A Deep Dive into Compressors Industrial Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for compressors industrial
In the dynamic world of industrial operations, sourcing reliable compressors is a critical challenge faced by businesses globally. From manufacturing plants in Brazil to construction sites in Nigeria, the need for high-performance compressors that meet specific operational demands is paramount. This comprehensive guide addresses the complexities of the global market for industrial compressors, offering insights into various types, applications, and essential criteria for supplier vetting.
International B2B buyers will find actionable information on evaluating compressor efficiency, understanding cost structures, and navigating the intricacies of logistics and compliance across different regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By equipping decision-makers with the knowledge to assess performance metrics and supplier reliability, this guide empowers organizations to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals and budgets.
Whether you are looking for rotary screw compressors for continuous operations or portable air compressors for on-the-go tasks, understanding the nuances of this market is essential. With a focus on practical insights and strategic sourcing, this guide serves as a vital resource for businesses aiming to optimize their compressor investments and enhance productivity in their respective industries.
Understanding compressors industrial Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
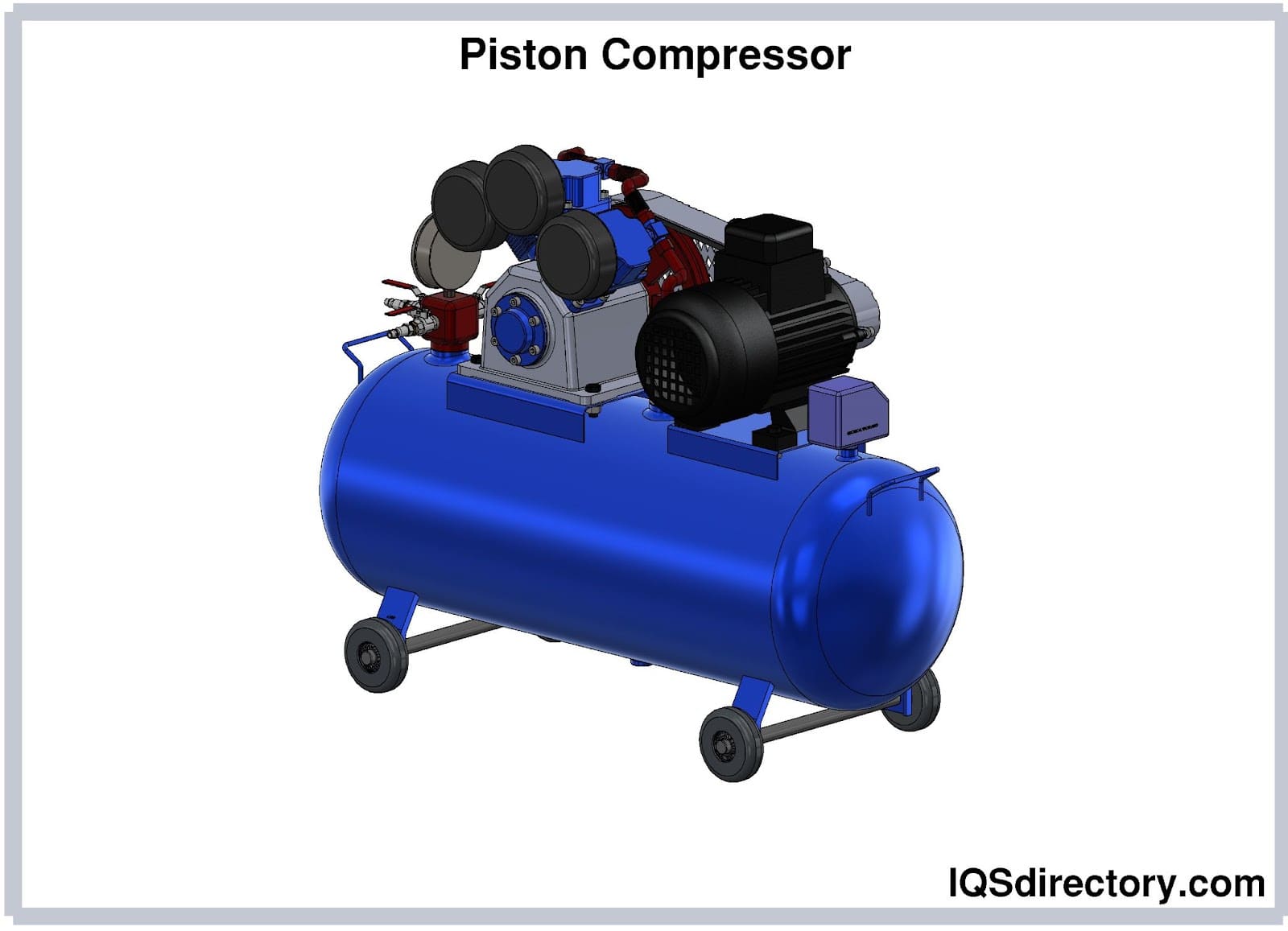
| Reciprocating Compressors | Uses pistons driven by a crankshaft; versatile and efficient for various pressures. | Automotive repair, manufacturing, construction | Pros: Cost-effective, wide range of sizes. Cons: Noisy, requires maintenance. |
| Rotary Screw Compressors | Utilizes two rotating screws to compress air; continuous operation and high efficiency. | Oil & gas, food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Low maintenance, energy-efficient. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Centrifugal Compressors | Employs a rotating disk to increase air velocity; ideal for high-volume air delivery. | HVAC systems, power generation, chemical plants | Pros: High flow rates, compact design. Cons: Not suitable for low-pressure applications. |
| Scroll Compressors | Utilizes two interleaved spirals; compact and quiet operation. | Refrigeration, air conditioning, medical devices | Pros: Quiet, low vibration. Cons: Limited capacity compared to other types. |
| Diaphragm Compressors | Uses a flexible diaphragm to compress gas; suitable for handling corrosive gases. | Laboratory applications, chemical processing | Pros: Excellent for gas purity, low contamination risk. Cons: Limited flow rate and pressure. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Reciprocating Compressors?
Reciprocating compressors are characterized by their use of pistons to compress air or gas, making them versatile for a range of applications. They are particularly suitable for operations requiring varied pressure levels, such as automotive repair and construction. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate their budget against the potential need for ongoing maintenance, as these units can be noisy and require regular upkeep.
How Do Rotary Screw Compressors Stand Out in Industrial Applications?
