The Definitive Guide to Serrano Vs Jalapeno: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for serrano vs jalapeno
Sourcing the right chili pepper can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly when navigating the distinct profiles of serrano and jalapeño peppers. Understanding the nuances of these two popular varieties is crucial for businesses in the food industry, as they each offer unique flavors and heat levels that cater to different culinary applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the key differences between serrano and jalapeño peppers, including their heat profiles, physical characteristics, and culinary uses, providing essential insights to help buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
In addition to outlining the types and applications of these peppers, this guide will equip buyers with practical knowledge on supplier vetting, pricing strategies, and best practices for sourcing. By exploring factors such as growing conditions and regional availability, businesses can better understand how to optimize their procurement processes and meet consumer demands effectively.
For buyers from diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Brazil and Germany—this guide serves as a vital resource to enhance their understanding of serrano and jalapeño peppers. Empowered with this information, businesses can confidently navigate the global market, ensuring they select the right products that align with their culinary needs and market trends.
Understanding serrano vs jalapeno Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serrano Pepper | Smaller, slender, 1-4 inches, heat: 10,000-25,000 SHU | Salsas, sauces, marinades, pickling | Pros: High heat, bold flavor; Cons: Limited availability in some regions. |
| Jalapeño Pepper | Medium-sized, 2-6 inches, heat: 2,500-8,000 SHU | Hot sauces, toppings, grilling, pickling | Pros: Versatile, widely available; Cons: Milder heat may not satisfy all spice lovers. |
| Red Jalapeño | Riper version of jalapeño, smokier flavor, heat: 3,500-10,000 SHU | Chipotle products, sauces, smoking | Pros: Unique flavor profile; Cons: Seasonal availability may affect supply. |
| Serrano Salsa | Blend of serrano peppers with other ingredients | Ready-to-use condiments, food service | Pros: Convenient, consistent flavor; Cons: Higher cost compared to fresh peppers. |
| Pickled Serrano | Serrano peppers preserved in vinegar | Snack foods, garnishes, culinary uses | Pros: Long shelf life, tangy flavor; Cons: Can be perceived as less fresh. |
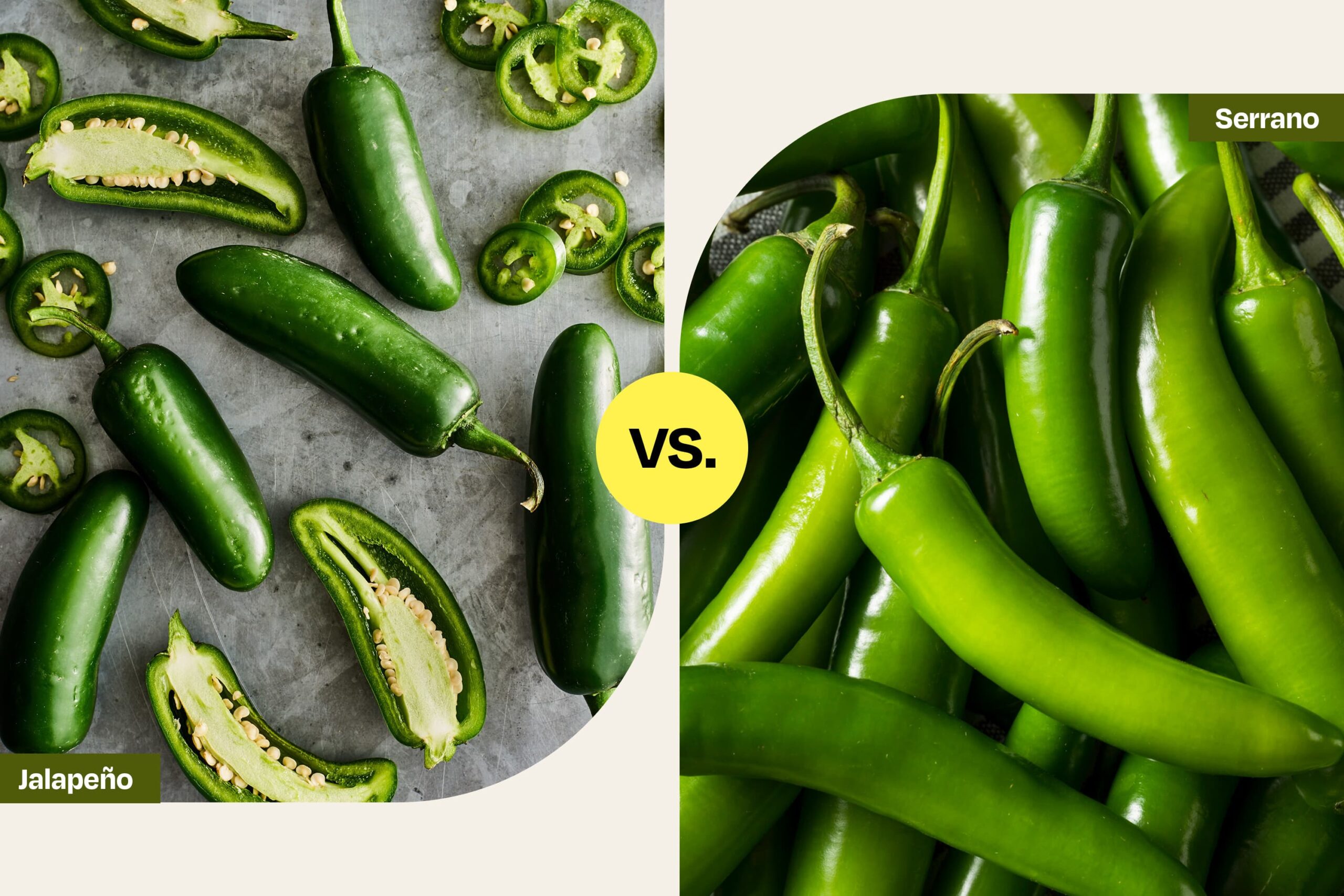
What Are the Key Characteristics of Serrano Peppers for B2B Buyers?
