Choosing Your What Is A Hydraulic Press Used For: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is a hydraulic press used for
In an increasingly competitive global market, understanding the diverse applications of a hydraulic press is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their manufacturing processes. Whether you are sourcing equipment for automotive production in Brazil or agricultural machinery in Nigeria, knowing what a hydraulic press is used for can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost management. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of hydraulic presses, their specific applications across industries such as automotive, agriculture, and consumer goods, and essential considerations for supplier vetting.
With an emphasis on empowering informed purchasing decisions, this resource equips buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe with actionable insights into the costs associated with hydraulic presses, maintenance requirements, and technology advancements. By understanding these elements, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce downtime, and achieve greater profitability. Furthermore, the guide highlights best practices for evaluating suppliers, ensuring that you can confidently select reliable partners who meet your quality and performance standards.
Explore the intricacies of hydraulic presses and discover how these powerful machines can transform your production capabilities while aligning with your strategic goals in an evolving marketplace.
Understanding what is a hydraulic press used for Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forging Press | Applies gradual pressure using a vertical ram | Metal forging, automotive parts manufacturing | Pros: High precision; suitable for complex shapes. Cons: High initial cost; requires skilled operators. |
| Power Press | Multi-functional for cutting, bending, and shaping | Appliance manufacturing, metal fabrication | Pros: Versatile; efficient for mass production. Cons: May require significant maintenance; setup time can be lengthy. |
| Hydraulic Lift | Moves heavy loads using hydraulic force | Warehousing, construction, automotive repair | Pros: Increases efficiency; safe lifting of heavy items. Cons: Space-consuming; potential hydraulic leaks. |
| Car Crusher | Compresses vehicles for recycling | Automotive recycling, scrap metal processing | Pros: Reduces storage space; increases recycling efficiency. Cons: Limited to end-of-life vehicles; requires heavy-duty construction. |
| Powder Press | Compacts powders into specific shapes | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics | Pros: Ensures consistent product quality; efficient for bulk production. Cons: Limited to powder materials; requires precise calibration. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of a Forging Press?
A forging press is characterized by its ability to apply controlled pressure through a vertical ram, making it ideal for shaping metal into complex forms. This type of hydraulic press is particularly suitable for industries like automotive manufacturing, where precision is critical for components such as gears and frames. When considering a forging press, buyers should assess the force capacity, compatibility with different materials, and the skill level required for operation to maximize productivity and safety.
How Does a Power Press Benefit Various Industries?
Power presses are known for their versatility, capable of cutting, bending, and shaping metal sheets into desired forms. They are commonly used in appliance manufacturing and metal fabrication, where efficiency and precision are paramount. Buyers should consider the machine’s operational speed, ease of setup, and maintenance requirements when selecting a power press, as these factors directly impact production timelines and costs.
Why Choose a Hydraulic Lift for Heavy Load Applications?
Hydraulic lifts utilize hydraulic force to elevate heavy items safely, making them essential in warehousing, construction, and automotive repair. Their design allows for efficient movement of materials and equipment, reducing manual labor and enhancing workplace safety. Buyers should evaluate the lift’s weight capacity, platform size, and space requirements to ensure it meets their operational needs without compromising safety.
What Is the Role of a Car Crusher in Recycling?
Car crushers are specialized hydraulic presses designed to compress end-of-life vehicles, facilitating their recycling. This equipment is pivotal in the automotive recycling industry, significantly reducing the space required for vehicle storage and enhancing material recovery rates. Buyers should focus on the crusher’s processing capacity, durability, and ease of maintenance to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
How Does a Powder Press Ensure Consistent Quality?
Powder presses are designed to compact powders into specific shapes, widely used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. Their ability to produce uniform products at scale makes them invaluable for manufacturers aiming for high quality and consistency. When purchasing a powder press, buyers should consider the machine’s compatibility with various powder types, its calibration capabilities, and the level of automation offered to optimize production efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of what is a hydraulic press used for
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is a hydraulic press used for | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Shaping and assembling car parts | Increases production efficiency and precision in part manufacturing | Reliability of machinery and availability of spare parts |
| Agriculture | Repairing farm equipment | Reduces downtime by facilitating quick repairs and maintenance | Compatibility with existing machinery and service support |
| Powder Manufacturing | Producing powdered products (e.g., cocoa, cosmetics) | Enhances product quality and consistency in powder form | Material quality and compliance with health regulations |
| Construction | Testing concrete strength | Ensures structural integrity and safety of building materials | Calibration accuracy and adherence to industry standards |
| Metal Fabrication | Metal stamping and shaping | Streamlines production processes and reduces waste | Tooling compatibility and customization options |
How is a hydraulic press used in automotive manufacturing, and what are the key benefits?