Rotary screw compressors are known for their efficiency and ability to provide continuous operation. They are ideal for industries like oil and gas, where reliability is crucial. Buyers should consider the initial investment against long-term energy savings, as these compressors generally have lower maintenance needs and operate more quietly than their reciprocating counterparts.
Why Choose Centrifugal Compressors for High-Volume Needs?
Centrifugal compressors are designed to handle high flow rates, making them perfect for HVAC systems and chemical plants. Their compact design allows for space-saving installations. However, buyers should note that they are less effective for low-pressure applications, which may limit their use in certain scenarios.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
What Benefits Do Scroll Compressors Offer for Specific Applications?
Scroll compressors are compact and operate quietly, making them suitable for refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Their design allows for lower vibration levels, which can enhance operational longevity. However, they may not deliver the same capacity as other compressor types, so it’s essential for buyers to assess their specific needs before choosing this option.
In What Scenarios Are Diaphragm Compressors the Best Choice?
Diaphragm compressors are particularly beneficial for laboratory and chemical processing applications due to their ability to handle corrosive gases without risk of contamination. They excel in providing gas purity, making them a preferred choice in sensitive environments. However, their limitations in flow rate and pressure mean that buyers should ensure their application requirements align with these capabilities.
Key Industrial Applications of compressors industrial
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of compressors industrial | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Pneumatic tools and equipment operation | Enhanced productivity and efficiency | Reliability, maintenance support, energy efficiency |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging and bottling processes | Improved product shelf life and quality | Compliance with health standards, energy costs |
| Oil and Gas | Gas compression for transportation | Increased operational safety and efficiency | Durability in harsh environments, service intervals |
| Construction | Concrete and asphalt compaction | Faster project completion and reduced costs | Portability, power source options, maintenance |
| Automotive | Paint spraying and assembly line operations | Higher quality finishes and reduced waste | Precision, compatibility with existing systems |
How Are Compressors Industrial Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, compressors are vital for powering pneumatic tools and equipment, which are essential for assembly lines and material handling. They significantly enhance productivity by providing consistent air pressure for various applications, such as drilling, fastening, and cutting. Buyers must consider reliability and energy efficiency when sourcing compressors, as downtime can lead to significant financial losses, especially in high-output environments.
What Role Do Compressors Play in the Food and Beverage Industry?
Compressors in the food and beverage industry are crucial for packaging and bottling processes, ensuring products remain fresh and safe for consumption. They aid in creating vacuum seals and pressurized environments that extend shelf life. International buyers, particularly from regions with strict health regulations, must ensure their compressors meet local compliance standards while also considering energy costs to maintain profitability.