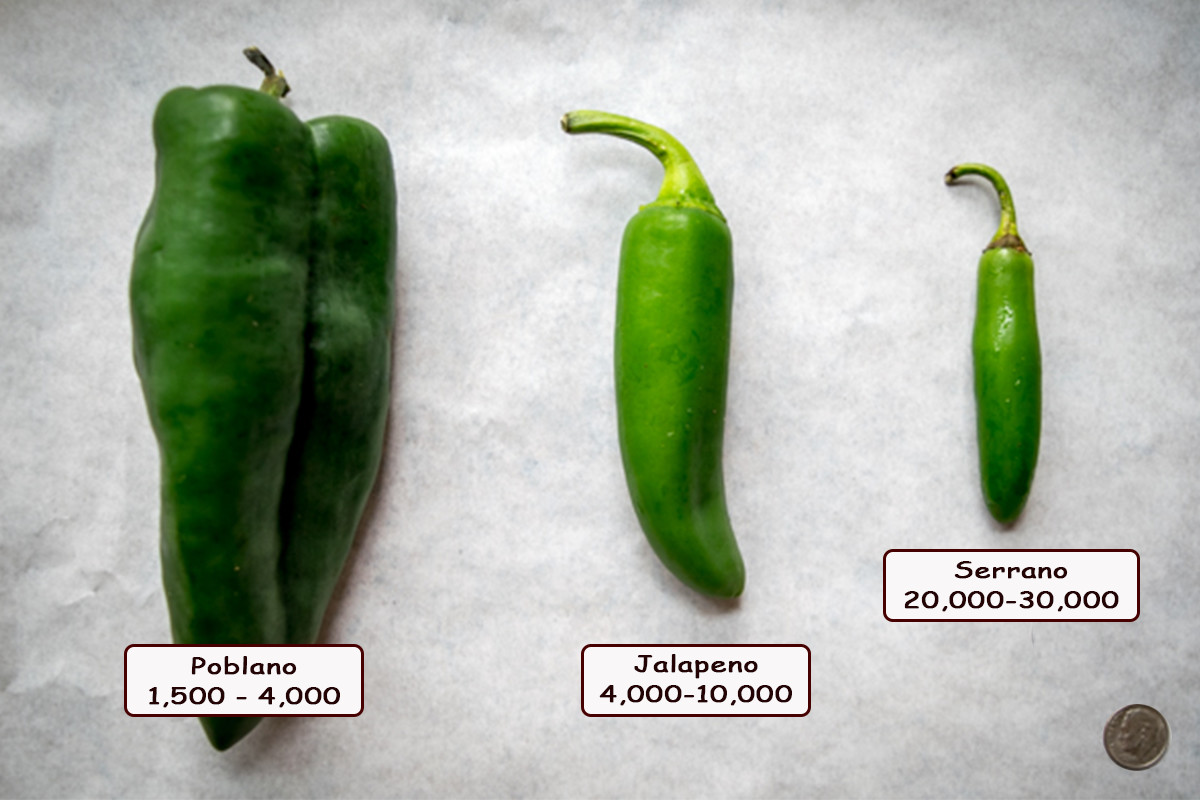
Serrano peppers are typically smaller and more slender than jalapeños, measuring between 1 to 4 inches in length. They boast a heat level ranging from 10,000 to 25,000 SHU, making them a favorite among those seeking a spicy kick. Their bold flavor profile, characterized by citrusy and earthy notes, makes them ideal for salsas, sauces, and marinades. For B2B buyers, sourcing serrano peppers can be advantageous for businesses focused on authentic Mexican cuisine or spicy condiment production. However, availability may vary by region, necessitating reliable supplier relationships.
How Do Jalapeño Peppers Fit into the B2B Market?
Jalapeño peppers are medium-sized, ranging from 2 to 6 inches, and offer a heat level of 2,500 to 8,000 SHU. This versatility makes them a staple in various culinary applications, including hot sauces, toppings for dishes, and grilling. Their mild spiciness appeals to a broader audience, making them suitable for mass-market products. B2B buyers should consider the consistent availability of jalapeños, as they are widely cultivated and recognized globally. However, the milder flavor may not cater to niche markets that demand higher heat levels.
What Are the Benefits of Red Jalapeños for Culinary Innovations?
Red jalapeños are simply ripe jalapeños that provide a smokier flavor, often used to create chipotle products. Their heat level ranges from 3,500 to 10,000 SHU, offering a unique flavor that can enhance sauces and marinades. For B2B buyers, incorporating red jalapeños into product lines can differentiate offerings and appeal to consumers seeking bold flavors. However, buyers should note that red jalapeños may have seasonal availability, which could impact consistent supply.
Why Consider Serrano Salsa in Your Product Line?
