships, as buyers grapple with timely deliveries and order fulfillment.
The Solution: To address this pain point, B2B buyers should implement a robust inventory management system that tracks usage trends of different ligation types. Utilizing software tools that analyze sales data can help predict future demands and optimize stock levels accordingly. Additionally, establishing strong relationships with multiple suppliers can mitigate the risk of stockouts and allow for quicker replenishment. Buyers should also consider negotiating flexible contracts that allow for adjustments based on demand forecasts, ensuring they can meet the needs of orthodontic practices efficiently.
Scenario 3: Communicating Differences to Patients Effectively
The Problem: Orthodontic practices often encounter challenges when explaining the differences between ligation methods to patients, especially in regions with varying levels of orthodontic awareness. Patients may not understand why they are being recommended one type of ligation over another, leading to confusion and resistance to treatment plans. This gap in communication can hinder patient satisfaction and trust, ultimately impacting a practice’s reputation and business.
The Solution: To bridge this communication gap, B2B buyers should develop comprehensive educational materials that clearly explain the differences between ties and brackets. This could include brochures, visual aids, and even interactive digital content that illustrates the mechanisms and benefits of each option. Additionally, training front-office staff and orthodontists on effective communication strategies can enhance the patient experience. Encourage practices to actively engage patients in discussions about their treatment options, emphasizing the personalized nature of care. By prioritizing clear and informative communication, orthodontic suppliers can foster stronger patient relationships and improve overall satisfaction with treatment outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for difference between a tie vs bracket
What Are the Key Materials Used in Ties and Brackets?
When considering the differences between ties and brackets in orthodontics, selecting the right materials is crucial for performance and patient satisfaction. Different materials exhibit unique properties that affect durability, cost, and application suitability. Below are four common materials used in ties and brackets, analyzed from a B2B perspective.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for orthodontic applications. It can withstand the mechanical stresses involved in tooth movement.
Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can endure the forces applied during orthodontic treatment. However, it is relatively heavy compared to other materials, which may affect patient comfort. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, with costs typically falling in the medium range.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including oral fluids, and is less likely to corrode over time. This makes it suitable for long-term use in orthodontics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and ISO is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the stainless steel used meets local health regulations.
2. Ceramic
Key Properties: Ceramic materials are lightweight and aesthetically pleasing, often available in tooth-colored options. They are less visible than metal counterparts, providing a cosmetic advantage.
Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of ceramic brackets is their aesthetic appeal, making them popular among adults and teens. However, they are more brittle than stainless steel, which can lead to breakage under excessive force. Manufacturing complexity is higher, and costs are generally higher than stainless steel.
Impact on Application: Ceramic is suitable for patients concerned about the visibility of orthodontic appliances. However, they may not be ideal for patients requiring significant force for tooth movement.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that ceramic materials comply with local regulations and standards, particularly in Europe, where strict guidelines on dental materials exist.

Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
3. Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and high corrosion resistance. It is biocompatible, making it suitable for medical applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium is its lightweight nature combined with strength, which enhances patient comfort. However, titanium can be more expensive than stainless steel, and its manufacturing process can be complex.
Impact on Application: Titanium is particularly useful in cases requiring minimal weight but maximum strength, such as in self-ligating brackets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like JIS and ASTM is critical. Buyers in the Middle East should consider the availability of titanium products in their local markets.
4. Plastic
Key Properties: Plastic materials are lightweight and can be manufactured in various colors. They are less durable than metal options but are cost-effective.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic is its low cost and aesthetic flexibility. However, plastic is less durable and may not withstand the same forces as metal materials, leading to potential failures during treatment.
Impact on Application: Plastic ties are often used in less demanding orthodontic applications where aesthetics are prioritized over strength.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic used is compliant with health and safety standards in their respective countries, particularly in regions with stringent regulations like Europe.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for difference between a tie vs bracket | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Traditional braces and ligation ties | High durability and strength | Heavier than other materials | Medium |
| Ceramic | Aesthetic braces for adults and teens | Less visible, tooth-colored | Brittle, higher cost | High |
| Titanium | Self-ligating brackets | Lightweight, strong | More expensive, complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Colorful ligation ties | Low cost, aesthetic flexibility | Less durable, potential failures | Low |
This analysis provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in diverse regions, enabling informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for difference between a tie vs bracket
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Ties and Brackets?
