3Phase Transformer Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3phase transformer
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electrical distribution, sourcing a reliable three-phase transformer can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. These critical components are essential for efficient power generation and transmission across various sectors, including manufacturing, construction, and renewable energy. With diverse configurations such as delta and star connections, understanding the intricacies of three-phase transformers is vital for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in your operations.
This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad aspects of three-phase transformers, encompassing types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations. It is designed to equip decision-makers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Nigeria—with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
By exploring the essential features and benefits of three-phase transformers, this guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of the global market confidently. From understanding the technical specifications to evaluating supplier credibility, you will gain the knowledge required to enhance your procurement strategy. Ultimately, the goal is to facilitate the selection of a transformer that not only meets your operational requirements but also aligns with your long-term business objectives in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Understanding 3phase transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delta-Delta (Dd) | All windings connected in a delta configuration. | Industrial motors, heavy machinery | Pros: Robust; continues operation if one unit fails. Cons: Requires high insulation; no neutral point. |
| Star-Star (Yy) | All windings connected in a star configuration. | Power distribution networks, commercial buildings | Pros: Allows neutral point; fewer turns needed. Cons: Vulnerable to total failure if one unit fails. |
| Star-Delta (Yd) | Primary windings in star, secondary in delta configuration. | Starting large motors, reducing starting current | Pros: Reduces starting current; versatile. Cons: More complex; requires additional wiring. |
| Delta-Star (Dy) | Primary windings in delta, secondary in star configuration. | Transformer stations, step-down applications | Pros: Provides a neutral point; good for load balancing. Cons: More expensive; requires careful design. |
| Zig-Zag (Zz) | Interconnected star configuration providing a neutral point. | Grounding systems, harmonic mitigation | Pros: Excellent for grounding; mitigates harmonics. Cons: Limited to specific applications; can be costly. |
What Are the Characteristics of Delta-Delta (Dd) Transformers?
Delta-Delta transformers connect all windings in a triangular formation, making them particularly robust for industrial applications. They are commonly used in powering heavy machinery and industrial motors due to their ability to maintain operation even if one transformer fails. However, they require high insulation levels, and their lack of a neutral point can complicate some applications.
How Do Star-Star (Yy) Transformers Stand Out?
Star-Star transformers connect all windings in a star formation, allowing for the establishment of a neutral point. This configuration is ideal for power distribution networks and commercial buildings, where the neutral connection can enhance safety and reliability. They require fewer turns in the windings compared to Delta configurations, but they are vulnerable to total failure if one transformer becomes inoperable.
What Are the Benefits of Star-Delta (Yd) Transformers?
Star-Delta transformers feature primary windings in a star configuration and secondary windings in a delta formation. This setup is particularly beneficial for starting large motors, as it reduces the initial starting current. The versatility of this configuration makes it popular in various industrial applications. However, it is more complex to install and requires additional wiring, which can increase costs.
Why Choose Delta-Star (Dy) Transformers?
In Delta-Star transformers, the primary windings are connected in delta while the secondary windings are in a star configuration. This allows for a neutral point, which is essential for load balancing in transformer stations and step-down applications. While they provide advantages in terms of safety and efficiency, the design can be more expensive, necessitating careful consideration during procurement.
What Are the Advantages of Zig-Zag (Zz) Transformers?
Zig-Zag transformers offer a unique interconnected star configuration that is particularly effective for grounding systems and harmonic mitigation. They provide an excellent neutral point, which is crucial for maintaining system stability. However, their application is somewhat limited, and the costs associated with these transformers can be higher, making them suitable for specific, high-requirement applications.
Key Industrial Applications of 3phase transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 3-phase transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Power supply for heavy machinery | Ensures reliable operation of equipment, reducing downtime | Voltage ratings, efficiency, and cooling methods |
| Oil & Gas | Transformer stations for remote drilling sites | Facilitates energy transmission over long distances, ensuring operational efficiency | Environmental ratings, ruggedness, and local compliance |
| Mining | Power distribution for extraction and processing | Enhances productivity by maintaining consistent power supply | Durability, load capacity, and ease of maintenance |
| Renewable Energy | Integration into wind and solar farms | Supports grid stability and energy conversion efficiency | Compatibility with renewable technologies and grid standards |
| Transportation | Electrification of rail systems | Reduces operational costs and enhances energy efficiency | Size, weight, and adaptability to existing infrastructure |
How is a 3-Phase Transformer Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, 3-phase transformers are essential for supplying power to heavy machinery, which requires substantial energy to operate efficiently. These transformers help in stepping down high voltages from the main supply to levels suitable for machinery use. By ensuring a stable power supply, they minimize downtime and enhance productivity. Buyers must consider voltage ratings, efficiency, and cooling methods when sourcing transformers to meet the specific demands of their manufacturing processes.
Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
What Role Do 3-Phase Transformers Play in Oil & Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas industry, 3-phase transformers are critical in transformer stations that support remote drilling sites. They enable the efficient transmission of electricity over long distances, which is vital in areas where access to reliable power is limited. By facilitating energy distribution, these transformers ensure that drilling operations run smoothly and efficiently. Buyers should focus on environmental ratings, ruggedness, and compliance with local regulations when procuring these transformers for use in challenging conditions.
How Do Mining Operations Benefit from 3-Phase Transformers?
Mining operations utilize 3-phase transformers for power distribution during extraction and processing activities. These transformers provide the necessary voltage and current to operate heavy mining equipment, ensuring consistent power supply crucial for productivity. Additionally, they help in managing the electrical load effectively, which is vital in a sector characterized by fluctuating power demands. Buyers need to prioritize durability, load capacity, and ease of maintenance to optimize their investment in transformers for mining applications.
How Are 3-Phase Transformers Integrated into Renewable Energy Systems?
In the renewable energy sector, 3-phase transformers play a pivotal role in integrating wind and solar farms into the power grid. They facilitate the conversion of generated energy into a form that can be effectively transmitted and distributed. By supporting grid stability and enhancing energy conversion efficiency, these transformers are vital for maximizing the output from renewable sources. Buyers should ensure compatibility with renewable technologies and adherence to grid standards when sourcing transformers for these applications.
What Benefits Do 3-Phase Transformers Provide in Transportation Electrification?
