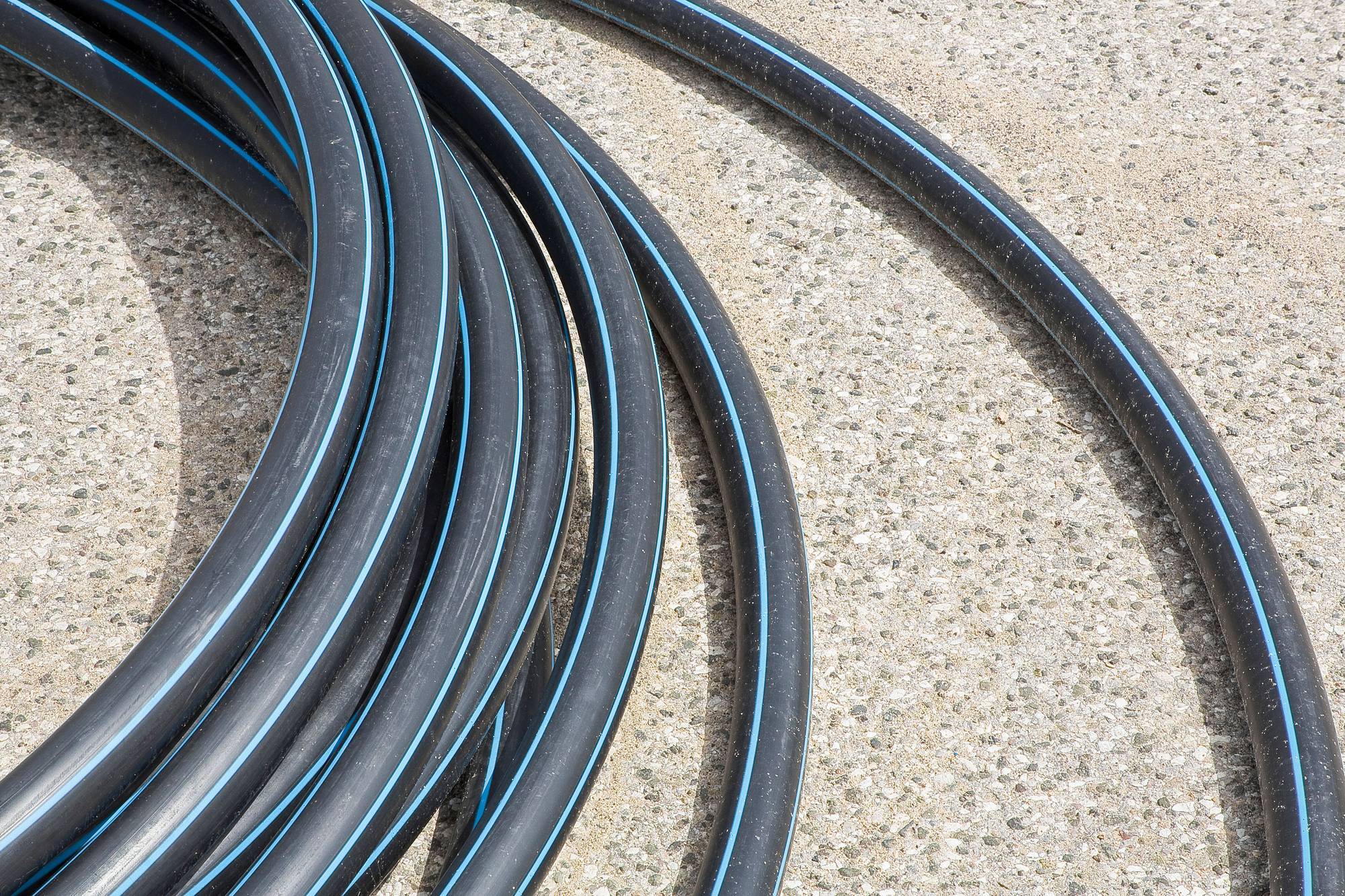
Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Poly Water Line Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for poly water line
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing high-quality poly water lines presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries strive to enhance their water management systems, understanding the nuances of polyethylene water piping becomes crucial. This guide offers a comprehensive overview, addressing various types of poly water lines, their applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting. With a focus on critical factors such as cost analysis and installation efficiencies, we empower decision-makers to navigate the complexities of this market confidently.
The diverse applications of poly water lines—from agricultural irrigation to municipal water supply—highlight their essential role in infrastructure development. However, the selection process can be daunting due to the variety of products available and the varying standards across different regions. By equipping buyers with the knowledge of product specifications, installation methods, and long-term performance metrics, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
Whether you are a contractor in Brazil seeking durable solutions for rural water projects or a municipal planner in Saudi Arabia looking for reliable piping systems, understanding the market landscape will enhance your procurement strategy. This resource is designed to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring that you invest in the right poly water lines that meet your specific operational needs while adhering to global standards.
