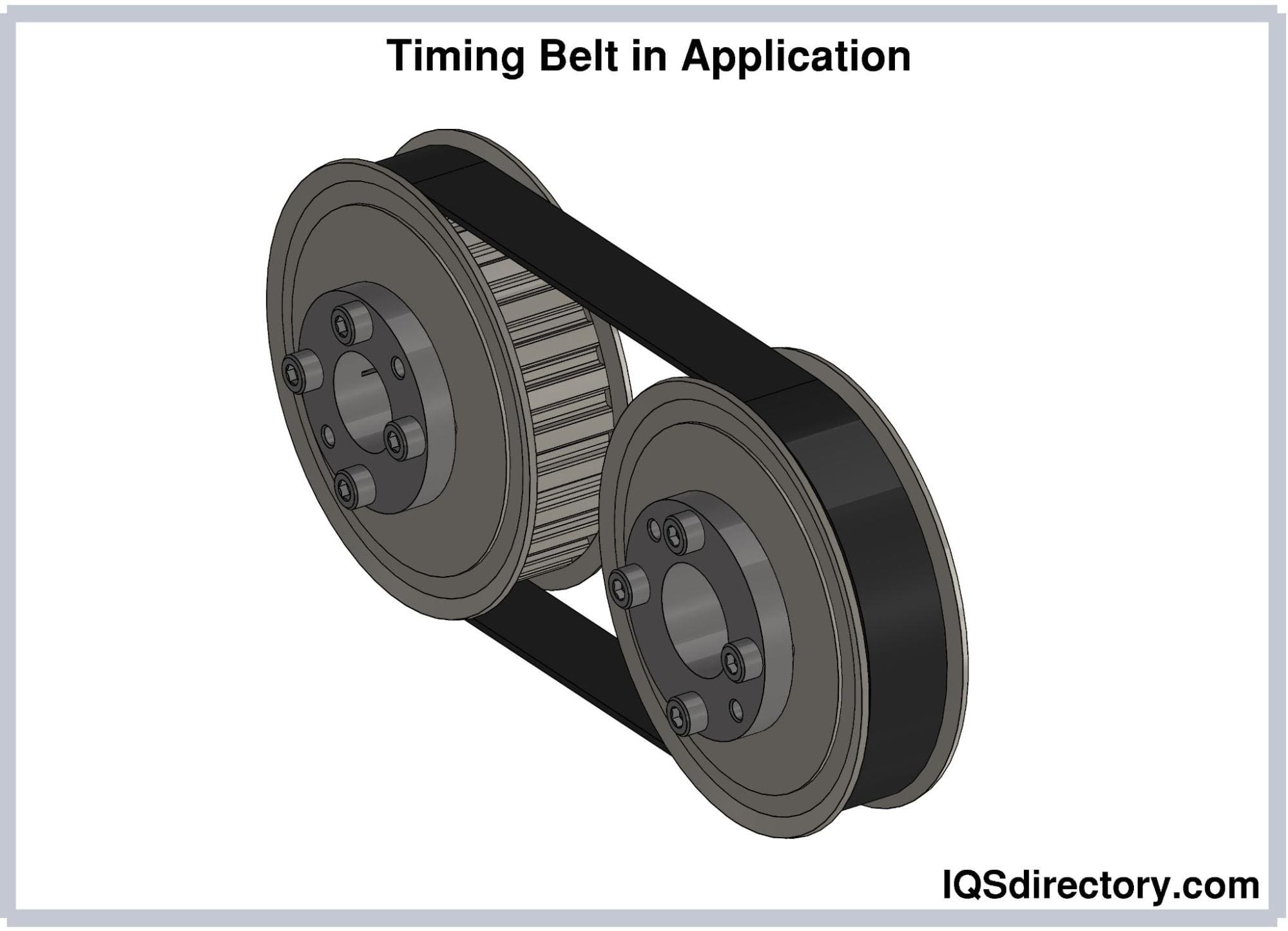
How to Source Timing Belt Types Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for timing belt types
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, sourcing the right timing belt types can pose a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Timing belts are essential components in a multitude of applications, from automotive engines to manufacturing machinery, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently. However, with various types of timing belts available, each suited for specific applications and conditions, navigating this landscape requires a keen understanding of the options available.
This comprehensive guide delves into the different types of timing belts, their specific applications, and the materials used in their construction. It also addresses critical aspects such as supplier vetting processes and cost considerations, empowering international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are a manufacturer in Brazil seeking robust solutions for your production line or a distributor in Germany looking for reliable suppliers, this guide offers valuable insights tailored to your unique market needs.
By exploring the nuances of timing belts, from the traditional rubber variants to advanced polyurethane and fabric options, this guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to optimize their procurement strategies. Understanding these factors will not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to long-term success in competitive markets.
