Is Your Garment Barcode Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for garment barcode
In an increasingly competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality garment barcodes presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The ability to effectively track inventory and enhance operational efficiency is crucial, particularly for businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including powerhouse markets like Germany and Vietnam). This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of garment barcodes, exploring various types, applications, and the latest trends in labeling technology.
Within these pages, you will find actionable insights on how to navigate the complexities of sourcing garment barcodes, including essential factors for supplier vetting, cost considerations, and compliance with international standards. Whether you are looking for iron-on labels, sew-on tags, or custom printed solutions, this guide equips you with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
By understanding the nuances of garment barcodes and their applications, you can enhance your supply chain management and improve customer satisfaction through better inventory tracking. Empower your business with the tools and information needed to thrive in the global market, ensuring that you remain competitive and responsive to ever-evolving consumer demands.
Understanding garment barcode Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| UPC Barcode | Universal Product Code, 12 digits, widely recognized | Retail sales, inventory management | Pros: Standardized, easy to scan. Cons: Limited data capacity. |
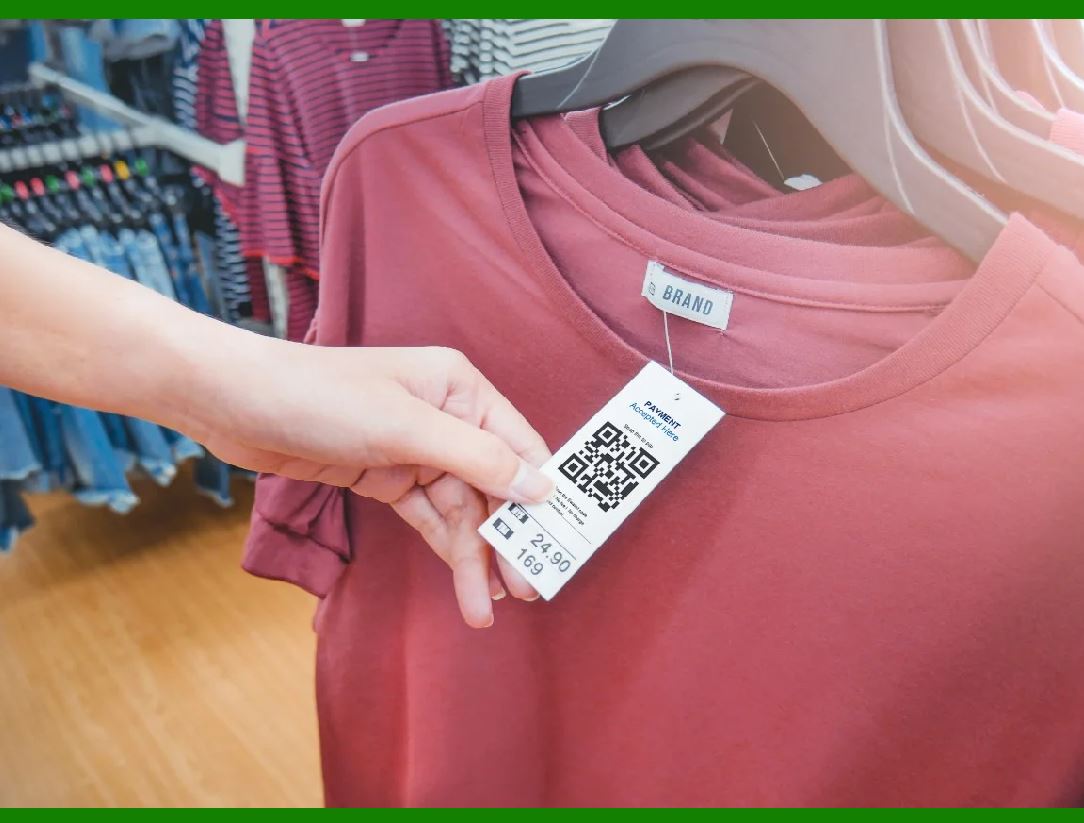
| QR Code Barcode | Square-shaped, can store URLs and additional data | Marketing, product information | Pros: High data capacity, interactive. Cons: Requires a scanner/app. |
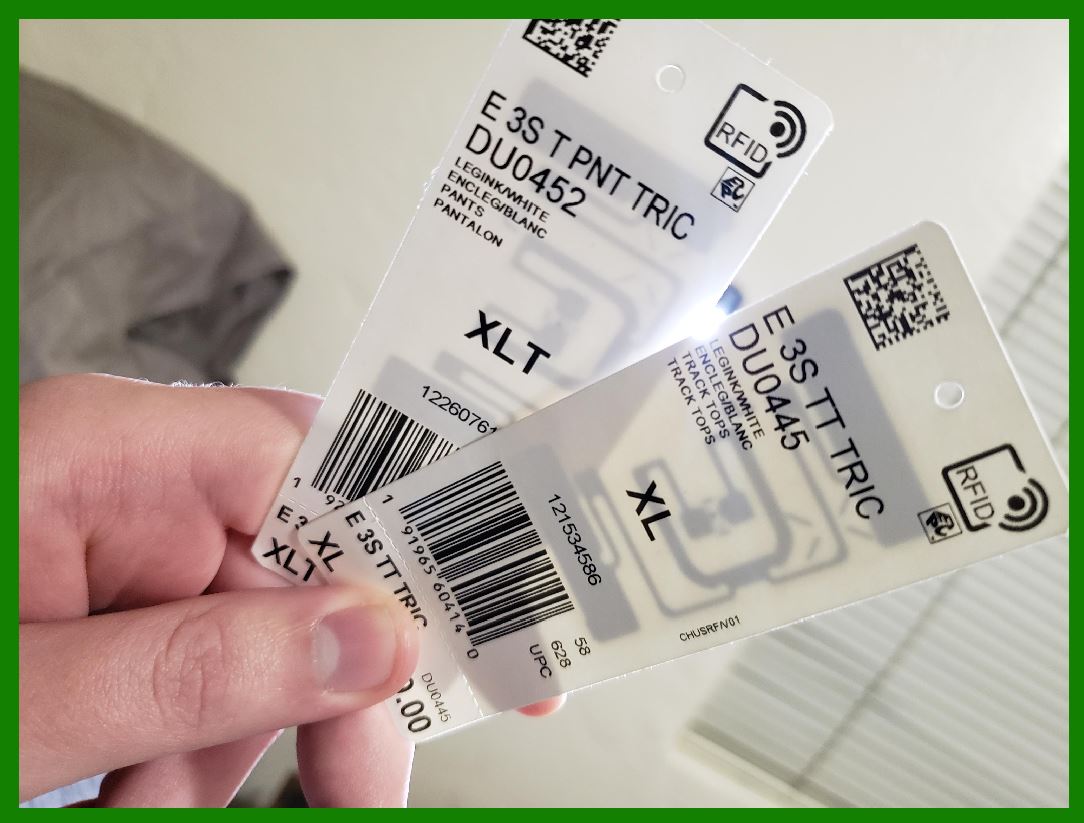
| Sew-On Barcode Tags | Durable fabric labels, can withstand washing | Textile tracking, rental garments | Pros: Long-lasting, customizable. Cons: More costly than adhesive options. |
| Iron-On Barcode Labels | Heat-applied labels, suitable for various fabrics | Garment manufacturing, asset tracking | Pros: Easy application, discreet. Cons: May not last as long as sew-on. |
| Sequential Barcode Labels | Unique identifiers in a sequential order | Inventory control, asset management | Pros: Easy tracking, minimizes errors. Cons: Requires careful management of sequences. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of UPC Barcodes for Garments?
Universal Product Codes (UPCs) are 12-digit barcodes that are universally recognized across various retail environments. These barcodes are primarily used for retail sales and inventory management, allowing businesses to streamline checkout processes and maintain accurate stock levels. When purchasing UPC barcodes, buyers should consider the initial cost of obtaining these codes and the need for consistent scanning technology to ensure efficiency.
How Do QR Code Barcodes Enhance Marketing and Consumer Engagement?