The manufacturing of orthodontic components such as ties and brackets involves a series of critical stages, each designed to ensure the highest quality and functionality of the final products. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Prepared?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of materials. Ties, often made from elastic materials or stainless steel, and brackets, typically crafted from stainless steel, ceramics, or composites, require careful sourcing. High-grade materials are essential for durability and effectiveness.
Material preparation involves cutting, cleaning, and sometimes pre-treating these materials to ensure optimal bonding and performance. For example, stainless steel brackets may undergo a passivation process to enhance corrosion resistance, while elastics used for ties must be sourced from suppliers that provide consistent elasticity and color stability.
How Are Ties and Brackets Formed?
The forming stage involves shaping the materials into their respective components. For brackets, this process often includes stamping or molding techniques. Metal brackets are typically stamped from sheets of stainless steel using high-precision dies, ensuring uniformity in size and shape. Ceramic brackets, on the other hand, may be molded and then sintered at high temperatures to achieve the required strength and aesthetic qualities.
Ties, particularly elastic ones, are manufactured through extrusion processes where raw rubber compounds are forced through a die to create continuous lengths of material, which are then cut into specific sizes. The manufacturing of steel ligatures involves wire drawing, where steel wire is pulled through dies to achieve the desired gauge and tensile strength.
What Steps Are Involved in the Assembly Process?
Assembly is a crucial phase where the individual components are brought together. For brackets, this may involve attaching hooks or other features designed to hold elastics or archwires. This process requires precision, as any misalignment can affect the orthodontic treatment’s effectiveness.
For ties, particularly elastic ligatures, the assembly might involve packaging them in bulk or as pre-cut lengths for ease of use in clinical settings. This stage may also include labeling and preparing the products for distribution, ensuring they meet regulatory requirements for medical devices.
How Is the Finishing Process Conducted?
The finishing stage involves final touches that enhance the product’s aesthetic and functional properties. For brackets, this may include polishing to remove any sharp edges, applying coatings for additional protection, or even color treatments for ceramic brackets to match tooth color.
For ties, the finishing process ensures that the elastic ligatures are uniform in size and elasticity. Quality checks at this stage help ensure that the products meet the required specifications before they are packaged and shipped.
What Quality Assurance Processes Are Essential for Ties and Brackets?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of orthodontic components. It encompasses various standards and checkpoints to guarantee that the products meet international and industry-specific regulations.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
For global B2B buyers, familiarity with international standards such as ISO 9001 is crucial. This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system and is applicable to any organization, regardless of its size or industry. Additionally, CE marking is essential for products sold within the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
In regions such as Africa and South America, buyers should also be aware of local certifications that may be necessary for the importation and sale of medical devices. This can include compliance with standards set by organizations like ANVISA in Brazil or NAFDAC in Nigeria.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint focuses on the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line. Suppliers must provide certificates of analysis (COA) to confirm that materials meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, regular inspections are conducted to monitor compliance with specifications. This can include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are packaged for shipment, a final inspection ensures that all items meet quality standards. This may involve functional testing of brackets and ties to ensure they perform as expected under typical usage conditions.
What Common Testing Methods Are Utilized?
Testing methods for orthodontic components can vary but typically include tensile strength tests for elastic ligatures, fatigue testing for brackets under simulated orthodontic forces, and biocompatibility tests to ensure materials do not cause adverse reactions in patients.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers. This includes requesting and reviewing quality assurance documentation, such as quality manuals and QC reports.
Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards. Buyers may also consider hiring third-party inspection services to conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing processes and finished products.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of the nuances associated with certifications and quality control in different regions. For instance, while ISO certifications are globally recognized, the specific requirements for CE marking can vary significantly from one country to another.
Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring compliance and minimizing risks associated with product recalls or legal issues. Engaging with local regulatory experts can provide invaluable guidance on navigating these complexities.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for orthodontic ties and brackets are multi-faceted and designed to ensure that these critical components meet the highest standards of performance and safety. By understanding these processes, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and choose suppliers that prioritize quality and compliance in their manufacturing practices. This knowledge is especially important for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory landscapes can vary significantly.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘difference between a tie vs bracket’
Introduction
Understanding the difference between ties and brackets is essential for B2B buyers involved in orthodontic supplies. This guide will help you navigate the procurement process by outlining key steps to ensure you make informed decisions when sourcing these essential components. Whether you are supplying orthodontists or clinics, knowing the technical distinctions and supplier capabilities will enhance your offerings.

Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications for the types of ties and brackets you need. Different orthodontic applications may require specific materials (e.g., metal, ceramic) or designs (e.g., self-ligating vs. elastic). Having a detailed list helps ensure that you only consider suppliers who can meet your exact needs.
Step 2: Research Material Options
Investigate the materials used in ties and brackets, as they significantly affect performance and patient comfort. For instance, ceramic brackets are less visible and preferred for aesthetic purposes, while metal brackets are known for their strength. Understanding the pros and cons of each material will guide your sourcing decisions.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Look for company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in your industry. Assess their experience in manufacturing ties and brackets to ensure they can deliver quality products that meet your specifications.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that suppliers comply with relevant regulations and standards. This includes certifications such as ISO or CE marking, which indicate adherence to quality and safety standards. Compliance not only assures product safety but also enhances your credibility as a supplier.
Step 5: Assess Product Range and Customization Options
Evaluate the range of products each supplier offers. Some may provide a limited selection, while others might offer customizable options. The ability to customize ties and brackets can be a significant advantage in meeting the unique needs of different orthodontic practices.
Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Step 6: Inquire About Quality Control Processes
Ask about the quality control measures that suppliers implement during manufacturing. Reliable suppliers should have stringent quality assurance protocols to minimize defects and ensure consistent product performance. Understanding their processes will help you choose a supplier committed to excellence.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you identify suitable suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Be clear about your budget constraints while ensuring that you do not compromise on quality. A well-negotiated contract can lead to long-term partnerships that benefit both parties.
By following this checklist, you can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing ties and brackets, ensuring that you make well-informed decisions that enhance your business offerings.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for difference between a tie vs bracket Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Ties vs Brackets?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing ties and brackets, several components must be considered. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects cost. Brackets, typically made from stainless steel, ceramic, or plastic, have varying price points depending on the material quality. Ties, whether elastic or metal, also vary in cost based on their composition and durability.
Labor: Labor costs depend on the manufacturing processes involved. Self-ligating brackets may require more skilled labor due to their complex design compared to simpler elastic ties. This can lead to higher labor costs for brackets.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility costs. The production of brackets may incur higher overhead due to the need for specialized machinery, while ties can often be produced using less complex equipment.
Tooling: The initial tooling costs for brackets can be significant, especially for custom designs. Ties typically have lower tooling costs, making them more economical for lower volume orders.
Quality Control: Ensuring the quality of orthodontic products is crucial, given the implications for patient health. Brackets may require more rigorous QC processes, impacting overall costs.
Logistics: Transporting brackets can be costlier due to their bulk and weight compared to ties. Additionally, international shipping can incur various tariffs and fees that affect the final price.
Margin: Suppliers will typically apply different profit margins based on the complexity of the product, market demand, and competitive landscape. Brackets may have a higher margin due to their perceived value and complexity.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Ties and Brackets?
Several factors influence the pricing of ties and brackets, which are vital for B2B buyers to consider.
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Suppliers often offer discounts for higher volume orders, making it more economical for buyers to purchase in bulk.
Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements can drive up costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
Material Quality/Certifications: Higher-quality materials and compliance with international standards can increase costs. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure suppliers meet necessary certifications to avoid future issues.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reliability, while newer suppliers may offer lower prices to gain market share.
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms affect the final cost as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. Understanding these terms is crucial for international B2B transactions.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency in Sourcing?
