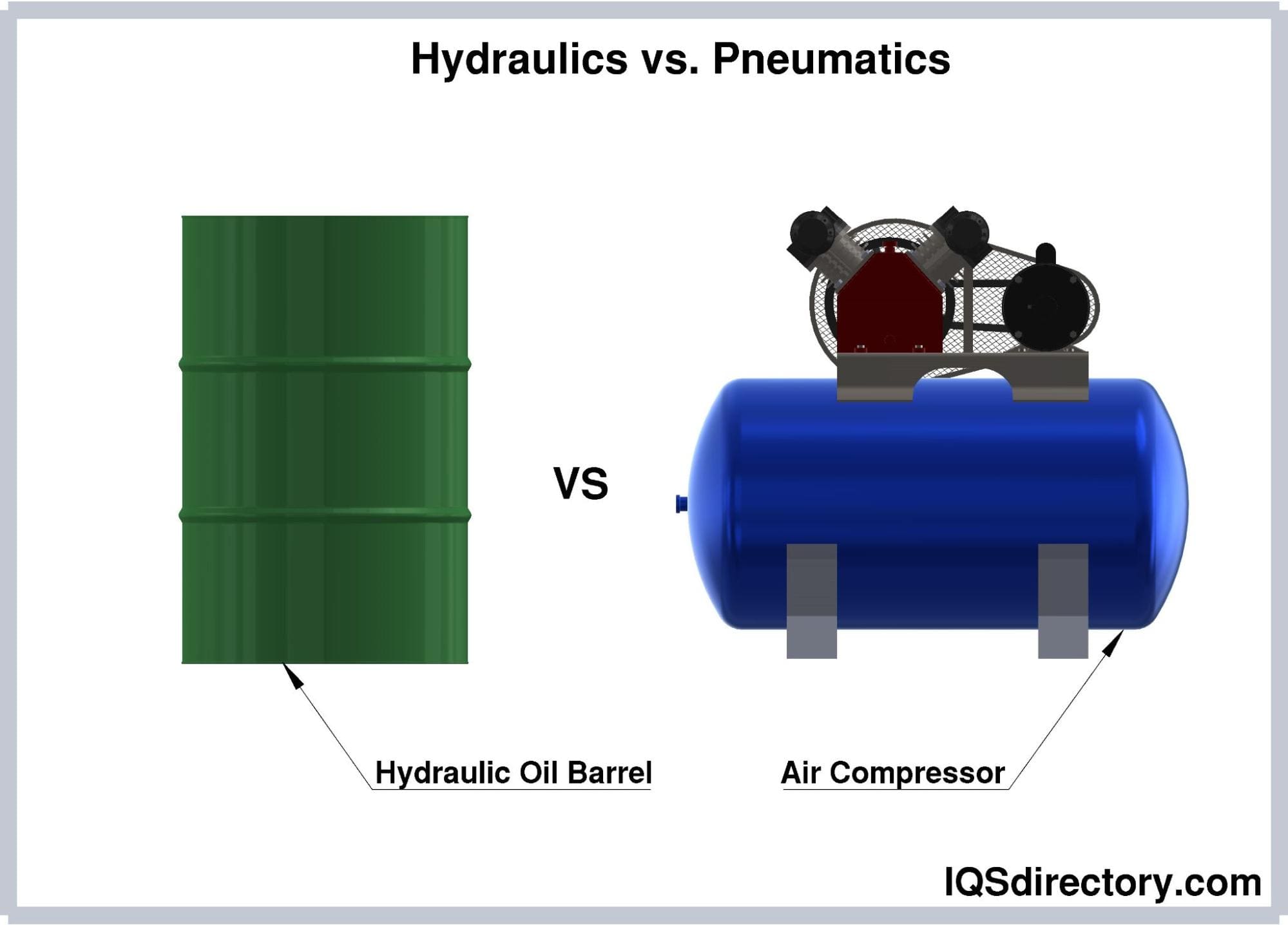
Is Your Pneumatic Vs Hydraulic Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pneumatic vs hydraulic
In today’s competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the critical challenge of choosing between pneumatic and hydraulic systems for their operations. Understanding the nuances of pneumatic versus hydraulic solutions is essential for sourcing the right equipment that meets specific project requirements, whether it’s for construction, manufacturing, or specialized applications. This guide provides a comprehensive analysis of both systems, exploring their types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations, empowering you to make informed purchasing decisions.
With detailed comparisons of performance metrics, such as strength, speed, energy efficiency, and maintenance needs, this resource is tailored for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By addressing the unique challenges and priorities of these regions, including environmental regulations and local market dynamics, this guide serves as a strategic tool to navigate the complexities of fluid power systems.
Moreover, we delve into the hygiene implications of each system, particularly relevant for industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where contamination risks are paramount. By leveraging the insights provided, you will be better equipped to select the optimal fluid power solution that aligns with your operational goals, enhances productivity, and ensures compliance with industry standards.
