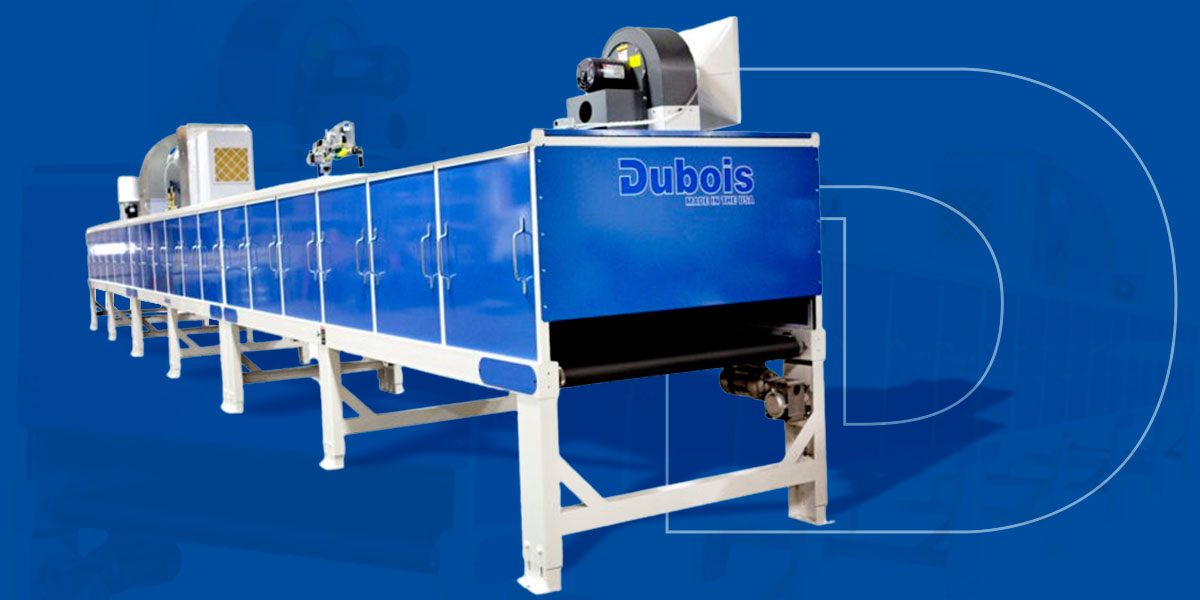
A Deep Dive into Curing Oven Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for curing oven
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, sourcing the right curing oven can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the nuances of different curing ovens—such as infrared, UV, and traditional convection models—can be the difference between streamlined production and costly setbacks. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, exploring various types of curing ovens, their applications across industries, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
From aerospace to automotive, the applications of curing ovens are vast, making it essential for buyers to grasp the specific requirements of their projects. This guide not only highlights the diverse functionalities of curing ovens but also offers insights into optimal temperature settings, curing times, and the materials best suited for each type. Additionally, we delve into cost considerations and procurement strategies that can help you make informed purchasing decisions.
By empowering you with actionable insights and a thorough understanding of the global market for curing ovens, this guide aims to facilitate smarter investments that enhance productivity and product quality. As you navigate this complex landscape, the knowledge contained within these pages will help you select the best solutions tailored to your unique business needs, ensuring that your operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding curing oven Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrared Curing Oven | Uses infrared radiation for rapid heating. | Automotive, electronics, and aerospace. | Pros: Fast curing times; energy-efficient. Cons: Limited penetration for thicker materials. |
| UV Curing Oven | Utilizes ultraviolet light for curing coatings. | Printing, electronics, and adhesive industries. | Pros: Quick curing; excellent finish quality. Cons: Requires UV-sensitive materials. |
| Forced Air Convection Oven | Employs forced air circulation for uniform heating. | General manufacturing and laboratory applications. | Pros: Consistent temperature; versatile. Cons: Slower than infrared or UV options. |
| Vertical Curing Oven | Compact design for inline production processes. | PCB assembly and electronics manufacturing. | Pros: Space-saving; continuous operation. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Vacuum Curing Oven | Operates under reduced pressure for sensitive materials. | Aerospace and high-tech industries. | Pros: Preserves material integrity; reduces oxidation. Cons: More complex setup and maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics of Infrared Curing Ovens?
Infrared curing ovens are designed to utilize infrared radiation, which allows for rapid heating and curing of materials. This type of oven is particularly suitable for applications in the automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries, where quick turnaround times are essential. When considering an infrared curing oven, buyers should evaluate the thickness of the materials being cured, as this method may not penetrate as deeply as other heating options, potentially limiting its effectiveness for certain applications.
How Do UV Curing Ovens Benefit B2B Operations?
UV curing ovens leverage ultraviolet light to initiate chemical reactions that cure coatings, inks, and adhesives almost instantaneously. This technology is prevalent in industries such as printing, electronics, and adhesives, where speed and finish quality are paramount. B2B buyers should consider the compatibility of their materials with UV curing processes, as only UV-sensitive materials will yield optimal results. The quick curing times and high-quality finishes make this option attractive, despite the limitation of requiring specific material types.
What Advantages Do Forced Air Convection Ovens Offer?
Forced air convection ovens utilize a fan to circulate hot air, ensuring even temperature distribution within the chamber. This type of oven is versatile and can be employed in various sectors, including general manufacturing and laboratory applications. When purchasing a forced air convection oven, buyers should note its slower curing times compared to infrared or UV options. However, its consistent temperature control makes it ideal for processes requiring precision, making it a reliable choice for many B2B operations.
Why Choose a Vertical Curing Oven for Your Production Line?
Vertical curing ovens are engineered for compact spaces and are particularly effective in inline production processes, such as PCB assembly in electronics manufacturing. They maintain a continuous curing operation, which enhances efficiency and reduces manual handling. Buyers should consider the initial investment cost, as vertical ovens can be pricier than batch ovens. However, their space-saving design and ability to improve production flow make them a compelling option for manufacturers facing space constraints.
