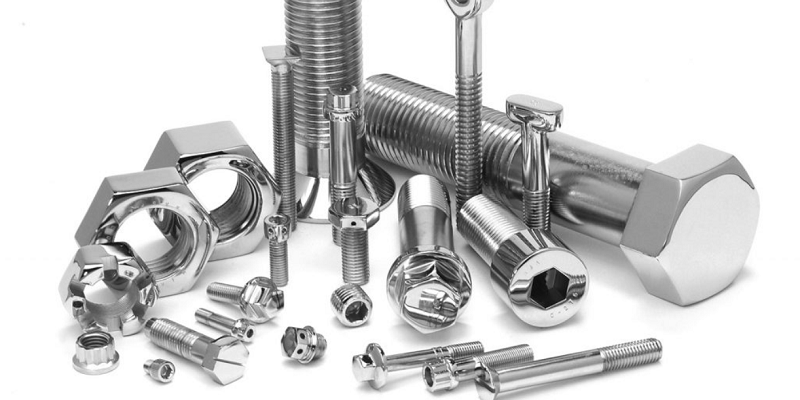
Top 8 Machine Bolts Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for machine bolts
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing machine bolts poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, the complexity of selecting the right fasteners can lead to costly delays and project setbacks. With numerous types of machine bolts available—ranging from standard steel options to specialized materials like stainless steel and brass—understanding their applications is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety in your projects.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the world of machine bolts by providing an in-depth look at the various types, their specific uses, and the critical factors to consider when sourcing them. We’ll cover essential aspects such as supplier vetting processes, pricing considerations, and industry standards to empower your purchasing decisions. By equipping yourself with the knowledge to navigate this intricate landscape, you can mitigate risks and enhance the efficiency of your procurement strategies.
As you explore the sections of this guide, you’ll find actionable insights tailored for your region, whether you’re based in Germany, Saudi Arabia, or beyond. Our goal is to support informed decision-making, ensuring you secure the right machine bolts for your operational needs while fostering long-term supplier relationships that drive success in your projects.
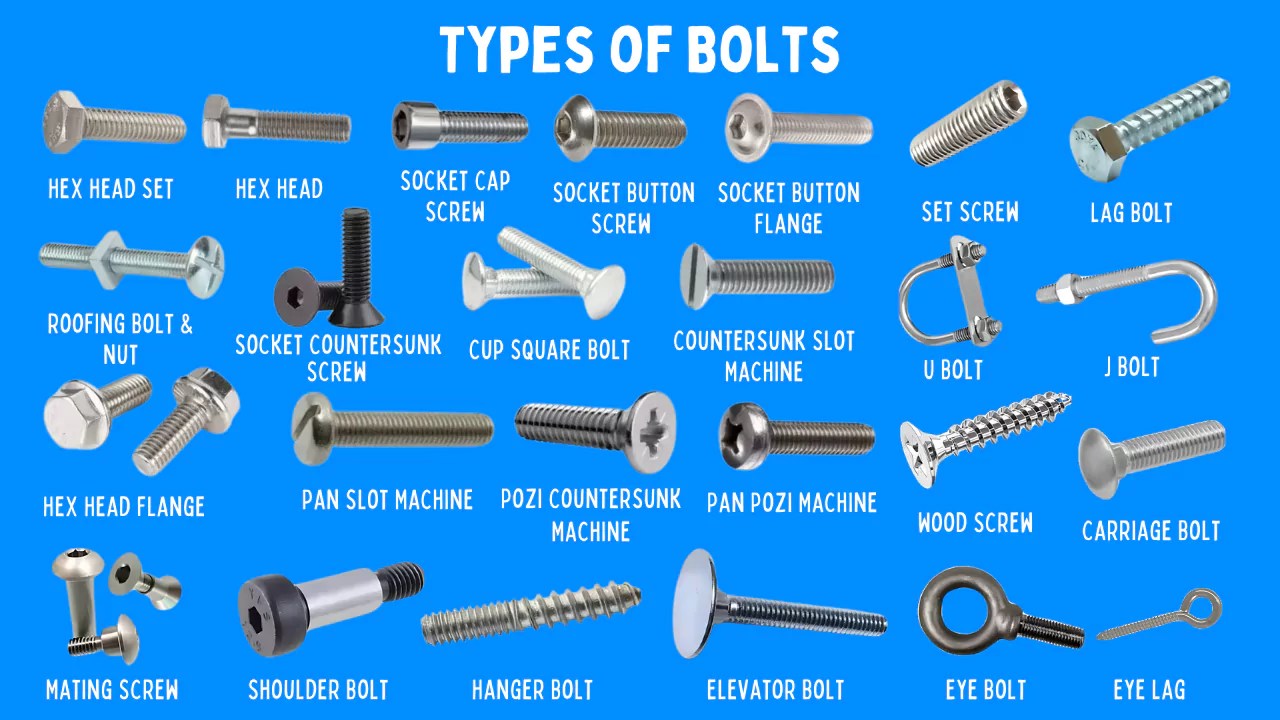
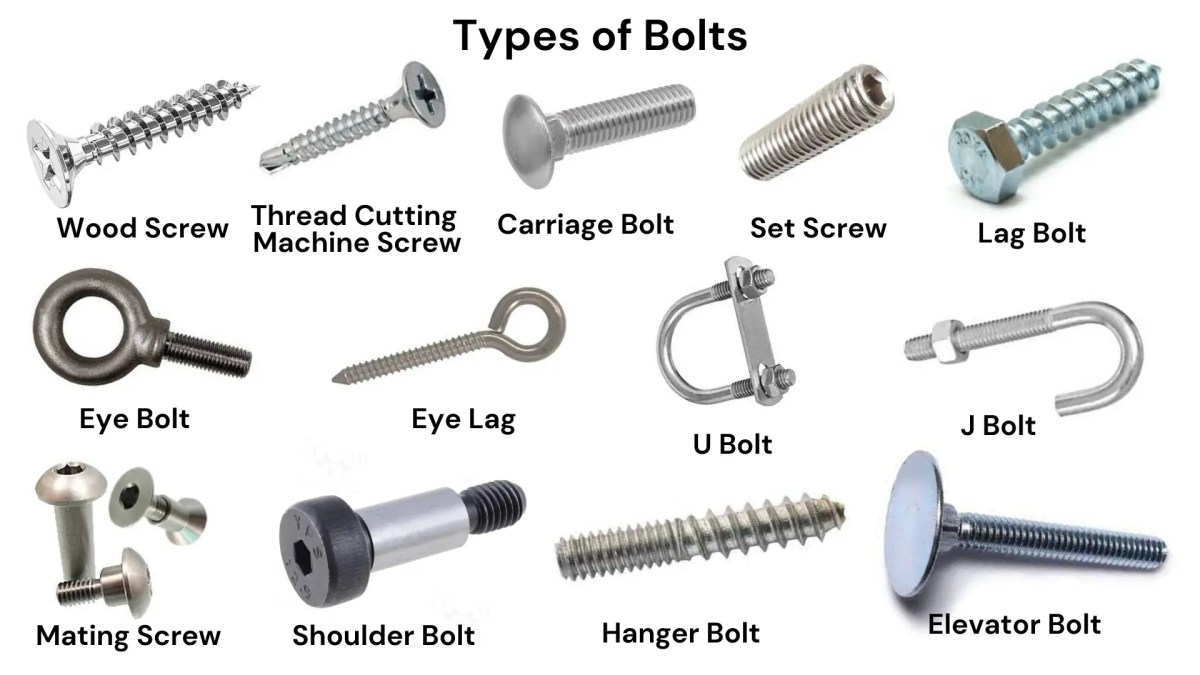
Understanding machine bolts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machine Screws | Machine threads, can be used with nuts or tapped holes | Electronics, automotive assembly, machinery | Pros: Versatile, high precision. Cons: May require specific head types for applications. |
| SEMS Machine Screws | Pre-assembled screws with a free-spinning washer | Automotive, electronics, appliance assembly | Pros: Convenient installation. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Type F Machine Screws | Self-tapping threads for ease of installation | Construction, metalworking | Pros: Reduces need for pre-drilling. Cons: May not work well in soft materials. |
| Socket Head Screws | Allen wrench drive, cylindrical head for high torque applications | Machinery, automotive, heavy equipment | Pros: High torque capability. Cons: Requires specific tools for installation. |
| Hex Bolts | Hexagonal head, driven with a wrench, often larger and stronger | Structural applications, heavy machinery | Pros: Strong and secure fastening. Cons: Requires more space for installation. |
