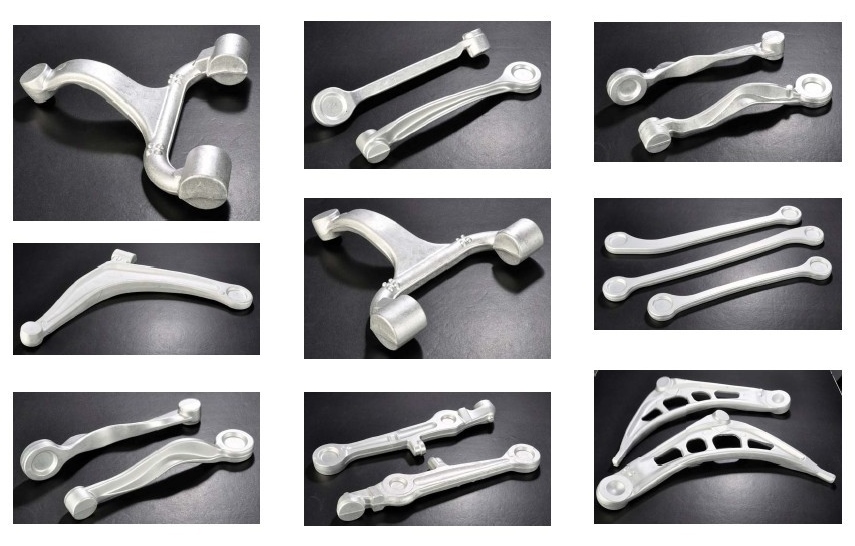
Is Your Forge Aluminium Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for forge aluminium
Navigating the complexities of sourcing forge aluminium presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications ranging from automotive components to architectural elements, the need for reliable information on the various types of aluminium alloys, their properties, and appropriate forging techniques is paramount. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the global market for forge aluminium, including insights on alloy selection, forging temperatures, and quality standards.
By understanding the nuances of aluminium forging, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Vietnam—can make informed purchasing decisions. The guide also covers essential aspects such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and market trends, ensuring that businesses can identify reputable partners and secure competitive pricing.
Equipped with this knowledge, B2B buyers will be better positioned to navigate the global aluminium forging landscape, enhancing their procurement strategies and ultimately driving operational efficiencies. Whether you are looking to expand your product offerings or streamline your supply chain, this guide serves as an invaluable resource for making strategic decisions in the forge aluminium market.
Understanding forge aluminium Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 Aluminum | High strength, excellent corrosion resistance | Aerospace, automotive, architectural | Pros: Strong, versatile; Cons: More expensive than lower-grade alloys. |
| 1100 Aluminum | Excellent workability, high ductility | Food processing, chemical handling | Pros: Easy to form and weld; Cons: Lower strength compared to other alloys. |
| 6063 Aluminum | Good extrudability, medium strength | Architectural components, window frames | Pros: Aesthetic finish; Cons: Not suitable for high-stress applications. |
| 7075 Aluminum | Very high strength, lightweight | Military, aerospace | Pros: Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio; Cons: Difficult to weld and machine. |
| 2024 Aluminum | High strength, fatigue-resistant | Aircraft structures, military vehicles | Pros: Excellent fatigue resistance; Cons: Prone to corrosion without treatment. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 6061 Aluminum for B2B Buyers?
6061 aluminum is known for its exceptional strength and versatility, making it a top choice in various industries, including aerospace and automotive. It has excellent corrosion resistance and can be easily forged or welded. When considering purchasing 6061, B2B buyers should evaluate the specific strength requirements of their applications, as well as the cost implications, since it tends to be pricier than lower-grade alternatives.
How Does 1100 Aluminum Stand Out for Industrial Applications?
1100 aluminum is characterized by its excellent workability and high ductility, making it ideal for applications requiring intricate shapes, such as in food processing and chemical handling. Its ability to be easily formed and welded allows for cost-effective manufacturing processes. However, buyers should note that while it is easy to work with, it does not offer the same strength as other alloys, which may limit its use in more demanding environments.
Why Choose 6063 Aluminum for Architectural Projects?
6063 aluminum is favored for its good extrudability and aesthetic finish, making it a popular choice in architectural applications, such as window frames and decorative elements. It offers a balance of strength and workability, but it is not suitable for high-stress applications. Buyers should assess whether the aesthetic benefits align with their project needs and consider the potential trade-offs in strength.
What Advantages Does 7075 Aluminum Provide in Critical Applications?
7075 aluminum is renowned for its very high strength and lightweight properties, making it the preferred choice for military and aerospace applications. Its strength-to-weight ratio is exceptional, which is critical in applications where weight savings are paramount. However, its difficulty in welding and machining may pose challenges for some manufacturers, making it essential for buyers to consider their fabrication capabilities when selecting this alloy.
How Does 2024 Aluminum Perform in Terms of Strength and Durability?
2024 aluminum is known for its high strength and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for aircraft structures and military vehicles. Its ability to withstand repeated stress makes it a reliable choice in demanding environments. However, buyers should be aware that it is prone to corrosion, necessitating protective treatments to enhance its durability. Understanding the balance between strength and corrosion resistance is crucial for B2B buyers in selecting the right alloy for their specific applications.