Understanding timing belt types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Timing Belts | Traditional material, often with teeth for precise timing | Automotive engines, general machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Prone to wear over time, less durable than modern materials. |
| Polyurethane Timing Belts | High elasticity, chemical resistance, and superior load capacity | Conveyor systems, packaging machinery | Pros: Long-lasting, low maintenance. Cons: Higher initial cost compared to rubber. |
| Fabric Timing Belts | High tensile strength, low friction, and high-temperature resistance | High-performance drives, robotics | Pros: Excellent for high torque applications. Cons: May require specialized handling and care. |
| Steel Reinforced Timing Belts | Enhanced durability and strength due to steel reinforcement | Heavy machinery, industrial automation | Pros: High load capacity, longer lifespan. Cons: Heavier and may require more complex installation. |
| Timing Chains | Metal construction, requires lubrication, and operates quietly | Automotive engines, heavy-duty machinery | Pros: Long lifespan, less frequent replacement. Cons: Can be noisy, more complex maintenance. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Rubber Timing Belts?
Rubber timing belts are the most common type found in automotive applications, especially in older models. Their design typically includes teeth that ensure precise synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft. While they are cost-effective and readily available, buyers should consider their susceptibility to wear and environmental factors such as heat and oil. When purchasing, it is essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the application, including operating conditions and replacement intervals.
How Do Polyurethane Timing Belts Compare in Durability and Performance?
Polyurethane timing belts are known for their high elasticity and resistance to a range of chemicals, making them suitable for various industrial applications. They excel in environments that require high load capacities and low maintenance. While they may come at a higher initial investment, the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs, particularly in terms of reduced downtime and maintenance needs. Buyers should assess their operational demands and consider the potential return on investment when choosing these belts.
In What Situations Are Fabric Timing Belts the Best Choice?
Fabric timing belts are designed for high-performance applications where extreme acceleration and torque are necessary. Their unique composition provides exceptional tensile strength and tear resistance, making them ideal for robotics and other demanding environments. However, these belts often require specialized handling and may not be suitable for all applications. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific performance criteria of their machinery to determine if fabric belts meet their needs.
What Advantages Do Steel Reinforced Timing Belts Offer for Heavy Machinery?
Steel reinforced timing belts are engineered for heavy-duty applications, offering enhanced durability and load-bearing capabilities. Their metal reinforcement allows them to withstand higher stresses, making them ideal for industrial automation and heavy machinery. While they provide a longer lifespan, they are heavier and may necessitate more complex installation processes. Buyers should consider the operational environment and the potential need for specialized equipment when selecting these belts.
Why Should Buyers Consider Timing Chains for Long-Term Use?
Timing chains are a robust alternative to timing belts, constructed from metal and designed for longevity. They operate quietly and require regular lubrication, making them suitable for heavy-duty machinery and automotive engines. While they typically have a longer lifespan and require less frequent replacement, they can be noisier and may involve more complex maintenance. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced replacement frequency against the need for ongoing maintenance when considering timing chains for their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of timing belt types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Timing Belt Types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine Timing Systems | Ensures precise timing for optimal engine performance | Material durability, temperature resistance, compatibility with engine types |
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Facilitates efficient material handling and processing | Load capacity, resistance to chemicals, ease of maintenance |
| Textile | Weaving and Knitting Machines | Enhances production speed and product quality | High tensile strength, low friction, resistance to wear |
| Food & Beverage | Packaging and Processing Equipment | Maintains hygiene and operational efficiency | Compliance with food safety standards, ease of cleaning |
| Robotics & Automation | Motion Control Systems | Increases precision and reliability in automated processes | Precision engineering, compatibility with existing systems |
How Are Timing Belt Types Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, timing belts are crucial for synchronizing the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft in internal combustion engines. This synchronization ensures that engine valves open and close at the correct times, which is vital for optimal performance and efficiency. Issues such as misalignment can lead to severe engine damage, making timely replacement essential. Buyers must consider the durability of materials, resistance to heat and oil, and compatibility with various engine types, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures or varying fuel qualities.
What Role Do Timing Belts Play in Manufacturing Conveyor Systems?
In manufacturing, timing belts are integral to conveyor systems, where they transport materials and products efficiently through various stages of production. Their design allows for precise control over the speed and timing of the conveyor, which is essential for maintaining productivity and reducing waste. Buyers should focus on the load capacity of the belts, resistance to chemicals, and ease of maintenance, especially in environments where they may be exposed to harsh conditions or require regular cleaning.
How Are Timing Belts Essential in Textile Machinery?
Timing belts are widely used in textile machinery, such as weaving and knitting machines, where they help maintain the speed and accuracy of production. These belts enable the synchronization of various machine components, which is crucial for producing high-quality textiles without defects. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize high tensile strength and low friction properties, as well as resistance to wear, to ensure long-lasting performance in high-speed operations.