How Are Compressors Utilized in the Oil and Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, compressors are used for gas transportation and processing, providing the necessary pressure to move gas through pipelines. Their role is critical in maintaining operational safety and efficiency, especially in remote locations. Buyers should focus on the durability of compressors to withstand harsh environments and consider service intervals to minimize downtime and ensure continuous operation.
Why Are Compressors Important in Construction?
Compressors are essential in the construction industry for applications like concrete and asphalt compaction. They enable faster project completion by powering heavy machinery, reducing labor costs and time. When sourcing compressors, buyers need to prioritize portability and power source options, as job sites can vary widely in accessibility and available resources.
How Do Compressors Enhance Operations in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, compressors facilitate paint spraying and assembly line operations, allowing for high-quality finishes and efficient production processes. The precision of air pressure delivered by these compressors directly impacts the quality of the final product, reducing waste and rework. Buyers should ensure compatibility with existing systems and consider the precision of the compressors to maintain production standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘compressors industrial’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Air Supply Disrupting Operations
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in sectors such as manufacturing and construction face the challenge of inconsistent air supply from their industrial compressors. This inconsistency can lead to unexpected downtime, affecting productivity and potentially causing delays in project timelines. For example, a construction company relying on pneumatic tools may find that their air compressor isn’t delivering the required pressure, resulting in halted operations and frustrated workers. This scenario not only hampers efficiency but can also lead to increased operational costs and dissatisfaction among clients.
The Solution: To combat this issue, it’s crucial for buyers to assess their specific air demand needs before selecting a compressor. They should conduct a thorough analysis of all tools and machinery that will require compressed air, considering peak usage times and potential expansion in operations. Investing in a compressor with adjustable pressure settings or one that can be scaled up as needed can provide the necessary flexibility. Additionally, regular maintenance checks, including monitoring for leaks and ensuring proper filtration, can help maintain consistent air quality and pressure. Forming a partnership with a reputable supplier who offers ongoing support and maintenance can further ensure reliability.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
Scenario 2: High Energy Costs from Inefficient Compressors
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the rising energy costs associated with outdated or inefficient compressors. In regions like Africa and South America, where energy prices can be volatile, businesses often find that their compressor systems consume more energy than anticipated, squeezing profit margins. For instance, a manufacturing plant operating multiple compressors may notice significant spikes in energy bills, which can threaten the overall financial health of the business.
The Solution: Buyers should consider investing in energy-efficient compressor models that are designed to reduce power consumption without sacrificing performance. Variable speed drive (VSD) compressors, for instance, adjust their power usage based on demand, leading to significant savings over time. It’s also advisable to implement regular energy audits to identify inefficiencies in existing systems and to explore government incentives for upgrading to greener technologies. Moreover, integrating smart monitoring systems can help track energy usage in real-time, allowing businesses to make informed decisions about their operations and further reduce costs.
Scenario 3: Complex Maintenance and Downtime Challenges
The Problem: Industrial compressors often require regular maintenance to operate efficiently, but many buyers face challenges related to complex maintenance schedules and the expertise required for repairs. This situation can result in prolonged downtime and increased repair costs, especially in regions where skilled technicians are scarce. A manufacturer may experience a compressor failure just before a crucial production deadline, leading to a loss of revenue and strained customer relationships.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize selecting compressors that come with comprehensive maintenance support and training from the manufacturer. Understanding the maintenance requirements upfront can help buyers create a proactive maintenance schedule, reducing the risk of unexpected failures. Additionally, investing in training for in-house personnel can empower teams to handle routine maintenance tasks and minor repairs, minimizing downtime. Engaging in preventive maintenance contracts with suppliers can also ensure that expert support is readily available, helping to keep operations running smoothly and efficiently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for compressors industrial
What Are the Key Materials Used in Industrial Compressors?
When selecting materials for industrial compressors, it is essential to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of compressors: aluminum, cast iron, stainless steel, and composite materials. Each material has distinct characteristics that can significantly influence operational efficiency and longevity.
Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
How Does Aluminum Perform in Compressor Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight material known for its excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and can withstand moderate pressure levels.
Pros: The primary advantages of aluminum include its lightweight nature, which facilitates easier installation and transportation, and its resistance to rust, making it suitable for humid environments. Additionally, aluminum is generally less expensive than some other metals.
Cons: However, aluminum’s lower tensile strength compared to steel means it may not be suitable for high-pressure applications. Moreover, its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized techniques to ensure durability.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in applications where weight savings are crucial, such as in portable compressors. However, it may not be ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications requiring high pressure.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local climate conditions that may affect aluminum’s performance. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM can also impact material selection.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Compressor Design?
