3 Way Solenoid Valve Diagram: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3 way solenoid valve diagram
In the intricate landscape of industrial automation, sourcing a reliable 3-way solenoid valve diagram is a pivotal challenge that many international B2B buyers face. Understanding the functionality and applications of these valves is essential for optimizing fluid control in diverse systems, ranging from manufacturing plants to HVAC installations. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of 3-way solenoid valves, their operational mechanisms, and practical applications across different industries.
Moreover, it equips buyers with critical insights on supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for integrating these components into existing systems. By providing detailed diagrams and explanations, this resource empowers decision-makers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany—to make informed purchasing choices.
The guide aims to demystify the complexities of solenoid valve selection, ensuring that buyers can confidently navigate the global market landscape. With clear visuals and expert recommendations, you will gain a deeper understanding of how 3-way solenoid valves function, enabling you to enhance efficiency and reliability in your operations. Whether you’re looking to upgrade existing systems or invest in new technologies, this guide serves as an essential tool for maximizing your investment in fluid control solutions.
Understanding 3 way solenoid valve diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard 3/2 Way Valve | Three ports, two positions; can be normally closed or open. | Pneumatic systems, HVAC applications | Pros: Versatile, simple design. Cons: Limited to two states. |
| Exhaust 3/2 Way Valve | Designed specifically for exhausting air; quick release. | Air compressors, pneumatic tools | Pros: Fast operation, efficient exhaust. Cons: Not suitable for liquids. |
| Universal 3/2 Way Valve | Configurable for various applications; can switch functions. | Robotics, automation systems | Pros: High adaptability, multifunctional. Cons: Complexity may require specialized knowledge. |
| Flow Control 3/2 Way Valve | Integrated flow control features for precision management. | Industrial processes, water treatment | Pros: Enhanced control over flow. Cons: More expensive due to additional features. |