What Are the Characteristics of Machine Screws and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Machine screws are essential fasteners with machine threads designed for use with nuts or in tapped holes. They come in various materials, including stainless steel and brass, and are available in fine or coarse threads. Their versatility makes them suitable for a range of applications, particularly in electronics and automotive assembly, where precision is crucial. B2B buyers should consider the specific head type and thread pattern required for their projects to ensure compatibility and effectiveness.
How Do SEMS Machine Screws Enhance Installation Efficiency?
SEMS machine screws are distinguished by their pre-assembled free-spinning washer, which facilitates quick and efficient installation. This feature is particularly advantageous in high-volume assembly environments, such as automotive and electronics manufacturing. Buyers should evaluate their assembly processes to determine if the convenience of SEMS screws can enhance productivity, though they may be limited to specific applications where this design is beneficial.
What Makes Type F Machine Screws Ideal for Construction?
Type F machine screws feature self-tapping threads that allow them to create their own holes in materials, making them particularly useful in construction and metalworking applications. Their ability to reduce the need for pre-drilling can save time and labor costs. However, B2B buyers should be cautious about using them in softer materials, where they may not provide adequate holding strength.
Why Choose Socket Head Screws for High Torque Applications?
Socket head screws are characterized by their cylindrical shape and require an Allen wrench for installation. They are designed for high torque applications, making them a preferred choice in machinery and automotive sectors. Buyers should consider the specific torque requirements of their applications, as these screws provide a strong and secure fastening solution but necessitate the use of specialized tools for installation.
When Should B2B Buyers Opt for Hex Bolts?
Hex bolts are recognized for their hexagonal heads and robust design, often utilized in structural applications and heavy machinery. They provide a strong and secure fastening solution, ideal for environments where high strength is required. However, B2B buyers must consider the space available for installation, as hex bolts typically require more room than other types of screws. This consideration is crucial for applications with limited access or confined spaces.
