Types Of Power Cords For Electronics Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of power cords for electronics
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing the right types of power cords for electronics presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The diverse range of power cord specifications, compliance standards, and regional electrical requirements can complicate purchasing decisions, particularly for businesses operating across multiple markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the complexities of power cord procurement by detailing the various types of power cords available, their specific applications, and the importance of adhering to local regulations.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the essential characteristics of AC and DC power cords, NEMA connectors, and specialized options like hospital-grade cords and surge protectors. Additionally, we will provide insights into effective supplier vetting processes, enabling you to assess quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. By equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the power cord landscape, this resource empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business needs and compliance requirements.
Whether you are looking to upgrade existing infrastructure, replace damaged cords, or expand your product offerings, understanding the nuances of power cord types will enhance your procurement strategy. With the right information at your fingertips, you can confidently source the best solutions for your electronic devices, ensuring seamless operations in a global marketplace.
Understanding types of power cords for electronics Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC Power Cord | Delivers alternating current; typically detachable | Computers, monitors, printers | Pros: Widely used, versatile; Cons: May require adapters for compatibility. |
| DC Power Cord | Supplies direct current; often used for low-voltage applications | Electronics, power tools, automotive devices | Pros: Efficient for specific devices; Cons: Limited to certain applications. |
| NEMA Connectors | Standardized connectors for AC power; various configurations | Industrial equipment, appliances | Pros: Reliable connections; Cons: Compatibility issues across regions. |
| IEC Power Cords | Internationally recognized standard; used for appliances | Medical devices, servers, audio equipment | Pros: Universally compatible; Cons: May be more expensive than local alternatives. |
| USB Power Cables | Supports data transfer and power; various types (A, B, C) | Mobile devices, peripherals | Pros: Multifunctional; Cons: Not suitable for high-power applications. |
What are AC Power Cords and Their Key Characteristics?
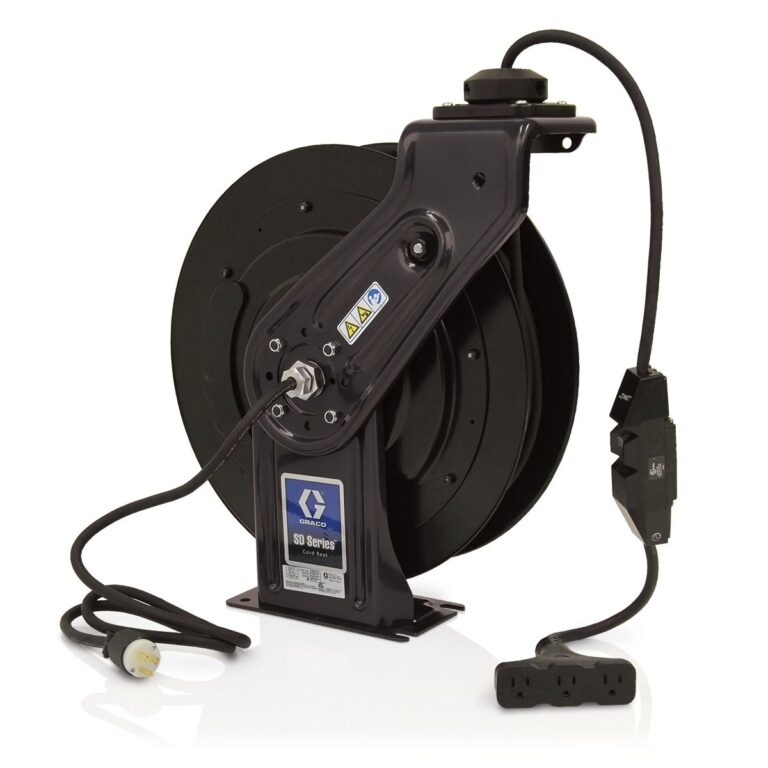
AC power cords are essential for delivering alternating current from a mains power supply to various electronic devices. These cords are commonly detachable, allowing for easy replacement or upgrades. They are predominantly used in office equipment, computers, and home appliances. When considering AC power cords for procurement, businesses should evaluate the length, gauge, and connector types to ensure compatibility with their devices. Additionally, buyers should be mindful of regional voltage standards to avoid electrical issues.
How Do DC Power Cords Differ in Usage?