International B2B buyers should adopt strategic approaches to maximize cost efficiency when sourcing ties and brackets.
Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure and market conditions can provide leverage during discussions.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of only considering the initial purchase price, evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, logistics, and potential replacement costs. This is especially important for long-term investments like orthodontic supplies.
Understand Pricing Nuances for Different Regions: Buyers from diverse regions, including Nigeria and Brazil, should be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and the impact of tariffs on imported goods.
Seek Long-term Relationships: Building a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority in production, and improved service.
Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of market trends and emerging technologies can provide insights into potential cost-saving opportunities.
Disclaimer
The pricing information provided is indicative and may vary based on specific circumstances, supplier negotiations, and market conditions. Buyers should conduct thorough research and consult with suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing difference between a tie vs bracket With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives: Understanding the Options Beyond Ties and Brackets
In the landscape of orthodontic solutions, the choice between using ties and brackets is just one of many considerations. Understanding the viable alternatives can equip international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with the insights needed to make informed decisions. This analysis contrasts the traditional method of ties and brackets with other innovative orthodontic approaches.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Difference Between A Tie Vs Bracket | Self-Ligating Brackets | Metal Ligation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides reliable tooth movement; may require frequent adjustments | Reduces friction; potentially faster tooth movement | Strong grip; effective for significant tooth adjustments |
| Cost | Generally lower cost; accessible to most patients | Higher upfront cost; premium technology | Moderate cost; traditional approach |
| Ease of Implementation | Familiar to most orthodontists; minimal learning curve | Requires specialized training for optimal use | Standard procedure; well-understood |
| Maintenance | Regular adjustments needed; potential plaque buildup | Less frequent adjustments; easier to maintain hygiene | Requires regular tightening; can lead to plaque accumulation |
| Best Use Case | Suitable for general orthodontic cases | Ideal for complex cases needing efficiency | Effective for rapid tooth movement and specific adjustments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Self-Ligating Brackets
Self-ligating brackets utilize a unique mechanism that allows the archwire to slide through the bracket with minimal friction. This design can lead to faster treatment times and fewer visits to the orthodontist, as patients may need adjustments less frequently. However, they often come at a higher price point, which might not be feasible for all practices or patient demographics. The ease of cleaning is a significant advantage, as there are no elastics to trap plaque.

Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
Metal Ligation
Metal ligation remains a traditional method where steel ties are used to secure the archwire to each bracket. This method is highly effective for significant tooth movement, making it a reliable choice for complex orthodontic cases. However, it does require more frequent adjustments and can lead to plaque accumulation around the metal ties, necessitating diligent oral hygiene. While the cost is moderate, the need for regular visits can be a drawback for some patients.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Orthodontic Needs
When considering the right orthodontic solution, B2B buyers must evaluate their specific needs against the features and benefits of each option. The choice between ties and brackets versus alternatives like self-ligating brackets or metal ligation can significantly influence treatment efficacy, patient satisfaction, and overall costs. By carefully assessing performance, cost, implementation ease, maintenance needs, and the best use cases, buyers can select the solution that aligns best with their operational goals and patient demographics. This comprehensive understanding not only enhances service delivery but also positions businesses for greater success in the competitive orthodontic market.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for difference between a tie vs bracket
What Are the Key Technical Properties Distinguishing a Tie from a Bracket?
When evaluating the differences between ties and brackets, especially in orthodontics, understanding their essential technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
The material used in ties and brackets can significantly influence their performance. Ties are often made from elastomeric materials or stainless steel, while brackets are commonly crafted from stainless steel, ceramic, or composite materials. The choice of material affects durability, aesthetics, and patient comfort. For instance, ceramic brackets are favored for their discreet appearance, making them popular among adult patients.
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength refers to the maximum amount of stress a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. Ties must have adequate tensile strength to maintain their function throughout the orthodontic treatment period. For brackets, a higher tensile strength ensures they can securely hold the archwire under various forces applied during tooth movement, which is essential for effective treatment.