3-phase transformers are increasingly used in the electrification of rail systems, providing the necessary power for trains to operate efficiently. This transformation not only reduces operational costs but also enhances energy efficiency, contributing to a more sustainable transportation system. When sourcing transformers for this application, buyers should consider factors such as size, weight, and adaptability to existing infrastructure to ensure seamless integration into current systems.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘3phase transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Power Supply Quality
The Problem: A manufacturing company in Brazil is experiencing frequent voltage fluctuations and power quality issues due to an inadequate power supply infrastructure. These fluctuations lead to equipment malfunctions, increased downtime, and ultimately higher operational costs. The buyer is concerned about the potential damage to sensitive machinery and the impact on production efficiency. Furthermore, the lack of a stable power supply makes it difficult to meet production schedules, which can jeopardize relationships with clients.
The Solution: To address this issue, the buyer should consider investing in a three-phase transformer with voltage regulation capabilities. A transformer equipped with Automatic Voltage Regulation (AVR) technology can help maintain a consistent output voltage, minimizing fluctuations and ensuring that machinery operates efficiently. When sourcing a transformer, the buyer should consult with suppliers to understand the specific voltage and current requirements of their machinery. It’s also crucial to consider the transformer’s kVA rating to ensure it can handle the load without overheating. Additionally, implementing proper installation and maintenance practices, such as regular inspections and load testing, can further enhance the reliability of the power supply.
Scenario 2: Complex Installation Challenges
The Problem: A construction firm in Nigeria is tasked with integrating a three-phase transformer into a new facility, but the team is facing challenges with the installation process. The complexity of the electrical connections, particularly distinguishing between star and delta configurations, has led to confusion among the technicians. As a result, the project timeline is at risk, and the company is concerned about incurring additional costs due to delays.
The Solution: To simplify the installation process, the buyer should invest in comprehensive training for the technical team on three-phase transformer configurations and installation techniques. Collaborating with experienced electrical engineers or consultants can also provide valuable insights and hands-on assistance during the installation phase. Furthermore, the buyer should ensure that the transformer comes with clear documentation outlining the wiring configurations and connection diagrams. Utilizing modular transformers designed for easier assembly can also mitigate installation difficulties, allowing the team to focus on efficient project completion.

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficiency
The Problem: An energy company in the Middle East is grappling with high operational costs attributed to inefficient energy use in their distribution network. The existing transformers are outdated and not optimized for energy efficiency, leading to higher energy losses and increased electricity bills. The buyer is looking for solutions that not only reduce costs but also align with sustainability goals.
The Solution: The buyer should consider upgrading to modern three-phase transformers designed with energy efficiency in mind, such as those with amorphous steel cores or higher-grade insulation materials. These advancements significantly reduce core losses and improve overall efficiency. When sourcing new transformers, the buyer should request performance data and energy efficiency ratings, such as the efficiency class (e.g., IE3 or IE4), to compare options. Additionally, conducting a thorough energy audit can help identify specific inefficiencies in the existing system and inform the buyer about the optimal transformer specifications required for their unique operational needs. Implementing a phased replacement strategy can also spread out costs while progressively improving energy efficiency across the network.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3phase transformer
What are the Key Materials Used in 3-Phase Transformers?
When selecting materials for 3-phase transformers, various factors such as performance, durability, cost, and regional compliance standards play a crucial role. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the construction of 3-phase transformers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
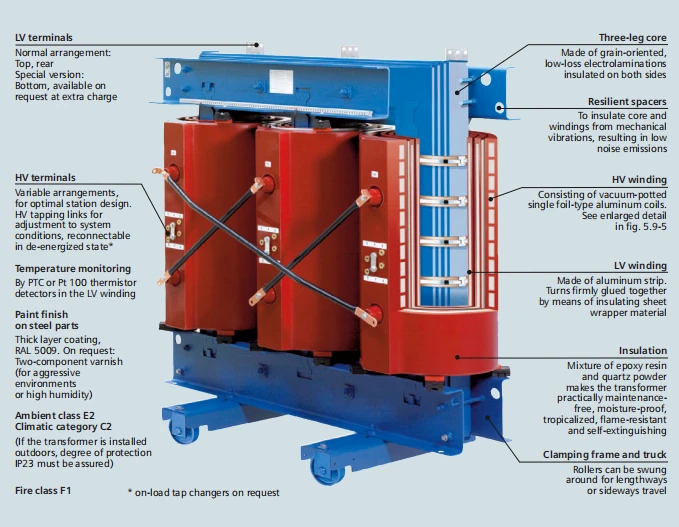
How Does Silicon Steel Impact Transformer Performance?
Silicon steel is widely used in transformer cores due to its excellent magnetic properties. Its key properties include high electrical resistivity, which reduces eddy current losses, and low hysteresis loss, enhancing energy efficiency. Silicon steel can typically withstand temperatures up to 150°C and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros: Silicon steel is cost-effective and readily available, making it a popular choice for manufacturers. Its lightweight nature also contributes to easier handling and installation.
Cons: However, silicon steel can be brittle, which may complicate manufacturing processes. Additionally, its performance can be affected by environmental factors, necessitating careful consideration in humid or corrosive settings.
Impact on Application: Silicon steel is particularly compatible with high-frequency applications, making it ideal for industrial settings. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local humidity levels and potential corrosion when selecting this material.
What Role Does Copper Play in Transformer Windings?
Copper is the preferred material for transformer windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal performance. It can handle high temperatures and has a melting point of around 1,085°C, making it suitable for high-load applications.
Pros: The high conductivity of copper leads to lower energy losses, which is crucial for efficiency in power distribution. Additionally, copper is highly durable and resistant to fatigue, ensuring long-term reliability.