How Do Vacuum Curing Ovens Enhance Material Integrity?
Vacuum curing ovens operate under reduced pressure, making them ideal for curing sensitive materials without the risk of oxidation or contamination. This technology is crucial in high-tech industries, such as aerospace, where material integrity is vital. When considering a vacuum curing oven, buyers should be prepared for a more complex setup and potential maintenance challenges. The benefits of preserving material properties and achieving uniform curing make vacuum ovens a valuable investment for companies prioritizing quality in their production processes.
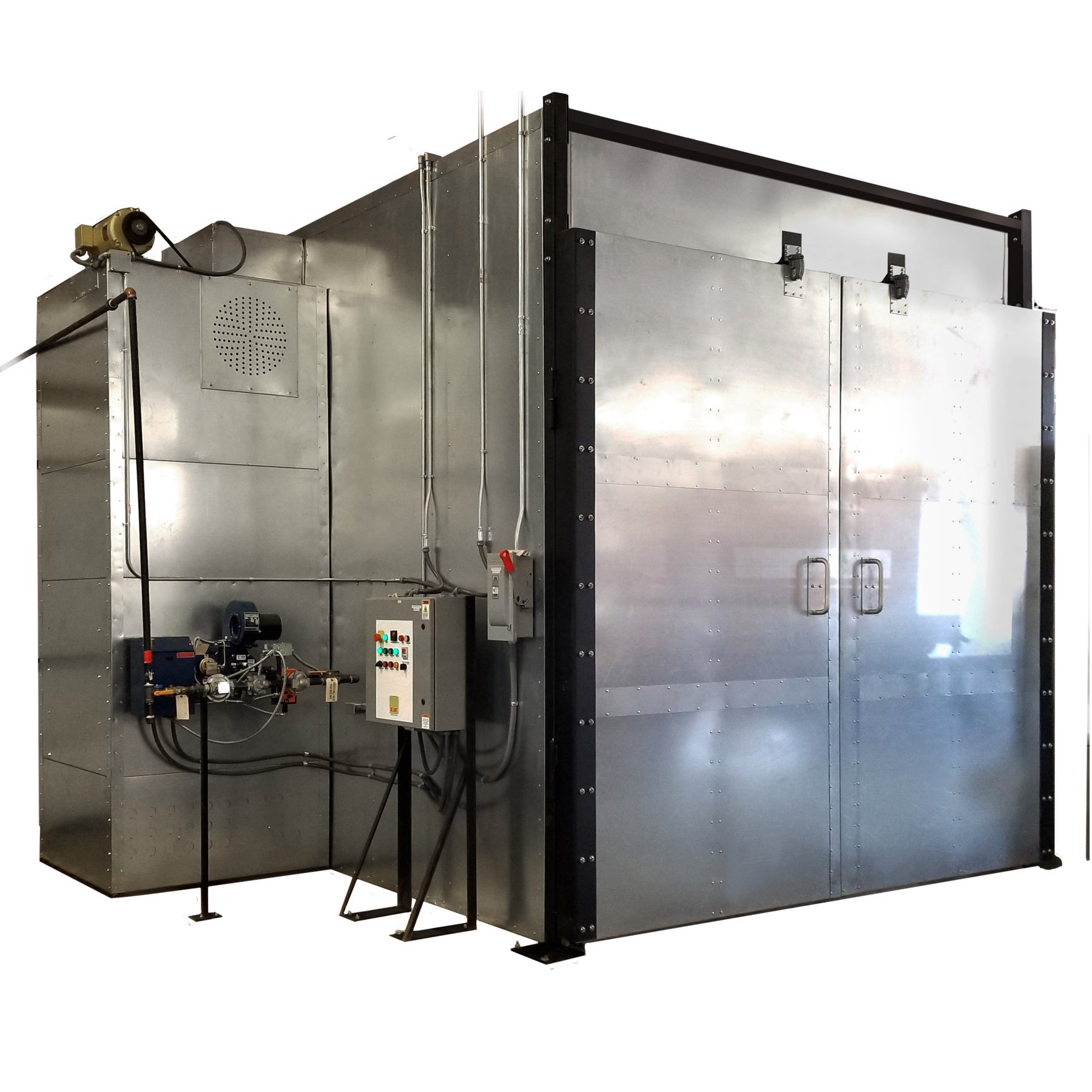

Illustrative image related to curing oven
Key Industrial Applications of curing oven
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Curing Oven | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Curing of powder coatings on vehicle parts | Enhanced durability and aesthetic finish of automotive components | Temperature control accuracy, size of the oven, energy efficiency |
| Electronics | Curing of adhesives in printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) | Improved bonding strength and reliability of electronic assemblies | Inline processing capabilities, cycle time, footprint requirements |
| Aerospace | Curing of composite materials and coatings | High-strength components that meet strict safety regulations | Compliance with industry standards, customization options |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Curing of sealants and adhesives for building materials | Increased longevity and performance of construction materials | Material compatibility, curing time, temperature range |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Curing of industrial coatings and polymers | Enhanced product quality and resistance to environmental factors | Customization for specific materials, automation features |
How is a Curing Oven Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, curing ovens are essential for applying and curing powder coatings on various vehicle components, such as wheels and chassis parts. These coatings enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of the products, providing a protective layer against corrosion and wear. Buyers in this industry should focus on ovens that offer precise temperature control and energy efficiency, as consistent curing is crucial for maintaining quality standards.
What Role Does a Curing Oven Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
Curing ovens are vital in electronics manufacturing, particularly for the curing of adhesives used in printed circuit board assemblies (PCBA). These ovens facilitate a rapid curing process that enhances the bonding strength and reliability of the components, which is critical in high-performance electronic devices. International buyers should consider ovens with inline processing capabilities to streamline production and minimize cycle times, ensuring efficient operation in their facilities.
