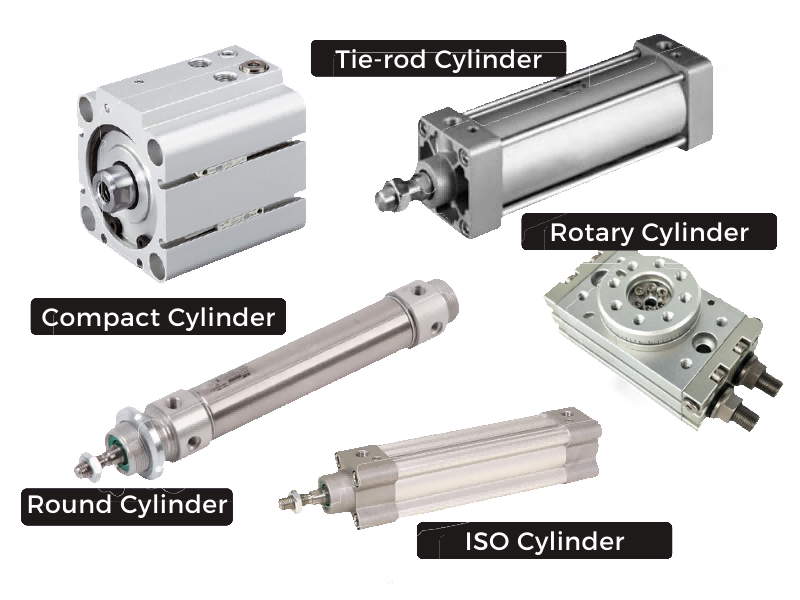
Types Of Pneumatic Cylinder: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of pneumatic cylinder
In today’s competitive global landscape, sourcing the right types of pneumatic cylinders can pose a significant challenge for B2B buyers. With various applications ranging from manufacturing automation to robotics, selecting the appropriate pneumatic cylinder is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring reliability. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of pneumatic cylinders, examining their unique characteristics, applications, and the factors influencing their performance.
International buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find invaluable insights into the nuances of pneumatic cylinder selection, including essential criteria for supplier vetting and cost considerations. By understanding the different types of pneumatic cylinders available—such as single-acting and double-acting cylinders, rodless designs, and compact models—buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Furthermore, this guide empowers B2B buyers by providing actionable insights and practical tips for navigating the complexities of the pneumatic cylinder market. With a focus on fostering informed purchasing decisions, readers will be equipped to enhance their procurement strategies, ultimately driving productivity and innovation within their organizations.
Understanding types of pneumatic cylinder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Acting Pneumatic Cylinder | Operates in one direction, uses a spring for return motion | Packaging, material handling | Pros: Cost-effective, simple design. Cons: Limited stroke, inconsistent output force. |
| Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinder | Moves in both directions using compressed air | Automation, robotics, assembly lines | Pros: Greater control, consistent force. Cons: Higher energy consumption. |
| Rodless Cylinder | No external rod; piston moves within the cylinder body | Compact machinery, tight spaces | Pros: Space-saving design, reduced wear. Cons: More complex, potentially higher cost. |
| Miniature Pneumatic Cylinder | Smaller diameter and compact size | Precision applications, medical devices | Pros: Ideal for tight spaces, lightweight. Cons: Limited force capabilities. |
| ISO Standard Pneumatic Cylinder | Adheres to international dimensions and specifications | General industry, interchangeable parts | Pros: Compatibility across brands, standardized performance. Cons: May not fit specialized applications. |
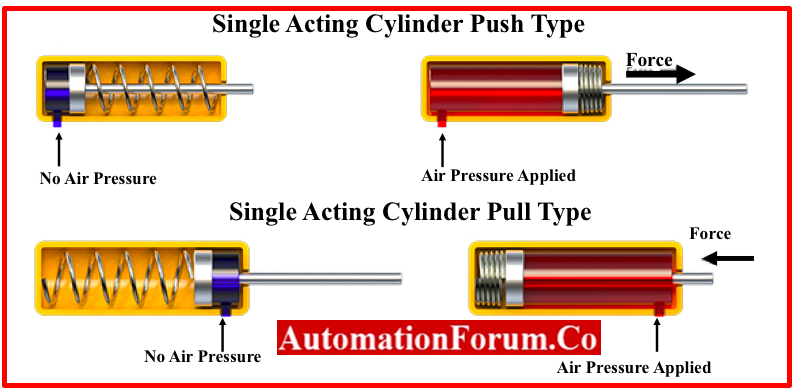
What are the Characteristics of Single-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders?
Single-acting pneumatic cylinders are designed to operate in a single direction, relying on a mechanical spring to return the piston to its original position. This simplicity makes them a cost-effective choice for applications where space and complexity need to be minimized. They are often utilized in packaging and material handling tasks where fail-safe mechanisms are crucial. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the limited stroke length and the inconsistent output force, which may not suit all operational needs.
How Do Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders Enhance Automation?
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders provide full control over the piston’s movement by utilizing compressed air to extend and retract the piston. This design allows for longer strokes and a consistent output force throughout its operation, making them ideal for applications in automation, robotics, and assembly lines. Buyers should consider the increased energy consumption and potential complexity of installation when selecting double-acting cylinders, but the benefits of precision and efficiency often outweigh these drawbacks.
Why Choose Rodless Cylinders for Compact Applications?
Rodless cylinders feature a unique design where the piston moves within the cylinder body, eliminating the need for an external rod. This makes them particularly suitable for compact machinery and applications where space is at a premium. Their design also reduces wear and tear since there are fewer moving parts exposed to external elements. However, buyers should be aware that rodless cylinders can be more complex and potentially carry a higher price tag than traditional designs.
What Advantages Do Miniature Pneumatic Cylinders Offer?
Miniature pneumatic cylinders are characterized by their smaller diameter and compact size, making them ideal for precision applications in tight spaces, such as in medical devices and small machinery. Their lightweight nature allows for easy integration into various systems. However, potential buyers should consider that these cylinders may have limited force capabilities, which could restrict their use in heavy-duty applications.
