Everything You Need to Know About Ir Oven Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ir oven
Navigating the complexities of sourcing infrared ovens can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in rapidly evolving markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Nigeria. As industries increasingly adopt advanced thermal processing technologies, understanding the diverse types of infrared ovens and their specific applications becomes essential. This guide is designed to demystify the intricacies of infrared oven selection, offering a comprehensive overview of various oven types—including conveyor ovens, curing ovens, and custom solutions—tailored to meet unique operational needs.
In this guide, we will explore critical considerations such as supplier vetting, cost factors, and the latest advancements in infrared technology. By providing detailed insights into the operational efficiencies and energy savings associated with different heating methods, we empower B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their production goals. Whether your focus is on enhancing product quality, improving throughput, or reducing energy consumption, our structured approach will equip you with the knowledge needed to successfully navigate the global market for infrared ovens.
Understanding ir oven Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conveyor Ovens | Continuous flow design with a conveyor system for uniform heating. | Food processing, automotive, electronics | Pros: High efficiency, consistent results. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Industrial Curing Ovens | Designed for enhancing material strength through thermal processing. | Coating, adhesives, composite curing | Pros: Improves product durability. Cons: Requires precise temperature control. |
| Electric Infrared Ovens | Uses electric infrared heaters, ideal for rapid heating. | Laminating, sintering, curing adhesives | Pros: Fast heating, energy-efficient. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Batch Ovens | Operates in discrete batches, suitable for smaller production runs. | Aerospace, pharmaceuticals, custom parts | Pros: Flexible, customizable. Cons: Slower throughput compared to conveyor types. |
| Tunnel Ovens | Multi-zone ovens designed for continuous product movement through heating zones. | Glass processing, metal coating | Pros: Efficient for large volumes, consistent results. Cons: Complex setup and maintenance. |
What Are Conveyor Ovens and Their B2B Relevance?
Conveyor ovens are characterized by their continuous flow design, featuring a conveyor belt that moves products through the oven. This design ensures uniform heating, making them ideal for high-volume applications in industries such as food processing and automotive. When considering a conveyor oven, B2B buyers should evaluate factors like production speed, energy efficiency, and the specific heating requirements of their products. While the initial investment may be higher, the operational efficiency can lead to significant long-term savings.
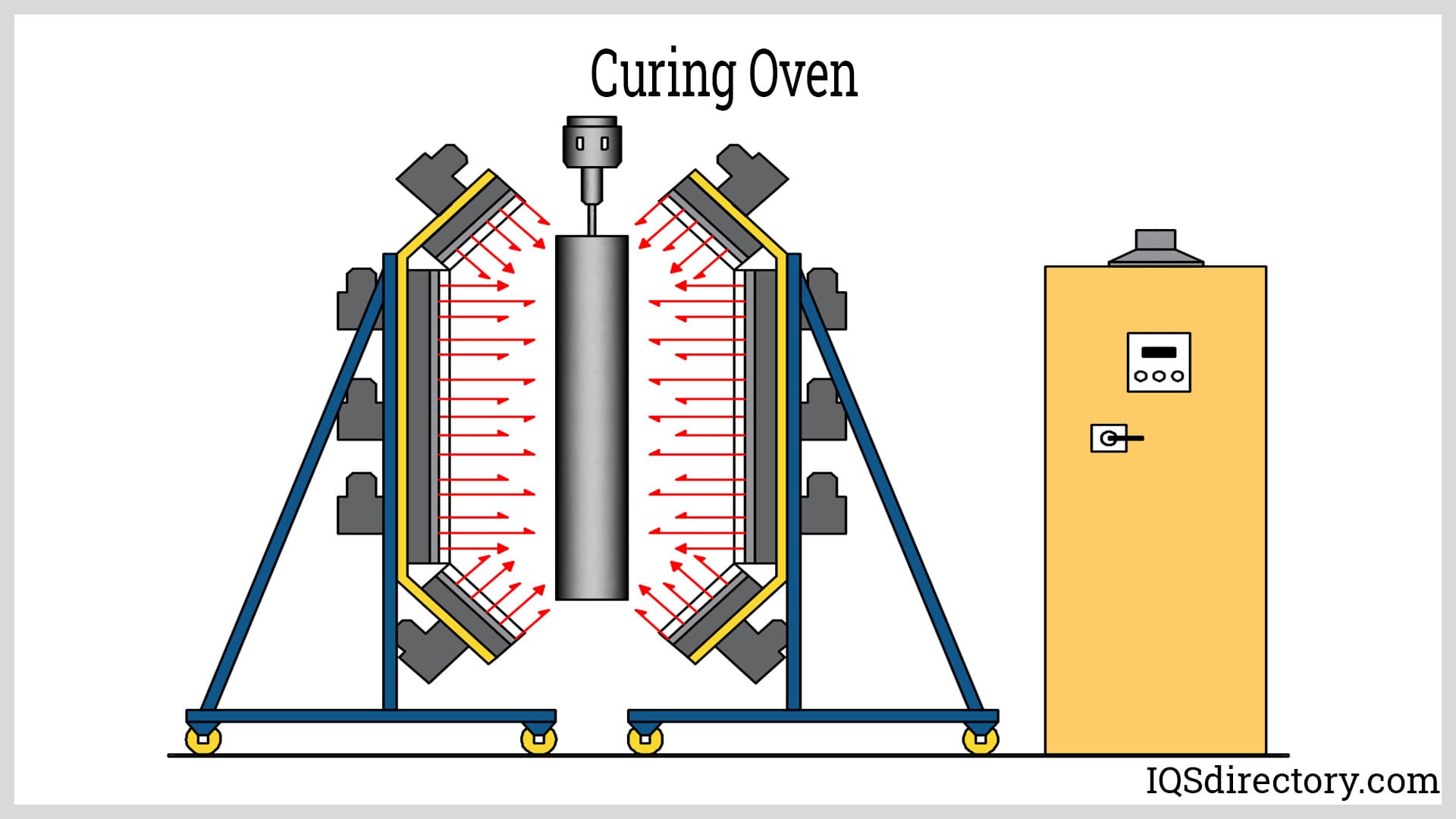
How Do Industrial Curing Ovens Enhance Material Strength?