DC power cords are designed to supply direct current, making them ideal for low-voltage applications such as electronics and automotive devices. These cords are often found in power tools and battery-operated devices. When purchasing DC power cords, businesses should consider the voltage requirements of their equipment and ensure that the cord is rated appropriately. This type of power cord is essential for efficient operation in specific applications but may not be suitable for all electronic devices.
What Are NEMA Connectors and Their Applications?
NEMA connectors are standardized connectors used primarily for AC power applications, offering various configurations to accommodate different power requirements. Commonly found in industrial equipment and appliances, these connectors provide reliable connections that ensure safety and performance. When sourcing NEMA connectors, businesses should assess compatibility with their existing infrastructure and consider the operational environment, as some connectors are designed for harsher conditions.
Why Choose IEC Power Cords for International Use?
IEC power cords are recognized globally and are commonly used in medical devices, servers, and audio equipment. Their international compatibility makes them an excellent choice for businesses operating in multiple regions. When purchasing IEC power cords, companies should consider the specific IEC standard needed for their devices, as there are several variations. While these cords may be more expensive, their reliability and versatility can justify the investment.
How Do USB Power Cables Enhance Connectivity?
USB power cables serve a dual purpose: they provide power and facilitate data transfer between devices. With various types available, including USB-A, USB-B, and USB-C, these cables are extensively used for mobile devices and peripherals. Businesses should evaluate the specific USB type required for their applications, as not all cables support the same power levels. While USB cables are multifunctional and widely available, they may not be suitable for high-power devices, limiting their use in certain industrial applications.
Key Industrial Applications of types of power cords for electronics
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of power cords for electronics | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Hospital-grade power cords for medical devices | Ensures safety and reliability in critical care | Compliance with medical standards, durability, length |
| Manufacturing | Power cords for industrial machinery | Supports continuous operation and reduces downtime | Voltage ratings, environmental resistance, cord length |
| Information Technology | Power cords for servers and networking equipment | Enhances data integrity and system uptime | Compatibility with equipment, certifications, length |
| Telecommunications | Power supplies for communication devices | Facilitates uninterrupted service and connectivity | Power specifications, connector types, geographic standards |
| Consumer Electronics | Power adapters for mobile devices and laptops | Provides versatility and convenience for users | Universal compatibility, safety certifications, length |
How Are Power Cords Used in the Healthcare Sector?
In healthcare settings, hospital-grade power cords are vital for connecting medical devices such as patient monitors, imaging equipment, and surgical tools. These cords must meet stringent safety and reliability standards to ensure they function correctly during critical procedures. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing power cords that comply with local healthcare regulations and international safety standards is crucial to maintaining patient safety and operational efficiency.
What Role Do Power Cords Play in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, robust power cords are essential for powering industrial machinery, including assembly lines and robotic systems. These cords must withstand harsh environments, including exposure to oils, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, ensuring continuous operation and minimizing downtime. Buyers from South America and Europe should prioritize sourcing cords that meet specific voltage ratings and environmental resistance standards to ensure optimal performance in their facilities.
Why Are Power Cords Critical for Information Technology?
Power cords are integral to IT infrastructure, connecting servers, workstations, and networking devices. Reliable power supply is crucial for maintaining data integrity and ensuring system uptime. International buyers, especially in Europe and Africa, must consider compatibility with various equipment and adhere to local electrical standards when sourcing these cords. Additionally, certifications for safety and efficiency can significantly impact operational reliability.
How Do Telecommunications Benefit from Power Supplies?
In the telecommunications industry, power supplies for communication devices, such as routers and base stations, are essential for ensuring uninterrupted service. These systems require consistent power to maintain connectivity across networks. Buyers in the Middle East and South America should focus on sourcing power cords that meet specific power specifications and connector types to align with their existing infrastructure and geographic standards.
What Advantages Do Power Adapters Offer for Consumer Electronics?
Power adapters for mobile devices and laptops provide essential versatility, allowing users to charge their devices across various settings. These adapters must be universally compatible to cater to diverse customer needs. For B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and Vietnam, sourcing power adapters that are certified for safety and efficiency is crucial to enhance user experience and ensure product reliability.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of power cords for electronics’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Incompatibility with International Standards
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing power cords that comply with various international standards. This issue is particularly prevalent for companies operating in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where electrical specifications differ significantly from those in Europe or North America. For instance, a buyer may order a bulk shipment of AC power cords that turn out to be incompatible with local outlets or voltage requirements, leading to costly delays and equipment failures.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should conduct thorough research on local electrical standards before sourcing power cords. Collaborating with suppliers who are knowledgeable about regional compliance can ensure that the power cords meet necessary specifications. It’s advisable to request samples or detailed product specifications that include voltage ratings, current capacities, and connector types. Additionally, leveraging certification markings (such as CE or UL) can help verify compliance with safety and performance standards. Establishing relationships with reputable manufacturers who specialize in international power solutions can streamline the sourcing process and minimize compatibility issues.
