Everything You Need to Know About Hydraulic Press Uses Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic press uses
In an increasingly competitive global landscape, sourcing the right hydraulic press can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers. With diverse applications ranging from automotive manufacturing to agricultural equipment repair, understanding the various hydraulic press uses is essential for optimizing production processes and ensuring operational efficiency. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of hydraulic presses, exploring their types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting and cost considerations.
For international buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the stakes are high. Choosing the wrong equipment can lead to costly downtimes and inefficiencies. This comprehensive resource empowers decision-makers by providing actionable insights into the hydraulic press market. By examining key factors such as performance specifications, durability, and supplier reliability, buyers can make informed choices that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
In this guide, you will gain a deeper understanding of how hydraulic presses can enhance productivity across various industries. From metal stamping to ceramic manufacturing, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of sourcing and utilizing hydraulic presses effectively. Prepare to streamline your procurement process and drive your business forward with confidence.
Understanding hydraulic press uses Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forging Press | Vertical ram applies gradual controlled pressure. | Metal forging, automotive component manufacturing. | Pros: Efficient for complex shapes; Cons: High initial investment. |
| Power Press | Versatile machine for cutting, bending, and shaping. | Sheet metal fabrication, appliance manufacturing. | Pros: Multi-functional; Cons: Requires skilled operators. |
| Hydraulic Lift | Utilizes fluid pressure for vertical movement. | Warehousing, construction, automotive repair. | Pros: Space-saving; Cons: Limited to vertical applications. |
| Car Crushing Press | Designed for compressing vehicles into smaller sizes. | End-of-life vehicle processing, recycling. | Pros: Reduces storage space; Cons: Requires significant power supply. |
| Ceramic Press | Compresses materials at room temperature. | Tile, brick, and ceramic manufacturing. | Pros: Energy-efficient; Cons: Slower production rates. |
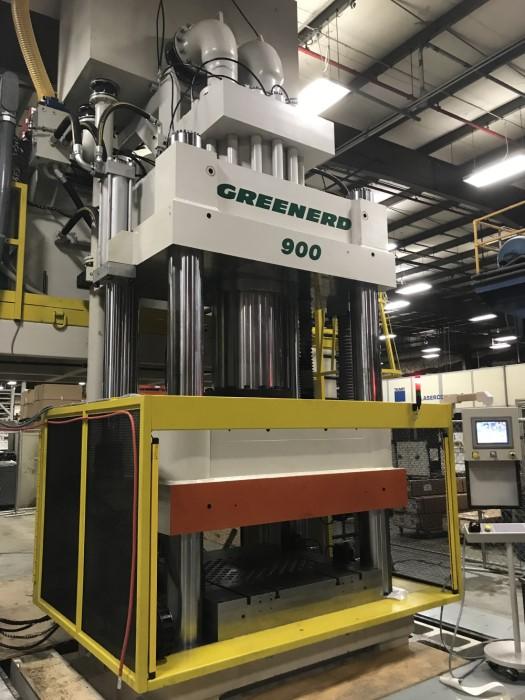
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of a Forging Press?
The forging press is characterized by its vertical ram that applies controlled pressure to a workpiece held in a die. This method is particularly effective for creating complex metal shapes with high precision, making it ideal for industries such as automotive and aerospace manufacturing. When considering a forging press, buyers should evaluate the required force capacity, die compatibility, and maintenance costs, as the initial investment can be significant.
How Does a Power Press Operate and What are Its Applications?
A power press is a versatile hydraulic machine designed to cut, bend, and shape metal sheets. It operates by using a hydraulic cylinder to generate a powerful stroke, allowing for the production of intricate parts for appliances, automotive components, and industrial machinery. Buyers should consider the machine’s stroke length, tonnage, and tooling options, as well as the availability of skilled operators to maximize its efficiency.
What Makes Hydraulic Lifts Essential for Various Industries?
Hydraulic lifts utilize hydraulic fluid to raise and lower a platform, making them essential in warehousing, construction, and automotive repair applications. Their ability to handle heavy loads and provide precise height adjustments enhances productivity and safety. When purchasing hydraulic lifts, businesses should assess load capacity, platform size, and safety features to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Why are Car Crushing Presses Important for Recycling Operations?
Car crushing presses are specifically designed to compact vehicles into smaller sizes for recycling purposes. They generate substantial force to ensure even compression, facilitating easier storage and transport of scrap metal. Buyers should evaluate the power requirements, operational efficiency, and maintenance needs of these presses, as they play a crucial role in reducing environmental impact and maximizing material recovery.
How Do Ceramic Presses Benefit Manufacturing Processes?