Serrano salsa, a blend of serrano peppers with other ingredients, offers a convenient option for food service and retail. This ready-to-use condiment provides a consistent flavor profile that can enhance various dishes. B2B buyers can benefit from offering serrano salsa as it caters to the growing demand for convenient, flavorful products. However, the cost may be higher than fresh peppers, which could affect pricing strategies.
What Are the Advantages of Pickled Serrano Peppers?
Pickled serrano peppers are preserved in vinegar, providing a tangy flavor that complements many dishes. With a long shelf life, they are ideal for snack foods and garnishes, making them a practical choice for businesses in the food industry. B2B buyers should consider the appeal of pickled products to consumers looking for convenient and flavorful options. However, some may perceive pickled peppers as less fresh, which could impact consumer preference.
Key Industrial Applications of serrano vs jalapeno
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of serrano vs jalapeno | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Ingredient in sauces and condiments | Enhances flavor profiles, catering to diverse culinary preferences | Consistency in heat levels, freshness, and sourcing location |
| Restaurant and Catering | Menu items featuring fresh or pickled peppers | Attracts customers seeking authentic, spicy dishes | Quality control, supplier reliability, and seasonal availability |
| Snack Manufacturing | Flavoring for spicy snacks and chips | Differentiates products in a competitive market | Capsaicin levels, sourcing origin, and cost-effectiveness |
| Export and Import Trade | Trading of dried and fresh peppers | Expands product offerings in international markets | Compliance with import regulations, quality standards, and logistics |
| Retail and Distribution | Retail packaging of fresh and processed pepper products | Meets consumer demand for variety and quality | Packaging standards, shelf life, and supply chain management |
How Are Serrano and Jalapeño Used in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, serrano and jalapeño peppers are essential ingredients in a variety of sauces, salsas, and condiments. Their distinct flavors and varying heat levels allow manufacturers to create products that cater to diverse consumer preferences. For international buyers, ensuring consistency in heat levels and freshness is crucial, as these factors directly impact product quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, sourcing from regions known for optimal growing conditions can enhance flavor profiles, making the product more appealing in global markets.
What Role Do Serrano and Jalapeño Play in the Restaurant and Catering Industry?
In the restaurant and catering sector, serrano and jalapeño peppers are frequently featured in menu items, both fresh and pickled. Their use in dishes such as tacos, nachos, and gourmet sauces attracts customers looking for authentic and spicy culinary experiences. For B2B buyers in this industry, quality control and supplier reliability are paramount, as the freshness of these peppers can significantly influence the overall dining experience. Moreover, understanding seasonal availability can help caterers plan their menus effectively, ensuring they offer the best products to their clientele.
How Are Serrano and Jalapeño Integrated into Snack Manufacturing?
Snack manufacturers utilize serrano and jalapeño peppers to create spicy flavor profiles in chips and other snack foods. The bold taste of these peppers can differentiate products in a crowded market, appealing to consumers who enjoy heat in their snacks. When sourcing these ingredients, manufacturers must consider the capsaicin levels to achieve the desired spiciness while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Additionally, establishing relationships with reliable suppliers can ensure a consistent supply of high-quality peppers, which is critical for maintaining product integrity.
What Are the Considerations for Export and Import Trade of Serrano and Jalapeño?
In the export and import trade, serrano and jalapeño peppers are traded both dried and fresh, allowing businesses to expand their product offerings in international markets. Buyers must navigate compliance with various import regulations and quality standards, which can vary significantly between countries. Establishing strong logistics partnerships is also essential to ensure timely delivery and product integrity. For businesses looking to enter new markets, understanding regional preferences for pepper types and heat levels can provide a competitive advantage.
How Do Retail and Distribution Benefit from Serrano and Jalapeño Products?
In the retail and distribution sector, serrano and jalapeño peppers are packaged for consumers in various forms, including fresh, dried, and processed products. The demand for diverse culinary options drives retailers to stock these peppers, catering to consumers’ growing interest in cooking and flavor experimentation. For B2B buyers, adhering to packaging standards and ensuring the products have an appropriate shelf life is crucial for maintaining quality and minimizing waste. Effective supply chain management also plays a vital role in ensuring that retailers can consistently meet consumer demand.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘serrano vs jalapeno’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Heat Level Confusion in Culinary Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers in the food service industry often face challenges when selecting ingredients that meet their customers’ heat preferences. The confusion between serrano and jalapeño peppers can lead to miscalculations in recipe formulation, resulting in dishes that are either too spicy or not spicy enough. This discrepancy can affect customer satisfaction and ultimately impact sales, as diners may return dishes or avoid ordering from a menu that fails to meet their heat expectations.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should invest in training for their culinary teams on the distinct heat profiles of serrano and jalapeño peppers. Detailed training sessions can include hands-on tastings and cooking demonstrations, helping chefs understand how to balance flavors and heat in their dishes. Additionally, buyers should consider sourcing both pepper types from reputable suppliers who can guarantee consistent quality and heat levels. Implementing a standardized heat measurement system, such as the Scoville scale, can also assist in maintaining consistency across menu items. By encouraging chefs to start with smaller quantities of serrano peppers and adjust incrementally, they can ensure the final dish aligns with customer expectations without overwhelming the palate.
Scenario 2: Ingredient Substitution Missteps
The Problem: In the fast-paced environment of food production, B2B buyers may often find themselves needing to substitute ingredients on short notice due to supply chain disruptions or changes in customer demand. The common assumption that serrano and jalapeño peppers can be used interchangeably may lead to significant flavor and heat discrepancies in final products, impacting the overall culinary experience. This can be especially problematic for businesses that pride themselves on authenticity and flavor integrity.