In the automotive sector, hydraulic presses are essential for shaping and assembling various car parts, including body panels and brake components. These machines apply controlled pressure to metal sheets, ensuring precision and uniformity in the manufacturing process. For B2B buyers, the key benefits include enhanced production efficiency and reduced material waste. Buyers should consider the reliability of the hydraulic press and the availability of spare parts, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where access to maintenance services may vary.
What role does a hydraulic press play in agriculture, and how does it solve industry-specific challenges?
In agriculture, hydraulic presses are utilized for repairing large farm equipment, allowing for the separation of rusted parts and the straightening of bent components. This capability significantly reduces equipment downtime, which is crucial for maintaining productivity during peak farming seasons. For international buyers, especially in the Middle East and Africa, sourcing presses that are compatible with existing machinery and come with robust service support is vital to ensure continuous operation.
How does a hydraulic press contribute to the powder manufacturing industry?
Hydraulic presses are widely used in powder manufacturing to produce items such as cocoa powder and cosmetic face powders. By applying high pressure, these presses help in extracting fats and creating a fine powder consistency. This process enhances product quality and ensures uniformity, which is critical in competitive markets. Buyers should focus on material quality and compliance with health regulations, particularly when sourcing equipment for food or cosmetic applications.
In what ways are hydraulic presses used in construction for concrete testing?
In the construction industry, hydraulic presses are employed to test the tensile strength of concrete, an essential procedure for ensuring the material’s structural integrity. This testing provides vital data that can influence concrete formulation, thereby enhancing safety and durability in construction projects. B2B buyers should prioritize calibration accuracy and adherence to industry standards when selecting hydraulic presses for concrete testing to ensure reliable results.
What benefits do hydraulic presses offer in metal fabrication, and what should buyers consider?
In metal fabrication, hydraulic presses are crucial for stamping and shaping metal parts, streamlining production processes, and minimizing waste. These machines enable manufacturers to achieve precise shapes and sizes, which is essential for high-quality end products. Buyers should evaluate tooling compatibility and customization options when sourcing hydraulic presses, ensuring that they can meet specific production needs in regions like Europe and South America, where manufacturing standards may differ.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is a hydraulic press used for’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges in Car Part Manufacturing with Hydraulic Presses
The Problem: In the automotive manufacturing industry, companies often face significant challenges in producing high-quality car parts consistently. These challenges include the need for precise shaping of components like body panels and brake pads, which can lead to production delays and increased costs if not managed effectively. Additionally, manufacturers may struggle with the wear and tear of their hydraulic presses, resulting in inconsistent pressure application and product defects that can compromise safety and performance.
The Solution: To address these challenges, automotive manufacturers should prioritize regular maintenance and calibration of their hydraulic presses. Implementing a scheduled maintenance program can significantly reduce downtime and ensure that the equipment operates at optimal performance. Furthermore, companies should invest in hydraulic presses with advanced pressure control technology, which can provide real-time monitoring and adjustments, ensuring uniform pressure application during the shaping process. Additionally, collaborating with suppliers who offer comprehensive training on the operation and maintenance of hydraulic presses can empower staff to identify issues early, minimizing production disruptions.
Scenario 2: Inefficiencies in Agricultural Equipment Repair
The Problem: Farmers and agricultural equipment manufacturers often encounter difficulties when repairing heavy machinery due to rusted or bent components. The traditional methods for separating and straightening parts can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, which affects productivity. Without an efficient repair process, equipment downtime can lead to significant financial losses, especially during critical planting or harvesting seasons.
The Solution: Utilizing a hydraulic press can streamline the repair process for agricultural machinery. By investing in a hydraulic press specifically designed for heavy-duty applications, farmers can easily and effectively separate rusted components and straighten bent parts with minimal effort. It’s essential to select a hydraulic press with the appropriate force rating and features suited for agricultural tasks, such as adjustable speed and pressure settings. Additionally, training staff on best practices for using hydraulic presses will enhance their skill set, allowing for quicker repairs and reduced downtime. Establishing a partnership with suppliers who specialize in hydraulic systems can also provide access to the latest technologies and maintenance support.
Scenario 3: Quality Control Issues in Metal Stamping Processes
The Problem: Manufacturers involved in metal stamping often face quality control issues, such as inconsistent product dimensions and defects due to improper use of hydraulic presses. These problems can arise from a lack of understanding of the hydraulic press’s operational capabilities or from inadequate machine settings, leading to increased scrap rates and customer dissatisfaction. Ensuring that products meet the required specifications while maintaining cost-effectiveness is a constant struggle.