Scenario 2: Short Cable Lengths Affecting Equipment Setup
The Problem: A frequent pain point for B2B buyers is the inadequacy of power cord lengths for their specific setups. In environments such as factories, data centers, or hospitals, where equipment is often dispersed over large areas, standard-length power cords may not suffice. This can result in the need for additional extension cords or even relocating equipment, which can be both impractical and unsafe.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should assess their operational layout and determine the optimal lengths required for all equipment prior to purchase. Suppliers often provide a range of lengths for power cords; therefore, it’s crucial to choose cords that not only meet the length requirements but also adhere to safety standards for the intended use. For instance, opting for heavy-duty cords with a higher gauge rating can prevent overheating over longer distances. Furthermore, consider investing in custom-length power cords, which many manufacturers offer. This tailored approach ensures that all equipment is powered safely and efficiently without compromising performance.
Scenario 3: Risk of Power Surges and Equipment Damage
The Problem: Businesses often overlook the risk of power surges that can damage sensitive electronic equipment. In regions with unstable power supply, this can be a significant concern. A B2B buyer may find themselves repeatedly replacing damaged devices due to inadequate protection from voltage fluctuations, leading to increased operational costs and downtime.
The Solution: To safeguard against power surges, it is essential to incorporate surge protectors into the power cord setup. Buyers should prioritize sourcing power cords that come with built-in surge protection features or utilize external surge suppressors that can be integrated into the power supply system. This not only protects valuable equipment but also prolongs its lifespan. Additionally, conducting a risk assessment of the power supply environment can help identify the need for more robust power solutions, such as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). Training staff on proper equipment handling and maintenance, including regular checks of power cords and connectors for wear and tear, can further minimize the risk of equipment damage.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of power cords for electronics
What Are the Key Materials Used in Power Cords for Electronics?
In the realm of power cords for electronics, the choice of materials significantly influences performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of power cords, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties: PVC is known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, flexibility, and resistance to moisture. It can operate effectively within a temperature range of -20°C to 70°C, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: PVC is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, which contributes to its widespread use. However, it has limitations in terms of durability, particularly in high-temperature applications where it can become brittle. Additionally, PVC is less environmentally friendly, raising concerns for companies focused on sustainability.
Impact on Application: PVC is commonly used in standard household and office power cords. However, its lower temperature tolerance may restrict its use in industrial applications where higher heat levels are present.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and IEC is crucial. Buyers should also consider the environmental regulations in their regions, as PVC is facing increasing scrutiny due to its environmental impact.
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer)
Key Properties: TPE offers excellent flexibility, resilience, and a wide operating temperature range (-40°C to 105°C). It is also resistant to UV light and ozone, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons: TPE is durable and can withstand harsher conditions compared to PVC. However, it is generally more expensive and may require more complex manufacturing processes. This can lead to higher costs for end products.
Impact on Application: TPE is ideal for power cords used in outdoor electronics and applications requiring flexibility and durability. Its resistance to environmental factors makes it suitable for regions with extreme weather.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with strict environmental regulations may prefer TPE due to its lower environmental impact. Compliance with standards like DIN and JIS is also important.
Silicone
Key Properties: Silicone is renowned for its exceptional heat resistance, withstanding temperatures from -60°C to 200°C. It is also highly flexible and resistant to aging, UV light, and ozone.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of silicone is its ability to perform in extreme conditions, making it suitable for high-performance applications. However, it is significantly more expensive than PVC and TPE, which can limit its use in budget-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: Silicone is often used in specialized applications, such as medical devices and high-temperature electronics, where safety and reliability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure that silicone materials comply with relevant safety standards, especially in regions like the EU where regulations are stringent. The higher cost may be justified in applications requiring superior performance.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
Rubber
Key Properties: Rubber provides excellent flexibility and durability, with a good range of temperature resistance (-30°C to 90°C). It is also resistant to abrasion and chemicals, making it suitable for industrial applications.