QR Code barcodes are distinct for their square shape and ability to store extensive data, including URLs and product information. They are increasingly used in marketing campaigns and product packaging to engage consumers directly. B2B buyers should evaluate the potential for customer interaction and data collection, recognizing that while QR Codes offer high data capacity, they require consumers to have scanning apps or devices.
Why Choose Sew-On Barcode Tags for Textile Tracking?
Sew-on barcode tags are made from durable fabric and are designed to withstand repeated wash cycles, making them ideal for textile tracking and rental garments. These tags can be customized with specific information and are sewn into the garment during manufacturing. Buyers should consider the higher upfront costs and labor involved in applying these tags, but the long-term durability and reliability can justify the investment.
What Are the Advantages of Using Iron-On Barcode Labels in Garment Production?
Iron-on barcode labels are heat-applied to garments, providing a versatile solution for various fabric types. They are especially useful in garment manufacturing and asset tracking, where quick application is essential. While these labels are easy to apply and can be placed discreetly, buyers should be aware that they may not offer the same longevity as sew-on options, making them better suited for less demanding environments.
How Do Sequential Barcode Labels Improve Inventory Management?
Sequential barcode labels feature unique identifiers arranged in a logical order, facilitating easy tracking of inventory and assets. This method is particularly beneficial for businesses managing large quantities of products, as it minimizes the risk of errors in stock management. Buyers should consider the importance of maintaining accurate records and the necessary systems for managing these sequences, as improper handling can lead to confusion and inefficiencies.
Key Industrial Applications of garment barcode
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of garment barcode | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Inventory Management | Streamlines stock tracking, reduces shrinkage, and enhances order accuracy. | Ensure barcode compatibility with existing POS systems and software. |
| Textile Manufacturing | Production Tracking | Improves efficiency by tracking materials and products through the supply chain. | Look for durable labels that withstand manufacturing processes. |
| Rental Services | Asset Management | Facilitates tracking of rental garments, reducing losses and improving turnover. | Choose labels that are easy to apply and remove without damage. |
| E-commerce | Order Fulfillment | Enhances picking accuracy and speeds up shipping processes. | Prioritize labels that can be printed on-demand and are easily scannable. |
| Healthcare | Patient Garment Tracking | Ensures proper identification and tracking of patient clothing, reducing mix-ups. | Select labels that are resistant to washing and sterilization. |
How is Garment Barcode Used in Retail for Inventory Management?