Key Industrial Applications of forge aluminium
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of forge aluminium | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft components and frames | Lightweight yet strong materials reduce fuel costs and improve efficiency. | Compliance with strict aviation regulations and standards. |
| Automotive | Engine components and structural parts | Enhanced performance and fuel efficiency due to reduced weight. | Need for high-quality alloys with precise specifications. |
| Construction | Architectural elements and structural supports | Durable and corrosion-resistant materials enhance longevity and safety. | Sourcing from certified suppliers to ensure material integrity. |
| Marine | Boat hulls and components | Resistance to corrosion in marine environments extends lifespan and reduces maintenance costs. | Availability of specialized marine-grade alloys. |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and housings for electronic devices | Improved thermal management enhances performance and reliability. | Precision in machining and thermal conductivity properties. |
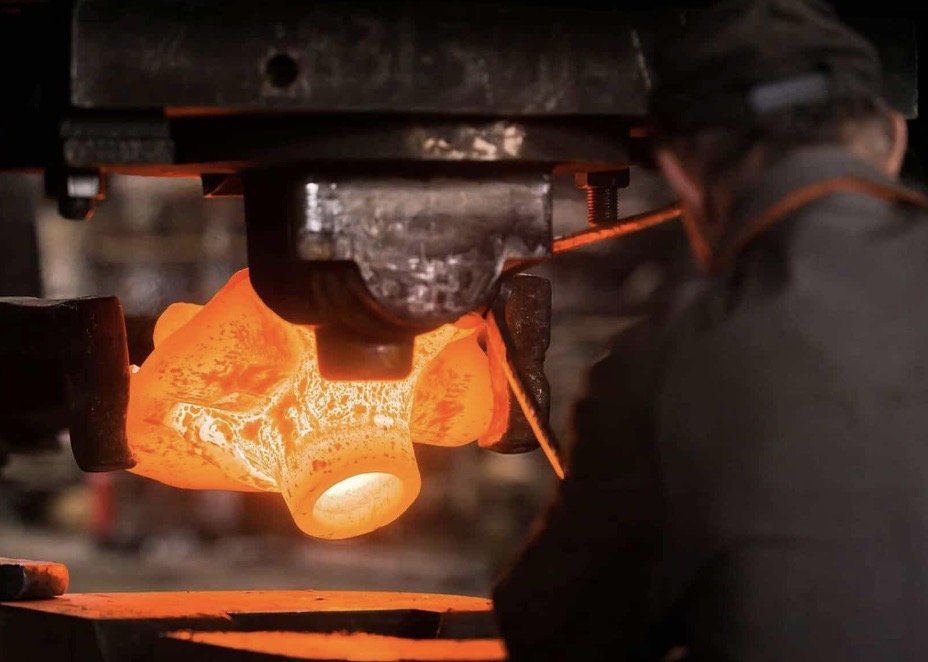
How Is Forge Aluminium Used in the Aerospace Sector?
In the aerospace industry, forged aluminum is critical for manufacturing lightweight yet robust components such as aircraft frames and landing gear. These parts must meet stringent safety and performance standards while minimizing weight to improve fuel efficiency. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that their suppliers comply with international aviation regulations, including certifications for materials and processes. Additionally, sourcing from manufacturers with expertise in aerospace-grade alloys can significantly impact the performance and longevity of aircraft components.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
What Are the Applications of Forge Aluminium in Automotive Manufacturing?
The automotive sector employs forged aluminum in engine components, chassis, and structural parts, where reducing weight is essential for enhancing fuel efficiency and performance. The unique properties of forged aluminum allow for the creation of complex shapes that traditional materials cannot achieve. Buyers must consider the specific alloy types and mechanical properties required for high-stress applications. Furthermore, suppliers should have a proven track record in delivering high-quality products that meet automotive industry standards, ensuring safety and reliability.
How Does Forge Aluminium Benefit the Construction Industry?
In construction, forged aluminum is utilized for architectural elements, such as window frames, doors, and structural supports. Its durability and resistance to corrosion make it an ideal choice for both aesthetic and functional applications in buildings. International buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who can provide certified materials that meet local building codes and standards. Additionally, understanding the specific alloy compositions suitable for different environmental conditions can enhance the longevity and safety of construction projects.
What Role Does Forge Aluminium Play in Marine Applications?
The marine industry relies on forged aluminum for boat hulls and various components due to its excellent resistance to corrosion in saltwater environments. This application significantly extends the lifespan of marine vessels while reducing maintenance costs. When sourcing forged aluminum for marine use, buyers must ensure that the alloys are specifically designed for marine applications, adhering to industry standards for performance and durability. Additionally, suppliers should offer guidance on the appropriate treatments and coatings to enhance corrosion resistance.
How Is Forge Aluminium Used in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics sector, forged aluminum is commonly used for heat sinks and housings. Its lightweight nature and superior thermal conductivity help manage heat efficiently, enhancing the performance and reliability of electronic devices. Buyers in this field should focus on sourcing aluminum with precise thermal and mechanical properties to meet specific device requirements. Collaborating with suppliers who understand the nuances of electronic applications can ensure that the materials provided meet the necessary standards for quality and performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘forge aluminium’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Aluminum Alloy for Forging Applications
The Problem: Choosing the right aluminum alloy can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, especially when considering the specific requirements of their applications. For instance, an automotive parts manufacturer might be unsure whether to use 6061 or 1100 aluminum for their forged components. The wrong choice can lead to product failures, increased costs, and delays in production, causing frustration and lost business opportunities.