Cast iron is a traditional choice for compressor components, known for its high strength and durability. It can handle high temperatures (up to 300°C) and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Cast iron’s key advantages include its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb vibrations, which helps in reducing noise levels during operation. It is also relatively cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing.
Cons: The main drawback is its weight, which can complicate transport and installation. Additionally, cast iron is more prone to corrosion if not properly coated or maintained.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is commonly used in stationary compressors that require high durability and strength. It is particularly effective in industrial settings where heavy-duty performance is necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with local regulations regarding emissions and noise levels. Understanding the local supply chain for cast iron components is also essential.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Compressors?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and high strength, making it an excellent choice for compressors exposed to various media, including corrosive gases and liquids. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 500°C.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and corrosion, which prolongs the lifespan of compressor components. It also maintains its structural integrity under high pressure.
Cons: On the downside, stainless steel is more expensive than aluminum and cast iron, which can impact the overall cost of compressor systems. Additionally, its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized welding techniques.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries, where cleanliness and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions with stringent safety and health regulations, such as Europe, must ensure compliance with standards like DIN and JIS when selecting stainless steel components.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Compressor Performance?
Composite materials, often a blend of polymers and fibers, are increasingly used in compressor design due to their lightweight and high-strength properties. They can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures.
Pros: The advantages of composites include their lightweight nature, which can lead to energy savings in transportation and installation. They also offer excellent corrosion resistance and can be molded into complex shapes.
Cons: However, composites can be more expensive than traditional materials and may not perform well under extreme temperatures or pressures.
Impact on Application: Composite materials are suitable for specialized applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace or portable compressors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of composite materials in their region and consider any specific certifications required for their applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Industrial Compressors
| Material | Typical Use Case for compressors industrial | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Portable compressors | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength for high-pressure | Low |
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty stationary compressors | High durability and wear resistance | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Med |
| Stainless Steel | Food and pharmaceutical applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Composite | Aerospace and specialized portable units | Lightweight and moldable | Expensive and limited temperature resistance | Med |
In conclusion, selecting the right material for industrial compressors is crucial for performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for compressors industrial
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Industrial Compressors?
The manufacturing process for industrial compressors typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials, such as steel, aluminum, and composite materials, which are essential for durability and performance. Suppliers often utilize advanced techniques like laser cutting or water jet cutting to ensure precision in material dimensions. This stage may also include heat treatment processes to enhance the material’s properties, like strength and resistance to wear.
-
Forming: Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes that can include forging, machining, and stamping. These techniques shape the components into their required forms. For instance, forging is commonly used for critical components like crankshafts and connecting rods, providing enhanced strength through the alignment of the material’s grain structure.
-
Assembly: The assembly stage involves the integration of various components into the compressor unit. This includes the installation of pistons, valves, and motors. Modern assembly lines often employ robotic automation to enhance efficiency and reduce human error, ensuring that components fit together with precision. During this phase, manufacturers may also implement lean manufacturing principles to minimize waste and optimize the workflow.
-
Finishing: The final stage focuses on surface treatments and coatings that improve the compressor’s performance and longevity. Techniques such as painting, anodizing, or powder coating are applied to protect against corrosion and wear. Quality checks during this stage ensure that the compressor meets aesthetic and functional standards before it is packaged for shipment.
Which Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Industrial Compressors?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of industrial compressors, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
-
International Standards: ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS). Compliance with ISO 9001 signifies that a manufacturer maintains consistent quality in their processes and products. This standard is especially relevant for B2B buyers looking for reliability in their suppliers.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Additional certifications like CE marking (for products sold in the European Economic Area) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are essential, particularly for compressors used in oil and gas applications. These certifications indicate that the products meet specific safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Compressor Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process with several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting the raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements. Any materials that do not comply are rejected or sent back to the supplier.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the production process. This may include dimensional checks, surface quality assessments, and functional tests of components as they are being assembled.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a comprehensive inspection is performed on the finished compressor units. This includes performance testing under simulated operating conditions, ensuring that the units operate efficiently and meet all specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Compressor Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the performance and reliability of industrial compressors:
-
Functional Testing: This involves running the compressor under load conditions to ensure it performs as expected. Parameters such as pressure output, noise levels, and energy consumption are monitored.
-
Leak Testing: Ensuring that there are no leaks in the compressor system is crucial. Manufacturers may utilize techniques like pressure decay testing or ultrasonic leak detection to confirm the integrity of the compressor.