Understanding poly water line Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Durable, flexible, resistance to corrosion and UV weathering | Agriculture, irrigation, construction | Pros: Long lifespan, easy installation; Cons: Higher initial cost compared to other materials. |
| Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | Lightweight, more flexible than HDPE, lower pressure ratings | Landscaping, low-pressure irrigation | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to handle; Cons: Less durable, lower PSI ratings limit applications. |
| Polybutylene (PB) | Affordable, easy to install, potential for chemical leaching | Residential plumbing, irrigation systems | Pros: Low installation cost; Cons: Prone to degradation, not suitable for high-pressure applications. |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Good chemical resistance, higher temperature tolerance | Industrial applications, chemical transport | Pros: Versatile, resistant to many chemicals; Cons: More expensive than HDPE and LDPE. |
| Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX) | Flexible, easy to install, resistant to scale and chlorine | Residential plumbing, radiant heating | Pros: Excellent for complex layouts; Cons: Can be more costly than traditional piping. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Water Lines?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are renowned for their robustness and flexibility, making them ideal for a range of applications, particularly in agriculture and construction. With a pressure rating of 200 PSI, HDPE pipes are suitable for both direct burial and surface installations. Their resistance to corrosion and UV weathering ensures longevity, with a projected lifespan of up to 100 years. Buyers should consider the initial investment, as HDPE tends to be more expensive than other materials, but the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and replacement costs can be significant.
How Does Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) Compare to Other Poly Water Lines?
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is valued for its lightweight and flexibility, making it easier to handle and install, especially in landscaping and low-pressure irrigation systems. While LDPE is more cost-effective than HDPE, it has lower pressure ratings, which limits its use in high-demand applications. Buyers should weigh the advantages of lower upfront costs against the potential need for more frequent replacements due to its reduced durability.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Polybutylene (PB) Pipes?
Polybutylene (PB) pipes are an economical choice for residential plumbing and irrigation systems. They are easy to install and connect, reducing labor costs. However, PB has faced scrutiny due to concerns about chemical leaching and degradation over time, particularly when exposed to chlorine. While PB may be suitable for low-pressure applications, buyers should consider the long-term implications of potential failures and the associated costs.
Why Choose Polypropylene (PP) for Industrial Applications?
Polypropylene (PP) offers excellent chemical resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, making it suitable for industrial applications and chemical transport. Its versatility allows it to be used in various environments; however, it typically comes at a higher price point than HDPE or LDPE. B2B buyers must evaluate the specific requirements of their applications against the cost of PP pipes to determine their overall value.
What Makes Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX) a Unique Option?
Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX) is increasingly popular for residential plumbing and radiant heating systems due to its flexibility and resistance to scale and chlorine. PEX allows for easier installation in complex layouts, reducing the need for joints and fittings. However, it may come at a higher cost compared to traditional piping materials. B2B buyers should consider their project needs and budget when evaluating PEX as an option, particularly in environments where durability is paramount.
Key Industrial Applications of poly water line
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of poly water line | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Irrigation systems for crops and livestock | Enhances water efficiency, reduces costs | Durability, resistance to UV and chemicals, local availability |
| Construction | Water supply lines for residential and commercial projects | Ensures reliable water delivery, reduces downtime | Compliance with local regulations, installation ease, pressure ratings |
| Mining | Dust suppression and water supply for mining operations | Improves operational safety, minimizes dust-related issues | Flexibility, resistance to abrasion, length options |
| Aquaculture | Water distribution systems for fish farms | Maintains optimal water quality, supports fish health | Non-toxic materials, ease of installation, local sourcing |
| Municipal Infrastructure | Water distribution networks for urban areas | Ensures safe drinking water supply, reduces leakage | Compliance with health standards, pressure ratings, sourcing logistics |
How is Poly Water Line Used in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, poly water lines are predominantly utilized for irrigation systems that supply water to crops and livestock. They offer enhanced water efficiency, enabling farmers to optimize their water usage and reduce costs associated with water supply. The durability of these pipes, combined with their resistance to UV rays and chemicals, ensures a long service life, making them a cost-effective choice for farmers. International buyers should consider local availability and compatibility with existing systems when sourcing these products.
What Role Does Poly Water Line Play in Construction?
In construction, poly water lines are essential for establishing reliable water supply systems in both residential and commercial projects. They ensure consistent water delivery, which is crucial for construction activities such as mixing concrete and providing potable water. The ease of installation and compliance with local regulations are vital for contractors, especially in international markets where standards may vary. Buyers should prioritize pressure ratings and the pipe’s ability to withstand environmental conditions when sourcing.
How is Poly Water Line Beneficial in Mining Operations?
The mining industry employs poly water lines primarily for dust suppression and water supply to mining operations. These pipes help maintain operational safety by minimizing dust-related health risks and ensuring that equipment remains functional. The flexibility of poly lines allows for easy installation in rugged terrains, and their resistance to abrasion is crucial for durability in harsh environments. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing options that offer various lengths and specifications suitable for their unique operational needs.
What is the Application of Poly Water Line in Aquaculture?
In aquaculture, poly water lines are critical for the distribution of water in fish farms. They help maintain optimal water quality, which is essential for fish health and growth. The non-toxic nature of the materials used in these pipes ensures that they do not negatively impact aquatic life. Buyers in the aquaculture sector should consider ease of installation and local sourcing to ensure compliance with environmental standards and operational efficiency.