Why Are Timing Belts Critical in Food & Beverage Processing?
In the food and beverage industry, timing belts are used in packaging and processing equipment to facilitate efficient operations while maintaining hygiene standards. These belts must be made from materials that comply with food safety regulations and are easy to clean to prevent contamination. Buyers should consider the belts’ resistance to oils and chemicals, as well as their ability to withstand frequent cleaning cycles, ensuring smooth and safe operations.
What Advantages Do Timing Belts Offer in Robotics & Automation?
In robotics and automation, timing belts are essential for motion control systems, providing precise and reliable movement for various robotic applications. They help enhance the efficiency and accuracy of automated processes, which is critical in industries such as electronics and assembly. When sourcing timing belts for these applications, buyers should focus on precision engineering, compatibility with existing systems, and the ability to handle varying loads and speeds, ensuring optimal performance in automated environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘timing belt types’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Compatibility Across Diverse Machinery
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges when sourcing timing belts for machinery that has been manufactured by different companies over the years. The diversity of timing belt types, sizes, and specifications can lead to compatibility issues. For instance, a buyer may discover that the timing belt they sourced does not fit the specific model of their equipment, resulting in costly downtime and the need for additional sourcing efforts. This problem is exacerbated in regions where access to a wide range of products is limited, making it crucial to ensure that the selected timing belt meets the necessary specifications.
The Solution:
To overcome compatibility challenges, buyers should implement a systematic approach to sourcing timing belts. First, they should compile a comprehensive inventory of their machinery, including model numbers and specifications for existing timing belts. With this data, they can consult with manufacturers or suppliers to identify compatible timing belt options. Utilizing digital tools or platforms that provide cross-reference capabilities can also streamline this process. Additionally, establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers who offer a diverse range of timing belts ensures that buyers can quickly access the products they need, minimizing downtime. Regular training for staff on the specifications and requirements of timing belts can further reduce the likelihood of sourcing errors.
Scenario 2: Navigating Material Selection for High-Performance Applications
The Problem:
In industries such as automotive or manufacturing, buyers may struggle with selecting the appropriate timing belt material for high-performance applications. Many buyers are unaware of how material properties, such as heat resistance and tensile strength, impact the performance and longevity of timing belts. Using the wrong material can lead to premature wear, breakdowns, and even catastrophic failures, resulting in significant costs and operational delays.

Illustrative image related to timing belt types
The Solution:
To navigate material selection effectively, buyers should conduct thorough research on the specific requirements of their applications. They should assess factors such as operating temperature, load conditions, and exposure to chemicals or abrasives. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in timing belts can provide valuable insights into the best material choices for specific applications. For example, polyurethane timing belts may be ideal for environments with high chemical exposure, while reinforced rubber belts might be better for standard automotive applications. Buyers should also consider requesting samples or conducting performance tests before making bulk purchases. This proactive approach not only ensures optimal performance but also enhances the longevity of the machinery involved.
Scenario 3: Implementing Effective Maintenance Strategies to Extend Lifespan
The Problem:
A frequent pain point for B2B buyers is the maintenance of timing belts, which is crucial for ensuring long-term performance and reliability. Many businesses do not have a structured maintenance program in place, leading to unexpected failures and costly repairs. As timing belts wear out or lose tension over time, the lack of regular inspections can result in operational inefficiencies and potential damage to connected components.
The Solution:
To implement effective maintenance strategies, buyers should develop a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections and replacements based on the manufacturer’s recommendations. This schedule should account for the specific conditions in which the machinery operates, such as temperature fluctuations and exposure to contaminants. Utilizing monitoring tools that track belt wear and tension can help identify issues before they lead to failure. Additionally, training maintenance personnel on the importance of timing belt upkeep and providing them with the necessary resources can enhance compliance with maintenance schedules. By prioritizing maintenance, buyers can significantly extend the lifespan of their timing belts and avoid unplanned downtime, ultimately contributing to a more efficient operational environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for timing belt types
What Are the Key Properties of Rubber Timing Belts?
Rubber timing belts are the traditional choice for many applications, particularly in internal combustion engines. They are known for their flexibility and ability to absorb vibrations, which is crucial in high-speed applications. The temperature rating typically ranges from -30°C to 80°C, making them suitable for various environments. However, they can degrade over time due to exposure to heat and oils, which can lead to a loss of tension and performance.
Pros include cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing, making them a popular choice for mass production. However, cons involve limited lifespan under extreme conditions, necessitating regular maintenance and replacement. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local climate conditions and the potential for oil exposure is vital for selecting the appropriate rubber timing belt.
How Do Polyurethane Timing Belts Compare?