The Solution: To effectively select the appropriate aluminum alloy, buyers should first assess their project’s requirements, including mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. For most forging applications that require strength and durability, 6061 aluminum is often the preferred choice due to its excellent mechanical properties and weldability. Conversely, if the project involves intricate designs or requires a softer, more malleable material, 1100 aluminum may be more suitable. Buyers should collaborate closely with their suppliers to obtain detailed technical data sheets and conduct tests to verify the properties of the chosen alloy. Additionally, considering the region-specific availability of alloys can help streamline the sourcing process.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Forging Temperatures Leading to Defects
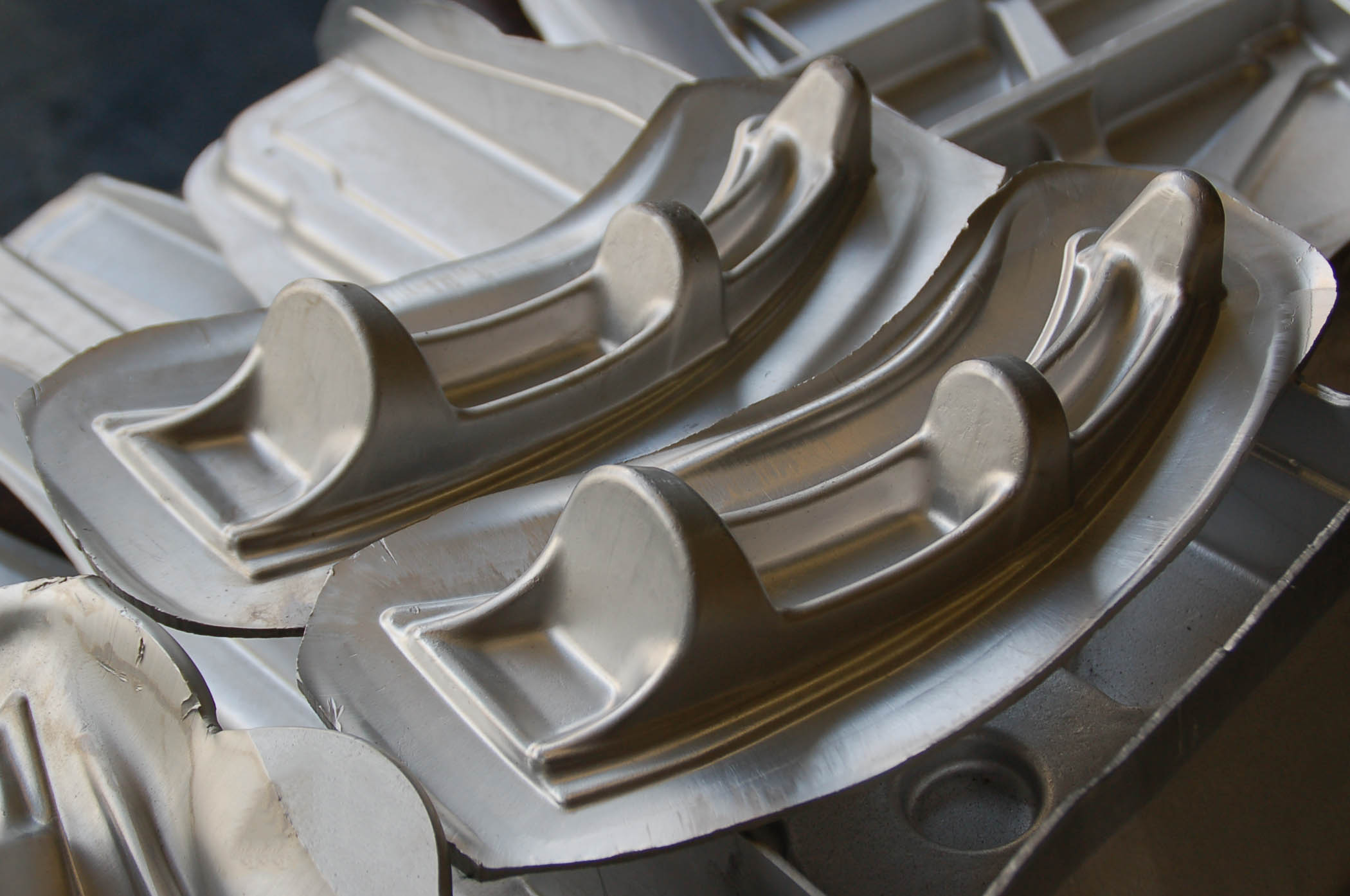
The Problem: Maintaining consistent forging temperatures is critical when working with aluminum, as fluctuations can lead to defects such as cracks or warping. For example, a metal fabrication company might struggle to achieve the ideal temperature range of 750°F to 900°F, resulting in inconsistent product quality. This not only affects customer satisfaction but also increases the need for rework and waste, straining resources and profitability.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
The Solution: To address temperature control challenges, companies should invest in reliable temperature monitoring equipment, such as infrared thermometers or pyrometers, to accurately gauge the temperature of the aluminum throughout the forging process. Implementing a robust training program for staff can also enhance their understanding of aluminum’s thermal properties and the importance of maintaining consistent temperatures. Additionally, developing a standardized operating procedure (SOP) for heating and forging aluminum can help streamline operations. Regularly reviewing and calibrating equipment will ensure optimal performance and minimize defects.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Heat Treatment and Annealing Processes
The Problem: Heat treatment and annealing are essential processes for optimizing the mechanical properties of forged aluminum, but they can be complex and time-consuming. A manufacturing plant may encounter difficulties in properly annealing 6061 aluminum, as it requires specific temperature control and timing to achieve desired results. Inadequate annealing can lead to brittleness or insufficient strength in finished products, which can be detrimental in high-stress applications.
The Solution: To effectively manage the annealing process, it’s crucial for B2B buyers to establish a clear annealing protocol that outlines the necessary temperatures and holding times. For 6061 aluminum, the recommended annealing temperature is around 775°F, held for 2 to 3 hours, followed by controlled cooling. Investing in advanced heating systems with programmable controls can significantly enhance the precision of the annealing process. Furthermore, conducting regular training sessions for the workforce on the nuances of heat treatment can help in achieving consistent results. Collaborating with suppliers to explore pre-annealed materials could also be a viable option, reducing the complexity of in-house processing while ensuring high-quality outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for forge aluminium
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Forge Aluminium?