| Pilot-Operated 3/2 Way Valve | Uses pilot pressure to control fluid flow; suitable for high pressures. | Heavy machinery, hydraulic systems | Pros: Handles high pressure, reliable. Cons: Requires more maintenance and understanding of operation. |
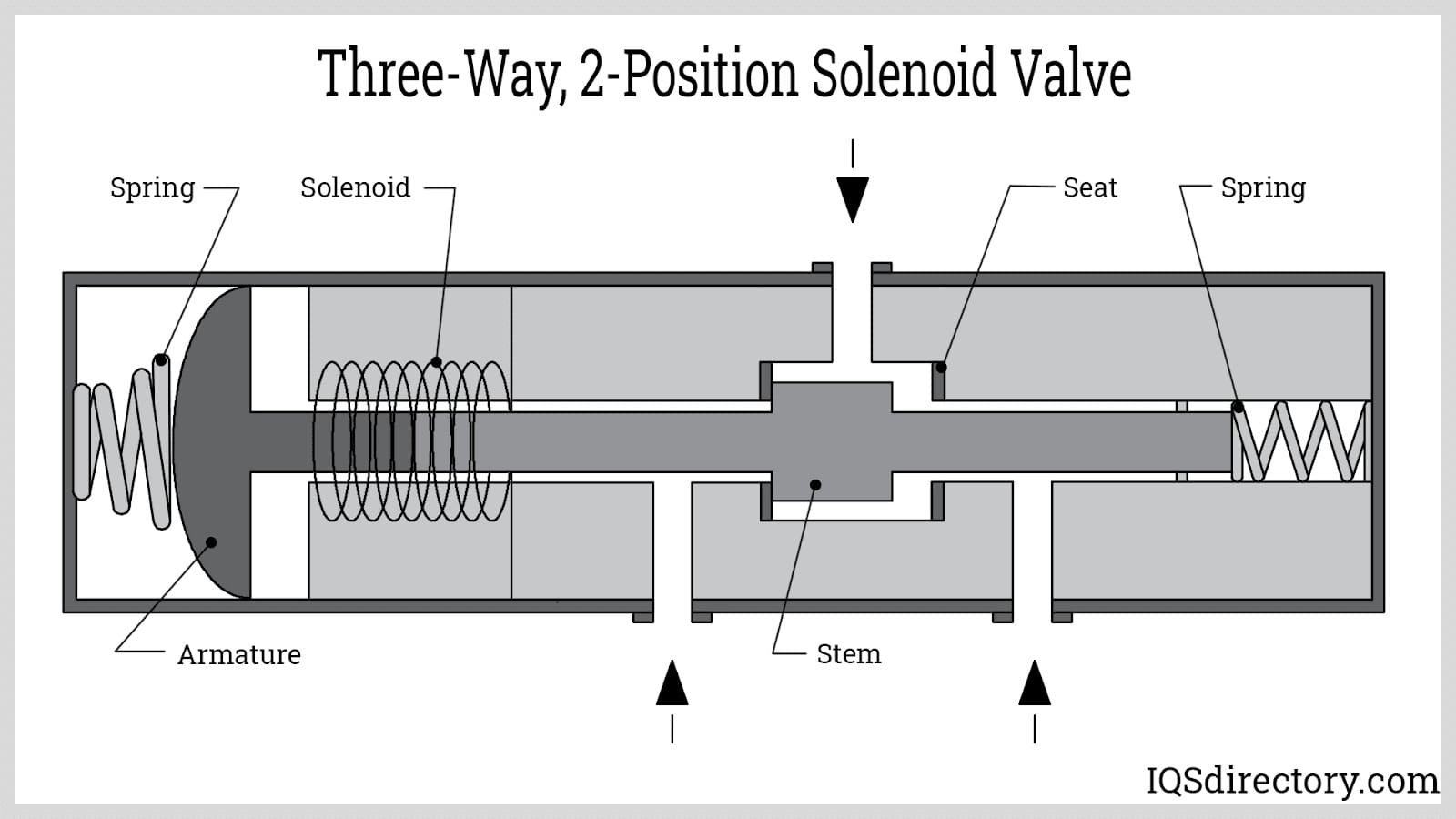
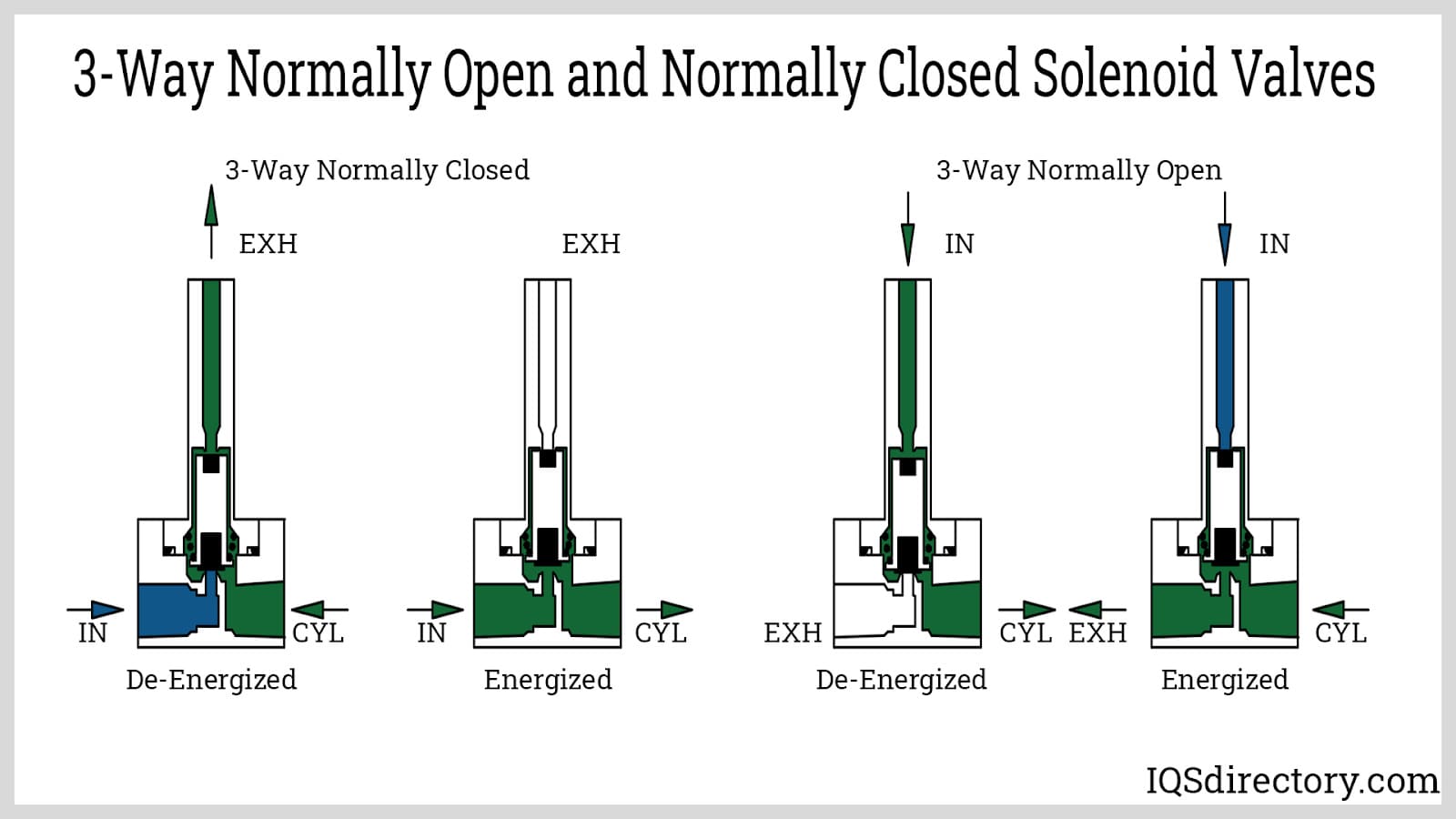
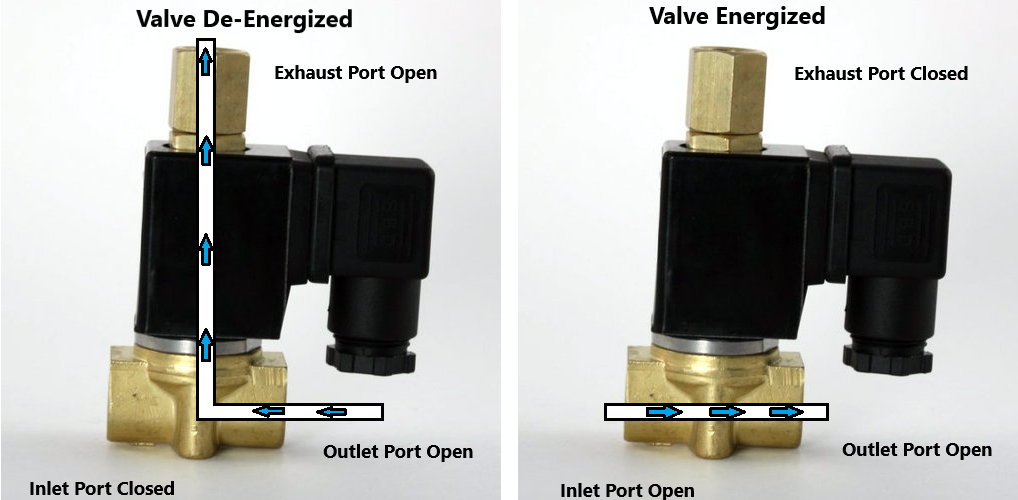
What Are the Key Characteristics of Standard 3/2 Way Valves?
Standard 3/2 way valves are characterized by their three ports and two positions, allowing for effective control of fluid flow in various systems. Typically, they can be configured as normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO), making them suitable for applications such as pneumatic systems and HVAC systems. When purchasing, buyers should consider factors like the valve’s actuation method, the medium being controlled, and compatibility with existing systems.
How Do Exhaust 3/2 Way Valves Operate?
Exhaust 3/2 way valves are specifically designed to facilitate rapid exhaust of air, making them ideal for applications involving pneumatic tools and air compressors. These valves ensure quick release of air pressure, enhancing the efficiency of pneumatic systems. Buyers should prioritize the valve’s response time and compatibility with their existing pneumatic setup when making a purchasing decision.
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
What Makes Universal 3/2 Way Valves Versatile?
Universal 3/2 way valves stand out due to their configurability for multiple applications. These valves can switch between various functions, making them suitable for use in robotics and automation systems. While their adaptability is a significant advantage, potential buyers should assess the complexity of installation and operation, as well as the need for specialized knowledge to maximize their functionality.
Why Choose Flow Control 3/2 Way Valves?
Flow control 3/2 way valves incorporate features that allow for precise management of fluid flow, making them particularly useful in industrial processes and water treatment applications. Their enhanced control capabilities can lead to improved efficiency and reduced waste. Buyers should consider the valve’s flow rate specifications and the potential for increased costs due to advanced features when evaluating options.