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with ingredient substitution, buyers should develop a comprehensive database of pepper varieties, highlighting their respective heat levels and flavor profiles. This database should include practical guidance on how to adjust recipes when substituting serrano for jalapeño and vice versa. For example, a recipe calling for one jalapeño could be modified to include half a serrano, depending on the desired heat level. Buyers should also establish relationships with multiple suppliers to ensure a steady availability of both pepper types, allowing for more flexible and reliable ingredient sourcing. Regular communication with suppliers about potential shortages can also help anticipate needs and make adjustments before they affect production.
Scenario 3: Cost Management and Sourcing Issues
The Problem: Fluctuating prices for serrano and jalapeño peppers can pose a significant challenge for B2B buyers aiming to maintain profitability while offering competitive pricing. Buyers often face the dilemma of sourcing quality peppers at reasonable prices, particularly when dealing with international suppliers. Price volatility can lead to budget overruns, complicating financial planning and affecting the bottom line.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs, buyers should adopt a strategic sourcing approach that includes diversifying their supplier base and exploring local sourcing options. Engaging with local farmers or cooperative groups can provide fresher options at lower prices, reducing reliance on international shipping and associated costs. Additionally, buyers should implement a seasonal purchasing strategy, purchasing larger quantities of peppers during peak harvest times when prices are typically lower, and preserving them for later use through freezing or pickling. Collaborating with suppliers to forecast demand and negotiate bulk pricing agreements can also help secure more favorable terms and stabilize costs. Finally, conducting regular market analysis will enable buyers to stay informed about pricing trends, allowing for more informed purchasing decisions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for serrano vs jalapeno
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Serrano and Jalapeño Processing?
When considering the processing of serrano and jalapeño peppers, several materials play a critical role in ensuring product quality and efficiency. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the food processing industry, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, durability, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 500°F (260°C) and is resistant to various food acids, making it ideal for processing peppers.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust and staining, which is crucial in food processing environments. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can increase costs.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with both serrano and jalapeño processing, ensuring that the flavors and heat levels are preserved. Its non-reactive nature means it won’t impart any unwanted flavors to the peppers.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with food safety standards such as ASTM or FDA regulations. In Europe, DIN standards may apply, and buyers should consider the local availability of specific stainless steel grades.
2. Polypropylene
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its chemical resistance and lightweight nature. It can withstand temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) and is resistant to many food acids.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of polypropylene makes it easy to handle and install, and it is generally more cost-effective than metals. However, it has lower temperature resistance and may not be suitable for high-heat applications.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is ideal for packaging and storage of both serrano and jalapeño peppers, especially in frozen or processed forms. Its chemical resistance ensures that the peppers remain uncontaminated.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with food safety regulations, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where local standards may vary. Understanding the recycling capabilities of polypropylene in different countries can also influence purchasing decisions.
3. Glass
Key Properties:
Glass is non-reactive, impermeable, and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for canning and storage. It does not leach chemicals into food, preserving the integrity of flavors.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of glass is its ability to maintain the quality of the product over time. However, it is heavier and more fragile than other materials, which can complicate transportation and storage.
Impact on Application:
Glass jars are commonly used for storing pickled jalapeños and serranos, ensuring that the peppers retain their flavor and heat. The visibility of the product also enhances marketing opportunities.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the shipping costs associated with glass and ensure compliance with packaging regulations in their respective regions. In Europe, for instance, glass recycling laws may affect the choice of packaging materials.
4. Food-Grade Silicone
Key Properties:
Food-grade silicone is flexible, durable, and can withstand extreme temperatures ranging from -40°F to 446°F (-40°C to 230°C). It is also resistant to moisture and various food substances.
Pros & Cons:
Silicone’s flexibility allows for easy handling and storage, making it ideal for molds and kitchen tools. However, it may not be as durable as metal options and can be more expensive than traditional plastics.
Impact on Application:
Silicone molds and tools can be used for preparing and serving both serrano and jalapeño dishes, allowing for creative culinary applications without affecting the peppers’ flavors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the silicone products meet international food safety standards and verify the certifications required in their specific markets, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for Serrano vs Jalapeño | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Processing equipment | Corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Polypropylene | Packaging and storage | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower temperature resistance | Low |
| Glass | Canning and storage | Non-reactive and preserves quality | Heavier and more fragile | Medium |
| Food-Grade Silicone | Kitchen tools and molds | Flexible and withstands extreme temps | Less durable than metals | Medium |
This comprehensive analysis will assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding material selection for processing serrano and jalapeño peppers, ensuring quality and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for serrano vs jalapeno
What Are the Main Manufacturing Processes for Serrano and Jalapeño Peppers?
In the production of serrano and jalapeño peppers, understanding the manufacturing processes is crucial for B2B buyers seeking quality products. The typical manufacturing stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection of high-quality seeds, which are sourced from reputable suppliers to ensure genetic consistency. Germination takes place under controlled conditions, allowing for optimal growth. Once seedlings are established, they are transplanted into fields with carefully managed soil conditions, including pH levels and nutrient content, to maximize yield and flavor.
Forming
During the growing phase, careful monitoring of environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and sunlight is essential. Both serrano and jalapeño peppers require specific watering schedules and pest control measures to prevent infestations that could compromise quality. This stage also involves regular pruning to encourage healthy growth and fruit development.