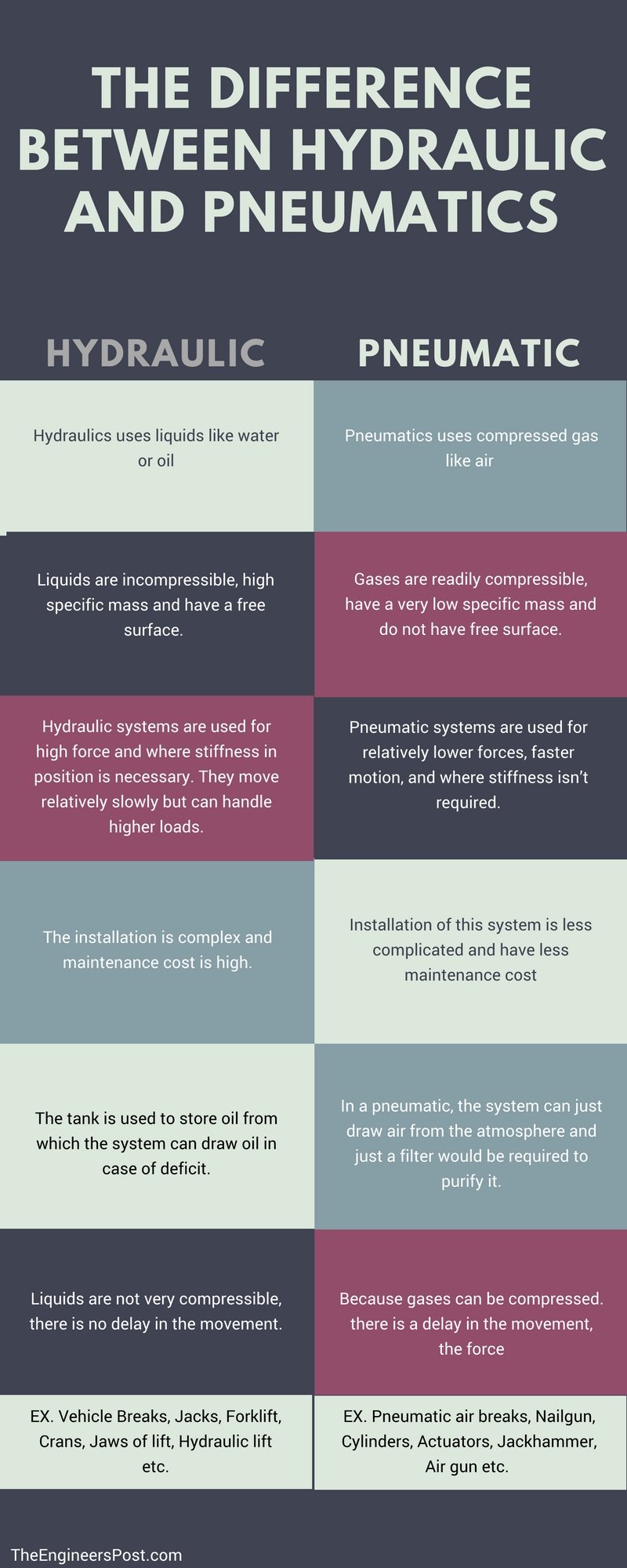
Understanding pneumatic vs hydraulic Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pneumatic Actuators | Operate using compressed air; quick response times; lower force capabilities. | Robotics, packaging, food processing, and medical devices. | Pros: Fast operation, minimal contamination risk. Cons: Limited lifting capacity, less suitable for heavy loads. |
| Hydraulic Cylinders | Utilize pressurized liquid to generate force; high pressure capabilities; more complex systems. | Construction, mining, heavy machinery, and automotive applications. | Pros: High force output, suitable for heavy lifting. Cons: Risk of leaks, requires more maintenance. |
| Pneumatic Conveying Systems | Transport materials using compressed air; ideal for bulk materials. | Food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and plastics industries. | Pros: Efficient for bulk handling, minimal contamination. Cons: Requires energy for air compression, limited distance for conveyance. |
| Hydraulic Power Units | Centralized power source for multiple hydraulic systems; energy-efficient when maintained. | Manufacturing plants, construction sites, and heavy equipment. | Pros: Versatile, can power multiple machines. Cons: Complexity in installation, potential for fluid leaks. |
| Pneumatic Tools | Handheld tools powered by compressed air; lightweight and portable. | Automotive repair, assembly lines, and maintenance operations. | Pros: Easy to use, low maintenance. Cons: Limited power compared to electric tools, dependency on air supply. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Pneumatic Actuators?
Pneumatic actuators are primarily characterized by their use of compressed air to generate movement. They are known for their rapid response times and ease of installation, making them ideal for applications requiring quick actuation, such as robotics and packaging. However, their lower force capabilities make them unsuitable for heavy lifting tasks. Buyers should consider the operational environment, as these systems are often favored in industries where hygiene is critical, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
How Do Hydraulic Cylinders Stand Out?
Hydraulic cylinders operate using pressurized liquids, enabling them to exert significant force, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications in construction and mining. Their ability to maintain high pressure allows them to handle substantial loads, but this comes with increased complexity and maintenance requirements. Buyers must evaluate the potential for leaks and corrosion, particularly in harsh environments, and ensure that proper safety measures are in place to mitigate risks associated with hydraulic fluid.
What Are Pneumatic Conveying Systems Used For?
Pneumatic conveying systems transport bulk materials using compressed air, making them effective for industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and plastics. Their design minimizes contamination risks, which is essential in sensitive environments. However, these systems require continuous energy input for air compression and may have limitations regarding the distance materials can be conveyed. B2B buyers should assess the efficiency of these systems in their specific applications, especially concerning energy consumption and material types.
What Benefits Do Hydraulic Power Units Offer?
Hydraulic power units serve as centralized sources of hydraulic power, enabling multiple machines to operate simultaneously. They are particularly energy-efficient when properly maintained, making them suitable for manufacturing and construction applications. However, their installation can be complex, and there is a risk of fluid leaks, which necessitates careful planning and maintenance. Buyers should weigh the advantages of versatility against the potential challenges of installation and upkeep.