What Are the Benefits of Pilot-Operated 3/2 Way Valves?
Pilot-operated 3/2 way valves utilize pilot pressure to manage fluid flow, making them suitable for high-pressure applications such as heavy machinery and hydraulic systems. Their reliability and ability to handle significant pressure differentials are key advantages. However, buyers must be aware of the maintenance requirements and the necessity for a thorough understanding of the valve’s operation to ensure optimal performance.
Key Industrial Applications of 3 way solenoid valve diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 3 way solenoid valve diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Fluid control in automated assembly lines | Enhances efficiency and reduces manual intervention | Reliability, compatibility with existing systems, and durability in high-cycle environments |
| Food and Beverage | Ingredient dosing and mixing control | Ensures precise measurements and consistency | Compliance with food safety standards and ease of cleaning |
| Oil and Gas | Pipeline switching and flow control | Improves operational safety and process efficiency | Resistance to corrosive environments and high-pressure ratings |
| HVAC Systems | Zone control for heating and cooling | Optimizes energy consumption and comfort levels | Energy efficiency, compatibility with HVAC systems, and ease of maintenance |
| Pharmaceutical | Process control in drug manufacturing | Ensures product quality and regulatory compliance | High precision, reliability, and compliance with industry regulations |
How is the ‘3 Way Solenoid Valve Diagram’ Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, the 3 way solenoid valve diagram plays a crucial role in controlling fluid dynamics within automated assembly lines. By enabling the switching of fluid flow between different paths, these valves enhance operational efficiency and minimize the need for manual intervention. Buyers should consider the reliability and durability of these valves, especially in high-cycle environments, to ensure seamless integration into existing systems.
What is the Role of 3 Way Solenoid Valves in Food and Beverage Applications?