Ceramic presses operate at room temperature to compress materials like clay and cement into desired shapes, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to traditional kiln methods. This technique is particularly advantageous for producing tiles, bricks, and sanitary ware. When considering a ceramic press, manufacturers should focus on the machine’s pressure capacity, cycle time, and the specific materials it can process, ensuring it aligns with production goals and efficiency targets.
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic press uses
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hydraulic press uses | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Forming and assembling car parts | Increased production efficiency and consistency | Reliability of hydraulic systems, maintenance support |
| Agriculture | Repair and maintenance of agricultural machinery | Reduced downtime and enhanced equipment longevity | Availability of spare parts, service network |
| Construction | Testing concrete tensile strength | Improved quality assurance and material optimization | Compliance with local standards, supplier certifications |
| Metal Fabrication | Metal stamping and shaping | Enhanced precision and reduced material waste | Tooling compatibility, customization options |
| Ceramics Production | Forming ceramic products without traditional kilns | Faster production cycles and lower energy costs | Equipment adaptability, raw material sourcing |
How is Hydraulic Press Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, hydraulic presses are integral for forming and assembling various car parts, such as body panels and brake components. These machines provide consistent pressure, ensuring that parts are shaped accurately and efficiently, which is crucial for meeting safety and quality standards. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing reliable hydraulic presses that can handle the specific demands of automotive manufacturing is vital. Additionally, considering the availability of local maintenance and spare parts can significantly reduce operational downtime.
What Role Does Hydraulic Press Play in Agriculture?
Agricultural machinery often requires regular maintenance and repair, where hydraulic presses prove invaluable. They are used for tasks such as straightening bent parts and pressing out bearings, which are essential for keeping equipment operational. By investing in a hydraulic press, farmers can minimize equipment downtime, thereby enhancing productivity. For B2B buyers in developing regions, it’s important to assess the availability of service support and spare parts to ensure that their investment remains functional over time.
How is Hydraulic Press Essential for Concrete Testing in Construction?
In construction, hydraulic presses are employed to test the tensile strength of concrete, providing critical data that helps in formulating stronger and more durable materials. This process is vital for ensuring that construction projects meet safety regulations and performance standards. For international buyers, understanding local compliance requirements and sourcing presses that can deliver precise testing results is essential. Additionally, selecting suppliers who can provide technical support and calibration services can further enhance the reliability of the testing process.
Why is Hydraulic Press Important in Metal Fabrication?
Hydraulic presses are widely used in metal fabrication for stamping and shaping metal sheets into specific designs. This process not only enhances precision but also reduces material waste, which is crucial for cost management. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing hydraulic presses that offer customizable tooling options can provide a competitive edge. It’s also essential to consider the supplier’s ability to provide ongoing support and maintenance to ensure operational efficiency.
How Does Hydraulic Press Benefit Ceramics Production?
In the ceramics industry, hydraulic presses are utilized to form products at room temperature, significantly reducing energy costs associated with traditional kiln firing. This method allows for faster production cycles and improved material quality. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, evaluating the adaptability of hydraulic presses to local raw materials and production methods is critical. Additionally, ensuring that suppliers can provide comprehensive training and support can optimize the production process and enhance product quality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘hydraulic press uses’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Consistent Quality in Manufacturing with Hydraulic Presses
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the manufacturing sector face the challenge of ensuring consistent quality in the components produced using hydraulic presses. Variability in pressure, temperature, or material can lead to defects such as incomplete forming or structural weaknesses, resulting in high rejection rates and costly rework. This issue is particularly pronounced in sectors like automotive and appliance manufacturing, where precision is critical for safety and performance.
The Solution: To overcome quality inconsistency, buyers should invest in hydraulic presses equipped with advanced monitoring systems. These systems can track parameters such as pressure levels, stroke length, and material temperatures in real-time. Buyers should also establish rigorous quality control protocols, including regular calibration and maintenance schedules for their equipment. Partnering with reliable suppliers who provide equipment with built-in diagnostic features will help ensure that machinery operates within specified tolerances. Additionally, conducting routine training for operators on the importance of these parameters can significantly reduce variability and enhance product quality.
Scenario 2: Reducing Downtime During Hydraulic Press Maintenance
The Problem: Hydraulic press downtime due to maintenance issues can be a significant pain point for manufacturers, leading to lost production time and financial losses. Components may wear out unexpectedly, and the complexity of hydraulic systems often results in lengthy repairs. This unpredictability affects not only production schedules but also supplier relationships and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To mitigate downtime, businesses should implement a proactive maintenance strategy that includes predictive maintenance techniques. Utilizing sensors and IoT technology can enable real-time monitoring of hydraulic press components, allowing for early detection of potential failures. Buyers should also establish partnerships with service providers who offer comprehensive maintenance plans, including regular inspections and rapid-response services for urgent repairs. Additionally, keeping a well-stocked inventory of critical spare parts can significantly reduce the time taken to resume operations after a breakdown, ensuring that production lines remain functional and efficient.