When selecting materials for forging aluminium, understanding the properties and performance characteristics is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we analyze several common materials used in the forging process, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
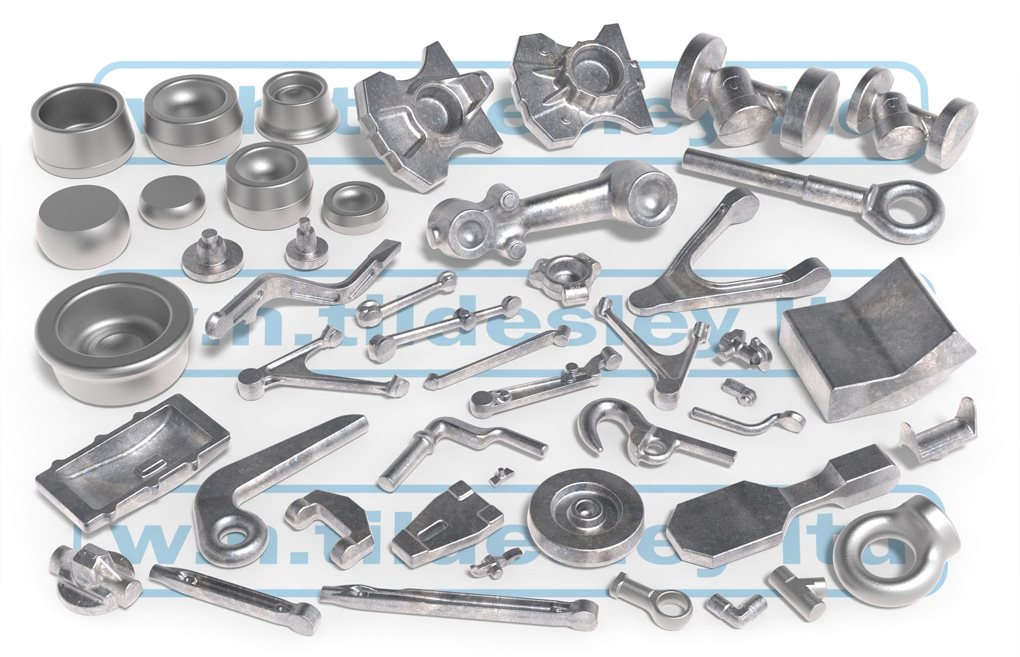

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
1. 6061 Aluminium Alloy
Key Properties:
6061 is a versatile aluminium alloy known for its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 900°F during forging, making it suitable for high-performance applications. Its tensile strength is around 310 MPa, which is beneficial for structural components.
Pros & Cons:
The alloy’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for applications in aerospace and automotive sectors. However, its cost can be higher than other alloys, and the forging process requires careful temperature management to avoid brittleness.
Impact on Application:
6061 is commonly used in structural components, marine applications, and automotive parts. Its compatibility with various media, such as seawater, enhances its appeal in coastal regions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B221. Additionally, understanding local availability and sourcing challenges is essential.
2. 1100 Aluminium Alloy
Key Properties:
1100 is a commercially pure aluminium alloy, offering excellent corrosion resistance and high thermal conductivity. It can be forged at lower temperatures, making it easier to work with, typically around 675°F for annealing.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of 1100 is its excellent ductility, which allows for intricate designs. However, its lower strength compared to 6061 limits its use in structural applications, making it more suitable for decorative and lightweight components.
Impact on Application:
This alloy is often used in applications requiring good thermal and electrical conductivity, such as heat exchangers and cooking utensils. Its compatibility with various environments makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should be aware of the specific grades and standards applicable in their regions, such as JIS in Japan or DIN in Europe, to ensure product quality and compliance.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
3. 6063 Aluminium Alloy
Key Properties:
6063 is known for its excellent extrudability and surface finish, making it ideal for architectural applications. It has a lower strength than 6061 but offers good corrosion resistance and is easily weldable.
Pros & Cons:
Its aesthetic appeal and ability to be anodized make it popular in construction and decorative applications. However, its lower strength limits its use in high-stress environments, and it may require additional treatments for enhanced durability.
Impact on Application:
6063 is widely used in window frames, door frames, and other architectural components. Its compatibility with various finishes allows for greater design flexibility.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must consider local regulations regarding building materials and ensure that the alloy meets specific architectural standards prevalent in their regions.
4. 7075 Aluminium Alloy
Key Properties:
7075 is one of the highest-strength aluminium alloys available, with a tensile strength exceeding 570 MPa. It is typically used in aerospace applications due to its high strength-to-weight ratio.
Pros & Cons:
The alloy’s exceptional strength makes it ideal for critical applications. However, it is more expensive and less corrosion-resistant than 6061 and 6063, requiring protective coatings in certain environments.
Impact on Application:
7075 is primarily used in aerospace and military applications where strength is paramount. Its use in high-stress situations necessitates careful consideration of environmental factors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should ensure compliance with aerospace standards, such as AMS and ASTM, particularly when sourcing for military applications in regions like the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Forge Aluminium
| Material | Typical Use Case for forge aluminium | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 Aluminium | Structural components, automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost, requires careful forging | High |
| 1100 Aluminium | Heat exchangers, cooking utensils | Excellent ductility and corrosion resistance | Lower strength limits applications | Medium |
| 6063 Aluminium | Architectural frames, decorative parts | Good extrudability and surface finish | Lower strength than 6061 | Medium |
| 7075 Aluminium | Aerospace, military applications | Exceptional strength | Higher cost, lower corrosion resistance | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their forging processes with aluminium, ensuring compliance and suitability for their specific applications.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for forge aluminium
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Forged Aluminium?
The manufacturing process of forged aluminum involves several critical stages that ensure the material’s integrity and suitability for various applications. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality forged aluminum products.
1. Material Preparation: How Is Aluminium Prepared for Forging?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy. Common choices include 6061, known for its high strength and versatility, and 1100, often used for its excellent workability. The chosen alloy is typically delivered in the form of billets or sheets, which are then cut to size based on the specifications of the end product.