Within the food and beverage industry, 3 way solenoid valves are utilized for precise ingredient dosing and mixing control. This application is vital for maintaining consistency and quality in production processes. International buyers must prioritize compliance with food safety standards, as well as the ease of cleaning and maintenance, to ensure hygienic operations and product integrity.
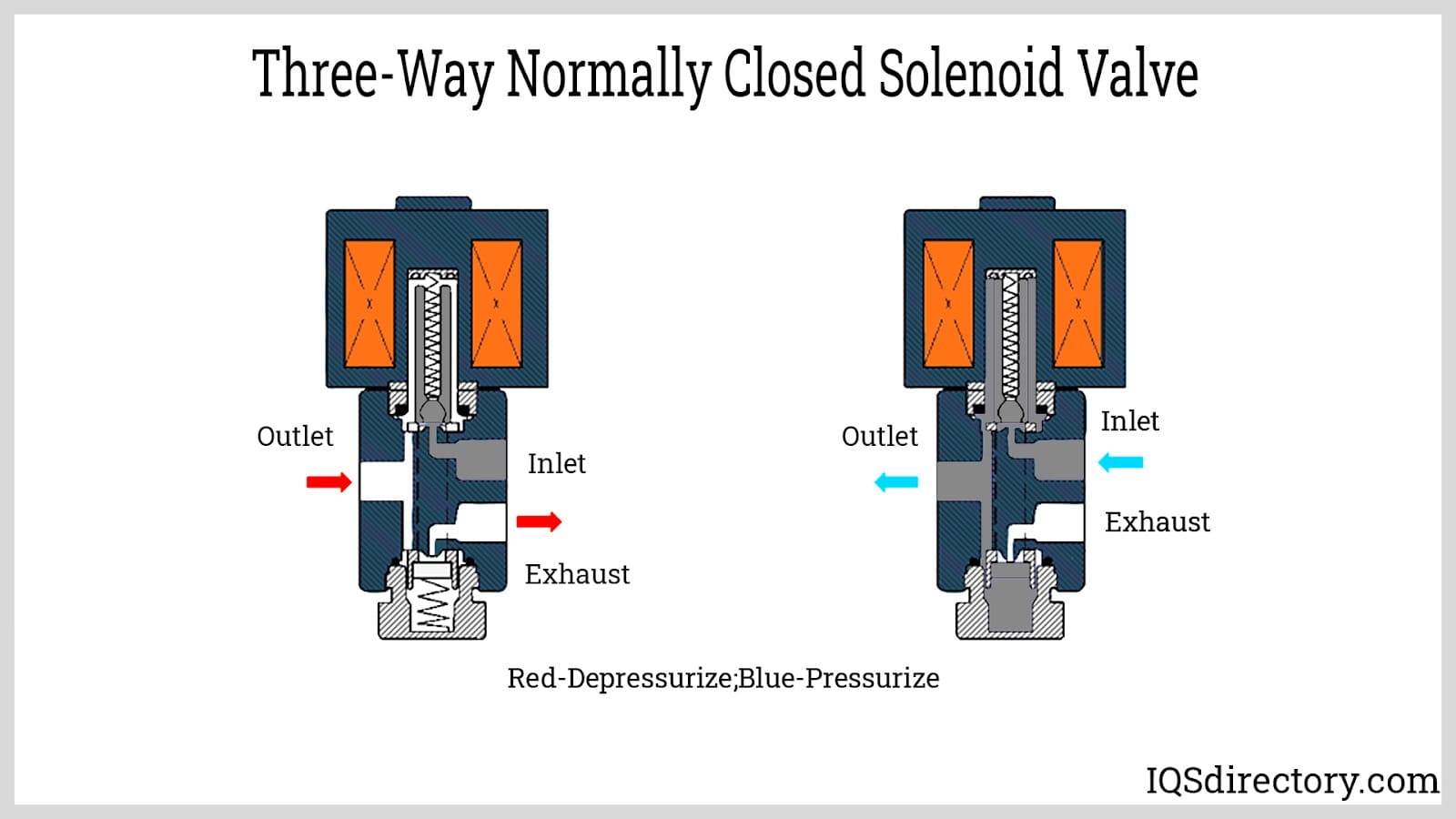
How Do 3 Way Solenoid Valves Enhance Oil and Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas industry, 3 way solenoid valves are essential for pipeline switching and flow control. These valves enhance operational safety by allowing for quick adjustments to fluid flow, which is critical in managing hazardous materials. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing valves that resist corrosive environments and meet high-pressure ratings to maintain safety and efficiency in their operations.
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
Why are 3 Way Solenoid Valves Important for HVAC Systems?
For HVAC systems, the 3 way solenoid valve diagram is integral to zone control, allowing for efficient heating and cooling distribution. By optimizing energy consumption and maintaining comfortable environments, these valves significantly enhance system performance. Key considerations for sourcing include energy efficiency ratings, compatibility with existing HVAC systems, and ease of maintenance to ensure long-term reliability.