Scenario 3: Addressing Safety Risks Associated with Hydraulic Presses
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern when operating hydraulic presses, as improper use can lead to severe injuries or accidents in the workplace. Many B2B buyers struggle with ensuring that operators adhere to safety protocols, which can vary based on the complexity of the machinery and the specific tasks being performed. This challenge is often exacerbated by a lack of training or insufficient safety equipment.
The Solution: To enhance safety in hydraulic press operations, businesses should develop comprehensive training programs for all operators that emphasize the importance of following safety protocols. Training should cover proper operational procedures, emergency shutdown processes, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Moreover, integrating machine guards and automated safety features—such as emergency stop buttons and pressure relief valves—can significantly reduce the risk of accidents. Regular safety audits and drills can reinforce the safety culture within the organization, ensuring that all staff members remain vigilant and informed about best practices in hydraulic press usage. By fostering a culture of safety and accountability, businesses can mitigate risks and create a safer working environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic press uses
What Are the Key Materials Used in Hydraulic Press Applications?
When selecting materials for hydraulic press applications, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This ensures optimal performance and longevity in various industrial contexts. Here, we analyze four common materials used in hydraulic presses: steel, aluminum, composite materials, and rubber.
How Does Steel Perform in Hydraulic Press Applications?
Steel is the most widely used material for hydraulic press components due to its high strength and durability. Key properties include excellent tensile strength, high-temperature resistance, and good wear resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel can withstand significant pressure, making it ideal for pressing operations involving metal shaping and forming.
Pros: Steel’s durability ensures a long lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements. It also offers good machinability, allowing for complex designs.
Cons: The primary drawback is its weight, which can complicate handling and installation. Additionally, steel is susceptible to corrosion unless treated, which could impact its longevity in humid or corrosive environments.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is crucial. Buyers should also consider local availability and transportation costs.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Hydraulic Press Uses?
Aluminum is increasingly used in hydraulic press applications due to its lightweight nature and good corrosion resistance. Key properties include a lower density compared to steel, which facilitates easier handling and transportation. Aluminum also has a decent strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for applications where weight savings are critical.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier installation and reduced energy consumption during operation. Its corrosion resistance makes it ideal for environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Cons: Aluminum has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-pressure applications. It also tends to be more expensive, impacting overall project costs.
For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 or EN AW-6060 is essential. Understanding local market preferences for aluminum grades can also influence purchasing decisions.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Hydraulic Press Performance?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastics, are gaining traction in hydraulic press applications due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Key properties include high tensile strength and low thermal expansion, which can enhance performance in temperature-variable environments.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, providing design flexibility. They also exhibit excellent resistance to chemicals and moisture, making them suitable for various applications.
Cons: The primary limitation is the higher manufacturing complexity and cost. Additionally, composites may not perform well under extreme temperatures compared to metals.
International buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties and ASTM D790 for flexural properties. Understanding local regulations regarding composite materials is also crucial.
What Role Does Rubber Play in Hydraulic Press Applications?
Rubber is often used in hydraulic presses for seals and gaskets due to its excellent elasticity and ability to withstand hydraulic fluids. Key properties include high resistance to wear and good compressibility, which help maintain effective sealing under pressure.
Pros: Rubber’s flexibility allows it to conform to various shapes, ensuring a tight seal that prevents fluid leakage. It is also cost-effective and readily available.
Cons: Rubber has limitations in high-temperature applications and can degrade over time when exposed to certain chemicals. This can lead to increased maintenance costs.
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Brazil and Nigeria, compliance with standards such as ASTM D2000 for rubber materials is important. Local sourcing of rubber components can also affect lead times and costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Hydraulic Press Uses
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic press uses | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Metal forming, heavy-duty applications | High strength and durability | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight components, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength and higher cost | High |
| Composite | Custom shapes, chemical resistance | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity and cost | Medium to High |
| Rubber | Seals and gaskets in hydraulic systems | Flexibility and cost-effective | Limited high-temperature resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on specific application needs and regional considerations.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic press uses
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic press uses
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Hydraulic Press Components?
The manufacturing of hydraulic presses involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets performance and quality standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Hydraulic Press Manufacturing?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials, typically steel or aluminum, which are essential for durability and strength. Suppliers must ensure that materials comply with international standards, such as ISO 9001, to guarantee consistency. This stage often involves cutting, machining, and treating the materials to remove impurities and enhance properties like tensile strength and ductility.