The Solution: To mitigate quality control issues, manufacturers should invest in advanced hydraulic press technology that incorporates automation and computer numerical control (CNC). This allows for precise adjustments in real-time, enhancing accuracy in the stamping process. Training operators on the specific requirements of the materials being processed and the capabilities of the hydraulic press can further improve outcomes. Implementing a robust quality assurance program that includes regular inspections and testing can help identify potential defects early in the production cycle. Collaborating with industry experts to optimize the metal stamping process can lead to significant improvements in both product quality and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is a hydraulic press used for
What Are the Key Materials Used in Hydraulic Press Applications?
Hydraulic presses are versatile machines used across various industries, from automotive manufacturing to agriculture. Selecting the right materials for hydraulic press applications is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials utilized in hydraulic press applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it an ideal choice for hydraulic press components that must withstand significant pressure and stress. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 500°F (260°C) and excellent corrosion resistance when treated.
Pros & Cons:
Steel offers exceptional durability and is relatively cost-effective. However, it can be heavy and may require additional manufacturing processes, such as heat treatment, to enhance its properties. The end products made from steel are generally robust but can be prone to rust if not properly maintained.
Impact on Application:
Steel’s compatibility with hydraulic fluids and its ability to handle high pressures make it suitable for various applications, including automotive part manufacturing and metal stamping.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN) for steel grades. Additionally, understanding the local availability of treated versus untreated steel can impact procurement decisions.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating of around 400°F (204°C). Its lower density compared to steel makes it easier to handle and transport.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of aluminum is its weight, which can lead to reduced operational costs in logistics and handling. However, it is less durable under high-pressure conditions compared to steel, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications. The manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is often used in applications requiring lighter components, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries for parts that do not bear heavy loads.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In Europe and the Middle East, compliance with specific aluminum alloy standards (such as EN 573) is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of aluminum in various grades and forms to meet their specific application needs.
3. Cast Iron
Key Properties:
Cast iron has excellent compressive strength and can withstand high temperatures, typically rated up to 1,200°F (650°C). It also offers good wear resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability and wear resistance of cast iron are significant advantages, especially in high-load applications. However, it is brittle and can crack under tensile stress, which limits its use in certain designs. Additionally, cast iron can be more expensive than steel due to the complexity of the casting process.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is commonly used in the manufacturing of molds and fixtures in hydraulic presses, particularly in industries such as construction and heavy machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the different grades of cast iron (e.g., gray, ductile) and their specific applications. Compliance with international standards (e.g., ASTM A48) is also essential for ensuring quality and performance.
4. Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, offer a unique combination of strength and lightweight characteristics. They can withstand a variety of temperatures and are often resistant to corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of composites is their lightweight nature and high strength-to-weight ratio, which can lead to improved efficiency in hydraulic press operations. However, they are generally more expensive and can require specialized manufacturing techniques, which may complicate production.
Impact on Application:
Composites are increasingly being used in specialized applications, such as aerospace and automotive industries, where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should consider the availability of composite materials in their regions and the associated costs. Compliance with specific industry standards (e.g., ASTM D3039 for tensile properties) is also important.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is a hydraulic press used for | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Automotive part manufacturing | High durability | Can rust if untreated | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components | Lightweight | Less durable under pressure | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Molds and fixtures in heavy machinery | Excellent wear resistance | Brittle under tensile stress | High |
| Composite Materials | Specialized applications in aerospace and automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive, complex to manufacture | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and considerations for various materials used in hydraulic press applications, facilitating informed purchasing decisions tailored to their specific needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is a hydraulic press used for
What Are the Key Stages of Manufacturing for Hydraulic Presses?
The manufacturing process for hydraulic presses is intricate and requires several critical stages to ensure the final product meets industry standards and client specifications. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers who need to ensure the reliability and functionality of the hydraulic presses they procure.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Hydraulic Press Manufacturing?
The first stage involves the careful selection and preparation of materials. Common materials used in hydraulic press construction include high-grade steel for the frame and components, which provides strength and durability. Other materials may include various alloys that enhance performance under high pressure.
During this phase, materials are inspected for quality and consistency, ensuring they meet the required specifications before moving forward. This can involve cutting, machining, and surface treatment to prepare the materials for assembly.
How Is the Forming Process Executed in Hydraulic Press Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming process begins. This stage involves shaping the components of the hydraulic press using techniques such as stamping, bending, and welding.
Metal stamping, for instance, is a prevalent technique used to create specific shapes and profiles from sheet metal. In this process, a die is used to cut or shape the metal under high pressure, ensuring precision and consistency. Additionally, hydraulic presses themselves are often used in this stage to assemble parts, demonstrating their versatility.
What Role Does Assembly Play in Hydraulic Press Production?
After forming, the assembly stage takes place. This critical phase involves fitting together the various components, including the hydraulic cylinders, pistons, and control systems. Each component must be aligned and secured properly to ensure optimal performance.