Industrial curing ovens are specifically engineered to improve the strength and durability of materials through controlled thermal processing. They are widely used in applications such as coating and adhesive curing, where precise temperature regulation is crucial. Buyers should consider the oven’s temperature range and control capabilities, as well as the material types they will be processing. While these ovens can enhance product performance, they require careful monitoring to avoid overheating or under-curing materials.
What Are the Advantages of Electric Infrared Ovens?
Electric infrared ovens utilize electric infrared heaters to provide rapid heating, making them particularly suitable for processes like laminating and curing adhesives. Their design allows for quick energy transfer, which is beneficial for operations with limited space or fast production lines. B2B purchasers should assess the oven’s energy efficiency, heating speed, and compatibility with their specific applications. Although they offer significant advantages in speed and energy use, their application may be limited to certain materials or processes.
Illustrative image related to ir oven
How Do Batch Ovens Function and What Are Their Benefits?
Batch ovens operate by processing products in discrete batches, making them ideal for industries that require flexibility and customization, such as aerospace and pharmaceuticals. These ovens can be tailored to specific heating needs, allowing for varied temperature profiles and processing times. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the slower throughput compared to conveyor systems. While batch ovens can accommodate unique production requirements, they may not be as efficient for large-scale operations.
What Makes Tunnel Ovens Suitable for High-Volume Production?
Tunnel ovens are designed with multiple heating zones, allowing for continuous product movement and efficient thermal processing. They are particularly effective for high-volume applications such as glass processing and metal coating. When considering tunnel ovens, B2B buyers should evaluate the complexity of setup and maintenance, as well as the specific heating requirements of their products. While they provide consistent results and can handle large volumes, the initial setup may require a more significant investment in time and resources.
Key Industrial Applications of ir oven
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ir oven | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Curing of coatings and adhesives in automotive parts | Enhances durability and performance of components | Oven size, temperature uniformity, energy efficiency |
| Electronics | Drying and curing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) | Reduces production time and increases reliability of products | Heat source type, control precision, compatibility with materials |
| Food Processing | Baking and drying of food products | Improves product quality and shelf life | Compliance with food safety standards, energy consumption |
| Aerospace | Composite curing for lightweight structures | Reduces weight while maintaining strength | Customization options, temperature control, processing speed |
| Textile | Heat setting of fabrics and coatings | Enhances fabric properties and production efficiency | Material compatibility, operational safety, maintenance needs |
In the automotive sector, infrared ovens are crucial for curing coatings and adhesives on automotive parts. These ovens provide uniform heat, ensuring that coatings adhere properly and enhance the durability of components. For B2B buyers, key considerations include the oven’s size to accommodate various parts, the uniformity of temperature distribution, and energy efficiency to reduce operational costs.
In electronics manufacturing, infrared ovens are employed for the drying and curing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). The rapid heating capabilities of these ovens minimize production time while ensuring the reliability of electronic components. Buyers should focus on the type of heat source, precision of temperature control, and compatibility with different PCB materials to ensure optimal performance.
In the food processing industry, infrared ovens are utilized for baking and drying food products. This technology enhances product quality by providing consistent heat, which is critical for achieving desired textures and flavors. Buyers must consider compliance with food safety standards, the energy consumption of the ovens, and the ability to handle various food types during their sourcing process.
The aerospace industry leverages infrared ovens for curing composites used in lightweight structures. These ovens facilitate the curing process, resulting in components that are both lightweight and strong, which is essential for fuel efficiency. B2B buyers should prioritize customization options, precise temperature control, and processing speeds to meet specific aerospace requirements.
In the textile industry, infrared ovens are used for heat setting fabrics and coatings, improving fabric properties and production efficiency. The application of infrared technology allows for quick and effective processing, which is vital in meeting production deadlines. Buyers should assess material compatibility, operational safety features, and maintenance needs to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the ovens in their production lines.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ir oven’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Production Bottlenecks with Infrared Ovens
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant production delays due to inefficient heating processes. Infrared ovens are intended to speed up heating and curing times, yet many users report that their existing systems do not meet the speed requirements needed for high-volume production. This can lead to slowdowns in the assembly line, increased labor costs, and ultimately, missed deadlines for customers. The challenge is compounded in industries like automotive or electronics, where precision and timing are critical.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should consider investing in advanced infrared oven technology that offers rapid heating capabilities. When sourcing an infrared oven, look for models specifically designed for high throughput, such as conveyor or tunnel ovens that allow for continuous production. Additionally, ensure the oven features adjustable heating zones that can be customized to the specific thermal requirements of different materials being processed. Collaborating with manufacturers that provide thorough testing and validation can also ensure that the selected system meets your production needs. Prioritize suppliers who offer comprehensive support and training to optimize usage, enabling your team to utilize the oven effectively for maximum efficiency.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Consistent Quality in Heat Treatment
The Problem: Quality control is a perennial pain point for B2B buyers, particularly in industries that require precise heat treatment processes. Inconsistent heating can lead to defects in materials, affecting product durability and performance. Buyers may struggle with ovens that do not provide uniform heat distribution, resulting in variations in product quality. This inconsistency can lead to increased waste, rework, and customer dissatisfaction.