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo inspection to confirm they meet specified criteria, such as hardness and thickness. Quality Control (QC) measures during this stage, known as Incoming Quality Control (IQC), help detect any issues before the manufacturing process continues.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Process of Hydraulic Presses?
The forming process is where the actual shaping of components occurs. Techniques such as metal stamping, die casting, and forging are commonly employed, depending on the complexity and design of the parts.
Metal stamping is a prevalent method for creating parts like plates and brackets, utilizing hydraulic presses to apply significant force to shape the metal accurately. Forging presses apply controlled pressure to produce parts with enhanced structural integrity. During this phase, In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) is crucial; operators routinely check dimensions and tolerances to ensure parts are within specifications.
How Does the Assembly of Hydraulic Presses Take Place?
Assembly involves integrating various components, such as pumps, cylinders, and control systems, into a cohesive unit. This stage often requires precision and attention to detail, as the performance of the hydraulic press relies on the proper functioning of each part.
During assembly, manufacturers may implement automated systems alongside manual labor to optimize efficiency and accuracy. Final assembly is followed by Functional Quality Control (FQC), where the assembled hydraulic press is tested under operational conditions to ensure it meets performance benchmarks.
What Are the Finishing Processes for Hydraulic Press Components?
Finishing processes enhance both the aesthetic and functional aspects of hydraulic presses. Techniques like painting, coating, or anodizing are employed to protect components from corrosion and wear.
Additionally, surface treatment methods such as shot peening or grinding improve the mechanical properties of parts. Before the final product is delivered, a comprehensive inspection ensures that all finishing aspects comply with industry standards and client specifications.
Which International Standards and Quality Assurance Practices Are Relevant?
For B2B buyers, understanding the quality assurance frameworks in hydraulic press manufacturing is paramount. International standards like ISO 9001 provide a framework for establishing effective quality management systems.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic press uses
Specific certifications, such as CE marking for compliance with European safety standards or API specifications for the oil and gas industry, may also be relevant depending on the application of the hydraulic press.
What QC Checkpoints Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality control in hydraulic press manufacturing involves multiple checkpoints to maintain high standards:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Routine checks during the manufacturing process to ensure that components meet dimensional and performance criteria.
-
Functional Quality Control (FQC): Final testing of the assembled hydraulic press to verify it operates correctly under load.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality control measures of suppliers. Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess compliance with international standards and the implementation of QC practices.
Requesting quality assurance reports, certification documents, and third-party inspection results can provide additional assurance regarding a supplier’s commitment to quality. Engaging third-party inspection agencies to conduct independent evaluations can further validate a supplier’s capabilities.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, understanding local regulations and certifications is crucial. Different countries may have specific compliance requirements that could affect the importation and use of hydraulic presses.
Buyers should be aware of the implications of certifications such as ISO and CE in their respective markets. Additionally, establishing clear communication with suppliers regarding these standards can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that the products meet local regulatory requirements.
Conclusion: The Importance of Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance in Hydraulic Presses
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for hydraulic presses are integral to ensuring that the products meet industry standards and customer expectations. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing hydraulic presses, ensuring they choose suppliers who adhere to stringent quality control measures. This diligence not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters long-term partnerships built on trust and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘hydraulic press uses’
In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing and production, hydraulic presses serve as indispensable tools across various industries. This guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe in effectively sourcing hydraulic presses tailored to their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. Determine the type of hydraulic press that fits your application—be it forging, power presses, or specialized models for specific tasks like metal stamping or car part manufacturing. Knowing the force requirements, size constraints, and material compatibility will streamline the selection process.
Step 2: Research Industry Applications
Understanding the different uses of hydraulic presses can inform your purchasing decision. Identify which industries align with your needs—automotive, agriculture, or manufacturing—and consider how hydraulic presses are utilized within those sectors. This knowledge will help you choose a press that meets your operational demands effectively.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering hydraulic presses and who can demonstrate expertise in your specific application.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure that suppliers possess relevant certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to quality and safety protocols.
- Assess After-Sales Support: Inquire about warranty options and technical support availability post-purchase, as this can significantly impact your long-term satisfaction.
Step 4: Examine Product Quality and Reliability
Quality is paramount when selecting a hydraulic press. Look for suppliers who provide detailed specifications and materials used in their presses.
- Request Samples or Demonstrations: If possible, see the equipment in action or obtain samples to evaluate performance and reliability.