-
Vibration Analysis: This method assesses the compressor’s operational stability. Excessive vibration can indicate misalignment or wear, which can lead to premature failure.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to ensure their suppliers maintain robust quality control practices:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand. This enables buyers to evaluate the supplier’s adherence to industry standards and their commitment to quality.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including results from recent inspections and tests. This transparency is crucial for buyers to understand the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies can conduct independent audits and testing, ensuring that products meet all specified standards before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Different regions may have varying regulations and standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local compliance requirements to ensure that imported compressors meet all necessary criteria.
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: Effective communication is essential when engaging with international suppliers. Buyers should ensure that both parties clearly understand quality expectations and certification requirements, potentially utilizing translation services if necessary.
-
Logistics and Certification Validity: The logistics of shipping and receiving products can impact certification validity. Buyers should confirm that the certifications held by suppliers are recognized in their respective countries and that the products can be imported without additional compliance issues.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing industrial compressors, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘compressors industrial’
Introduction
When sourcing industrial compressors, it is essential to follow a systematic approach to ensure you acquire the right equipment for your operational needs. This checklist will guide international B2B buyers through the critical steps in the procurement process, from defining specifications to ensuring supplier reliability. By adhering to these steps, you can streamline your purchasing decision and minimize risks associated with investment in industrial compressors.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements of the compressors you need. This includes factors such as pressure ratings, flow rates, power supply requirements, and intended applications.
– Consider specific features: Identify whether you need a single-stage or two-stage compressor based on your operational demands.
– Assess energy efficiency: Look for models that meet local energy efficiency standards to reduce operational costs.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Technologies
Stay informed about the latest trends and technologies in the compressor market. Understanding advancements can help you choose a model that enhances productivity and efficiency.
– Review industry reports: Access publications or market analysis reports that highlight emerging technologies and innovations.
– Consider environmental regulations: Ensure that the compressors you consider comply with any relevant emissions standards in your region.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. This step is vital for ensuring the reliability and quality of the compressors you intend to buy.
– Request documentation: Ask for company profiles, certifications, and case studies from similar industries to assess their credibility.
– Seek references: Connect with other businesses that have purchased from the supplier to gauge their satisfaction and product performance.
Step 4: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing effectively. However, don’t make decisions based solely on cost; consider total value, including warranties and after-sales support.
– Understand payment options: Investigate financing options and payment terms that could ease your cash flow.
– Inquire about hidden costs: Clarify shipping fees, installation costs, and any other potential expenses that may arise.
Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the compressors meet local safety and environmental regulations. This step is crucial to avoid legal issues and ensure operational safety.
– Check certifications: Look for compliance with international standards such as ISO or CE marking.
– Review local regulations: Familiarize yourself with any additional compliance requirements specific to your region.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance Services
Evaluate the after-sales support and maintenance services offered by the supplier. Reliable support can significantly impact the longevity and performance of your compressors.
– Inquire about warranties: Understand the warranty terms and what is covered.
– Evaluate service response times: Consider suppliers that offer prompt service and maintenance to minimize downtime.
Step 7: Make an Informed Decision
Compile all the information gathered and make a decision based on a comprehensive analysis of your findings. Ensure that the selected compressor aligns with your operational needs and budget constraints.
– Review all documentation: Ensure that contracts and agreements are clear and align with your expectations before signing.
– Prepare for delivery and installation: Plan for logistics and installation to ensure a smooth transition to using the new equipment.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complex process of sourcing industrial compressors, ultimately leading to more informed purchasing decisions and successful operational outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for compressors industrial Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in the Pricing of Industrial Compressors?
Understanding the cost structure of industrial compressors is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing compressors significantly influence costs. High-grade metals and specialized components often lead to higher prices but can enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and skill level required for assembly and quality assurance. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, the overall pricing may reflect this.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive prices.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific compressor designs can add to initial costs. However, suppliers may amortize these costs over larger production volumes, potentially reducing the price per unit.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure the reliability of compressors but can add to the overall cost. Buyers should consider the value of quality assurance in their pricing evaluations.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling expenses can vary significantly, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and local tariffs can influence the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and ensure sustainability. Understanding the typical margins in the compressor market can aid buyers in recognizing fair pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Industrial Compressors?
