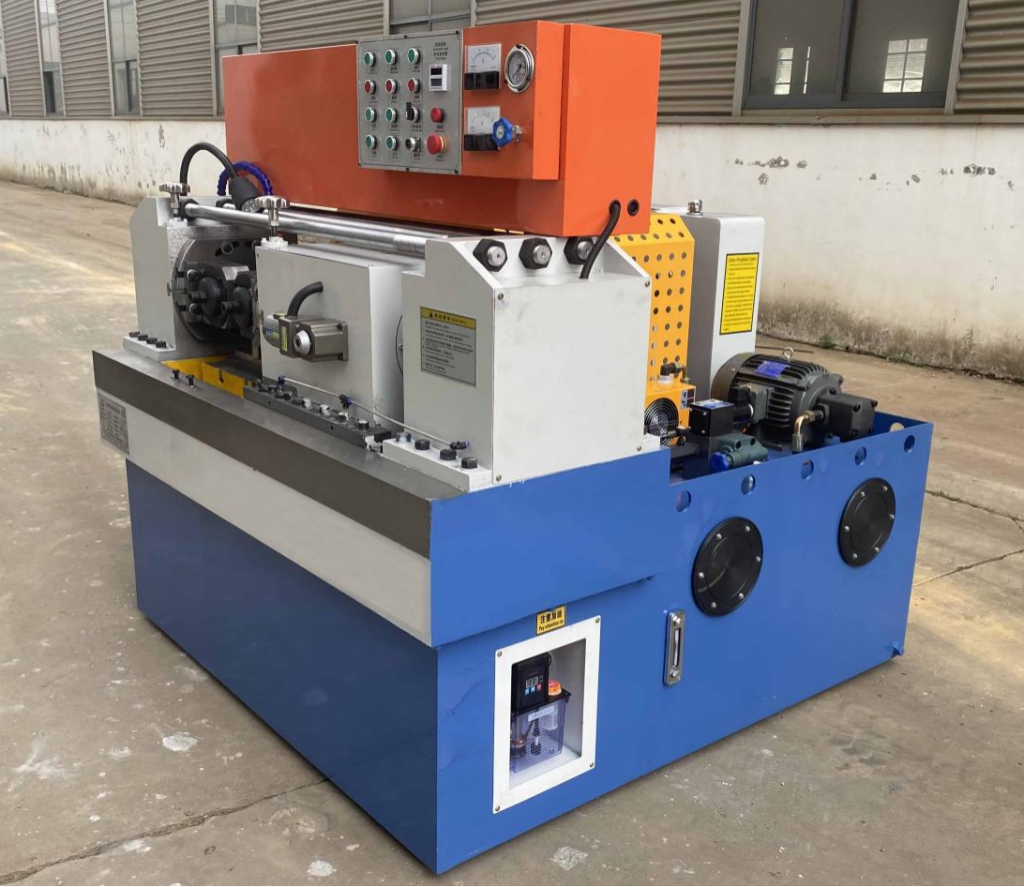
Thread Rolling Machine Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thread rolling machine
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing the right thread rolling machine can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With the growing demand for precision components across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, understanding the nuances of thread rolling technology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse range of thread rolling machines, including their types, applications, and key features, while also addressing critical factors like supplier vetting and cost considerations.
As buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of global sourcing, this guide serves as an essential resource. It empowers them to identify reliable suppliers, evaluate machine specifications, and assess the long-term value of their investments. By delving into the intricacies of thread rolling processes, materials, and the latest technological advancements, B2B buyers will gain valuable insights that can enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Whether you’re looking for a robust two-die machine for high-volume production or a specialized three-die system for intricate designs, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make strategic decisions tailored to your business needs. By leveraging the expertise provided herein, manufacturers can optimize their procurement strategies and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving market.
Understanding thread rolling machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Die Thread Rolling | Utilizes two dies for rolling; suitable for large volumes | Fasteners, screws, bolts, automotive components | Pros: High efficiency; Cons: Limited to certain shapes |
| 3-Die Thread Rolling | Employs three dies for more complex profiles; high precision | Aerospace fasteners, pipe fittings, automotive parts | Pros: Greater precision; Cons: Higher cost and complexity |
| Flat Die Thread Rolling | Uses flat dies for shaping; simpler design | General manufacturing, low-volume production | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited to simpler shapes |
| Horizontal Thread Rolling | Horizontal axis design for ease of operation | Heavy machinery, construction applications | Pros: High throughput; Cons: Requires more floor space |
| Vertical Thread Rolling | Vertical axis for compact design and easy loading | Aerospace, automotive, and precision parts | Pros: Space-saving; Cons: May have lower throughput than horizontal |
What are the Characteristics of 2-Die Thread Rolling Machines?
2-die thread rolling machines are designed for high-volume production, making them ideal for manufacturing fasteners, screws, and bolts. They operate by using two dies that compress the material, forming threads with minimal waste. Buyers should consider the machine’s rolling force, which typically ranges from 50kN to 1000kN, as this affects the types of materials that can be processed. While highly efficient, these machines are best suited for simpler thread profiles.
How Do 3-Die Thread Rolling Machines Stand Out?
3-die thread rolling machines offer enhanced precision and versatility, capable of rolling complex profiles such as splines and knurls. They are particularly beneficial for industries like aerospace and automotive, where high-quality components are critical. The ability to handle hollow components with thin walls makes them a preferred choice for intricate designs. However, potential buyers should weigh the higher investment and maintenance costs against the benefits of precision and flexibility.