- Understand Maintenance Requirements: Ensure you are aware of the maintenance protocols to keep the press functioning optimally.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
While it may be tempting to go for the lowest price, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
- Obtain Detailed Quotations: Ensure that all costs, including delivery and installation, are included in the quotes you receive.
- Evaluate Financing Options: Some suppliers may offer financing plans that can ease the burden of upfront costs.
Step 6: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Assess potential risks associated with the procurement process. This includes evaluating the financial stability of the supplier, delivery timelines, and any geopolitical factors that may affect international transactions.
- Review Contract Terms: Before finalizing, ensure that contract terms are clear regarding delivery, warranties, and liabilities.
- Consider Insurance Options: Look into insurance for your equipment during shipping and installation, safeguarding your investment.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Plan for Integration
Once you’ve selected a supplier, finalize your purchase and develop a plan for integrating the hydraulic press into your operations.
- Coordinate with Your Team: Ensure that your team is trained on the new equipment and understands its operational requirements.
- Schedule Installation and Testing: Plan for a thorough installation process followed by testing to confirm that the press operates as expected.
By following these steps, you can make an informed decision when sourcing hydraulic presses, ensuring that your investment supports your operational goals effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic press uses Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Hydraulic Presses?
When sourcing hydraulic presses, several cost components come into play that significantly influence the overall pricing structure. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the cost. High-grade steel, hydraulic fluids, and specialized components can elevate expenses. For example, presses made with advanced alloys may offer better durability but at a higher price point.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both manufacturing and assembly. Labor costs vary significantly across regions, with countries in Africa or South America often having lower wage rates compared to Europe. This variance can affect the total cost and may lead buyers to consider outsourcing production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, but these efficiencies may require initial investment in technology.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific press designs can be a significant expense. Buyers should factor in these costs, especially if they require unique specifications or adaptations for their operations.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the hydraulic presses meet industry standards. While this adds to the cost, it is crucial for minimizing failures and ensuring safety, especially in high-stakes environments like automotive manufacturing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary widely based on the location of the supplier and the delivery terms. International buyers must consider shipping fees, import duties, and potential delays.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin that reflects their operational costs and profit expectations. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide leverage during negotiations.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Hydraulic Press Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of hydraulic presses, making it essential for buyers to understand these elements:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can impact pricing; larger orders often lead to discounts. Buyers should evaluate their needs carefully to optimize order sizes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized hydraulic presses tend to be more expensive due to the additional engineering and manufacturing processes involved. Buyers should balance the need for customization with their budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can increase costs but also enhance the reliability and performance of the hydraulic press.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence price. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to proven quality and service levels.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterm can significantly impact the total cost of ownership, as it dictates the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics. Understanding these terms is crucial for international transactions.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Hydraulic Press Sourcing?
B2B buyers can implement several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing hydraulic presses:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing. Understanding their cost structure may reveal areas where concessions can be made, particularly on bulk orders.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. This holistic view can lead to better long-term investments.
-
Consider Regional Differences: When sourcing from different regions, be aware of local economic conditions, labor costs, and material availability. For instance, sourcing from local suppliers in Brazil or Nigeria may reduce shipping costs and lead times.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about industry trends and economic conditions that may affect pricing. For example, fluctuations in material costs or changes in trade policies can impact overall pricing strategies.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service over time. Loyalty can often translate into preferential treatment in terms of pricing and availability.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for hydraulic presses can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they receive competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.

