Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Flash Freezer Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for flash freezer
In the fast-paced global market, sourcing a reliable flash freezer can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With the increasing demand for high-quality food preservation and the need for efficiency in operations, businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—specifically in countries like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—must navigate a complex landscape of options. Flash freezers, known for their ability to rapidly chill and freeze products while maintaining their quality, are essential tools for enhancing productivity and extending shelf life.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of flash freezers available, their applications across different industries, and critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers. We will explore cost implications, energy efficiency, and technological advancements that can significantly impact your purchasing decisions. Additionally, we will provide insights on best practices for installation and maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
By leveraging the information within this guide, B2B buyers will be empowered to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Whether you are looking to improve your food service operations or enhance your cold storage capabilities, understanding the nuances of flash freezers will enable you to invest wisely in this vital equipment.
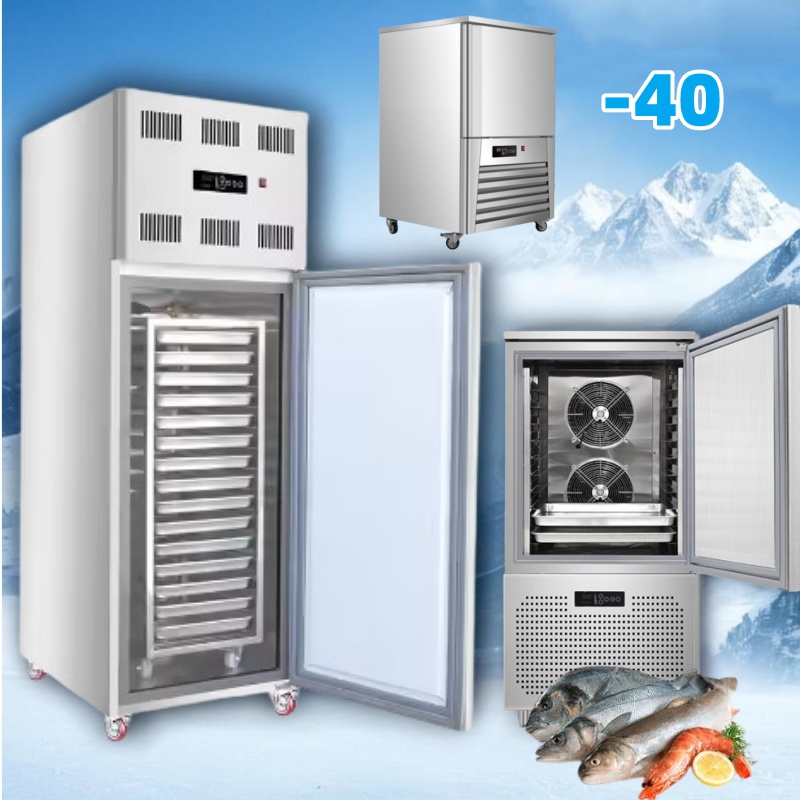
Understanding flash freezer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Blast Freezer | High-capacity, rapid freezing, often with multiple trays | Restaurants, catering, food processing | Pros: Efficient for bulk freezing; preserves food quality. Cons: Higher initial investment; requires space. |
| Shock Freezer | Extremely low temperatures, often below -30°C, quick freeze | Seafood processing, bakeries | Pros: Excellent for delicate foods; minimal ice crystal formation. Cons: Energy-intensive; maintenance can be complex. |
| Portable Flash Freezer | Compact design, suitable for mobile operations | Food trucks, events, small businesses | Pros: Versatile and easy to transport; lower cost. Cons: Limited capacity; may lack advanced features. |
| Industrial Tunnel Freezer | Continuous freezing process, conveyor belt system | Large-scale food production | Pros: Ideal for high volume; automated operation. Cons: Significant space and energy requirements; high cost. |
| Blast Chiller/Freezer | Dual functionality (chilling and freezing), user-friendly controls | Bakeries, restaurants, food storage | Pros: Multi-functional; maintains food integrity. Cons: May not reach extreme temperatures; moderate capacity. |
What Are the Characteristics of Commercial Blast Freezers?
Commercial blast freezers are designed for high-capacity food freezing, making them essential for restaurants, catering services, and food processing facilities. These units can accommodate multiple trays and rapidly freeze large quantities of food, preserving texture and flavor. When considering a purchase, businesses should evaluate energy efficiency, space requirements, and the ability to maintain consistent low temperatures, as these factors directly influence operational costs and food quality.
How Do Shock Freezers Enhance Food Preservation?
Shock freezers operate at extremely low temperatures, often below -30°C, allowing them to freeze foods quickly and effectively. This is particularly beneficial for seafood processing and bakeries, where the preservation of delicate textures and flavors is crucial. B2B buyers should consider the energy consumption, maintenance needs, and the specific freezing capabilities required for their products when evaluating shock freezers.
What Advantages Do Portable Flash Freezers Offer?
Portable flash freezers are compact and designed for mobility, making them ideal for food trucks, events, and small businesses. These units provide a cost-effective solution for businesses that require on-the-go freezing capabilities. Buyers should assess the unit’s capacity, freezing speed, and ease of transport to ensure it meets their operational needs while maintaining food quality.