What Makes Flat Die Thread Rolling Machines Cost-Effective?
Flat die thread rolling machines are characterized by their straightforward design and lower operational costs. They are suitable for general manufacturing tasks, particularly in low-volume production runs. While they provide a cost-effective solution for simpler shapes, buyers should be aware that their capabilities are limited compared to more advanced machines. These machines are ideal for businesses looking to enter the thread rolling market without significant capital investment.
What are the Advantages of Horizontal Thread Rolling Machines?
Horizontal thread rolling machines are designed for high throughput, making them a popular choice in heavy machinery and construction applications. Their horizontal axis allows for easier operation and part handling, which can enhance productivity. However, buyers should consider the space requirements, as these machines may occupy more floor space than vertical alternatives. The investment in a horizontal machine can yield significant returns in efficiency for large-scale operations.
Why Choose Vertical Thread Rolling Machines?
Vertical thread rolling machines offer a compact design that saves valuable floor space while maintaining high quality in thread production. They are particularly advantageous for industries requiring precision parts, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. The vertical axis allows for easier loading and unloading of components, but buyers should consider that these machines may have lower throughput compared to horizontal designs. The initial investment can be justified by the space-saving benefits and operational efficiencies.
Key Industrial Applications of thread rolling machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Thread Rolling Machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of fasteners such as bolts and screws | Enhanced strength and durability of components | Consider machine capacity, automation options, and die types for specific fasteners. |
| Aerospace | Rolling threads on turbine studs and fittings | Improved precision and reduced material waste | Look for machines capable of handling high tolerances and specialized tooling. |
| Oil & Gas | Manufacturing pipe fittings and connectors | Increased reliability and performance under pressure | Ensure compatibility with various pipe sizes and materials; assess automation capabilities. |
| Construction | Rolling threads on foundation bolts and rebar | Strengthened structural integrity and faster assembly | Evaluate machine speed, ease of operation, and maintenance support. |
| Electronics | Production of precision screws and connectors | High-quality finishes and reduced production costs | Focus on machines with CNC capabilities for intricate designs and automation features. |
How Is a Thread Rolling Machine Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, thread rolling machines are essential for producing high-strength fasteners like bolts and screws that are critical for vehicle assembly. The cold rolling process enhances the mechanical properties of the fasteners, making them more durable and resistant to wear. Buyers in this industry should prioritize machines with high throughput and the ability to accommodate various fastener sizes, ensuring they meet production demands while maintaining quality standards.
What Are the Applications in Aerospace Manufacturing?
Aerospace applications require precision-engineered components, such as turbine studs and fittings. Thread rolling machines are employed to create these components with exacting tolerances, reducing material waste and improving overall part quality. International buyers should seek machines that offer advanced control systems and the capability to handle specialized dies, ensuring compliance with stringent aerospace standards.
How Do Thread Rolling Machines Benefit the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, thread rolling machines are used to manufacture pipe fittings and connectors that must withstand extreme pressures and harsh environments. The rolling process creates strong, uniform threads that enhance the reliability of these critical components. Buyers should consider machines that can handle a variety of pipe sizes and materials while providing options for automation to streamline production processes.
Why Are Thread Rolling Machines Important for Construction?
In construction, thread rolling machines are utilized for creating foundation bolts and rebar, which are vital for structural integrity. The machines provide consistent quality and strength, enabling faster assembly on job sites. Buyers should evaluate machine speed and ease of operation, as well as the availability of support and maintenance services, to ensure long-term productivity.
What Role Do Thread Rolling Machines Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
The electronics industry relies on thread rolling machines for producing precision screws and connectors used in various devices. The machines facilitate high-quality finishes and can significantly reduce production costs by optimizing material usage. Buyers should focus on machines equipped with CNC capabilities for intricate designs, as well as automation features that enhance efficiency in high-volume production environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘thread rolling machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Complicated Setup and Changeover Processes
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with the setup and changeover of thread rolling machines, particularly when switching between different product lines or specifications. This can lead to significant downtime, impacting production efficiency and increasing operational costs. In industries like automotive and aerospace, where precision is paramount, lengthy changeover processes can also result in quality issues or non-compliance with stringent industry standards. Buyers may feel overwhelmed by the complexity of adjusting dies, settings, and machine configurations, especially if they lack experienced personnel.

Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, it is crucial for buyers to invest in thread rolling machines designed for quick changeovers, such as those with user-friendly interfaces and automated settings. When sourcing machines, look for features like quick-release die systems and intuitive control panels that simplify the setup process. Additionally, providing comprehensive training for operators can significantly reduce the learning curve. Consider partnering with manufacturers who offer ongoing support and resources, such as detailed manuals and troubleshooting guides. This proactive approach can streamline operations and minimize downtime, ultimately enhancing productivity.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Thread Quality and Dimensional Accuracy
The Problem: Inconsistent thread quality and dimensional accuracy is a common pain point for manufacturers using thread rolling machines. Variability in thread dimensions can lead to issues such as poor fitment, increased rejection rates, and costly rework. This inconsistency often arises from improper machine calibration, inadequate maintenance, or subpar raw materials. Buyers may find it challenging to maintain quality control, especially when producing high-precision components for critical applications.