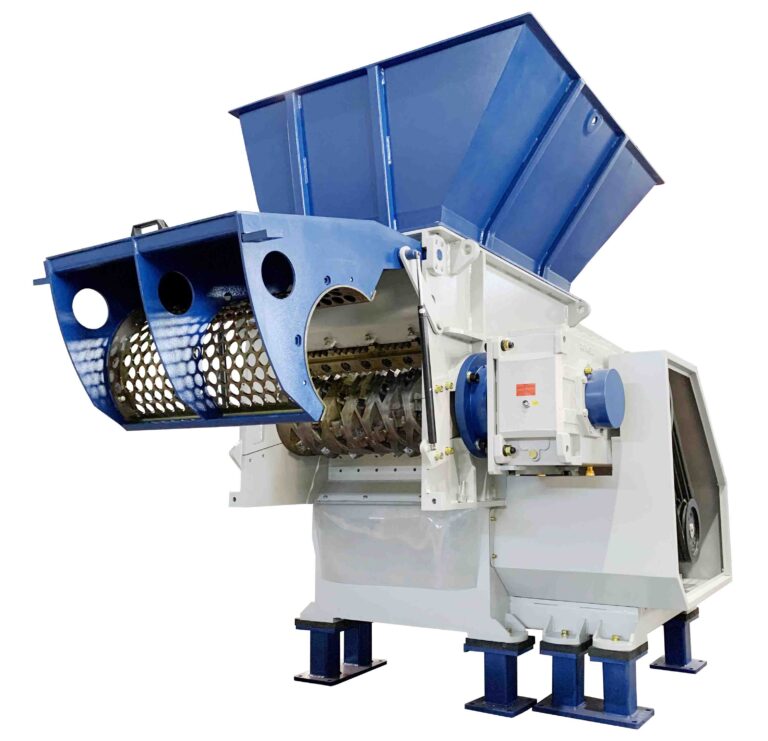
Illustrative image related to hydraulic press uses
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing hydraulic press uses With Other Solutions
Understanding the Importance of Alternatives in Hydraulic Press Applications
In the industrial landscape, hydraulic presses are widely recognized for their versatility and efficiency in shaping and manipulating materials. However, there are alternative solutions that can also fulfill similar functions, offering varying benefits based on specific operational needs. This analysis compares hydraulic press uses against other viable technologies, providing B2B buyers with insights into the best options for their applications.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Hydraulic Press Uses | Mechanical Presses | Pneumatic Presses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High force application with precision | Excellent for high-speed operations | Moderate force; best for lighter tasks |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, high ROI | Generally lower initial cost | Lower initial cost, but higher operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires hydraulic system setup | Easier setup; often plug-and-play | Simple installation, but requires air supply |
| Maintenance | Requires regular hydraulic fluid checks | Low maintenance; fewer components | Regular air compressor maintenance needed |
| Best Use Case | Metal forming, automotive parts, ceramics | Mass production, high-speed stamping | Lightweight assembly, packaging, textiles |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are Mechanical Presses and When Are They Most Effective?
Mechanical presses operate using a mechanical advantage to generate high-speed stamping and shaping actions. They excel in mass production environments, where speed and efficiency are paramount. With a generally lower initial investment compared to hydraulic presses, mechanical presses can be more cost-effective for high-volume production lines. However, their performance may not match the precision of hydraulic presses when dealing with complex shapes or materials requiring gradual pressure application. They are best suited for applications such as metal stamping and part manufacturing in industries like automotive and appliance production.
How Do Pneumatic Presses Compare in Performance and Cost?
Pneumatic presses utilize compressed air to exert force, making them an appealing option for lighter tasks and applications where speed is essential. These presses are often less expensive to install and operate than hydraulic systems. However, they typically offer lower force output, making them unsuitable for heavy-duty applications. The ongoing operational costs associated with air supply can add up, particularly in environments where air leaks are common. Pneumatic presses are ideal for tasks such as assembly, packaging, and textile applications, where precision is less critical than speed.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the right solution requires a thorough assessment of specific operational needs, including the types of materials processed, production volume, and budget constraints. Hydraulic presses are ideal for high-force applications needing precision, while mechanical presses offer speed for mass production scenarios. Pneumatic presses serve well in lightweight applications with lower force requirements. By evaluating these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational objectives, ensuring they invest in the most appropriate technology for their business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic press uses
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Hydraulic Presses?
Understanding the essential technical properties of hydraulic presses is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating equipment for manufacturing or production processes. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Force Capacity (Tonnage)
The force capacity, often measured in tons, indicates the maximum load a hydraulic press can handle. This specification is vital for determining whether a press is suitable for specific applications, such as forming metal sheets or crushing components. Buyers should assess their production needs to select a press with adequate tonnage to ensure efficiency and safety. -
Stroke Length
Stroke length refers to the distance the ram travels downwards during operation. This property is significant because it affects the depth of the workpiece that can be processed. A longer stroke length can accommodate larger items or more complex operations, making it essential for buyers in industries like automotive and aerospace, where varying part sizes are common. -
Operating Pressure
Operating pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates the pressure at which the hydraulic system functions optimally. It is essential for the effectiveness of the press, as higher pressures can lead to faster processing times and the ability to work with denser materials. Understanding operating pressure helps buyers match the press to their material requirements. -
Material Grade
The material grade of the hydraulic press’s construction affects its durability and resistance to wear and tear. Common materials include steel and cast iron, which provide strength and stability. Buyers should consider the operating environment and the types of materials being processed when selecting a press with the appropriate material grade to ensure longevity and reliability. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension during the manufacturing process. In hydraulic presses, tight tolerances are crucial for precision applications such as die stamping and metal forming. Understanding tolerance requirements can help buyers ensure that the hydraulic press will meet their production standards without excessive rework or waste.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Hydraulic Presses?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in B2B transactions. Here are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of hydraulic presses, buyers often seek OEM components for reliability and compatibility. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing quality parts for their operations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it can affect purchasing decisions, especially for smaller companies. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better terms or plan their inventory management more effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. This process is essential for buyers looking to compare prices and terms from different vendors. A well-crafted RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms in the procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and freight. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions, especially when importing or exporting hydraulic presses. Knowledge of Incoterms can help buyers clarify shipping costs, delivery responsibilities, and risk management. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This term is particularly important for buyers who rely on hydraulic presses for production schedules. Understanding lead times can help businesses plan their operations and avoid delays in their supply chain. -
Hydraulic Fluid Type
The type of hydraulic fluid used in a press affects its performance, efficiency, and maintenance requirements. Various fluids may have different properties, such as viscosity and temperature tolerance. Buyers should be aware of the hydraulic fluid requirements for their presses to ensure optimal operation and longevity.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding hydraulic presses, optimizing their procurement processes and enhancing operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the hydraulic press uses Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting Hydraulic Press Uses?