Why Choose Industrial Tunnel Freezers for Large-Scale Operations?
Industrial tunnel freezers utilize a conveyor belt system for continuous freezing, making them suitable for large-scale food production. These systems are automated, allowing for high-volume processing while maintaining consistent freezing temperatures. However, B2B buyers must consider the substantial space, energy requirements, and initial investment needed for installation, as these factors can significantly impact operational budgets.
What Makes Blast Chiller/Freezers a Versatile Option?
Blast chiller/freezers offer dual functionality, allowing businesses to chill and freeze food products efficiently. They are user-friendly and designed to maintain food integrity while providing rapid cooling. This versatility makes them popular in bakeries, restaurants, and food storage facilities. When purchasing, companies should evaluate the temperature range, capacity, and features that align with their specific food preservation needs.
Key Industrial Applications of flash freezer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Flash Freezer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Rapid freezing of meat and seafood | Preserves quality, texture, and extends shelf life | Capacity, energy efficiency, temperature control, maintenance |
| Bakeries | Freezing dough and baked goods | Maintains freshness and prevents spoilage | Size, programmable settings, ease of operation |
| Pharmaceuticals | Preservation of biological samples | Ensures integrity and efficacy of temperature-sensitive products | Compliance with safety standards, energy consumption |
| Catering Services | Quick freeze for bulk meal prep | Enhances productivity and reduces food waste | Volume capacity, speed of freezing, reliability |
| Supermarkets | Flash freezing of fruits and vegetables | Extends shelf life and improves product quality | Sourcing of eco-friendly refrigerants, maintenance requirements |
How is Flash Freezer Used in Food Processing and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the food processing industry, flash freezers are essential for rapidly freezing meat and seafood, ensuring that products retain their quality and texture. The swift freezing process minimizes the formation of ice crystals, which can compromise the structural integrity of food. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, it’s crucial to consider the capacity and energy efficiency of these machines to meet local demand and operational costs.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
What Role Do Flash Freezers Play in Bakeries?
Bakeries utilize flash freezers to freeze dough and finished products such as pastries and bread. This technology allows bakers to maintain the freshness of their products while reducing spoilage. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it’s important to evaluate the size and programmable settings of flash freezers to align with production schedules and operational workflows, ensuring that the equipment can handle peak demand efficiently.
How Do Flash Freezers Benefit the Pharmaceutical Industry?
In the pharmaceutical sector, flash freezers are used to preserve biological samples, vaccines, and other temperature-sensitive products. The ability to quickly lower temperatures helps maintain the integrity and efficacy of these critical items. Buyers in this field must prioritize compliance with safety standards and consider energy consumption, as these factors directly impact operational efficiency and regulatory adherence.
Why Are Flash Freezers Important for Catering Services?
Catering services benefit from flash freezers by enabling quick freezing of bulk meal preparations. This capability not only enhances productivity but also significantly reduces food waste by allowing caterers to prepare meals in advance without compromising quality. For businesses in regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria, sourcing reliable equipment with a focus on volume capacity and freezing speed is essential to meet diverse client demands and event schedules.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
How Do Supermarkets Utilize Flash Freezers for Fruits and Vegetables?
Supermarkets employ flash freezers to quickly freeze fruits and vegetables, extending their shelf life and enhancing overall product quality. This rapid freezing process preserves the nutritional value and texture of fresh produce, making it more appealing to consumers. Buyers in the retail sector should consider sourcing eco-friendly refrigerants and understanding maintenance requirements to ensure long-term operational sustainability and compliance with environmental regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘flash freezer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Freezing Quality Affecting Product Integrity
The Problem: A food processing company in Nigeria is experiencing issues with the quality of frozen products. Their current freezing methods are leading to the formation of large ice crystals, which compromise the texture and taste of seafood and meat products. This inconsistency is not only disappointing customers but also impacting the company’s reputation and sales. The challenge becomes even more pronounced during peak seasons when rapid freezing is crucial to meet demand.
The Solution: To address this issue, the company should invest in a high-quality flash freezer equipped with advanced features such as Micro-Wind System technology. This system circulates cold air gently but rapidly around the food, promoting quick freezing while minimizing ice crystal formation. When sourcing a flash freezer, buyers should prioritize models that offer programmable settings tailored to specific food types, ensuring optimal freezing conditions. Additionally, conducting regular freezing tests will help the company determine the best practices for their specific products, ensuring quality is maintained even at high volumes.
Scenario 2: High Energy Costs and Inefficiency in Operations
The Problem: A bakery in Brazil is struggling with escalating energy costs due to the inefficiency of their existing freezing equipment. The current freezers take too long to freeze dough and finished goods, which not only increases energy consumption but also slows down production cycles. The management is concerned that without a solution, profitability will continue to dwindle as operational costs rise.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
The Solution: Upgrading to an energy-efficient flash freezer can significantly reduce energy costs while enhancing operational efficiency. When selecting a new unit, the bakery should consider models that are designed for energy efficiency, featuring high-quality insulation and modern compressors. Moreover, implementing a regular maintenance schedule will ensure the equipment operates at peak efficiency. The bakery might also explore leasing options for flash freezers, allowing them to test various models and select the most suitable one without committing to a large upfront investment.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Meeting Food Safety Regulations
The Problem: A meat processing facility in Saudi Arabia faces challenges in complying with stringent food safety regulations. Their current freezing methods do not meet the rapid freezing standards required to prevent bacterial growth, and the facility risks incurring penalties or losing certification. This compliance issue poses a significant threat to their business continuity and market position.