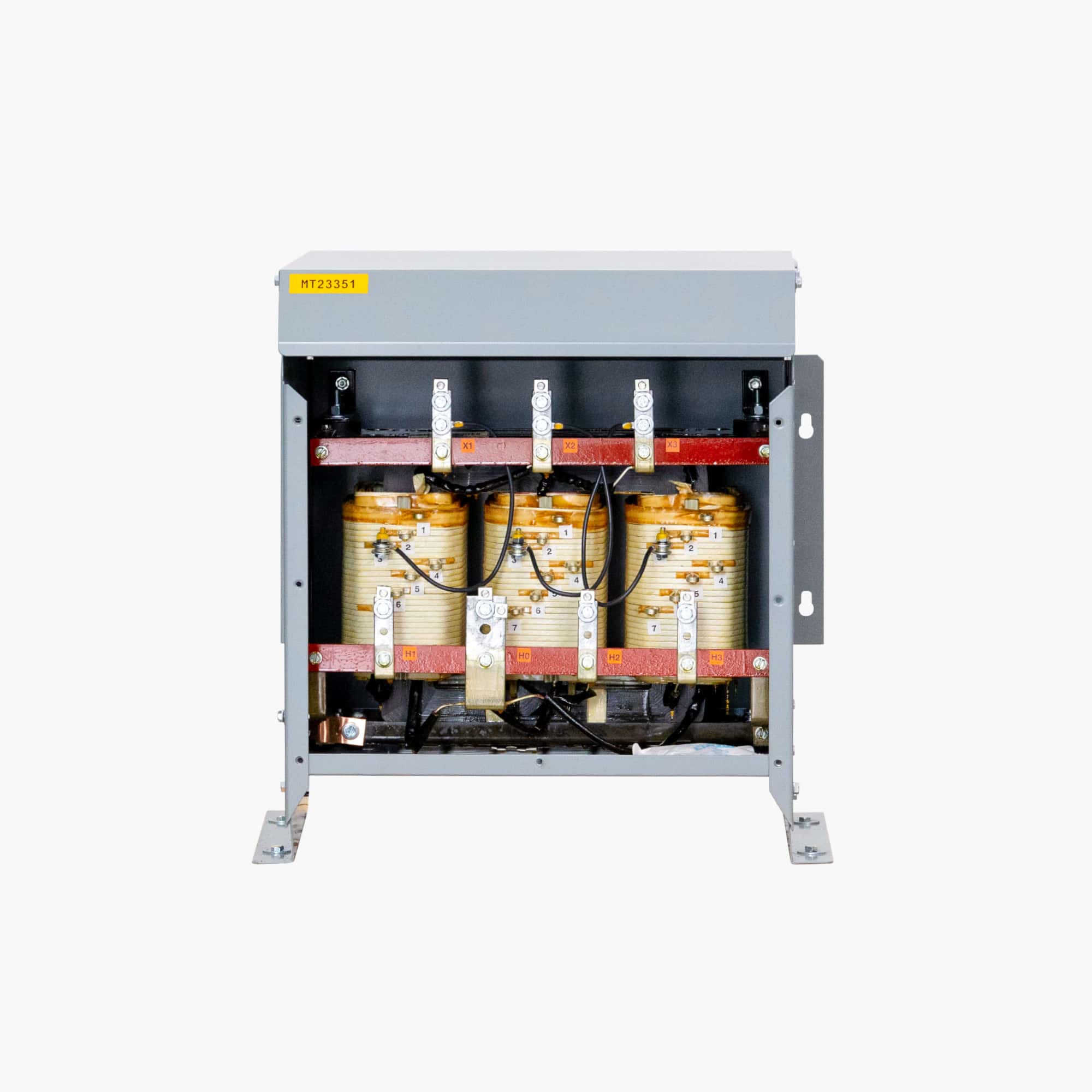

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
Cons: The primary drawback is the cost; copper is significantly more expensive than aluminum, which is often used as an alternative. Furthermore, copper’s weight can complicate installation and increase shipping costs.
Impact on Application: Copper windings are essential for applications requiring high efficiency and low resistance. B2B buyers should consider local pricing fluctuations and availability, especially in markets like Nigeria and Brazil.
How Does Aluminum Compare to Copper for Windings?
Aluminum is frequently used as a cost-effective alternative to copper in transformer windings. It has lower electrical conductivity than copper but is lighter and less expensive, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects.
Pros: The reduced weight of aluminum can simplify installation and lower transportation costs. It is also more abundant and can be sourced more easily in various regions.
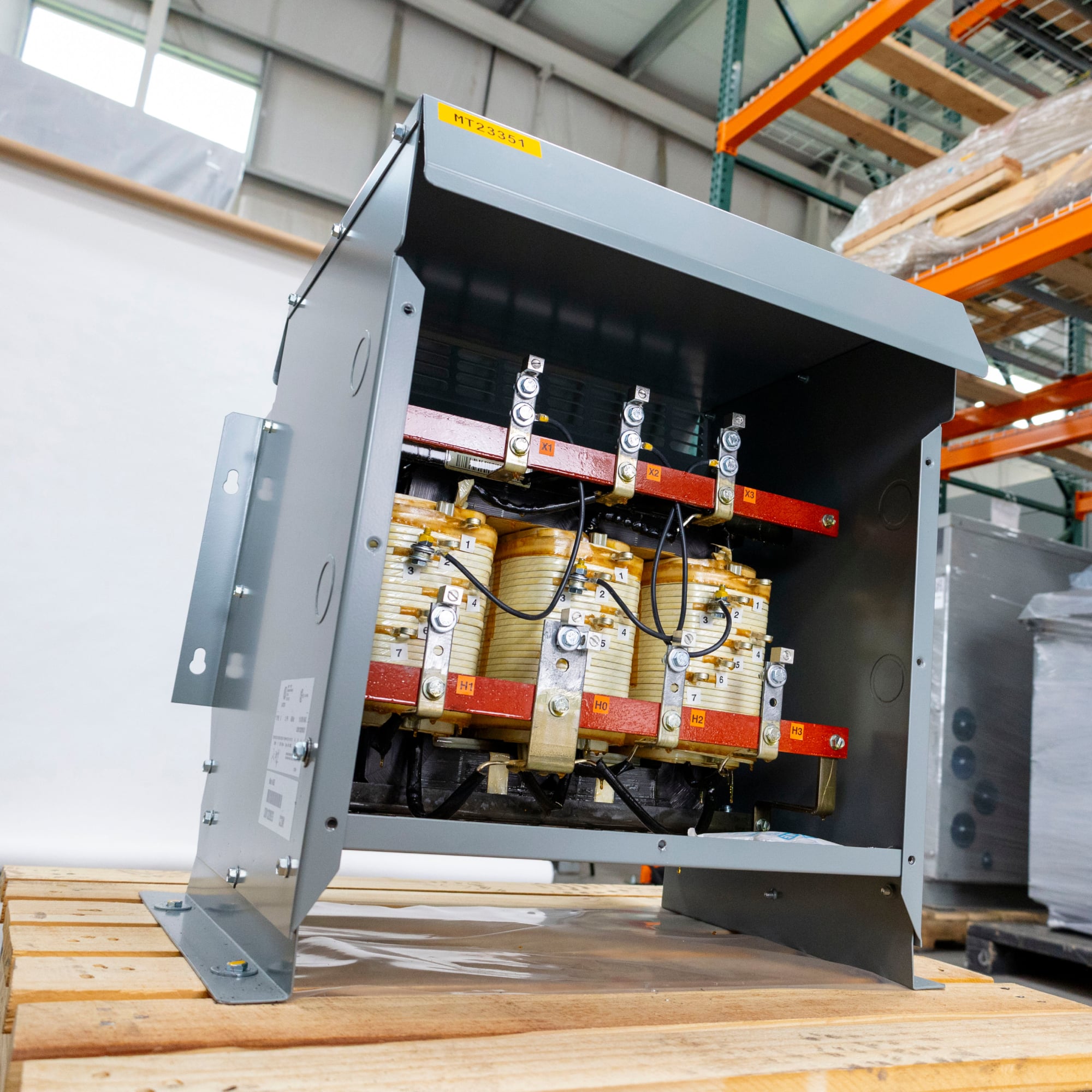

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
Cons: The downside is that aluminum has a higher resistance, leading to greater energy losses compared to copper. Additionally, aluminum is more prone to oxidation, which can impact performance and longevity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight and cost are more critical than efficiency. Buyers in the Middle East and South America should be aware of the trade-offs between cost and performance when considering aluminum for windings.