How Do 3 Way Solenoid Valves Support Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, 3 way solenoid valves are critical for process control, ensuring the accurate mixing and dosing of chemicals. This precision is vital for maintaining product quality and adhering to regulatory standards. Buyers in this industry should prioritize valves that offer high precision, reliability, and compliance with stringent industry regulations to ensure safety and efficacy in drug production.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘3 way solenoid valve diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding 3-Way Solenoid Valve Diagrams
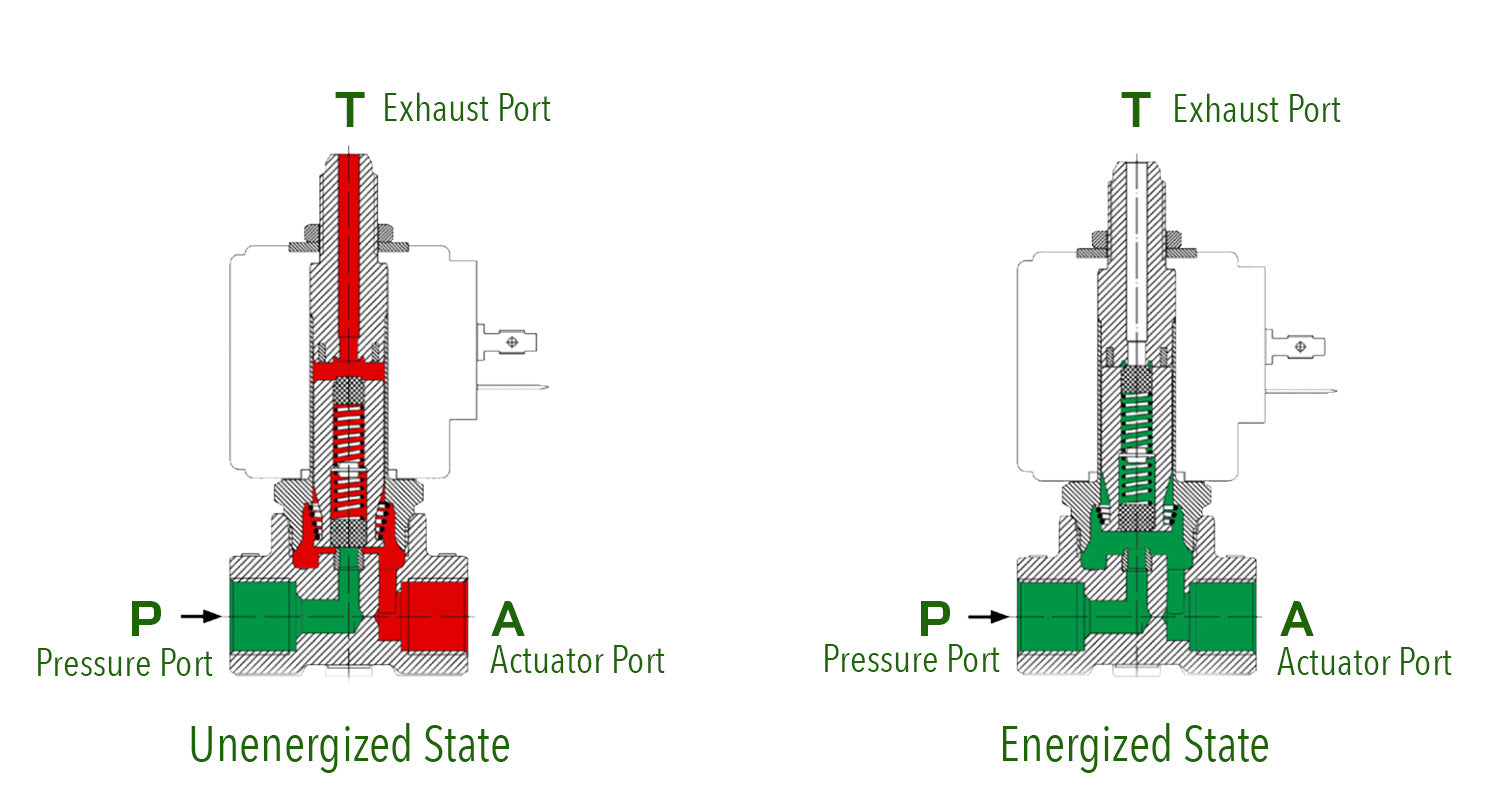
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those new to fluid control systems, often struggle to interpret 3-way solenoid valve diagrams. The symbols used can be complex and vary between manufacturers, leading to confusion when trying to understand how a valve operates within a system. This lack of clarity can result in miscommunication with engineering teams and costly errors during installation or maintenance.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should invest time in familiarizing themselves with standard symbols used in 3-way solenoid valve diagrams. Resources such as technical guides and industry standards (like ISO 1219) can provide clarity on these symbols. Additionally, purchasing from reputable suppliers who provide comprehensive documentation—including detailed diagrams and symbol legends—can help eliminate ambiguity. When placing orders, buyers should request specific diagrams and operational manuals for the valves they intend to use, ensuring that all team members are on the same page regarding installation and operation.