The Solution: The facility should invest in a flash freezer that is specifically designed to meet food safety standards by ensuring rapid temperature drops to below -18°C within the required timeframe. Features such as AI Smart Freeze technology can automate the freezing process, reducing human error and maintaining consistent quality. It’s crucial for the facility to work closely with suppliers to ensure that the chosen equipment is compliant with local regulations and can handle their production volumes. Additionally, staff training on the proper use of the flash freezer can further enhance compliance and operational safety, ensuring that all food safety protocols are strictly followed.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for flash freezer
What Are the Common Materials Used in Flash Freezers and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for flash freezers, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The right material can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the equipment, making it crucial for B2B buyers to understand their options.
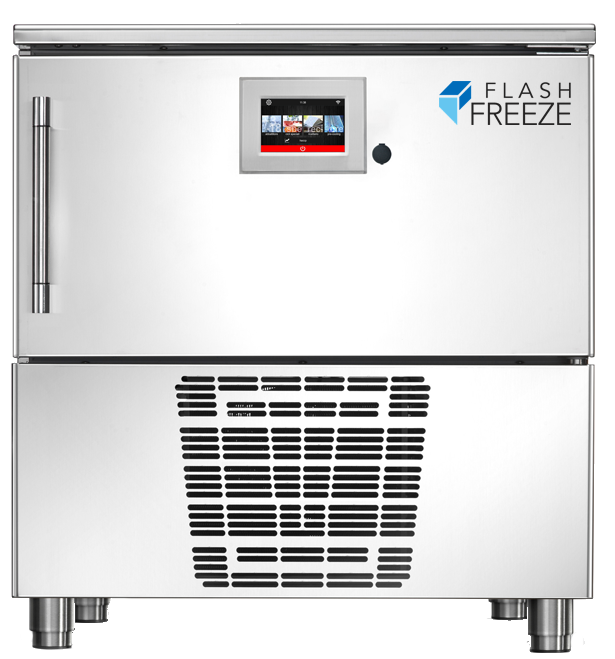

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
Stainless Steel: The Industry Standard
Stainless steel is a prevalent choice for flash freezers due to its excellent corrosion resistance and ability to withstand low temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of -40°C and can handle high pressure, making it suitable for various freezing applications.
Pros: Stainless steel is durable and easy to clean, which is vital for maintaining hygiene in food processing environments. It also has a long lifespan, providing good value over time.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be higher than other materials like aluminum. Additionally, it can be heavier, which may complicate installation and mobility.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of food products, ensuring that there is no contamination. Its robustness makes it ideal for high-volume operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards, such as those from the FDA or EFSA, is vital. Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should also consider local regulations regarding material safety and hygiene.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Alternative
Aluminum is another common material used in flash freezers, known for its lightweight properties and good thermal conductivity. It can typically handle temperatures down to -20°C.
Pros: Its lightweight nature makes it easier to transport and install, reducing overall operational costs. Aluminum also has good resistance to corrosion, especially when anodized.
Cons: While aluminum is less expensive than stainless steel, it may not be as durable in high-stress environments. It can also warp at extreme temperatures, which may affect the integrity of the freezer over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for less demanding freezing applications, such as freezing fruits and vegetables, but may not be ideal for meat or seafood.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet international standards such as ASTM for material quality. In regions with high humidity, additional coatings may be necessary to prevent corrosion.
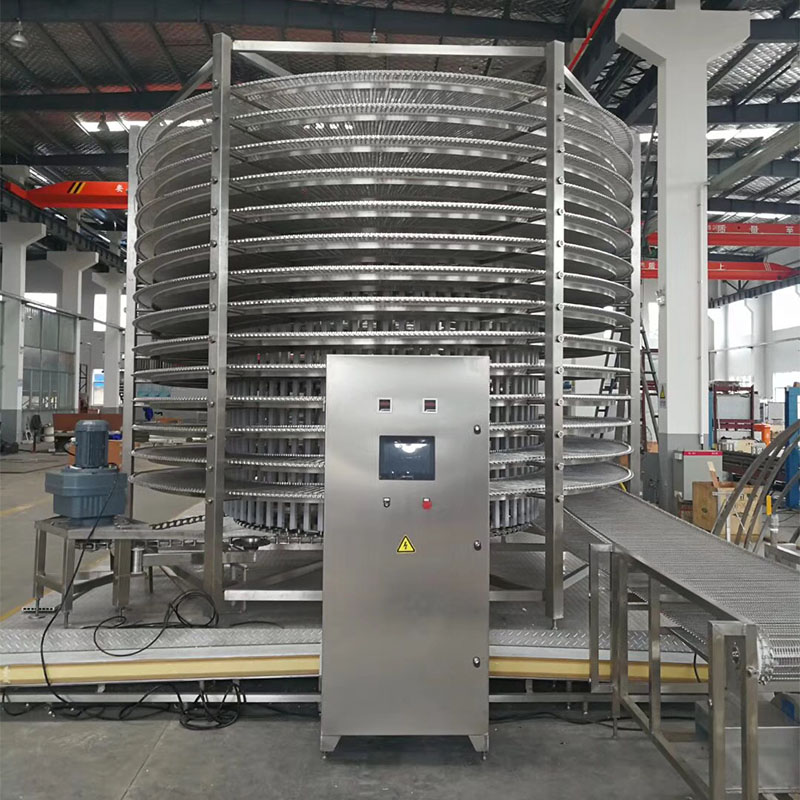

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
Polyurethane Foam: Insulation Material
Polyurethane foam is often used as insulation in flash freezers due to its excellent thermal resistance and lightweight characteristics. It can maintain temperatures as low as -50°C.