What Benefits Does Insulating Material Provide in Transformers?
Insulating materials, such as oil and resin, are crucial for the safe operation of transformers. These materials provide electrical insulation and thermal management, with properties that can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Pros: Insulating materials enhance safety by preventing electrical shorts and overheating. They also improve the overall efficiency of the transformer by maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
Cons: The main limitation is the potential environmental impact, particularly with oil-based insulations. Regulatory compliance can be a concern, especially in Europe where strict environmental standards apply.
Impact on Application: Insulating materials must be compatible with the specific operating conditions of the transformer. B2B buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations, such as ASTM or DIN standards, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 3-Phase Transformers
| Material | Typical Use Case for 3-phase transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Steel | Transformer cores | High magnetic efficiency | Brittle, sensitive to environmental factors | Medium |
| Copper | Windings | Excellent conductivity | High cost, heavier than aluminum | High |
| Aluminum | Windings | Lightweight, cost-effective | Higher resistance, prone to oxidation | Low |
| Insulating Material | Electrical insulation | Enhances safety and efficiency | Environmental concerns, regulatory compliance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the various materials used in 3-phase transformers, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3phase transformer
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a 3-Phase Transformer?
The manufacturing process of a three-phase transformer is intricate and involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets performance standards and customer requirements. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers effectively.
Material Preparation: What Is Involved?
The manufacturing process begins with the careful selection and preparation of raw materials. The primary materials include:
- Core Materials: High-grade silicon steel is typically used for the transformer core due to its superior magnetic properties. This steel is cut into sheets to minimize energy loss due to eddy currents.
- Winding Materials: Copper and aluminum wires are commonly used for windings. The choice between these materials often depends on cost, weight, and conductivity requirements.
- Insulation Materials: Insulating materials, such as polyester film and varnish, are essential for preventing short circuits and ensuring the durability of the transformer under high voltage conditions.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo rigorous testing for quality and compliance with international standards. This ensures that all components are suitable for the intended application.
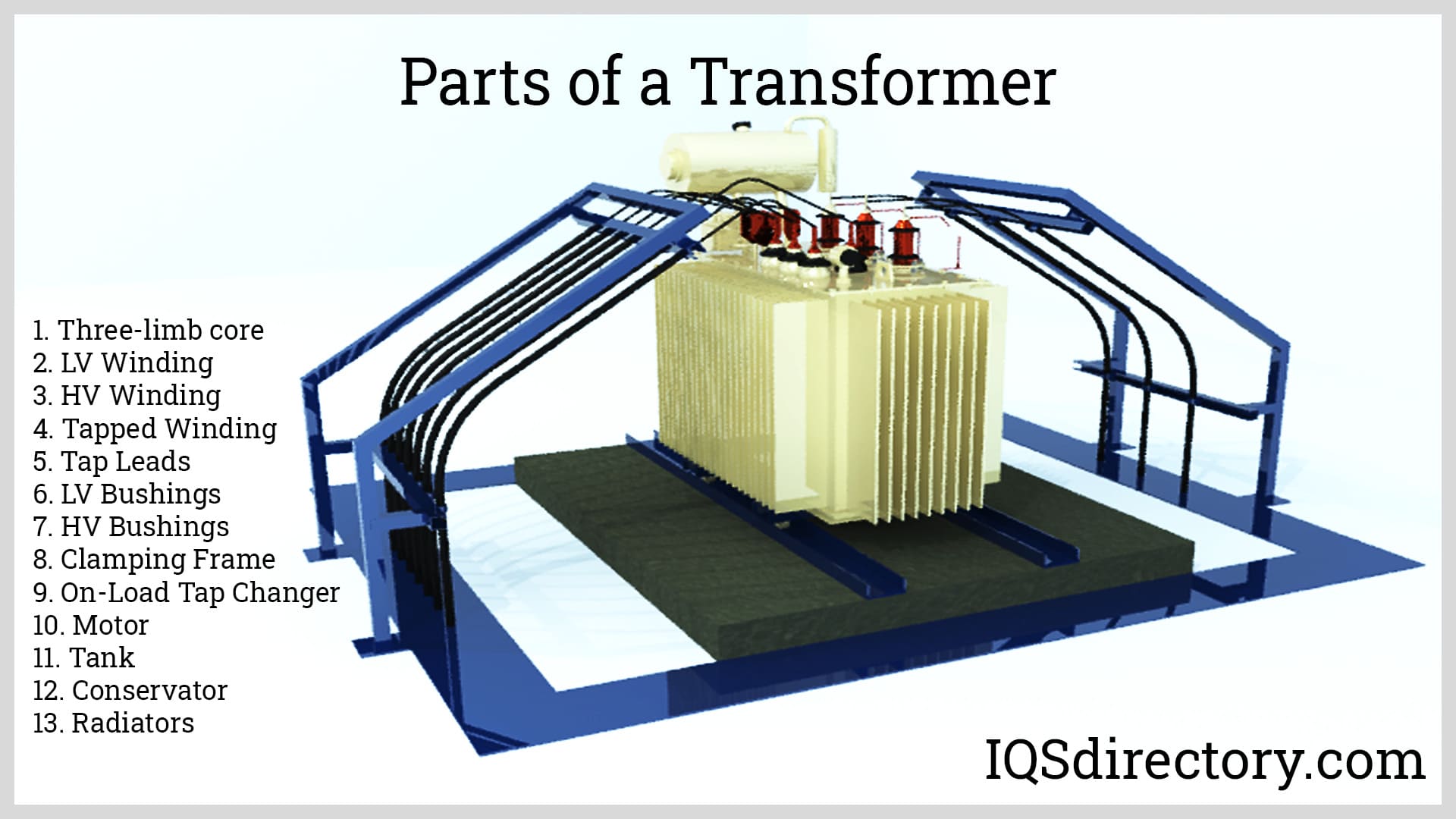
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
The forming stage involves shaping the core and windings to prepare for assembly. This stage includes:
Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
- Core Assembly: The core is assembled from pre-cut sheets, which are stacked and joined to form a robust magnetic structure. This assembly is typically done using a process called stacking, which helps to minimize air gaps that could lead to energy loss.