Illustrative image related to ir oven
The Solution: To mitigate quality issues, buyers should invest in infrared ovens that utilize advanced temperature control systems. Look for models equipped with multi-zone control capabilities, which allow for different temperatures in various sections of the oven to ensure uniform heating. Conducting thorough research on suppliers who offer ovens with built-in sensors and real-time monitoring can also enhance consistency. Implementing regular maintenance schedules and performance audits will help identify any deviations in heating patterns early on. Additionally, consider collaborating with suppliers that provide detailed training for operators on how to maintain optimal conditions for heat treatment.
Scenario 3: Navigating the Complexity of Customization
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find themselves overwhelmed by the need for customized solutions to meet their specific manufacturing processes. Off-the-shelf infrared ovens may not adequately cater to unique product dimensions or specialized heating requirements. This lack of customization can lead to inefficiencies, production delays, and increased costs as companies attempt to adapt standard equipment to their needs.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that specialize in custom infrared oven solutions. When engaging with suppliers, provide detailed specifications of your heating requirements, including material types, size, and production volume. A collaborative approach during the design phase can result in an oven tailored to your precise needs, which in turn enhances productivity and efficiency. Additionally, inquire about the flexibility of the oven to accommodate future changes in production demands, ensuring long-term utility. Look for manufacturers that offer comprehensive post-installation support, including maintenance and troubleshooting, to facilitate smooth operation and minimize downtime.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ir oven
What Are the Key Materials Used in Infrared Ovens?
When selecting materials for infrared (IR) ovens, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with the specific needs of international B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of IR ovens: stainless steel, aluminum, ceramic, and composite materials.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Infrared Ovens?
Stainless steel is a widely used material in IR ovens due to its excellent durability and resistance to corrosion. It can withstand high temperatures, typically rated up to 1000°F (538°C), making it suitable for various thermal processes. The key advantage of stainless steel is its strength and longevity, which translates into lower maintenance costs over time. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require more complex manufacturing processes, especially for custom designs.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Germany and Nigeria, compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial. Stainless steel components must meet specific grades, such as 304 or 316, to ensure they can withstand the operational demands and environmental conditions.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Infrared Oven Applications?
Aluminum is another popular choice for IR ovens, known for its lightweight and excellent thermal conductivity. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 750°F (399°C) and is often used in applications requiring rapid heating and cooling cycles. The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication, which can lead to lower manufacturing costs.
However, aluminum is less durable than stainless steel and can be prone to warping under extreme heat. For international buyers, particularly in regions with varying environmental conditions, it’s important to assess the suitability of aluminum for specific applications. Compliance with local standards and regulations is also a must.
How Do Ceramic Materials Enhance Infrared Oven Performance?
Ceramic materials are increasingly being utilized in IR ovens, particularly for their ability to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock. They can operate at temperatures exceeding 2000°F (1093°C), making them ideal for specialized applications like sintering and curing. The key advantage of ceramics is their exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion.
On the downside, ceramics can be brittle and may require careful handling during installation and operation. For international buyers, understanding the specific ceramic grades and their compliance with industry standards is vital, especially in regions like South America, where material sourcing can be challenging.
What Are the Benefits of Composite Materials in Infrared Ovens?
Composite materials, often made from a combination of polymers and fibers, are becoming popular in IR oven construction due to their lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. They can withstand moderate temperatures and provide excellent insulation properties. The primary advantage of composites is their versatility, allowing for custom designs that can meet specific operational needs.
However, composites may not be suitable for extremely high-temperature applications and can be more costly than traditional materials. International buyers need to consider the specific properties of the composite materials used and ensure they meet relevant standards in their respective regions, especially in the Middle East, where compliance with local regulations is critical.
Summary Table of Material Selection for IR Ovens
| Material | Typical Use Case for ir oven | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | General-purpose IR ovens | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Rapid heating applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable, prone to warping | Medium |
| Ceramic | High-temperature applications | Exceptional thermal stability | Brittle and requires careful handling | High |
| Composite | Custom-designed applications | Versatile and lightweight | Limited high-temperature suitability | Medium |
Selecting the right material for an infrared oven is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring compliance with regional standards. By understanding the properties and implications of each material, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ir oven
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Infrared Ovens?
The manufacturing process for infrared ovens involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate suppliers more effectively.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing of infrared ovens is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality materials that can withstand high temperatures and provide effective heat transfer. Common materials used include stainless steel for the oven casing and specialized alloys for heating elements. Suppliers often conduct material inspections to ensure compliance with international standards, such as ASTM and ISO specifications.
Forming Techniques
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This typically involves cutting, bending, and shaping the metal sheets into the desired oven components. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are frequently employed to ensure precision. This step is critical, as any inaccuracies can affect the oven’s efficiency and durability. Quality checks during this phase might include dimensional inspections and material property tests to confirm that the components meet design specifications.
Assembly Process
The assembly stage is where the various components come together. This includes installing heating elements, electrical wiring, and control systems. Skilled technicians often perform this work to ensure all parts are correctly integrated and functioning. During assembly, quality control checkpoints are established to verify that each component is correctly positioned and connected. Buyers should inquire about the assembly methods used and whether they allow for easy maintenance and repair in the future.
Finishing Touches
After assembly, the ovens undergo a finishing process, which may involve powder coating or other surface treatments to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal. This stage is essential for preventing corrosion and ensuring longevity, particularly in harsh industrial environments. A final round of quality checks ensures that the surface finish meets specifications and that all functional elements operate as intended.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Infrared Oven Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of infrared oven manufacturing, ensuring that products meet the required standards for performance and safety. Various international and industry-specific standards guide this process.