Key Industrial Applications of machine bolts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of machine bolts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Assembling engine components | Enhanced durability and performance of vehicles | Material grade, corrosion resistance, and certifications |
| Construction | Securing structural elements in buildings | Ensures safety and integrity of structures | Load capacity, compliance with local standards, and availability |
| Electronics | Mounting circuit boards and enclosures | Precision fastening for reliability and performance | Size specifications, material compatibility, and lead times |
| Machinery Manufacturing | Fastening parts in heavy machinery | Increases operational efficiency and longevity | Tolerance levels, strength specifications, and bulk purchasing options |
| Aerospace | Attaching components in aircraft | High reliability and safety standards | Weight considerations, aerospace-grade materials, and traceability |
How Are Machine Bolts Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, machine bolts are crucial for assembling engine components, ensuring that parts like cylinder heads and intake manifolds are securely fastened. The use of high-strength machine bolts minimizes the risk of failure under high-stress conditions, enhancing vehicle performance and safety. Buyers should prioritize sourcing bolts made from high-grade materials, such as stainless steel or alloy, which offer superior corrosion resistance and longevity. Compliance with automotive industry standards and certifications is also critical to ensure quality and reliability.
What Role Do Machine Bolts Play in Construction?
In construction, machine bolts are employed to secure structural elements, such as beams and columns, providing stability and safety to buildings. Their ability to handle heavy loads and resist shear forces makes them indispensable in this sector. Buyers must consider the load capacity and compliance with local building codes when sourcing machine bolts. Additionally, the availability of different sizes and grades is essential to meet the specific requirements of various construction projects.
How Are Machine Bolts Utilized in Electronics?
Machine bolts are widely used in the electronics industry for mounting circuit boards and enclosing sensitive components. Precision fastening is vital to ensure that electronic devices function reliably without the risk of loose connections or damage. Buyers should focus on sourcing bolts that meet specific size and material compatibility requirements, as well as those that can be delivered within tight lead times to accommodate rapid production schedules.
Why Are Machine Bolts Important in Machinery Manufacturing?
In machinery manufacturing, machine bolts are integral for fastening parts in heavy machinery, ensuring that assemblies can withstand high operational stresses. By using machine bolts, manufacturers can enhance the efficiency and longevity of their equipment. Sourcing considerations include tolerance levels and strength specifications, as well as the option for bulk purchasing to reduce costs. Ensuring that bolts meet industry standards for strength and durability is essential to maintaining operational performance.
How Do Machine Bolts Contribute to Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, machine bolts are critical for attaching components in aircraft, where safety and reliability are paramount. The use of aerospace-grade machine bolts ensures compliance with stringent safety standards and regulations. Buyers must consider weight constraints and the need for traceability in sourcing these fasteners. Additionally, selecting materials that can withstand extreme conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and corrosion, is vital for ensuring the safety and performance of aerospace applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘machine bolts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing the Right Machine Bolt for Diverse Applications
The Problem: A construction manager in South America is tasked with overseeing multiple projects that require different types of machine bolts. With varying specifications—such as thread types, materials, and lengths—finding the right machine bolts can be overwhelming. Additionally, local suppliers may not offer the full range needed, leading to delays in procurement and increased costs. This not only affects project timelines but also the overall quality of the assembly, risking structural integrity.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of sourcing machine bolts, it’s essential to develop a detailed understanding of the specific requirements for each project. Create a comprehensive list of specifications, including thread type (coarse or fine), length, material (such as stainless steel for corrosion resistance), and any relevant standards (like ISO or ASTM). Next, engage with reputable suppliers who specialize in fasteners and can provide a diverse inventory. Online platforms that aggregate multiple suppliers can also simplify the search process. Consider ordering samples to test compatibility before making bulk purchases, ensuring that the selected machine bolts meet the performance criteria for each unique application.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality and Compliance in Machine Bolts
The Problem: An automotive parts manufacturer in Europe faces challenges with the quality of machine bolts sourced from local suppliers. Instances of rust and breakage have led to costly recalls and damaged reputation. The lack of compliance with international standards adds another layer of complexity, as many clients require certifications that verify the quality and safety of components used in their products.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, implement a rigorous supplier evaluation process focusing on quality assurance. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and ISO 14001 for environmental standards from potential suppliers. Additionally, establish a comprehensive quality control checklist that includes checks for material integrity, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy. Regular audits of supplier facilities can also ensure adherence to compliance requirements. Consider building long-term relationships with suppliers who demonstrate consistent quality and reliability, as this can lead to better pricing and priority during supply chain disruptions.