The Solution: To address quality concerns, implement a robust maintenance and calibration schedule for your thread rolling machines. Regular inspections and adjustments can help ensure that machines operate within specified tolerances. When sourcing machines, prioritize those equipped with advanced monitoring systems that provide real-time feedback on parameters like pressure, speed, and die wear. Additionally, investing in high-quality raw materials and conducting regular quality checks on inputs can significantly enhance the final product’s reliability. Consider adopting statistical process control (SPC) techniques to track variations and proactively identify issues before they escalate into larger problems.
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Production Processes
The Problem: Many buyers find that their operational costs escalate due to inefficient production processes related to their thread rolling machines. Factors such as energy consumption, excessive material waste, and labor inefficiencies can contribute to inflated costs. In regions like Africa and South America, where competitive pricing is crucial, manufacturers must find ways to optimize their operations without compromising quality or throughput.
The Solution: To improve operational efficiency, consider investing in energy-efficient thread rolling machines that utilize advanced technologies to reduce energy consumption. Look for machines with features like variable speed drives and optimized rolling parameters that can minimize waste and maximize output. Additionally, integrating automation solutions, such as robotic part handling and in-line inspection systems, can streamline production workflows and reduce labor costs. Collaborating with machine manufacturers to customize equipment according to specific production needs can also lead to more efficient processes. By focusing on these strategies, buyers can significantly lower operational costs while maintaining high-quality standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thread rolling machine
What Are the Key Materials Used in Thread Rolling Machines?
When selecting materials for thread rolling machines, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for specific applications. The following analysis covers four common materials used in the construction of thread rolling machines: carbon steel, stainless steel, tool steel, and aluminum.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Thread Rolling Machines?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and excellent wear resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 400°C and can withstand moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its durability and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for many manufacturers. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to maintenance issues over time.

Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for rolling applications involving non-corrosive materials. However, its performance may be compromised in high-humidity environments typical in some regions of Africa and South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is crucial. Buyers should also consider local conditions that may affect the longevity of carbon steel components.
What Are the Advantages of Stainless Steel in Thread Rolling Machines?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance (up to 800°C), and good mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for environments where moisture is prevalent. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel and may require specialized manufacturing processes, increasing production costs.

Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly suitable for rolling applications involving corrosive media or in industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240. Given its higher cost, buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and longevity.
Why Choose Tool Steel for Thread Rolling Machines?
Key Properties: Tool steel is designed for high hardness and wear resistance, with temperature ratings often exceeding 500°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of tool steel is its ability to maintain sharp cutting edges and resist deformation under heavy loads. However, it is more expensive and can be challenging to machine, leading to longer production times.
Impact on Application: Tool steel is ideal for high-precision applications where durability and performance are critical, such as aerospace and automotive components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as JIS G4404 is essential, especially for buyers in Japan and other Asian markets. The higher upfront cost may be justified by the extended lifespan and reduced downtime.
How Does Aluminum Compare in Thread Rolling Machines?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, with good corrosion resistance and a temperature rating of around 200°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce operational costs in terms of energy and handling. However, it has lower strength compared to steel and may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications.

Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in the aerospace industry. However, it may not perform well in high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and South America should ensure compliance with standards such as EN AW-6060. The cost of aluminum can vary significantly based on market conditions, so buyers should monitor pricing trends.
Summary of Material Selection for Thread Rolling Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for thread rolling machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General fasteners and non-corrosive parts | Cost-effective and durable | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Tool Steel | Aerospace and automotive components | High hardness and wear resistance | Expensive and difficult to machine | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications in aerospace | Low weight and good corrosion resistance | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for thread rolling machines, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thread rolling machine
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Thread Rolling Machines?
The manufacturing of thread rolling machines involves several critical stages that ensure the machinery meets the precise specifications and quality standards demanded by industries worldwide. Here are the primary stages:
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Thread Rolling Machines?
The initial phase of manufacturing thread rolling machines involves careful selection and preparation of materials. Typically, high-quality alloy steels are used for the machine frame and components, ensuring durability and resistance to wear. The selection of materials is crucial because the performance and longevity of the machine depend heavily on the quality of the raw materials. Manufacturers often use advanced metallurgical techniques to enhance the properties of these materials, making them suitable for high-stress applications.
Forming: How Is the Machine Assembled and Shaped?
During the forming stage, the prepared materials undergo various processes, such as machining, welding, and casting. Precision machining is employed to create the intricate components required for the thread rolling machines, including the dies, gears, and control systems. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology is frequently utilized to achieve the high tolerances necessary for effective operation. Additionally, die manufacturing is a specialized process, where dies are shaped to create specific thread profiles, ensuring the threads produced are uniform and meet the required specifications.
Assembly: What Steps Are Involved in the Assembly Process?
The assembly stage involves integrating all the components into a cohesive machine. This stage requires skilled technicians who ensure that all parts fit together correctly and function as intended. Key components, such as the hydraulic systems, drive mechanisms, and control panels, are carefully aligned and tested during assembly. Ensuring precise alignment is critical, as misalignments can lead to decreased performance or even mechanical failure.
Finishing: How Are Thread Rolling Machines Prepared for Delivery?
The final stage, finishing, includes processes such as surface treatment, painting, and quality checks. Surface treatments, such as hardening or coating, enhance the machine’s resistance to wear and corrosion, extending its lifespan. After the finishing touches, machines undergo rigorous quality assurance checks to confirm that they meet both internal standards and international specifications. This stage often involves both visual inspections and functional tests to ensure that the machine operates smoothly and efficiently.

Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Thread Rolling Machines?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of thread rolling machines to ensure reliability and performance. Here are the key aspects of quality assurance that B2B buyers should be aware of:
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
Manufacturers of thread rolling machines often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a company is committed to maintaining high-quality standards in its processes and products. Additionally, other certifications like CE mark (for European markets) and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications for specific industries further assure buyers of the machine’s compliance with safety and performance standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical at various stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting the raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet required specifications. This step helps prevent defects in the final product by ensuring that only quality materials are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing checks are conducted to monitor the quality of the assembly and machining processes. This may include measuring tolerances and verifying machine settings.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the machines undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they function correctly. This includes operational tests, stress tests, and performance evaluations to ensure they meet all specified criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of potential suppliers is crucial. Here are some effective strategies:
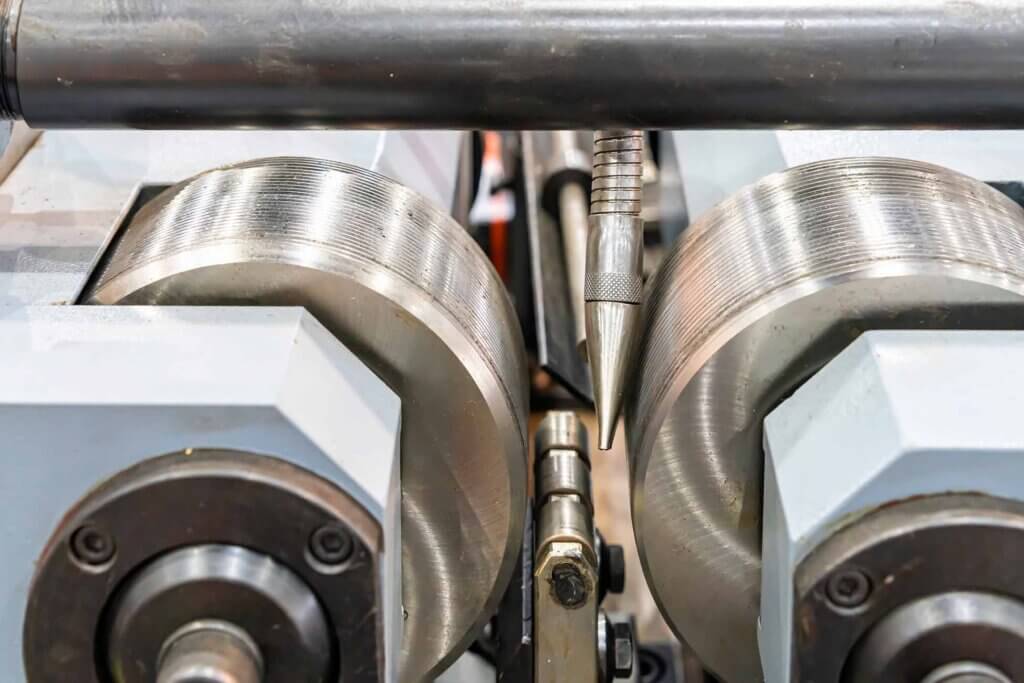

Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
What Methods Can Buyers Use to Assess Supplier Quality?
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facility allows buyers to assess the quality control measures and manufacturing processes firsthand. During an audit, buyers can evaluate the machinery, technology, and workforce capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports provides insight into the supplier’s QC processes and any historical data on product defects or failures. These reports can help buyers gauge the reliability of the supplier.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can offer an objective evaluation of the manufacturing process and quality standards. These inspectors can provide detailed reports on compliance with international standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Transactions?
Understanding the nuances of quality control is essential for B2B buyers, especially when dealing with international suppliers. Here are some considerations:
How Do Cultural and Regulatory Differences Impact Quality Assurance?
Buyers should be aware that quality assurance practices may vary significantly across regions. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have stringent regulations compared to those in other regions. Understanding these differences can help buyers set appropriate expectations and negotiate better terms.
What Should Buyers Know About Warranty and Support Services?
When purchasing thread rolling machines, it is vital to inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support. A robust warranty can indicate the manufacturer’s confidence in their product quality. Additionally, support services such as maintenance and training can significantly impact the machine’s long-term performance and reliability.
Conclusion: Why Quality Assurance Is Critical for Thread Rolling Machines
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for thread rolling machines is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, buyers can appreciate the complexities involved in producing these machines. Moreover, by ensuring suppliers adhere to international standards and robust quality control processes, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure that their investments yield high-quality, reliable machinery.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘thread rolling machine’
Introduction
This guide provides a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in sourcing a thread rolling machine. Whether you are manufacturing fasteners or precision components, selecting the right machine is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and product quality. Follow these steps to ensure a successful procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by detailing the technical requirements for the thread rolling machine. Consider the types of threads you need to produce, material specifications, and production volume.
– Common Specifications: Identify whether you need a two-die or three-die machine based on the complexity of the threads.
– Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine can handle the materials you intend to use, such as steel or aluminum.
Step 2: Research Different Machine Types
Explore the various types of thread rolling machines available in the market. Each type has unique features tailored for specific applications.
– Cold vs. Hot Rolling: Decide if you need a cold rolling machine for tighter tolerances or a hot rolling machine for larger components.
– Automation Options: Consider machines with automation capabilities to enhance throughput and reduce labor costs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to assess their reliability and product quality. Request detailed company profiles and product catalogs.
– Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or other quality assurance indicators that demonstrate a commitment to industry standards.