Why Choose Pneumatic Tools for Operations?
Pneumatic tools are lightweight, portable, and powered by compressed air, making them highly convenient for automotive repair, assembly lines, and maintenance tasks. Their ease of use and low maintenance requirements appeal to many businesses. However, they may lack the power of electric tools and are dependent on a consistent air supply. B2B buyers should consider the specific tasks at hand and the availability of air supply when deciding on pneumatic tools for their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of pneumatic vs hydraulic
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pneumatic vs hydraulic | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines (pneumatics) | Increased speed and efficiency in production | Reliability of components, availability of spare parts |
| Construction | Heavy machinery operation (hydraulics) | High lifting capacity for heavy loads | Quality of hydraulic fluid, maintenance support |
| Food & Beverage | Packaging and bottling (pneumatics) | Enhanced hygiene and reduced contamination risk | Compliance with food safety standards, filtration systems |
| Mining | Excavation and material handling (hydraulics) | Ability to operate in harsh environments with power | Durability of equipment, local service availability |
| Medical Devices | Surgical tools and equipment (pneumatics) | Precision and control in medical procedures | Regulatory compliance, reliability of air supply systems |
How Are Pneumatics Used in Manufacturing Automation?
In the manufacturing sector, pneumatic systems are widely utilized in automated assembly lines for tasks such as clamping, lifting, and moving components. The rapid actuation and high-speed motion of pneumatic actuators enhance production efficiency, allowing manufacturers to meet high demand with minimal downtime. For international B2B buyers, sourcing reliable pneumatic components is crucial, as any failure can lead to production halts. Additionally, ensuring the availability of spare parts and maintenance services is essential to sustain operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
What Role Do Hydraulics Play in Construction?
Hydraulic systems are the backbone of heavy machinery used in construction, including excavators, cranes, and bulldozers. Their ability to generate substantial lifting force makes them ideal for moving heavy materials and performing demanding tasks. For businesses in regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure projects are prevalent, selecting high-quality hydraulic fluids and ensuring proper maintenance protocols are vital. Buyers should consider the local availability of parts and service support to minimize downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
Why Are Pneumatic Systems Preferred in Food & Beverage Industries?
In the food and beverage industry, pneumatic systems are favored for packaging and bottling processes due to their clean operation and minimal contamination risk. Compressed air, which is the primary medium, does not pose a hazard of contamination, making it suitable for environments that require strict hygiene standards. International buyers must focus on sourcing systems that comply with food safety regulations and incorporate effective filtration units to ensure product quality. Moreover, the ability to maintain equipment without the risk of spills or residues is a significant advantage.
How Are Hydraulics Essential in Mining Operations?
The mining industry relies heavily on hydraulic systems for excavation and material handling due to their ability to operate under extreme conditions. Hydraulic equipment can exert high force, making it essential for tasks like drilling and transporting heavy loads. For buyers in the Middle East and Africa, where mining is a critical economic driver, ensuring the durability of hydraulic components and local service availability is paramount. Additionally, understanding the local climate’s impact on equipment performance can guide procurement decisions.
What Advantages Do Pneumatic Systems Offer in Medical Devices?
Pneumatic systems are integral to the operation of various medical devices, including surgical tools and dental equipment, where precision and control are paramount. The quick response times and clean operation of pneumatic systems are critical in medical settings, where contamination can have severe consequences. International buyers must prioritize compliance with healthcare regulations and reliability in air supply systems when sourcing these technologies. Ensuring that pneumatic components are designed for easy maintenance can further enhance operational reliability in medical environments.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pneumatic vs hydraulic’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Weight Capacity in Industrial Applications
The Problem: A manufacturing plant in Brazil relies heavily on pneumatic systems for automation. However, as production demands increase, they find their pneumatic equipment struggling to lift heavier loads. The limitations of compressed air lead to inefficiencies and increased downtime, as operators frequently adjust processes to accommodate the system’s constraints. The challenge is compounded by the need for rapid product changeovers, which pneumatic systems struggle to handle, leading to frustration among the workforce and delays in production schedules.
The Solution: To address this issue, the company should conduct a thorough assessment of its lifting requirements and consider integrating hydraulic systems for heavy-duty applications. Unlike pneumatic systems, hydraulic solutions can generate significantly higher pressure and force, making them ideal for heavy lifting. By sourcing hydraulic cylinders and pumps tailored to their specific load requirements, the plant can enhance efficiency and minimize downtime. Additionally, training staff on the operational differences between pneumatic and hydraulic systems will ensure a smooth transition and optimal use of new equipment. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in hydraulic solutions can also provide insights on best practices for implementation and maintenance, ensuring the system operates effectively from the start.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over Contamination in Sensitive Environments
The Problem: A pharmaceutical company in Vietnam operates in a cleanroom environment where even minor contamination can lead to significant compliance issues and product recalls. The existing hydraulic systems pose a risk, as they can leak oil or other fluids, jeopardizing the cleanliness of the workspace. This concern leads to heightened anxiety among the quality assurance team, who must constantly monitor for potential contamination sources, diverting their focus from other critical tasks.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, the company should transition to a pneumatic system, which utilizes air as its operational medium and is less likely to introduce contaminants. When specifying the new pneumatic system, it is crucial to invest in high-quality filtration units to ensure that the compressed air is free from oil, water, and particulates. Selecting components that meet cleanroom standards will further enhance system reliability. Collaborating with vendors who have experience in cleanroom applications will help the company identify suitable pneumatic solutions that maintain air purity. Furthermore, regular maintenance and monitoring of the pneumatic system will help uphold the necessary hygiene standards, allowing the company to focus on production without the constant worry of contamination.