How Do ISO Standard Pneumatic Cylinders Ensure Compatibility?
ISO standard pneumatic cylinders conform to internationally recognized dimensions and specifications, ensuring compatibility across different brands and manufacturers. This standardization simplifies the procurement process for B2B buyers, allowing for easier replacement and maintenance of equipment. While they are versatile and widely applicable in general industry settings, buyers should assess whether ISO standards meet the specific requirements of specialized applications.
Key Industrial Applications of types of pneumatic cylinder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of pneumatic cylinder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automation of assembly lines using double-acting cylinders | Increased efficiency and precision in production | Compatibility with existing systems and ISO standards |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging and filling processes with rodless cylinders | Enhanced hygiene and space-saving designs | Corrosion resistance and compliance with food safety |
| Automotive | Actuation of robotic arms for material handling | Improved speed and reliability in production | Load capacity and cycle rate specifications |
| Pharmaceuticals | Controlled movement in tablet pressing and packaging equipment | Consistency and accuracy in production | Cleanroom compatibility and material certifications |
| Construction and Heavy Equipment | Lifting and moving heavy loads with pneumatic hoists | Reduction in manual labor and increased safety | Durability under harsh conditions and load ratings |
How are pneumatic cylinders utilized in manufacturing applications?
In the manufacturing sector, double-acting pneumatic cylinders are crucial for automating assembly lines. These cylinders allow for precise control of linear motion, enabling machines to assemble components with high accuracy. This automation reduces labor costs and minimizes human error, enhancing overall production efficiency. International buyers should consider the compatibility of these cylinders with existing machinery and ensure they meet ISO standards for seamless integration.
What role do pneumatic cylinders play in the food and beverage industry?
Rodless pneumatic cylinders are increasingly used in the food and beverage industry for packaging and filling applications. Their design allows for a compact footprint, which is essential in environments where space is limited. Additionally, these cylinders are typically made from materials that resist corrosion and are compliant with hygiene regulations, ensuring safe handling of food products. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide cylinders with certifications that meet food safety standards.
How are pneumatic cylinders applied in the automotive sector?
In the automotive industry, pneumatic cylinders are integral to the operation of robotic arms used for material handling. These cylinders provide the necessary force to lift and manipulate heavy components, significantly speeding up production processes. The reliability of pneumatic systems is critical in this sector, as downtime can lead to substantial losses. Buyers must evaluate the load capacity and cycle rate of the cylinders to ensure they meet the demands of their specific applications.
Why are pneumatic cylinders important in pharmaceuticals?
Pneumatic cylinders are essential in the pharmaceutical industry for equipment such as tablet presses and packaging machines. They offer precise control over the movement of components, which is vital for maintaining consistency and accuracy in production. Given the stringent regulatory environment in pharmaceuticals, international buyers should focus on sourcing cylinders that are compatible with cleanroom standards and have the necessary material certifications to ensure product safety.
How do pneumatic cylinders enhance efficiency in construction and heavy equipment?
In the construction and heavy equipment sectors, pneumatic cylinders are often used in hoists to lift and move heavy loads. This application reduces the reliance on manual labor, significantly enhancing safety and productivity on job sites. The durability of pneumatic cylinders in harsh environments is crucial, and buyers should consider factors such as load ratings and resistance to environmental conditions when sourcing these components.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of pneumatic cylinder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Pneumatic Cylinder Type
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with selecting the appropriate type of pneumatic cylinder for their specific application. For instance, a manufacturing facility may require a cylinder that can handle varying loads and speeds, yet they are overwhelmed by the multitude of options such as single-acting, double-acting, and rodless cylinders. The stakes are high; selecting the wrong type can lead to inefficiencies, increased downtime, and ultimately, financial losses.
The Solution: To tackle this challenge, buyers should start by conducting a thorough analysis of their application requirements, including load capacity, stroke length, and operating speed. Utilize a systematic approach to define the specifications. For example, if the application requires a consistent output force and higher cycling rates, a double-acting cylinder may be ideal. Conversely, if the operation needs a fail-safe mechanism where the cylinder returns to a default position upon air loss, a single-acting cylinder should be considered. Collaborating with suppliers who offer technical support can also provide invaluable insights into the nuances of different cylinder types, ensuring that the chosen solution aligns perfectly with operational needs.
Scenario 2: Maintenance Challenges Leading to Downtime
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant downtime due to inadequate maintenance of pneumatic cylinders. For example, a factory in South America may experience frequent malfunctions because the maintenance schedules were not adhered to or because operators lack the knowledge on how to properly service the cylinders. This not only disrupts production but also incurs additional costs for repairs and lost productivity.
The Solution: Implementing a proactive maintenance strategy is essential. Buyers should establish a detailed maintenance schedule that includes regular inspection and servicing of pneumatic cylinders. This could involve checking for leaks, ensuring proper lubrication, and monitoring wear on critical components like seals and pistons. Additionally, training operators on best practices for maintenance can help in identifying potential issues before they escalate. Engaging with suppliers who provide maintenance kits and clear guidelines can also enhance the longevity and reliability of pneumatic cylinders. This comprehensive approach not only minimizes downtime but also fosters a culture of operational excellence.
Scenario 3: Incompatibility with Existing Systems
The Problem: Another common issue is the incompatibility of new pneumatic cylinders with existing machinery. For instance, a European manufacturing company might invest in a new pneumatic system only to find that the cylinders do not integrate seamlessly with their current automation setup. This can lead to costly retrofitting or even a complete overhaul of existing systems, which is often not feasible within budget constraints.
The Solution: To avoid this pitfall, buyers should prioritize compatibility during the purchasing process. This involves a detailed assessment of existing systems and requirements before sourcing new pneumatic cylinders. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in custom solutions can be beneficial. They can provide insight into standardized cylinder designs that adhere to ISO specifications, ensuring interoperability with existing machinery. Additionally, buyers should consider modular designs that can be easily adapted to various systems, thus offering flexibility for future upgrades. By taking these steps, businesses can ensure smoother integration and maintain operational efficiency without incurring unnecessary costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of pneumatic cylinder
What Are the Key Materials Used in Pneumatic Cylinders?