Prior to forging, the aluminum may undergo processes such as heating or annealing to enhance its malleability. For instance, 6061 aluminum is generally heated to temperatures between 750°F to 900°F to achieve optimal forging conditions. This heating process ensures that the material can be shaped effectively without cracking or losing structural integrity.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
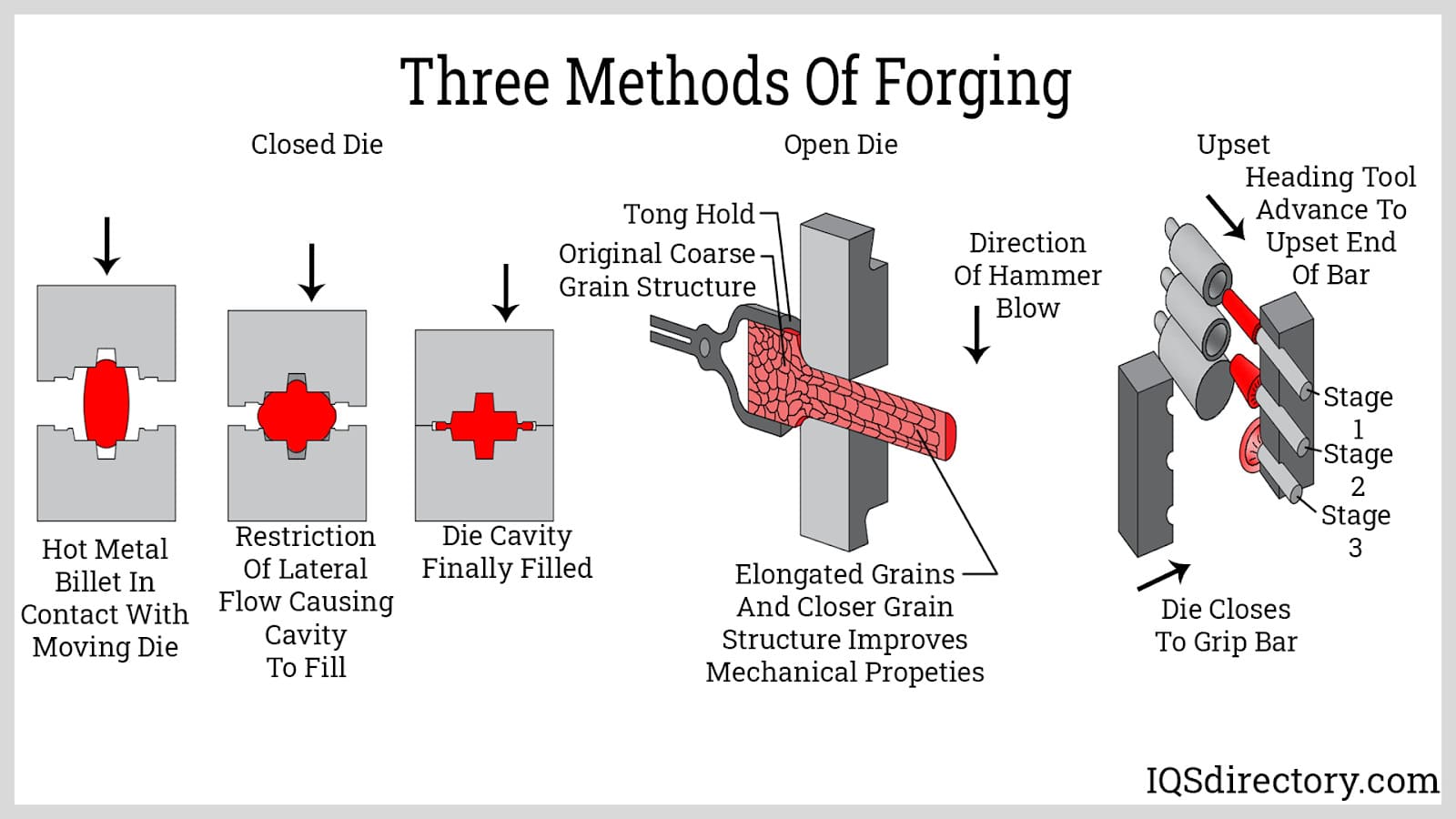
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used in Forging Aluminium?
The forming stage is where the actual forging occurs. Various techniques can be employed, including:
- Open Die Forging: This method involves compressing the aluminum between two flat dies. It is versatile and suitable for large components.
- Closed Die Forging: In this process, the aluminum is placed in a die with a specific shape, allowing for greater detail and tighter tolerances. This technique is often used for smaller, more complex parts.
- Upset Forging: Here, the material is compressed axially to increase its diameter, often used for creating fasteners or flanges.
During forging, careful monitoring of temperature is essential. Aluminum melts quickly, so operators must ensure that the material remains within the ideal temperature range to avoid defects. Techniques like using a wooden stick to test the surface temperature can help operators maintain control over the process.
3. Assembly: How Is Forged Aluminium Assembled into Final Products?
Once the forging process is complete, the next step is assembly. This stage may involve additional processes such as machining, welding, or anodizing to enhance the product’s functionality and appearance. Machining may include milling or turning to achieve precise dimensions, while anodizing provides a protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance.
Assembly can also involve the integration of forged aluminum parts into larger structures or systems. For instance, components may be assembled into frameworks for automotive applications or architectural installations. Effective assembly techniques are crucial for ensuring that the final product meets performance specifications.
4. Finishing: What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Used for Forged Aluminium?
Finishing processes are essential for improving the aesthetic and functional qualities of forged aluminum products. Common finishing techniques include:
Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
- Anodizing: This electrochemical process enhances corrosion resistance and can add color to the aluminum surface.
- Powder Coating: A dry finishing process that provides a durable and attractive finish, ideal for outdoor applications.
- Polishing: This technique is used to create a smooth, reflective surface, often required for decorative applications.
Finishing not only improves the appearance of the product but also increases its lifespan, making it a critical step in the manufacturing process.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Forged Aluminium Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for forged aluminum, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications. B2B buyers should be aware of the various QA measures in place throughout the production cycle.
1. What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
International standards play a significant role in quality assurance for forged aluminum. Some of the most relevant include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS), focusing on consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Particularly important for products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For buyers in the oil and gas sector, API standards ensure that products meet rigorous safety and performance requirements.
Understanding these standards helps buyers assess the credibility of potential suppliers.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical for maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the forging and finishing stages to detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product to verify that it meets all specifications before shipment.