How Do Municipal Infrastructure Projects Utilize Poly Water Line?
Municipal infrastructure projects rely on poly water lines for the construction of water distribution networks in urban areas. These pipes are vital for ensuring a safe drinking water supply and minimizing leakage, which is a significant concern for municipalities. Compliance with health standards and appropriate pressure ratings are essential factors for sourcing these products. International buyers should also consider the logistics of sourcing and transporting these materials to ensure timely project completion.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘poly water line’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Delays Due to Supply Chain Issues
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant delays in acquiring poly water lines due to unpredictable supply chain disruptions. These disruptions can stem from various factors such as geopolitical tensions, raw material shortages, or logistical challenges. For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, where infrastructure may already be strained, these delays can halt critical projects, impact operational timelines, and lead to increased costs.
The Solution:
To mitigate supply chain issues, B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach by diversifying their supplier base. Instead of relying on a single supplier, consider establishing relationships with multiple manufacturers across different geographical areas. This diversification can provide backup options in case of delays from one supplier. Moreover, implementing a just-in-time inventory strategy can help manage stock levels effectively, reducing the likelihood of overstocking or stockouts. Regular communication with suppliers about their production capabilities and lead times will enable buyers to anticipate potential delays and make informed decisions about order quantities and timing.

Illustrative image related to poly water line
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Product Quality
The Problem:
Quality inconsistency is a common concern when sourcing poly water lines, especially when suppliers do not adhere to industry standards or when there is a lack of stringent quality control measures. Buyers may find themselves dealing with pipes that do not meet the specified pressure ratings or exhibit premature wear, leading to costly repairs and project delays.
The Solution:
To ensure consistent product quality, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who have established certifications, such as NSF or ISO. These certifications demonstrate adherence to industry standards and rigorous testing processes. Additionally, conducting site visits to manufacturing facilities can provide insights into production practices and quality control measures. Buyers should also request samples for testing before making large orders, ensuring that the product meets their specific requirements. Establishing a clear quality agreement with suppliers, outlining expectations and responsibilities, can further safeguard against quality issues.
Scenario 3: Complications with Installation and Maintenance
The Problem:
Many buyers encounter complications during the installation and maintenance of poly water lines, which can result from a lack of proper training or inadequate tools. Improper installation may lead to leaks or system failures, while maintenance challenges can increase operational costs and reduce system lifespan.
The Solution:
Investing in training for installation and maintenance personnel can significantly reduce complications. Buyers should collaborate with suppliers who offer comprehensive training programs, either in-person or online, focusing on best practices for installation and maintenance of poly water lines. Additionally, providing teams with the right tools and equipment, such as specialized fusion machines for connecting pipes, can enhance installation efficiency. Furthermore, creating a detailed maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the water lines.
By addressing these common pain points with actionable solutions, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement processes, ensuring the successful deployment of poly water lines in their projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for poly water line
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Poly Water Lines?
When selecting materials for poly water lines, it is essential to consider their properties, pros and cons, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX).
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Key Properties:
HDPE pipes are known for their high strength-to-density ratio, making them ideal for high-pressure applications. They typically have a pressure rating of up to 200 PSI and can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°F to 140°F. HDPE is also resistant to corrosion, UV weathering, and chemical exposure.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of HDPE offers a projected service life of up to 100 years, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run. However, the initial manufacturing costs can be higher than other materials. Installation is straightforward, but the need for specialized fusion equipment can complicate the process.
Impact on Application:
HDPE is suitable for potable and non-potable water applications. Its resistance to corrosion and chemicals makes it ideal for various environments, including agricultural and municipal water systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN. HDPE’s widespread acceptance in international markets makes it a reliable choice.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
Key Properties:
LDPE is characterized by its flexibility and lower density compared to HDPE, making it suitable for low-pressure applications. It typically has a pressure rating of around 60 PSI and can operate effectively in temperatures up to 120°F.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of LDPE is its flexibility, which allows for easier installation in tight spaces. However, it is less durable than HDPE and has a shorter lifespan, typically around 50 years. LDPE is also more susceptible to environmental stress cracking.
Impact on Application:
LDPE is often used for irrigation systems and low-pressure water distribution. Its flexibility makes it suitable for applications where bending and maneuverability are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers:
LDPE is less commonly regulated than HDPE, but buyers should still check for compliance with local standards. Its lower cost may appeal to budget-conscious buyers in developing regions.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Key Properties:
PVC is a rigid plastic that offers good chemical resistance and a pressure rating of up to 150 PSI. It can handle temperatures up to 140°F but is not recommended for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons:
PVC is cost-effective and easy to install, making it a popular choice for various plumbing applications. However, it is less flexible than polyethylene options, which can limit its use in certain installations. Additionally, PVC can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application:
PVC is commonly used for non-potable water systems, drainage, and irrigation. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for transporting a variety of fluids.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the environmental regulations surrounding PVC, particularly in Europe, where there are stringent standards for plastic materials.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX)
Key Properties:
PEX is a flexible tubing that can withstand temperatures up to 200°F and pressure ratings of up to 80 PSI. Its cross-linking process enhances its durability and resistance to temperature fluctuations.