When selecting pneumatic cylinders, the choice of material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity in various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of pneumatic cylinders, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: A Lightweight and Cost-Effective Option
Aluminum is frequently used in pneumatic cylinder construction due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. Key properties include a temperature rating of up to 150°C and a pressure rating that can exceed 10 bar, making it suitable for various environments.
Illustrative image related to types of pneumatic cylinder
Pros: Aluminum cylinders are durable and easy to manufacture, often resulting in lower production costs. Their lightweight characteristic allows for faster movement and reduced energy consumption.
Cons: However, aluminum may not be suitable for high-stress applications due to its lower tensile strength compared to steel. Additionally, it can be more prone to wear in abrasive environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum cylinders are ideal for applications involving air or non-corrosive fluids. However, they may not be the best choice for environments with aggressive chemicals.
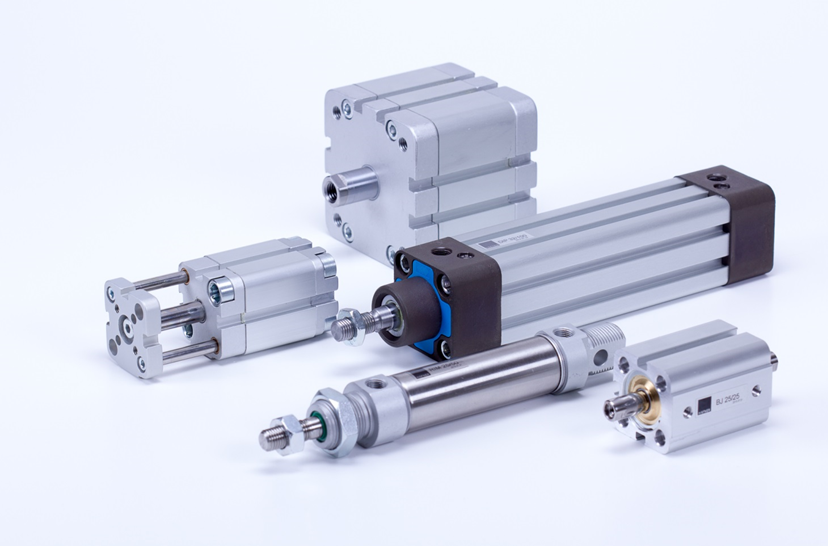

Illustrative image related to types of pneumatic cylinder
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ISO standards is essential for ensuring compatibility across different regions. Buyers in Europe, Africa, and South America should ensure that the aluminum used meets local regulations regarding material quality and safety.
Stainless Steel: Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel is another popular material for pneumatic cylinders, known for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and pressure ratings similar to aluminum.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability, making it suitable for harsh environments and applications involving corrosive substances. Its robust nature ensures a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Cons: The main drawback is the higher cost compared to aluminum. Additionally, manufacturing processes for stainless steel can be more complex, leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel cylinders are perfect for food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with ASTM standards, especially in regions like Germany, where stringent regulations apply to materials used in industrial applications.
Composite Materials: Innovation in Lightweight Design
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, are emerging in the pneumatic cylinder market. These materials offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and can operate in a wide range of temperatures and pressures.