Harvesting
Harvesting techniques vary slightly between serrano and jalapeño peppers due to their differing maturity stages. Serranos are typically harvested when they are still green, whereas jalapeños can be harvested at both green and red stages. Handpicking is the preferred method to minimize damage to the fruit, ensuring that only the best specimens are selected for further processing.
Finishing
After harvesting, the peppers undergo washing and sorting to remove any debris or damaged fruits. This is followed by grading based on size, color, and ripeness, which is crucial for maintaining product quality. The final step involves packaging, where care is taken to use materials that prevent spoilage and maintain freshness during transit.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should Be in Place for Serrano and Jalapeño Peppers?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing process to ensure that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. For serrano and jalapeño peppers, adherence to relevant international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
ISO 9001 provides a framework for quality management systems, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. For agricultural products, compliance with food safety standards such as HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) is also critical. In regions like Europe, CE marking may be necessary, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Quality Control Checkpoints
In the manufacturing process, several quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials (seeds and fertilizers) upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring occurs throughout the growing and harvesting phases. Regular assessments of plant health, pest control measures, and environmental conditions are conducted to ensure compliance with quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the peppers are harvested and processed, they undergo rigorous testing for size, color, flavor, and any contaminants. This may involve laboratory testing for pesticide residues and microbial contamination.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable steps to ensure that suppliers meet necessary quality standards:
Supplier Audits
Conducting regular audits of suppliers is one effective way to verify their adherence to quality standards. During these audits, buyers should assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards.
Quality Reports and Certifications
Requesting quality reports and certifications from suppliers can provide insight into their QA processes. Certifications from recognized organizations, such as ISO or HACCP, serve as evidence of a supplier’s commitment to quality.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can further validate the quality of the peppers. Independent inspectors can conduct assessments at various stages of the supply chain, from growing to processing, ensuring that the products meet the buyer’s quality expectations.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing serrano and jalapeño peppers from international suppliers, there are specific nuances that buyers should be aware of:
Cultural and Regional Considerations
Understanding regional agricultural practices is essential, as these can impact the quality and availability of the product. For instance, climate conditions in South America may differ significantly from those in Europe, affecting the flavor and heat profile of the peppers.
Regulatory Compliance
Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations regarding pesticide use, food safety, and labeling. This is particularly important for markets in Europe, where regulations are stringent.
Supply Chain Transparency
Maintaining transparency in the supply chain is essential for trust and accountability. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide detailed information about their sourcing, production, and quality control practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for serrano and jalapeño peppers is critical for B2B buyers looking to source these products effectively. By focusing on quality control checkpoints, verifying supplier practices, and navigating the unique nuances of international sourcing, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality peppers that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘serrano vs jalapeno’
Introduction
This guide provides a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure serrano and jalapeño peppers. Understanding the distinct characteristics of these two peppers is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that meet culinary needs and customer preferences. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they select the right products, enhancing their offerings in the marketplace.
1. Identify Your Requirements
Before beginning the sourcing process, clearly define your culinary or commercial needs. Consider factors such as the desired heat level, flavor profile, and intended use (fresh, dried, or processed). Knowing whether you need serrano or jalapeño peppers will streamline your search and help you communicate effectively with suppliers.
2. Research Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to find reputable suppliers that specialize in chili peppers. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in quality and reliability, particularly those who can meet your specific regional requirements. Utilize platforms like trade directories and industry-specific websites to gather a list of potential suppliers.
3. Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold the necessary certifications, such as Global GAP or ISO standards. These certifications ensure that the peppers are grown and processed under strict quality control measures. Confirming this can help mitigate risks related to food safety and compliance with international regulations.
4. Assess Product Quality
Request samples of both serrano and jalapeño peppers to evaluate their quality firsthand. Pay attention to factors such as size, color, and firmness. High-quality peppers should be vibrant in color and free from blemishes, ensuring they meet your standards for freshness and flavor.
5. Understand Pricing and Payment Terms
Discuss pricing structures and payment terms with potential suppliers to ensure they align with your budget and financial practices. Look for transparency in pricing, including any additional costs such as shipping or handling fees. Establishing clear payment terms can prevent misunderstandings and foster a positive supplier relationship.
6. Inquire About Supply Chain Reliability
Assess the supplier’s ability to deliver products consistently and on time. Ask about their supply chain logistics, including sourcing, storage, and distribution capabilities. A reliable supply chain is crucial for maintaining inventory levels and meeting customer demand without interruption.
7. Request Customer References
Finally, ask for references from other businesses that have purchased from the supplier. Speaking with previous clients can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reliability, quality, and customer service. This step is essential for ensuring that you choose a supplier who will meet your business’s expectations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for serrano and jalapeño peppers, ensuring they make informed decisions that enhance their product offerings and satisfy their customers’ needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for serrano vs jalapeno Sourcing
When analyzing the cost structure and pricing dynamics for sourcing serrano and jalapeño peppers, several factors come into play that can significantly impact the total cost for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Serrano and Jalapeño Peppers?
The primary cost components in sourcing these chili peppers include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The base cost is influenced by the price of the peppers themselves, which can vary based on supply, demand, and seasonal fluctuations. Serrano peppers typically command a higher price due to their intense flavor and heat levels, which are often preferred in gourmet cooking.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of farm workers involved in planting, harvesting, and packing the peppers. This can vary based on the region of production and local labor laws. For example, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs may yield savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment used in processing the peppers. The scale of production can affect these costs; larger operations might benefit from economies of scale.