Polyurethane timing belts have gained popularity due to their superior elasticity and resistance to wear and tear. They can withstand temperatures ranging from -20°C to 80°C and are resistant to chemicals and oils, making them ideal for various industrial applications. Their high tensile strength and load capacity enable them to perform well in demanding environments.
The advantages of polyurethane belts include their durability and lower maintenance needs, which can translate to cost savings in the long run. However, they tend to be more expensive than rubber belts, which could be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers. For B2B buyers in Europe, compliance with standards such as DIN or ASTM for material safety and performance is crucial when selecting polyurethane belts.

Illustrative image related to timing belt types
What Are the Benefits of Fabric Timing Belts?
Fabric timing belts are engineered for high-performance applications, particularly where high torque and acceleration forces are required. They are designed to operate efficiently in extreme conditions, with temperature ratings often exceeding those of rubber and polyurethane belts. Their unique construction allows for low friction and high tear resistance.
The key advantage of fabric belts is their ability to handle high loads without significant wear, making them suitable for specialized machinery. However, their disadvantage lies in their higher manufacturing complexity and cost. For international buyers, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, ensuring that fabric timing belts meet specific industry standards is essential for operational reliability.
What Should Buyers Consider When Selecting Timing Belt Materials?
When selecting timing belt materials, buyers must consider the specific application and environmental conditions. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stress play a significant role in material performance. Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS, is also critical for ensuring product quality and safety.
In regions with diverse climates, such as Africa and South America, it is essential to choose materials that can withstand local conditions. Additionally, understanding the supply chain and availability of specific materials can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
| Material | Typical Use Case for Timing Belt Types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Internal combustion engines, general machinery | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited lifespan under extreme conditions | Low |
| Polyurethane | Industrial applications, conveyor systems | High durability and chemical resistance | Higher initial cost compared to rubber | Med |
| Fabric | High-performance machinery, robotics | Excellent tensile strength and low friction | More complex manufacturing process | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for timing belt types
What Are the Main Stages of Timing Belt Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing of timing belts is a multi-stage process that requires precision and quality control to ensure optimal performance in various applications. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to timing belt types
How Is Material Prepared for Timing Belt Production?
Material preparation is the foundational step in timing belt manufacturing. This stage involves selecting high-quality materials that meet specific performance requirements. Common materials used include rubber, polyurethane, and fabric composites.
For rubber belts, a mixture of natural and synthetic rubber compounds is formulated, often incorporating additives to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors. Polyurethane belts undergo a similar process, where the formulation is adjusted based on the desired elasticity and temperature resistance. Quality assurance starts here, as the materials are tested for consistency, tensile strength, and other properties before moving to the next stage.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Process of Timing Belts?
The forming process involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired belt configuration. This is typically achieved through extrusion or molding techniques.
In extrusion, the rubber or polyurethane is forced through a die to create a continuous length of belt with specific tooth profiles. The teeth are essential for the belt’s function, as they engage with corresponding pulleys to maintain timing. For molded belts, materials are poured into pre-shaped molds and cured under controlled conditions to achieve the final shape and properties.

Illustrative image related to timing belt types
How Are Timing Belts Assembled?
Once formed, timing belts may require assembly, particularly if they incorporate additional components like tensioners or reinforcements. This stage often involves sewing or bonding fabric layers to enhance strength and flexibility.
For specialized applications, such as high-torque settings, additional reinforcements may be added to the belt. Assembly is critical, as any misalignment or improper bonding can lead to performance failures.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Applied to Timing Belts?
Finishing processes include cutting the belts to specific lengths, applying surface treatments for additional protection, and conducting final inspections. The finishing stage ensures that all belts meet the exact specifications required by customers.
Quality checks during this phase often involve measuring the belt’s width, length, and tooth profile accuracy. Any deviations from standards can result in reworking or rejection of the product.

Illustrative image related to timing belt types
What Are the Key Quality Control Standards for Timing Belts?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in timing belt manufacturing, particularly for B2B buyers concerned with reliability and performance. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for effective quality management systems.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications, such as CE for safety and compliance in the European market or API for oil and gas applications, may also be relevant. These certifications ensure that the products not only meet quality benchmarks but also comply with regulatory requirements.
How Is Quality Control Implemented Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line. Testing may include tensile strength tests, chemical composition analysis, and dimensional inspections.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, real-time monitoring is conducted to ensure that the production parameters remain within specified limits. This includes checking the temperature and pressure in molding processes or measuring dimensions during extrusion.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the timing belts are finished, a comprehensive inspection is performed. This may involve functional testing, visual inspections, and measurement of critical dimensions to ensure they conform to specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Timing Belt Quality?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure that timing belts meet performance standards. These include:
-
Tensile Testing: This assesses the strength of the belt materials and determines how much load they can withstand before failure.