Why is a Curing Oven Important in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, curing ovens are used to cure composite materials and protective coatings that meet stringent safety regulations. The curing process significantly increases the strength and durability of components, which is vital for aircraft performance and safety. Buyers should prioritize sourcing ovens that comply with aerospace industry standards and offer customization options to accommodate specific material requirements.
How Do Curing Ovens Benefit Construction and Infrastructure Projects?
Curing ovens play a crucial role in the construction and infrastructure sectors by curing sealants and adhesives used in building materials. This process enhances the longevity and performance of these materials, ensuring they can withstand environmental stressors. Buyers should look for ovens that provide optimal temperature ranges and compatibility with various materials to ensure effective curing processes.
What Advantages Do Curing Ovens Offer in Industrial Manufacturing?
In industrial manufacturing, curing ovens are utilized for curing coatings and polymers, which enhances product quality and resistance to environmental factors. This is particularly important in industries where products are exposed to harsh conditions. Buyers should consider ovens with automation features and the ability to customize settings for specific materials, as these factors contribute to increased efficiency and product performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘curing oven’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Curing Results Leading to Product Defects
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of inconsistent curing results, which can lead to defects in the final product. This inconsistency may arise from fluctuations in temperature, uneven airflow, or improper loading of materials into the curing oven. For industries such as automotive and electronics, where precision is critical, these defects can result in costly recalls, wasted materials, and damaged reputations.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should invest in curing ovens equipped with advanced temperature control systems and uniform airflow technology. When sourcing a curing oven, look for models that feature multiple heating zones and programmable settings to ensure precise temperature management throughout the curing process. Additionally, consider ovens with real-time monitoring capabilities that provide alerts for temperature deviations. Proper loading techniques, such as ensuring even spacing and avoiding overcrowding, can also enhance airflow and heat distribution, leading to more consistent curing results.
Scenario 2: High Energy Costs Associated with Curing Processes
The Problem: High operational costs can significantly impact the profitability of manufacturing businesses. Curing ovens, especially older models, can consume excessive energy, leading to inflated utility bills. This issue is particularly pressing for companies operating in regions where energy prices are high or fluctuating. Buyers often struggle to balance the need for efficient curing with the demands of cost-effectiveness.
The Solution: To address energy inefficiencies, consider investing in modern curing ovens that utilize advanced insulation technologies and energy-efficient heating methods, such as infrared or ultraviolet curing. These systems often require lower energy inputs while achieving faster curing times. When evaluating options, request energy consumption data and operational costs from suppliers. Additionally, implementing a scheduled maintenance program can help ensure ovens operate at peak efficiency, further reducing energy costs over time.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Meeting Production Demands
The Problem: As market demands increase, businesses often struggle to keep up with production schedules, particularly when using batch curing ovens that require manual loading and unloading. This can lead to bottlenecks in the production line, delayed deliveries, and ultimately dissatisfied customers. Buyers in fast-paced industries, such as consumer electronics or automotive parts, may find their current curing solutions inadequate for scaling operations.
The Solution: To overcome production bottlenecks, consider transitioning to inline curing ovens that automate the curing process. These systems can integrate seamlessly into existing production lines, allowing for continuous operation and reduced manual intervention. When selecting an inline curing oven, assess the throughput capabilities and ensure it aligns with your production goals. Additionally, look for ovens that offer flexible configurations to accommodate various product sizes and shapes. Investing in automation not only enhances efficiency but also allows for better quality control, ensuring that products meet the required standards consistently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for curing oven
What Are the Key Materials Used in Curing Ovens?
When selecting materials for curing ovens, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and the specific needs of international buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of curing ovens: stainless steel, aluminum, ceramic, and composite materials.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Curing Ovens?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for environments where chemical exposure is a concern. It can withstand temperatures typically up to 1,500°F (815°C) without losing structural integrity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and corrosion, which prolongs the lifespan of the oven. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials, and its weight can complicate manufacturing and installation processes.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of curing processes, including those involving corrosive chemicals or high humidity. It is often used in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where stringent quality standards are necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East may need to ensure compliance with specific standards such as ASTM or DIN for material quality and safety. The high initial cost may be justified by the longevity and reduced maintenance needs of stainless steel ovens.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Curing Oven Construction?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for rapid heating and cooling cycles. It can endure temperatures up to about 1,200°F (650°C).
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easier to manufacture and transport. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may be prone to warping or corrosion, especially in harsh environments.

Illustrative image related to curing oven
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly beneficial for applications requiring quick temperature changes, such as in electronics manufacturing. Its lower thermal mass allows for efficient energy use.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with high humidity, such as parts of South America, should consider the potential for corrosion. Compliance with local standards regarding material safety and performance is also crucial.
How Do Ceramic Materials Enhance Curing Ovens?
Key Properties: Ceramics are capable of withstanding extremely high temperatures (up to 2,500°F or 1,370°C) and have excellent thermal insulation properties.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of ceramics is their ability to maintain high temperatures without degrading. However, they can be brittle and may require careful handling during installation and operation.