Pros & Cons: Rubber is robust and can withstand rough handling, making it ideal for industrial environments. However, it is heavier and bulkier than other materials, which can affect the design and usability of power cords.
Impact on Application: Rubber is commonly used in heavy-duty power cords for industrial machinery and outdoor equipment. Its durability makes it a preferred choice in demanding environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying quality of rubber materials and ensure compliance with industry standards. The weight and bulkiness of rubber cords may also impact shipping costs and logistics.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Power Cords
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of power cords for electronics | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Standard household and office power cords | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Lower durability in high temperatures | Low |
| TPE | Outdoor electronics and flexible applications | Excellent flexibility and UV resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Silicone | Medical devices and high-performance electronics | Exceptional heat resistance and durability | Significantly more expensive | High |
| Rubber | Heavy-duty industrial power cords | Robust and abrasion-resistant | Heavier and bulkier than alternatives | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for power cords, equipping international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of power cords for electronics
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Power Cords for Electronics?
The manufacturing process of power cords for electronics involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets safety and performance standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to procure high-quality power cords.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Power Cord Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality power cords typically consist of insulated copper wire, which is known for its excellent conductivity. The insulation material, often PVC or rubber, is selected based on its durability and resistance to environmental factors. Manufacturers must also source connectors, such as NEMA or IEC types, made from robust materials that can withstand frequent use and environmental exposure.
How Are Power Cords Formed and Assembled?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming and assembling the power cords. This involves several sub-processes, including:
- Wire Stripping: The copper wire is stripped of its insulation at the ends to prepare for connection.
- Connector Attachment: Connectors are then molded or crimped onto the ends of the wire. This step may involve automated machinery to ensure precision and consistency.
- Cable Assembly: The insulated wires are assembled into a cable, often twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference.
- Insulation: Additional layers of insulation may be applied to protect against wear and tear, ensuring safety in diverse environments.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed in Power Cord Manufacturing?
Finishing is the final stage in the manufacturing process, which includes quality checks and packaging. Power cords are often subjected to:
- Marking and Labeling: Each cord is labeled with specifications, including voltage ratings and compliance marks.
- Packaging: Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transit. This often involves using protective materials and ensuring the cords are coiled correctly.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance for Power Cords?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of power cords is governed by several international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these standards is crucial to ensure product reliability and safety.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
How Does ISO 9001 Impact Power Cord Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard for quality management systems. Manufacturers adhering to ISO 9001 are required to implement a systematic approach to managing their processes, which enhances the quality and consistency of their products. B2B buyers should verify whether their suppliers possess ISO 9001 certification, as it indicates a commitment to quality.
What Other Certifications Should Buyers Look for?
In addition to ISO 9001, buyers should look for certifications relevant to their specific markets, such as:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- UL Certification: Commonly required in North America, this certification ensures that the power cords have been tested for safety.
- RoHS Compliance: Ensures that the cords do not contain hazardous substances.
What Are the Critical Quality Control Checkpoints in Power Cord Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet established standards and specifications. Here are the main QC checkpoints:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
IQC involves the inspection of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This ensures that all components meet quality standards before production begins. Buyers should inquire about IQC processes to confirm that only high-quality materials are used.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During production, IPQC measures are implemented to monitor the manufacturing process. This includes regular inspections of wire stripping, connector attachment, and cable assembly. Manufacturers often use statistical process control (SPC) techniques to identify and rectify any deviations from quality standards in real-time.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
FQC is the last step before packaging and shipment. It typically includes comprehensive testing of the finished power cords to check for electrical performance, safety compliance, and physical integrity. Common testing methods include:
- Electrical Testing: Measures the voltage and current carrying capacity.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses durability under stress and environmental conditions.
- Safety Testing: Ensures compliance with international safety standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures, B2B buyers should take several steps:
What Audits and Reports Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should request access to quality management system audits and performance reports. These documents provide insight into the manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards and the effectiveness of their QC processes.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can be beneficial for verifying supplier quality control. These independent audits can offer an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and product quality. Buyers should consider including third-party inspections as part of their procurement strategy, especially when dealing with international suppliers.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and market demands is vital. Buyers should be aware of:
- Import Regulations: Different countries have varying regulations regarding product safety and compliance. It’s essential to ensure that the power cords meet local standards.