These checkpoints are essential for identifying issues early in the production process, minimizing waste, and ensuring high-quality outcomes.
3. What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the quality of forged aluminum products. Common methods include:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of the material.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the material’s resistance to deformation.
- Ultrasonic Testing: Detects internal defects that may not be visible on the surface.
These testing methods provide valuable data on the material’s performance characteristics and help ensure that the final product meets industry standards.
4. How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Effective strategies include:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of supplier facilities to assess their adherence to quality standards and practices.
- Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of quality control procedures and results from previous production runs.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the quality of products before shipment.
These measures provide assurance that suppliers maintain high standards of quality and reliability in their manufacturing processes.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, additional quality control considerations may apply. These include:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding the local regulations and quality standards in the supplier’s country is crucial for compliance and risk management.
- Logistical Challenges: Ensuring that quality is maintained throughout the shipping process, including handling and storage conditions.
- Communication Barriers: Establishing clear lines of communication with suppliers to address any quality concerns promptly.
By considering these factors, international buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing forged aluminum products while ensuring quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘forge aluminium’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing high-quality forged aluminum is a critical process that demands attention to detail and strategic planning. This guide provides actionable steps for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to effectively procure forged aluminum that meets their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the aluminum you need. This includes selecting the appropriate alloy (such as 6061 for strength or 1100 for sheet applications) and defining mechanical properties like tensile strength and ductility. Establishing these specifications upfront ensures that suppliers understand your needs and can provide suitable products.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Investigate the market to identify potential suppliers of forged aluminum. Focus on regions known for aluminum production and forging capabilities, such as Europe and the Middle East. Utilize industry reports, trade shows, and online platforms to gather information on supplier capabilities, technologies, and product offerings.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies that demonstrate their experience with forged aluminum. Additionally, seek references from other B2B buyers in similar industries to gain insights into the supplier’s reliability and quality.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Standards
Ensure that suppliers comply with international quality standards and certifications relevant to forged aluminum production. Look for certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management and specific industry standards (e.g., ASTM or EN) that pertain to aluminum products. This verification is crucial for ensuring the quality and consistency of the materials you procure.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the forged aluminum for evaluation. Conduct tests to assess mechanical properties, surface finish, and overall quality against your specifications. This step allows you to confirm that the supplier’s products meet your requirements and helps mitigate risks before larger investments.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in negotiations with your chosen supplier to establish pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Consider factors like bulk order discounts or long-term partnership agreements that could provide cost savings. Clear communication during this stage is vital to ensure mutual understanding and satisfaction.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a robust quality control process for incoming shipments of forged aluminum. Define acceptance criteria based on your specifications and ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation, such as material test reports. Regularly review and communicate quality issues to your supplier to maintain a high standard of materials.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing forged aluminum more effectively, ensuring they secure high-quality materials that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for forge aluminium Sourcing
When sourcing forged aluminum, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The cost components involved in this process include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin. Each of these elements plays a significant role in determining the final price of forged aluminum products.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Forged Aluminum Sourcing?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in forged aluminum is the raw material itself. Aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 1100, are commonly used due to their favorable properties. Prices for aluminum can fluctuate based on global market conditions, so it’s essential to stay informed about current prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region and skill level required for the forging process. Skilled labor is often necessary for quality assurance and for handling complex designs, which can increase overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production facility, such as utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, making it beneficial to evaluate potential suppliers based on their operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: The tools used for forging aluminum, including dies and molds, represent a significant upfront investment. Custom tooling can be particularly expensive, so it’s important to assess whether a supplier can provide cost-effective tooling solutions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the forged aluminum meets industry standards and specific buyer requirements involves rigorous QC processes. The costs associated with inspections and certifications can add to the overall price, particularly for buyers requiring certified materials.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on the distance from the supplier, the volume of the order, and the chosen Incoterms. Understanding these factors is critical for calculating the total landed cost of the product.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a markup to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Forged Aluminum Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in the forged aluminum market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to lower per-unit costs. Understanding a supplier’s minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products can significantly increase costs due to the additional design and tooling requirements. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Materials and Quality: Higher quality materials or specific alloys may command higher prices. Buyers should assess the long-term benefits of investing in quality against initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and operational efficiency of a supplier can greatly affect pricing. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can influence the total cost of ownership by affecting shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs. Understanding these terms is essential for accurate budgeting.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Navigate Forged Aluminum Pricing?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Always be prepared to negotiate prices, especially for large orders. Leveraging volume can often lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the purchase price but also logistics, quality assurance, and potential rework costs. This holistic view can lead to better decision-making.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and tariffs that can impact overall costs.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Comparing quotes from different suppliers can provide insights into market pricing and help identify the best value for your needs.
-
Stay Informed: Keeping up with market trends and changes in the aluminum industry can provide valuable insights into when to buy and how to negotiate effectively.
Conclusion
While indicative prices can provide a baseline, they should be treated with caution as costs can vary based on numerous factors. Engaging in thorough research and maintaining open communication with suppliers can lead to more favorable outcomes in sourcing forged aluminum.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing forge aluminium With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Forge Aluminium
When considering the use of forged aluminum in manufacturing and engineering applications, it is essential to evaluate alternative methods that may offer similar benefits or cater to specific needs. This analysis compares forged aluminum with two viable alternatives: cast aluminum and 3D printing with aluminum alloys. Each method has distinct characteristics that can influence decision-making for B2B buyers in various industries.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Forge Aluminium | Cast Aluminium | 3D Printing with Aluminium Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength and durability; excellent mechanical properties | Good strength; often lower than forging | Variable strength; depends on the process and materials used |
| Cost | Moderate; tooling and labor-intensive | Generally lower for large volumes | High initial cost; variable based on complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and specialized equipment | Easier for mass production; simpler setup | Requires advanced technology and skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Low; durable finished products | Moderate; can require additional finishing | Moderate; depends on post-processing needs |
| Best Use Case | High-performance applications (aerospace, automotive) | Large, complex shapes (furniture, machinery) | Prototyping and custom parts with complex geometries |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Cast Aluminium
Casting involves pouring molten aluminum into a mold to create parts. This method allows for intricate shapes and is often more cost-effective for large production runs. The primary advantage of cast aluminum is its ability to produce complex geometries that may be difficult to achieve with forging. However, cast aluminum typically exhibits lower mechanical properties compared to forged aluminum, making it less suitable for applications requiring high strength and durability.