-
Abrasion Testing: This evaluates the durability of the belt under conditions that simulate real-world wear and tear.
-
Temperature Resistance Testing: Belts are exposed to extreme temperatures to ensure they can operate effectively in diverse environments.
-
Fatigue Testing: This checks how well the belt can endure repeated flexing and stress over time, which is particularly important in high-performance applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Buyers can take several steps to ensure compliance and quality:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insight into the supplier’s quality management practices. This includes evaluating their adherence to international standards and internal QC processes.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and compliance certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can add an additional layer of assurance. These agencies can perform evaluations at various stages of production and provide objective reports.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certifications is vital. Different regions may have varying requirements for compliance and safety standards. For instance:
-
European Standards: CE marking is mandatory for products sold in the EU, ensuring they meet safety and environmental requirements.
-
Middle Eastern and African Markets: Local regulations may vary significantly, and buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with regional standards that may not be as stringent as those in Europe.
-
Documentation and Transparency: Buyers should insist on clear documentation of quality control processes and certifications. This transparency can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing from international suppliers.
By being diligent in assessing manufacturing processes and quality control measures, B2B buyers can ensure they procure reliable and high-performing timing belts suitable for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘timing belt types’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure various types of timing belts. Timing belts are critical components in numerous applications, particularly in power transmission systems and internal combustion engines. Understanding the nuances of timing belt types and their specifications will ensure you make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clarify the technical specifications of the timing belts you need. Consider factors such as size, material, tooth profile, and load capacity.
– Material Considerations: Decide whether rubber, polyurethane, or fabric belts best suit your application.
– Operational Environment: Assess temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical load to determine durability requirements.

Illustrative image related to timing belt types
Step 2: Research Available Timing Belt Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of timing belts available in the market. Each type serves unique functions and has distinct characteristics.
– Rubber Timing Belts: Common in traditional applications, but may degrade over time.
– Polyurethane Timing Belts: Known for their elasticity and resistance to chemicals, making them suitable for high-load applications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
– Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials to gauge reliability and customer satisfaction.
– Certifications: Ensure suppliers have relevant industry certifications that reflect quality and safety standards.
Step 4: Analyze Pricing and Terms of Supply
Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Take into account not only the initial cost but also the terms of supply, including delivery timelines and payment conditions.
– Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing for larger orders, which could result in significant savings.
– Warranty and Return Policies: Understand the warranty coverage for the timing belts and return policies in case of defects.
Step 5: Conduct Quality Assurance Checks
Implement quality assurance measures to ensure the timing belts meet your specifications and standards. Request samples for testing before finalizing any orders.
– Testing Protocols: Develop a testing protocol to assess tensile strength, durability, and compatibility with your equipment.
– Inspection Standards: Establish clear inspection criteria to evaluate the belts upon delivery.
Step 6: Confirm After-Sales Support and Technical Assistance
After securing your supplier, verify the availability of after-sales support and technical assistance. This is vital for ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting.
– Technical Documentation: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive documentation, including installation guides and maintenance instructions.
– Customer Support: Assess the responsiveness and expertise of the customer support team in addressing any issues that may arise.
Step 7: Establish Long-Term Relationships with Suppliers
Building long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can enhance your procurement strategy. Regular communication fosters collaboration and can lead to better pricing and support.
– Feedback Loop: Create a mechanism for providing feedback on product performance and service quality.
– Partnership Opportunities: Explore opportunities for joint ventures or exclusive deals for future projects.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing timing belts, ensuring they select the right products for their operational needs while establishing reliable supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for timing belt types Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Timing Belt Types Sourcing?
When sourcing timing belts, it’s essential to understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly influences cost. Traditional rubber belts are generally less expensive than high-performance polyurethane or fabric belts. Advanced materials may also incur additional costs due to their enhanced durability and specific applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location and the complexity of the timing belt design. Regions with lower labor costs can provide competitive pricing, but this may come at the expense of quality control.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, ultimately impacting pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for tooling can be substantial, especially for custom designs. This cost can be amortized over larger production runs, making it essential to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs).
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability, particularly for critical applications in engines. Enhanced QC measures can increase costs but are crucial for maintaining standards and certifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are vital considerations, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and the chosen Incoterms can significantly affect the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market conditions. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Timing Belt Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of timing belts, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to volume discounts, while low MOQs can drive up individual unit costs. B2B buyers should assess their needs to optimize order sizes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements can lead to higher prices. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the choice of materials directly affects pricing. High-performance materials may offer long-term savings through reduced maintenance and longer lifespans.