In the retail sector, garment barcodes play a crucial role in inventory management. They enable businesses to track stock levels in real-time, minimizing the risk of overstocking or stockouts. This system not only enhances order accuracy but also reduces shrinkage caused by misplacement or theft. For international buyers, it is essential to ensure that the barcodes are compatible with existing point-of-sale (POS) systems and inventory management software to maximize efficiency.
What Benefits Does Garment Barcode Provide in Textile Manufacturing?
In textile manufacturing, garment barcodes are utilized for effective production tracking. By tagging raw materials and finished products, manufacturers can monitor their items throughout the supply chain, leading to improved operational efficiency. This tracking system helps identify bottlenecks and facilitates better resource allocation. Buyers should consider sourcing durable labels that can withstand various manufacturing processes, including washing and dyeing.
How Do Rental Services Leverage Garment Barcode for Asset Management?
For rental services, garment barcodes are essential for asset management. They simplify the tracking of rental garments, ensuring that items are returned on time and in good condition. This technology reduces losses and improves turnover rates, significantly impacting profitability. When sourcing barcodes for rental applications, it is vital to select labels that can be easily applied and removed without damaging the garment, as well as those that maintain readability after multiple uses.
In What Ways Does Garment Barcode Enhance E-commerce Order Fulfillment?
In the e-commerce sector, garment barcodes streamline order fulfillment processes. By using barcodes for picking and packing, businesses can enhance accuracy and speed, ensuring that the correct items are shipped to customers. This efficiency is crucial in maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty. Buyers should prioritize sourcing labels that can be printed on-demand and are designed for easy scanning to facilitate rapid processing.
How is Garment Barcode Important for Patient Garment Tracking in Healthcare?
In healthcare, garment barcodes are vital for patient garment tracking, ensuring that each patient’s clothing is accurately identified and tracked. This reduces the risk of mix-ups and enhances the overall patient experience. For international buyers in the healthcare sector, it is important to select labels that can withstand multiple washings and sterilization processes while maintaining their scannability. This ensures compliance with healthcare standards and promotes operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘garment barcode’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Label Durability for Garment Tracking
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the garment industry face significant challenges with label durability. Traditional barcodes can wear off or become unreadable after multiple wash cycles, especially in high-volume laundry settings such as hotels or rental services. This leads to issues with inventory management, as garments can become untrackable, resulting in lost revenue and increased operational costs. Buyers often find themselves replacing labels frequently, which not only affects their bottom line but also disrupts supply chain efficiency.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should consider investing in high-quality, durable garment barcode labels. Options like iron-on or sew-on barcode tags provide superior durability, ensuring that the labels remain intact even after repeated laundering. When sourcing these labels, buyers should look for manufacturers that guarantee their products can withstand various environmental conditions, such as moisture, abrasion, and heat. Additionally, implementing a robust quality control process during the labeling phase can help ensure that only labels that meet durability standards are used. Collaborating with suppliers who offer verification services for barcode readability can further enhance tracking accuracy and reliability.
Scenario 2: Incompatibility with Existing Inventory Management Systems
The Problem: Another common pain point arises when garment barcodes are incompatible with a buyer’s existing inventory management systems. This can lead to inefficiencies in tracking and processing garments, especially when businesses are integrating new products or technologies. Buyers may experience frustration when their barcodes fail to scan or do not sync properly with their software, resulting in time-consuming manual entry and potential errors in inventory data.
The Solution: To mitigate this compatibility issue, buyers should conduct thorough research on their inventory management systems before selecting garment barcode solutions. It’s essential to ensure that the barcodes adhere to industry standards such as UPC or EAN, which are widely recognized and compatible with most systems. Working closely with software providers to understand the specific requirements for barcode formats can streamline this process. Additionally, buyers can benefit from investing in customizable barcode solutions that allow them to generate labels tailored to their system’s specifications, thus ensuring seamless integration and reducing the risk of operational disruptions.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Data Management for Barcode Labeling
The Problem: Managing the data associated with garment barcodes can be a significant challenge for B2B buyers. As businesses expand and diversify their product lines, the complexity of maintaining accurate and up-to-date data for each garment increases. This often leads to inconsistencies in labeling, such as incorrect product information or missing barcodes, which can create confusion during inventory audits and sales processes.
The Solution: Implementing a comprehensive data management strategy is crucial for overcoming these challenges. Buyers should utilize advanced barcode label printing systems that allow for dynamic data imports from existing databases or spreadsheets. This enables automatic updates and reduces the likelihood of errors associated with manual entry. Collaborating with data technicians or third-party services that specialize in barcode data management can provide valuable support in organizing and cleansing product data. Additionally, regular audits and training for staff on data entry best practices can help maintain the integrity of the information linked to each garment barcode, ensuring smooth operations and accurate inventory tracking.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for garment barcode
What Are the Key Materials Used in Garment Barcodes?
When selecting materials for garment barcodes, it’s essential to consider various factors such as durability, cost, and compatibility with the intended application. Below are analyses of four common materials used for garment barcodes, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Properties of Polyester for Garment Barcodes?