3. Elasticity
Elasticity is a critical property for ties, particularly elastic ligatures. This property allows ties to stretch and return to their original shape, which is essential for maintaining consistent pressure on teeth. In contrast, brackets need to be rigid to provide stable anchorage for the archwire. Understanding the elasticity of ties can help buyers select the right product based on the specific treatment goals.
4. Dimensions and Tolerances
The dimensions of ties and brackets, including width, height, and thickness, play a vital role in their fit and functionality. Tolerances refer to the acceptable limits of variation in these dimensions. Proper tolerances ensure that ties fit snugly around the brackets without excessive force, which can lead to discomfort or ineffective treatment. Buyers must consider these specifications to ensure compatibility with existing orthodontic systems.
5. Surface Finish
The surface finish of brackets can impact both aesthetics and hygiene. A smoother surface finish on brackets reduces plaque accumulation, making them easier to clean. Ties, especially elastomeric ones, often come in various colors, enhancing the patient experience but may require more maintenance to prevent discoloration. Buyers should assess surface finish properties to align with patient preferences and clinical requirements.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand Regarding Ties and Brackets?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and procurement processes for B2B buyers. Here are some common terms relevant to ties and brackets:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of orthodontics, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reputable sources for ties and brackets, ensuring they receive high-quality products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. It can impact purchasing decisions, especially when exploring new suppliers or products.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs when sourcing ties and brackets to ensure they receive competitive pricing and detailed information about product specifications.

Illustrative image related to difference between a tie vs bracket
4. Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, especially for international buyers looking to import orthodontic supplies.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. In orthodontics, understanding lead times for ties and brackets can help B2B buyers effectively plan inventory and ensure timely treatment for patients.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when navigating the differences between ties and brackets, ultimately enhancing their procurement strategies and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the difference between a tie vs bracket Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends Impacting the Difference Between a Tie and a Bracket?
The global market for orthodontic materials, specifically the distinctions between ties and brackets, is influenced by several key drivers. With an increasing awareness of dental aesthetics, particularly among consumers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a growing demand for discreet orthodontic solutions. Self-ligating brackets, which eliminate the need for elastic ligatures, are gaining popularity due to their aesthetic appeal and efficiency in treatment time. Moreover, advancements in materials technology are leading to the development of lighter, more durable brackets that enhance patient comfort and treatment outcomes.
Emerging B2B tech trends, such as digital orthodontics and 3D printing, are revolutionizing the sourcing process. Digital tools allow orthodontists to customize treatment plans more effectively, leading to the creation of personalized brackets and ligation options. This shift towards customization is critical for international buyers seeking to differentiate their offerings in competitive markets. Additionally, cloud-based platforms are facilitating global sourcing, enabling buyers from diverse regions to access a broader range of suppliers and negotiate better terms.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regulatory changes and the need for compliance with international standards, particularly in regions with stringent health regulations. Buyers must stay informed about these developments to ensure their sourcing strategies align with global best practices. In summary, understanding these market trends is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their purchasing decisions in the evolving orthodontic landscape.
How Is Sustainability Reshaping Sourcing in the Tie vs. Bracket Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern for B2B buyers in the orthodontic market, particularly in relation to the sourcing of materials for ties and brackets. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. This shift is not just a trend but a response to increasing consumer demand for ethical products, which is particularly strong in markets across Europe, Africa, and South America.
Ethical supply chains are crucial for ensuring that materials used in orthodontics are sourced responsibly. Buyers should look for suppliers that provide transparency about their sourcing practices and that have established certifications for sustainable materials. For instance, brackets made from recycled metals or biocompatible polymers are becoming more prevalent. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ certifications can serve as a valuable benchmark for buyers looking to align with environmentally conscious brands.
Investing in sustainable sourcing not only addresses environmental concerns but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty. As global consumers become increasingly aware of the environmental footprint of their choices, B2B buyers must adapt their sourcing strategies to reflect these values. This transition to sustainable practices is not merely an ethical obligation but a strategic advantage in today’s competitive market.
How Has the Tie vs. Bracket Market Evolved Over Time?