Pros & Cons:
PEX offers excellent flexibility and is resistant to scale and chlorine, making it suitable for various water applications. However, it is more expensive than traditional polyethylene options and may require specific fittings and installation techniques.
Impact on Application:
PEX is increasingly used in residential plumbing and heating systems due to its flexibility and ease of installation. It is also suitable for both hot and cold water applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should check for compliance with local building codes and standards, as PEX is not universally accepted in all regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Poly Water Lines
| Material | Typical Use Case for poly water line | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Potable and non-potable water systems | Long service life (up to 100 years) | Higher initial costs and need for fusion equipment | High |
| Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | Irrigation and low-pressure applications | Flexible and easy to install | Shorter lifespan and lower pressure rating | Low |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Non-potable water systems and drainage | Cost-effective and easy to install | Brittle over time and less flexible | Medium |
| Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX) | Residential plumbing and heating systems | Excellent flexibility and temperature resistance | Higher cost and specific installation requirements | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for poly water lines, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for poly water line
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Poly Water Lines?
The manufacturing of poly water lines, particularly those made from High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the stringent requirements of durability and performance.

Illustrative image related to poly water line
Material Preparation
The first stage of the manufacturing process involves sourcing and preparing raw materials. HDPE resin, characterized by its high strength-to-density ratio, is typically sourced from reputable suppliers. During this stage, the resin undergoes rigorous quality checks to ensure that it meets the required specifications. This includes testing for melt flow index, density, and other physical properties.
Once the resin is confirmed to meet quality standards, it is compounded with additives that enhance its performance characteristics, such as UV resistance and color. This compounding process is crucial as it directly impacts the longevity and usability of the pipes in various environmental conditions.
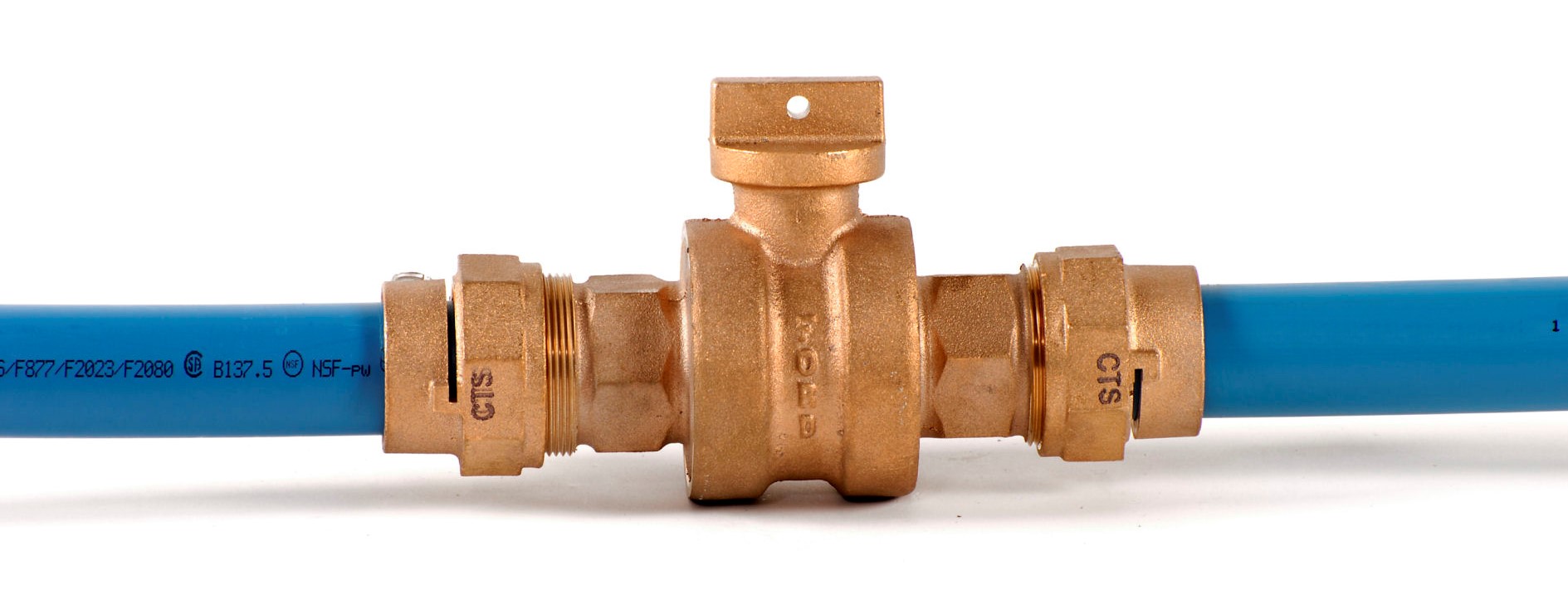
Forming Techniques: How Are Poly Water Lines Shaped?
After material preparation, the next step is forming the HDPE into the desired pipe shapes. The most common techniques used in this stage include extrusion and rotational molding.