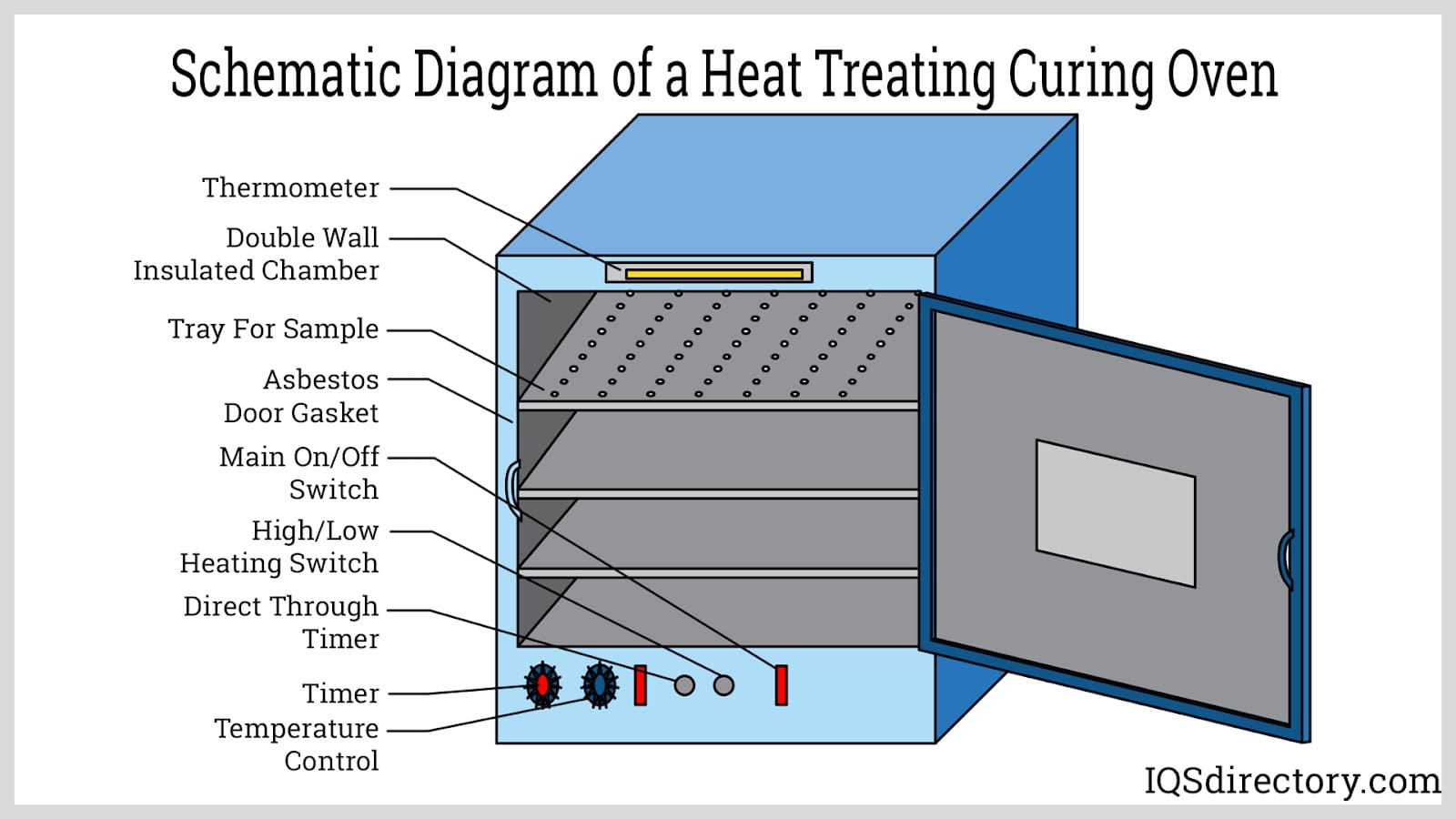
Illustrative image related to curing oven
Impact on Application: Ceramics are ideal for specialized applications requiring high thermal stability, such as in the aerospace industry. They can enhance the performance of curing ovens by improving energy efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the fragility of ceramic materials, especially in regions where transportation may be challenging. Additionally, compliance with international standards for thermal performance is essential.
What Are the Benefits of Using Composite Materials in Curing Ovens?
Key Properties: Composite materials combine various materials to achieve superior strength and thermal resistance while being lightweight.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their versatility and ability to be tailored for specific applications. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized knowledge for maintenance.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in the automotive and aerospace sectors. Their customizable nature allows for specific thermal properties to be engineered.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of the varying standards for composite materials across regions. Ensuring that the composites meet local regulations can be a challenge, especially in emerging markets in Africa and South America.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Curing Ovens
| Material | Typical Use Case for curing oven | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Aerospace, automotive | High durability and corrosion resistance | High cost and heavy weight | High |
| Aluminum | Electronics manufacturing | Lightweight and excellent thermal conductivity | Less durable, prone to warping | Medium |
| Ceramic | Aerospace, high-temperature applications | Extremely high-temperature resistance | Brittle and requires careful handling | High |
| Composite | Automotive, aerospace | Versatile and customizable | Higher manufacturing costs and maintenance complexity | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions regarding curing ovens, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for curing oven
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Curing Ovens?
The manufacturing process of curing ovens involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications.
1. Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Chosen and Processed?
The first stage involves selecting high-quality materials suitable for the construction of curing ovens. Common materials include steel for the frame and housing, as well as specialized insulation materials that can withstand high temperatures. The selection process typically includes a review of material specifications, ensuring they comply with relevant international standards such as ISO 9001. After selection, materials undergo cutting, shaping, and surface treatment processes, such as sandblasting or coating, to enhance durability and performance.
2. What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Process?
Once materials are prepared, they move to the forming stage. Techniques such as laser cutting, CNC machining, and welding are employed to create the various components of the curing oven. Precision is crucial during this phase, as even minor discrepancies can affect the oven’s performance. Manufacturers often utilize 3D modeling software to design components, which allows for adjustments before physical production, minimizing waste and ensuring accuracy.
3. How Is the Assembly of Curing Ovens Conducted?
The assembly process is where the individual components come together. This stage involves fitting the oven’s housing, insulation, heating elements, and control systems. Advanced assembly techniques include automated processes for consistent quality and manual inspections to address any irregularities. Skilled technicians often conduct this assembly, ensuring that all parts fit correctly and function as intended. This phase is critical, as proper assembly directly impacts the oven’s thermal efficiency and overall performance.