Several factors can influence the pricing of industrial compressors, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to discounted pricing. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize their purchasing costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized compressors tailored to specific applications can incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Compressors built with higher-quality materials or those that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) typically command higher prices. Buyers should assess whether the additional investment aligns with their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better warranty terms and customer service, justifying a higher price point.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers. The chosen shipping terms can affect the total landed cost, including duties, taxes, and shipping fees.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
International B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing industrial compressors:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Buyers should aim to consolidate purchases to achieve volume discounts. Engaging in long-term contracts may also encourage suppliers to offer better pricing.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and downtime costs. This holistic view can lead to better investment decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional pricing trends, currency fluctuations, and economic factors that may influence compressor pricing.
-
Establish Clear Communication: Open dialogue with suppliers regarding budget constraints and expectations can lead to more favorable pricing arrangements. Transparency often fosters trust and leads to better deals.
Conclusion: Why is it Important to Understand Pricing Dynamics in Industrial Compressor Sourcing?
Gaining insight into the cost structure and pricing dynamics of industrial compressors empowers B2B buyers to make strategic purchasing decisions. By considering the various cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, buyers can optimize their sourcing processes and ensure they receive value for their investments. Always remember that pricing can fluctuate based on market conditions; thus, remaining informed and adaptable is key to successful procurement.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing compressors industrial With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Compressors Industrial
In the realm of industrial operations, the selection of equipment is critical for optimizing performance and efficiency. While compressors industrial play a vital role in various applications, buyers should also consider alternative technologies that may offer specific advantages depending on their operational needs. This analysis compares compressors industrial with two viable alternatives: vacuum pumps and gas generators.
| Comparison Aspect | Compressors Industrial | Vacuum Pumps | Gas Generators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High pressure, suitable for pneumatic tools and machinery | Effective for creating vacuums for various industrial processes | Provides electrical power for operations |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment; ongoing energy costs | Generally lower initial cost but can incur high maintenance | High initial investment; variable fuel costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires a dedicated space and installation | Easier to install with less space requirement | Requires infrastructure for fuel supply and exhaust management |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance | Less frequent maintenance but specific to vacuum systems | Regular maintenance needed; fuel system checks are crucial |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for manufacturing, automotive, and construction sectors | Best for packaging, chemical processing, and laboratories | Suitable for remote operations, construction sites, and backup power |
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum pumps are designed to remove air and gases from a sealed environment, thus creating a vacuum. Their efficiency is particularly beneficial in applications like packaging, where maintaining a controlled atmosphere is crucial. The initial investment for vacuum pumps is typically lower than that for industrial compressors, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to minimize upfront costs. However, the maintenance can be unique to the specific vacuum system in use, requiring specialized knowledge.
Evaluating Gas Generators as an Alternative
Gas generators convert fuel into electrical energy, making them essential for operations that require a reliable power source, especially in remote areas. They can serve as a backup power source or provide electricity for pneumatic tools in locations without grid access. While the initial investment in gas generators can be high, they offer flexibility in power supply. However, they require ongoing fuel management and maintenance, which can add complexity to operations.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate solution for your industrial needs involves a careful evaluation of your specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Compressors industrial provide robust performance for applications requiring high pressure, but alternatives like vacuum pumps and gas generators can offer distinct advantages depending on the context. By thoroughly assessing the pros and cons of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals and operational efficiencies.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for compressors industrial
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Industrial Compressors?
When assessing industrial compressors, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Pressure Rating (PSI)
The pressure rating, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates the maximum pressure the compressor can generate. This is vital for applications that require specific pressure levels to operate machinery efficiently. Selecting a compressor with an appropriate pressure rating ensures optimal performance and prevents equipment failure. -
Flow Rate (CFM)
The flow rate, expressed in cubic feet per minute (CFM), measures the volume of air the compressor can deliver. It is essential for determining whether a compressor can support the air demand of your tools and machinery. A compressor with a higher CFM rating can accommodate multiple tools simultaneously, enhancing productivity in industrial settings. -
Motor Power (HP)
The horsepower (HP) of the motor indicates the compressor’s ability to perform work. A higher HP rating typically translates to greater efficiency and capacity. For industrial applications, selecting a compressor with adequate motor power is critical to ensure it can handle the workload without overheating or underperforming. -
Tank Size (Gallon)
The tank size, measured in gallons, affects how much compressed air the system can store. Larger tanks provide a buffer for high-demand applications, allowing for continuous operation without frequent cycling. This is particularly important in industries where air supply consistency is crucial for production processes. -
Noise Level (dBA)
Noise level, measured in decibels (dBA), indicates how loud the compressor operates. This is especially relevant in environments where noise regulations exist or in workplaces aiming to enhance employee comfort. Selecting a quieter compressor can lead to a more pleasant working environment and compliance with local noise ordinances.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Industrial Compressor Market?