– Customer References: Ask for references from other businesses in your region or sector to gauge their experiences with the supplier.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
After narrowing down your options, request quotes from multiple suppliers. Comparing pricing is essential to ensure you are getting the best deal.
– Cost Breakdown: Pay attention to what is included in the price, such as installation, training, and after-sales support.
– Financing Options: Inquire about financing plans if upfront costs are a concern, especially for large investments.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Evaluate the after-sales support and warranty options provided by the supplier. A solid support system can greatly influence long-term operational efficiency.
– Technical Support: Ensure the supplier offers timely technical assistance and spare parts availability.
– Warranty Terms: Review warranty terms carefully to understand what is covered and for how long, as this can protect your investment.
Step 6: Visit Production Facilities (If Possible)
If feasible, arrange a visit to the supplier’s production facilities. This step can provide invaluable insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
– Quality Assurance Practices: Observe their quality assurance protocols to ensure they align with your standards.
– Machine Demonstrations: Request demonstrations of the machines you are interested in to see their performance firsthand.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, carefully review and finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure all terms are clearly outlined to avoid misunderstandings.
– Payment Terms: Clarify payment terms, including deposit requirements and payment schedules.
– Delivery and Installation: Confirm delivery timelines and installation responsibilities to ensure a smooth transition to production.
By following this checklist, you can make an informed decision when sourcing a thread rolling machine that meets your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thread rolling machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Thread Rolling Machine Sourcing?
When sourcing thread rolling machines, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The main cost components include:

Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in the manufacturing of thread rolling machines significantly influence the overall cost. High-grade steel and advanced alloys used in dies and machine frames can enhance durability but may increase initial costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct labor involved in the assembly and indirect labor related to design and engineering. The geographic location of the manufacturer can affect labor rates, with regions in Europe typically having higher labor costs compared to some South American or African countries.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment depreciation, and factory maintenance. Manufacturers with advanced technology may have higher overheads, but this often results in better product quality and efficiency.
-
Tooling: The cost of dies and tooling is a significant factor in thread rolling machine pricing. Custom tooling can be expensive but is often necessary for specific applications. Regular maintenance and regrinding of dies also add to the total cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Quality assurance processes ensure that the machines meet industry standards. Rigorous QC can add to the cost but is crucial for ensuring machine reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly based on the machine’s size and weight, distance from the supplier, and chosen shipping method. International buyers must consider customs duties and taxes that may apply.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin can vary based on their brand reputation, market position, and relationship with buyers. Established brands may command higher prices due to perceived reliability and service.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Thread Rolling Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of thread rolling machines:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Ordering in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often have tiered pricing based on the quantity purchased.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-built machines tailored to specific needs typically cost more than standard models. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines built with premium materials and those that meet specific industry certifications (e.g., ISO) may be priced higher, reflecting their reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and location of the supplier can impact pricing. Local suppliers may offer lower logistics costs, while overseas suppliers may provide better pricing but involve additional shipping and customs complexities.
-
Incoterms: The agreed Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage their total costs effectively.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Thread Rolling Machines?
To maximize cost-efficiency and ensure a favorable purchase, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices, especially when purchasing in bulk or if you have existing relationships with suppliers. Leverage competitive quotes to secure better terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront costs but also long-term expenses, including maintenance, downtime, and operational efficiency. A cheaper machine may lead to higher TCO if it requires frequent repairs or has lower productivity.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: International buyers must be aware of exchange rates, potential tariffs, and local regulations that can affect costs. Conduct thorough research on the supplier’s reliability and customer service, especially for overseas transactions.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes break down costs clearly, including all components and shipping details. This transparency will help identify hidden fees and facilitate better comparisons between suppliers.
-
Assess Local Support and Service: Consider the availability of local support and spare parts, which can minimize downtime and additional costs related to machine servicing.
By understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and leveraging effective sourcing strategies, international buyers can make informed decisions when investing in thread rolling machines, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and profitability.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing thread rolling machine With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Thread Rolling Machines
In the manufacturing landscape, thread rolling machines serve a specialized purpose in producing high-quality threads on various components. However, businesses may consider alternative methods to achieve similar results, depending on specific operational requirements, production volumes, and cost constraints. Below, we explore two viable alternatives to thread rolling machines: tapping and thread cutting.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Thread Rolling Machine | Tapping | Thread Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed production, durable threads | Moderate speed, good for small batches | Lower speed, excellent for intricate designs |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower operational costs | Lower initial cost, moderate operational costs | Moderate initial cost, higher operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled setup, training needed | Simple setup, minimal training | Requires skilled labor for setup |
| Maintenance | Moderate, needs regular checks | Low, minimal upkeep needed | Moderate, tool wear can be significant |
| Best Use Case | Mass production of uniform threads | Small to medium batch sizes | Custom or complex threading needs |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What are the Pros and Cons of Tapping?
Tapping is a widely used method for creating internal threads in materials. It involves rotating a tool with cutting edges to form the thread profile directly into the workpiece.
Pros:
– Cost-effective: Tapping tools are generally less expensive compared to rolling machines, making it an attractive option for businesses with limited budgets.
– Ease of Use: The setup is straightforward, and operators can quickly learn the technique, allowing for faster implementation in production environments.
Cons:
– Speed Limitations: While tapping is suitable for smaller batches, it does not match the high-speed capabilities of thread rolling machines.