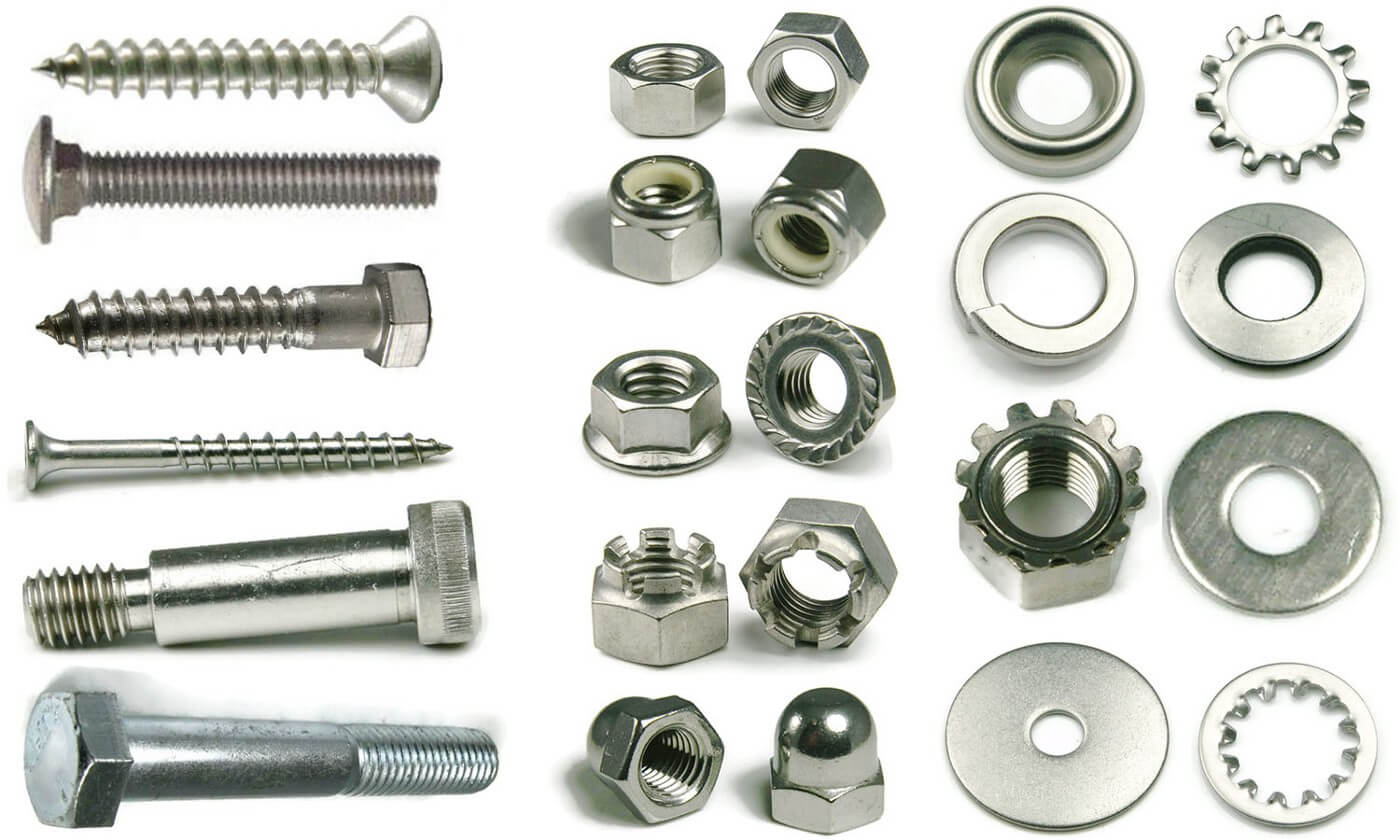

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
Scenario 3: Managing Inventory and Reducing Waste with Machine Bolts
The Problem: A manufacturing firm in Africa struggles with excess inventory of machine bolts, leading to increased storage costs and waste. Fluctuating demand and inconsistent project requirements mean that they often over-order, resulting in a surplus of unused fasteners. This not only ties up capital but also complicates inventory management and can lead to obsolescence.
The Solution: To optimize inventory management, implement a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system that aligns procurement with actual project needs. Utilize inventory management software to track usage patterns and forecast demand more accurately. Establish strong communication channels with project managers to ensure that bolt requirements are clearly understood and communicated in advance. Additionally, consider collaborating with suppliers to create a consignment stock arrangement, where suppliers maintain ownership of inventory until it’s used. This approach reduces storage costs and minimizes waste, ensuring that your firm only pays for what it actually uses while maintaining flexibility to meet project demands.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for machine bolts
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Machine Bolts?
When selecting materials for machine bolts, it’s essential to consider their properties, as these directly affect performance in various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and zinc-plated steel.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Machine Bolt Applications?
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals. It typically maintains performance at high temperatures, withstanding pressures up to 1500 psi depending on the grade. The most common grades for machine bolts are 304 and 316, with 316 offering superior resistance to chlorides.
Pros: Stainless steel bolts are durable, resistant to rust, and maintain structural integrity over time. They are ideal for marine applications, food processing, and environments with high humidity.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to carbon steel. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to machine, potentially leading to increased manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel bolts are compatible with a wide range of media, including water, steam, and various chemicals. However, buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A193 for high-temperature applications.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Carbon Steel?
Carbon steel is a popular choice for machine bolts due to its excellent strength and versatility. It can handle high loads and is often used in structural applications. Carbon steel bolts can be treated for increased hardness and wear resistance, making them suitable for heavy machinery.

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
Pros: Carbon steel is cost-effective and readily available, making it a go-to option for many applications. It can be heat-treated to enhance performance characteristics.
Cons: The main limitation is its susceptibility to corrosion, which can lead to failure in humid or chemically aggressive environments unless properly coated.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel bolts are typically used in construction, automotive, and general manufacturing. Buyers in regions with high humidity or corrosive environments should consider protective coatings or alternative materials.

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
Why Choose Brass for Machine Bolts?
Brass is often selected for its aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance, particularly in decorative applications. It has good machinability and is commonly used in electrical applications due to its conductivity.
Pros: Brass bolts are resistant to corrosion and have a pleasing appearance, making them suitable for visible applications. They also provide good resistance to galling, which is beneficial in threaded connections.
Cons: Brass is generally weaker than stainless or carbon steel, making it unsuitable for high-load applications. Additionally, it can be more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Brass bolts are ideal for electrical components and decorative hardware. Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B16 for brass fasteners.
What Role Does Zinc-Plated Steel Play in Machine Bolt Selection?