Pros: Composites are incredibly lightweight, which enhances efficiency and speed in applications. They also provide excellent resistance to corrosion and chemicals.
Cons: However, the manufacturing complexity and cost of composite materials can be prohibitive. Additionally, they may not be as widely accepted or understood in traditional industries.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for specialized applications in aerospace and automotive industries, where weight savings are critical.
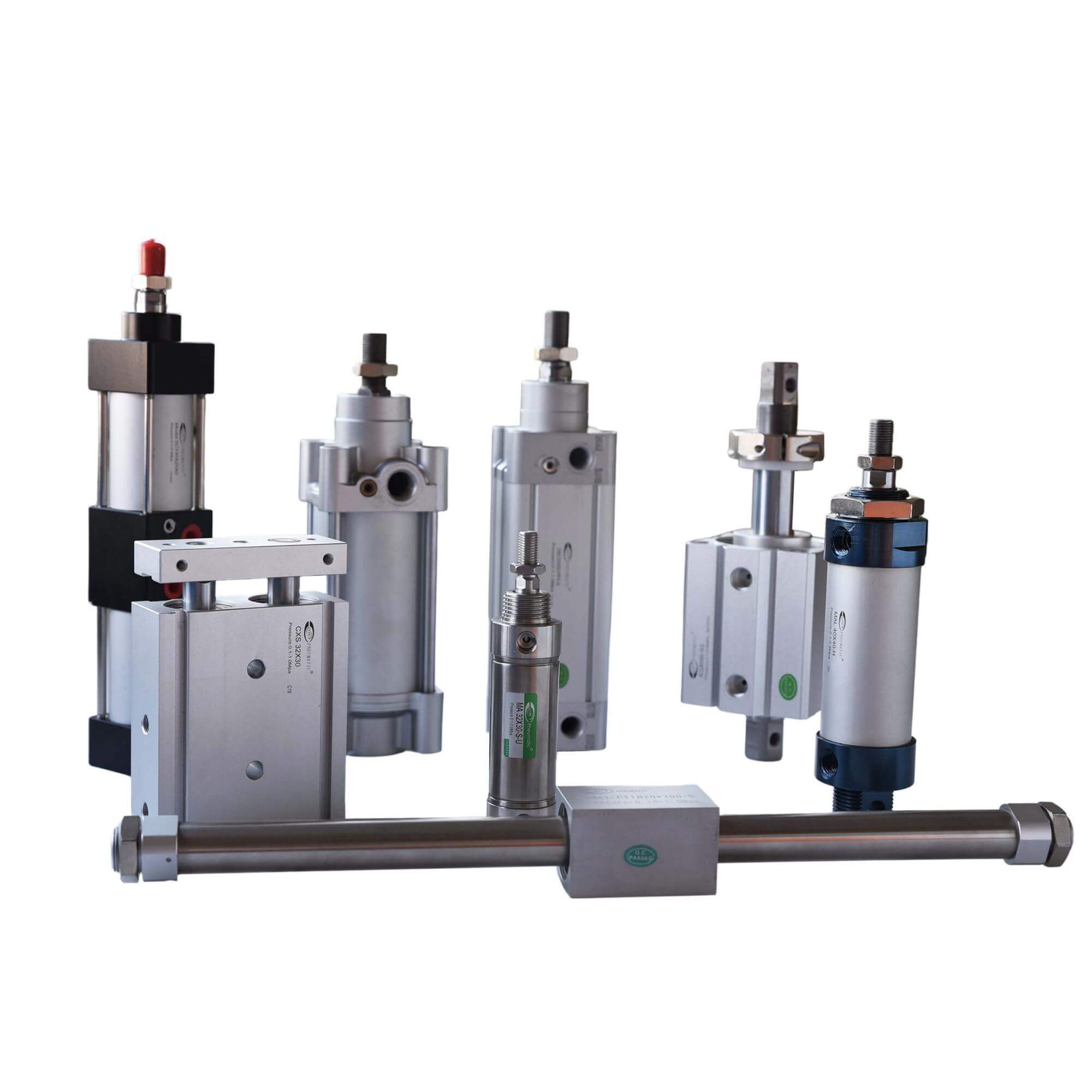

Illustrative image related to types of pneumatic cylinder
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the evolving standards and regulations surrounding composite materials, particularly in Europe, where certification processes may be more rigorous.
Brass: A Traditional Choice with Unique Properties
Brass is often used in pneumatic cylinders for specific applications, particularly where low friction and good machinability are required. It typically operates well at temperatures up to 200°C.
Pros: The primary advantage of brass is its excellent machinability, allowing for intricate designs and components. It also offers good corrosion resistance in non-aggressive environments.
Cons: However, brass is generally more expensive than aluminum and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications. Its lower strength compared to steel can also limit its use.
Impact on Application: Brass cylinders are often used in applications requiring precise movement and low friction, such as in small machinery or instruments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with JIS standards is crucial for buyers in regions like Japan and South Korea, where specific material properties are mandated.
Summary of Material Selection for Pneumatic Cylinders
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of pneumatic cylinder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | General industrial applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower tensile strength | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Exceptional durability | Higher cost and complexity | High |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace, automotive | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Brass | Precision machinery and instruments | Good machinability | Limited pressure rating | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in pneumatic cylinders, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific application requirements and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of pneumatic cylinder
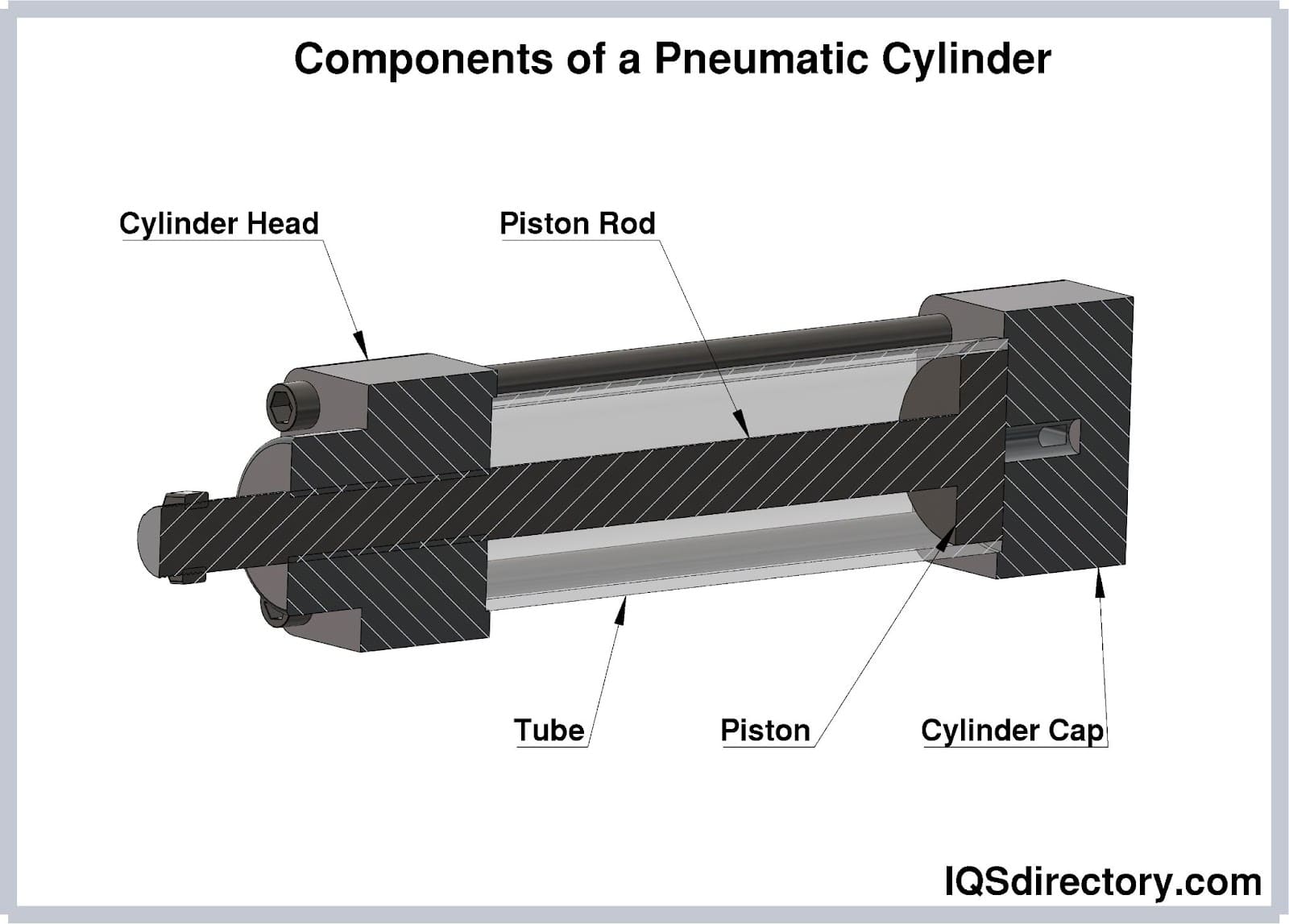
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Pneumatic Cylinders?