Illustrative image related to poly water line
-
Extrusion: This is the primary method for producing poly water lines. The compounded HDPE resin is heated until it melts and is then forced through a die to create a continuous pipe. This method allows for the production of pipes in various diameters and lengths, often in coils for easier transport and installation.
-
Rotational Molding: Although less common for water lines, this technique is sometimes used for creating fittings or specialized components. The process involves heating a mold filled with the resin, allowing it to coat the inside and form the desired shape as it cools.
What Is Involved in the Assembly and Finishing of Poly Water Lines?
After forming, pipes may require assembly with various fittings or connectors. This stage often involves the use of fusion welding techniques to ensure a seamless and leak-proof connection.
Once assembled, the pipes go through a finishing process that may include cutting to specified lengths, surface treatment, and additional quality checks. This ensures that any surface irregularities are addressed and that the product meets aesthetic and functional standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Poly Water Line Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for international B2B buyers who require assurance of product reliability and compliance with industry standards.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers of poly water lines often adhere to various international standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For manufacturers involved in the oil and gas sector, compliance with American Petroleum Institute standards is crucial.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is typically segmented into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. It prevents subpar materials from entering the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections ensure that processes remain within defined parameters. This can include monitoring temperatures, pressures, and dimensions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the production process, final inspections are conducted. This includes physical testing of the pipes for pressure resistance, leakage, and dimensional accuracy.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Common testing methods employed in the QC process for poly water lines include:
- Hydrostatic Testing: Used to test the pressure capacity of the pipes.
- Impact Testing: Assesses the toughness of the material, especially in colder temperatures.
- Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR) Testing: Evaluates the material’s ability to withstand environmental stressors.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are several approaches:

Illustrative image related to poly water line
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can help buyers assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures implemented by the supplier. This direct observation can reveal the operational standards maintained by the manufacturer.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can provide insight into the testing methods used and the results obtained. This documentation should ideally include evidence of compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These organizations typically have established protocols for evaluating manufacturing processes.
What Are the Specific QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances related to QC and certification.
-
Regional Standards: Different countries may have unique requirements regarding certifications. For example, buyers in the European Union may prioritize CE marking, while those in the Middle East may look for compliance with local standards.
-
Language and Documentation: Ensuring that all quality documentation is available in a language that is understandable to the buyer is essential for transparency.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate better communication and negotiation regarding quality expectations.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing poly water lines, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘poly water line’
This sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in procuring high-quality polyethylene (poly) water lines. The procurement process can be complex, especially when dealing with varying standards and supplier capabilities across different regions. This checklist will help you navigate through the essential steps to ensure a successful purchase.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for selecting the right poly water line for your needs. Consider factors such as pipe diameter, pressure rating (e.g., 200 PSI), and the type of polyethylene (HDPE vs. LDPE). This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure you receive products that meet your operational requirements.
- Key Considerations:
- Intended use (potable vs. non-potable water)
- Installation method (direct burial vs. surface)
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Understanding local regulations and standards is essential when sourcing poly water lines. Different countries may have specific certifications required for materials used in water supply systems, such as NSF or ISO certifications. Ensuring compliance with these regulations will help avoid legal issues and ensure safety.
- Look for:
- Supplier certifications that align with your region’s requirements
- Documentation to verify compliance with international standards
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Look for companies with a proven track record in supplying poly water lines, especially in your target regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from existing clients to gauge their reliability.
- Assessment Criteria:
- Years in business and industry reputation
- Customer testimonials and case studies
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request product samples. This step is vital to evaluate the physical quality of the poly water lines. Inspect the samples for flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental factors such as UV exposure and chemical interaction.
- Focus On:
- Material thickness and overall construction
- Any signs of wear or defects in the sample
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Pricing is a critical factor in the sourcing process. Once you are satisfied with the quality, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Ensure that you account for shipping costs, especially if you are importing from distant suppliers.
- Important Points:
- Clarify bulk purchase discounts
- Discuss warranty and return policies
Step 6: Verify Logistics and Delivery Options
Ensure that your supplier can meet your delivery timelines and logistical needs. This is particularly important for international shipments, where delays can significantly impact project schedules. Confirm shipping methods and estimated delivery times.
- Key Factors:
- Shipping terms (FOB, CIF, etc.)
- Availability of tracking options during transit
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Documentation
After agreeing on terms, finalize your order with all necessary documentation. Ensure that contracts detail product specifications, pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. This will protect both parties and facilitate a smooth transaction.
- Documentation Checklist:
- Purchase order
- Compliance certificates and warranties
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for poly water lines, ensuring they select the right products and suppliers for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for poly water line Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Poly Water Lines?