Zinc-plated steel bolts are carbon steel bolts that have been coated with zinc to improve corrosion resistance. This makes them suitable for a variety of indoor and outdoor applications.
Pros: The zinc coating provides a cost-effective barrier against rust, making these bolts suitable for use in less aggressive environments. They are widely available and easy to source.
Cons: The zinc coating can wear off over time, especially in harsh conditions, leading to potential corrosion of the underlying steel. They are not recommended for long-term exposure to moisture.
Impact on Application: Zinc-plated steel bolts are commonly used in construction and automotive applications. Buyers should consider the environmental conditions and ensure that the selected bolts meet relevant standards like ASTM B633 for coatings.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Machine Bolts
| Material | Typical Use Case for machine bolts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Marine applications, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, machining complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel | Construction, automotive | Cost-effective, high strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Brass | Electrical components, decorative uses | Aesthetic appeal, good machinability | Weaker than steel, higher cost | Medium |
| Zinc-Plated Steel | General construction, automotive | Cost-effective corrosion barrier | Coating can wear off | Low |
By understanding the properties and implications of each material, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and environmental conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for machine bolts
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Machine Bolts?
The manufacturing process of machine bolts involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary strength, durability, and precision requirements. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
-
Material Preparation: The first stage involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, typically high-quality steel or stainless steel, which are then cut into specified lengths. The material undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets the required specifications. This stage may also include processes like annealing, which improves the ductility of the metal and reduces brittleness.
-
Forming: After preparation, the material is shaped into bolts using techniques such as cold heading or hot forging. Cold heading is preferred for its efficiency and ability to produce precise dimensions without significant material loss. In contrast, hot forging is used when larger bolts are required, allowing for better material flow and reducing residual stresses. The forming process also involves threading, which can be done through rolling or cutting, depending on the desired finish and application.
-
Assembly: In some cases, machine bolts may require additional components, such as washers or nuts, to be assembled. This step is crucial for ensuring the bolts function correctly in their intended applications, particularly in heavy-duty environments. Automated assembly lines are often employed to increase efficiency and maintain consistent quality.
-
Finishing: The finishing process may include surface treatments like plating (zinc or nickel) to enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetics. Other treatments, such as passivation or phosphating, are also common to further increase durability. Quality checks are performed at this stage to ensure that the finishing meets industry standards.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Machine Bolt Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for machine bolts, which are often used in critical applications. Adhering to international standards and implementing rigorous quality control measures are essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
International Standards: Many manufacturers comply with ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. This certification ensures that the organization consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking and API standards are crucial for certain applications, particularly in the oil and gas sector.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, random samples are checked for dimensional accuracy, strength, and surface finish.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo comprehensive testing to verify performance and compliance with standards before shipment. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of machine bolts. These include:
– Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of the bolts.
– Hardness Testing: Assesses the material’s hardness to ensure it meets specifications.
– Dimensional Inspection: Verifies that the bolts conform to specified dimensions and tolerances using precise measuring instruments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
When sourcing machine bolts, especially for international projects, B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Here are several strategies to verify quality control:

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. An audit checklist should include aspects such as equipment maintenance, employee training, and adherence to safety regulations.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports from suppliers provides insight into their quality control practices. These reports should detail inspection results, testing methodologies, and any corrective actions taken for non-conforming products.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and quality control. These services can perform inspections at various stages of production, ensuring that the final product meets all specifications and standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control that may impact their sourcing decisions:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying quality standards and certifications. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential legal issues. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East might look for compliance with local regulations.
-
Cultural Differences: Communication and business practices vary across cultures. Establishing clear lines of communication with suppliers and understanding cultural nuances can help mitigate misunderstandings regarding quality expectations.
-
Supply Chain Reliability: The reliability of the supply chain is essential for consistent quality. Buyers should evaluate the supplier’s track record, including their ability to meet delivery schedules and manage inventory effectively.
-
After-Sales Support: Quality control does not end at the point of sale. B2B buyers should inquire about the supplier’s after-sales support, including warranty policies, return processes, and availability of replacement parts. This support can be critical in maintaining operational efficiency and minimizing downtime.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for machine bolts is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, along with rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure they source reliable and high-quality machine bolts for their projects.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘machine bolts’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring machine bolts, a critical component in various industrial applications. By following this step-by-step checklist, you will ensure that your procurement process is thorough, compliant, and tailored to your specific operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for ensuring that the machine bolts meet your project requirements. Consider factors such as size, material (e.g., stainless steel, brass), thread type (coarse vs. fine), and head style (pan, flat, or round). Documenting these specifications will facilitate better communication with suppliers and help avoid costly errors.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reliable suppliers that specialize in machine bolts. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry and regions of interest, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Utilize platforms like trade shows, industry directories, and online marketplaces to compile a list of potential partners.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, it’s essential to vet suppliers comprehensively. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to assess their capabilities. Additionally, seek references from other businesses in your industry to understand their reliability and service quality. This will help mitigate risks associated with supplier selection.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensuring that your suppliers adhere to international standards and possess relevant certifications is vital for quality assurance. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems. Compliance with regional regulations, such as RoHS or REACH, is also crucial, especially when sourcing from different international markets.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the machine bolts for testing. This step allows you to assess the quality, strength, and compatibility of the bolts with your applications. Evaluate the samples under real-world conditions to ensure they meet your performance criteria and can withstand operational stresses.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, initiate negotiations on pricing and terms. Consider factors such as minimum order quantities, payment terms, and delivery timelines. A clear understanding of these terms will help prevent misunderstandings and ensure that both parties are aligned on expectations.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Plan
Effective communication is key to a successful procurement process. Establish a plan for regular updates and check-ins with your supplier. This will help address any concerns promptly and keep the project on track, ensuring that you receive your machine bolts on time and as per your specifications.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing machine bolts more effectively, ensuring they select the right products and suppliers for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for machine bolts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Machine Bolt Sourcing?