Scenario 2: Incompatibility with Existing Systems
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring that new 3-way solenoid valves are compatible with their existing systems. This issue arises when the specifications of the new valves do not match the existing piping or control systems, leading to delays in project timelines and increased costs for retrofitting.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their current system before sourcing new 3-way solenoid valves. This includes reviewing the existing piping diagrams, valve specifications, and control system requirements. Collaborating with engineers or consultants during this phase can provide insights into necessary adaptations. Furthermore, when sourcing valves, buyers should look for suppliers that offer customization options or technical support to tailor the valves to their existing systems. This proactive approach can save time and resources in the long run.
Scenario 3: Overlooking Maintenance and Serviceability
The Problem: After installation, many B2B buyers neglect the long-term maintenance requirements of 3-way solenoid valves, which can lead to operational failures and increased downtime. Without clear maintenance guidelines outlined in the valve diagrams, users may not perform necessary checks and service, resulting in costly repairs or replacements.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing 3-way solenoid valves that come with comprehensive maintenance guidelines included in their documentation. These guidelines should clearly outline the frequency of inspections, recommended service procedures, and troubleshooting steps for common issues. Additionally, establishing a routine maintenance schedule based on these guidelines can help ensure the longevity and reliability of the valves. Training staff on these maintenance protocols, perhaps through supplier-led workshops, can further enhance operational reliability and minimize unexpected failures. This proactive maintenance strategy not only ensures smooth operation but also extends the lifespan of the equipment, yielding better ROI over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3 way solenoid valve diagram
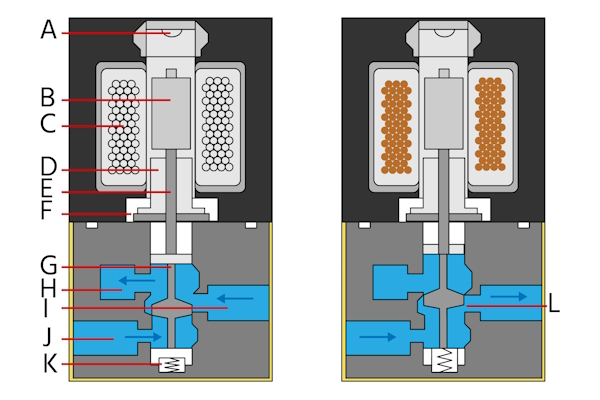
What Are the Key Materials Used in 3 Way Solenoid Valves?
When selecting materials for 3-way solenoid valves, several factors must be considered, including performance characteristics, cost, and application suitability. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the manufacturing of these valves.
How Does Brass Perform in 3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Brass is a popular choice for solenoid valve components due to its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and can handle moderate pressure levels, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros: Brass is durable and provides good sealing properties, which is essential for preventing leaks. Its relatively low cost compared to other metals makes it an attractive option for many manufacturers.
Cons: While brass is resistant to corrosion, it can be susceptible to dezincification in certain environments, particularly in the presence of chlorides. This can limit its use in applications involving aggressive media.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with water, air, and some oils, making it ideal for HVAC systems and general fluid control applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that the brass used meets local regulations regarding lead content.
What Are the Benefits of Stainless Steel in 3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Stainless steel is another widely used material for solenoid valves, known for its high corrosion resistance and strength. It can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and high pressure, making it suitable for harsh environments.
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
Pros: The durability and resistance to corrosion make stainless steel an excellent choice for applications involving aggressive chemicals or high temperatures. Its longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements.
Cons: The higher cost of stainless steel compared to brass can be a drawback for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, its manufacturing process is more complex, which can lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are ideal for chemical processing and food and beverage applications where hygiene is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with international standards such as JIS and ISO, especially in markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia, where stringent regulations are enforced.
Why Choose Plastic for 3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Plastic materials, particularly PVC and PTFE, are increasingly used for solenoid valves due to their lightweight and excellent chemical resistance. They can operate effectively at temperatures up to 80°C and moderate pressure levels.
Pros: Plastic valves are generally less expensive and easier to manufacture, which can lead to cost savings for large-scale applications. Their resistance to corrosion makes them suitable for a wide range of chemicals.
Cons: Plastic materials may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications, limiting their use in certain industrial environments. They can also be less durable than metal options.
Impact on Application: Plastic solenoid valves are commonly used in water treatment and chemical processing applications where corrosive substances are handled.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic materials used comply with relevant standards, especially in food applications, where certifications like FDA approval may be necessary.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in 3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Aluminum is a lightweight and cost-effective alternative for solenoid valve components. It has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and is suitable for low to moderate pressure applications.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easy to handle and install. Its cost-effectiveness can be appealing for large-scale manufacturing.