The manufacturing process of pneumatic cylinders involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets stringent performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers, as they can directly impact reliability and operational efficiency.
How Is Material Prepared for Pneumatic Cylinder Manufacturing?
The first step in manufacturing pneumatic cylinders is material preparation. Typically, high-grade aluminum, stainless steel, or composite materials are chosen for their strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. The materials undergo rigorous inspections to verify their chemical composition and mechanical properties. This ensures that they meet industry standards before moving on to the next stage.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
Forming techniques vary based on the type of pneumatic cylinder being produced. Common methods include:
- Extrusion: Often used for the barrel of the cylinder, this process involves forcing material through a die to create a specific cross-sectional profile.
- Machining: Precision machining is employed to create components such as the piston and end caps. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are typically used for their accuracy and efficiency.
- Casting: For larger or complex components, casting techniques can be utilized, allowing for intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve through machining alone.
Each forming technique is selected based on the design specifications and performance requirements of the pneumatic cylinder.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted?
Once the individual components are manufactured, assembly begins. This stage often involves the following steps:
- Component Inspection: Each part is inspected for defects or deviations from specifications before assembly.
- Joining Techniques: Components are assembled using methods like welding, bolting, or adhesive bonding. The choice depends on the material and application requirements.
- Integration of Accessories: Accessories such as pneumatic solenoid valves, cushions, and mounting brackets are integrated into the assembly, enhancing functionality.
Assembly is a critical stage where quality control measures are put in place to ensure that all components fit and function correctly.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Pneumatic Cylinders?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of pneumatic cylinders. Common finishing techniques include:
- Anodizing: This electrochemical process is used primarily on aluminum components to increase corrosion resistance and improve surface hardness.
- Painting or Coating: Protective coatings can be applied to prevent wear and tear, especially in harsh environments.
- Polishing: For aesthetic purposes, polishing may be employed to create a smooth surface finish.
These finishing techniques not only improve the product’s lifespan but also contribute to its overall performance in various applications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Pneumatic Cylinder Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that pneumatic cylinders meet performance and safety standards. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these processes.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
The most recognized quality management standard is ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements. Other relevant certifications include:
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For manufacturers involved in the oil and gas sector, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial for ensuring equipment reliability.
B2B buyers should seek suppliers with these certifications as they reflect a commitment to quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in pneumatic cylinder manufacturing typically includes three main checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the facility. Any non-conformities are addressed before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to ensure that components are being produced according to specifications. This includes monitoring tolerances and dimensions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a final inspection is performed. This includes functional testing to ensure the cylinder operates as intended under specified conditions.
These checkpoints are essential for identifying defects early in the production process, reducing waste and ensuring a high-quality end product.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Testing methods for pneumatic cylinders vary based on the application and expected performance. Common testing methods include:
Illustrative image related to types of pneumatic cylinder
- Pressure Testing: To verify that the cylinder can withstand the maximum operating pressure without leaking.
- Cycle Testing: Simulates the operational conditions the cylinder will face, verifying its durability and performance over time.
- Leak Testing: Ensures that all seals and joints are airtight, preventing loss of compressed air.
These tests provide critical data on the reliability and safety of the pneumatic cylinders, which is vital for B2B buyers in sectors where safety is paramount.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturer’s quality control processes.
By implementing these verification methods, B2B buyers can ensure that they are partnering with reliable suppliers who adhere to the highest quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and standards is crucial. Different regions may have specific requirements that manufacturers must meet, which can affect the choice of suppliers.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with experience in international trade and compliance with regional standards to mitigate these challenges.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for pneumatic cylinders are intricate and vital for ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced risk in their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of pneumatic cylinder’
When sourcing pneumatic cylinders, a systematic approach can significantly streamline the procurement process. This checklist aims to guide international B2B buyers through the essential steps to ensure they select the right type of pneumatic cylinder for their specific applications, while also considering regional nuances and supplier reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating any procurement process, clearly outline the technical requirements of the pneumatic cylinders you need. Consider factors such as:
– Type of Cylinder: Identify whether you need single-acting, double-acting, or rodless cylinders based on your application.
– Stroke Length and Force Requirements: Calculate the necessary stroke length and the force needed to move the intended load efficiently.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Compliance
Understanding the industry standards for pneumatic cylinders is crucial for ensuring compatibility and safety. Look for:
– ISO Certifications: Ensure that the cylinders adhere to ISO 15552 or ISO 6432 standards, which indicate quality and interoperability.
– Regional Compliance: Verify that the products meet specific regulations or certifications relevant to your region, particularly if you’re sourcing from international suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Focus on:
– Company Reputation: Request case studies and references from similar industries to assess reliability and performance.
– Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about the supplier’s quality control measures to ensure they can consistently deliver high-quality products.
Step 4: Compare Product Features and Pricing
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, compare the features and pricing of their pneumatic cylinders. Pay attention to:
– Technical Features: Assess specifications like maximum pressure ratings, materials used, and operational speed.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the purchase price but also factors like maintenance costs and expected lifespan to evaluate long-term value.
Step 5: Request Samples or Prototypes
Before finalizing your order, request samples or prototypes of the pneumatic cylinders. This step is vital because:
– Functionality Testing: It allows you to test the cylinders in your specific application to ensure they meet performance expectations.