- Cultural and Market Differences: Understanding the specific needs and preferences of different markets can guide purchasing decisions and supplier evaluations.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing power cords for electronics. This knowledge not only helps in selecting reliable suppliers but also ensures that the products meet necessary safety and performance standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of power cords for electronics’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing the right types of power cords for electronics, this guide provides a systematic checklist to ensure all critical aspects are addressed. Understanding the specifications, compliance standards, and supplier credibility is essential in making informed purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by identifying the specific technical requirements for the power cords you need. Consider factors such as voltage rating, current capacity, and connector types (e.g., NEMA, IEC). Documenting these specifications will help narrow down your options and ensure compatibility with your electronic devices.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the power cords can handle the required voltage and current to avoid overheating or equipment failure.
- Connector Types: Specify the necessary connectors based on the equipment in use, such as C13, C14, or USB types.
Step 2: Understand Regional Standards and Compliance
Different regions may have specific electrical standards and certifications that power cords must meet. Familiarize yourself with local regulations and international standards (like IEC, UL, or CE) relevant to your target markets.
- Safety Certifications: Look for cords that are certified for safety and performance to prevent hazards.
- Environmental Regulations: Ensure compliance with standards that may affect the materials used in the cords, such as RoHS in Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs reliably. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and references from other businesses in your industry.
- Supplier Reputation: Investigate the supplier’s history, customer reviews, and case studies to gauge their reliability.
- Production Capabilities: Assess whether they can handle your order volume and meet delivery timelines.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the power cords to conduct performance tests. This step is crucial to ensure the cords meet your quality standards and operational requirements.
- Functionality Testing: Check for compatibility with your equipment and confirm that the cords perform under expected load conditions.
- Durability Assessment: Evaluate the materials used for insulation and connectors to ensure they withstand your operational environment.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions with your chosen supplier to establish favorable terms, including pricing, payment conditions, and delivery schedules. Clear agreements help prevent misunderstandings later.
- Pricing Structures: Understand the pricing model, including bulk discounts and additional costs for shipping or customs.
- Delivery Timelines: Ensure that the supplier can meet your required delivery dates, especially if you have tight project deadlines.
Step 6: Verify After-Sales Support and Warranty
Assess the after-sales support offered by the supplier, including warranty terms and customer service responsiveness. Strong support is critical in addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase.
- Warranty Coverage: Look for warranties that cover defects and performance issues, ensuring you’re protected in case of manufacturing faults.
- Customer Service Accessibility: Confirm that the supplier offers reliable channels for support, such as dedicated account managers or technical assistance.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for power cords, ensuring they select the best products to meet their needs while minimizing risks and optimizing costs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of power cords for electronics Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of power cords for electronics is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their procurement strategies. This analysis delves into the various cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for buyers.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Power Cord Manufacturing?
The cost structure of power cords typically includes several key components:
-
Materials: The primary material costs come from the insulated copper wire, plastic connectors, and additional components like fuses or surge protectors. The price can vary significantly based on the type of material used (e.g., copper vs. aluminum) and market fluctuations.
-
Labor: Labor costs depend on the region of production. For example, manufacturing in low-wage countries may reduce labor expenses, while countries with higher labor standards may incur higher costs, impacting the overall pricing strategy.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can help lower overhead costs, which can be beneficial for pricing flexibility.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for specialized connectors or custom designs can be significant. These costs are often amortized over a larger production volume, making them less impactful per unit for bulk orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with international standards and certifications (e.g., UL, CE) incurs additional costs. These expenses are critical for maintaining product reliability and safety, especially in industries where standards are stringent.
-
Logistics: Shipping, customs, and warehousing expenses can vary greatly depending on the shipping terms (Incoterms) and the geographic location of the buyer. Effective logistics management can minimize these costs.