What International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with key international standards that govern industrial equipment manufacturing. ISO 9001 is a fundamental quality management standard, focusing on process efficiency and customer satisfaction. Additionally, CE marking may be required for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
For specific applications, other certifications like API (American Petroleum Institute) may be relevant, especially if the ovens are used in oil and gas applications. Understanding these standards helps buyers assess the credibility and reliability of potential suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in infrared oven manufacturing typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications. This may involve checking the material’s physical and chemical properties.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are carried out to monitor compliance with design specifications and operational standards. This includes dimensional checks and functional tests of components as they are assembled.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the oven is fully assembled, a comprehensive testing phase occurs. This includes functional testing of heating elements, control systems, and safety features. Buyers should inquire about the specific tests performed, such as temperature uniformity tests and energy efficiency assessments.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Infrared Oven Manufacturing?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure infrared ovens perform reliably under operational conditions. Some common methods include:
-
Thermal Testing: This assesses the oven’s ability to maintain consistent temperatures across different zones. It ensures that the heating elements distribute heat evenly, which is crucial for processes like curing and drying.
-
Electrical Safety Testing: This ensures that all electrical components meet safety standards, reducing the risk of electrical failures during operation. This testing often includes insulation resistance tests and ground continuity checks.
-
Performance Testing: This evaluates the oven’s efficiency and effectiveness in real-world applications. It may involve running the oven under load and measuring performance metrics such as energy consumption and processing time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
When sourcing infrared ovens, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify suppliers’ quality control practices. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. An audit should assess compliance with relevant standards and the effectiveness of their quality management systems.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide quality control reports detailing inspection results, testing outcomes, and compliance with international standards. This documentation can help buyers gauge the reliability of a supplier.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspectors can evaluate the manufacturing process, conduct tests, and verify that the products meet the agreed-upon specifications.
What Nuances Exist for International B2B Buyers Seeking Quality Assurance?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances when evaluating suppliers. Differences in regulatory requirements, cultural expectations, and quality standards can impact the procurement process.
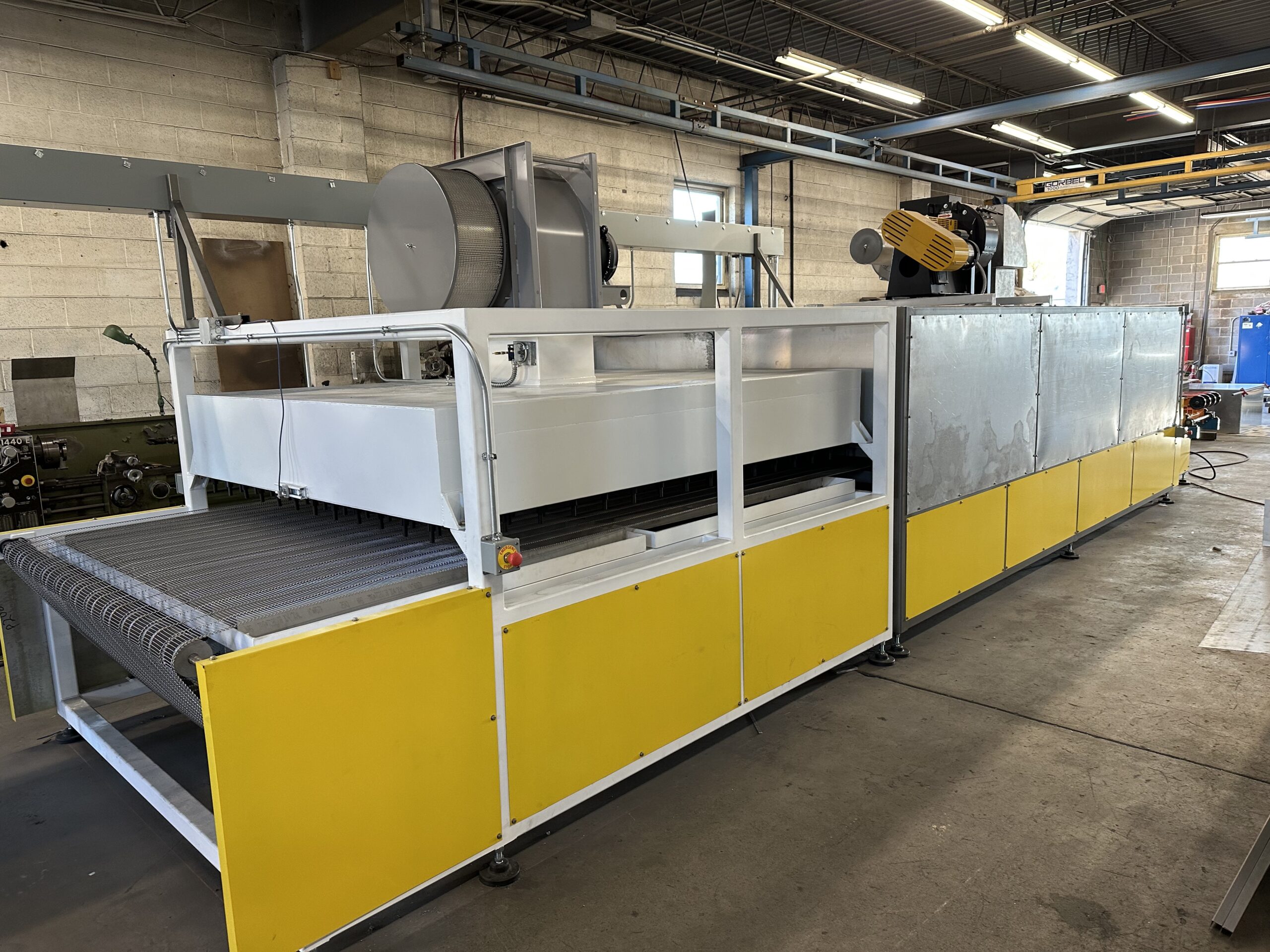

Illustrative image related to ir oven
Understanding regional certifications and compliance requirements is crucial. For example, while CE marking is essential for European buyers, other regions may have different requirements. Additionally, cultural factors can influence communication and negotiation processes, making it essential to establish clear expectations regarding quality standards and delivery timelines.