-
Tooling: For operations that involve cutting, packaging, or processing the peppers, tooling costs can be significant. Custom machinery may be required for specific products, especially if buyers are looking for tailored cuts or packaging.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality can incur additional costs, especially for certifications that guarantee food safety and organic status. Buyers should consider the implications of these certifications on overall pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs can vary widely depending on the distance from the source to the buyer. Factors like shipping method, customs duties, and storage conditions in transit are crucial to consider.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This can vary by supplier and may be negotiable depending on order volume.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Serrano and Jalapeño Sourcing?
Several key price influencers must be considered when sourcing these peppers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to bulk discounts, while smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Specific requirements, such as organic certification or custom packaging, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: The quality of the peppers and associated certifications (e.g., organic, fair trade) can impact pricing. High-quality peppers will generally cost more but may offer better flavor and appeal to premium markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge a premium but offer more consistent quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) will dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance, affecting overall costs. Understanding these terms is crucial for accurate cost assessments.
What Are the Best Tips for Buyers Sourcing Serrano and Jalapeño Peppers?
-
Negotiation: Buyers should leverage their purchasing power, especially when placing large orders. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyzing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is essential. Consider not just the purchase price, but also logistics, storage, and potential waste due to spoilage.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, local tariffs, and import regulations that may affect final costs.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: It is important to note that prices for serrano and jalapeño peppers can vary widely based on market conditions, sourcing regions, and other factors. Buyers should request quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure they are getting competitive pricing.
By understanding the cost structure, pricing influences, and strategic negotiation tactics, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing serrano and jalapeño peppers, ultimately enhancing their supply chain efficiency and product offerings.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing serrano vs jalapeno With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Serrano and Jalapeño Peppers
When considering the culinary applications of peppers, particularly serrano and jalapeño, it’s essential to explore alternative options that offer similar heat and flavor profiles. This analysis will help international B2B buyers identify which pepper best fits their specific needs, whether for food production, culinary ventures, or product development. In this comparison, we will examine serrano and jalapeño peppers against two alternatives: Fresno peppers and banana peppers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Serrano Vs Jalapeño | Fresno Pepper | Banana Pepper |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Higher heat (10,000-25,000 Scoville units); versatile in various dishes. | Moderate heat (2,500-10,000 Scoville units); great for salsas and grilling. | Mild heat (0-500 Scoville units); excellent for salads and pickling. |
| Cost | Moderate cost; availability may vary by region. | Generally affordable; similar availability to jalapeños. | Lower cost; widely available, especially in salads. |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to incorporate into recipes; can be used interchangeably. | Simple to use; similar application as jalapeños. | Very easy to use in various dishes without altering heat. |
| Maintenance | Requires proper storage; fresh usage preferred. | Minimal maintenance; lasts well when stored properly. | Very low maintenance; easy to store and use. |
| Best Use Case | Spicy dishes, salsas, marinades, and sauces. | Salsas, grilling, and as a topping for various dishes. | Salads, pickling, and as a mild ingredient in various recipes. |
In-Depth Look at Alternatives
What Are Fresno Peppers and Their Benefits?
Fresno peppers are a viable alternative to serrano and jalapeño peppers, offering a moderate heat level that ranges from 2,500 to 10,000 Scoville units. Their vibrant red color and fruity flavor make them an appealing option for salsas, sauces, and grilling. One significant advantage of Fresno peppers is their versatility; they can be used fresh, roasted, or pickled. However, they may not provide the same intensity of heat that some culinary applications require, making them less suitable for heat-seeking consumers.
How Do Banana Peppers Compare?
Banana peppers are another alternative that offers a very mild heat level, typically ranging from 0 to 500 Scoville units. These peppers are particularly popular in salads, sandwiches, and as a pickled condiment. Their mild flavor allows them to enhance dishes without overwhelming them with spice. While banana peppers are easy to incorporate and maintain, they lack the heat profile that may be necessary for certain recipes, which could limit their use in spicy dishes.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between serrano and jalapeño peppers or considering alternatives like Fresno and banana peppers, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific requirements. If the goal is to add significant heat and flavor to dishes, serrano peppers are the ideal choice. For moderate spice levels, Fresno peppers offer a balanced option, while banana peppers are perfect for those who prefer milder flavors. Ultimately, understanding the characteristics and culinary applications of each pepper will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and consumer preferences.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for serrano vs jalapeno
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Serrano and Jalapeño Peppers?
Understanding the technical specifications of serrano and jalapeño peppers is crucial for B2B buyers involved in food distribution, culinary businesses, and food production. Here are some critical specifications:
1. Scoville Heat Units (SHU)
The Scoville scale measures the spiciness or heat of chili peppers. Serrano peppers typically range from 10,000 to 25,000 SHU, while jalapeños are milder, falling between 2,500 and 8,000 SHU. This metric is essential for buyers to determine which pepper meets their culinary needs and to manage customer expectations regarding heat levels in products.
2. Size and Weight
Serrano peppers are generally smaller, measuring between 1 to 4 inches in length, whereas jalapeños are larger, ranging from 3 to 6 inches. This size difference can affect packaging and shipping logistics, as well as how the peppers fit into various culinary applications. Buyers need to account for these specifications when planning inventory and pricing.
3. Flavor Profile
Serrano peppers have a sharper, more grassy flavor, while jalapeños offer a distinct bright and zesty taste. Understanding these flavor profiles is vital for culinary professionals and product developers aiming to create specific taste experiences in their dishes or food products. This knowledge can influence recipe development and product marketing strategies.