- Winding Formation: Copper or aluminum wires are wound around the core in precise configurations. This can be done using automated winding machines that ensure consistent tension and alignment, which are critical for maintaining the transformer’s efficiency.
What Assembly Techniques Are Commonly Used?
The assembly of a three-phase transformer is a meticulous process that requires attention to detail. The assembly stage involves:
- Connecting Windings: The primary and secondary windings are connected based on the desired configuration (e.g., Delta or Star). This is crucial as it determines the voltage transformation ratio and the overall performance of the transformer.
- Insulation Application: After the windings are connected, insulation materials are applied to prevent electrical leakage and enhance safety. This step is vital, especially in high-voltage transformers.
- Final Assembly: The entire unit is then assembled within a protective casing, which may include additional insulation and cooling features. The casing is designed to withstand environmental factors and mechanical stresses.
What Finishing Processes Ensure Quality?
Finishing processes are essential to ensure that the transformer meets all performance specifications and industry standards. Key finishing steps include:
- Surface Treatment: The outer surfaces of the transformer may undergo treatments such as painting or powder coating to enhance corrosion resistance and durability.
- Final Assembly Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that all components are correctly installed and that there are no visible defects.
- Testing: Prior to shipping, the transformer undergoes a series of tests, including insulation resistance tests, power frequency tests, and temperature rise tests, to verify that it operates within specified parameters.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for 3-Phase Transformers?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of three-phase transformers, especially for international B2B buyers. Suppliers often adhere to various quality management systems and standards, including:
- ISO 9001: This international standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that organizations meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently.
- CE Certification: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For transformers used in oil and gas applications, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints play a vital role in maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic inspections are conducted to monitor the production process and identify any deviations from established standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, a comprehensive inspection and testing process ensures that the finished transformer meets all specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for 3-Phase Transformers?
A variety of testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability and performance of three-phase transformers:
- Insulation Resistance Testing: This test assesses the integrity of insulation materials and checks for potential faults that could lead to electrical failures.
- Power Frequency Testing: Conducted to evaluate the transformer’s ability to withstand high voltage conditions without failure.
- Temperature Rise Testing: This ensures that the transformer operates within safe temperature limits during normal and overload conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is essential. Here are some strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed QC reports, including test results and certifications, to validate the supplier’s compliance with relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality assurance processes and product integrity.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control when sourcing three-phase transformers. These include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements, so it is critical to ensure that the transformer complies with local regulations.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and foster stronger supplier relationships.
- Logistics and Transportation: Consideration must be given to the logistics of transporting transformers, as this can impact their quality if not handled properly.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for three-phase transformers, ensuring they receive high-quality, reliable products tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘3phase transformer’
To assist B2B buyers in the procurement of three-phase transformers, this guide provides a practical checklist designed to ensure informed decision-making and successful sourcing. By following these steps, buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of selecting the right transformer for their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining your technical requirements for the three-phase transformer. This includes determining the power rating (kVA), voltage levels, and whether a delta or star connection suits your application best. Understanding these specifications is crucial, as they directly influence the transformer’s performance and compatibility with your existing systems.
Step 2: Research Compliance and Standards
Ensure that the transformers you are considering comply with international and local standards, such as IEC or ANSI. This step is essential to guarantee safety, reliability, and performance. Additionally, verify whether the transformers meet environmental regulations, particularly if you are sourcing from regions with strict compliance requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers within similar industries or regions. A supplier’s track record in delivering quality products and services is indicative of their reliability and capability to meet your needs.
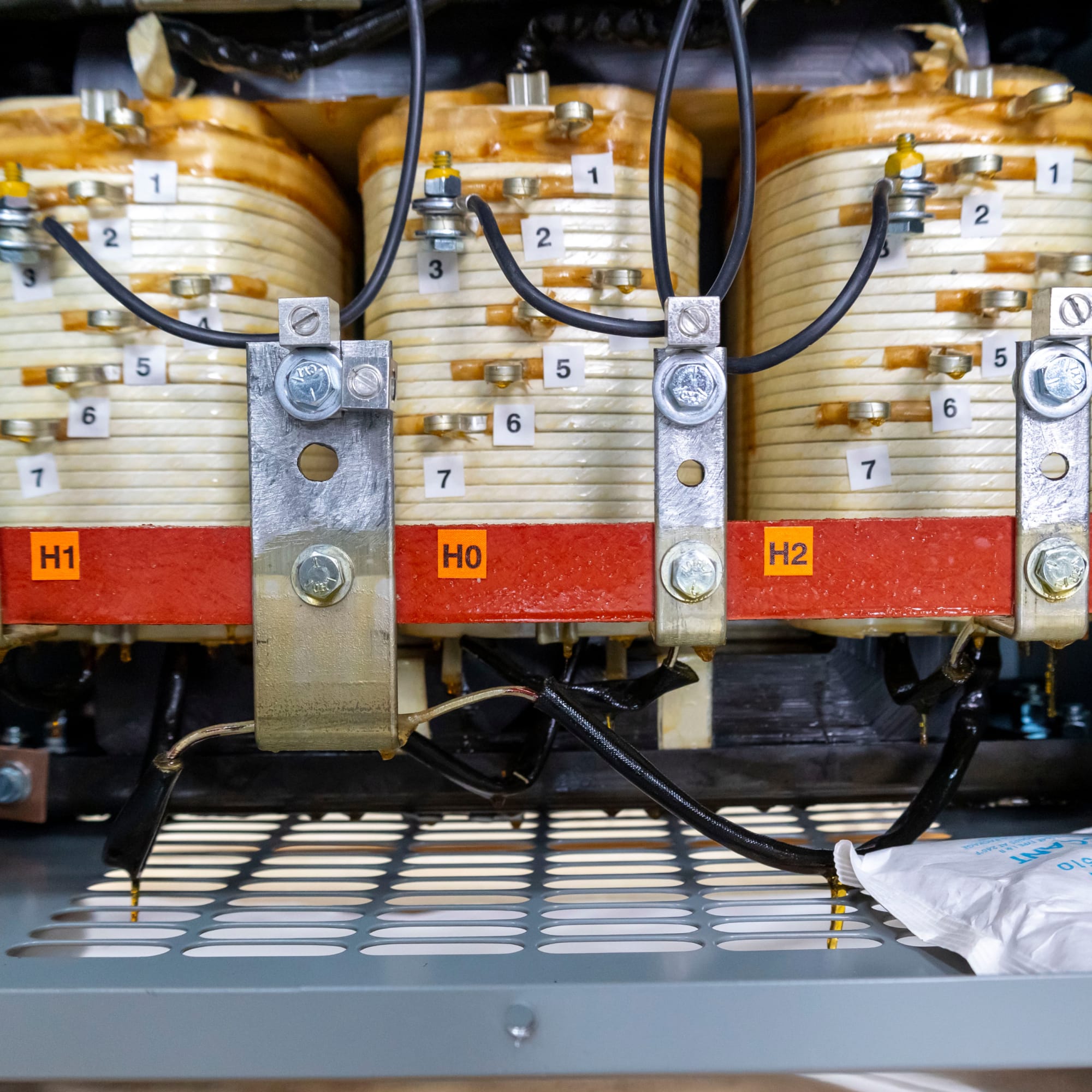

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
Step 4: Assess Warranty and After-Sales Support
Review the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by the suppliers. A robust warranty can protect your investment, while responsive after-sales service ensures that any issues can be resolved quickly. Look for suppliers that provide technical support, installation guidance, and maintenance services.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
While pricing is an important factor, consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes installation, maintenance, and operational costs. Request detailed quotations from multiple suppliers to facilitate a comprehensive comparison. Understanding the TCO will help you make a more informed decision that balances upfront costs with long-term value.
Step 6: Inspect Manufacturing Capabilities
Evaluate the manufacturing capabilities of potential suppliers. This includes assessing their production processes, quality control measures, and technological advancements. A supplier with modern facilities and stringent quality control is more likely to deliver a reliable product that meets your specifications.