– Fit and Compatibility: Verify that the dimensions and connection points align with your existing machinery and systems.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier and tested the products, engage in negotiations regarding terms and conditions. Important aspects include:
– Payment Terms: Discuss flexible payment options that align with your budget and cash flow.
– Warranty and Support: Ensure clear terms regarding warranties, service, and support to protect your investment.
Step 7: Finalize Order and Monitor Delivery
After reaching an agreement, finalize your order and establish a delivery timeline. Key considerations include:
– Shipping Logistics: Confirm shipping methods and estimated delivery dates, particularly if sourcing internationally.
– Tracking and Communication: Maintain open communication with your supplier during the shipping process to address any potential issues promptly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing pneumatic cylinders, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional requirements.

Illustrative image related to types of pneumatic cylinder
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of pneumatic cylinder Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Pneumatic Cylinders?
When sourcing pneumatic cylinders, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials—such as aluminum, stainless steel, or composite materials—affects both the durability and price of the cylinder. Higher-grade materials typically command higher prices but may offer longer lifespans and better performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region of manufacture. In countries with higher labor costs, such as Germany, the manufacturing process may be more expensive compared to regions like Vietnam or some parts of Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help reduce overhead costs, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs can be a substantial upfront investment. However, this cost is amortized over larger production runs, making it critical to consider expected order volumes when calculating overall costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures product reliability, which can justify higher prices. Certifications such as ISO can also add to costs but may be necessary for compliance in certain markets.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the destination, with international freight often being a significant expense. Understanding the implications of Incoterms is essential for budgeting logistics effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This can vary based on market competition, supplier reputation, and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Pneumatic Cylinders?
Several factors can influence the pricing of pneumatic cylinders:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating for bulk discounts can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specific design requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and recognized certifications can elevate prices. Buyers should balance their need for quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms can help buyers minimize additional charges.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Pneumatic Cylinder Prices?
International B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Establish clear communication with suppliers regarding pricing structures and seek transparency in cost breakdowns. Strong negotiation can lead to better terms and prices.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, evaluate maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A more expensive but durable cylinder may prove cost-effective in the long run.
-
Research Market Prices: Understanding the market landscape for pneumatic cylinders can provide leverage in negotiations. Price comparisons from various suppliers can help identify competitive offers.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Factors such as tariffs, currency fluctuations, and international shipping can affect the final cost. Buyers should account for these elements in their budget.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the cost and pricing dynamics of pneumatic cylinders, actual prices may vary based on specific requirements, supplier negotiations, and market conditions. It is advisable for buyers to request quotes from multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate pricing for their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of pneumatic cylinder With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Pneumatic Cylinders
In the realm of industrial automation and motion control, pneumatic cylinders are a popular choice for many applications due to their efficiency and simplicity. However, several alternative technologies exist that can also deliver similar functionality. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and specific application needs.
Illustrative image related to types of pneumatic cylinder
Comparison Table of Pneumatic Cylinders and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Types of Pneumatic Cylinder | Electric Actuators | Hydraulic Cylinders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed operation; suitable for repetitive tasks | High precision; suitable for complex motions | High force output; suitable for heavy loads |
| Cost | Generally low initial cost; ongoing air supply costs | Higher initial investment; lower operating costs | Higher initial cost; fluid maintenance required |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively simple setup; requires air compressor | Requires electrical infrastructure; may need programming | Requires hydraulic setup; more complex installation |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular checks on air supply and seals | Low; minimal wear parts | High; needs fluid checks and potential leaks |
| Best Use Case | Assembly lines, packaging, and light-duty applications | Robotics, CNC machines, and applications requiring precise control | Heavy machinery, construction, and applications needing high force |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Actuators
Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion and are known for their precision and control. They are suitable for applications where fine-tuned movement is essential, such as robotics or CNC machining. The initial investment is typically higher than that of pneumatic cylinders, but the operating costs are lower since they do not require compressed air. Maintenance is minimal, making them a reliable choice in environments where uptime is critical. However, the reliance on electrical infrastructure may pose challenges in certain industrial settings, especially where power supply is inconsistent.
Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders use pressurized hydraulic fluid to produce linear motion and are ideal for applications that require significant force. They excel in heavy-duty operations, such as construction and heavy machinery, where lifting and pushing large loads are necessary. While hydraulic systems can deliver more power than pneumatic cylinders, they come with higher initial costs and require more complex installations. Maintenance can also be demanding, as hydraulic fluids need regular checks to prevent leaks and ensure system integrity. Their best use cases often involve scenarios where high force and heavy lifting are paramount.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate motion control solution involves evaluating specific operational requirements, including load capacity, precision, and budget constraints. Pneumatic cylinders offer an economical and efficient option for many standard applications, while electric actuators provide precision for more complex tasks. Hydraulic cylinders are unmatched for heavy-duty applications requiring significant force. By considering the performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance needs of each solution, B2B buyers can make informed choices that align with their operational goals and industry standards.
Illustrative image related to types of pneumatic cylinder
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of pneumatic cylinder
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Pneumatic Cylinders?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of pneumatic cylinders is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when selecting the right component for their applications. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Stroke Length
The stroke length refers to the maximum distance that a pneumatic cylinder can extend or retract. This measurement is vital for determining how far a load can be moved. In applications where precise positioning is required, selecting a cylinder with the appropriate stroke length ensures that operational needs are met without overextending the equipment.
2. Force Output
The force output of a pneumatic cylinder is determined by its diameter and the pressure of the compressed air used. Understanding the force output is essential for ensuring that the cylinder can move the intended load effectively. B2B buyers must select a cylinder that offers a force rating slightly above the required load force to ensure reliable operation and avoid potential failures.
3. Operating Pressure
Operating pressure indicates the range of air pressure that a pneumatic cylinder can handle. This specification is crucial for maintaining efficiency and safety in operations. B2B buyers should consider the pressure requirements of their systems to avoid underperformance or damage to the cylinder.