Scenario 3: High Energy Costs Leading to Budget Constraints
The Problem: A construction firm in South Africa has noticed a significant increase in energy costs associated with running its hydraulic machinery. The constant need for hydraulic fluid circulation to maintain system pressure results in high operational expenses, straining the company’s budget. Additionally, unplanned maintenance due to equipment wear and tear caused by energy inefficiencies adds to their financial burden, creating a need for a more cost-effective solution.
The Solution: To combat rising energy costs, the firm should evaluate the feasibility of incorporating pneumatic systems for less demanding applications. Pneumatic systems can be more energy-efficient for tasks that do not require the high force output of hydraulic systems. Moreover, implementing energy recovery solutions, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) in hydraulic pumps, can optimize energy usage in existing hydraulic systems. By working with an engineering consultant, the firm can determine which applications can be effectively serviced by pneumatics without compromising performance. Finally, investing in preventive maintenance programs for hydraulic equipment will enhance system longevity and reduce unexpected costs. By strategically balancing pneumatic and hydraulic systems based on specific application needs, the firm can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pneumatic vs hydraulic
What Are the Key Materials Used in Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
When selecting materials for pneumatic and hydraulic systems, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of each application. The choice of materials can significantly impact performance, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in these systems: steel, aluminum, plastic, and rubber.
How Does Steel Perform in Pneumatic and Hydraulic Applications?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high strength and durability, with a temperature rating that can exceed 300°C and pressure ratings that can handle thousands of psi. It also offers excellent corrosion resistance when treated or coated.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
Pros & Cons: Steel’s durability makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, especially in hydraulic systems that require high pressure. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require additional treatments to prevent corrosion, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of fluids, including hydraulic oils and water. Its strength makes it suitable for applications in mining and construction, where heavy lifting is common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with ASTM standards for steel grades. Additionally, understanding local corrosion conditions is crucial, as environmental factors can affect the longevity of steel components.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating up to 150°C. Its pressure rating is lower than steel but still adequate for many pneumatic applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which reduces the overall system weight and can lead to cost savings in transportation and installation. However, it is less durable under high pressure compared to steel, making it less suitable for heavy-duty hydraulic applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in pneumatic systems and applications requiring lightweight components, such as robotics and automotive parts. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for environments where moisture is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of JIS standards for aluminum components, especially in markets like Japan and South Korea. Additionally, aluminum’s recyclability can be a selling point for environmentally conscious companies.
How Do Plastics Compare in Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
Key Properties: Plastics, such as PVC and nylon, are lightweight and offer excellent chemical resistance. They typically have lower temperature ratings (around 60-80°C) and pressure ratings compared to metals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastics is their resistance to corrosion and chemicals, making them suitable for various fluids. However, they are less durable under high pressure and can deform under extreme temperatures, limiting their use in hydraulic applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for pneumatic systems and applications where weight and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in food processing and medical devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA or EU regulations) is essential for buyers in the food and beverage industry. Understanding local regulations regarding plastic use is also vital in regions like the Middle East.
What Are the Benefits of Using Rubber in Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
Key Properties: Rubber materials, such as nitrile and neoprene, provide excellent flexibility and sealing capabilities. They can withstand temperatures from -40°C to 100°C and are effective at sealing against various fluids.
Pros & Cons: Rubber’s flexibility makes it ideal for seals and gaskets in both pneumatic and hydraulic systems. However, it may degrade over time due to exposure to oils or extreme temperatures, necessitating regular maintenance and replacement.
Impact on Application: Rubber is crucial for sealing applications in both systems, ensuring leak-free operations. It is particularly effective in hydraulic systems where fluid containment is critical.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific rubber grades that comply with ASTM or DIN standards, especially in Europe and the Middle East, where quality assurance is paramount.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Pneumatic vs. Hydraulic Systems
| Material | Typical Use Case for Pneumatic vs Hydraulic | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty hydraulic systems | High strength and durability | Higher cost and corrosion treatment needed | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight pneumatic systems | Low weight and good corrosion resistance | Lower pressure rating than steel | Medium |
| Plastic | Pneumatic systems in food processing | Excellent chemical resistance | Limited pressure and temperature ratings | Low |
| Rubber | Seals in pneumatic and hydraulic systems | Flexibility and sealing capabilities | Degrades over time with exposure | Medium |
Selecting the right materials for pneumatic and hydraulic systems is crucial for ensuring performance, safety, and compliance with international standards. Understanding the pros and cons of each material will help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pneumatic vs hydraulic
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
The manufacturing processes for pneumatic and hydraulic systems differ significantly due to the distinct properties of air and fluid media they utilize. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source quality equipment.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
How Is Material Prepared for Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
The preparation of materials is the foundational stage in manufacturing both pneumatic and hydraulic systems. For pneumatic systems, lightweight materials such as aluminum and polymers are often preferred due to their lower density, which aids in speed and efficiency. Conversely, hydraulic systems require materials with higher tensile strength, such as steel or reinforced plastics, to withstand the high pressures of hydraulic fluids.
During this stage, raw materials undergo quality checks to ensure they meet industry standards. This may involve chemical analysis for metals and tensile testing for composites. Buyers should look for suppliers who maintain rigorous testing protocols in line with international standards such as ISO 9001.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Pneumatic and Hydraulic Manufacturing?