During assembly, manufacturers often utilize jigs and fixtures to maintain accuracy. The integration of electrical and hydraulic systems also occurs at this stage, requiring skilled technicians to ensure that all parts function harmoniously.
Why Is Finishing Important in the Manufacturing of Hydraulic Presses?
The finishing stage involves several processes designed to enhance the performance and aesthetics of the hydraulic press. This can include painting, powder coating, and applying protective finishes to prevent corrosion.
Additionally, finishing processes often include quality checks to ensure that the surface treatments meet the desired specifications. This stage is crucial as it not only affects the longevity of the press but also its operational efficiency.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Hydraulic Press Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a non-negotiable aspect of hydraulic press manufacturing. Adhering to international standards and implementing rigorous quality control (QC) measures ensures that the final product is safe, reliable, and effective for its intended use.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards, such as ISO 9001, play a vital role in guiding manufacturers in their quality management processes. ISO 9001 focuses on ensuring consistent quality in production and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for compliance with European safety standards and API standards for the oil and gas industry, are crucial for buyers to consider.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Hydraulic Press Production?
Quality control in hydraulic press manufacturing typically includes several checkpoints throughout the production process:

Illustrative image related to what is a hydraulic press used for
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial phase involves inspecting raw materials and components as they arrive at the manufacturing facility. Any subpar materials are rejected to prevent defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various checks are conducted to monitor the quality of the components being produced. This could include measurements of pressure, alignment, and surface finishes.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a thorough inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing of hydraulic systems and ensuring that all components meet the specified tolerances and standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Hydraulic Press Manufacturing?
Testing methods vary but often include:
-
Hydraulic Testing: Verifying the integrity and performance of the hydraulic system under pressure.
-
Load Testing: Assessing the press’s ability to handle specified loads, ensuring it operates within safe limits.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Using tools such as calipers and micrometers to ensure components meet design specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for ensuring the reliability of hydraulic presses. Here are effective strategies:
What Should Buyers Look for During Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess quality control measures. During an audit, buyers can evaluate the manufacturing processes, quality assurance practices, and adherence to international standards.
How Can Buyers Request Quality Control Reports?
Buyers should request detailed QC reports that outline the results of inspections and tests conducted during the manufacturing process. These documents provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and any corrective actions taken for issues identified.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Ensuring Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can verify compliance with international standards and provide an additional layer of assurance for buyers, especially in regions where local regulations may vary.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances in quality control. These may include:

Illustrative image related to what is a hydraulic press used for
-
Understanding Local Standards: Familiarizing themselves with local regulations and standards that may differ from international ones.
-
Navigating Language Barriers: Ensuring clear communication regarding quality specifications and expectations, which can be particularly important in multinational transactions.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Being aware of cultural differences that may affect business practices and negotiations, particularly regarding quality assurance and compliance.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with hydraulic presses is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside robust quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure the reliability and efficiency of their hydraulic presses.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is a hydraulic press used for’
To effectively procure a hydraulic press that meets your operational needs, it’s essential to follow a systematic approach. This guide offers a checklist to ensure you make informed decisions tailored to your specific industry requirements. Here’s how to navigate the procurement process.
Step 1: Identify Your Application Needs
Understanding the specific applications for which you need a hydraulic press is crucial. Different industries utilize hydraulic presses for various purposes, such as metal forming, car part manufacturing, or agricultural equipment repairs. Define whether you need a press for high-volume production, custom applications, or prototyping to guide your selection process.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Once you’ve clarified your application needs, outline the technical specifications required for the hydraulic press. Consider factors such as:
– Force Requirements: Determine the maximum force needed for your applications.
– Size and Dimensions: Ensure the press fits within your operational space and can accommodate the materials you’ll be working with.
– Speed and Cycle Time: Evaluate how quickly the press needs to operate to meet production demands.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your requirements. Look for:
– Company Reputation: Research supplier backgrounds, including their experience and market presence.
– Customer References: Request case studies and testimonials from businesses in your industry to gauge satisfaction levels.
– Service and Support: Assess the level of after-sales support and maintenance services they offer.

Illustrative image related to what is a hydraulic press used for
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensuring that suppliers adhere to industry standards is essential for safety and performance. Check for:
– ISO Certifications: Look for ISO 9001 certification, which indicates a commitment to quality management.
– Compliance with Local Regulations: Confirm that the equipment meets safety and environmental standards specific to your region, such as CE marking in Europe or ANSI standards in the U.S.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
After narrowing down your options, request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers. When comparing pricing, consider:
– Total Cost of Ownership: Beyond the initial purchase price, evaluate installation costs, maintenance, and potential downtime.
– Warranty and Service Plans: A robust warranty and service plan can save costs in the long run, so factor these into your decision.