Polyester is a synthetic fabric known for its durability and resistance to environmental factors. It typically withstands temperatures ranging from -40°C to 150°C, making it suitable for various climates. Polyester labels are resistant to moisture, abrasion, and fading, which is crucial for garments that undergo frequent washing.
Pros: Polyester is cost-effective and offers high durability, making it ideal for long-term use. Its resistance to various chemicals ensures that barcodes remain legible even after multiple washes.
Cons: While polyester is durable, it may not be as environmentally friendly as natural fibers. Additionally, it may require specific adhesives for optimal application, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Polyester is compatible with thermal transfer printing, ensuring high-quality barcode resolution. However, buyers should verify that their printing equipment can handle polyester labels.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D5034 (breaking strength) is essential. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East often prefer materials that meet REACH regulations regarding chemical safety.
How Does Cotton Perform as a Material for Garment Barcodes?
Cotton is a natural fiber that offers breathability and comfort, making it a popular choice for clothing labels. It can withstand temperatures up to 200°C, which is beneficial for high-temperature laundering processes.
Pros: Cotton labels are soft, making them suitable for garments where comfort is a priority. They are also biodegradable, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Cons: Cotton is less durable than synthetic materials and may degrade faster when exposed to harsh chemicals or high temperatures. This can lead to barcode fading over time.
Impact on Application: Cotton labels are compatible with both direct thermal and thermal transfer printing methods, but they may require special coatings to enhance durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that cotton labels meet the relevant standards for textile labeling in their region, such as the Oeko-Tex Standard 100, which tests for harmful substances.
What Are the Advantages of Vinyl for Garment Barcodes?
Vinyl is a synthetic material known for its flexibility and resistance to moisture, making it a popular choice for outdoor garments and items exposed to various elements. Vinyl can withstand temperatures from -10°C to 60°C.
Pros: Vinyl labels are waterproof and resistant to tearing, ensuring that barcodes remain intact in challenging environments. They are also easy to clean, making them suitable for garments that require frequent washing.
Cons: Vinyl can be more expensive than other materials, and its production process may have a higher environmental impact. Additionally, it may not be as breathable as natural fibers.
Impact on Application: Vinyl is ideal for thermal transfer printing, providing high-resolution barcodes that are easy to scan. However, it may not be suitable for all garment types due to its weight and feel.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations is crucial, especially in regions with strict plastic use laws. Buyers should also check for compatibility with local textile standards.
Why Choose Paper for Garment Barcodes?
Paper labels are commonly used for temporary tagging and promotional items. They are lightweight and can be printed in high resolution, making them visually appealing.
Pros: Paper is cost-effective and readily available, making it a popular choice for short-term applications. It can be easily printed with various designs and information.
Cons: Paper labels are less durable than synthetic options and may not withstand moisture or frequent washing. They are generally suitable for non-washable garments.
Impact on Application: Paper labels are best suited for direct thermal printing. However, they may not be appropriate for long-term use where durability is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that paper labels comply with local regulations regarding labeling and packaging, especially in regions where recycling is prioritized.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Garment Barcodes
| Material | Typical Use Case for garment barcode | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester | Long-term garment labels | High durability and moisture resistance | Less environmentally friendly | Medium |
| Cotton | Comfortable garment labels | Biodegradable and soft | Less durable, prone to fading | Low |
| Vinyl | Outdoor and moisture-resistant garments | Waterproof and tear-resistant | Higher cost, less breathable | High |
| Paper | Temporary tags and promotions | Cost-effective and easy to print | Not durable for washing | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used for garment barcodes, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for garment barcode
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Garment Barcodes?
The manufacturing of garment barcodes involves several critical stages designed to ensure durability, readability, and compliance with international standards. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages:
Material Preparation: Selecting Quality Substrates
The first step in manufacturing garment barcodes is material preparation, which involves selecting appropriate substrates. Common materials include polyester, nylon, and paper-based options, each chosen based on the intended application and environmental conditions. For instance, polyester is favored for its moisture resistance and durability, making it ideal for garments that undergo frequent washing. The selected materials must meet specific industry standards to ensure they can withstand wear and tear while maintaining barcode readability.
Forming: Printing Techniques for Clarity and Longevity
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming, which typically involves printing the barcode. High-quality thermal transfer printing is often employed to create sharp, clear barcodes that are resistant to fading and abrasion. This technique uses heat to transfer ink from a ribbon onto the substrate, ensuring high-resolution images that meet the necessary scanning requirements. Additionally, advanced printing technologies, such as digital printing, can be utilized for custom designs and rapid prototyping.
Assembly: Affixing Barcodes to Garments
The assembly stage involves affixing the printed barcodes to the garment. This can be achieved through various methods, including sewing, ironing, or adhesive application. Sew-on tags are preferred when durability is essential, as they can withstand extensive washing and handling. Iron-on labels provide a quick application method but should be placed in non-visible areas to maintain the garment’s aesthetic. The choice of attachment method will depend on the garment type, usage, and specific buyer requirements.