– Thread Strength: The threads produced via tapping may not be as strong or durable as those created through rolling, potentially impacting the performance of the final product in critical applications.

Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
How Does Thread Cutting Compare?
Thread cutting is another alternative that involves using a cutting tool to remove material and form threads. This method allows for the creation of intricate thread profiles, making it valuable in specialized applications.
Pros:
– Versatility: Thread cutting can produce a wide range of thread types and sizes, making it ideal for custom or complex threading needs.
– Precision: This method allows for precise control over thread dimensions, which is essential for applications requiring tight tolerances.
Cons:
– Slower Production Rates: Thread cutting is generally slower than both rolling and tapping, making it less suitable for high-volume production.
– Higher Tool Wear: The cutting tools can wear out quickly, leading to increased maintenance costs and downtime for tool replacement.
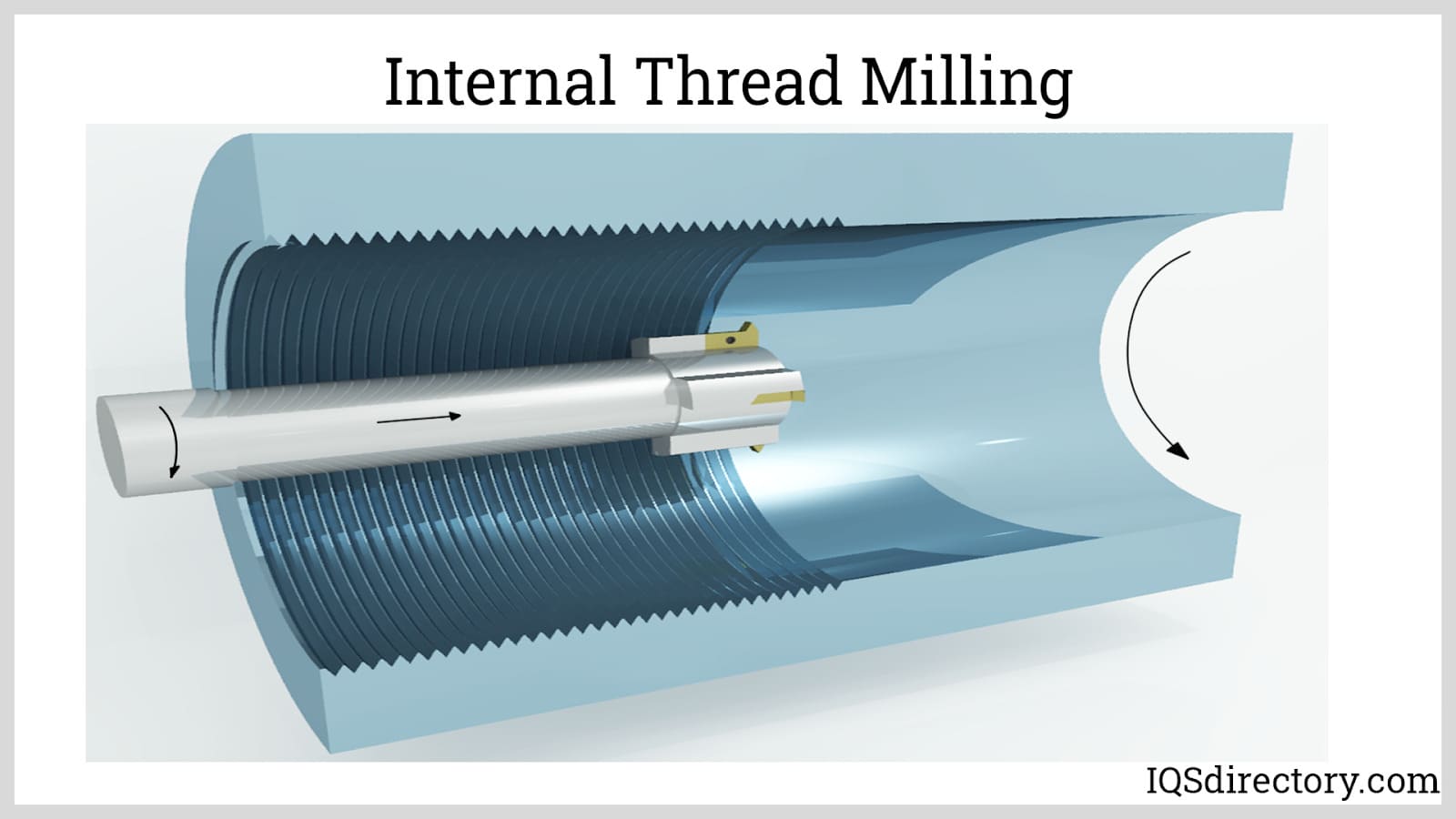
Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the most appropriate threading method, B2B buyers should assess their specific production needs and constraints. Considerations include the volume of parts required, the strength and durability of the threads needed, and budgetary limitations. For high-volume production with stringent quality requirements, a thread rolling machine is often the best choice. However, for smaller batches or custom applications, tapping or thread cutting may provide a more cost-effective and flexible solution. Engaging with manufacturers and suppliers can provide insights into the best practices and help identify the right technology for your operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thread rolling machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Thread Rolling Machines?