The forming techniques employed in the production of pneumatic and hydraulic components vary based on the material properties and intended application.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
-
Pneumatic Systems:
– Extrusion: Common for producing tubes and hoses, allowing for consistent wall thickness and flexibility.
– Injection Molding: Used for creating complex shapes in plastic components, such as valves and fittings. -
Hydraulic Systems:
– Casting: Often utilized for creating complex shapes in pump housings and valve bodies, ensuring strength and durability.
– Machining: Precision machining techniques are applied to components like cylinders and valves, ensuring tight tolerances necessary for high-pressure applications.
Buyers should assess whether suppliers use advanced forming technologies like CNC machining or 3D printing, which can enhance precision and reduce waste.
How Are Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems Assembled?
Assembly is a critical stage where components are integrated into functional systems. For pneumatic systems, assembly often involves connecting lightweight tubes and fittings. The process is generally less complex, allowing for quicker assembly times.
In contrast, hydraulic systems require careful assembly to prevent leaks under pressure. This involves fitting seals, gaskets, and valves precisely to ensure a tight seal. Hydraulic assemblies may also require torque specifications to be met, ensuring that connections are secure.
Buyers should inquire about the assembly process used by suppliers, including any automation or quality checks employed to ensure reliability.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used for Pneumatic and Hydraulic Components?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the performance and longevity of pneumatic and hydraulic components.
-
Surface Treatments:
– Anodizing: Common in pneumatic systems to improve corrosion resistance of aluminum parts.
– Coating: Hydraulic components may receive oil-resistant coatings to protect against fluid leaks and environmental factors. -
Quality Checks During Finishing:
– Components are often subjected to visual inspections and surface roughness tests to ensure they meet specifications.
Buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to these finishing processes to maintain quality and durability.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Practices for Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in ensuring that both pneumatic and hydraulic systems meet industry standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider for Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
Adherence to international standards is vital for ensuring quality and safety in manufacturing. The following standards are particularly relevant:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries, including manufacturing.
- CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with safety and environmental requirements.
- API Standards: For hydraulic systems used in oil and gas applications, API standards ensure that products meet specific performance and safety criteria.
B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers are certified and compliant with these standards, as this can significantly impact the reliability of the products.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process help in identifying defects early. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing to catch any deviations from standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Final inspections are conducted before products are shipped to ensure they meet all requirements.
Buyers should ask suppliers about their QC processes and how they document inspections and tests.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
Testing methods vary based on the application and industry standards. Common testing methods include:
- Pressure Testing: Ensures that hydraulic systems can withstand operational pressures without leaking.
- Functional Testing: Assesses the performance of pneumatic systems to ensure they operate within specified parameters.
- Leak Testing: Detects any potential leaks in both pneumatic and hydraulic systems, which is crucial for safety and efficiency.
Buyers should request test reports and certifications from suppliers to validate these methods.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they are sourcing reliable products. Here are some strategies:

Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and QC practices directly.
- Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of quality tests and compliance certifications can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors can help validate the supplier’s claims and provide an unbiased assessment of quality.
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be particularly diligent in verifying QC, as variations in standards and practices can impact product performance and safety.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control, including:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can influence communication and expectations regarding quality.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding product safety and environmental impact, which can affect quality assurance processes.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Evaluating the reliability of a supplier’s logistics and distribution can impact the timeliness and quality of product delivery.
By considering these factors, B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of sourcing pneumatic and hydraulic systems from international suppliers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pneumatic vs hydraulic’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers navigating the procurement of pneumatic and hydraulic systems. By following these steps, you can make informed decisions that align with your operational needs, budget constraints, and industry standards. This checklist will help clarify the differences between the two systems, ensuring that you choose the right technology for your application.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing your technical requirements is critical for selecting the appropriate system. Consider factors such as load capacity, speed, and operational environment.
– Identify whether your application requires high force (favoring hydraulics) or speed and flexibility (favoring pneumatics).
– Document the specific pressures and flow rates needed for your operations.
Step 2: Assess Environmental Considerations
Evaluate the operating environment where the system will be implemented.
– For clean rooms or environments sensitive to contamination, pneumatics is generally preferred due to its cleaner operation.
– If your application involves heavy lifting or rugged conditions, hydraulics may be more suitable despite the risk of fluid leaks.
Step 3: Evaluate Energy Efficiency and Costs
Understanding the energy consumption of each system can significantly impact your operational costs.
– Pneumatic systems often require continuous air supply, leading to higher energy costs due to compressor operation.
– Hydraulic systems can be more energy-efficient over time if well-maintained but may have high initial setup costs.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Selecting reputable suppliers is crucial for ensuring reliability and compliance with industry standards.
– Request documentation for certifications such as ISO 9001 or other relevant quality management systems.
– Ensure that suppliers can provide evidence of past performance and compliance with safety regulations specific to your industry.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
Step 5: Conduct Supplier Evaluations
Before making a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your needs.
– Ask for case studies or references from companies in similar sectors to gauge the supplier’s capability and reliability.
– Consider conducting site visits or audits to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
Step 6: Review Maintenance and Support Services
Understanding the maintenance requirements and support services offered by suppliers can save you time and costs in the long run.
– Inquire about the availability of spare parts and service contracts for both pneumatic and hydraulic systems.
– Evaluate the supplier’s response time for repairs and support to minimize downtime in your operations.