Finishing: Quality Control and Final Touches
The finishing stage encompasses several processes, including trimming excess material, applying protective coatings, and conducting quality checks. Protective coatings can enhance the barcode’s resistance to moisture and chemicals, ensuring longevity. This stage is crucial for ensuring that every label not only looks good but also functions correctly.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Garment Barcode Production?
Quality assurance is vital in the production of garment barcodes, ensuring that each label meets international standards and performs reliably in various environments.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Garment Barcodes?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in the quality assurance process. ISO 9001 outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS), ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) for industrial applications may apply depending on the barcode’s usage.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Barcode Manufacturing?
Quality control in garment barcode production typically involves several checkpoints, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage verifies that all raw materials meet specified quality standards before production begins. This includes checking substrate durability, ink quality, and adhesion properties.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring ensures that printing and assembly processes remain within established tolerances. This may involve regular checks of barcode readability and adherence to specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, each batch undergoes rigorous testing to ensure that all barcodes are functional and meet quality standards. This includes scanning tests to confirm that barcodes can be read by standard scanners.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure barcode quality:
-
Readability Testing: This involves scanning the barcodes with various types of scanners to ensure they are easily readable under different conditions.
-
Durability Testing: Barcodes are subjected to wear tests, including exposure to moisture, abrasion, and chemicals, to ensure they maintain their integrity over time.
-
Adhesion Testing: For iron-on and adhesive labels, testing is conducted to ensure that the barcode remains affixed to the garment after multiple wash cycles.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensuring consistent product quality. Here are several methods to consider:
Conducting Supplier Audits: What to Look For
One of the most effective ways to verify a supplier’s QC processes is through on-site audits. Buyers should look for compliance with international quality standards, proper documentation of quality checks, and evidence of continuous improvement practices. An audit can also reveal the supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices, which is increasingly important in the global marketplace.
Requesting Quality Control Reports: What Should Be Included?
Buyers should request detailed quality control reports from suppliers, which should include data on IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports provide insights into the frequency of quality checks, the outcomes of those checks, and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services: Why Is It Beneficial?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control processes. These services can conduct audits, perform testing, and provide certifications that confirm compliance with international standards. This additional layer of verification is particularly beneficial for buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where local regulations and standards may differ significantly from European or Middle Eastern markets.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
When sourcing garment barcodes internationally, buyers must navigate various nuances that can affect quality assurance. For example, understanding regional regulations and compliance requirements is essential. Buyers should also be aware of cultural differences that may influence manufacturing practices and quality perceptions.
Additionally, language barriers can complicate communication about quality requirements. It is advisable to establish clear specifications and expectations in advance, possibly using visual aids or samples to ensure mutual understanding.
By focusing on these manufacturing and quality assurance processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for garment barcodes, ultimately ensuring that their products meet market demands and customer expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘garment barcode’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of the garment industry, effective labeling is crucial for inventory management, sales tracking, and compliance with international standards. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers looking to source garment barcodes, ensuring that they make informed decisions while optimizing their supply chain processes.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements for garment barcodes. Consider factors such as size, type (UPC, QR code, etc.), material (iron-on, sew-on, heat seal), and the environmental conditions the labels will face.
- Why it matters: Having well-defined specifications helps streamline the sourcing process and ensures that the labels will meet your operational needs.
- What to look for: Ensure the specifications align with your inventory management systems and any regulatory requirements for your target markets.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in garment barcodes. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of candidates.
- Why it matters: A diverse supplier pool increases your chances of finding the best fit for your needs.
- What to look for: Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in the garment industry, positive customer reviews, and relevant certifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Once you have a list of potential suppliers, assess their capabilities to meet your specific requirements. Request samples of their products and inquire about their production processes.
- Why it matters: Understanding a supplier’s capabilities can prevent future issues related to quality or delivery.
- What to look for: Ensure that suppliers can provide labels that are durable and scan accurately under various conditions.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
It is essential to ensure that your suppliers comply with industry standards and regulations. Request documentation of certifications such as ISO, GS1, or other relevant accreditations.
- Why it matters: Compliance with industry standards guarantees that your products will meet the necessary quality and safety benchmarks.
- What to look for: Certifications specific to textile labeling and barcode printing should be prioritized.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Terms
Request detailed quotes from shortlisted suppliers, including pricing, minimum order quantities, lead times, and payment terms. Compare these quotes to evaluate which supplier offers the best overall value.
- Why it matters: Transparent pricing enables you to budget effectively and avoid unexpected costs.
- What to look for: Pay attention to additional costs such as shipping, taxes, and potential tariffs, especially when sourcing internationally.
Step 6: Request References and Case Studies
Before finalizing a supplier, ask for references and case studies from previous clients, especially those in the garment industry. This will provide insights into their reliability and quality of service.
- Why it matters: References can validate a supplier’s claims and provide reassurance of their capabilities.
- What to look for: Look for feedback on the supplier’s responsiveness, quality consistency, and ability to meet deadlines.
Step 7: Finalize the Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, draft a comprehensive agreement that outlines all terms, including product specifications, pricing, delivery schedules, and quality assurance measures.
- Why it matters: A clear agreement protects both parties and sets expectations from the outset.