Pros: This material provides exceptional insulation, which helps reduce energy costs by minimizing heat transfer. It is also lightweight, making it easier to handle during installation.
Cons: Polyurethane foam can be sensitive to certain chemicals, which may limit its applications. Additionally, it may not provide the structural integrity required for heavy-duty use.
Impact on Application: Ideal for maintaining low temperatures in flash freezers, polyurethane foam is commonly used in the walls of the units to enhance energy efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with fire safety regulations is crucial, especially in regions like Europe where stringent standards apply. Buyers should also consider the foam’s environmental impact, as some formulations may not be eco-friendly.
High-Performance Plastics: Emerging Options
High-performance plastics, such as polycarbonate or PEEK, are emerging materials in flash freezer construction. These materials can withstand extreme temperatures and offer good chemical resistance.
Pros: High-performance plastics are lightweight and resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making them versatile for various applications. They also provide good thermal insulation properties.
Cons: The cost of high-performance plastics can be significantly higher than traditional materials, which may deter budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, their long-term durability in extreme conditions is still being evaluated.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
Impact on Application: These materials are suitable for specialized applications, such as freezing delicate items that require careful handling.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that high-performance plastics meet relevant international standards and regulations, particularly in food safety and environmental impact.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Flash Freezers
| Material | Typical Use Case for flash freezer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | General food freezing | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Freezing fruits and vegetables | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Polyurethane Foam | Insulation in freezer walls | Excellent thermal insulation | Sensitive to chemicals, limited structural integrity | Medium |
| High-Performance Plastics | Specialized freezing applications | Chemical resistance and lightweight | High cost and uncertain long-term durability | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the materials used in flash freezers, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs and regional considerations.
Illustrative image related to flash freezer
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for flash freezer
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Flash Freezers?
The manufacturing process of flash freezers involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall quality and efficiency of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they are selecting equipment that meets their operational needs.
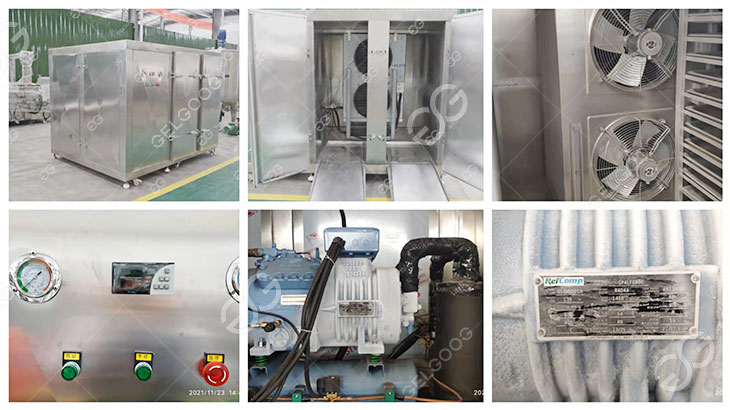
Material Preparation: What Are the Key Components?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality materials are essential for durability and performance. Common materials used include stainless steel for the exterior and interior components, which resist corrosion and facilitate hygiene. Insulation materials are also critical, as they minimize energy loss and maintain internal temperatures. Manufacturers often source these materials from certified suppliers to ensure compliance with international standards.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This involves cutting, bending, and shaping the materials into the required components of the flash freezer. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are commonly employed for precision and consistency. This stage may also involve welding parts together, which is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of the unit.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
The assembly process involves putting together the individual components, including the refrigeration system, evaporators, and fans. This stage is often automated to enhance efficiency, but skilled technicians oversee it to ensure accuracy. Key components are tested during assembly to confirm their functionality. For instance, the refrigerant lines are checked for leaks, and electrical connections are verified for safety.
How Is the Finishing of Flash Freezers Achieved?
Finishing is the final stage of manufacturing, where the flash freezers undergo painting or coating processes to enhance aesthetics and protect against corrosion. Additionally, quality checks are performed to ensure that all components meet the specified standards. This may include visual inspections, measurements, and functional tests to verify that the unit operates as intended.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Flash Freezers?
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring that flash freezers operate efficiently and safely. International standards, such as ISO 9001, provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards signifies that the manufacturer has established processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Which Industry-Specific Certifications Should B2B Buyers Consider?