Step 7: Make Informed Comparisons
Compile all gathered data to make a comprehensive comparison between pneumatic and hydraulic systems.
– Create a decision matrix that weighs the pros and cons based on your specific criteria, such as strength, speed, cost, and maintenance.
– Engage stakeholders within your organization to ensure that the chosen solution aligns with overall business goals and operational strategies.
By following this checklist, you will be better equipped to make a well-informed decision when procuring pneumatic or hydraulic systems, ultimately enhancing your operational efficiency and productivity.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pneumatic vs hydraulic Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Pneumatic vs Hydraulic Systems?
When evaluating the cost structure of pneumatic versus hydraulic systems, it’s essential to break down the various cost components involved:
-
Materials: Pneumatic systems typically use lighter materials due to lower pressure requirements, resulting in lower material costs. Conversely, hydraulic systems require robust materials capable of withstanding high pressures, leading to higher material expenses. The choice of materials also affects durability and maintenance costs.
-
Labor: Installation and maintenance labor costs can vary significantly. Pneumatic systems often require less skilled labor for installation due to their simpler design. In contrast, hydraulic systems may necessitate specialized technicians for installation and ongoing maintenance, increasing labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: The complexity of hydraulic systems often results in higher manufacturing overhead. This includes costs associated with specialized equipment and longer production times. Pneumatic systems, being less complex, tend to have lower overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial for both systems but tend to be higher for hydraulic systems due to the need for precision components and custom tooling to handle high-pressure applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Given the risks associated with hydraulic fluid leaks and the potential for contamination, hydraulic systems often require more rigorous quality control measures, adding to the overall cost. Pneumatic systems, while still requiring QC, generally have lower associated costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the weight and size of components. Hydraulic systems are often bulkier and heavier, leading to higher logistics costs. Additionally, the need for special handling due to the potential hazards of hydraulic fluids can further inflate these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers may apply different markup percentages based on the complexity and demand for each system. Hydraulic systems, due to their higher manufacturing costs and specialized nature, might carry a higher margin compared to pneumatic systems.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Pneumatic and Hydraulic System Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of pneumatic and hydraulic systems:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often results in lower unit prices. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, which can significantly affect overall costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-designed systems generally incur higher costs due to additional engineering and manufacturing processes. Standardized components are typically more cost-effective.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only impacts the initial costs but also the long-term maintenance and durability of the systems. Higher-quality materials can lead to higher upfront costs but may reduce total ownership costs over time.
-
Quality/Certifications: Systems with higher quality standards or certifications can command premium prices. Buyers should assess the importance of these certifications in relation to their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better support and warranty options, which can be crucial for international buyers.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping, insurance, and tariffs, affecting the total landed cost of the equipment.
What Are Key Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Pneumatic and Hydraulic Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing power, especially if buying in bulk. Negotiating terms, prices, and payment plans can lead to significant savings.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A cheaper upfront cost might lead to higher TCO if the system is less reliable.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and shipping costs that can affect pricing. Additionally, local regulations in regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East may impact the choice of pneumatic versus hydraulic systems.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on suppliers, considering their service offerings, customer reviews, and warranties. This can help ensure that you select a supplier that aligns with your quality and cost expectations.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times, providing additional advantages in terms of support and maintenance.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for pneumatic and hydraulic systems can vary widely based on factors such as specifications, supplier, and market conditions. It’s crucial for buyers to obtain quotes tailored to their specific requirements and to consider all cost components when making a purchasing decision.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pneumatic vs hydraulic With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternative Solutions to Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
When evaluating fluid power systems for industrial applications, businesses often consider pneumatic and hydraulic solutions. However, several alternative technologies exist that can provide similar functionalities while catering to specific needs. Understanding these alternatives helps B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and suitability for particular use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Pneumatic Vs Hydraulic | Electric Actuators | Mechanical Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High speed, lower force | High precision, moderate force | Variable speed and force |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, ongoing energy costs | Higher upfront cost, lower operating costs | Low initial cost, potential wear and tear costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation, requires air supply | Moderate complexity, needs electrical infrastructure | Straightforward installation, no external power required |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, air filtration needed | Low maintenance, mostly plug-and-play | Moderate maintenance, depends on mechanical wear |
| Best Use Case | Clean environments, fast operations | Precision applications, robotics | Simple lifting and movement tasks |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Actuators
Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, providing precise control over speed and position. They are particularly advantageous in applications requiring high accuracy, such as robotics and automated machinery. While the initial investment can be higher than pneumatic or hydraulic systems, electric actuators typically have lower operating costs due to reduced energy consumption and minimal maintenance needs. However, they may not be suitable for applications requiring high force output, making them less ideal for heavy lifting tasks.
Mechanical Systems
Mechanical systems rely on gears, levers, or other mechanical components to achieve movement. They often represent a cost-effective solution for simple applications that do not require complex control systems. Their straightforward design allows for easy implementation and operation without the need for external power sources. However, mechanical systems can suffer from wear and tear over time, leading to increased maintenance needs and potentially reduced performance. They are best suited for tasks involving simple lifting and movement where precision is not a primary concern.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right system—whether pneumatic, hydraulic, electric actuators, or mechanical—depends on your specific application requirements. Consider the performance needs, initial and ongoing costs, ease of implementation, and maintenance capabilities. Additionally, evaluate the environment in which the system will operate. For instance, if hygiene is critical, pneumatic systems might be preferable, while electric actuators could be more suitable for precision tasks. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and limitations of each alternative will empower B2B buyers to make informed choices that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pneumatic vs hydraulic
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
When evaluating pneumatic and hydraulic systems, several critical specifications influence their performance and suitability for specific applications. Understanding these properties helps B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
1. Pressure Rating
Pressure rating is a measure of the maximum pressure a system can safely operate under. Hydraulic systems typically operate at much higher pressures (1,000-10,000 psi) compared to pneumatic systems (80-100 psi). This property is crucial for applications requiring significant lifting or force, such as construction and mining, where hydraulics excel. In contrast, low-pressure pneumatic systems are ideal for lighter tasks, such as in packaging or automation.