3D Printing with Aluminium Alloys
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, allows for the creation of parts layer by layer. This method is highly versatile and can produce intricate designs that are challenging to forge or cast. The main advantage of 3D printing is its ability to rapidly prototype and customize parts, making it ideal for low-volume, high-complexity applications. However, the initial setup costs and the need for skilled operators can be significant drawbacks. Additionally, the mechanical properties of 3D printed aluminum parts can vary widely based on the printing method and materials used.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
In selecting the appropriate method for aluminum fabrication, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the specific application requirements, production volume, and budget constraints. Forged aluminum is ideal for high-performance applications demanding strength and durability, while cast aluminum may be better suited for larger parts with complex geometries at a lower cost. For those needing rapid prototyping and customization, 3D printing offers unique advantages, albeit at a higher cost and with varying mechanical properties. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and limitations of each method will guide buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational needs and goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for forge aluminium
What are the Critical Technical Properties of Forge Aluminium?
When evaluating forge aluminium, understanding its technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grades, such as 6061 and 1100, are pivotal in determining the performance characteristics of forged aluminium. Grade 6061 is known for its high strength and is commonly used in structural applications, while 1100 is more malleable and better suited for complex shapes. Choosing the right grade ensures that the final product meets the required strength and durability standards for specific applications.
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures how much pulling force a material can withstand before failing. For example, 6061 aluminium typically has a tensile strength of around 310 MPa. This property is crucial for applications where the material will experience significant stress, such as automotive or aerospace components. Higher tensile strength often translates to better performance and longer-lasting products.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
3. Elongation Percentage
Elongation percentage indicates how much a material can stretch before breaking. This property is vital in forging processes as it affects how easily the aluminium can be shaped without fracturing. For instance, 6061 aluminium typically exhibits an elongation of about 12% to 17%, making it suitable for applications requiring complex shapes and intricate designs.
4. Fatigue Strength
Fatigue strength refers to the material’s ability to withstand repeated loading and unloading cycles without failure. This property is particularly important in sectors like automotive and aerospace, where components may experience cyclic stresses. Selecting aluminium with high fatigue strength can lead to improved reliability and reduced maintenance costs over time.
5. Heat Treatment Response
The ability of aluminium alloys to be heat treated significantly impacts their mechanical properties. For instance, 6061 can be heat treated to enhance its strength, making it more suitable for high-performance applications. Understanding heat treatment responses helps buyers select the right alloy for processes like forging, welding, and machining.
What are Common Trade Terms in the Forge Aluminium Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and transactions in the forge aluminium sector. Here are several essential terms:

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of forge aluminium, OEMs often require specific grades and properties to ensure compatibility with their products. Understanding OEM requirements can help buyers align their sourcing strategies accordingly.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps companies plan their purchases and avoid overstocking or understocking situations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process in which buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is essential in the B2B landscape, as it facilitates price comparison and helps in negotiating better terms. Providing detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. They cover aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms ensures that both parties understand their obligations, minimizing the risk of disputes and miscommunication.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. In the forge aluminium sector, understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and meeting customer demands. Longer lead times may necessitate adjustments in inventory management and project timelines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing forge aluminium more effectively, ensuring that their procurement aligns with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the forge aluminium Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Global Forge Aluminium Market?
The global forge aluminium market is witnessing significant transformations driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for lightweight materials, and a heightened focus on sustainability. One of the primary drivers is the automotive and aerospace industries’ push for lightweight solutions that enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. As a result, alloys such as 6061 and 6063 are gaining traction due to their superior strength-to-weight ratios and versatility.
Emerging B2B technology trends, including digital platforms for sourcing and procurement, are reshaping how companies engage with suppliers. International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly leveraging e-commerce platforms to streamline their purchasing processes. The use of data analytics and AI in forecasting demand and managing inventory is also becoming prevalent, enabling buyers to make informed decisions and optimize costs.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
Market dynamics are further influenced by geopolitical factors, trade policies, and fluctuations in raw material prices. Buyers need to stay informed about potential disruptions in the supply chain, such as tariffs or trade restrictions, that could affect the availability and pricing of forge aluminium products. As the market continues to evolve, staying agile and adaptable is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to capitalize on opportunities in the forge aluminium sector.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Forge Aluminium?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the forge aluminium sector. The environmental impact of aluminium production is significant, with energy-intensive processes contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Consequently, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing recycled aluminium and employing energy-efficient manufacturing techniques.
Ethical supply chains are paramount for international buyers, particularly in regions where regulatory standards may vary. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough audits of their suppliers to ensure compliance with environmental and labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) certification can provide assurance of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ materials is on the rise. Buyers should consider sourcing forge aluminium from suppliers who utilize renewable energy sources and implement waste reduction strategies. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally-conscious customers.
What Is the Historical Context of Forge Aluminium in B2B Markets?
The history of forge aluminium dates back to the early 20th century when aluminium’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties began to be recognized. Initially used in the aerospace and automotive industries, the material’s versatility quickly led to its adoption across various sectors, including construction and consumer goods.
As forging techniques evolved, the introduction of advanced alloys like 6061 and 6063 further expanded the applications of forge aluminium. The development of modern forging processes, including hot and cold working techniques, has improved the efficiency and quality of aluminium products.
Today, the forge aluminium market is characterized by continuous innovation and adaptation to meet the changing needs of B2B buyers globally. Understanding this historical context is essential for businesses looking to navigate the complexities of sourcing and leveraging forge aluminium in their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of forge aluminium
-
How do I select the right aluminum alloy for forging applications?