Step 6: Test the Equipment
If possible, arrange for a demonstration or trial of the hydraulic press before finalizing your purchase. This step allows you to:
– Assess Performance: Evaluate the press’s capabilities in real-time and ensure it meets your application needs.
– Check Usability: Ensure the controls and features align with your operational requirements and are user-friendly for your team.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract
Once you’ve selected a supplier, ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in a contract. Pay attention to:
– Delivery Schedules: Confirm timelines for delivery and installation.
– Payment Terms: Discuss payment options and any financing arrangements.
– Service Agreements: Outline the scope of maintenance and support included in the purchase.
By following this checklist, you can confidently procure a hydraulic press that aligns with your business goals, ensuring efficiency and productivity in your operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is a hydraulic press used for Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing a Hydraulic Press?
When sourcing a hydraulic press, understanding the cost structure is vital for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as steel and hydraulic components, significantly impacts the overall price. High-quality materials can enhance durability and performance but may increase initial costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and maintenance. Skilled labor is essential for ensuring that the hydraulic press meets industry standards and specifications.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications can lead to higher upfront costs but may improve efficiency and output in the long run. This is particularly relevant for specialized presses designed for unique tasks.
-
Quality Control: Investing in rigorous QC processes ensures that the hydraulic presses meet safety and performance standards. While this adds to the cost, it can prevent costly failures and repairs later.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the destination. International shipping may involve tariffs, insurance, and freight charges, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. Understanding the average margins in your specific market can aid in negotiating better pricing.
What Factors Influence the Price of Hydraulic Presses?
Several price influencers can affect the overall cost of a hydraulic press, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounts. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQs) can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-built hydraulic presses tailored to specific applications will generally incur higher costs compared to standard models. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to avoid overspending on unnecessary features.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts both cost and quality. For instance, presses made with high-grade steel may offer better performance but come at a premium.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet international safety and quality standards may be more expensive but provide assurance of reliability. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in certified equipment.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and geographical location of the supplier can influence pricing. Local suppliers may offer competitive rates, while international suppliers may present logistical challenges.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions, as they define responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This knowledge can significantly impact the final cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Hydraulic Press Prices?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure they secure the best pricing when sourcing hydraulic presses:
-
Negotiate: Always be prepared to negotiate. Leverage quotes from multiple suppliers to create a competitive bidding environment.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions that may affect pricing.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about trends in hydraulic press pricing and demand in your region. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to exclusive deals.
By understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing hydraulic presses, ultimately leading to more cost-effective and efficient operations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is a hydraulic press used for With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Hydraulic Presses
In various industrial applications, the hydraulic press serves as a vital tool for shaping, forming, and compressing materials. However, there are alternative technologies and methods that can achieve similar results. Understanding these options can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on specific operational needs, budget constraints, and application requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is A Hydraulic Press Used For | Mechanical Press | Pneumatic Press |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High force application, precise control | Moderate force, variable control | Lower force, faster operation |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Generally lower cost | Lower initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires hydraulic setup and space | Simpler mechanical setup | Easy to implement, less space required |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for hydraulic fluid | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance, reliant on air supply |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty applications, metal forming | High-volume production of metal parts | Light to moderate applications, quick operations |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Mechanical Presses?
Mechanical presses utilize a mechanical system to apply force to materials, often through a flywheel mechanism. They are particularly effective for high-volume production runs where speed and consistency are essential. The primary advantage is their lower initial cost and reduced maintenance requirements. However, they may not provide the same level of force control or versatility as hydraulic presses, making them less suitable for intricate or heavy-duty applications. B2B buyers focused on mass production of simpler components might find mechanical presses more appealing.
How Do Pneumatic Presses Compare to Hydraulic Presses?
Pneumatic presses use compressed air to generate force, making them ideal for lighter applications where speed is more crucial than sheer power. Their setup is typically simpler, and they require less space compared to hydraulic systems. While they can operate quickly, pneumatic presses generally produce lower force levels than hydraulic presses, which may limit their use in heavy manufacturing tasks. B2B buyers looking for efficient, fast solutions for softer materials may benefit from pneumatic presses, especially in assembly lines where rapid processing is critical.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Selecting the appropriate solution for material shaping and forming hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your business. Hydraulic presses excel in heavy-duty applications requiring significant force and precision, while mechanical presses offer cost-effective options for high-volume production. Pneumatic presses provide a quick solution for lighter applications but may not suit every manufacturing need. By analyzing performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance requirements, B2B buyers can align their operational goals with the most suitable technology, ensuring efficient and effective production processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is a hydraulic press used for
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Hydraulic Press?