By leveraging a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality infrared ovens that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ir oven’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure infrared ovens. Given the diverse applications and technological nuances of these ovens, following a structured approach will ensure you make an informed decision that aligns with your operational needs and budget.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is essential before initiating the procurement process. Determine the intended application of the infrared oven, such as curing, drying, or heat treating, as this will influence the type and design of the oven you need. Additionally, consider factors like the required temperature range, size, and production capacity to ensure the oven meets your operational demands.
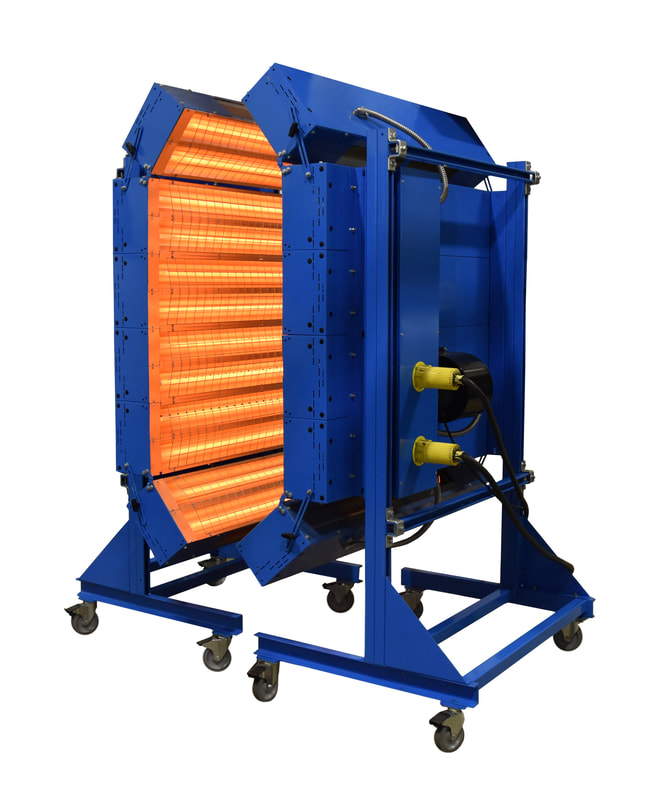

Illustrative image related to ir oven
Step 2: Research Different Types of Infrared Ovens
Familiarize yourself with the various types of infrared ovens available, such as conveyor ovens, batch ovens, and custom designs. Each type offers unique benefits; for instance, conveyor ovens provide continuous processing, while batch ovens may be more suitable for smaller production runs. Understanding these differences will help you choose an oven that best fits your workflow.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a strong track record in manufacturing quality infrared ovens and those who can provide ongoing support and maintenance services.
- Check for industry certifications: Ensure the supplier complies with relevant industry standards and regulations, which can vary by region.
- Examine customer feedback: Online reviews and testimonials can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability and product performance.
Step 4: Assess Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
Energy consumption is a critical factor in the overall cost of operating an infrared oven. Evaluate the energy efficiency of the models you are considering, as more efficient ovens can lead to significant savings over time. Additionally, factor in the cost of utilities in your region, as this can impact your total operational expenses.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes and Specifications
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include technical specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines. This step allows for direct comparisons between different models and suppliers. Be sure to clarify any additional costs, such as installation and training, to get a complete picture of your investment.
Step 6: Inquire About Customization Options
If your application has specific requirements, discuss customization options with potential suppliers. Many manufacturers offer tailored solutions that can enhance the performance of the oven for your unique processes. This could include modifications to size, heating technology, or control systems to better fit your operational needs.
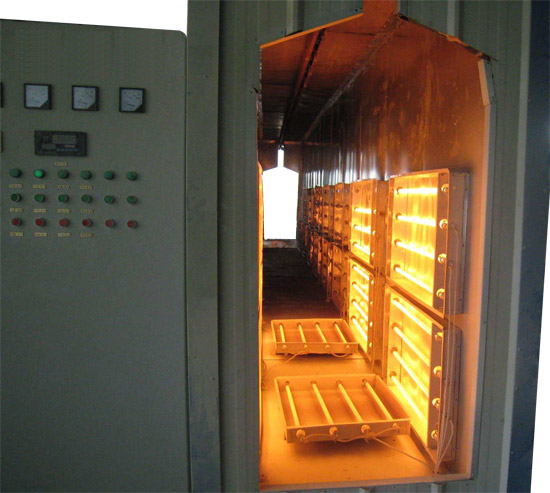

Illustrative image related to ir oven
Step 7: Plan for After-Sales Support and Maintenance
After securing your infrared oven, ensure that the supplier provides robust after-sales support. This includes maintenance services, warranty details, and availability of spare parts. A supplier with a strong service reputation can significantly reduce downtime and ensure the longevity of your investment.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process for infrared ovens with confidence, ensuring they select the right equipment to enhance their production capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ir oven Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Infrared Ovens?