-
Margin: The profit margin applied by manufacturers and suppliers can vary. Understanding the typical margin in your industry can help in negotiating better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Power Cord Costs?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of power cords:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) play a pivotal role in pricing. Larger orders typically lead to reduced per-unit costs, making bulk purchasing an attractive option for buyers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized tooling and materials. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and compliance with certifications can lead to increased costs but may provide long-term savings through durability and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, but they often offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the total landed cost. Buyers should consider whether they prefer to handle shipping and customs or if they want the supplier to take on those responsibilities.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Optimize Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate payment terms, delivery schedules, and pricing. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts for larger volumes or long-term contracts.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes not only the purchase price but also logistics, maintenance, and potential replacement costs. This holistic view can lead to smarter purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Regional Advantages: Understand regional manufacturing strengths and potential cost savings. For example, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs can significantly impact overall expenses.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Nuances: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade agreements that can affect pricing. Keeping abreast of these factors can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to assess quality and compatibility. This can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the final products meet your specifications.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing dynamics of power cords can empower B2B buyers to make informed procurement decisions. By considering the various cost components, price influencers, and strategic negotiation tips, buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies to achieve better value in their purchases.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of power cords for electronics With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Power Cords for Electronics
In the realm of electronics, power cords are essential for connecting devices to a power source. However, there are alternative solutions that can also provide energy transfer or connectivity, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. This analysis explores how traditional power cords compare to wireless charging solutions and Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Types of Power Cords for Electronics | Wireless Charging Solutions | Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, reliable power supply | Variable efficiency, dependent on distance and alignment | High efficiency, provides data and power |
| Cost | Generally low-cost per unit | Higher initial setup costs | Moderate setup costs, cost-effective for integrated systems |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple plug-and-play functionality | Requires compatible devices, may need infrastructure upgrades | Requires network infrastructure, installation of PoE switches |
| Maintenance | Minimal, replace when damaged | Low maintenance, but less durable over time | Low, but requires network management |
| Best Use Case | Standard electronics, appliances | Mobile devices, convenience-focused applications | Network devices, IP cameras, VoIP phones |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Pros and Cons of Wireless Charging Solutions?
Wireless charging has gained traction, particularly for mobile devices. The primary advantage is convenience—users can simply place their device on a charging pad without worrying about cords. However, the efficiency of wireless charging can be affected by distance and alignment, leading to slower charging times compared to traditional cords. Additionally, not all devices support wireless charging, which can limit its applicability in a B2B context where multiple device types are used.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
How Does Power over Ethernet (PoE) Technology Compare?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology allows network cables to deliver both data and power to devices, such as IP cameras and VoIP phones. This dual capability can simplify installations by reducing the number of cables needed, which is particularly advantageous in commercial environments. While the initial costs for PoE switches may be moderate, the long-term savings from reduced cabling and enhanced network management can be significant. However, PoE requires a robust network infrastructure, which may not be feasible for all organizations.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the appropriate solution for powering electronics ultimately depends on the specific needs and infrastructure of the business. For straightforward applications, traditional power cords remain a reliable and cost-effective choice. However, for organizations looking to streamline installations or enhance mobility, exploring wireless charging or Power over Ethernet technologies may provide additional benefits. Buyers should consider factors such as device compatibility, installation complexity, and long-term costs when making their decision, ensuring that their choice aligns with both current and future operational requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of power cords for electronics
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Power Cords for Electronics?
When sourcing power cords for electronic applications, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance. Here are some essential properties to consider:

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
-
Material Grade: Power cords are typically constructed from copper or aluminum conductors, with PVC or rubber insulation. Copper is preferred for its superior conductivity, which reduces energy loss and improves efficiency. Choosing the right material can impact the durability and flexibility of the cord, making it essential for international buyers to consider local environmental conditions.
-
Voltage Rating: This specification indicates the maximum voltage that a power cord can handle safely. Common ratings include 125V, 250V, or even higher for industrial applications. Selecting the appropriate voltage rating is vital to prevent overheating or electrical failures, which can lead to costly downtime.
-
Current Rating (Amperage): The current rating specifies the maximum amount of electrical current a cord can carry. This is typically expressed in amperes (A). Understanding the current requirements of your devices ensures that the power cords you select will not be overloaded, thereby enhancing safety and reliability.
-
Cable Length: The length of the power cord can affect installation flexibility and accessibility. Longer cords may be necessary for larger setups, while shorter cords can reduce clutter. Buyers should evaluate their spatial requirements to determine the optimal cord length for their applications.
-
Connector Type: Different connectors, such as NEMA, IEC, or USB, are designed for specific applications and regions. It is critical for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility with existing equipment. The wrong connector can result in operational inefficiencies and increased costs.