Understanding the technical specifications of hydraulic presses is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in or utilize these machines effectively. Here are some essential properties:
-
Pressure Rating (PSI)
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the hydraulic press can safely handle, typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). This specification is critical as it directly affects the types of materials and applications the press can accommodate. Selecting a press with an appropriate pressure rating ensures that it can perform the desired tasks without risk of failure or damage. -
Stroke Length
Stroke length refers to the distance the ram travels when the press is activated. This measurement influences the size of the workpieces that can be processed. A longer stroke length allows for greater versatility in applications, making it essential for manufacturers needing to work with various material sizes. -
Ram Size and Configuration
The size and configuration of the ram impact the force distribution during operation. A larger ram can exert more force, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Additionally, the ram configuration (e.g., single or double-acting) can affect the speed and efficiency of the pressing process, allowing businesses to choose a model that best fits their production needs. -
Material Grade
The material grade of the hydraulic press components, such as the frame and ram, determines the overall durability and longevity of the machine. High-grade materials can withstand higher stress levels and ensure reliable operation in demanding environments. For B2B buyers, investing in presses made from premium materials can reduce maintenance costs and downtime. -
Cycle Time
Cycle time is the duration it takes for the hydraulic press to complete one full operation, including pressing and returning to the starting position. Shorter cycle times enhance productivity, making this a vital specification for businesses with high-volume production needs. Understanding cycle time helps buyers evaluate the efficiency of different models. -
Power Source
Hydraulic presses can be powered by various sources, including electric, pneumatic, or manual options. The choice of power source affects operational costs, ease of use, and maintenance requirements. For international buyers, understanding local power infrastructure and availability is essential in selecting the most suitable hydraulic press.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Hydraulic Presses?
Familiarity with industry terminology can help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process more effectively. Here are key terms to know:
Illustrative image related to what is a hydraulic press used for
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of hydraulic presses, working with reputable OEMs ensures that businesses receive high-quality, compatible components and machines. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for buyers, as it can impact inventory levels and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This process helps businesses compare costs and services from multiple vendors. An effective RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, making it a vital part of the procurement strategy. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, ensuring smoother transactions across borders. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is essential for production planning and inventory management, especially for businesses relying on timely delivery of hydraulic presses. -
Tonnage
Tonnage refers to the maximum load capacity of a hydraulic press, indicating how much weight it can compress or shape. This measurement is vital for ensuring that the press can handle the specific applications intended, allowing buyers to choose a model that meets their operational requirements.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding hydraulic presses, aligning their investments with their operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is a hydraulic press used for Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for Hydraulic Presses in International B2B Trade?
The hydraulic press sector is witnessing significant growth driven by industrial advancements and the increasing demand for efficient manufacturing processes. Key markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly impacted by the rising need for automation and precision in manufacturing. Industries such as automotive, agriculture, and appliance manufacturing are leveraging hydraulic presses for tasks ranging from metal forming to component assembly. Emerging trends include the integration of smart technologies and IoT capabilities into hydraulic systems, enabling remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. This shift not only enhances operational efficiency but also minimizes downtime, a critical factor for international buyers looking to optimize production capabilities.
Furthermore, the demand for custom hydraulic presses tailored to specific industry needs is on the rise. Buyers are increasingly interested in suppliers who can provide specialized equipment that meets their unique operational requirements. The trend toward modular designs is also gaining traction, allowing for easy upgrades and maintenance. In regions such as Nigeria and Brazil, where manufacturing sectors are rapidly evolving, the ability to adapt hydraulic presses to local market conditions can significantly enhance competitiveness.
How Is Sustainability Reshaping the Hydraulic Press Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a central focus in the hydraulic press market, with an increasing number of buyers prioritizing environmentally friendly practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, has prompted businesses to seek hydraulic solutions that minimize their carbon footprint. Ethical sourcing and transparent supply chains are now critical considerations for B2B buyers, particularly in regions where regulatory standards are tightening.
The adoption of ‘green’ certifications and materials is a vital trend influencing purchasing decisions. Hydraulic press manufacturers that utilize recyclable materials and energy-efficient technologies are gaining a competitive edge in the market. Moreover, innovations such as hydraulic fluids that are biodegradable or less harmful to the environment are becoming more prevalent, aligning with the broader shift towards sustainability. Buyers are encouraged to evaluate suppliers not only based on price and performance but also on their commitment to sustainable practices.