In addition to ISO standards, various industry-specific certifications are essential for flash freezers. The CE mark indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, making it crucial for buyers in Europe. For buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East, certifications from local regulatory bodies can also be significant. Understanding these certifications can help buyers ensure that they comply with local regulations.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each flash freezer meets established standards. Various checkpoints are implemented throughout the production cycle:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of materials received from suppliers. Testing may involve checking the chemical composition of metals or the thermal insulation properties of materials.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the assembly process, regular checks are performed to ensure that components are being assembled correctly and that any defects are identified early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the assembly is complete, a comprehensive inspection is conducted. This includes functional tests to ensure that refrigeration cycles are operating correctly and that temperature settings can be accurately achieved.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in Quality Control?
Testing methods play a pivotal role in verifying the quality of flash freezers. Common methods include:
-
Thermal Testing: This ensures that the unit can achieve and maintain the specified temperatures under various operational conditions.
-
Pressure Testing: For refrigeration systems, pressure tests confirm that there are no leaks in the refrigerant lines.
-
Performance Testing: This assesses the overall efficiency of the freezer, including its freezing speed and energy consumption.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
When sourcing flash freezers, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Periodic audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their quality assurance processes. Buyers should assess the adherence to ISO standards and other relevant certifications during these audits.
-
Request Quality Control Reports: Manufacturers should be willing to provide documentation that outlines their QC processes and results from recent inspections. This transparency is vital for building trust.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: For buyers unfamiliar with the manufacturing landscape, hiring independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances when it comes to quality control. Differences in regulations and standards can significantly impact purchasing decisions:
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Each region may have specific regulations regarding food safety and equipment standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Perception: Different cultures may have varying expectations regarding quality and safety. Buyers should consider these differences when evaluating suppliers.
-
Shipping and Handling Considerations: Ensure that quality control extends beyond manufacturing to include how the flash freezers are packaged and shipped. Damages during transit can affect performance, so it’s important to verify that suppliers have robust shipping protocols in place.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms in place for flash freezers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘flash freezer’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring a flash freezer, this guide provides a comprehensive checklist to ensure you make an informed decision. Flash freezers are critical for industries that demand rapid freezing capabilities, such as food processing, catering, and restaurants. This checklist will guide you through the essential considerations to maximize your investment.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clarify your technical requirements. Consider factors such as freezing capacity, temperature range, and the types of products you intend to freeze.
– Freezing Capacity: Determine how much product you need to freeze at once. This will influence the size of the freezer you require.
– Temperature Range: Ensure the freezer can achieve the necessary low temperatures for your products, ideally below -30°C for optimal preservation.
Step 2: Research and Identify Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers. Look for companies with a strong track record in manufacturing and supplying flash freezers.
– Supplier Reputation: Check online reviews, industry forums, and trade publications for feedback on potential suppliers.
– Experience: Consider suppliers with experience in your specific industry to ensure they understand your unique requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Certifications: Verify that the supplier adheres to relevant industry standards and certifications, such as ISO or CE.
– Customer Support: Assess the level of after-sales support they provide, including maintenance and service agreements.
Step 4: Request Product Demonstrations
Whenever possible, request demonstrations of the flash freezer in action. This is an invaluable step to assess performance and features.
– Freezing Speed: Observe how quickly the unit can freeze various products and ensure it meets your operational demands.
– Ease of Use: Evaluate the user interface and controls to ensure they are intuitive and user-friendly.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
While initial costs are important, consider the total cost of ownership, including energy consumption, maintenance, and potential downtime.
– Energy Efficiency: Look for models with high energy ratings to reduce operational costs over time.
– Maintenance Needs: Factor in the frequency and cost of maintenance required to keep the unit running efficiently.
Step 6: Assess Warranty and Support Options
A strong warranty and support system can save you from unexpected expenses. Ensure you understand the terms and conditions.
– Warranty Duration: Look for a warranty that covers critical components for an extended period.
– Support Availability: Confirm the availability of technical support and the response times for service requests.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Arrange Logistics
Once you’ve selected a supplier, finalize the purchase agreement and discuss logistics. Ensure that delivery timelines and installation services meet your operational needs.
– Delivery Terms: Clarify shipping costs and timelines to avoid delays in your operations.
– Installation Support: Confirm whether the supplier provides installation services or if you need to arrange for this separately.
By following this checklist, you can confidently source a flash freezer that meets your business needs while ensuring quality and efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for flash freezer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Flash Freezers?
When evaluating the cost structure of flash freezers, several components come into play. Materials represent a significant portion of the cost, including high-quality stainless steel for durability, advanced insulation materials for energy efficiency, and specialized refrigeration components. Labor costs are incurred during manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. Manufacturing overhead encompasses expenses related to factory operations, including utilities, rent, and administrative costs.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
Moreover, tooling costs for specialized machinery to produce flash freezers can be substantial. Quality control (QC) processes ensure that each unit meets safety and performance standards, adding to overall costs. Finally, logistics expenses, which include transportation and warehousing, play a crucial role, especially for international shipments. These factors collectively influence the final margin that suppliers set on their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Flash Freezer Costs?
Several price influencers can impact the cost of flash freezers. Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQ) are critical; larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Customization and specific specifications can also drive prices up, as tailored solutions require additional materials and engineering time.