When sourcing infrared ovens, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. High-quality metals, insulation, and heating elements can increase initial costs but lead to better durability and efficiency.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the manufacturing location. Regions with higher wages may lead to increased production costs, while countries with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses associated with production. Understanding these costs can provide insights into the pricing of the final product.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific oven designs or features can add to the initial investment. Buyers should consider whether standard designs meet their needs to minimize tooling costs.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous quality assurance processes ensure the ovens meet industry standards. While this may increase costs, it is essential for maintaining product reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely depending on the location of the supplier and the destination country. Factors such as freight charges, insurance, and customs duties must be considered.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin can vary based on market conditions and competition. Understanding this can aid in negotiations and ensure the buyer is receiving fair pricing.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Infrared Oven Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of infrared ovens, which buyers should consider to optimize their procurement strategies:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQ to benefit from economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom ovens tailored to specific processes or product types can be more expensive. Buyers should evaluate whether standard models can meet their needs to reduce costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Ovens constructed from premium materials or those that comply with specific quality certifications may command higher prices. However, these can lead to lower operational costs and longer lifespans.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and service offerings can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better support and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) used in the contract is vital. They determine the responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect the total landed cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Infrared Oven Pricing?
For B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, implementing strategic negotiation techniques can lead to better pricing outcomes:

Illustrative image related to ir oven
-
Conduct Market Research: Knowledge of current market prices and competitor offerings can empower buyers during negotiations. This information can help establish realistic pricing expectations.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than focusing solely on the purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. This approach can justify higher initial costs for more efficient ovens.
-
Leverage Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, favorable payment terms, and improved service. Suppliers may be more willing to negotiate with repeat customers.
-
Explore Financing Options: Consider financing solutions that can spread the cost over time, making high-quality ovens more accessible without straining cash flow.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying cost structures due to economic conditions, labor costs, and regulatory environments. Understanding these nuances can assist in making informed decisions when sourcing ovens from international suppliers.
Conclusion
While the costs associated with sourcing infrared ovens can be multifaceted, understanding the various components and pricing influencers can empower buyers to make strategic purchasing decisions. By leveraging negotiation tactics and focusing on total cost of ownership, international buyers can optimize their procurement processes, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment. Always consider that prices may fluctuate based on market conditions, making it essential to seek updated quotes and detailed specifications from suppliers.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ir oven With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to IR Ovens in Industrial Applications
In the industrial sector, particularly for processes requiring precise heating and curing, infrared (IR) ovens have become a popular choice. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications or operational needs. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their production goals, budget constraints, and efficiency requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | ‘IR Oven’ | Electric Convection Oven | Industrial Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Fast heating with focused energy | Moderate heating, uniform heat distribution | High-temperature applications, versatile heating methods |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower operating costs | Moderate initial cost, higher energy consumption | High initial investment, variable operating costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific installation and calibration | Easier to install and integrate | Complex setup, may require significant infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, but specific to IR components | Moderate maintenance; regular cleaning needed | High maintenance; frequent checks on heating elements |
| Best Use Case | Curing coatings, drying, laminating | Baking, drying, and general heating | Metal treatment, high-temperature processing |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Convection Oven
Electric convection ovens utilize fans to circulate hot air, providing a consistent temperature throughout the cooking or heating process. One of the main advantages is their ease of installation and operation, making them suitable for diverse applications, from baking to drying materials. However, they consume more energy than IR ovens and may not heat as rapidly, which can be a disadvantage in fast-paced production environments. They are typically more affordable upfront but incur higher ongoing energy costs.
Industrial Furnace
Industrial furnaces are designed for high-temperature applications, often exceeding 400°C (752°F). They are highly versatile and can accommodate a variety of materials, making them ideal for metal treatment and heat processing. While they offer significant performance advantages in terms of temperature control and material processing capabilities, they come with high initial costs and complex installation requirements. Additionally, maintenance can be demanding due to the need for regular inspections and repairs of heating elements.

Illustrative image related to ir oven
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Heating Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a heating solution, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific production requirements, including the type of materials being processed, desired temperature ranges, and production speed. Each heating technology presents distinct advantages and challenges that should align with operational capabilities and financial considerations. For instance, if rapid heating and energy efficiency are paramount, an IR oven may be the best choice. Conversely, if the application involves high-temperature metal treatment, an industrial furnace could be more suitable. By assessing these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and profitability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ir oven
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Infrared Ovens?
When selecting an infrared (IR) oven, understanding key technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Temperature Range
The temperature range of an IR oven indicates the minimum and maximum temperatures it can achieve. Most industrial infrared ovens operate between 100°C to 500°C (212°F to 932°F). This property is vital as it determines the oven’s suitability for various applications, such as curing, drying, or heat treating materials. B2B buyers should align the oven’s temperature capabilities with their specific production needs to ensure optimal performance.
2. Heating Method
IR ovens may use electric or gas heating elements. Electric infrared ovens are known for their efficiency and rapid heating capabilities, making them ideal for processes requiring quick temperature changes. Gas infrared ovens can be more cost-effective for larger operations but may have longer warm-up times. Understanding the heating method helps businesses evaluate operational costs and energy consumption, which can significantly impact overall production expenses.
3. Oven Size and Capacity
The physical dimensions and internal volume of the oven are critical for accommodating the size and quantity of products being processed. A larger capacity oven can handle more products simultaneously, enhancing throughput. B2B buyers must assess their production volumes and workspace constraints to select an appropriately sized oven that maximizes efficiency without incurring unnecessary costs.
4. Control Systems
Modern IR ovens often feature advanced control systems that enable precise temperature regulation and monitoring. These systems can include digital displays, programmable settings, and automated alarms. The ability to maintain consistent temperatures is crucial for quality control, especially in industries like food processing or electronics manufacturing. Buyers should prioritize ovens with user-friendly controls that facilitate easy operation and maintenance.
5. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is increasingly important for businesses aiming to reduce operational costs and minimize their environmental footprint. Infrared ovens that utilize advanced heating technologies can significantly lower energy consumption compared to traditional heating methods. B2B buyers should seek ovens with energy-efficient ratings and features, which not only reduce costs but can also enhance their sustainability initiatives.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand When Sourcing Infrared Ovens?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and procurement processes. Here are several essential trade terms:

Illustrative image related to ir oven
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of infrared ovens, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the equipment, as OEMs often adhere to stringent manufacturing standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Understanding the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchasing strategies and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For infrared ovens, an RFQ allows buyers to compare different suppliers’ offerings and determine the most cost-effective option that meets their technical requirements.

Illustrative image related to ir oven
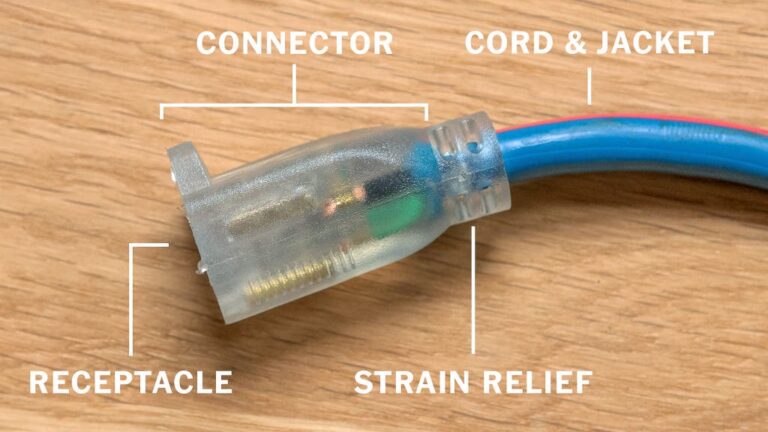
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms used in international trade that specify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thereby reducing the risk of misunderstandings.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the context of infrared ovens, shorter lead times can significantly impact production schedules. B2B buyers should inquire about lead times during negotiations to align their supply chain needs effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing infrared ovens that align with their operational requirements and business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ir oven Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends in the Global IR Oven Market?
The infrared (IR) oven market is experiencing notable growth, driven by advancements in manufacturing processes and increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions. Global drivers include the rise of industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, which require precise heat treatment for various applications. In regions like Africa and South America, the industrial sector is expanding, leading to an uptick in demand for reliable thermal processing equipment. Furthermore, the Middle East and Europe are witnessing an increase in the adoption of custom-designed IR ovens that cater to specific operational needs, enabling manufacturers to optimize their production efficiency.
Current and emerging trends in B2B sourcing include a shift towards automation and smart technology integration. Many companies are investing in IoT-enabled ovens that provide real-time data on performance metrics, thus enhancing operational transparency and efficiency. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration in procurement decisions, with buyers seeking suppliers who offer energy-efficient, low-emission solutions. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers from Germany and Nigeria, where regulatory frameworks are tightening around environmental standards. As a result, sourcing from manufacturers that prioritize advanced technologies and sustainability is increasingly seen as a competitive advantage.
How Is Sustainability Impacting the Sourcing of IR Ovens in B2B Markets?
Sustainability is a key concern for B2B buyers in the IR oven sector, reflecting a broader shift towards environmentally responsible practices. The environmental impact of traditional industrial heating methods, which often rely on fossil fuels, is prompting manufacturers to seek greener alternatives. Electric infrared ovens, for instance, are recognized as a more sustainable option, as they produce lower emissions and can be powered by renewable energy sources.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction among international buyers. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to responsible labor practices and sustainable resource management is increasingly becoming a priority. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Energy Star for energy efficiency are valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. B2B buyers from Europe and the Middle East, in particular, are leveraging these certifications to assess supplier credibility and align with their corporate social responsibility goals. The emphasis on green materials and processes not only supports environmental stewardship but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.

Illustrative image related to ir oven
What Is the Evolution of IR Oven Technology and Its Significance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of IR oven technology has been marked by significant advancements since its inception. Initially, IR ovens were primarily used for simple heating applications. However, technological innovations have transformed them into sophisticated thermal processing systems capable of handling a variety of functions, including curing, drying, and heat treatment for complex materials.
Over the years, the introduction of electric infrared heating elements has revolutionized energy efficiency and precision in thermal applications. Modern IR ovens are designed to cater to specific industry needs, offering custom configurations and controls that enhance process reliability. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers, as it allows for tailored solutions that improve operational efficiency and reduce energy costs. As industries increasingly prioritize innovative and sustainable practices, understanding the historical context of IR oven technology can provide valuable insights into current market offerings and future potential.
By recognizing these trends and implications, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals, positioning themselves favorably in a competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ir oven
-
How do I choose the right infrared oven for my manufacturing process?
Choosing the right infrared oven involves assessing your specific manufacturing needs, including the type of materials you work with, the required temperature range, and the production volume. Consider the heating method (electric vs. gas), oven type (conveyor, batch, or tunnel), and size. Collaborate with suppliers who can provide custom solutions tailored to your process. Request samples and detailed specifications to evaluate how well a particular oven aligns with your operational requirements. -
What are the advantages of electric infrared ovens compared to gas infrared ovens?