4. Color Variations
Both peppers can be found in various colors, including green and red. The color often indicates ripeness and flavor intensity; red jalapeños tend to be sweeter and smokier when dried into chipotle peppers. Buyers should consider these color variations when sourcing peppers for specific culinary uses or product formulations, as color can impact consumer appeal.
5. Shelf Life and Storage
The shelf life of serrano and jalapeño peppers can vary based on handling and storage conditions. Typically, fresh peppers have a shorter shelf life than dried or pickled versions. For B2B buyers, understanding the storage requirements and shelf life is crucial for inventory management and minimizing waste.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Serrano and Jalapeño Peppers?
Familiarity with trade terminology is vital for B2B transactions, ensuring clarity and efficiency in communication. Here are some commonly used terms in the industry:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
In the context of food production, OEM refers to companies that produce goods that are sold under another company’s brand name. For buyers, knowing potential OEM partners can expand sourcing options for serrano and jalapeño products, such as sauces or processed foods.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to ensure they can meet purchasing requirements without overcommitting to stock that may not sell quickly.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products, such as serrano and jalapeño peppers. This process helps buyers compare costs and negotiate better terms, ensuring they receive competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, insurance, and risk management when importing peppers from different regions.
5. CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight)
CIF is a trade term indicating that the seller is responsible for the cost, insurance, and freight of the goods until they reach the buyer’s designated port. This term is crucial for buyers to understand the total landed cost of importing serrano and jalapeño peppers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, streamline their sourcing processes, and effectively manage their supply chains related to serrano and jalapeño peppers.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the serrano vs jalapeno Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers for Serrano and Jalapeño Peppers?
The global demand for serrano and jalapeño peppers has seen a steady increase due to the growing popularity of spicy foods and the culinary versatility of these peppers. This trend is particularly evident in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where culinary traditions increasingly incorporate these ingredients. The rise of international cuisines and the expansion of food service sectors have also fueled this demand. As global trade networks evolve, B2B buyers are leveraging technology to streamline sourcing processes, with digital platforms facilitating direct connections between producers and buyers.
Emerging trends such as clean labeling and the demand for authentic flavors are influencing sourcing decisions. Buyers are increasingly seeking high-quality, sustainably sourced peppers that not only meet culinary needs but also align with consumer preferences for transparency and quality. Additionally, advancements in agricultural technology, including precision farming and improved pest management, are optimizing yields and quality, further enhancing the market dynamics for serrano and jalapeño peppers.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing?
Sustainability has become a focal point for B2B buyers in the food sector, including those sourcing serrano and jalapeño peppers. The environmental impact of pepper cultivation is significant, with factors such as water usage and pesticide application posing challenges. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adopt sustainable farming practices, such as organic farming, integrated pest management, and water conservation techniques.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers seek to ensure fair labor practices within their supply chains. Certifications like Fair Trade and Rainforest Alliance are gaining traction, providing assurance that products are sourced responsibly. By choosing suppliers with these certifications, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation while contributing to environmental sustainability and social equity. Emphasizing these values not only meets consumer demand but also prepares businesses for regulatory changes that prioritize sustainability.
What is the Historical Context of Serrano and Jalapeño Peppers in the Market?
Serrano and jalapeño peppers have deep roots in Mexican cuisine, dating back centuries. Historically, these peppers were cultivated in the regions of Puebla and Veracruz, where they became staples in traditional dishes. Over time, their popularity spread globally, influenced by the rise of Mexican cuisine in the United States and beyond.
In recent decades, the global market for these peppers has expanded significantly, driven by the increasing interest in spicy foods and diverse culinary experiences. Today, they are not only integral to traditional recipes but also feature prominently in fusion cuisines, sauces, and snacks. This evolution highlights the adaptability of serrano and jalapeño peppers, making them vital components for B2B buyers looking to cater to a wide array of culinary preferences.
Understanding these market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical context can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions in sourcing serrano and jalapeño peppers, ensuring they align with both market trends and consumer expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of serrano vs jalapeno
-
How do I choose between serrano and jalapeño peppers for my product line?
When deciding between serrano and jalapeño peppers, consider the intended flavor profile and heat level of your products. Serrano peppers range from 10,000 to 25,000 Scoville units, making them significantly hotter than jalapeños, which measure between 2,500 and 8,000 units. If your target market prefers a milder flavor, jalapeños may be the better choice. However, if your product aims to attract heat enthusiasts, serranos can add a fiery kick. Additionally, assess local culinary trends and customer preferences in your target regions to make an informed decision. -
What are the key differences in culinary uses for serrano vs jalapeño peppers?
Serrano peppers are often favored in fresh salsas, sauces, and dishes requiring a more intense heat, thanks to their sharper, grassy flavor. They are also effective when pickled, adding a vibrant kick to various recipes. Jalapeños, on the other hand, are versatile and commonly used in nachos, tacos, and as a base for hot sauces. Their milder heat allows them to be used in a broader range of cuisines, making them a staple in many kitchens. Understanding these uses can help you tailor your offerings to meet customer demands effectively. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing serrano and jalapeño peppers internationally?
When sourcing these peppers internationally, consider factors such as the origin, quality, and supplier reliability. Research the growing conditions in the supplier’s region, as climate and soil significantly impact flavor and heat levels. Additionally, assess the supplier’s certifications, quality control processes, and ability to meet your specifications regarding size and freshness. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers who understand your market can also enhance the quality of your product line. -
How can I ensure consistent quality in serrano and jalapeño peppers from suppliers?