When considering the purchase of a thread rolling machine, it’s essential to understand the technical specifications that influence performance, efficiency, and suitability for specific applications. Here are some critical properties:
-
Rolling Force (kN)
This measures the maximum force the machine can exert during the rolling process, typically ranging from 50 kN to 1000 kN. A higher rolling force allows for the processing of tougher materials and larger components, making it crucial for industries such as automotive and aerospace. Understanding this specification helps buyers ensure the machine can handle their specific production demands. -
Die Configuration (2-Die vs. 3-Die)
Thread rolling machines can come in various configurations, primarily 2-die and 3-die systems. A 2-die machine is suitable for simpler threads, while a 3-die machine provides more precise rolling for complex profiles, including threads on hollow components. Selecting the right configuration is vital for achieving desired thread quality and production efficiency. -
Spindle Diameter (mm)
The spindle diameter affects the type and size of the components that can be processed. A larger spindle diameter typically accommodates larger workpieces, while smaller diameters are ideal for precision applications. This property is crucial for buyers looking to ensure compatibility with their existing production lines. -
Automation Capability
Many modern thread rolling machines come equipped with automation features such as CNC controls and robotic part handling. Automation enhances productivity by reducing labor costs and increasing throughput. Buyers should assess their production needs and consider the level of automation required to remain competitive in their market. -
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of the machine, often high-grade iron or steel, impacts durability and performance. Machines built with superior materials are likely to withstand the rigors of continuous operation, offering better longevity and lower maintenance costs. Evaluating material quality is essential for buyers prioritizing investment longevity. -
Production Rate (pieces/min)
This metric indicates the number of components that can be produced in a given timeframe. A higher production rate is essential for meeting market demands and optimizing operational efficiency. Buyers should evaluate their production targets against the machine’s capabilities to ensure alignment with their business objectives.
What Common Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know?
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some key terms to familiarize yourself with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, knowing the OEM can help in sourcing reliable components or machines that fit specific requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively, especially when sourcing components or machinery from international suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products. This is a critical step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare offers and negotiate terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers navigate logistics and reduce risks associated with international transactions. -
Lead Time
This refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and ensuring timely project execution. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which a manufacturer guarantees the machine’s performance and covers repairs or replacements for defects. Knowing the warranty terms can provide buyers with peace of mind and protection against unforeseen issues.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing thread rolling machines that align with their operational needs and business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the thread rolling machine Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Thread Rolling Machine Market?
The thread rolling machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for fasteners across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. As manufacturers seek to enhance productivity and precision, there is a notable shift towards advanced technologies such as CNC-controlled machines and automation solutions. These innovations not only improve the quality of the threaded products but also streamline production processes, making them more cost-effective.
International B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly interested in machines that can handle a variety of materials and thread types. The trend towards customization is also gaining traction, as companies aim to meet specific client requirements. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is prompting manufacturers to integrate smart technologies into their thread rolling machines, facilitating real-time monitoring and data analytics for improved operational efficiency.
Sourcing trends are increasingly leaning towards suppliers who can provide comprehensive solutions, including machine maintenance, spare parts, and training services. In emerging markets, affordability and reliability remain key decision-making factors. Buyers are advised to consider the total cost of ownership when selecting machines, focusing not only on initial purchase price but also on operational efficiency and long-term service support.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Thread Rolling Machine Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for B2B buyers in the thread rolling machine sector. As environmental regulations tighten globally, manufacturers are pressured to adopt practices that minimize their ecological footprint. This includes using energy-efficient machines and sourcing materials responsibly.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and ensuring fair labor practices throughout their supply chains. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management can provide buyers with confidence in their suppliers’ sustainability claims.
Moreover, the trend towards ‘green’ materials is becoming prominent. Manufacturers are exploring the use of biodegradable lubricants and recyclable components in their machines. This shift not only meets regulatory requirements but also appeals to environmentally conscious customers, enhancing brand reputation and marketability.
How Has the Thread Rolling Machine Sector Evolved Over Time?
The thread rolling machine sector has undergone significant evolution since its inception. Initially, thread rolling was a manual process, heavily reliant on human skill and mechanical prowess. Over the decades, advancements in engineering and materials science have transformed the industry, leading to the development of automated and CNC-controlled machines that offer unprecedented precision and efficiency.
The introduction of cold rolling technology revolutionized the manufacturing of fasteners, allowing for stronger and more durable threads. As the global demand for fasteners surged, particularly in the automotive and aerospace sectors, manufacturers have increasingly focused on innovation and automation to meet production challenges. Today, companies are not only prioritizing high-performance machines but are also integrating smart technologies that align with the principles of Industry 4.0, ensuring that they remain competitive in an ever-evolving marketplace.
In conclusion, understanding these market dynamics and sourcing trends is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to make informed purchasing decisions in the thread rolling machine sector. By focusing on technology, sustainability, and the historical context of this industry, businesses can better navigate the complexities of sourcing and supply chain management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thread rolling machine
-
How do I choose the right thread rolling machine for my production needs?
Selecting the right thread rolling machine involves assessing your production volume, the materials you are working with, and the specific thread profiles you need. Consider the machine’s capacity, such as rolling force and die configuration, to ensure it meets your requirements. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s flexibility for different applications and its compatibility with automation systems to enhance efficiency. Consulting with manufacturers about your needs can provide tailored recommendations. -
What are the benefits of investing in a high-quality thread rolling machine?