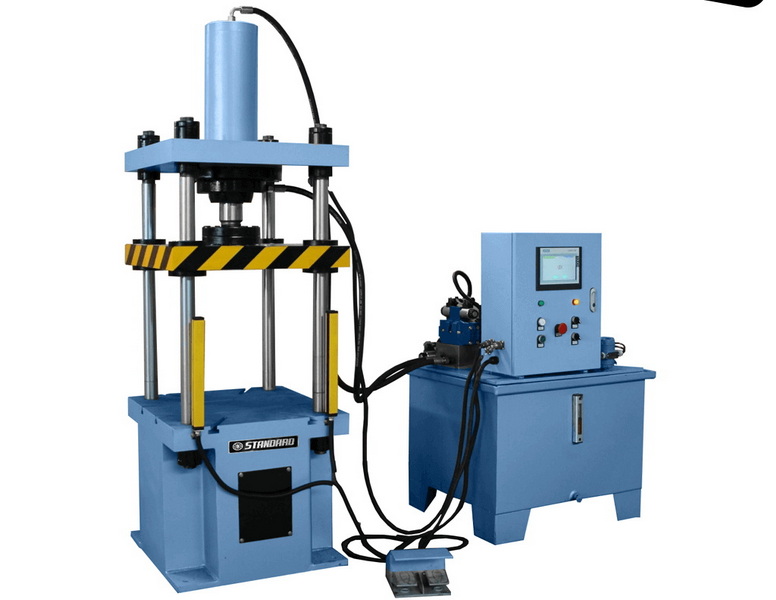

Illustrative image related to what is a hydraulic press used for
What Is the Historical Context Behind Hydraulic Press Technology?
The hydraulic press has a rich history dating back to the late 18th century, with Joseph Bramah’s invention in 1795 marking a pivotal moment in manufacturing technology. Initially designed for the production of metal components, hydraulic presses have evolved dramatically over the centuries. The integration of hydraulic systems into various industries has revolutionized production methods, enabling the efficient shaping and assembly of materials.
As industries expanded, the versatility of hydraulic presses found applications beyond metalworking, extending to sectors such as agriculture and construction. The ongoing development of hydraulic technology has led to enhanced performance and reliability, making these machines indispensable in modern manufacturing. Understanding this evolution is essential for B2B buyers as it underscores the importance of selecting equipment that not only meets current needs but also anticipates future demands in an ever-changing market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is a hydraulic press used for
-
How do I determine the right hydraulic press for my manufacturing needs?
To select the appropriate hydraulic press, assess the specific applications and materials you intend to work with. Consider factors such as the maximum tonnage required, the size and shape of the workpieces, and the type of operation (e.g., forging, stamping, or crushing). Additionally, evaluate the available space in your facility, as well as the power supply requirements. Consulting with manufacturers or suppliers can provide insights on models best suited to your operational needs. -
What are the typical applications of hydraulic presses in various industries?
Hydraulic presses are versatile machines used across several sectors. In automotive manufacturing, they shape and assemble parts such as body panels and brake pads. The agriculture sector utilizes them for equipment repairs and part separations. Additionally, they play a crucial role in metal stamping, powder manufacturing, and even blacksmithing for sword-making. Understanding these applications can help you identify how a hydraulic press can enhance your production processes. -
What customization options are available when sourcing hydraulic presses?
When sourcing hydraulic presses, many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific operational requirements. Customizations may include adjustments in tonnage capacity, stroke length, and frame design. Some manufacturers can also modify controls for automation or integrate additional safety features. Discuss your unique needs with suppliers to explore available options that can optimize the performance of the hydraulic press in your facility. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for hydraulic presses?
When vetting suppliers, evaluate their experience and reputation in the industry. Look for certifications or quality assurance standards that ensure reliability and safety in manufacturing. Request references or case studies from previous clients, especially those in your region, to gauge their service quality. Additionally, assess their customer support capabilities and after-sales services, as ongoing maintenance and support are crucial for hydraulic press operations. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for hydraulic presses?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for hydraulic presses can vary widely based on the manufacturer and the specific model. Some suppliers may offer single-unit sales, while others may require bulk orders to reduce costs. When negotiating, inquire about MOQs and discuss your requirements to find a supplier willing to accommodate your needs. Understanding MOQs is essential for budgeting and aligning your procurement strategy with production goals. -
What payment terms are typically offered when purchasing hydraulic presses?
Payment terms for hydraulic presses can differ among suppliers, often influenced by the order size and client relationship. Common terms include upfront payments, partial payments during production, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger purchases. It’s essential to clarify payment terms before finalizing any agreements to ensure they align with your financial capabilities. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for the hydraulic press I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications from your supplier regarding the hydraulic press. Look for ISO certifications or compliance with international safety standards. Additionally, inquire about the testing procedures the manufacturer employs before shipping. Some suppliers may offer warranties or service agreements that further guarantee the quality and reliability of their products, providing peace of mind for your investment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing a hydraulic press?
When importing hydraulic presses, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Assess the total landed cost, which includes shipping, duties, and handling fees. Work with logistics partners experienced in heavy machinery to ensure proper handling and compliance with international shipping standards. Also, confirm the supplier’s ability to provide necessary documentation for customs clearance to avoid delays in delivery.