Step 7: Finalize Logistics and Delivery Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, clarify the logistics and delivery terms. Discuss shipping options, lead times, and any potential import/export duties that may apply. Establishing clear terms upfront will help avoid unexpected delays and costs, ensuring a smoother procurement process.

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies for three-phase transformers, ensuring they select the right products that meet their operational requirements while also securing reliable partnerships with suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3phase transformer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 3-Phase Transformers?
When sourcing 3-phase transformers, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as copper, steel, and insulation materials is a significant factor. Copper prices can fluctuate based on global demand, while the quality of steel used in the core affects both durability and efficiency.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region where manufacturing occurs. In areas with higher wages, such as parts of Europe, the labor component can be substantial. In contrast, countries with lower labor costs may provide a more competitive pricing option.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs related to production, including factory utilities, equipment maintenance, and salaries of supervisory staff. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting the overall cost.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling is crucial, especially for custom specifications. Buyers should consider the amortization of these costs over the expected production volume to evaluate their impact on pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product reliability through rigorous QC processes adds to the cost. Certifications such as ISO can enhance credibility but may also elevate prices due to compliance costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and insurance, can vary based on the destination. Buyers should factor in these costs, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s financial health.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of 3-Phase Transformers?
Several factors influence the pricing of 3-phase transformers, making it essential for buyers to understand these dynamics:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, which can significantly impact overall pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs and specifications can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized materials and additional engineering. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials directly impacts the price. Transformers built with high-quality materials that meet specific certifications are usually more expensive but can offer better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their brand, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) between the buyer and supplier can affect the total cost. Different terms can shift responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs, impacting overall expenditure.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help Buyers Reduce Costs?
Effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings when sourcing 3-phase transformers. Here are some actionable tips:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: When possible, consolidate orders to meet or exceed MOQs, allowing for more favorable pricing from suppliers.
-
Request Multiple Quotations: Soliciting bids from multiple suppliers not only provides comparative pricing but also strengthens your negotiating position.
-
Discuss Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Emphasize the long-term benefits of quality transformers, including reduced maintenance costs and energy efficiency, which may justify a higher initial price.
-
Be Clear on Specifications: Clearly communicate your requirements to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to costly changes later in the process.
What Are the Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers in Emerging Markets?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, face unique challenges:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of exchange rate volatility, as it can significantly impact the final costs. Consider locking in exchange rates when feasible.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Research local regulations regarding import duties, taxes, and potential tariffs that could affect the total cost of acquisition.
-
Supply Chain Reliability: Ensure the supplier has a reliable logistics network to avoid delays that could lead to additional costs or operational disruptions.
Disclaimer
The prices and strategies discussed herein are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and consult with industry experts to determine accurate pricing for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 3phase transformer With Other Solutions
When considering electrical power distribution systems, B2B buyers often seek alternatives to three-phase transformers. These alternatives may offer unique benefits depending on specific operational requirements, regional infrastructure, or budget constraints. This analysis compares the three-phase transformer against two viable alternatives: single-phase transformers and static frequency converters.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 3Phase Transformer | Single-Phase Transformer | Static Frequency Converter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency for industrial loads | Suitable for smaller applications | Excellent for variable loads |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost | Moderate cost, depends on capacity |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled installation | Easier installation | Complex installation |
| Maintenance | Moderate, skilled labor required | Low, simpler systems | High, requires specialized knowledge |
| Best Use Case | Large industrial applications | Residential and small businesses | Renewable energy integration |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Single-Phase Transformers?
Single-phase transformers are often less complex and more cost-effective, making them suitable for residential and small-scale commercial applications. They are easier to install and maintain, which can be a significant advantage for smaller businesses or projects with limited budgets. However, their performance is limited in larger industrial applications, as they cannot efficiently handle the power demands that a three-phase system can.
What are the Benefits and Challenges of Using Static Frequency Converters?
Static frequency converters are an attractive alternative for applications requiring variable frequency and voltage. They excel in renewable energy systems and variable speed drives, allowing for better control over power delivery. However, they tend to be more complex and costly to install and maintain, requiring specialized knowledge and training. This makes them less accessible for companies without the necessary technical expertise.