- What to look for: Ensure that the contract includes provisions for handling disputes and guarantees regarding product quality and delivery timelines.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively source garment barcodes that meet their operational needs while ensuring compliance and quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for garment barcode Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Garment Barcode Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure associated with garment barcode sourcing is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their purchasing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of material used for barcodes can significantly influence pricing. Options such as heat seal labels, sew-on tags, or iron-on labels vary in cost based on durability and application method. For instance, high-quality synthetic materials may incur higher costs but offer better longevity and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs are incurred during the manufacturing process, including design, printing, and application. These costs can vary based on the complexity of the design and the skill level required for production.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. A well-structured manufacturing facility can help mitigate these costs, leading to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for specialized printing equipment or dies can be significant, especially for custom designs. Buyers should inquire about these costs upfront, particularly when requesting custom barcodes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each barcode meets industry standards is critical. QC processes may add to the overall cost but are necessary to prevent issues related to barcode readability and compliance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can fluctuate based on the destination and the volume of the order. Understanding local and international shipping nuances can aid in accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs. This margin can vary depending on the supplier’s market position and the relationship they maintain with the buyer.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Garment Barcode Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of garment barcodes, which buyers should consider to enhance their procurement strategies:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact unit costs. Larger orders often lead to reduced pricing per unit, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific barcode types (e.g., UPC, QR codes) may incur additional costs. Providing clear specifications upfront can help suppliers offer more accurate quotes.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects costs. For example, eco-friendly materials may be more expensive but can appeal to environmentally conscious brands, potentially offering a marketing edge.
-
Quality and Certifications: Labels that meet specific quality standards or certifications (like ISO) may come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can all influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge more but can offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international buyers. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect overall costs and responsibilities during shipping.
What Buyer Tips Can Optimize Garment Barcode Sourcing Costs?
To achieve cost-efficiency in garment barcode sourcing, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can lead to more favorable pricing and terms. Don’t hesitate to negotiate on volume discounts or long-term contracts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider long-term costs associated with durability, maintenance, and potential replacements to gauge the true value of your investment.
-
Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions that may affect pricing.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough research on various suppliers to compare costs and offerings. Leverage online tools and resources to gather insights on market prices and product specifications.
By understanding the comprehensive cost structure, price influencers, and actionable strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals while optimizing their garment barcode sourcing process.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing garment barcode With Other Solutions
When considering the implementation of garment barcodes, it’s essential to evaluate other available solutions that can fulfill similar functions in inventory management, tracking, and operational efficiency. Below, we compare garment barcodes with two viable alternatives: RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags and QR codes (Quick Response codes). Each solution has its unique strengths and weaknesses, making it critical for B2B buyers to analyze which option aligns best with their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Garment Barcode | RFID Tags | QR Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy in scanning | Very high accuracy, no line of sight needed | Moderate accuracy, requires a camera |
| Cost | Low initial cost | Higher initial cost | Low to moderate cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to apply | Requires specialized readers | Easy to generate and print |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance required | Moderate, may need battery replacements | Minimal, but needs a scanner |
| Best Use Case | Retail and inventory tracking | Warehouse management, asset tracking | Marketing, quick access to information |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Garment Barcodes?
Garment barcodes are a well-established method for tracking apparel through a straightforward scanning process. They are cost-effective and easy to implement, as they can be printed and applied directly to garments. However, the scanning process requires line-of-sight, which can slow down operations during busy periods. Additionally, while they are reliable, they may not provide as much data as RFID tags, which can capture more information without direct scanning.
How Do RFID Tags Compare to Garment Barcodes?
RFID tags offer a significant advantage over garment barcodes in terms of performance. They can be read without needing a direct line of sight, allowing for quicker inventory checks and asset tracking. This technology is ideal for large warehouses and retail environments where speed is critical. However, the initial cost of RFID systems is higher, and they require specialized reading equipment. Maintenance can also be more complex due to the need for battery replacements in active RFID tags.
What Makes QR Codes a Viable Alternative?
QR codes present a flexible solution that can be used for various purposes, including marketing and inventory tracking. They are inexpensive to produce and easy to implement, as they can be printed on any surface. However, QR codes rely on cameras for scanning, which may not be as efficient as traditional barcode scanners. Their primary use case is in consumer engagement and information sharing rather than detailed inventory management, making them less suitable for comprehensive garment tracking compared to barcodes and RFID.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting between garment barcodes, RFID tags, and QR codes, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including budget, operational needs, and the scale of their inventory. For businesses focused on cost-effectiveness and simplicity, garment barcodes may be the best choice. In contrast, companies that prioritize speed and efficiency in large-scale inventory management might find RFID tags more beneficial. QR codes can serve a dual purpose but may lack the robust tracking capabilities required for detailed garment management. Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific operational goals and technological capabilities of the business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for garment barcode
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Garment Barcodes?
When selecting garment barcodes, understanding the essential technical properties is critical for ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry standards. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of barcode labels significantly affects their durability and application. Common materials include synthetic films (like polyester) and paper. Synthetic labels are typically more resistant to moisture and abrasion, making them ideal for garments that undergo frequent washing. Choosing the right material ensures that the barcode remains legible throughout the product’s lifecycle, which is essential for inventory management and tracking.