The hydraulic press market is experiencing notable growth due to increasing industrial applications across various sectors such as automotive, agriculture, and manufacturing. The drive for automation and precision in production processes is propelling demand for advanced hydraulic systems that offer efficiency and reliability. In regions like Africa and South America, where industries are evolving rapidly, international B2B buyers are looking for hydraulic presses that can handle diverse applications—from metal stamping to concrete testing.
Emerging technologies, such as Industry 4.0, are enhancing the capabilities of hydraulic presses with smart automation and predictive maintenance features. These innovations not only improve operational efficiency but also reduce downtime, a critical factor for manufacturers aiming to optimize production. Additionally, the rise of electric and hybrid hydraulic systems is reshaping sourcing strategies, as businesses prioritize energy-efficient solutions to mitigate operational costs.
In the Middle East and Europe, stringent regulations regarding emissions and environmental impact are influencing the design and sourcing of hydraulic presses. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with these regulations, thus driving a trend toward more sustainable manufacturing practices. As international buyers navigate these market dynamics, understanding local industry needs and regulatory frameworks is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Hydraulic Press Uses?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone in the sourcing strategies of hydraulic press buyers. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt eco-friendly practices. This includes utilizing hydraulic presses that minimize waste and energy consumption during production.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, especially for international buyers who are increasingly concerned about the origin of their equipment and materials. Sourcing from suppliers who prioritize ethical labor practices and sustainable materials can enhance a company’s reputation and compliance with global standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are crucial indicators that buyers should look for when vetting suppliers.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials—such as recycled metals or biodegradable lubricants—can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with hydraulic press operations. By prioritizing sustainable sourcing, businesses not only meet regulatory requirements but also align with consumer expectations for environmentally responsible practices, ultimately leading to a competitive advantage in the market.
What Is the Historical Context of Hydraulic Press Technology in B2B Applications?
The hydraulic press has a rich history that dates back to the 18th century, initially used for applications such as wine pressing. Over time, advancements in hydraulic technology have transformed the press into a versatile tool essential across numerous industries. The industrial revolution marked a significant turning point, as hydraulic presses became pivotal in metalworking, enabling mass production and greater precision in forming metal parts.
As industries evolved, so did the design and functionality of hydraulic presses, leading to innovations such as programmable controls and enhanced safety features. Today, hydraulic presses are integral to various manufacturing processes, from automotive part production to the creation of consumer goods. Their evolution reflects the broader trends in manufacturing technology, emphasizing efficiency, sustainability, and automation—key considerations for modern B2B buyers navigating the hydraulic press market.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic press uses
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic press uses
-
How do I choose the right hydraulic press for my manufacturing needs?
Choosing the right hydraulic press involves assessing your specific manufacturing requirements, including the type of materials you’ll be working with, the size of the components, and the desired output. Consider factors such as the press’s tonnage, stroke length, and speed of operation. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s versatility for future applications and its compatibility with existing equipment. Engaging with suppliers for demos or technical specifications can provide further clarity on which model best suits your production line. -
What are the primary applications of hydraulic presses in various industries?
Hydraulic presses are widely used across multiple sectors, including automotive for shaping and assembling parts, agriculture for equipment repair, and the manufacturing of appliances like washing machines and microwaves. Other notable applications include metal stamping, powder production in food and cosmetics, and even in construction for concrete testing. Understanding these applications can help you identify the most suitable press for your operational needs. -
What customization options are available when sourcing hydraulic presses?