-
Quality and Certifications: Timing belts that meet international standards or specific certifications (e.g., ISO, SAE) may come at a premium. However, they often provide assurance of quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer companies may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can affect the total landed cost. For instance, DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) includes all shipping and customs fees, while FOB (Free On Board) places more responsibility on the buyer, potentially affecting cost calculations.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Timing Belt Prices?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency in timing belt sourcing:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for bulk orders. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts based on order size or long-term contracts.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, including maintenance, replacement frequency, and operational efficiency, rather than just the upfront cost. This holistic approach can lead to better long-term investments.
-
Research Market Prices: Conduct thorough market research to understand prevailing prices for different types of timing belts. This knowledge can bolster negotiation efforts.
-
Assess Supplier Capabilities: Investigate suppliers’ manufacturing capabilities and quality assurance processes. A supplier with robust QC might justify a higher price due to their reliability.
-
Factor in International Pricing Nuances: For international buyers, currency fluctuations, local tariffs, and import duties can significantly affect pricing. Keep these factors in mind when budgeting.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for timing belts can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. The information provided serves as a general guideline, and buyers are encouraged to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing timing belt types With Other Solutions
Introduction to Timing Belt Alternatives
In the realm of mechanical systems, timing belts are crucial components that ensure precise synchronization between various moving parts. However, there are alternative solutions that can achieve similar objectives, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives is essential for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their operations and make informed purchasing decisions.
Comparison of Timing Belt Types with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Timing Belt Types | Timing Chain | Gear Drive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in synchronization; ideal for applications requiring exact timing. | Durable and long-lasting; less prone to slippage but can be noisier. | Excellent load capacity and torque transmission; suited for heavy-duty applications. |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate cost; replacement required at intervals. | Higher initial cost due to complexity; lower long-term replacement costs. | Higher upfront investment; potentially lower maintenance costs over time. |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward installation; requires tensioning adjustments. | More complex installation; requires precise alignment and lubrication. | Installation can be intricate; may require custom fittings and adjustments. |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections and periodic replacements recommended; sensitive to environmental factors. | Requires regular lubrication; generally low maintenance. | Minimal maintenance; robust design leads to longer intervals between servicing. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for automotive engines and conveyor systems where precision is critical. | Best for high-performance engines where durability is key. | Suitable for industrial applications that require high torque and load handling. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Timing Chain
Timing chains offer a robust alternative to timing belts, particularly in high-performance automotive applications. Made from metal, they provide greater durability and are less susceptible to wear and tear compared to rubber belts. However, they are often noisier and require regular lubrication to function optimally. The initial installation cost can be higher due to the complexity of the system, but they tend to last longer, which can offset replacement costs over time.
Gear Drive
Gear drives are another viable alternative that excels in heavy-duty applications where high torque and load capacities are essential. They provide a direct means of power transmission without the slippage that belts might experience. While gear drives can be more costly upfront and may require custom designs for specific applications, their long lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements make them an attractive option for industries focused on durability and reliability.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between timing belt types and their alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Timing belts are ideal for situations where precision is paramount, while timing chains and gear drives may be more suitable for applications demanding durability and high torque. By evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and ensure optimal performance in their mechanical systems.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for timing belt types
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Timing Belts?
Understanding the critical technical properties of timing belts is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. These properties can significantly impact the performance, longevity, and overall efficiency of the systems in which they are employed.
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a timing belt often dictates its performance characteristics. Common materials include rubber, polyurethane, and fabric composites. Each material offers unique properties like elasticity, temperature resistance, and chemical durability. For instance, polyurethane belts excel in high-load applications and are resistant to oils and chemicals, making them suitable for diverse industrial environments. Selecting the right material grade ensures compatibility with operational demands, thereby reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of the timing belt, particularly in its width, length, and thickness. Tight tolerances are crucial for applications requiring precise synchronization, such as automotive engines. In contrast, looser tolerances may be acceptable in less critical applications. Understanding tolerances is vital for ensuring that belts fit correctly within their systems, which minimizes wear and maximizes efficiency.
3. Tooth Profile
The tooth profile of a timing belt is designed to engage with corresponding pulleys effectively. Different profiles (e.g., trapezoidal, rounded, or curvilinear) affect how the belt transmits power and maintains tension. The right tooth profile is essential for optimal performance, as it influences the belt’s grip and resistance to slippage. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate tooth profile can lead to improved energy efficiency and reduced operational noise.
4. Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum load a timing belt can withstand during operation without failure. This property is critical for applications where high torque is involved. Different applications—such as automotive engines versus industrial machinery—will have varying load requirements. By understanding load capacity, buyers can choose belts that meet their specific operational needs, ultimately enhancing system reliability.
5. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range defines the extremes of temperature within which the timing belt can function effectively. Some belts are designed to operate in high-temperature environments, while others may be suited for colder conditions. It’s crucial to select a timing belt that aligns with the specific temperature conditions of the application to prevent premature wear or failure.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Associated with Timing Belts?