When sourcing poly water lines, understanding the cost structure is essential for informed decision-making. Key cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary material for poly water lines is high-density polyethylene (HDPE), known for its durability and resistance to corrosion. The price can vary based on quality and certifications, such as NSF approval for potable water applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce required for manufacturing, installing, and maintaining the water lines. These costs can fluctuate significantly based on the region and local wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses associated with the manufacturing process.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom or specialized production can be substantial, particularly for unique diameters or specifications. These costs are often amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of poly water lines is vital, especially for applications involving potable water. QC processes can add to costs but are essential for compliance and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, shipping method, and weight. International buyers should factor in customs duties and potential tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that can vary based on their business model and market competition.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Poly Water Line Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of poly water lines, impacting the total cost for buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk often leads to significant discounts. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing models based on order size, incentivizing larger purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom dimensions, pressure ratings, or additional features (such as UV resistance) can increase costs. Buyers should clarify requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications (like NSF for drinking water) can command a premium price but may be necessary for compliance and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service level can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and customer support.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, affecting the total landed cost of products.
What Tips Should Buyers Consider for Cost Efficiency in Poly Water Line Sourcing?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies for cost-efficient sourcing:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and potential discounts for bulk orders. Building a good relationship can lead to better terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider long-term costs such as installation, maintenance, and potential replacement. HDPE pipes often have lower TCO due to their durability.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of market conditions, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical factors that can affect pricing. This knowledge can aid in timing purchases effectively.
-
Compare Multiple Suppliers: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide insight into market pricing and help identify the best deals. Pay attention to the total cost, not just the unit price.
-
Leverage Local Regulations: Understanding local regulations and certifications can guide the selection of appropriate products and ensure compliance, potentially avoiding costly penalties or project delays.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for poly water lines can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors, and the figures provided in this analysis are indicative. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain tailored quotes to ensure accurate budgeting for their specific projects.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing poly water line With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Poly Water Lines
When considering water transportation systems, B2B buyers must evaluate various solutions to identify the best fit for their needs. Poly water lines, typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offer several advantages, but alternative technologies may present comparable benefits depending on specific project requirements. This analysis explores how poly water lines stack up against two prominent alternatives: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) piping and steel piping. Each option presents unique characteristics that influence performance, cost, and ease of implementation.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Poly Water Line | PVC Piping | Steel Piping |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly flexible, resistant to corrosion and UV | Good pressure tolerance, less flexible | High pressure and temperature resistance |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, long-term savings | Generally lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost, maintenance can be expensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to install, lightweight, can be coiled | Moderate installation complexity, rigid | Heavy, requires skilled labor for installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable (up to 100 years) | Moderate; prone to cracking under stress | High; susceptible to rust and corrosion |
| Best Use Case | Agricultural and ranching applications | Residential and commercial plumbing | Industrial applications requiring high durability |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
PVC Piping
PVC piping is widely used in various applications due to its cost-effectiveness and availability. Its lightweight nature and ease of handling make it a popular choice for residential plumbing and irrigation systems. However, while PVC is generally cheaper than poly water lines, it lacks the flexibility and UV resistance that poly lines provide. PVC can become brittle over time, especially when exposed to extreme temperatures, leading to potential failure. This makes poly water lines a more durable and reliable option for long-term projects.
Steel Piping
Steel piping is known for its robustness and ability to handle high pressure and temperature conditions, making it ideal for industrial applications. However, its weight and susceptibility to corrosion necessitate protective coatings and regular maintenance, which can escalate costs over time. While steel may be suitable for specific high-demand environments, poly water lines offer a significant advantage in terms of installation ease and longevity, making them a more practical choice for agricultural and ranching operations where flexibility and minimal maintenance are critical.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right water transportation solution hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your project. Poly water lines provide a compelling mix of durability, flexibility, and low maintenance, making them particularly well-suited for agricultural applications. In contrast, PVC piping may be a more economical choice for smaller, less demanding installations, while steel piping excels in high-pressure industrial contexts despite its higher long-term costs. B2B buyers should carefully assess their unique needs, including installation environment, long-term maintenance considerations, and budget constraints, to make an informed decision that aligns with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for poly water line
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Poly Water Lines?
When sourcing poly water lines, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the critical specifications that international B2B buyers should be aware of:
1. Material Grade: What Does HDPE Mean?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is the most common material used for poly water lines. Its high tensile strength and resistance to impact make it suitable for various applications, including agricultural and municipal water supply systems. HDPE’s durability ensures longevity, often projected to last up to 100 years, which is vital for cost-effective long-term investments.
2. Pressure Rating: Why is PSI Important?
Pressure ratings, such as 200 PSI (pounds per square inch) at 73°F, indicate the maximum pressure the pipe can handle without failure. This specification is crucial for buyers to ensure the selected poly water line can withstand operational conditions without risk of leaks or bursts. Choosing the appropriate pressure rating can significantly influence system reliability and maintenance costs.
3. Pipe Size and Dimensions: How Do They Affect Installation?
Poly water lines come in various sizes, typically measured in inches (IPS—Iron Pipe Size). Common diameters range from 3/4” to 2”, affecting flow rates and installation requirements. Selecting the right size is essential for optimizing water delivery efficiency and ensuring compatibility with existing systems.
4. SDR Rating: What Does SDR Stand For?
Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR) represents the ratio of the pipe’s diameter to its wall thickness. An SDR of 11 indicates a balance between flexibility and strength, making it suitable for various applications. Understanding SDR helps buyers gauge the pipe’s capacity to withstand external pressures, such as soil load or hydrostatic pressure.