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Choosing the right electrical distribution solution requires a thorough understanding of operational needs, budgetary constraints, and technical capabilities. For businesses with high power demands, three-phase transformers remain the industry standard due to their efficiency and performance. However, for smaller operations or those needing flexibility, single-phase transformers or static frequency converters may provide the necessary functionality at a more manageable cost. Evaluating the specific application and consulting with technical experts can guide B2B buyers toward the most suitable option for their unique circumstances.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3phase transformer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a 3-Phase Transformer?
When evaluating 3-phase transformers, understanding their critical technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key specifications:
-
KVA Rating (Kilovolt-Amperes)
The KVA rating indicates the transformer’s capacity to handle electrical loads. It’s crucial for determining how much power a transformer can supply without overheating. Buyers should match the KVA rating to their application needs, as undersized transformers can lead to inefficiencies and potential failures. -
Winding Configuration
Transformers can be configured in delta (Δ) or star (Y) arrangements. The choice impacts voltage transformation and system reliability. Delta configurations are often used for industrial applications requiring high power, while star configurations are suitable for systems needing a neutral point. Understanding these configurations helps buyers choose the right transformer for specific applications. -
Material Grade
The core and winding materials significantly influence performance and efficiency. High-grade silicon steel is commonly used for cores to minimize losses, while copper is preferred for windings due to its excellent conductivity. Selecting a transformer with high-quality materials ensures durability and operational efficiency, which is vital for long-term investment. -
Temperature Class
The temperature class indicates the maximum operating temperature of the transformer. Common classes include A (up to 105°C), B (up to 130°C), and F (up to 155°C). This specification is crucial for ensuring that the transformer operates reliably in various environmental conditions, especially in regions with extreme climates. -
Impedance
Impedance affects the voltage regulation and fault current levels in a transformer. It is typically expressed as a percentage. A transformer with appropriate impedance helps in maintaining system stability during load changes and fault conditions, making this an essential factor for buyers concerned about system reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 3-Phase Transformers?
Understanding industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms used in the context of 3-phase transformers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of transformers, buyers may work directly with OEMs to procure customized transformers that meet specific operational requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For transformers, this may affect purchasing decisions, especially for smaller companies or projects with limited budgets. Understanding MOQ helps buyers negotiate better terms or plan their procurement strategy effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific products, including 3-phase transformers. This process allows buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they obtain the best value and terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They specify who pays for shipping, insurance, and duties. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and manage risks effectively when importing transformers from overseas suppliers. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. In transformer procurement, understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring timely delivery, especially when dealing with large-scale installations. -
Transformer Bank
This term refers to a group of three single-phase transformers connected to function as a single three-phase transformer. Buyers may encounter this term when looking for flexible solutions that can be adapted to specific load requirements or redundancy needs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of 3-phase transformer procurement with greater confidence and precision.
Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 3phase transformer Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends Shaping the 3-Phase Transformer Market?
The global 3-phase transformer market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for electricity in emerging economies, particularly in Africa and South America. With rapid urbanization and industrialization, countries like Nigeria and Brazil are investing heavily in electrical infrastructure to support their economic growth. This surge in demand is accompanied by a shift toward renewable energy sources, necessitating advanced transformer technologies that can efficiently manage variable loads and integrate with smart grid systems.
Emerging technologies such as IoT and AI are revolutionizing the way transformers are monitored and managed, leading to increased operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. For B2B buyers, this means sourcing transformers equipped with smart capabilities that enhance reliability and performance. Additionally, the market is witnessing a trend toward prefabricated and modular transformer solutions, allowing for quicker installation and flexibility in deployment, which is particularly advantageous for projects in remote areas.
Another significant trend is the rise of digital procurement platforms. These platforms streamline the sourcing process, enabling international buyers to compare products, prices, and suppliers more efficiently. As competition intensifies, transparency in pricing and supplier capabilities becomes crucial for B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the 3-Phase Transformer Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the procurement of 3-phase transformers. With growing awareness of environmental issues, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. This includes sourcing materials that are environmentally friendly and ensuring that the manufacturing processes comply with international environmental standards.
Ethical sourcing is closely linked to sustainability and involves ensuring that the materials used in transformers are obtained from responsible suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations. Buyers should look for certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or similar green certifications that indicate a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, as energy efficiency standards become stricter globally, transformers that meet or exceed these standards are becoming more attractive. Investing in high-efficiency transformers not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with corporate social responsibility goals. For B2B buyers, incorporating sustainability into sourcing strategies can enhance brand reputation and foster long-term relationships with environmentally conscious partners.
What Is the Historical Context of 3-Phase Transformers in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of 3-phase transformers dates back to the late 19th century, coinciding with the advent of electrical power generation and distribution. Initially, transformers were primarily used to step up voltage for long-distance transmission, a necessity for the burgeoning electrical infrastructure. The introduction of alternating current (AC) systems marked a significant advancement, allowing for more efficient power distribution.
As industries expanded, the demand for reliable and efficient power sources grew, leading to innovations in transformer design and technology. The development of different winding configurations—such as delta and star—enabled transformers to cater to various applications, enhancing their versatility in industrial settings. Over the decades, the focus has shifted towards improving energy efficiency and reliability, paving the way for modern 3-phase transformers that integrate advanced technologies and meet stringent environmental standards.

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
Today, the historical context of 3-phase transformers serves as a foundation for understanding current market dynamics and sourcing trends. Buyers who appreciate this evolution are better equipped to make informed decisions that align with both technological advancements and sustainability goals in their procurement strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3phase transformer
1. How do I choose the right 3-phase transformer for my application?
Selecting the right 3-phase transformer involves understanding your specific electrical requirements, including voltage ratings, power capacity (kVA), and the type of load you will be serving (resistive, inductive, or mixed). Consider whether you need a star or delta connection based on your existing system and future scalability. Additionally, check the transformer’s efficiency and cooling requirements, as these factors can impact operational costs. Engaging with a knowledgeable supplier can also help tailor the selection to your unique needs.
2. What are the key advantages of using a 3-phase transformer?
3-phase transformers offer several benefits over single-phase units, including increased efficiency in power distribution and reduced copper losses due to the balanced load. They can handle larger power loads, making them ideal for industrial applications. Additionally, they provide a more stable power supply, which is crucial for sensitive equipment. Their compact design also saves space compared to using three single-phase transformers.