Navigating the terminology associated with timing belts can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication with suppliers.

Illustrative image related to timing belt types
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand name. In the context of timing belts, OEM parts are typically made to the exact specifications of the original components. B2B buyers often prefer OEM timing belts for their reliability and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure that they are not over-committing to stock that may not be needed. This term is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to optimize shipping costs and inventory levels.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process in which a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products. For timing belts, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, delivery times, and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better purchasing decisions.
Illustrative image related to timing belt types
4. Incoterms
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are standardized terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers, particularly those involved in cross-border transactions, as these terms define who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transit.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in industries where timing belts are integral to production processes. Effective lead time management helps ensure that operations remain uninterrupted.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions that align with their operational needs, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the timing belt types Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Timing Belt Types Sector?
The timing belt market is experiencing significant transformation driven by several global factors. Increased automotive production, particularly in emerging markets such as Brazil and South Africa, is amplifying demand for both traditional rubber timing belts and advanced materials like polyurethane. Additionally, advancements in technology are leading to more efficient manufacturing processes, enabling suppliers to offer high-performance timing belts with enhanced durability and reduced noise levels.
Another notable trend is the shift towards automation in manufacturing and industrial applications, which is increasing the reliance on precision-engineered timing belts. As industries seek to improve efficiency and reduce downtime, the demand for timing belts that can withstand higher loads and offer longer service life is growing. Moreover, international B2B buyers are increasingly sourcing from suppliers that demonstrate agility and innovation in their product offerings, particularly those that can customize timing belts for specific applications.
Sourcing strategies are also evolving, with a focus on building resilient supply chains. This includes diversifying suppliers and integrating digital tools for better visibility and tracking of components. As a result, B2B buyers are keenly interested in understanding the sourcing landscape to ensure they can meet their operational needs effectively.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Timing Belt Types Sector?
Environmental sustainability is becoming a critical concern within the timing belt industry. The production of timing belts can have significant environmental impacts due to the materials used and the processes involved. Consequently, many companies are now prioritizing sustainable practices and materials in their supply chains. This includes the adoption of eco-friendly rubber compounds and the use of recycled materials, which help to reduce the overall carbon footprint.
Ethical sourcing has also gained traction, as buyers increasingly demand transparency in their supply chains. Suppliers that adhere to ethical standards and can provide certifications for their materials—such as those indicating low environmental impact or fair labor practices—are viewed more favorably. This trend is particularly strong among buyers in Europe, where regulatory pressures for sustainability are intensifying.
Furthermore, the push for “green” certifications is influencing product design and development. Manufacturers are exploring alternative materials that not only perform well but also align with environmental goals. As a result, international B2B buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers that emphasize sustainability, as this can enhance brand reputation and ensure compliance with global environmental standards.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Timing Belts and Their Significance in B2B?
The evolution of timing belts has been marked by significant advancements in materials and technology. Traditionally, timing belts were made from thick rubber compounds, which were adequate for the automotive industry for decades. However, as engine designs became more complex and performance demands increased, the limitations of rubber became apparent, particularly in terms of durability and heat resistance.
In response, manufacturers began experimenting with advanced materials such as polyurethane and reinforced composites, which provide superior tensile strength and longevity. This evolution has not only improved the reliability of timing belts but has also expanded their applications beyond automotive use into sectors like manufacturing, robotics, and automation.
As the market continues to evolve, understanding these historical trends enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions about sourcing timing belts that meet their specific operational requirements. The focus on innovation and the integration of advanced materials have positioned timing belts as essential components in modern machinery and systems, making them a critical consideration in any B2B procurement strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of timing belt types
-
How do I choose the right timing belt type for my application?
Selecting the appropriate timing belt type involves considering several factors including the application requirements, load capacity, and environmental conditions. For example, rubber belts are suitable for standard automotive applications, while polyurethane belts are ideal for high-load and abrasive environments. Assess the speed, torque, and temperature ranges that your application will encounter, and consult with suppliers to understand material specifications and recommended uses. Additionally, consider the compatibility with existing machinery to ensure optimal performance. -
What is the best timing belt material for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, polyurethane timing belts are often the best choice due to their superior elasticity and heat resistance compared to rubber belts. They maintain performance under extreme conditions and offer higher tensile strength, making them suitable for industries like manufacturing and automotive where temperature fluctuations are common. Always verify the specific temperature ratings provided by manufacturers to ensure the selected material meets your operational needs. -
How can I ensure the quality of timing belts from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of timing belts from suppliers, look for certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards that indicate adherence to quality management systems. Request samples for testing and validate their performance in your specific application. Additionally, check customer reviews and references, and consider suppliers with a proven track record in your industry. Establishing clear communication regarding your quality expectations is also essential. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for timing belts?