The choice of materials affects not only the initial cost but also the longevity and efficiency of the freezer. Higher quality materials may command a premium but can result in lower energy costs and longer lifespans, which are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. Supplier factors, such as reputation, reliability, and delivery times, can also influence pricing. Finally, understanding Incoterms is essential, as they define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect overall costs.
What Tips Should Buyers Consider for Cost-Efficiency in Flash Freezer Procurement?
International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing flash freezers. Negotiation is key; buyers should engage suppliers to discuss pricing, potential discounts for bulk purchases, or long-term contracts that may yield better terms.
Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is vital. This includes not only the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs. Buyers should evaluate energy efficiency ratings, as a more efficient model may offer substantial savings over time.
Additionally, it is advisable to be aware of pricing nuances specific to different regions. Economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and local regulations can affect pricing. In regions like Saudi Arabia or Nigeria, understanding local market dynamics and establishing relationships with local suppliers can facilitate better pricing and service.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Indicative Prices?
While evaluating flash freezers, it’s essential to recognize that prices can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. Suppliers may provide indicative prices, but these should be viewed as starting points. Final pricing can be influenced by negotiations, specific buyer requirements, and market conditions at the time of purchase.
In conclusion, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research and engage in proactive discussions with suppliers to ensure they secure the best possible deal on flash freezers while considering the broader implications of their purchase decisions.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing flash freezer With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Flash Freezers in the Food Industry
In the competitive landscape of food preservation, businesses often seek efficient freezing solutions to maintain product quality and extend shelf life. Flash freezers are renowned for their rapid freezing capabilities, but several alternative technologies also offer viable benefits. This analysis compares flash freezers with blast chillers and traditional freezers, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Flash Freezer | Blast Chiller | Traditional Freezer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Freezes food quickly, preserving texture and nutrients | Rapid chilling but slower than flash freezers | Slower freezing, larger ice crystal formation |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate investment | Lower upfront cost, but higher energy costs over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized setup | Generally easy to install and use | Widely available and easy to use |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed, tech-savvy operation | Moderate maintenance, easier operation | Low maintenance but requires regular defrosting |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume commercial operations needing quality preservation | Suitable for smaller batches and diverse applications | Good for general household or low-volume commercial use |
Exploring the Alternatives in Detail
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Blast Chillers?
Blast chillers rapidly reduce the temperature of food, but they do so at a slower rate than flash freezers. They are more versatile for various applications, including chilling, freezing, and preserving cooked foods. The moderate cost of blast chillers makes them accessible for small to medium-sized operations. However, they may not achieve the same level of quality preservation as flash freezers, particularly for delicate items that require extremely rapid freezing to maintain texture and flavor.
How Do Traditional Freezers Compare to Flash Freezers?
Traditional freezers are the most familiar option, generally found in both households and commercial settings. They offer a lower initial investment and straightforward operation, making them a common choice for smaller businesses. However, they are less efficient in terms of freezing speed, which can lead to the formation of larger ice crystals that negatively impact food quality. Additionally, traditional freezers require regular defrosting, which can disrupt operations, particularly in commercial settings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
Selecting the appropriate freezing solution hinges on understanding your operational requirements, budget, and product types. For high-volume enterprises focused on quality, investing in flash freezers is advantageous despite the higher upfront cost. Conversely, businesses with less demanding freezing needs might find blast chillers or traditional freezers more suitable, balancing cost and performance. Ultimately, evaluating the specific use cases and potential ROI will guide B2B buyers in choosing the best freezing technology for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for flash freezer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Flash Freezers?
When considering the procurement of flash freezers for commercial applications, understanding their key technical properties is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications to evaluate:

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
-
Cooling Capacity
This refers to the amount of product a flash freezer can cool or freeze within a specific timeframe. Measured in pounds per hour (lb/hr) or kilograms per hour (kg/hr), cooling capacity directly impacts operational efficiency. Businesses must select a freezer with adequate capacity to meet their production needs without overloading the system, which can lead to inefficiencies and product quality issues. -
Temperature Range
The temperature range of a flash freezer indicates the lowest temperature it can achieve, often below -30°C (-22°F), and the maximum temperature for effective freezing. A wider temperature range allows for versatility in freezing various food items, from delicate fruits to dense meats. It’s crucial for buyers to assess whether the temperature range meets their specific product preservation requirements. -
Energy Efficiency Rating
Energy efficiency is increasingly important for businesses seeking to reduce operational costs. Look for models with high energy efficiency ratings, which can save significant costs over time. Flash freezers designed with advanced insulation and energy-efficient compressors are typically more sustainable, aligning with eco-friendly business practices. -
Airflow System
The airflow system is responsible for distributing cold air evenly throughout the freezer. A robust airflow system prevents uneven freezing and ensures that all products maintain their quality. Buyers should consider flash freezers that utilize high-velocity fans for optimal air circulation, as this significantly enhances freezing speed and product integrity. -
Control Systems
Modern flash freezers often come with digital control systems that allow for precise temperature settings and monitoring. Features such as programmable settings and alarms for temperature deviations are crucial for maintaining product safety and quality. A user-friendly interface is essential for ease of operation, especially in busy commercial environments.