4. Material Grade
The material grade of a pneumatic cylinder affects its durability and resistance to wear and corrosion. Common materials include aluminum and stainless steel. Selecting the right material is essential for ensuring that the cylinder can withstand the specific environmental conditions it will face, such as exposure to moisture or chemicals, thus prolonging its lifespan.
5. Cushioning
Cushioning refers to the mechanisms used to slow down the piston at the end of its stroke, reducing impact and increasing service life. Different cushioning types, such as adjustable or non-adjustable, allow for customization based on application requirements. Effective cushioning can enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Pneumatic Cylinders?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is crucial for buyers who need components that fit into existing systems without compatibility issues.
Illustrative image related to types of pneumatic cylinder
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it can affect inventory levels and cash flow. Buyers should assess their demand against the MOQ to optimize their procurement strategy.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the purchasing process, allowing buyers to compare costs and negotiate better terms based on detailed specifications.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are standardized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for managing logistics, including shipping costs and risk during transit.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period required from placing an order to receiving the goods. This term is crucial for project planning, as longer lead times can affect production schedules. Buyers should consider lead times when placing orders to ensure timely delivery and avoid disruptions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that the pneumatic cylinders they select meet their operational requirements efficiently and effectively.
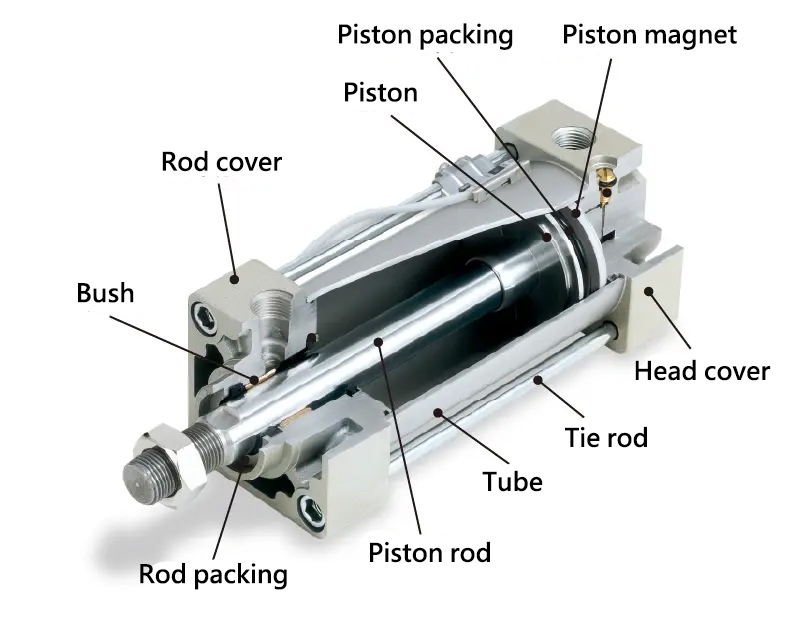
Illustrative image related to types of pneumatic cylinder
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of pneumatic cylinder Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Driving the Types of Pneumatic Cylinder Sector?
The global pneumatic cylinder market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and packaging. As international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, seek efficiency and cost-effectiveness, pneumatic cylinders have become essential components for linear motion applications. The rise of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing technologies has further accelerated this trend, encouraging the adoption of advanced pneumatic systems integrated with IoT capabilities for real-time monitoring and control.
Emerging technologies, such as electric actuators and proportional solenoid valves, are reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer innovative products that combine traditional pneumatic capabilities with modern digital features. Additionally, the focus on customization and modular systems allows companies to tailor solutions that meet specific operational requirements, enhancing flexibility and reducing lead times.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regional factors. For instance, in Europe, stringent regulations regarding energy efficiency and emissions are prompting manufacturers to invest in more sustainable pneumatic solutions. Conversely, emerging markets in Africa and South America are witnessing rapid industrialization, presenting opportunities for suppliers to introduce cost-effective pneumatic technologies that can boost productivity in local industries.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Types of Pneumatic Cylinder Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the pneumatic cylinder sector. As companies strive to reduce their environmental footprint, the demand for eco-friendly materials and processes is on the rise. This shift is prompting manufacturers to explore sustainable sourcing options, such as recycled materials and low-emission production methods, which can significantly reduce the environmental impact of pneumatic cylinders.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction, with buyers increasingly favoring suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to establish credibility and trust with international buyers. By prioritizing suppliers that adhere to these standards, businesses can ensure that their pneumatic cylinders are produced in a manner that respects both the environment and the workforce.
Additionally, as consumers and regulatory bodies push for greener practices, suppliers who invest in “green” certifications and materials are likely to gain a competitive advantage. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing demand for sustainable solutions, making it a strategic consideration for international buyers.
What Is the Historical Context of Pneumatic Cylinder Development?
The evolution of pneumatic cylinders dates back to the late 18th century when the principles of pneumatics began to gain traction. Early applications were primarily focused on simple tasks, but as industrialization progressed in the 19th and 20th centuries, pneumatic technology advanced significantly. The introduction of the first pneumatic actuators revolutionized various manufacturing processes, providing reliable and efficient means of automation.
In the latter half of the 20th century, the development of standardized designs, such as ISO-compliant cylinders, facilitated global trade and interoperability among manufacturers. This standardization has enabled international B2B buyers to source pneumatic cylinders with confidence, knowing that they meet established performance and safety criteria. Today, the sector continues to innovate, integrating digital technologies and sustainable practices to meet the demands of a rapidly changing industrial landscape.
Understanding the historical context of pneumatic cylinders not only highlights their importance in modern manufacturing but also informs current sourcing strategies and market dynamics for international buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of pneumatic cylinder
-
How do I select the right type of pneumatic cylinder for my application?