2. Adhesive Type
The type of adhesive used on garment barcodes is crucial for their application. There are permanent adhesives, which are designed for long-term adhesion, and removable adhesives, which allow for easier label removal without leaving residue. Understanding the adhesive’s performance in various environmental conditions, such as heat and humidity, helps in selecting the right label for specific garment types, ensuring that barcodes remain intact during processing and use.
3. Print Quality
Print quality is determined by the resolution (measured in dots per inch or DPI) and the printing technology used. High-resolution printing is essential for barcodes to be scanned accurately, especially in retail environments where speed is critical. A minimum of 300 DPI is recommended for garment barcodes to ensure clarity. This is especially important for international markets where barcode scanning accuracy can directly impact sales and inventory management.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in the barcode’s dimensions, including width and height. It is vital for ensuring compatibility with various scanning equipment and systems. A standard tolerance ensures that barcodes can be read across different devices, reducing the risk of scanning errors that can lead to inventory discrepancies. Ensuring the correct tolerance minimizes operational disruptions and enhances efficiency in supply chain management.
5. Durability
Durability encompasses the barcode’s resistance to factors like heat, moisture, and abrasion. Garment barcodes must withstand various conditions, including washing, ironing, and exposure to chemicals. Selecting labels that meet specific durability standards can prevent loss of information and scanning failures, which is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency in logistics and inventory management.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Garment Barcodes?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and decision-making processes. Here are some essential trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of garment barcodes, an OEM might provide barcode printing equipment or software that integrates with a retailer’s inventory management system.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum quantity of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to negotiate better pricing and manage inventory levels effectively. It can significantly impact production costs, especially for businesses looking to optimize their supply chain.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. When sourcing garment barcodes, buyers often use RFQs to compare costs, services, and delivery timelines, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to manage shipping costs, risks, and logistics effectively, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
5. SKU (Stock Keeping Unit)
SKU is a unique identifier for each distinct product and service that can be purchased. For garment barcodes, SKUs help in tracking inventory and sales, enabling businesses to manage their stock efficiently.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure the successful implementation of garment barcode systems in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the garment barcode Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends in the Garment Barcode Sector?
The garment barcode sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by advancements in technology and the increasing need for efficient inventory management. As global supply chains become more complex, the adoption of automated tracking systems, including barcode technology, is essential for optimizing operations. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly focusing on solutions that enhance traceability and streamline logistics. Emerging trends include the integration of QR codes for enhanced consumer interaction and the use of RFID technology to improve inventory accuracy and reduce shrinkage.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in sourcing decisions. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that offer eco-friendly materials and processes in their barcode solutions. For instance, using recycled materials for labels and ensuring that the printing processes are low-impact can significantly enhance a company’s marketability. Additionally, the rise of omnichannel retailing is pushing businesses to invest in versatile barcode solutions that can cater to both online and offline channels seamlessly.
How Is Sustainability Shaping B2B Sourcing in the Garment Barcode Sector?
Sustainability is no longer a trend but a necessity in the garment barcode sector. B2B buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impacts of their sourcing decisions. The textile industry is notorious for its ecological footprint, and integrating sustainable practices into the supply chain is crucial for long-term viability. This includes choosing barcode solutions that utilize biodegradable or recycled materials, reducing waste, and lowering carbon emissions during production.
Furthermore, ethical sourcing is becoming a priority. Buyers are seeking suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and provide transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or OEKO-TEX® can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. Incorporating these values not only mitigates risks associated with consumer backlash but also enhances brand loyalty among environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of Garment Barcodes and Their Evolution?
The evolution of garment barcodes can be traced back to the 1970s when the first UPC (Universal Product Code) was introduced. Initially used for retail, barcodes quickly became integral in inventory management across various sectors, including textiles. As technology advanced, the introduction of 2D barcodes and QR codes offered enhanced data capacity and versatility, paving the way for more sophisticated applications in garment tracking and consumer engagement.
Today, garment barcodes are not just about tracking products; they are vital tools for improving operational efficiencies, enhancing customer experiences, and supporting sustainability initiatives. This historical context highlights the importance of adapting to technological advancements and consumer expectations in the garment barcode sector, emphasizing the need for B2B buyers to stay informed about ongoing innovations.
In conclusion, understanding the market dynamics, sustainability imperatives, and historical context of garment barcodes equips international B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of garment barcode
-
How do I choose between sew-on and iron-on garment barcodes?
When selecting between sew-on and iron-on garment barcodes, consider the application method and the durability required. Sew-on labels are ideal for garments that undergo frequent washing and wear, as they provide a secure attachment and withstand harsh conditions. Conversely, iron-on labels are suitable for quick application where sewing is impractical, and they can be affixed to non-visible areas. Evaluate your production capabilities and garment types to determine the best choice for your labeling needs. -
What are the benefits of using barcodes on garments for inventory management?
Implementing barcodes on garments enhances inventory management by enabling accurate tracking and real-time data collection. This facilitates efficient stock management, reducing errors associated with manual entry. Barcodes also streamline the checkout process, improve order fulfillment accuracy, and provide valuable insights into sales patterns. Overall, they contribute to operational efficiency and help maintain optimal inventory levels. -
What customization options are available for garment barcodes?