High-quality thread rolling machines offer superior durability, precision, and efficiency, which can significantly enhance production quality. They reduce scrap rates and rework, ultimately lowering manufacturing costs. Moreover, advanced features like automation integration and programmable settings allow for consistent output and scalability. Investing in a reputable brand can also provide long-term support, including training and maintenance, which is crucial for optimizing performance. -
What customization options are available for thread rolling machines?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor thread rolling machines to specific applications. Custom features may include specialized dies for unique thread profiles, adjustable speed settings, and enhanced automation capabilities. Additionally, you can request modifications in machine size or configuration to fit your workspace or production line. Discussing your specific requirements with suppliers will help ensure you get a machine that meets your operational needs. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for thread rolling machines?
The minimum order quantity for thread rolling machines can vary significantly between manufacturers and the complexity of the machine. Generally, MOQs can range from a single unit for standard machines to several units for custom or specialized equipment. It’s important to clarify MOQs with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to ensure your purchasing strategy aligns with their production capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a thread rolling machine?
Payment terms for thread rolling machines can vary based on the supplier and the buyer’s location. Common terms include a deposit upon order confirmation, followed by the balance before shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide sufficient security for both parties and ensure clarity on currency exchange rates and payment methods. -
How can I ensure the quality of the thread rolling machines I purchase?
To ensure quality, consider sourcing from reputable manufacturers with a track record of producing reliable machinery. Request certifications such as ISO standards, and inquire about their quality control processes. Visiting the production facility or seeking third-party inspections can also provide assurance. Additionally, reviews and testimonials from other B2B buyers can offer insights into the machine’s performance and the supplier’s reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I take into account when importing thread rolling machines?
When importing thread rolling machines, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure you have a reliable freight forwarder who understands the complexities of international shipping. It’s essential to factor in lead times for production and delivery, as well as the availability of local support for installation and maintenance. Proper planning can mitigate delays and additional costs associated with logistics. -
How do I vet suppliers for thread rolling machines in the international market?
Vetting suppliers involves researching their reputation, production capabilities, and customer service history. Look for manufacturers with established certifications and positive reviews from other international buyers. Request references and assess their responsiveness and willingness to provide technical support. It may also be beneficial to attend industry trade shows or use B2B platforms to connect with verified suppliers, allowing for direct communication and negotiation.
Top 5 Thread Rolling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Profiroll – Thread and Profile Rolling Machines
Domain: profiroll.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Profiroll Thread and Profile Rolling Machines are designed for high-quality thread manufacturing using cold rolling technology. Key features include:
– Statically and dynamically stiff iron cast C-frame
– High accessibility for part insertion and extraction
– Rolling force range from 50kN to 1000kN
– Infeed and through-feed rolling capabilities
– Custom drive and control systems tailored for …
2. Waterbury-Farrel – APT #YC-3T Thread Roller
Domain: surplusrecord.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Used Thread Rollers for Sale from various manufacturers including Waterbury-Farrel, Hartford, Kinefac, Warren, and others. Key models include APT #YC-3T, Hartford #0-500, and Waterbury-Farrel #00. Specifications include thread diameters ranging from 3/32″ to 1/2″, thread lengths up to 1″, production rates from 150 to 1100 PPM, and motor specifications such as 2 HP and 3-phase power. Locations of s…
3. Fette – Key Product
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Key product details for thread roller products on eBay include various brands such as Fette, Winter Works, and Swisher, with a range of conditions (new and pre-owned). Prices vary from under $1,300 to over $3,620. Specific models listed include FETTE F2SL, FETTE E8 A00, Winter Works Machine Thread Roller, and WHARCO THREAD ROLLER. Sizes and specifications vary, with options for different thread si…
4. Bhavya Machine Tools – Hydraulic Thread & Form Rolling Machines
Domain: bhavyamachinetools.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Thread & Form Rolling Machine
Model Numbers: TR-25, TR-30, TR-40, TR-50, TR-80, TR-190, TR-120
Max. Pitch Can Be Rolled (in mm): 3, 25, 35, 4, 5, 6, 8
Max. Dia can be Rolled in Feed (in mm): 25, 30, 40, 50, 80, 100, 120
Max. Dia can be Rolled in Through Feed (in mm): 18, 20, 28, 35, 40, 50, 70
Max. Rolling Length in Feed (in mm): 80, 100, 100, 150, 150, 150, 70
Max. Rolling Length Throug…
5. Videx – Hi-Tensile Thread & Form Rollers
Domain: videx-machine.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Thread & Form Rollers for Hi-Tensile Fasteners. Key features include: higher die life, faster PPM, fully automatic, threading any shape and size up to 300-200mm long thread. The VA series operates 24/7 with no clutches, slides, or hydraulics, requiring minimal maintenance. It offers perfect thread quality, excellent die life, and high production rates. Closed structure design improves thread lengt…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thread rolling machine
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, strategic sourcing of thread rolling machines is paramount for optimizing production efficiency and enhancing product quality. By understanding the diverse machine types—such as two-die and three-die configurations—and their specific applications, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. The integration of automation and innovative features in modern machines not only reduces labor costs but also significantly increases throughput and precision.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic sourcing can lead to substantial cost savings and improved supply chain resilience. Engaging with reputable manufacturers ensures access to the latest technologies, which can drive competitive advantages in the marketplace.
As you consider your next investment in thread rolling machinery, prioritize partnerships that emphasize reliability, technical support, and adaptability to your unique requirements. The future of manufacturing is here—embrace it by selecting the right equipment to propel your business forward and enhance your production capabilities. Take the next step in your sourcing journey today, and unlock the potential of advanced thread rolling technology.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to thread rolling machine
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.