The distinction between ties and brackets in orthodontics has evolved significantly over the decades, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. Historically, traditional metal ligatures were the standard for securing archwires to brackets. However, the introduction of elastic ligatures provided patients with a fun, customizable element to their braces, allowing for a variety of colors and styles. This shift not only enhanced patient experience but also made orthodontic treatment more appealing, particularly among younger demographics.
The emergence of self-ligating brackets in the 1980s marked a notable turning point in orthodontic treatment. These brackets eliminated the need for elastic ties, leading to shorter treatment times and improved patient comfort. As orthodontic technology continues to advance, newer materials and designs are being introduced, allowing for even greater customization and efficiency in treatment. This evolution reflects the ongoing commitment within the orthodontic industry to enhance patient care while meeting the demands of a more discerning consumer base.
Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as it highlights the trajectory of product development and the importance of staying abreast of innovations that can influence sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of difference between a tie vs bracket
-
How do I choose between a tie and a bracket for orthodontic applications?
Choosing between a tie and a bracket largely depends on the specific orthodontic treatment needs. Ties, often made from elastic or metal, secure the archwire to the brackets, allowing for tooth movement. Brackets, on the other hand, are the fixed components that hold the archwire in place. Consider factors such as treatment goals, aesthetics, and the complexity of the case. Self-ligating brackets may offer advantages in terms of hygiene and comfort, while traditional ties may be more cost-effective. Consulting with orthodontic professionals can provide tailored recommendations. -
What are the key differences in functionality between a tie and a bracket?
The primary difference lies in their roles in orthodontic treatment. Brackets are the attachments bonded to each tooth, designed to hold and guide the archwire. Ties, whether elastic or metal, are used to secure the archwire within the brackets. While brackets determine the movement direction, ties influence how tightly the wire is held, affecting the treatment’s effectiveness and comfort. Understanding these roles can help in selecting the right components for optimal results. -
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using elastic ties versus metal ties?
Elastic ties offer a colorful, customizable option that appeals to younger patients, making orthodontic visits more engaging. However, they are more prone to plaque accumulation and may require more frequent adjustments. Metal ties, while less visually appealing, provide a tighter grip on the archwire, enhancing control during treatment. They may also be more durable, though they require more skill to apply. The choice between these options should consider patient preferences, treatment needs, and maintenance concerns. -
What customization options are available for ties and brackets in international sourcing?
Many suppliers offer customization options for both ties and brackets, allowing for tailored solutions to meet specific orthodontic needs. Customization may include different materials (such as ceramic or stainless steel), colors for elastic ties, or specialized shapes for brackets. When sourcing internationally, verify supplier capabilities for customization and ensure they can meet regulatory standards in your target market. Engaging with manufacturers directly can often yield the best results for bespoke solutions. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect when sourcing orthodontic ties and brackets?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Typically, MOQs for orthodontic components like ties and brackets may range from 100 to 1,000 units, depending on the manufacturer. It’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront to avoid unexpected costs. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for first-time orders or sample requests, so negotiating can be beneficial, especially for new buyers looking to test products before making larger commitments. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing orthodontic components internationally?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing ties and brackets, it’s crucial to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to international standards. Request certifications such as ISO or CE marking, which indicate compliance with safety and quality regulations. Conducting factory audits and requiring product samples for testing before bulk orders can also mitigate risks. Building a strong relationship with suppliers and maintaining open communication about quality expectations is key to successful sourcing. -
What payment terms are common in international trade for orthodontic supplies?
Payment terms in international trade can vary but often include options such as letters of credit, advance payments, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). It’s important to discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to ensure both parties are protected. Many suppliers may request a deposit before production begins, with the balance due upon completion or shipment. Understanding these terms can help in budgeting and managing cash flow effectively. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing orthodontic brackets and ties?
When importing orthodontic components, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger orders but takes longer. Ensure compliance with local regulations regarding medical devices, as this may affect the import process. Working with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline logistics and help navigate customs procedures, ensuring timely delivery and minimizing delays.