Familiarizing yourself with industry-specific terminology can streamline communication and negotiation processes. Here are some common terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components or products that are used in another company’s end product. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers who seek quality and compatibility in their compressors. Working with reputable OEMs can enhance reliability and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, especially for businesses that may not require large quantities. This term often affects pricing, as larger orders may lead to discounts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that potential buyers send to suppliers to solicit pricing and other details for specific products. Crafting a clear RFQ helps ensure you receive accurate and comparable quotes, facilitating better purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for managing shipping costs and liabilities, ensuring that both parties are clear about who is responsible for various aspects of the shipping process. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the compressor against defects in materials or workmanship. Knowing the warranty terms can provide peace of mind and protect your investment, making it an important consideration when selecting a compressor. -
Service Interval
The service interval specifies how often a compressor should be maintained or serviced to ensure optimal performance. Understanding this helps businesses plan maintenance schedules and budget for downtime, which is crucial for operational efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the industrial compressor market more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the compressors industrial Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Global Compressors Industrial Market?
The global compressors industrial market is experiencing significant growth, driven by rising demand across various sectors such as manufacturing, construction, and oil & gas. Key drivers include the increasing need for energy efficiency and the growing adoption of automation technologies. B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a shift towards more advanced compressor systems that not only enhance performance but also reduce energy consumption.
Emerging trends include the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) in compressor systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which minimizes downtime and maintenance costs. Additionally, the trend toward modular compressor designs offers flexibility and scalability, enabling businesses to adapt to changing operational demands. Another noteworthy trend is the increasing focus on digital procurement solutions. B2B buyers are leveraging online platforms for sourcing, which streamlines the procurement process and enhances transparency in pricing and availability.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors, particularly in the Middle East and Africa, where infrastructure development is a priority. Buyers in these regions should consider the impact of local regulations and trade agreements on sourcing strategies, as these can affect product availability and pricing.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Operations in the Compressors Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the compressors industrial sector, as environmental regulations tighten globally. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and environmental impact. This includes sourcing compressors that incorporate energy-efficient technologies and sustainable materials.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are encouraged to partner with manufacturers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials in compressor production is gaining traction. Manufacturers are exploring alternative materials that reduce environmental impact without compromising performance. For instance, the adoption of recyclable components and eco-friendly lubricants can significantly enhance the sustainability profile of compressors.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
In summary, aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals not only mitigates risks associated with regulatory compliance but also strengthens brand reputation, making it an essential consideration for B2B buyers in the compressors industrial sector.
What Is the Historical Context of the Compressors Industrial Sector?
The compressors industrial sector has evolved significantly over the last century, transitioning from simple mechanical devices to sophisticated systems integrated with advanced technologies. Early compressors were primarily used in mining and construction, focusing on basic functionality. However, as industries developed and automation became prevalent, the demand for more efficient and reliable compressor systems surged.
The 1970s oil crisis catalyzed innovations in energy efficiency, prompting manufacturers to design compressors that used less power while maintaining output. By the 1990s, digital technologies began to influence compressor design, leading to the development of smart compressors capable of real-time performance monitoring.
Today, the focus has shifted towards sustainability, with manufacturers investing in eco-friendly technologies and practices. This historical context highlights the ongoing evolution of the compressors industrial sector, emphasizing the importance of adaptability for B2B buyers seeking to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of compressors industrial
-
How do I choose the right industrial compressor for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate industrial compressor hinges on several factors including your specific application, required pressure levels, and airflow capacity. First, assess the tools and machinery that will be powered by the compressor to determine the necessary horsepower and tank size. Additionally, consider the type of compressor—such as reciprocating, rotary screw, or centrifugal—based on the operational efficiency and maintenance costs. Finally, evaluate energy efficiency ratings to reduce long-term operational expenses, especially in energy-sensitive regions like Africa and South America. -
What are the key features to look for in a commercial air compressor?
When sourcing a commercial air compressor, focus on essential features such as reliability, ease of maintenance, and energy efficiency. Look for compressors with high-quality components that promise longevity, as well as those that offer user-friendly maintenance options. Noise levels are also critical; consider models designed for quiet operation if your business environment demands it. Additionally, features like variable speed drives can enhance efficiency, making them a worthwhile investment for businesses aiming to reduce energy costs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for industrial compressors?