Selecting the right pneumatic cylinder involves understanding the specific requirements of your application, including load size, stroke length, and operating environment. Consider whether a single-acting or double-acting cylinder is needed; single-acting cylinders are suitable for simpler tasks, while double-acting cylinders offer greater control and power. Additionally, evaluate factors like speed, force requirements, and available space. Consulting with suppliers or using selection tools can further ensure you make an informed choice tailored to your operational needs. -
What are the advantages of using double-acting pneumatic cylinders?
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders provide several advantages, including continuous force in both extension and retraction, which enhances operational efficiency. They allow for longer stroke lengths and quicker cycling rates, making them ideal for applications requiring precision and speed. Furthermore, they maintain consistent output force throughout the stroke, ensuring reliable performance. However, they consume more energy than single-acting cylinders, so assess your application’s energy requirements when making a decision. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pneumatic cylinders?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pneumatic cylinders can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the specific type of cylinder. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units for standard models to several dozen for customized solutions. When sourcing internationally, it’s crucial to discuss MOQs with suppliers upfront to ensure that your purchasing strategy aligns with your operational needs and budget constraints. Additionally, consider the impact of shipping costs on smaller orders. -
How can I ensure the quality of pneumatic cylinders when sourcing from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by vetting suppliers through their certifications (e.g., ISO standards) and customer reviews. Request samples to assess product performance and durability before placing a bulk order. It’s also beneficial to inquire about their quality assurance processes, such as testing protocols and warranty policies. Establishing clear communication about your quality expectations and maintaining ongoing dialogue can help mitigate risks associated with international sourcing. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing pneumatic cylinders internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary widely, but common options include letters of credit, advance payments, and payment upon delivery. Discussing terms during negotiations is essential to ensure both parties are comfortable and secure. Be mindful of currency fluctuations and additional fees that may arise from international transactions. Establishing a clear agreement on payment terms can help prevent misunderstandings and facilitate smoother transactions. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing pneumatic cylinders?
When importing pneumatic cylinders, consider the shipping methods available, as well as lead times for delivery. Factor in customs regulations and potential tariffs that may apply to your shipment, which can affect your overall costs. It’s advisable to work with logistics partners who are experienced in handling industrial equipment to ensure compliance and efficiency. Proper packaging and handling are also critical to avoid damage during transit. -
Can pneumatic cylinders be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for pneumatic cylinders to meet unique application requirements. Customizations may include variations in stroke length, mounting options, materials, and additional features like cushioning. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and inquire about their capabilities in delivering tailored solutions. Custom cylinders can enhance performance and efficiency, making them a valuable investment for specialized applications. -
What are the common applications for pneumatic cylinders in industrial settings?
Pneumatic cylinders are widely used across various industries, including manufacturing, packaging, automotive, and robotics. They are essential for automating processes such as material handling, assembly, and packaging tasks. Their ability to provide reliable linear motion makes them suitable for applications requiring precise control and speed. Understanding your industry’s specific needs can help you identify the right type of pneumatic cylinder for optimal performance in your operations.
Top 5 Types Of Pneumatic Cylinder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SMC – Air Cylinders
Domain: smcworld.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Air Cylinders: Standard Air Cylinders (Round Type), Standard Air Cylinders (Square Cover), Compact Air Cylinders, Environment Resistant Cylinders, Stainless Steel Made to Order, Water Resistant Cylinder, Dust Resistant Cylinder, Mechanically Jointed Rodless Cylinders, Magnetically Coupled Rodless Cylinders, Table Cylinders, Guide Cylinders, Dual Rod Cylinders, Lock Cylinders/Cylinder with An End L…
2. Trimantec – Single Acting Pneumatic Cylinder
Domain: trimantec.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Single Acting Pneumatic Cylinder: 1 port for pressurized air, uses a spring or load for retraction, suitable for clamping, positioning, and punching. Types: Push Type (air pushes piston out) and Pull Type (air pulls piston in). Advantages: simple design, low cost, reduced valve and piping costs. Disadvantages: requires proper air management. Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinder: 2 ports for air, allow…
3. Howard Precision – Pneumatic Cylinders
Domain: howardprecision.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic cylinders are mechanical devices that utilize compressed gas for reciprocating linear motion. They are preferred for their cleaner and quieter operation. Applications include air compressors, air brakes, dental drills, HVAC systems, and more. Advantages include reliability, simple control, and safety. Types include single-acting, double-acting, and telescoping cylinders. Materials used r…
4. Festo – Pneumatic Cylinders
Domain: festo.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic cylinders are components that perform movement using compressed air, also known as compressed air cylinders. They are cost-effective solutions for various applications, characterized by simple commissioning and speeds between 10 mm/s and 3 m/s. There are two main types: single-acting cylinders (movement in one direction using compressed air and a spring for return) and double-acting cyli…
5. Artec Pneumatic – Pneumatic Cylinders
Domain: artec-pneumatic.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Artec Pneumatic specializes in the production of various types of pneumatic cylinders for industrial automation, including: ISO Standard Cylinders, Stainless Steel Cylinders, Compact Cylinders, Round and Short Stroke Cylinders, Rodless Cylinders, Cnomo Cylinders, Pneumatic Grippers, and Accessories. The ISO Standard Cylinders are essential for industrial pneumatic systems, ensuring efficiency and …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of pneumatic cylinder
In conclusion, understanding the various types of pneumatic cylinders is essential for optimizing operational efficiency in industrial applications. By strategically sourcing pneumatic cylinders—be it double-acting, single-acting, or specialized variants—businesses can enhance automation, reduce downtime, and ensure consistent performance. This knowledge allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs, thereby maximizing return on investment.
As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of sourcing, it is crucial to prioritize suppliers who adhere to ISO standards and offer comprehensive support. This will not only facilitate smoother integration into existing systems but also ensure scalability as market demands evolve.
Looking ahead, the pneumatic cylinder market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in automation technology and increasing industrial demand. Now is the time to leverage these insights and engage with reliable suppliers to secure the best solutions for your operations. Embrace the future of automation by making strategic sourcing decisions that propel your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.