Customization options for garment barcodes include size, color, material, and printing techniques. You can opt for different label types such as thermal transfer, direct thermal, or resin printing depending on your durability requirements. Additionally, you may include specific information such as brand logos, care instructions, or unique identifiers. Discuss your specific needs with suppliers to explore available customization options that align with your branding and operational needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for garment barcode labels?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly among suppliers, often ranging from a few hundred to several thousand labels. Factors influencing MOQs include the type of label, customization requirements, and the supplier’s production capabilities. It’s advisable to communicate your needs clearly and negotiate with suppliers to find a solution that meets your budget while ensuring you have enough stock for your production schedule. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing garment barcodes internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing typically vary based on supplier policies and the buyer’s location. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). It’s crucial to establish clear agreements upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods to protect your financial interests during international transactions. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for garment barcodes?
To ensure quality assurance for garment barcodes, request samples before placing a bulk order. Verify that the barcodes are scannable and meet your specifications in terms of durability and print quality. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer barcode verification services to confirm that all labels meet industry standards. Establishing a clear quality control process can help mitigate risks associated with subpar products. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing garment barcodes?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, delivery times, and customs regulations. Ensure that your supplier can provide reliable shipping options that meet your timeline, especially if you are operating on a tight schedule. Additionally, familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes that may apply to your shipments. Coordinating with logistics providers can streamline the delivery process and minimize delays. -
How can I vet suppliers for garment barcode sourcing?
Vetting suppliers involves assessing their reputation, production capabilities, and compliance with industry standards. Check online reviews, request references from past clients, and evaluate their certifications (e.g., ISO). It’s also beneficial to visit their facilities if possible or conduct virtual audits to understand their operations better. Engaging in direct communication to discuss your requirements can help gauge their responsiveness and reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Garment Barcode Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cleaner Supply – Custom Printed Barcode Heat Seal Labels
Domain: cleanersupply.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Custom Printed Barcode Heat Seal Labels, Size: 0.6875″ x 0.25″, Quantity: 1000 per roll, Free shipping on orders over $99, Customer service contact: 1-800-388-5410.
2. WePrintBarcodes – Iron-On & Sew-On Barcode Labels
Domain: weprintbarcodes.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: WePrintBarcodes offers Iron-On and Sew-On Barcode Labels designed for textile products, including rentals and internal assets. The labels are guaranteed to be readable and verified for quality. Sew-On Barcode Tags feature a sewing flap for easy attachment and resist moisture, abrasion, heat, fading, and washing. Iron-On Barcode Labels use a heat-activated adhesive and also resist similar environme…
3. Unitherm Inc. – Iron On Barcode Labels
Domain: unitherminc.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Iron On Barcode Labels from Unitherm Inc. are designed for tracking clothing and fabric items. They are available as preprinted labels or blank labels for self-printing, with multiple sizes in stock and custom sizes available upon request. The labels are launderable and are applied using the U35 Label Press, bonding permanently to clothing through a Heat Seal Film process. They are printed with wa…
4. MyAssetTag – Customizable Barcode Labels
Domain: myassettag.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Print Barcode Labels For Free – Printable Barcode Labels Review 4.8 stars from 9,628 reviews. The #1 Choice for Asset Tags. Free Shipping for US orders of $15.00 and more. Customizable options include size, design, color, and numbering. Available sizes: 0.5″ x 1.0″ to 3″ x 5″ and various shapes (rectangle, square, circle, ovals). Materials include vinyl, destructible vinyl, removable polyester, ta…
5. WavePLM – Garment Barcodes Explained
Domain: blog.waveplm.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Garment barcodes are unique identifiers attached to clothing items that store vital information such as size, color, style, and price. Types of barcodes include UPC (12-digit), EAN (8 or 13 digits), QR Codes (two-dimensional), and RFID Tags (electronic data storage). Benefits of garment barcodes include improved inventory management, enhanced accuracy, faster checkouts, efficient supply chain mana…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for garment barcode
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Garment Barcoding?
In today’s competitive garment industry, strategic sourcing of barcode solutions is essential for enhancing operational efficiency and inventory management. By opting for high-quality labels—such as sew-on or iron-on barcodes—businesses can ensure durability and readability, even under challenging environmental conditions. The integration of advanced printing technologies and data services allows for seamless tracking and management of textile products, catering to a variety of needs from retail to rental sectors.
How Can Buyers Leverage Strategic Sourcing for Competitive Advantage?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize suppliers who offer customizable, reliable, and eco-friendly barcode solutions. Engaging with vendors that provide comprehensive data services and quick turnaround times can significantly streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance supply chain transparency.
What’s Next for B2B Buyers in the Garment Barcode Market?
As the garment industry evolves, so too will the requirements for effective tracking and management solutions. Buyers are encouraged to explore innovative barcode technologies and forge partnerships with suppliers who can adapt to their unique needs. By investing in strategic sourcing now, businesses can position themselves for success in a rapidly changing market landscape. Embrace the future of garment barcoding to unlock new efficiencies and drive growth.