4. What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Curing Ovens?
After assembly, curing ovens undergo finishing processes, which may include painting, anodizing, or applying protective coatings. These finishes not only improve aesthetics but also enhance the oven’s resistance to environmental factors such as humidity and corrosion. Quality assurance checks are integrated into this stage to ensure that the finishes meet specified durability standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Curing Oven Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of curing oven manufacturing, ensuring that every unit meets stringent performance and safety standards.
What International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Curing ovens must adhere to several international standards that dictate quality and safety. ISO 9001 is a critical standard focusing on quality management systems, ensuring manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Other relevant certifications may include CE marking for compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, as well as API standards for specific applications in the oil and gas sector.
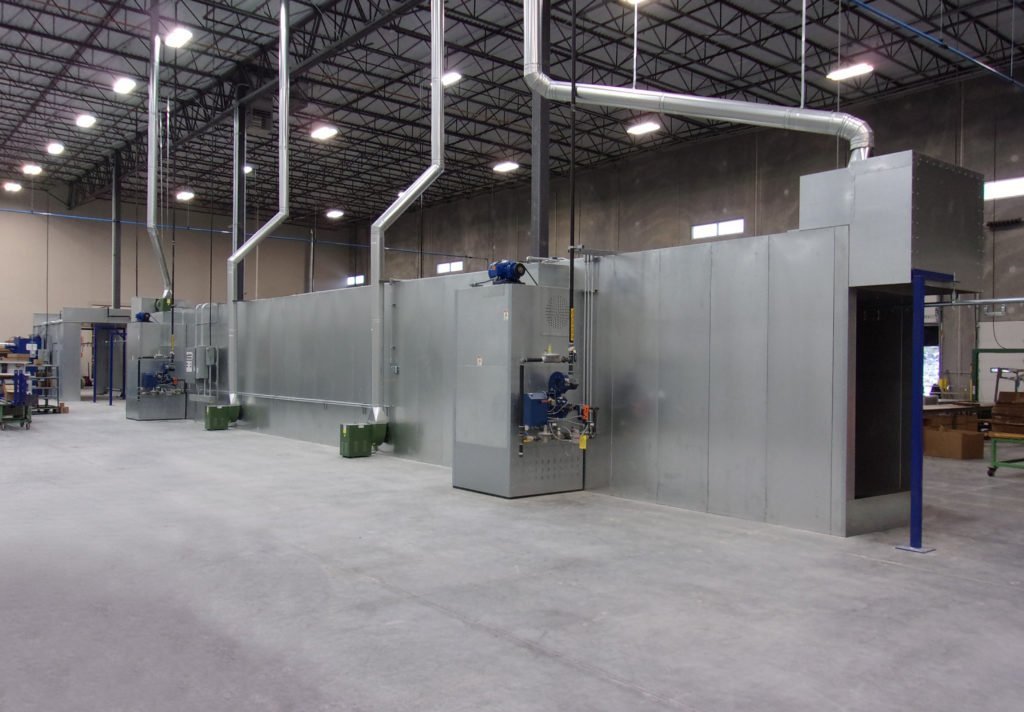

Illustrative image related to curing oven
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria before processing begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly, regular inspections are conducted to verify that components are assembled correctly and meet design specifications. This includes monitoring temperature controls and ensuring proper insulation.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, each curing oven undergoes rigorous testing to verify its performance. This may involve functional testing, temperature calibration, and safety checks.
How Are Common Testing Methods Employed?
Testing methods may include:
-
Thermal Cycling Tests: Assessing the oven’s ability to maintain consistent temperatures over extended periods.
-
Load Testing: Evaluating how well the oven performs under expected operational loads.
-
Safety Tests: Ensuring that all safety mechanisms function properly, including emergency shut-off systems.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are several strategies:
What Steps Can Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers is an effective way to assess their quality control processes. This can include:
-
On-Site Visits: Arranging visits to the manufacturing facility to observe production processes and quality checks firsthand.
-
Documentation Review: Requesting quality assurance documentation, including ISO certifications, testing reports, and maintenance records.
How Can Buyers Utilize Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control systems. These services can conduct thorough inspections and testing to confirm that products meet specified standards before shipment.
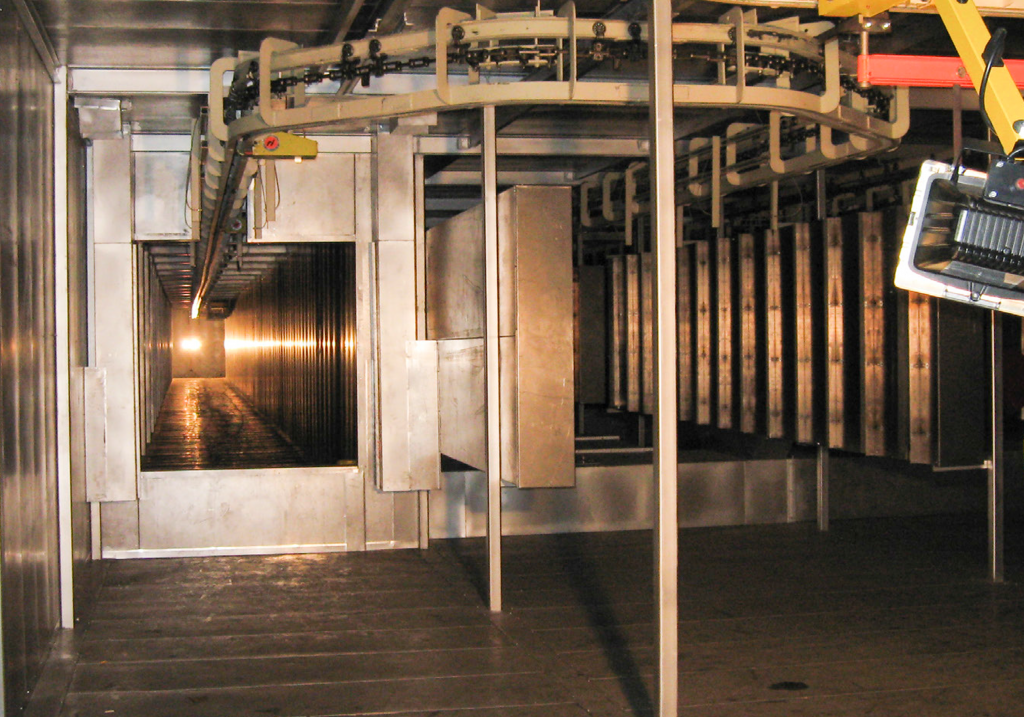

Illustrative image related to curing oven
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Compliance with Local Regulations: Different countries may have unique compliance requirements that must be met in addition to international standards. It’s crucial to understand these regulations to avoid issues with customs or product acceptance.