Customization options for hydraulic presses can vary significantly between manufacturers. Common modifications include adjustments to tonnage capacity, stroke length, and control systems. Some suppliers may also offer tailored features such as specific die configurations or software for automation. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their capabilities for customization to ensure the press meets your unique production requirements. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect when purchasing hydraulic presses?
Minimum order quantities can vary by supplier and the complexity of the hydraulic press. Typically, larger manufacturers may require higher MOQs, especially for customized machines, while smaller suppliers might accommodate smaller orders. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your production schedule and budget. -
How can I vet suppliers when sourcing hydraulic presses internationally?
When sourcing hydraulic presses from international suppliers, it’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence. Verify the supplier’s credentials, including certifications and industry experience. Request references from previous clients and check online reviews. Additionally, consider visiting their facility if possible or engaging third-party inspection services to ensure quality and compliance with international standards before placing an order. -
What payment terms are typically offered for hydraulic press purchases?
Payment terms for hydraulic press purchases can vary widely depending on the supplier and the order size. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance due upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that provide security for both parties, especially when dealing with international transactions. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and provide protection against fraud. -
What quality assurance processes should I expect from hydraulic press manufacturers?
Reputable hydraulic press manufacturers typically implement stringent quality assurance processes. These may include material inspections, in-process quality checks, and final testing before shipment. Request detailed information on the manufacturer’s quality control measures, including certifications like ISO 9001. Understanding their QA processes can provide assurance of the equipment’s reliability and performance. -
How do logistics and shipping work for international hydraulic press orders?
Logistics for international orders of hydraulic presses involve several key steps, including customs clearance, freight forwarding, and delivery coordination. It’s important to work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to navigate regulations and tariffs effectively. Discuss shipping methods, estimated delivery times, and who will bear the shipping costs upfront. Ensuring a clear logistics plan can help mitigate delays and unexpected costs during the import process.
Top 5 Hydraulic Press Uses Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Hydraulic Press – Versatile Shaping Tool
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: A hydraulic press is used for shaping sheet metal into objects like kitchen sinks and car body panels, reshaping cars and garbage in car crushers and trash compactors, punching holes out of thick materials, and squeezing metal through a die to shape it. It can also be used to determine the strength of materials by crushing samples.
2. IQS Directory – Hydraulic Press
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Press: A mechanical apparatus that uses static pressure of a liquid to form, reshape, and alter materials like metals, plastics, rubber, and wood. Key components include the mainframe, power system, and control mechanisms. Operates by forcing hydraulic fluid into a double-acting piston, relying on Pascal’s Law to multiply force. Typical components include: Main Cylinder (Ram), Plunger, P…
3. Carolina Hose and Hydraulics – Hydraulic Presses
Domain: carolinahoseandhydraulics.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic presses are used in various industries including agriculture for repairing equipment, car part manufacturing for making and assembling parts, appliance manufacturing for shaping and assembling parts, car crushing for compressing vehicles, sword making for blacksmithing, powder making in food and cosmetics, concrete testing for assessing tensile strength, and ceramic making for producing …
4. XRF Scientific – Hydraulic Presses
Domain: xrfscientific.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: XRF Scientific supplies a range of manual, power, motorized and automatic hydraulic presses for XRF sample preparation. The Power Hydraulic Press operates in ranges between 8 and 25 tons. It is microprocessor controlled and loadable in metric and imperial tons for XRF and IR sample preparations.
5. Specac – Laboratory Hydraulic Presses
Domain: specac.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Laboratory hydraulic presses are machines that use fluid pressure to generate force for compressing or molding materials. They are smaller than industrial hydraulic presses, offering precision and control, and are commonly used for testing material strength and durability, creating pellets for FTIR and XRF spectroscopy, and powder compaction for composite materials. Key applications include making…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic press uses
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Hydraulic Press Procurement?
In conclusion, the diverse applications of hydraulic presses across industries—from automotive manufacturing to agriculture—underscore their essential role in modern production processes. For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, strategic sourcing of hydraulic presses can lead to significant cost savings, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced product quality. By partnering with reputable suppliers, businesses can ensure access to cutting-edge technology and reliable service.
Moreover, investing in high-quality hydraulic presses can enhance your production capabilities, enabling you to meet increasing market demands while maintaining competitive pricing. As industries evolve and the global market becomes more interconnected, it is crucial for buyers to stay ahead of technological advancements and supplier innovations.
Looking ahead, the potential for growth in hydraulic press applications is vast. Companies are encouraged to explore opportunities for collaboration and investment in this essential machinery. Embrace the future of manufacturing by prioritizing strategic sourcing—your business’s success depends on it. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure the hydraulic press solutions that will drive your operations forward.

Illustrative image related to hydraulic press uses
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.