When sourcing machine bolts, it is essential to understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The type of material used significantly influences the price of machine bolts. Stainless steel, brass, and zinc-plated options vary in cost, with stainless steel generally being the most expensive due to its corrosion resistance and strength. The choice of material should align with the application requirements.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of workers involved in manufacturing the bolts. This can vary based on the geographical location of the manufacturing plant. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Asia or Eastern Europe, can offer competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and other indirect expenses of running a manufacturing facility. Efficient operations and modern machinery can help reduce these overheads.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and tools for production can be significant. Custom tooling for specific bolt designs will add to the cost but may be necessary for specialized applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality checks ensure that the bolts meet industry standards and specifications. Investing in quality control can prevent costly defects but adds to the overall production cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling expenses are crucial, especially for international shipments. Costs can vary based on distance, shipping method, and any tariffs or duties imposed on imports.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary significantly among suppliers based on their market positioning and value-added services.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Machine Bolt Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of machine bolts, impacting how buyers approach sourcing decisions:

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it beneficial for buyers to assess their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed bolts or those with specific specifications (e.g., unique thread patterns or finishes) usually incur higher costs due to the complexity and additional tooling required.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (like ISO or ASTM standards) can raise costs. Buyers should evaluate the balance between quality and price based on their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a solid reputation may charge more due to perceived reliability and service quality. However, new or lesser-known suppliers could offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international buyers. They define responsibilities regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer, which can affect the total cost of ownership.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Machine Bolts?
B2B buyers should adopt several strategies to optimize their sourcing of machine bolts:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions to explore discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts. Establishing a good relationship can also yield better pricing and terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the initial purchase price. Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, replacement, and potential downtime costs associated with lower-quality bolts.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that can affect overall costs. Additionally, consider the impact of shipping times and logistics on project timelines.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and assess their offerings based on quality, price, and delivery timelines. This competitive analysis can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keep abreast of trends in the fastener industry, including raw material price changes and technological advancements in manufacturing. This knowledge can provide leverage in negotiations.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of machine bolts is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By considering these factors and employing strategic sourcing methods, buyers can optimize their procurement processes and achieve better value for their investments. Prices can vary widely based on numerous factors, so conducting thorough market research and supplier evaluations is essential.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing machine bolts With Other Solutions
In the realm of fastening solutions, machine bolts are a popular choice for their reliability and strength. However, there are alternative methods and products available that can also serve similar functions. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions that align with their specific project requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Machine Bolts | Self-Tapping Screws | Rivets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High tensile strength, reliable | Good for thin materials, quick use | Permanent joint, excellent shear strength |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to installation tools |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires nut or tapped hole | Simple installation, no pre-drilling | Requires specialized tools for installation |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance | Low maintenance | No maintenance after installation |
| Best Use Case | Heavy machinery, automotive | Sheet metal, plastics | Aircraft, structural applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Self-Tapping Screws?
Self-tapping screws are designed to create their own threads when driven into material, making them particularly useful for quick installations in thin materials. Their ease of use is a significant advantage, as they eliminate the need for pre-drilling, allowing for faster assembly times. However, they may not provide the same level of strength as machine bolts, particularly in heavy-duty applications. This makes them ideal for lighter projects, but less suitable where high tensile strength is required.
How Do Rivets Compare to Machine Bolts?
Rivets are a permanent fastening solution that excels in applications requiring high shear strength, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. Their installation typically requires specialized tools like rivet guns, which can add to the initial cost and complexity. While rivets provide a robust and durable connection, they are not adjustable once installed, making them less versatile than machine bolts. They are best used in situations where a permanent, strong bond is necessary, but may not be the best choice for projects needing ongoing adjustments.

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Fastening Solution?
When selecting a fastening solution, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific project needs, including the materials involved, the required strength, and the environment in which the fasteners will be used. Machine bolts offer robust performance and reliability for heavy-duty applications, while self-tapping screws provide quick installation for lighter materials. Rivets are ideal for permanent solutions requiring high strength. By assessing these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that not only meet their technical requirements but also align with their budget and operational efficiencies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for machine bolts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Machine Bolts?
When sourcing machine bolts, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring the right fit and performance in your application. Here are some critical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade indicates the strength and corrosion resistance of the bolt. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and brass, each offering different mechanical properties. For example, stainless steel bolts (like grades 304 and 316) provide excellent resistance to rust and are ideal for outdoor or corrosive environments. Selecting the appropriate material grade is essential to ensure longevity and reliability in your applications. -
Thread Type
Machine bolts can feature various thread types, such as coarse and fine threads. Coarse threads provide faster assembly and are less likely to strip, making them suitable for softer materials. Fine threads offer better tension control and are more effective in high-stress applications. Understanding the thread type is vital for compatibility with nuts and tapped holes, influencing the bolt’s performance in specific environments. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions. For machine bolts, tight tolerances ensure a secure fit and minimize movement, which is critical in load-bearing applications. A tighter tolerance can lead to improved precision and reliability, reducing the risk of failure in critical systems. -
Length and Diameter
The length and diameter of machine bolts are fundamental specifications that dictate their suitability for various projects. Length affects the bolt’s grip on the materials being fastened, while diameter influences the bolt’s strength. Knowing the appropriate dimensions helps prevent issues such as over-tightening, which can lead to material damage or bolt failure. -
Surface Treatment
Surface treatments such as galvanization or plating enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics. For instance, zinc-plated bolts are commonly used in environments where moisture is a concern, while black oxide finishes can be selected for a more polished appearance. The choice of surface treatment is pivotal for ensuring the bolt’s performance in specific environmental conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Machine Bolts?