Top 8 Difference Between A Tie Vs Bracket Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SoCal Ortho Assisting – Types of Ligation in Orthodontics
Domain: socalorthoassisting.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Types of ligation in orthodontics include: 1. Self Ligation: – Brackets do not need elastic ligatures, making them easier to clean. – Less visible, suitable for older teens and adults. – Cons: More expensive, can be difficult in finishing stages. 2. Elastic Ligation: – Uses colored rubber bands, making visits fun for patients. – Brackets tend to be less noticeable. – Cons: Attracts more plaque, re…
2. Cream Ridge Ortho – Orthodontic Essentials
Domain: creamridgeortho.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Bracket – Small metal or ceramic attachment glued to the teeth so the wire can be placed in the slot of the bracket. Archwire – The main wire that connects all the brackets and guides the direction the teeth move. Elastics – Rubber bands used to apply pressure to the jaw, aligning the top and bottom teeth. Molar Band – Thin metal ring around back teeth, usually with a hook for elastics. Headgear t…
3. Burke Redford Orthodontists – Key Components of Braces
Domain: burkeredfordorthodontists.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Braces consist of several key components that work together to align teeth and improve oral health. The main parts include: 1. **Brackets**: Small metal or ceramic squares bonded to the teeth, holding the archwire in place. They can be made of stainless steel (metallic appearance) or ceramic (clear or tooth-colored). 2. **Archwire**: The wire that runs through the brackets and connects all the tee…
4. ScrapingDog – Instagram Data Scraping
Domain: instagram.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Contact us at [email protected] for scraping Instagram. Let us know how many pages you want to scrape per month.
5. Marlboro Kids Dentist – Self-Ligating Braces
Domain: marlborokidsdentist.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Self-ligating braces are orthodontic brackets that do not use elastics or metal ties to connect the archwire. Key benefits include: 1. Aesthetics – They may appear smaller than traditional brackets. 2. Cleaning – Easier to maintain oral hygiene due to the absence of elastics and ties. 3. Appointment Time – Adjustment appointments are often shorter. 4. Treatment Time – Overall treatment time is oft…
6. Grant Ortho – Braces
Domain: grantortho.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Braces are orthodontic appliances that help straighten and align teeth, available in metal, ceramic, plastic, or invisible options. Key components include: 1. Brackets: Made of metal, ceramic, or plastic, glued to the front of each tooth, attached to the archwire. Types include stainless steel, colored ceramic, and clear plastic. 2. Banding: Metal bands placed around each tooth to secure brackets….
7. Renick Ortho – Traditional Bands & Brackets
Domain: renickortho.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Traditional Bands & Brackets are a traditional orthodontic system that allows for the application of directional force on teeth. Bands are rings placed around molars, serving as anchors for wires and appliances, while brackets (or braces) house the wire to provide force. Dr. Renick uses low profile, mini twin brackets, which are smaller, more aesthetic, and comfortable. The metal brackets have pol…
8. Healthline – Self-Ligating Braces
Domain: healthline.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Self-ligating braces are a type of orthodontic treatment that differ from traditional braces by using a built-in system in the brackets to hold the archwire, eliminating the need for elastic ties. There are two types of self-ligating brackets: active (which apply active force) and passive (which do not press on the archwire). Benefits include shorter orthodontist visits, easier cleaning, and poten…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for difference between a tie vs bracket
In the competitive landscape of orthodontic supplies, understanding the nuanced differences between ties and brackets is crucial for informed decision-making. Ties, whether elastic or metal, play distinct roles in securing archwires to brackets, impacting treatment efficacy and patient comfort. Elastic ligatures offer customization and ease of use but may present hygiene challenges, while metal ligatures provide robust stability during critical treatment phases.
Strategic sourcing of these components not only enhances the quality of orthodontic treatments but also optimizes inventory management and cost efficiency for suppliers. By partnering with reputable manufacturers and distributors, businesses can ensure they are equipped with the latest advancements in orthodontic technology, thus enhancing service offerings.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should leverage these insights to strengthen their supply chains. By prioritizing quality and innovation in sourcing decisions, organizations can position themselves as leaders in the orthodontic market. Embrace the opportunity to refine your procurement strategies today—your future success in the dynamic orthodontic landscape depends on it.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.