Minimum order quantities for timing belts can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of belt being ordered. Generally, MOQs can range from 50 to 1,000 units depending on the material, size, and customization requirements. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their flexibility on MOQs, especially if you are testing a new product line or entering a new market. Some suppliers may offer reduced MOQs for first-time orders or larger contracts. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing timing belts internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of timing belts typically range from 30% upfront payment to full payment upon shipment. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms depending on your relationship and order size. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring mutual security. Utilizing letters of credit or escrow services can also provide additional protection for both parties in international transactions. -
How do logistics impact the sourcing of timing belts?
Logistics play a critical role in the sourcing of timing belts, affecting lead times, shipping costs, and overall supply chain efficiency. When selecting a supplier, consider their location, shipping methods, and reliability in meeting delivery schedules. International buyers should also be aware of customs regulations, import duties, and potential delays. Collaborating with logistics providers can help streamline the process and mitigate risks associated with international shipping. -
Can I customize timing belts for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for timing belts to meet specific application requirements. Customizations can include alterations in size, material composition, tooth profiles, and even branding. When seeking customization, provide detailed specifications and intended use to the supplier. This ensures that the final product aligns perfectly with your operational needs and enhances performance. -
What should I consider when replacing timing belts in machinery?
When replacing timing belts in machinery, consider factors such as the operating conditions, the age of other components (like tensioners), and the recommended replacement intervals provided by the manufacturer. Ensure that the new belt matches the specifications of the original to maintain compatibility. Additionally, use this opportunity to inspect related components for wear and tear, which can prevent future breakdowns and optimize machinery performance.
Top 6 Timing Belt Types Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. RS Components – Timing Belts
Domain: uk.rs-online.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Timing belts, also known as cambelts, are devices fitted to rotary mechanisms in power transmission systems, primarily found in internal combustion engines. They connect the crankshaft to the camshafts to maintain precise alignments. Commonly made from thick rubber, modern variants can be constructed from high-tech materials. Timing belts are crucial for the smooth operation of engines, ensuring o…
2. Tyma – Timing Belts Identification Guide
Domain: tyma.eu
Introduction: Timing Belts Identification Guide: 1. Material: Common materials are rubber (black, usually fiberglass) and polyurethane (light plastic, usually with steel fiber). 2. Types and Pitch: Common types include HTD (rounded teeth) and STD (squared teeth). Pitch measurements vary: HTD pitch is typically 8mm, while plastic belts are often 10mm. Common belt types by pitch include HTD: 3M, 5M, 8M, 14M; STD:…
3. FEC Consulting – Neoprene Timing Belts
Domain: fecconsulting.dk
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: This company, FEC Consulting – Neoprene Timing Belts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. GlobalSpec – Timing Belts (Metric)
Domain: globalspec.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Timing belts (metric) are designed for power transmission systems where maintenance-of-speed ratio is crucial. Key specifications include:
– Pitches: T (2.5mm, 5mm, 10mm, 20mm), AT (5mm, 10mm, 20mm), GT (2mm, 3mm, 5mm), HTD (3mm, 5mm, 8mm, 14mm, 20mm), Super-Torque (2mm to 14mm), FHT (1mm, 2mm, 3mm).
– Types: Double-sided, truly endless, and open-ended.
– Materials: Neoprene, Polyurethane, Rubber…
5. AllData – Timing Belt Engine Types
Domain: alldata.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, AllData – Timing Belt Engine Types, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Megadyne Group – Timing/Synchronous Belts
Domain: megadynegroup.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Timing/Synchronous Belts are used to modify speeds and relay torque from electric motors to driven equipment. They require proper alignment for longevity and offer safety and efficiency benefits. Key features include:
– Positive engagement with toothed sprockets to prevent speed loss and slippage.
– Belt teeth shapes: trapezoidal, curvilinear, or modified curvilinear.
– Resistance to corrosion and…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for timing belt types
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of timing belts is essential for maintaining operational efficiency across various industries. Understanding the differences between types such as rubber, polyurethane, and fabric belts enables buyers to select the most appropriate solutions for their specific applications. Moreover, recognizing the importance of timely replacements can prevent costly downtimes and extend the lifecycle of machinery.
As B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize their operations, prioritizing high-quality timing belts and reliable suppliers becomes crucial. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, companies can ensure they are equipped with the best materials suited for their unique environments, whether in automotive, industrial machinery, or other sectors.
Looking forward, the evolution of timing belt technology presents new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. As materials advance, incorporating energy-efficient and durable options will be key to maintaining competitive advantage. We encourage international buyers to actively engage with suppliers to explore the latest advancements in timing belt solutions, ensuring that their operations remain at the forefront of industry standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.