3. How can I verify the reliability of a 3-phase transformer supplier?
To assess a supplier’s reliability, start by checking their industry certifications and quality standards (ISO, IEC). Review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge their performance history. Additionally, request references from previous clients, especially those in your region or industry. Consider conducting site visits or audits to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Strong after-sales support and warranty terms are also indicators of a trustworthy supplier.

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
4. What customization options should I consider when sourcing a 3-phase transformer?
Customization can significantly enhance the performance of your 3-phase transformer. Key options include voltage ratings, winding configurations (star or delta), and cooling methods (oil-immersed or dry-type). You might also want to consider specific features such as built-in protection devices, noise reduction, and size constraints based on your installation environment. Discussing your requirements with the supplier can lead to tailored solutions that meet your operational needs.
5. What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for 3-phase transformers?
The MOQ for 3-phase transformers varies by supplier and can depend on factors such as production capacity and customization requirements. Generally, MOQs can range from a single unit for standard models to larger quantities for customized or high-demand configurations. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your purchasing capabilities and project timelines, and to inquire about potential flexibility in order sizes.
6. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a 3-phase transformer internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common options include advance payments, letter of credit, or staggered payments based on delivery milestones. Ensure you clarify the terms before finalizing the order to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using secure payment methods that protect your financial interests, especially for large transactions.
7. How do logistics and shipping affect the cost of a 3-phase transformer?
Logistics and shipping can significantly impact the total cost of acquiring a 3-phase transformer, especially for international buyers. Factors to consider include shipping method (air vs. sea), customs duties, and insurance costs. Additionally, the transformer’s weight and dimensions will affect freight charges. It’s essential to work closely with your supplier to understand the logistics involved and to budget for these additional expenses in your procurement process.
8. What quality assurance measures should be in place for 3-phase transformers?
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing 3-phase transformers. Ensure that the supplier conducts rigorous testing, including insulation resistance tests, load testing, and temperature rise tests, to verify performance and safety. Look for compliance with international standards such as IEC or ANSI. Additionally, a robust warranty and after-sales service can provide peace of mind regarding long-term reliability and support in case of issues post-purchase.
Top 8 3Phase Transformer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Electronics Tutorials – Three-Phase Transformers
Domain: electronics-tutorials.ws
Introduction: Three-phase transformers are essential for electrical power distribution, used for generating and transmitting electric power over long distances. They can be connected in various configurations: Delta (D), Star (Y), and Interconnected-Star (Z). Three-phase transformers can be constructed by connecting three single-phase transformers or using a pre-assembled three-phase transformer with three pair…
2. Bel Fuse – 3-Phase Transformers
Domain: belfuse.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 3-Phase Transformers are electrical devices that transform power between circuits at the same frequency, typically changing voltage and current values. They are crucial for long-distance power distribution and are constructed by winding three single-phase transformers on a single core, making them smaller, more cost-effective, and lighter than three individual single-phase transformers. 3-phase tr…
3. Grainger – Three Phase Transformers
Domain: grainger.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, Grainger – Three Phase Transformers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. The Engineering Mindset – Three Phase Transformers
Domain: theengineeringmindset.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Three Phase Transformers: Rated for 2kVA, with a delta primary and a wye secondary configuration. They convert one AC voltage into another, producing multiple voltages (480V, 277V, 240V, 208V, and 120V). Types include pad mounted and pole mounted transformers. They consist of three single phase transformers combined, utilizing a steel core to enhance efficiency and reduce energy loss. Configuratio…
5. North America Phase Converters – Single to Three Phase Transformers
Domain: northamericaphaseconverters.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Single Phase to Three (3) Phase Power Converter Transformers include: 1. 240 X 480V to 120/240V Single Phase Transformers – Price range: $578.00 – $2,824.00 2. 240 Delta to 208Y/120 Volt Wye 3-Phase Transformer – Price range: $1,594.00 – $5,994.00 3. 480V to 208Y/120V Transformers – 3 Phase – Price range: $1,298.00 – $4,299.00 4. 240-480Y/277 Volt 3 Phase Transformers – Price range: $1,594.00 – $5…
6. Maddox – 3-Phase 240V Delta Transformer
Domain: store.maddox.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “3-Phase 240V Delta – 208 Y 120”, “SKU”: “MIT-DRY-125”, “sizes_available”: [“15 kVA”, “30 kVA”, “45 kVA”, “75 kVA”, “112.5 kVA”, “150 kVA”, “225 kVA”, “300 kVA”, “500 kVA”], “prices”: {“15 kVA”: {“new”: “$1,670”, “used”: “$1,336”}, “30 kVA”: {“new”: “$2,697”, “used”: “$2,158”}, “45 kVA”: {“new”: “$3,181”, “used”: “$2,545”}, “75 kVA”: {“new”: “$4,481”, “used”: “$3,585”}, “112.5 kVA…
7. Larson Electronics – 3 Phase Delta Buck/Boost Step-Up Transformer
Domain: larsonelectronics.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “3 Phase Delta Buck/Boost Step-Up Transformer”, “Primary Voltage”: “208V”, “Secondary Voltage”: “230V”, “Amperage”: “20.83 Amps”, “Frequency”: “50/60Hz”, “Transformer Type”: “Buck/Boost Step-Up Autotransformer”, “Phase”: “Three Phase”, “NEMA Rating”: “NEMA 3R”, “Input Voltage”: “208 V Delta”, “Primary Amps”: “22.94 A @ 208 V Delta”, “kVA Rating”: “8.26”, “Output Voltage”: “230 V D…
8. Square D – Low Voltage Distribution Transformers
Domain: se.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Low Voltage Distribution Transformers, Three Phase; DOE 2016 Efficiency; EX offering; Square D; 100 years of transformer design and manufacturing; latest technology in core, coil, and enclosure.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3phase transformer
As we conclude this guide on three-phase transformers, it’s essential to highlight the pivotal role strategic sourcing plays in optimizing procurement for international businesses. By understanding the various configurations—such as Delta and Star connections—buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Engaging with reliable suppliers not only ensures access to high-quality transformers but also fosters partnerships that can adapt to evolving technological advancements and market demands.
The growing energy needs across regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe present a significant opportunity for businesses to invest in robust and efficient power solutions. As these markets continue to expand, the demand for reliable three-phase transformers will only increase.
We encourage B2B buyers to proactively seek suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to quality, innovation, and sustainability. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, companies can secure a competitive edge in their operations. The future of power distribution is bright—embrace it by forging strong partnerships today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to 3phase transformer
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.