5. UV Resistance: Why Is This Critical for Outdoor Applications?
Polyethylene pipes are often exposed to UV radiation, which can degrade lesser-quality materials. A high UV resistance rating ensures that the pipe maintains its integrity and performance over time, especially in regions with intense sunlight, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East.
6. Coiling and Length: What Are the Benefits of Coiled Pipes?
Coiled poly water lines, typically available in lengths of 500 feet, offer advantages in transportation and installation. They are easier to handle and can be joined using connectors or fusion techniques, allowing for seamless integration into extensive systems. This feature is particularly beneficial for large agricultural projects where long runs of pipe are required.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Poly Water Line Industry?
Understanding trade terminology is vital for B2B buyers to navigate contracts and negotiations effectively. Here are some common terms used in the poly water line industry:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): What Does It Imply?
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the poly water line sector, knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can impact product quality and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): How Does It Affect Purchasing?
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for businesses looking to maintain a steady supply without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation): Why Is It Necessary?
An RFQ is a standard business process wherein a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers. This process helps buyers compare offers and make informed decisions regarding costs and supplier capabilities.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): How Do They Influence Shipping?
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and logistics. Familiarity with these terms can help buyers understand shipping costs, delivery timelines, and risk management, ensuring smoother transactions across borders.
5. NSF Certification: What Does It Guarantee?
NSF (National Sanitation Foundation) certification assures that the product meets public health and safety standards. For poly water lines, NSF certification is crucial for ensuring that the materials are safe for potable water applications, which is particularly important in regions with strict health regulations.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their investments in poly water lines meet their operational needs and standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the poly water line Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Poly Water Line Sector?
The global poly water line market is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient and sustainable water management solutions. Factors such as urbanization, agricultural expansion, and the need for reliable water infrastructure are propelling the market forward. In regions like Africa and South America, where water scarcity is a pressing issue, polyethylene (PE) pipes are increasingly favored due to their durability, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion. This shift is further supported by advancements in manufacturing technologies, which are lowering costs and improving product availability.
Emerging trends in sourcing for B2B buyers include the adoption of digital platforms for procurement, allowing for more streamlined and transparent supply chains. E-commerce solutions and online marketplaces are becoming vital, enabling buyers to compare products, negotiate prices, and manage orders efficiently. Additionally, the rise of ‘smart’ water management technologies—integrating IoT and data analytics—offers opportunities for enhanced monitoring and maintenance of water distribution systems. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Saudi Arabia and Europe, the focus is also on sourcing high-quality materials that meet stringent industry standards, ensuring reliability in their water infrastructure projects.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Poly Water Line Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the poly water line sector. The environmental impact of plastic waste has prompted buyers to prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. This includes using recycled materials in the production of polyethylene pipes and implementing eco-friendly manufacturing processes. Certifications such as NSF (National Sanitation Foundation) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization) are increasingly sought after, as they provide assurance of product safety and environmental compliance.
Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining traction, with an emphasis on supply chain transparency. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and maintain responsible sourcing of raw materials. This not only mitigates reputational risks but also aligns with the values of consumers and stakeholders who are increasingly aware of corporate social responsibility. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, this shift toward sustainability and ethical sourcing can enhance brand loyalty and open doors to new market opportunities.
What Is the Historical Context of the Poly Water Line Sector?
The poly water line sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by traditional materials such as metal and concrete, the introduction of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) revolutionized the industry. Its lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties made it an ideal choice for water distribution systems, particularly in agricultural and municipal applications.
As the global demand for efficient and durable water solutions grew, so did the development of innovative manufacturing techniques and product offerings. The shift toward more sustainable materials and practices has now positioned polyethylene as a preferred option in many markets worldwide. This evolution reflects the broader trends of modernization in infrastructure and heightened awareness of environmental issues, shaping the future of the poly water line sector for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of poly water line
-
How do I choose the right poly water line for my project?
Selecting the appropriate poly water line involves considering factors such as diameter, pressure rating, and application type. For agricultural or industrial use, High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are often preferred due to their durability and resistance to corrosion. Assess your project’s specific requirements, including the length of the installation and environmental conditions. Consulting with suppliers about your needs can provide valuable insights, ensuring you select a pipe that meets regulatory standards and is suitable for your intended use. -
What is the best pressure rating for poly water lines in different applications?