What Common Trade Terms Should Buyers Know When Purchasing Flash Freezers?
Understanding industry terminology is critical for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several essential terms related to flash freezers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When purchasing flash freezers, knowing the OEM can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the equipment, as well as understand potential warranty and support options. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially when budgeting for initial stock or evaluating supplier flexibility. It also impacts cash flow management for businesses looking to minimize inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. Buyers should prepare a comprehensive RFQ detailing their requirements, including specifications and quantities, to receive accurate and competitive pricing for flash freezers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for buyers to understand shipping costs and risks associated with importing flash freezers from overseas suppliers. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from placing an order to its delivery. It encompasses manufacturing time, shipping, and any customs clearance. For businesses that rely on timely inventory replenishment, understanding lead times can help in planning and avoiding operational disruptions. -
Warranty and Service Agreements
Warranties cover repairs or replacements for faulty equipment within a specified period. Service agreements may include regular maintenance and support. Buyers should carefully review these agreements to ensure they receive adequate protection and support for their investment in flash freezers.
In summary, a thorough understanding of both the technical properties and trade terminology associated with flash freezers enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right equipment for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the flash freezer Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Flash Freezer Sector?
The global flash freezer market is experiencing robust growth driven by an increasing demand for high-quality frozen food products and the need for efficient food preservation methods. Key drivers include the rise of food delivery services, which necessitate rapid freezing techniques to maintain product integrity and extend shelf life. Additionally, the growing awareness of food safety standards among consumers and regulatory bodies is pushing businesses to adopt advanced freezing technologies that minimize bacterial growth and preserve nutritional value.
Emerging trends in sourcing reflect a technological shift toward automation and AI integration in flash freezer operations. These innovations enhance operational efficiency, allowing businesses to optimize freezing cycles and reduce energy consumption. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics is crucial. Buyers should consider factors such as local energy costs, climatic conditions, and transportation logistics when sourcing flash freezers. The ability to test equipment performance on specific food products through freezing tests is also essential in ensuring compatibility with operational needs.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
How Can B2B Buyers Embrace Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Flash Freezer Procurement?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point in the procurement of flash freezers. The environmental impact of refrigeration technologies is significant, making it vital for businesses to seek out energy-efficient models that utilize eco-friendly refrigerants, such as R290, which have a lower global warming potential compared to traditional refrigerants.
Moreover, ethical sourcing in the flash freezer sector entails ensuring that suppliers adhere to responsible manufacturing practices, including fair labor standards and minimal environmental harm. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and energy efficiency labels can guide buyers toward making responsible purchasing decisions. Additionally, investing in equipment made from recyclable materials can further enhance a company’s sustainability profile, appealing to a growing consumer base that values environmentally-conscious practices.
What Is the Evolution of Flash Freezer Technology and Its Significance for B2B Buyers?
Flash freezer technology has evolved significantly since its inception, transitioning from basic freezing methods to sophisticated systems capable of rapid temperature reductions. Initially developed for industrial applications, flash freezing technology is now widely adopted across various sectors, including food service, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. The introduction of features such as anti-frost systems and AI-driven automation has further refined the process, enhancing efficiency and product quality.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial as it informs their purchasing decisions. The advancements in technology not only improve freezing capabilities but also ensure compliance with stringent food safety regulations. As the market continues to innovate, businesses that invest in state-of-the-art flash freezers can gain a competitive edge by ensuring product quality, reducing waste, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of flash freezer
-
How do I choose the right flash freezer for my business needs?
Selecting the right flash freezer involves evaluating your operational requirements, including the type of food you freeze, volume capacity, and freezing speed. Consider features such as energy efficiency, temperature range, and ease of maintenance. Additionally, assess the freezer’s footprint to ensure it fits within your facility. Engaging in a freezing test with sample products can provide insights into the performance and suitability of the equipment for your specific needs. -
What is the best flash freezer for preserving the quality of seafood?
For seafood preservation, look for flash freezers that offer rapid freezing capabilities and advanced air circulation systems. Models equipped with anti-frost technology are particularly effective, as they prevent ice crystal formation, which can compromise texture and flavor. Additionally, ensure the freezer can reach temperatures below -30°C (-22°F) to maintain optimal quality. Brands specializing in commercial-grade equipment often provide the best options for seafood processing. -
What are the typical payment terms when purchasing flash freezers internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include a deposit (usually 30% upfront) with the balance due prior to shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans based on credit history. It’s essential to clarify terms in the purchase agreement and consider using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit, to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How can I ensure the quality of the flash freezer I am purchasing?
To ensure quality, request certifications such as ISO, CE, or UL from potential suppliers. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and service support, as well as references from previous customers. A thorough vetting process, including factory visits or third-party inspections, can also help verify the manufacturer’s credibility and the equipment’s performance standards. Engaging in discussions about the materials and technology used in the freezer’s construction is advisable. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for flash freezers?
The MOQ for flash freezers can vary based on the manufacturer and the specific model. Some suppliers may have a MOQ of one unit for standard models, while others might require larger orders for customized or specialized units. It’s important to clarify MOQ policies during initial discussions with suppliers. If you’re unsure about your volume needs, consider starting with a single unit to assess performance before scaling up orders. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing flash freezers?