-
Cultural Differences in Business Practices: Understanding cultural nuances can facilitate better communication and expectations regarding quality control. For instance, the emphasis on documentation and traceability may vary across regions.
-
Logistical Considerations: International shipping can introduce variables that affect product quality. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers have robust logistics processes in place to mitigate risks during transport.
Conclusion
Manufacturing curing ovens is a complex process that requires careful attention to detail at every stage, from material preparation to final quality assurance. By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality control measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing curing ovens that meet their operational needs. Adhering to international standards and conducting thorough due diligence on suppliers will ensure that investments in curing ovens yield reliable, high-quality results for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘curing oven’
When sourcing a curing oven, it’s essential to approach the process methodically to ensure you select a solution that meets your operational requirements and budget. This guide outlines a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procuring a curing oven.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes understanding the types of materials you will be curing—such as coatings, adhesives, or polymers—and the specific temperatures and times required for effective curing. Consider factors like oven size, heating method (e.g., infrared, convection, or UV), and whether you need features like programmable controls or multiple heating zones.
Step 2: Research Different Curing Oven Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of curing ovens available on the market. Each type serves distinct applications:
– Infrared (IR) Ovens: Ideal for rapid curing with high energy efficiency.
– UV Curing Ovens: Best for quick curing of UV-sensitive materials.
– Convection Ovens: Provide uniform heating, suitable for larger batches.
Understanding these differences will help you make informed decisions tailored to your specific needs.

Illustrative image related to curing oven
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with proven expertise and reliable customer service, as these attributes can significantly impact your long-term satisfaction with the equipment.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the curing ovens you are considering comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This may include safety certifications, energy efficiency ratings, and environmental regulations. Compliance not only ensures the quality and safety of the equipment but also protects your business from potential legal issues.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Costs
Once you have identified suitable suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline all costs involved, including shipping, installation, and any additional features. Compare these quotes not just based on price, but also on the value offered, such as warranty terms, after-sales support, and maintenance services. This holistic view will help you make a cost-effective decision.

Illustrative image related to curing oven
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance Options
Inquire about the after-sales support provided by the supplier. A good supplier should offer training, maintenance, and spare parts availability. Consider how easily you can access technical support in case of issues with the oven, as this can greatly influence your operational efficiency.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Plan for Installation
Once you have selected a supplier and agreed on terms, finalize your purchase. Plan for the installation process, including any site preparations needed to accommodate the oven. Ensure that your team is trained on its operation and maintenance to maximize the longevity and performance of your curing oven.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for curing ovens, ensuring that they select the right equipment to enhance their manufacturing capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for curing oven Sourcing
When sourcing curing ovens, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will explore key cost components, price influencers, and practical buyer tips to facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components of Curing Ovens?
The cost structure of curing ovens typically encompasses several components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality steel, insulation, and electronic components can raise the price but enhance durability and efficiency. Custom materials for specific applications (e.g., high-temperature resistance) can further increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and manufacturer. Skilled labor is often necessary for assembly and quality control, particularly for custom or complex oven designs. It’s essential to consider the labor market dynamics in the supplier’s location, as this can influence pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can lead to lower overhead costs, which may be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specialized ovens, impacting initial costs. For standard models, the tooling cost is often amortized over larger production runs, making the unit price more competitive.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that ovens meet industry standards and customer specifications. This can involve additional testing and certification costs, which are reflected in the final price.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on the destination and the chosen Incoterms. International shipping may incur tariffs, duties, and insurance costs, which should be factored into the total purchase price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that reflects their market position, product uniqueness, and overall demand. Understanding the average margins in the industry can aid buyers in negotiations.
What Influences the Pricing of Curing Ovens?
Several factors can influence the pricing of curing ovens, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchasing often leads to significant discounts. Buyers should assess their production needs to leverage volume pricing effectively.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as specific temperature ranges or automation capabilities, can increase costs. Clearly defining requirements upfront can help in obtaining accurate quotes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Ovens with higher-grade materials or certifications (e.g., CE, ISO) typically command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits of investing in quality against initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and after-sales service can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record and support services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential, as they determine who bears shipping costs and risks. This can affect the final landed cost of the oven.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can implement various strategies to optimize costs:
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and warranties. Suppliers may be willing to adjust prices based on order size or long-term partnerships.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes operational costs like energy consumption and maintenance over the oven’s lifespan. Investing in energy-efficient models may lead to substantial long-term savings.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations due to local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and economic factors. Researching local suppliers can also provide competitive alternatives.