Top 9 What Is A Hydraulic Press Used For Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Hydraulic Presses
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic presses are used for shaping sheet metal into products like kitchen sinks and car body panels, reshaping cars and garbage in car crushers and trash compactors, punching holes out of thick materials, and squeezing metal through a die for shaping. They can also be used to test the strength of materials, such as crushing concrete to determine PSI.
2. IQS Directory – Hydraulic Press
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Press: A mechanical apparatus that uses static pressure of a liquid to form, reshape, and alter materials like metals, plastics, rubber, and wood. Key components include the mainframe, power system, and control mechanisms. Operates by forcing hydraulic fluid into a double-acting piston, multiplying force for heavy-duty tasks. Typical components: Main Cylinder (Ram), Plunger, Pipes and Ho…
3. Carolina Hose and Hydraulics – Hydraulic Presses
Domain: carolinahoseandhydraulics.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic presses are used in various industries including agriculture for equipment repair, car part manufacturing for creating and assembling parts, appliance manufacturing for shaping and assembling parts, car crushing for compressing vehicles, sword making for blacksmithing, powder making in food and cosmetics, concrete testing for assessing tensile strength, and ceramic making for producing c…
4. XRF Scientific – Power Hydraulic Press
Domain: xrfscientific.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: XRF Scientific supplies a range of manual, power, motorized and automatic hydraulic presses for XRF sample preparation. The Power Hydraulic Press operates in ranges between 8 and 25 tons. It is microprocessor controlled and loadable in metric and imperial tons for XRF and IR sample preparations.
5. Grainger – Hydraulic Presses
Domain: grainger.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Types of Hydraulic Presses: 1. H-Frame: Large floor units with a steel frame, press cylinder, pump, and movable bolster; used in repair, maintenance, and production lines. 2. Roll Frame: Similar to H-frame but features a long table for large materials; allows for calculated presses and safer material handling. 3. Bench Frame: Smaller than H-frame, can mount to tabletops; used for high-volume assem…
6. DakeCorp – Hydraulic Presses
Domain: blog.dakecorp.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic presses are versatile and reliable machines used in the manufacturing industry. They come in various designs including Vertical H-frame, C-frame, Horizontal, Movable table, Tire presses, Movable frame, and Lab presses. Hydraulic presses can have single or double acting workheads and can be operated manually, by air, or electrically. Key advantages include smooth and even pressure, pressu…
7. AllPhase Hydraulics – Hydraulic Presses
Domain: allphasehydraulics.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic presses are mechanical devices used to crush, flatten, and compress materials. They consist of two connected cylinders containing hydraulic fluid: a larger cylinder (ram) and a smaller cylinder (plunger). Common components include a hydraulic pump, control valve, and cylinder. Hydraulic presses can generate pressures from several hundred PSI to thousands of PSI, depending on the applicat…
8. Specac – Laboratory Hydraulic Presses
Domain: specac.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Laboratory hydraulic presses are machines that use fluid pressure to generate force for compressing or molding materials. They are smaller than industrial hydraulic presses, offering precision and control, and are commonly used for: 1. Sample preparation for spectroscopy, specifically creating KBr pellets for FTIR and general sample pellets for XRF. 2. Powder compaction for composite material stud…
9. Ingenia – Hydraulic Press Solutions
Domain: ingenia.org.uk
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic presses are integral components of manufacturing, used for assembling and disassembling tight components, moulding, forming, compacting, and more. They operate on the principle of Pascal’s principle, using a small force to generate a large force through a hydraulic circuit. The system consists of two syringes connected by a pipe filled with incompressible fluid (usually oil). The smaller…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is a hydraulic press used for
What Are the Key Benefits of Investing in a Hydraulic Press?
In conclusion, the hydraulic press is a versatile tool that plays a pivotal role across various industries, from automotive manufacturing to agricultural equipment maintenance. By harnessing Pascal’s principle, it provides efficient and consistent force, making it indispensable for tasks such as metal shaping, material testing, and even food processing. For B2B buyers, understanding the diverse applications of hydraulic presses can lead to enhanced operational efficiency and product quality.
Strategic sourcing of hydraulic presses can significantly impact your supply chain, enabling you to select suppliers that offer reliable, high-quality equipment tailored to your specific needs. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for advanced hydraulic solutions is expected to grow, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, where infrastructure and manufacturing are on the rise.
Now is the time for international B2B buyers to evaluate their hydraulic press needs and explore partnerships with reputable suppliers. Investing in the right hydraulic press can not only streamline production processes but also position your business competitively in the global marketplace. Take the next step and connect with suppliers who can provide the innovative hydraulic solutions your operations require.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.