When importing flash freezers, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply. It’s essential to work with a logistics partner familiar with international shipping, particularly for heavy or oversized equipment. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of delivery timelines and handling requirements, as flash freezers may require special care during transport. Additionally, prepare for any necessary inspections or certifications upon arrival. -
What are the common customization options available for flash freezers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options, including size adjustments, specific temperature ranges, and additional features like programmable controls or enhanced insulation. Customization may also extend to aesthetics, such as color and branding. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options. Custom solutions can be particularly beneficial if your business has unique operational needs or space constraints. -
How often should I perform maintenance on my flash freezer?
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance of your flash freezer. It is recommended to conduct routine checks every three to six months, including cleaning the interior, inspecting seals, and checking air filters. Additionally, schedule professional maintenance annually to address any mechanical issues and ensure the unit operates efficiently. Keeping a maintenance log can help track service dates and any potential issues that arise over time.
Top 6 Flash Freezer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Flash Freeze – Ultra-Fast Freezing Solutions
Domain: flash-freeze.net
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Flash Freezers by Flash Freeze offer ultra-fast freezing technology designed for superior efficiency in food preservation. Key products include: 1. Blast Freezers & Blast Chillers 2. Ultra-Low Temperature Tunnel Freezer 3. Ultra-Low Temperature Medical Freezer 4. Cryogenic Freezing 5. Ultra Low Temperature Spiral Freezer. Key benefits include: extended food shelf life, optimized and automated free…
2. Avantco Refrigeration – Commercial Blast Chillers
Domain: webstaurantstore.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Commercial Blast Chillers and Flash Freezers designed for safe food handling by rapidly cooling food through the temperature danger zone where bacteria grows. Features include:
– Brands: Avantco Refrigeration, Alto-Shaam, Beverage-Air, Delfield, Eurodib, Techfrost
– Installation Types: Countertop, Freestanding
– Widths: 22-26 inches, 27-31 inches, 32-35 inches, 40-57 inches
– Chill Capacities:…
3. U-Line – Commercial Blast Chillers & Shock Freezers
Domain: u-line.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: U-Line Commercial Blast Chillers & Shock Freezers are designed to rapidly chill and shock freeze ingredients and prepared food down to safe temperatures. Key features include:
– Reduces food waste
– Minimizes preparation times
– Improves production efficiency and profitability
– Available models include:
– UCBF432-STAND: Commercial Cook and Chill Stand
– UCBF432-SS11A: Commercial 5 Tray Blast …
4. Ampto – Blast and Shock Freezers
Domain: ampto.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Blast freezers rapidly cool down hot or warm food to around 0°C (32°F) within a few hours, ideal for temporary storage of food for 24 to 48 hours, preventing bacterial growth and preserving food quality. Shock freezers rapidly freeze food to below -18°C (-0.4°F) in 30 minutes or less, suitable for long-term storage of food for weeks or months, maintaining cellular structure, taste, and appearance …
5. Get Maine Lobster – Premium Seafood & Chowder
Domain: getmainelobster.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Four 4-5 Ounce Lobster Tails – $69.99
2 Pints of Wicked Good Clam Chowda – $29.99
1 Pint of Wicked Good Clam Chowda – $16.99
Twin 4-5 Ounce Lobster Tails – $39.99
1 Pint of Lobster Bisque – $16.99
4 Whoopies – $14.99
8 Lobster Rolls – Special Price For You – $149.99
2 Pints of Lobster Bisque – $29.99
4 Grandeur 6-7oz Lobster Tails – $119.99
2 Crab Cakes – $14.99
48 Club Membership – $99.99
Momofuk…
6. Ultra-Low Temperature Freezer – Key Product
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Flash Freezer listings on eBay include various models and specifications. Key details extracted from the listings are: 1. Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers with temperatures as low as -123°F (-86°C). 2. Capacities available: 20L, 28L, and 50L. 3. Price range: $999.00 to $2,599.00. 4. Condition: Brand New. 5. Locations: Various sellers located in Chino, CA and Walnut, CA. 6. Delivery options: Some lis…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for flash freezer
In summary, the strategic sourcing of flash freezers represents a pivotal investment for businesses aiming to enhance food preservation, extend shelf life, and improve overall operational efficiency. By leveraging advanced technologies such as AI Smart Freeze and Anti-Frost systems, companies can optimize their freezing processes, ensuring that product quality remains uncompromised while boosting productivity. Furthermore, the ability to operate these machines with ease makes them accessible for various commercial settings, from large-scale food production to specialized culinary enterprises.
As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe consider their sourcing options, it’s essential to evaluate not only the initial cost but also the long-term benefits that flash freezers can provide. Look for solutions that align with your specific operational needs, ensuring energy efficiency and reliability.
In the evolving landscape of food preservation technology, embracing flash freezer solutions will not only enhance your competitive edge but also position your business for sustainable growth. Take the next step—explore the market, assess your requirements, and invest in a flash freezer that meets your needs today for a more efficient tomorrow.

Illustrative image related to flash freezer
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.