-
Temperature Rating: This refers to the maximum temperature the cord can withstand during operation. Power cords with higher temperature ratings are typically designed for heavy-duty applications or environments with extreme conditions. Choosing the right temperature rating is essential for ensuring longevity and safety.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Power Cord Procurement?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are several key terms often encountered in the power cord trade:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For B2B buyers, understanding OEM relationships can help identify reliable suppliers and ensure the quality of components used in their products.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers to understand as it affects purchasing decisions and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and forecasting needs.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. This is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple vendors.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to clarify shipping responsibilities, insurance, and risk management throughout the supply chain.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for planning and inventory management, particularly in industries with tight production schedules.
-
Certification Standards: Power cords often need to comply with specific safety and performance standards, such as UL, CE, or RoHS. Familiarity with these certifications helps buyers ensure they are sourcing safe and compliant products, reducing the risk of liability and enhancing brand reputation.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing power cords, ensuring their investments meet both performance and compliance standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of power cords for electronics Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends for Power Cords in the Electronics Sector?
The global market for power cords is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for electronic devices across various sectors, including consumer electronics, healthcare, and industrial applications. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, continue to embrace digital transformation, the need for reliable and efficient power solutions is paramount. One notable trend is the shift towards universal power cords, which cater to a wide range of devices, thereby reducing inventory complexity and costs for businesses.
Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce has enabled buyers to source power cords more conveniently. However, it also necessitates a keen awareness of quality standards and certifications, such as NEMA and IEC, to ensure safety and compatibility with local electrical systems. Emerging technologies, including smart power management systems and IoT integration, are also shaping sourcing strategies, as they require innovative power solutions to enhance functionality and energy efficiency.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing Power Cord Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B sourcing strategies in the power cord industry. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of plastic waste and energy consumption, has prompted buyers to prioritize ethical sourcing practices. Companies are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to green certifications and use eco-friendly materials in their products, such as recycled plastics and low-impact manufacturing techniques.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
Furthermore, the emphasis on circular economy principles is gaining traction, encouraging businesses to consider the entire lifecycle of power cords, from production to disposal. This includes exploring options for power cords that are designed for recyclability and reduced environmental footprint. As a result, international buyers are not only evaluating cost-effectiveness but are also assessing suppliers based on their commitment to sustainable practices, which can enhance brand reputation and align with corporate social responsibility goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Power Cords in the Electronics Industry?
The evolution of power cords can be traced back to the early days of electrical engineering, where the need for safe and effective power transmission was first recognized. Initially, power cords were rudimentary, often comprising bare wires that posed significant safety risks. Over the decades, advancements in materials science led to the development of insulated cables and standardized connectors, significantly enhancing safety and reliability.
The introduction of international standards, such as NEMA in the United States and IEC in Europe, revolutionized the industry by providing guidelines that ensure compatibility and safety across different regions. Today, the market is characterized by a wide variety of power cords, including AC, DC, and universal types, catering to an increasingly diverse array of electronic devices. This historical context underscores the importance of adhering to established standards while also embracing innovation to meet the evolving needs of B2B buyers in the global marketplace.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical context of power cords is essential for international B2B buyers. By staying informed about trends and sourcing strategies, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and align with sustainability goals, ultimately driving success in the competitive electronics sector.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of power cords for electronics
-
How do I choose the right power cord for my electronic devices?
When selecting a power cord, consider the voltage and current requirements of your device, along with the connector type needed for compatibility. Ensure the cord meets international safety standards relevant to your region, such as IEC or NEMA specifications. Additionally, factor in the length of the cord for your installation needs and whether you require features like surge protection or hospital-grade certification, especially for critical applications. -
What is the best power cord for industrial equipment?
For industrial applications, high-quality AC power cords with robust insulation and connectors designed to handle high voltages and currents are recommended. Look for cords that comply with industry standards and certifications, such as UL or CE, to ensure safety and reliability. Additionally, consider cords with features like strain relief and durability against environmental factors such as moisture or temperature extremes. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers for power cords?
When vetting suppliers, assess their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and compliance with international standards. Check their certifications, such as ISO 9001, and request product samples to evaluate quality firsthand. Additionally, inquire about their experience in international shipping and logistics to ensure they can meet your delivery timelines and handle customs regulations effectively. -
What customization options are available for power cords?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for power cords, including length, gauge, connector types, and colors. You can also request specific labeling or branding for your products. Discuss your requirements upfront with suppliers, as minimum order quantities (MOQs) may apply for customized orders. This flexibility allows you to tailor cords to suit your specific applications or branding needs. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for power cords in B2B transactions?