2. Flow Rate
Flow rate refers to the volume of fluid (air or liquid) that can move through the system in a given time. Pneumatic systems have a higher flow rate due to the lower viscosity of air, allowing for faster operation and quicker actuation of components. This speed can enhance productivity in applications like assembly lines. Hydraulic systems, while slower, offer sustained force, making them suitable for applications requiring continuous power.
3. Medium Used
The operational medium defines the system’s functionality. Pneumatics utilize compressed air, which is clean and non-toxic, making them suitable for food processing and pharmaceutical applications. Hydraulics, on the other hand, use oil or water, which can pose contamination risks if leaks occur. Understanding the medium helps buyers determine the right system based on hygiene and environmental considerations.
4. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency varies significantly between pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Pneumatics may waste energy through air leaks and require continuous compressor operation. However, they often have lower operational costs since air is free. Hydraulics can be more energy-efficient in long-term use due to the recirculation of hydraulic fluid, provided the system is well-maintained. Buyers should assess the long-term operational costs against the initial investment.
5. Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance needs differ significantly between the two systems. Pneumatic systems generally require less maintenance, focusing on filters and air quality. In contrast, hydraulic systems demand regular checks for leaks, fluid quality, and component wear due to the corrosive nature of hydraulic fluids. Understanding maintenance implications can impact long-term operational costs and system reliability.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions involving pneumatic and hydraulic systems.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of pneumatic and hydraulic systems, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source quality components tailored to their specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost calculations. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their operational needs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. This term is crucial for procurement processes, enabling buyers to compare offers and select the best value.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers as they clarify costs, risks, and obligations in international trade, ensuring smoother transactions.
5. Tolerances
Tolerances refer to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension of a component. In pneumatic and hydraulic applications, maintaining precise tolerances is critical for system performance and reliability. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can meet specified tolerances to avoid operational issues.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, fostering better supplier relationships and optimizing their operational efficiencies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pneumatic vs hydraulic Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Pneumatic vs Hydraulic Sector?
The global market for pneumatic and hydraulic systems is shaped by several key drivers, including advancements in technology, increasing automation, and the need for efficient energy solutions. In sectors such as construction, manufacturing, and agriculture, the demand for robust and reliable systems remains strong. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is critical.
Emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are revolutionizing the pneumatic and hydraulic sectors. These technologies facilitate predictive maintenance, enhance operational efficiency, and reduce downtime. For instance, smart sensors can monitor system performance in real-time, allowing for proactive interventions before failures occur. Additionally, the rising trend of miniaturization in pneumatic components is expanding their applicability in high-precision environments like electronics and pharmaceuticals, where space and cleanliness are paramount.
Market dynamics also reflect a growing emphasis on energy efficiency. Buyers are increasingly looking for systems that minimize energy consumption while maximizing output. Hydraulics, despite their energy demands, are evolving with advancements in pump technology that improve efficiency. Conversely, pneumatic systems are being designed to optimize air consumption and reduce leakage, further enhancing their appeal in environmentally conscious markets.

Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Pneumatic vs Hydraulic Sector?
As global awareness of environmental issues escalates, the pneumatic and hydraulic sectors are facing increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of products are now critical considerations for B2B buyers. Pneumatic systems generally have a lower environmental footprint due to their use of air as a medium, which eliminates the risks associated with fluid leaks common in hydraulic systems.
Ethical sourcing is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of procurement. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through transparent supply chains and responsible sourcing practices. The use of ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, is gaining traction. Manufacturers that utilize recycled materials or develop biodegradable hydraulic fluids are increasingly favored, particularly in regions where environmental regulations are stringent.
Moreover, companies are encouraged to engage with suppliers who not only focus on product quality but also on the ethical implications of their sourcing practices. This includes evaluating the impact of their supply chain on local communities and ecosystems, which is particularly relevant in developing regions like Africa and South America.
What is the Evolution and Historical Context of Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems in B2B?
The evolution of pneumatic and hydraulic systems has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing market demands. Pneumatic systems, which harness compressed air, have roots in the 18th century, primarily utilized in simple tools and transportation systems. With the advent of industrialization, their application expanded to include automation in manufacturing processes.
Hydraulic systems, on the other hand, emerged in the 19th century, leveraging the incompressibility of liquids to transmit power effectively. They quickly became integral to heavy machinery and construction equipment, where high force and precision were essential. Over the decades, both systems have undergone substantial innovations, driven by the need for increased efficiency, reliability, and safety.
Today, both pneumatic and hydraulic technologies continue to evolve, with a focus on integrating smart technologies and sustainable practices, ensuring they remain relevant in a rapidly changing global market. Understanding this historical context enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions about the systems that best meet their operational needs while aligning with modern sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pneumatic vs hydraulic
-
How do I determine whether to choose pneumatic or hydraulic systems for my application?