MOQs for industrial compressors vary significantly between suppliers and can depend on the type of compressor and customization options. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs ranging from one unit to multiple units based on production capabilities and market demand. For international buyers, it’s advisable to negotiate MOQs based on your purchasing capacity and frequency of orders. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses, so it’s beneficial to discuss your needs upfront. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing compressors internationally?
Payment terms for international compressor purchases can vary, often depending on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness. Common options include advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may also offer financing options or installment plans for larger orders. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods and associated fees upfront, especially when dealing with international transactions, to avoid unexpected costs or delays in shipment. -
How can I vet suppliers when sourcing industrial compressors?
To effectively vet suppliers, conduct thorough research that includes checking their industry reputation, customer reviews, and case studies. Request references from other businesses that have procured compressors from them. Additionally, evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, compliance with international quality standards, and after-sales support. A site visit or virtual tour of their facilities can also provide insights into their operational practices and product quality. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from compressor manufacturers?
Reputable compressor manufacturers typically implement stringent quality assurance (QA) processes that include testing for performance, safety, and durability. Look for suppliers that provide certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to international quality management standards. Additionally, inquire about the warranty and return policies to ensure that you are covered in case of defects. A robust QA process is indicative of a manufacturer’s commitment to delivering reliable and efficient compressors. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international compressor shipments?
When importing compressors, logistics play a crucial role in ensuring timely delivery. Consider the shipping method—air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for large shipments but takes longer. Be aware of customs regulations and ensure all necessary documentation, such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, are in order. Collaborating with a freight forwarder familiar with your destination country’s import requirements can streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. -
Can I customize compressors to meet specific operational needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for industrial compressors to suit specific operational requirements. Customizations may include modifications to tank size, pressure settings, or additional features like soundproofing or integrated dryers. When discussing customization, clearly outline your needs and ask about the associated costs and lead times. Custom solutions can significantly enhance operational efficiency and ensure that the compressor aligns perfectly with your business processes.
Top 5 Compressors Industrial Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Atlas Copco – Air Compressors and Industrial Solutions
Domain: atlascopco.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Atlas Copco offers a wide range of air compressors and industrial solutions, including oil-free compressors, oil-injected compressors, piston compressors, rotary screw compressors, and centrifugal compressors. Their products are designed for various industries such as aquaculture, automotive, biogas production, breweries, cement, chemical/petrochemical, food and beverage, mining, oil and gas, phar…
2. Compressor Pros – Industrial Gold Two Stage Air Compressors
Domain: compressorpros.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: This company, Compressor Pros – Industrial Gold Two Stage Air Compressors, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Sullair – Industrial Air Compressors
Domain: america.sullair.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Sullair Industrial Air Compressors are designed for reliability, durability, and performance. Key features include:
– Oil flooded industrial air compressors
– 10-Year Diamond Warranty for models up to 150 psi (except ShopTek)
– 5-Year Warranty for models above 150 psi and ShopTek
– Factory filled with genuine Sullube® compressor fluid
– Sullair Touch Screen (STS) Controller for performance mo…
4. Quincy – QGS 7.5 HP Rotary Screw Air Compressor
Domain: aircompressors.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Air Compressors for Industrial Use, including Piston Compressors, Oil Injected Rotary Screw Compressors, Oil-Free Scroll Air Compressors, and various Air Dryers (Refrigerated and Desiccant). Featured products include: Quincy QGS 7.5 Horsepower 60 Gallon Tank Mounted Rotary Screw Air Compressor (Original Price: $8,244.00), Quincy QT MAX Duplex Continuous Use Piston Air Compressor (Original Price: $…
5. Industrial Air – Air Compressors
Domain: industrialairusa.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: This company, Industrial Air – Air Compressors, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for compressors industrial
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Compressor Procurement?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing in the industrial compressor sector is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By leveraging detailed market insights, international buyers can identify suppliers who not only meet their technical specifications but also provide competitive pricing and reliable service. Establishing strong relationships with reputable manufacturers facilitates access to advanced technologies and innovations, ensuring that your operations remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Furthermore, with global supply chains becoming increasingly interconnected, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must remain proactive in their sourcing strategies. This includes evaluating potential suppliers based on their sustainability practices, responsiveness, and ability to meet local regulations.
As we look ahead, the demand for high-performance compressors is set to rise, driven by industrial growth and technological advancements. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to refine their sourcing strategies and align with suppliers that can deliver not just products, but comprehensive solutions. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your operational capabilities and secure your position in the global marketplace. Take action today—invest in strategic sourcing to future-proof your business and drive sustainable growth.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to compressors industrial
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.