MOQs for power cords can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the order. Standard MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units, especially for customized options. However, some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for standard products. It’s essential to communicate your needs with potential suppliers to find a solution that aligns with your purchasing capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing power cords internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region but typically include options like advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60/90 days after delivery. Ensure you clarify payment methods and currency before finalizing orders. It’s advisable to establish trust and verify the supplier’s credibility, especially for significant transactions, to mitigate risks associated with international trade. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for the power cords I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request certifications and test reports from your supplier that demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards. Consider establishing a QA process that includes random sampling and testing of received goods. Additionally, collaborating with third-party inspection services can provide an independent assessment of product quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipments of power cords?
When shipping power cords internationally, consider the logistics involved, including freight forwarding, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Ensure that your supplier has experience with international shipping and can provide documentation like invoices and packing lists. Additionally, be aware of import regulations in your country to avoid delays and ensure smooth customs processing.
Top 6 Types Of Power Cords For Electronics Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Power Cords
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Power cords, also known as line cords or power cables, connect electronic devices to power sources, facilitating electricity transmission. They typically consist of copper wires insulated and covered by a non-conductive layer. Power cords are categorized into basic power cords (plug at one end, bare wires at the other) and connector power cords (connector at one end, wires at the opposite end). Th…
2. Cables.com – Essential Power Cords and Connectors
Domain: cables.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Power cords and cables are essential for delivering electricity to devices, with various specifications including voltage and current ratings, connectors, and material construction. Key types include AC power cords, C14 to C13 connectors for data centers, C19 to C20 for high-power devices, and 5-15P to C13 for office electronics. Specialty options include colored power cables for quick identificat…
3. XLR – Connector Overview
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, XLR – Connector Overview, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. MSL – Power Cable Solutions
Domain: msl-tw.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Power Cable Types: IEC, NEMA, CEE. Key components of power cables include conductors (copper or aluminum), insulation (XLPE, PVC, EPR), shielding (metallic tapes or braids), and sheath/jacket (PVC, TPU, polyethylene). Types of connectors include IEC 60320 (C5/C6, C7/C8), NEMA (5-15P, 5-20P), and CEE. IEC connectors are standardized for global use, NEMA for North America, and CEE for Europe. AC pow…
5. CableWholesale – Power Cords & Connectors
Domain: cablewholesale.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: NEMA and IEC power cord types; NEMA connectors range from 15-60 amps and 125-600 volts; NEMA classifications: straight-blade and locking; common NEMA designations: 5-15P (grounded, 125V, 15A), 5-20P, 14-30, 14-50 (for dryers/stoves), TT-30 (for RVs); IEC connectors: C13 (for computers), C14, C15 (for hot appliances), C17, C18 (no grounding), C19, C20 (for servers), C7 (figure-eight), C5 (clover-le…
6. DigiKey – Desktop Power Supplies
Domain: forum.digikey.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Many Desktop Power Supplies sold at DigiKey do not come with an input power cord. The input type is listed under Product Attributes on individual product pages. To determine the necessary cable, check the Input Connector section. For example, an IEC 320-C8 connector requires a power cable with an IEC 320-C7 connector. Common plugs in North America include Nema 5-15P (3-Prong) and Nema 1-15P (2-Pro…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of power cords for electronics
In the evolving landscape of electronics, the strategic sourcing of power cords is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reliability. Buyers must recognize the diverse types of power cords available, such as AC power cords, NEMA connectors, and DC power supplies, each tailored for specific applications. Understanding these classifications not only aids in selecting the right products but also ensures compliance with regional standards, which is particularly vital for international markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
The emphasis on quality and compatibility cannot be overstated, as subpar power cords can lead to equipment failures and safety hazards. Thus, establishing relationships with reputable suppliers is essential for securing durable and compliant products that meet the demands of various electronic devices.
Looking forward, the global market for power cords is set to expand, driven by innovations in technology and increasing demand for electronic devices. International buyers should leverage this growth by exploring new sourcing avenues and investing in high-quality power solutions. By doing so, they can ensure their operations remain competitive and aligned with industry advancements. Take action now to enhance your sourcing strategy and position your business for success in the dynamic electronics market.

Illustrative image related to types of power cords for electronics
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.