When deciding between pneumatic and hydraulic systems, assess your specific application requirements. Pneumatics are ideal for lighter tasks where speed and cleanliness are crucial, such as in food processing or pharmaceutical environments. In contrast, hydraulics excel in high-force applications like heavy machinery or construction, where strength is paramount. Consider factors such as the materials being moved, operational pressure needs, space constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Engaging with suppliers for detailed specifications can further inform your decision. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing pneumatic or hydraulic equipment?
Key factors include the application requirements, system compatibility, and supplier reputation. Evaluate the specifications of the equipment, such as pressure ratings and flow rates, to ensure they meet your operational needs. Additionally, consider the availability of spare parts, warranty terms, and the supplier’s experience in your industry. Researching supplier certifications and customer reviews can also provide insights into quality and reliability, helping you make an informed purchasing decision. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for pneumatic and hydraulic systems?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of equipment. Generally, MOQs for pneumatic systems tend to be lower, often starting at a few units for standard components. Hydraulic systems, particularly custom or specialized units, may have higher MOQs due to manufacturing constraints. Always inquire directly with suppliers about their MOQs to ensure that they align with your project scale and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing pneumatic or hydraulic equipment internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after installation. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or financing options for larger orders. Ensure clarity on payment methods, currency, and any applicable taxes or tariffs, especially when dealing with international transactions. Establishing a clear agreement in advance can prevent misunderstandings and facilitate smoother transactions. -
How can I vet suppliers for pneumatic and hydraulic systems effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their certifications and industry standards compliance, such as ISO certifications. Request references from previous clients, and evaluate their experience in your specific industry. Conducting site visits or virtual audits can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Additionally, assess their customer service responsiveness and support capabilities, as reliable communication is crucial for long-term partnerships. -
What customization options are available for pneumatic and hydraulic systems?
Customization options can vary by supplier but often include modifications to size, pressure ratings, and component materials to suit specific applications. Some suppliers may also offer tailored solutions such as specialized fittings or configurations for unique operational environments. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand what customization is available and any associated costs or lead times. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in pneumatic and hydraulic equipment?
Quality assurance measures can include supplier certifications, adherence to industry standards, and documented testing procedures for equipment. Request information on the supplier’s quality control processes, such as routine inspections and performance testing of their products. Additionally, inquiring about warranties and service agreements can provide insights into their commitment to product quality and customer satisfaction. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing pneumatic or hydraulic systems?
When importing equipment, consider shipping methods, lead times, and potential customs duties or tariffs. Ensure that the supplier can provide all necessary documentation, such as certificates of origin and compliance, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, assess the reliability of the shipping partners and their track record with international deliveries. Planning for potential delays and having contingency plans can help mitigate risks associated with logistics.
Top 4 Pneumatic Vs Hydraulic Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Aztec Bolting – Pneumatic and Hydraulic Tools
Domain: aztecbolting.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Pneumatic and hydraulic tools are used for transporting power to equipment, with hydraulics utilizing fluids like oils and pneumatics using compressed gases. Pneumatics are preferred for maintenance of valves and flanges due to controllable pressure, rapid movement, and smaller sizes. They are cleaner, suitable for food manufacturing, and can quickly change direction. However, pneumatics operate a…
2. IQS Directory – Hydraulics Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Hydraulics: Utilizes pressurized fluids (typically hydraulic oil or water) for mechanical operations, capable of generating significant force (up to nine times the initial force), easy control, consistent power, cost-effective with fewer moving parts, and greater safety. Common applications include hydraulic lifts, braking systems, and aircraft components. Pneumatics: Uses gas (primarily compresse…
3. SMC Pneumatics – Pneumatic Actuators
Domain: smcpneumatics.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: SMC Pneumatics offers a full line of pneumatic automation products, including pneumatic actuators with standard bore sizes ranging from ½-8 inches, capable of generating upwards of 7,500 lb. of force, and solid steel actuators that can generate close to 40,000 lbf. Pneumatic equipment is noted for its simplicity, lightweight design, and lower initial investment compared to hydraulic systems. It is…
4. Nature – Actuation System Comparison
Domain: nature.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: The study compares hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric linear actuation systems under controlled conditions with a maximum input power of 1.1 kW. Key findings include: 1. Electric systems showed the most consistent response and lowest power consumption. 2. Hydraulic systems are known for their high force-torque ratio and are commonly used in heavy machinery and construction equipment. 3. Pneumatic …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pneumatic vs hydraulic
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers When Choosing Between Pneumatics and Hydraulics?
In the decision-making process for pneumatic versus hydraulic systems, B2B buyers must consider several critical factors. Hydraulics excel in high-force applications, making them suitable for heavy machinery and construction tasks, while pneumatics offer advantages in speed and cleanliness, ideal for environments where contamination is a concern. Understanding the specific demands of your application—such as required force, speed, and environmental conditions—will guide your choice effectively.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement Process?
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in optimizing costs and ensuring the selection of the right technology. By evaluating suppliers based on reliability, maintenance requirements, and total cost of ownership, companies can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. This is particularly vital in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where access to high-quality components can significantly impact productivity.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers in Fluid Power Solutions?
As industries continue to evolve, staying informed about advancements in fluid power technologies will be crucial. Investing in the right system now will position your business to meet future demands effectively. Engage with trusted suppliers and explore new innovations to ensure your operations are not only efficient but also adaptable to changing market conditions. Your strategic sourcing decisions today will shape your competitive edge tomorrow.
Illustrative image related to pneumatic vs hydraulic
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.