Electric infrared ovens offer faster heating times and are generally more energy-efficient, making them an environmentally friendly option. They provide precise temperature control and can be customized to fit specific part profiles, maximizing heat absorption. Gas infrared ovens may be less expensive initially but can incur higher operational costs over time due to gas prices and maintenance. For industries focused on sustainability and operational efficiency, electric infrared ovens are often the preferred choice. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for infrared ovens?
When vetting suppliers, evaluate their industry experience, reputation, and customer testimonials. Investigate their manufacturing capabilities, including the range of products they offer and their ability to customize equipment. Check for compliance with international quality standards and certifications. Additionally, inquire about their after-sales support, warranty terms, and lead times to ensure they can meet your needs effectively. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for infrared ovens?
Minimum order quantities for infrared ovens can vary significantly by manufacturer and the specific model you require. Some suppliers may accommodate smaller orders, particularly for custom solutions, while others may have higher MOQs based on production costs and logistics. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your business scale and budget. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by infrared oven manufacturers?
Payment terms vary by supplier but typically include options such as full payment upfront, a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery, or installment payments based on milestones. Some manufacturers may offer financing options for larger purchases. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts to ensure they are manageable for your cash flow and project timelines. -
How can I ensure the quality of infrared ovens before purchasing?
To ensure quality, request detailed product specifications, including materials used and performance testing results. Ask for references or case studies from previous customers to assess their satisfaction with the product. Some manufacturers offer product testing and demonstrations before purchase, which can provide insights into the oven’s performance. Additionally, verify the manufacturer’s adherence to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing infrared ovens?
When importing infrared ovens, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the supplier can provide the necessary documentation for customs clearance, including certificates of origin and compliance. It’s also wise to evaluate the logistics capabilities of the supplier, including their experience in handling international shipments and their ability to provide support during the delivery process. -
What industries commonly use infrared ovens, and what are their specific applications?
Infrared ovens are widely used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, food processing, and textiles. In automotive manufacturing, they are used for curing paint and coatings. In food processing, they serve for drying and curing products. The textile industry utilizes them for fabric treatment. Understanding your industry’s specific applications can help you select the right oven type and features to optimize your production processes.
Top 6 Ir Oven Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Infrared Ovens
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Introduction: Infrared ovens utilize infrared radiation to heat or cook items, differing from traditional conduction and convection ovens. They are used in commercial kitchens, residential spaces, and industrial settings. Infrared ovens heat food directly without heating the surrounding air, making them more energy-efficient and compact. They operate using electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between 780 …
2. Infrared Heating Technologies – Industrial Ovens & Furnaces
Domain: infraredheating.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Industrial Ovens & Furnaces – Infrared Heating Technologies offers a variety of products including: Composite Stack Furnaces, Infrared Convection Conveyor Oven, Roller Hearth Industrial Oven, Composite Cure Tunnel Oven, Industrial Conveyor Oven, Flat Glass Conveyor Oven, Mastic Oven and Cooler. They provide complete turn-key solutions for industrial oven applications, with custom and standard desi…
3. Powder Buy The Pound – 44 Infrared Oven Model FPB44-H1-14-4
Domain: powderbuythepound.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”:”44″ Infrared Oven Model FPB44-H1-14-4″,”sku”:”21087″,”features”:[“Infrared cooking technology”,”Energy efficient design”,”Compact size”,”Easy to use controls”,”Versatile cooking options”],”dimensions”:”44 inches”,”weight”:”Varies”,”wattage”:”Varies”,”color”:”Varies”,”material”:”Varies”}
4. BBC Industries – Infrared Ovens
Domain: bbcind.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Infrared Ovens – BBC Industries, Inc. are available in over 50 standard configurations with optional conveyors, exhaust blowers, and vestibules. Custom designed ovens can be manufactured for specific surface finishing requirements. Key features include:
– Programmable Individual Heat Zones for complete temperature control
– Easy-to-use controls for simplified operation
– Energy efficient, conve…
5. PROTHERM – Electric Infrared Ovens
Domain: pro-therm.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: PROTHERM Electric Infrared Ovens are high quality, cost-effective systems designed for industrial applications. They include infrared heaters, controls, and a frame, often with insulated housings, conveyors, exhaust hoods, air ducting, cooling tunnels, and other peripherals. The ovens are designed to reduce emissions and utilize clean energy, aligning with government “GREEN” initiatives. They are …
6. Catalytic Ovens – Gas Catalytic Infrared Heaters
Domain: catalyticirovens.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Gas Catalytic Infrared Industrial Powder Coating Ovens; High efficiency industrial process heaters & ovens; Custom designed and manufactured; Gas catalytic infrared heaters in multiple sizes and duties; Microprocessor-based PLC with color HMI control panels; Single or multi-zone gas trains; Ventilation systems tailored to applications; Cures up to 10 times faster than convection; Reduces process t…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ir oven
Strategic sourcing of infrared (IR) ovens is essential for businesses looking to enhance their thermal processing capabilities while optimizing operational efficiency. Key considerations include understanding the specific applications—such as curing, drying, and heat treating—alongside evaluating oven types such as conveyor or batch ovens. The choice of energy source, whether electric or gas, plays a crucial role in determining the environmental impact and operational costs, especially for companies in regions like Africa and South America where energy costs can vary significantly.
By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can negotiate better terms, ensure high-quality manufacturing standards, and access innovative technologies tailored to their unique needs. This proactive approach not only streamlines procurement but also aligns with sustainability goals, which are increasingly important in today’s global market.

Illustrative image related to ir oven
As we look to the future, international buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who offer customized solutions and robust support services. Embracing advancements in infrared heating technology will empower organizations to stay competitive and responsive to market demands. Begin your journey towards enhanced production efficiency today—connect with leading manufacturers and explore how infrared ovens can transform your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.