Conclusion
In summary, a thorough understanding of the cost structure and pricing dynamics of curing ovens is essential for B2B buyers. By considering key cost components, influencing factors, and employing strategic purchasing techniques, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remember to consult multiple suppliers for quotes and be cautious of indicative prices, as they can fluctuate based on market conditions and supplier capabilities.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing curing oven With Other Solutions
When evaluating industrial curing methods, it’s crucial to consider various alternatives that can achieve similar results in terms of solidifying coatings, adhesives, or polymers. This section presents a comparison of curing ovens against two viable alternatives: UV curing systems and infrared (IR) curing systems. Each solution has its unique benefits and limitations, making the selection process dependent on specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Curing Oven | UV Curing System | Infrared Curing System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for various materials; requires specific temperature and time settings for optimal curing. | Rapid curing process; ideal for UV-sensitive materials; achieves high bond strength quickly. | Fast heating with good energy efficiency; ideal for heat-sensitive materials. |
| Cost | Generally higher initial investment; long-term operational costs can be moderated with efficient use. | Moderate initial cost; lower operational costs due to shorter curing times. | Typically lower initial investment; energy-efficient, but may require more maintenance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup of temperature controls and monitoring; suitable for batch processing. | Simple integration into existing production lines; minimal operator intervention needed. | Easy to implement but requires proper alignment and positioning for effective curing. |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning and calibration needed; can be labor-intensive. | Low maintenance; requires occasional bulb replacements. | Moderate maintenance; heating elements may need periodic replacement. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for a wide range of industries including automotive and aerospace; suitable for batch processing. | Best for high-speed production environments; suitable for coatings, inks, and adhesives. | Suitable for applications requiring quick heating; ideal for textiles, plastics, and certain composites. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of UV Curing Systems?
UV curing systems utilize ultraviolet light to cure inks, coatings, and adhesives almost instantaneously. The primary advantage is the speed of the curing process, which significantly enhances productivity and throughput in high-volume applications. However, they are limited to materials that can respond to UV light, potentially restricting their applicability in certain sectors. Moreover, the initial investment may still be moderate, but operational costs are lower due to reduced curing times and energy consumption.
How Do Infrared Curing Systems Compare to Curing Ovens?
Infrared curing systems use radiant heat to quickly raise the temperature of the material, leading to efficient curing. They are particularly advantageous for heat-sensitive materials, as they can be adjusted to provide localized heating without overheating surrounding areas. While the initial investment is typically lower than that of curing ovens, the systems may require more frequent maintenance due to wear on heating elements. Additionally, the alignment of products within the system is crucial for optimal performance, which can complicate implementation in some settings.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Curing Solution?
Selecting the appropriate curing solution requires a thorough understanding of operational needs, budget constraints, and material compatibility. Buyers should assess the types of materials being cured, production volumes, and available floor space for equipment. While curing ovens provide versatility across various applications, UV and infrared systems may offer enhanced efficiency and speed for specific operations. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s strategic goals and production capabilities, ensuring a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for curing oven
When considering the acquisition of a curing oven, understanding its technical specifications and trade terminology is crucial for making informed decisions. Here’s a breakdown of essential properties and terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Curing Oven?
1. Temperature Range
The temperature range indicates the operational limits of the curing oven, typically ranging from ambient to 500°F (260°C) or higher. This is vital for ensuring that the oven can adequately cure different materials, such as powder coatings, adhesives, and polymers. Buyers should align the oven’s temperature capabilities with the specific requirements of their applications to avoid processing issues.
2. Heating Method
Curing ovens utilize various heating methods, including convection, infrared (IR), and ultraviolet (UV). Convection ovens use forced air circulation for even heat distribution, while IR ovens provide rapid heating through infrared radiation. Understanding the heating method is essential for optimizing the curing process for specific materials and production speeds.
3. Curing Time
Curing time refers to the duration needed for a material to reach its desired hardness and chemical properties after being subjected to heat. This time can vary significantly depending on the material and the oven’s specifications. For businesses, minimizing curing time can lead to increased production efficiency and reduced operational costs.
4. Capacity and Size
Capacity is determined by the oven’s internal dimensions and load capacity, which dictates how many products can be cured simultaneously. Buyers must assess their production needs to ensure that the oven can handle the expected workload, thus optimizing space and resources in their manufacturing processes.
Illustrative image related to curing oven
5. Control Systems
Modern curing ovens often come equipped with advanced control systems, including programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and touch-screen interfaces. These systems allow for precise temperature control, time settings, and monitoring of curing processes. A robust control system enhances operational efficiency and product quality by ensuring consistent curing results.
6. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency ratings are critical for long-term operational cost savings. Curing ovens with high energy efficiency use less electricity while maintaining performance, which is especially important for manufacturers looking to reduce their carbon footprint and operational expenses.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Curing Ovens?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture products for other companies to rebrand. Understanding OEM relationships is important for buyers seeking custom solutions or specific equipment tailored to their needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant for B2B transactions, as it can affect inventory management and budgeting for companies looking to purchase curing ovens or related equipment.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting price estimates from suppliers for specific products or services. This is a critical step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare pricing and terms from different manufacturers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping agreements, clarifying who is responsible for transportation costs, insurance, and customs duties. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, ensuring smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for production planning and inventory management, helping businesses align their operations with supply chain capabilities.
6. Warranty and Service Agreements
These terms encompass the commitments made by manufacturers regarding product performance and post-sale support. Buyers should carefully review warranty terms and available service agreements to ensure they are protected against potential defects and have access to maintenance support.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting curing ovens, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the curing oven Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Curing Oven Sector?
The global curing oven market is experiencing significant growth driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and the increasing demand for efficient production processes across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate this landscape, they will find that the shift towards automation and energy efficiency is paramount. The integration of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled curing ovens, allows for real-time monitoring and optimization of curing processes, enhancing productivity and reducing operational costs.
Emerging trends also highlight the importance of customization in curing solutions. Buyers are increasingly seeking ovens that can be tailored to specific materials and production needs, such as UV and infrared curing technologies that cater to specialized applications. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling buyers to compare specifications, pricing, and reviews across a wider array of suppliers, thus facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing in the Curing Oven Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the curing oven sector. As environmental regulations tighten and consumer awareness grows, companies are under pressure to adopt eco-friendly practices. This includes sourcing equipment that minimizes energy consumption and emissions during operation. For instance, modern curing ovens often come equipped with energy-efficient technologies that significantly reduce their carbon footprint.
The importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and ensuring fair labor practices throughout their supply chains. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and energy star ratings for efficiency can serve as reliable indicators of a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability. By investing in ‘green’ technologies, businesses not only comply with regulations but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Curing Ovens and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of curing ovens has been marked by significant technological advancements. Initially designed for basic heating applications, these ovens have transformed into sophisticated machinery capable of precise temperature control and automation. The introduction of convection heating and recirculating hot air systems has improved the efficiency and uniformity of the curing process, catering to a variety of materials from paints to polymers.
As industries have evolved, so too have the applications of curing ovens. Modern versions are equipped with features such as programmable controls and multi-zone heating capabilities, allowing for greater flexibility in production. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers who seek equipment that can adapt to changing manufacturing demands and improve overall production efficiency. Understanding the historical context of these advancements can help buyers make informed decisions regarding the technology and features they require for their specific applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of curing oven
-
How do I solve issues with inconsistent curing results in my production?
To address inconsistent curing results, first ensure that your curing oven is properly calibrated and maintained. Regularly check the temperature and airflow to confirm they meet the specifications for the materials you are using. Additionally, consider using a data logging system to track temperature fluctuations during the curing process. If problems persist, consult with the oven manufacturer for troubleshooting tips or potential upgrades to your equipment that enhance temperature uniformity. -
What is the best curing oven for powder coatings?
The ideal curing oven for powder coatings is one that can consistently reach and maintain temperatures around 200°C (390°F). Look for ovens with forced air circulation to ensure even heat distribution, as this is crucial for achieving a durable finish. Additionally, consider the size and capacity of the oven based on your production volume. High-quality models often feature programmable settings for different materials, allowing for flexibility in production. -
How do I evaluate suppliers for curing ovens internationally?
When evaluating suppliers for curing ovens, focus on their reputation and experience in the industry. Check for certifications that indicate adherence to international standards, such as ISO. Request references from existing clients and assess their customer service responsiveness. It’s also wise to inquire about warranties and after-sales support. Engaging in a direct conversation can provide insights into their reliability and capability to meet your specific needs. -
What customization options are available for curing ovens?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for curing ovens to better fit specific production processes. These can include adjustable temperature zones, conveyor systems, and programmable curing cycles. Some suppliers may also provide tailored designs for unique applications, such as vertical ovens for limited space environments. Always discuss your requirements with the supplier to explore available modifications that enhance performance and efficiency. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for curing ovens?
The minimum order quantity for curing ovens can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, MOQs range from one unit for small-scale operations to several units for larger manufacturers. It’s important to communicate your needs to the supplier to negotiate terms that fit your production scale. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for initial orders, especially if you express intentions for future bulk purchases. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing curing ovens?
Payment terms can vary by supplier but typically include options such as full payment upfront, a deposit with the balance due upon delivery, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It’s crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing your order to avoid any misunderstandings. Additionally, inquire about potential financing options if you require more flexible payment arrangements. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing curing ovens?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications for the curing ovens you are considering. Look for suppliers that conduct rigorous testing and quality control throughout the manufacturing process. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible or request a factory acceptance test (FAT) before shipment. Establishing clear communication regarding your quality standards will help ensure that the final product meets your expectations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing curing ovens?
When importing curing ovens, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply. Engage a logistics partner experienced in handling industrial equipment to navigate these complexities effectively. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides proper documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Planning for potential delays in shipping and customs processing is also advisable to avoid disruptions in your production schedule.
Top 3 Curing Oven Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reliant Finishing Systems – Industrial Curing Ovens
Domain: reliantfinishingsystems.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Industrial Curing Ovens are essential in advanced manufacturing processes, particularly for powder coating. They ensure precise temperature control and uniformity, leading to high-quality finishes. Key features include:
– Types: Compact batch ovens, large-scale conveyor ovens, vertical curing ovens.
– Technology: Infrared oven technology for rapid curing processes.
– Options: Electric powder coati…
2. Despatch – Industrial Curing Ovens
Domain: despatch.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Despatch offers a selection of industrial curing ovens including benchtop, cabinet, walk-in, and conveyor ovens ideal for curing applications. Key features include fast ramping and cool down rates, tight temperature tolerance, precise control, and uniform airflow. Applications include coatings, adhesives, rubber, thermoset plastics, and composites, particularly in the electronics and semiconductor…
3. Thermal Product Solutions – Gruenberg Truck-In Oven
Domain: thermalproductsolutions.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Curing Ovens by Thermal Product Solutions include a variety of models designed for different curing applications. Key products include:
1. Gruenberg Truck-In Oven: Ideal for powder coating, drum heating, aging, core hardening, drying, preheating, curing, and component testing. Chamber Size: 12 to 96 cubic feet (some models 144 to 480 cubic feet). Maximum Temperature Range: 450°F to 1200°F.
2. Gru…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for curing oven
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Curing Ovens?
In the rapidly evolving industrial landscape, strategic sourcing of curing ovens is paramount for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency and product quality. By understanding the diverse types of curing ovens—such as infrared, UV, and forced air convection—buyers can select equipment that aligns with their specific applications, whether for automotive, aerospace, or electronics sectors. The right oven not only optimizes production processes but also minimizes energy consumption and operational costs.
How Can International Buyers Benefit from Curing Oven Investments?
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in advanced curing ovens can lead to significant competitive advantages. These ovens facilitate a range of applications, from curing coatings to hardening polymers, thereby enhancing product durability and performance. Moreover, leveraging local suppliers can streamline logistics, reduce lead times, and foster partnerships that are vital for sustainable growth.
What Does the Future Hold for Curing Oven Technology?
As technology advances, the future of curing ovens promises innovations such as increased automation and energy efficiency. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about market trends and emerging technologies that could further enhance their production capabilities. By making informed sourcing decisions now, businesses can position themselves for success in the years to come. Explore your options today to harness the full potential of curing ovens in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.