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
Cons: Aluminum is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel and brass, which may limit its application in certain environments. It can also be prone to wear and tear over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum valves are often used in pneumatic applications and systems where weight is a critical factor.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the aluminum used meets relevant international standards, particularly in regions with specific material regulations, such as Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 3 Way Solenoid Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for 3 way solenoid valve diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | HVAC systems, general fluid control | Good machinability and cost-effective | Susceptible to dezincification | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, food and beverage applications | High corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Water treatment, chemical processing | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-temperature applications | Medium |
| Aluminum | Pneumatic applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less corrosion resistance | Medium |
This material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3 way solenoid valve diagram
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for 3-Way Solenoid Valves?
The manufacturing of 3-way solenoid valves involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can aid B2B buyers in selecting reliable suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for 3-Way Solenoid Valves?
Material preparation is the foundation of the manufacturing process. Typically, manufacturers begin by sourcing high-quality materials such as brass, stainless steel, or plastic, depending on the valve’s application. These materials are then subjected to rigorous testing to verify their mechanical properties and compatibility with fluids.
Cutting techniques, including CNC machining, are commonly employed to achieve the precise dimensions required for valve components. This stage may also involve surface treatments to enhance corrosion resistance, especially important for valves used in harsh environments.
What Forming Techniques Are Utilized in 3-Way Solenoid Valve Production?
The forming stage includes various techniques such as forging, casting, and machining. Forging is often used for metal components to improve strength and durability. Casting allows for complex shapes to be created, particularly for valve bodies.
Once the initial forms are created, machining processes like milling and turning refine the components to exact specifications. This precision is crucial, as even minor deviations can affect the valve’s performance and reliability.
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
How Are 3-Way Solenoid Valves Assembled?
Assembly involves integrating various components, including the solenoid coil, valve body, and internal seals. Automated assembly lines are frequently employed to enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
During this stage, it’s vital to ensure that all components fit perfectly to prevent leaks and ensure smooth operation. Assembly techniques may involve the use of adhesives, welding, or mechanical fastening, depending on the design and material of the valve.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for 3-Way Solenoid Valves?
Finishing processes enhance the valve’s appearance and functionality. Techniques such as powder coating or anodizing may be applied to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Additionally, quality checks are performed during this stage to ensure that the surface finish meets specified standards. This step is essential for maintaining the valve’s integrity over time, especially in demanding applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for 3-Way Solenoid Valves?
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring that 3-way solenoid valves perform reliably and meet international standards. Various checkpoints and testing methods are employed throughout the manufacturing process.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems. Compliance with industry-specific standards like CE (for European markets) and API (for oil and gas applications) is also crucial.
These certifications indicate that the manufacturer follows rigorous quality control processes and is committed to continuous improvement.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several key checkpoints, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage verifies that the raw materials meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing ensure that any deviations are identified and corrected immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the products are shipped, a comprehensive inspection checks the valves against performance specifications and quality standards.
These checkpoints help minimize defects and ensure that only high-quality products reach the market.
How Are 3-Way Solenoid Valves Tested for Quality?
Common testing methods include pressure testing, leak testing, and functional testing.
- Pressure Testing assesses the valve’s ability to withstand the operational pressures it will encounter in service.
- Leak Testing ensures that there are no leaks in the valve, which is critical for maintaining system integrity.
- Functional Testing verifies that the valve operates as intended under various conditions, including different temperatures and pressures.
These tests help ensure that the valve will perform reliably in real-world applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can implement several verification strategies:
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures directly. This can include reviewing documentation related to quality certifications and processes.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality assurance reports that outline their QC processes, testing results, and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased review of the supplier’s quality control practices. These organizations can perform independent tests and audits, offering additional assurance to buyers.
-
Certification Checks: Buyers should verify that suppliers hold necessary certifications, such as ISO 9001, CE, or API, and ensure these are current and applicable to the products being sourced.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in quality assurance.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local regulations and international standards applicable to their markets.
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: Communication can be a challenge when dealing with international suppliers. Buyers should ensure that they have clear and effective communication channels to discuss quality standards and expectations.
-
Logistics and Shipping Considerations: The quality of products can be affected during transit. Buyers should consider suppliers that provide robust packaging and shipping solutions to minimize damage during transportation.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing 3-way solenoid valves, ensuring they select suppliers that prioritize quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘3 way solenoid valve diagram’
To effectively source a 3-way solenoid valve diagram, B2B buyers must navigate a series of critical steps. This checklist is designed to guide you through the procurement process, ensuring that you select the right components for your operational needs while minimizing risks associated with supplier quality and product specifications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining the technical requirements for the 3-way solenoid valve you need. This includes identifying the type of fluid to be controlled, the required flow rates, and the operating pressure. Be specific about the valve’s actuation method (e.g., normally open or normally closed) and any environmental considerations, such as temperature ranges and material compatibility.
Step 2: Research Applicable Standards and Regulations
Familiarize yourself with industry standards and regulations that govern solenoid valve specifications in your region. Compliance with standards such as ISO, ANSI, or local safety codes is crucial, as they ensure that the valves meet safety and operational criteria. Investigating these standards will also help you understand the certifications your supplier should have.