Choosing the appropriate aluminum alloy depends on your specific application requirements. For structural applications requiring high strength, 6061 is often recommended due to its excellent mechanical properties and versatility. If you are working with sheet metal, 1100 is a good choice as it is easy to form and has good corrosion resistance. Additionally, consider your project’s temperature requirements, as different alloys have varying forging and annealing temperatures that can affect workability and performance. -
What are the ideal forging temperatures for aluminum alloys?
The ideal forging temperatures for aluminum alloys vary. Generally, 6061 and 6063 should be forged at temperatures between 750°F and 900°F for optimal results. For 1100 aluminum, it can often be forged cold, but it’s essential to monitor temperatures closely to avoid melting, which can happen quickly. Using a temperature-checking method, such as rubbing a dry stick on the aluminum, can help ensure you are within the correct range for forging without damaging the material. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing forged aluminum?
Minimum order quantities for forged aluminum can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the parts being produced. Typically, MOQs may range from 100 to 1,000 units. However, some suppliers may accommodate smaller orders, especially if you are willing to pay a premium for lower quantities. Always discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that suit your business requirements. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in forged aluminum products?
To ensure quality assurance in your forged aluminum products, request detailed certifications and testing reports from your suppliers. Look for ISO certifications, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Consider implementing an inspection process that includes visual checks, dimensional inspections, and material testing. Regular audits of your suppliers can also help maintain quality standards and ensure compliance with your specifications. -
What payment terms are commonly offered in international aluminum trade?
Payment terms in international aluminum trade can vary widely. Common options include letters of credit, advance payments, or net terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). It is crucial to establish clear payment terms before entering into a contract to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using escrow services for larger transactions to ensure both parties fulfill their obligations before funds are released. -
How do I vet suppliers for forged aluminum internationally?
To vet suppliers for forged aluminum, start by researching their reputation in the industry through online reviews and testimonials. Request references from previous clients, and consider visiting their facilities if feasible. Evaluate their production capabilities, quality control processes, and compliance with international standards. Additionally, verify their financial stability and whether they have experience exporting to your region, as this can impact logistics and communication. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing forged aluminum?
When importing forged aluminum, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international trade to navigate customs clearance efficiently. Ensure that you have all necessary documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, to avoid delays. Additionally, factor in shipping costs and potential tariffs that may affect your overall budget. -
Can forged aluminum products be customized for specific applications?
Yes, forged aluminum products can be highly customized to meet specific application requirements. Many suppliers offer services to modify dimensions, shapes, and finishes according to your needs. Discuss your project details with suppliers to explore available customization options, including alloy selection, surface treatments, and additional machining processes. Engaging in early collaboration can lead to optimized designs that meet your operational requirements effectively.
Top 5 Forge Aluminium Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Instructables – Aluminum Forging Solutions
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Aluminum forge, aluminum melting furnace, coffee can aluminum foundry, blow dryer and red brick aluminum forge, zero cost aluminum furnace, sand-cast aluminum, natural gas burner, aluminum casting foundry, cheap and effective aluminum forge.
2. QC Forge – Forged vs. Cast Aluminum
Domain: qcforge.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Forged Aluminum vs. Cast Aluminum: The key differences between forged and cast aluminum involve the manufacturing processes. Forging does not melt the material; instead, it deforms solid aluminum through hammering or pressing, enhancing its internal microstructure and eliminating impurities. This results in improved durability and toughness. Cast aluminum, on the other hand, involves melting the m…
3. Scot Forge – Aluminum Forgings
Domain: scotforge.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Forgings: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and durable. Excellent for various forging techniques and applications. Custom Material Inventory includes Aluminum Forgings (Highlander 613), Copper Forgings, Stainless Steel Forgings, Titanium Forgings, Inconel, Monel, Incoloy Forgings, Carbon, Alloy & Tool Steel Forgings. Market expertise in Aerospace, Mining, Defense, Semiconductor, Power Ge…
4. IQS Directory – Aluminum Forging Techniques
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Aluminum forging is a method used to process aluminum alloys by applying pressure and heat to manufacture strong and durable parts. Key types of aluminum forging include hot forging and cold forging, with advanced techniques such as drop forging, press forging, upset forging, roll forging, rolled ring forging, isothermal forging, open die forging, and closed die forging. Aluminum alloys commonly u…
5. Forge Aluminium – Custom Aluminium Products
Domain: forgealuminium.com.au
Introduction: Forge Aluminium specializes in high-quality, custom-made aluminium products including Aluminium Trays, Aluminium Canopies, and 12Volt Power Systems. Key offerings include:
– Aluminium Trays: Available in Dual Cab, Single Cab, American, and NPS/Truck configurations.
– Aluminium Canopies: Options include Chassis Mount, Jack Off, Dog Box, and Custom Canopies.
– Internal Fit-out and Accessories:…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for forge aluminium
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Forged Aluminum Procurement?
In today’s dynamic global market, strategic sourcing for forged aluminum is not just advantageous; it is essential. By understanding the unique properties of alloys like 6061 and 1100, buyers can make informed decisions that meet their specific application needs, whether for construction, automotive, or aerospace. Leveraging local suppliers and manufacturers from regions like Africa and South America can also reduce lead times and costs, while fostering sustainable practices.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
Moreover, as industries increasingly prioritize lightweight and durable materials, the demand for forged aluminum is set to rise. This presents an opportunity for B2B buyers to establish long-term partnerships with suppliers who are committed to quality and innovation. Engaging in proactive sourcing strategies will ensure that you remain competitive and responsive to market changes.
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing forged aluminum, consider investing in supplier relationships that align with your strategic goals. Embrace the potential of this versatile material and position your business for future growth. Start exploring your options today to secure a robust supply chain that supports your operational needs and sustainability objectives.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to forge aluminium
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.