Navigating the B2B landscape involves familiarizing oneself with industry jargon. Here are some essential terms that can impact your purchasing decisions:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of machine bolts, an OEM may require specific bolt specifications to ensure compatibility with their machinery. Understanding OEM requirements is crucial for maintaining quality and performance in your supply chain. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For machine bolts, MOQs can affect inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases and manage stock levels effectively, particularly in regions with varying demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer seeking price quotes from suppliers for specific products. When dealing with machine bolts, an RFQ allows businesses to compare prices, specifications, and lead times from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, covering aspects like shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as it can influence overall costs and logistics in sourcing machine bolts. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning, particularly in industries where delays can lead to increased costs or project overruns. -
Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ISO or ASTM, ensure that machine bolts meet specific quality and safety requirements. Recognizing the importance of certification can help buyers avoid substandard products and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing machine bolts, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and reduced risks in their projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the machine bolts Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Machine Bolts Sector Globally?
The machine bolts market is undergoing significant transformations driven by global industrialization, technological advancements, and evolving consumer demands. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe expand, the demand for reliable and high-quality fasteners, including machine bolts, continues to surge. One of the primary drivers is the rapid growth of construction and manufacturing sectors, particularly in emerging markets, where infrastructure development is paramount.
Illustrative image related to machine bolts
In addition to traditional sourcing methods, B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms and e-commerce solutions to streamline their procurement processes. The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies—such as IoT, AI, and automation—enables companies to optimize inventory management and enhance supply chain transparency. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to ensure timely delivery and minimize costs.
Moreover, the shift towards customization is reshaping buyer expectations. Companies are now seeking machine bolts that not only meet standard specifications but also cater to specific project requirements, which necessitates flexibility from suppliers. As a result, manufacturers are investing in advanced production techniques, including additive manufacturing, to offer tailored solutions efficiently.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Machine Bolts Market?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor for B2B buyers in the machine bolts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has prompted companies to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. This includes the use of recycled materials, energy-efficient production methods, and waste reduction strategies. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing the carbon footprint of their supply chains, making it essential for suppliers to adopt sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing has also gained prominence, with businesses emphasizing the importance of transparency in their supply chains. Buyers are looking for partners who comply with international labor standards and engage in fair trade practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade compliance are becoming critical differentiators in supplier selection.

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
Additionally, the demand for ‘green’ materials is rising. Machine bolts made from sustainable materials, such as recycled steel or eco-friendly coatings, are gaining traction. Suppliers who can provide these options not only meet regulatory demands but also appeal to environmentally conscious buyers, enhancing their competitive edge in the market.
What Is the Historical Context of Machine Bolts in B2B Transactions?
The evolution of machine bolts can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, which marked the beginning of mass production and standardization of fasteners. Initially, machine bolts were crafted manually, making them costly and inconsistent. The introduction of machinery and later advancements in metallurgy allowed for the production of more reliable and standardized bolts, catering to the burgeoning demands of various industries.
In recent decades, the advent of global supply chains has transformed the sourcing landscape for machine bolts. With the rise of international trade, companies can now access a broader range of products at competitive prices. This globalization has also introduced challenges, such as quality control and ethical sourcing, which are increasingly influencing buyer decisions. As the market continues to evolve, understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers aiming to navigate the complexities of sourcing machine bolts effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of machine bolts
1. How do I choose the right machine bolts for my project?
Selecting the appropriate machine bolts involves understanding the specific requirements of your project, such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and material compatibility. Consider factors like the type of load (static or dynamic), the presence of corrosive elements, and the required strength grade of the bolts. Additionally, assess the dimensions, thread type (fine or coarse), and head style that best suits your application. Consulting technical data sheets and collaborating with suppliers can also provide valuable insights for making the right choice.

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
2. What is the best material for machine bolts in outdoor applications?
For outdoor applications, stainless steel is typically the best choice due to its excellent corrosion resistance and durability. Grade 316 stainless steel is particularly suited for environments exposed to saltwater or chemicals, while Grade 304 offers good protection in less severe conditions. If cost is a concern, galvanized steel bolts provide a balance of strength and corrosion resistance but may require replacement sooner in harsh environments. Always evaluate the specific conditions your application will face to ensure longevity and reliability.
3. How can I ensure the quality of machine bolts from suppliers?
To ensure quality, vet suppliers by checking their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request samples and review their manufacturing processes, including material sourcing and testing methods. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance practices, such as regular inspections and compliance with industry standards. Establishing a long-term relationship with reliable suppliers can further enhance your confidence in the quality of the machine bolts you source.