To maintain consistent quality, establish clear quality assurance (QA) protocols with your suppliers. This includes setting specific criteria for size, color, and heat level, as well as conducting regular inspections and taste tests. Implementing a traceability system can help monitor the peppers’ journey from farm to table, ensuring they meet your standards. Additionally, consider working with suppliers who have established quality certifications, as this can provide an extra layer of assurance regarding product consistency. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for serrano and jalapeño peppers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for serrano and jalapeño peppers can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific market. Generally, MOQs may range from 100 kg to several tons, particularly for bulk purchases. For smaller businesses or those testing new products, some suppliers may offer more flexible options. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly and negotiate terms that suit your business model while ensuring you can maintain inventory levels that meet customer demand. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing peppers internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include payment in advance, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms for established relationships. It’s crucial to clarify payment expectations upfront and consider using secure payment methods to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. Establishing trust and transparency with your suppliers can facilitate smoother financial interactions. -
How does logistics impact the sourcing of serrano and jalapeño peppers?
Logistics play a critical role in the sourcing of serrano and jalapeño peppers, particularly given their perishable nature. Efficient supply chain management is essential to minimize transit times and maintain product freshness. Consider factors such as shipping methods, storage conditions, and customs regulations in your target markets. Partnering with experienced logistics providers can enhance your ability to navigate these challenges, ensuring timely delivery while preserving the quality of your peppers. -
What are the potential challenges when importing serrano and jalapeño peppers?
Importing serrano and jalapeño peppers can present challenges, including compliance with local food safety regulations, tariffs, and seasonal availability. Understanding the import regulations in your target market is crucial to avoid delays or penalties. Additionally, fluctuations in supply due to climate conditions can impact availability and pricing. Building strong relationships with multiple suppliers can help mitigate these risks, providing alternative options if one source faces challenges.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Serrano Vs Jalapeno Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Mexican Please – Serrano vs. Jalapeno Peppers
Domain: mexicanplease.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Serrano and Jalapeno peppers are often confused, but they can be used interchangeably in recipes. Serrano peppers are 3-4 times hotter than Jalapenos, with a higher concentration of capsaicin. Serranos are typically smaller and thinner, and have a grassier and sharper taste. When substituting, use less Serrano due to its higher heat. The heat of peppers can vary based on growing conditions, and th…
2. Yahoo – Jalapeño vs. Serrano Peppers
Domain: yahoo.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Jalapeño and Serrano peppers are two types of peppers that differ in appearance and spiciness. Jalapeños are plumper with a rounded end, while Serranos are longer, thinner, and have a pointed tip. Both are commonly sold green, but mature Serranos can be red, brownish-orange, or yellow, while Jalapeños can be red or brown. Serrano peppers are significantly hotter, ranging from 10,000 to 25,000 Scov…
3. Facebook – Spicy Pepper Comparison
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Spicy Pepper Comparison, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Cuisine at Home – Chili Pepper Varieties
Domain: cuisineathome.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Jalapeño chiles: Lower heat on the Scoville scale, popular, color changes from dark green to scarlet as they ripen. Serrano chiles: Smaller and hotter than jalapeños, color changes from bright green to scarlet to yellow. Thai chiles: Small, exotic, pack a lot of heat that doesn’t dissipate with cooking, color changes from green to red when ripe. Habanero chiles: Among the hottest, shaped like smal…
5. Serrano – Jalapeno Substitute Guide
Domain: cooking.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Serrano pepper is considered an acceptable substitute for jalapeno, but it is usually hotter. When substituting, it is recommended to use one Serrano pepper instead of two jalapenos and to remove the seeds and internal membranes to reduce heat. Jalapenos can vary widely in heat (1000 to 20000 Scoville heat units), while Serranos are more consistent in heat level. If a milder flavor is desired, oth…
6. MasterClass – Serrano Peppers
Domain: masterclass.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Serrano Peppers:
– Scientific Name: Capsicum annuum
– Size: Slender, about the length of a finger
– Color: Green (most common), yellow, orange, red
– Origin: Mexico, specifically Puebla and Hidalgo
– Heat Level: 10,000–20,000 SHU (Scoville Heat Units)
– Culinary Uses: Marinades, salsas, glazes for proteins, Indian cuisine substitute for hot green chilies.
Jalapeño Peppers:
– Scientific Na…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for serrano vs jalapeno
In the dynamic landscape of culinary ingredients, understanding the nuances between serrano and jalapeño peppers is crucial for international B2B buyers. Both peppers offer unique flavor profiles and heat levels, making them versatile options for various cuisines. Serrano peppers, with their higher Scoville rating, are ideal for products targeting heat-seeking consumers, while jalapeños serve as a milder alternative suitable for a broader audience.
Strategic sourcing of these peppers can lead to enhanced product offerings and customer satisfaction. Buyers should consider regional preferences, availability, and pricing strategies when selecting between these two varieties. Engaging with reliable suppliers who understand the local market dynamics can further streamline procurement processes and ensure consistent quality.
As global culinary trends continue to evolve, the demand for both serrano and jalapeño peppers is expected to rise. By leveraging insights into their distinct characteristics and applications, buyers can position themselves advantageously in the marketplace. Embrace the opportunity to diversify your product lines and cater to a wider audience by incorporating these peppers into your sourcing strategy. Reach out to trusted suppliers today to explore the best options for your business needs.