The pressure rating of poly water lines, typically expressed in PSI, is crucial for ensuring safe and effective operation. For most agricultural applications, a 200 PSI rating is standard and sufficient for handling water supply. However, for high-pressure scenarios, such as in industrial settings, you may need pipes with higher ratings. Always evaluate the specific conditions of your application, including potential pressure fluctuations, to select the most appropriate rating. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for poly water lines?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, product quality, certifications, and customer service reputation. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in international trade and those who understand the regulatory requirements of your region. Request samples to evaluate product quality and inquire about their manufacturing processes to ensure compliance with safety standards. Additionally, check reviews and testimonials from other B2B buyers to gauge their reliability and service levels. -
Can I customize poly water lines to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for poly water lines, including variations in diameter, length, and pressure ratings. You can also request specific additives for UV protection or enhanced chemical resistance, depending on your application. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available customization options and any associated costs. This can help ensure the final product meets your project specifications and operational demands. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for poly water lines?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among suppliers, typically depending on the type of product and the supplier’s production capabilities. Many suppliers may have an MOQ ranging from a few hundred feet to several thousand, particularly for custom orders. When sourcing poly water lines, inquire about the MOQ upfront, as well as any discounts available for bulk purchases. This information can aid in budget planning and ensure you meet your project needs efficiently. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing poly water lines internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary, but common practices include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may also offer letters of credit or escrow services to secure transactions. Ensure you clarify payment terms, including accepted currencies and payment methods, before finalizing your order. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect your investment while allowing flexibility for large purchases. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in poly water lines?
Quality assurance (QA) measures are vital for ensuring that poly water lines meet safety and performance standards. Look for suppliers who adhere to international quality certifications, such as ISO 9001 or NSF certification, which indicates compliance with health and safety regulations. Request documentation of testing protocols, including pressure testing and material inspections. Reliable suppliers should be transparent about their QA processes and willing to provide certifications upon request. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping when sourcing poly water lines internationally?
Logistics and shipping can be complex when sourcing poly water lines internationally. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including freight costs, delivery times, and customs requirements. It’s crucial to understand the shipping terms (Incoterms) that apply to your order, as they dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and duties. Consider partnering with a freight forwarder experienced in handling international shipments to streamline the process and minimize potential delays.
Top 5 Poly Water Line Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. PowerFlex Fence – HDPE Water Pipe 200 PSI
Domain: powerflexfence.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: HDPE Water Pipe 200 PSI-Underground Polyethylene Water Coils
– Material: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
– Pressure Rating: 200 PSI @ 73 degrees Fahrenheit
– Sizes Available: 3/4 Inch, 1 Inch, 1-1/4 Inch, 1-1/2 Inch, 2 Inch
– Length: 500-foot coils
– Benefits: Durable, flexible, resistant to corrosion, UV weathering, and chemical exposure, no need for glue joints or special coatings, quick instal…
2. PlumbersStock – Polyethylene Pipe
Domain: plumbersstock.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Polyethylene Pipe available in sizes ranging from .75” to 2”. Advantages include water conservation, flexibility without breaking, and corrosion resistance. Common uses include liquid transfer and corrosion protection for steel piping.
3. Adspipe – PolyFlex Pressure Pipe
Domain: adspipe.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: PolyFlex Pressure Pipe is designed for utility and potable water service applications, including agricultural and landscape irrigation. It is available in three variations: Utility IPS, Potable IPS, and Potable Water Service Tubing CTS. Key features include: lightweight and chemically resistant composition, resistance to vibrations, surface loads, and pressure surges, flexibility for installation …
4. Southern Pipe – Polyethylene Water Service Tubing
Domain: southernpipe.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Poly Tubing Products: 1 inch CTS x 300 ft NSF SDR 9 Polyethylene Water Service Tubing (Mfg.Part #: UPEBCTS1300), 1 inch CTS x 500 ft NSF SDR 9 Polypropylene Water Service Tubing (Mfg.Part #: UPEBCTS1500), 3/4 inch x 100 ft NSF SDR 9 Polyethylene Water Service Tubing (Mfg.Part #: UPEBCTS34100), 1 inch CTS x 100 ft NSF SDR 9 Polyethylene Water Service Tubing (Mfg.Part #: UPEBCTS1100). Manufacturer: …
5. Reddit – Pipe Materials for Water Main Replacement
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Pipe Materials: PVC and Polyethylene (specifically HDPE) are discussed for water main line replacement. 2. Recommended Size: 3/4″ line is mentioned, but some suggest using 1″ CTS SDR-9 HDPE for better pressure management. 3. Length: The line will be approximately 90′ from the street to the house, with a 75′ straight shot and a 90-degree turn for the last 15′. 4. Installation Considerations: HDP…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for poly water line
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Poly Water Line Procurement?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in optimizing the procurement of poly water lines for businesses across various sectors, particularly in agriculture, construction, and municipal projects. By focusing on high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes, buyers can capitalize on their durability, resistance to corrosion, and ease of installation. These attributes not only reduce long-term operational costs but also ensure compliance with international standards, a crucial factor for B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As global demand for reliable water supply solutions continues to rise, the ability to source quality products at competitive prices becomes essential. Buyers should consider establishing relationships with multiple suppliers to leverage better pricing and availability, particularly for large orders. Furthermore, understanding local regulations and the logistics of shipping can significantly enhance the sourcing strategy.

Illustrative image related to poly water line
Looking ahead, the market for poly water lines is poised for growth, driven by increasing infrastructure investments and a shift towards sustainable solutions. International buyers are encouraged to act now, aligning their sourcing strategies with trusted suppliers to secure the best products and pricing for their projects. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your supply chain and ensure your projects run smoothly and efficiently.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.