4. What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for machine bolts?
Minimum order quantities for machine bolts can vary significantly based on the supplier, type of bolt, and customization requirements. Typically, MOQs can range from as low as 100 pieces for standard products to thousands for specialized or custom bolts. When negotiating with suppliers, discuss your specific needs and see if they can accommodate smaller orders, especially for initial tests or samples. Understanding the MOQ will help you manage inventory and cash flow effectively.
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing machine bolts internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among international suppliers, often influenced by the buyer’s location, order size, and supplier policies. Common terms include advance payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon shipment. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide a balance of security for the supplier and flexibility for your business. Additionally, consider using escrow services for larger orders to mitigate risks associated with international transactions.

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
6. How can I handle logistics for sourcing machine bolts from overseas?
Managing logistics for international sourcing requires careful planning. Start by choosing a reliable freight forwarder familiar with customs regulations in both the exporting and importing countries. Understand the shipping options available, such as air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is prepared to avoid delays at customs. Establishing clear communication with your supplier and freight forwarder will streamline the process and mitigate potential issues.
7. Can machine bolts be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for machine bolts, including dimensions, materials, thread types, and coatings. Customization can enhance performance for specific applications, ensuring compatibility with your machinery or assembly processes. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and, if possible, samples of existing bolts. Be aware that custom orders may involve longer lead times and higher costs, so plan accordingly to align with your project timelines.
8. What are the best practices for storing machine bolts?
Proper storage of machine bolts is crucial to maintaining their quality and usability. Store bolts in a dry, cool environment to prevent corrosion and degradation of materials. Use labeled bins or containers to organize different sizes and types, making it easier to access them when needed. Additionally, consider using desiccants or moisture-absorbing packets in storage areas to reduce humidity. Regularly inspect stored bolts for any signs of rust or damage, and rotate inventory to ensure older stock is used first.
Illustrative image related to machine bolts
Top 8 Machine Bolts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bolt Depot – Machine Screws
Domain: boltdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Machine screws have machine threads for use with a nut or in a tapped hole. SEMS machine screws are pre-assembled with a permanently attached, free-spinning washer for convenient installation. Type F machine screws are thread cutting machine screws that tap their own threads. Metric machine screws also have machine threads for use with a nut or in a tapped hole. Socket screws are screws with an Al…
2. Fastenere – Machine Screws
Domain: fastenere.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Machine screws are fasteners designed for use in various applications, typically featuring a uniform diameter and a sharp point for easy insertion. They are available in a range of materials, including stainless steel, brass, and nylon, and come in various sizes and thread types to suit different needs. Machine screws are commonly used in machinery, electronics, and construction, providing secure …
3. Blacksmith Bolt – Unslotted Machine Screws
4. ASTM Bolts – Machine Bolts
Domain: astmbolts.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: {“Product Type”: “Machine Bolts”, “Head Styles”: [“Hex Head”, “Square Head”], “Thread Types”: [“UNC”, “UNF”, “ISO”, “BSW”, “ACME”], “Dimensions”: {“Metric Size”: “M10 to M100”, “Imperial Size”: “3/8 to 8”}, “Standards”: [“ASME”, “BS”, “DIN”, “ISO”, “UNI”, “DIN-EN”], “Sub Types”: [“Fully Threaded Machine Bolts”, “Partial Threaded Machine Bolts”, “Metric Machine Bolts”, “Imperial Machine Bolts”], “M…
5. Portland Bolt – Crossarm Bolts
Domain: portlandbolt.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Machine bolts, also known as crossarm bolts, are used in the pole line industry. They feature square heads and a semi-cone point, typically assembled with a square nut. These bolts are usually hot-dip galvanized for steel protection. Portland Bolt manufactures crossarm bolts up to 1-1/2″ in diameter, adhering to thread length guidelines for pole line fasteners. Dimensions for machine bolts include…
6. Monster Bolts – Machine Screws
Domain: monsterbolts.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Machine screws have a uniform diameter along the entire length of the shaft, making them very similar to bolts and socket screws. They can be secured with nuts but are often driven into tapped holes. Commonly used to fasten machine components, they are frequently found in automotive applications, appliances, and more. Available types include Phillips Flat head and Pan head screws, with materials s…
7. McMaster – Machine Bolts
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Machine Bolts, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. Earnest Machine – Fasteners and Key Products
Domain: earnestmachine.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Key product details include a wide range of fasteners such as bolts, screws, washers, nuts, clamps, plugs, clips, timberjack pins, rods, studs, and anchors. Specific offerings include hex head cap screws with diameters from 1/4″ to 2 1/2″, hex nuts available in multiple sizes, grades, and finishes with diameters from 1/4″ to 3″, and serrated flange screws with diameters from #10 to 5/8″ and length…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for machine bolts
In the realm of machine bolts, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal approach for international B2B buyers. By understanding the diverse types of machine screws and bolts—ranging from stainless steel to zinc-plated options—buyers can ensure they select the most suitable fasteners for their specific applications. The right choice not only enhances the durability and safety of projects but also optimizes operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
As market dynamics continue to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the importance of a well-planned sourcing strategy cannot be overstated. Buyers should leverage supplier partnerships, prioritize quality standards, and stay informed about technological advancements in fastener production to remain competitive.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality machine bolts will only increase as industries expand and innovate. Engaging with reputable suppliers and exploring new sourcing opportunities will be essential for businesses aiming to thrive. We encourage international buyers to act now—evaluate your fastener needs, assess your supply chain, and embark on a strategic sourcing journey that will secure your projects’ future success.

Illustrative image related to machine bolts
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.