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Review their company profiles, request case studies, and seek references from other buyers in similar industries. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your region, particularly those familiar with the specific applications of 3-way solenoid valves in your industry.
Step 4: Request Detailed Product Information
When you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed product catalogs that include diagrams, specifications, and performance data. Ensure that the diagrams clearly illustrate the valve’s operation and configuration. This information will help you assess whether the product aligns with your technical specifications.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Evaluate the level of after-sales support offered by your suppliers. Reliable customer service is crucial, especially for technical products like solenoid valves that may require installation support or troubleshooting. Ensure that the supplier provides warranties, technical assistance, and easy access to replacement parts.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications
It is essential to verify that your chosen supplier holds relevant certifications. Look for quality management system certifications such as ISO 9001, as well as product-specific certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards. This verification process helps mitigate risks associated with product quality and performance.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Finally, before finalizing your order, negotiate terms and conditions, including pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Ensure that you have clarity on the return policy and warranty coverage. A well-structured agreement can protect your interests and foster a long-term partnership with your supplier.
By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions when sourcing a 3-way solenoid valve diagram, ensuring that you select a product that meets your operational requirements while minimizing potential risks.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3 way solenoid valve diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 3-Way Solenoid Valves?
When considering the sourcing of 3-way solenoid valves, understanding the underlying cost structure is vital for effective budget management. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The selection of materials significantly influences the overall cost. Common materials for solenoid valves include brass, stainless steel, and plastics. Each material comes with different price points, durability, and performance characteristics. For international buyers, sourcing from regions where these materials are abundant can reduce costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary greatly depending on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs can provide competitive pricing, but this can sometimes come at the expense of quality. Evaluating the labor environment in potential sourcing countries is crucial.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facilities, utilities, and other indirect expenses involved in production. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs, impacting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are associated with the equipment needed to produce the valves. If custom designs are required, these costs can rise significantly. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs upfront, particularly for custom specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product reliability is paramount, especially for critical applications. QC processes can add to the cost but are essential for maintaining standards. Look for suppliers with certifications like ISO 9001, which can influence pricing due to the rigorous QC processes involved.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are a significant factor in the total cost of ownership. International buyers must consider the logistics costs associated with transportation, customs duties, and potential tariffs, particularly when sourcing from regions like Europe or Asia.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competition. Understanding typical margins in different regions can aid in negotiation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of 3-Way Solenoid Valves?
Several factors can influence the price of 3-way solenoid valves, making it essential for buyers to be aware of them when sourcing.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and consider bulk purchases to maximize savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications may lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized tooling and materials. It’s advisable to clearly outline requirements to avoid unexpected expenses during production.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: The choice of materials and the level of quality assurance certifications can also impact pricing. Higher quality materials will often command higher prices but can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer lifespan.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality and service, potentially justifying a higher price. Conducting due diligence on suppliers is critical.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (Incoterms) can help buyers anticipate additional costs. For example, terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can impact the total cost depending on who is responsible for shipping and insurance.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Prices for 3-Way Solenoid Valves?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, employing strategic negotiation tactics can lead to more favorable pricing.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than focusing solely on upfront costs, evaluate the total cost of ownership. Consider factors such as maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan when assessing value.
-
Negotiate Terms: Be open to discussing payment terms, delivery schedules, and potential discounts for early payment or bulk purchases. Flexibility in negotiation can yield better pricing.
-
Research Market Prices: Understanding the market price range for 3-way solenoid valves can empower buyers during negotiations. Utilize industry reports and competitor pricing to inform discussions.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing over time. Consider loyalty and repeat business when negotiating.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local economic conditions, tariffs, and market demand. Being informed about these nuances can provide leverage in negotiations.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always seek updated quotes and conduct thorough market research before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 3 way solenoid valve diagram With Other Solutions
When considering fluid control systems, the 3 way solenoid valve diagram serves as a vital component for directing flow in various applications. However, several alternatives exist that can achieve similar outcomes. This analysis aims to compare the 3 way solenoid valve diagram with two viable alternatives: pneumatic actuators and motorized ball valves.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 3 Way Solenoid Valve Diagram | Pneumatic Actuator | Motorized Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed actuation, precise control | Moderate speed, robust control | High flow rates, precise control |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, lower operating costs | Higher initial cost, variable operating costs | Higher initial cost, low maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple integration in most systems | More complex installation | Moderate complexity, requires electrical setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, occasional coil replacement | Moderate maintenance, depends on air supply | Low maintenance, infrequent checks needed |
| Best Use Case | Switching between two circuits or actuating cylinders | Applications needing rapid response and flexibility | Applications requiring on/off control with high flow |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to create motion, making them suitable for applications where quick actuation is required. They can handle high pressures and provide robust control over the operation. However, their initial setup can be complex, requiring dedicated air supply systems and potential ongoing costs related to air compression. Maintenance needs are moderate, as they rely on the quality of the compressed air and regular checks to ensure optimal performance.
Motorized Ball Valves
Motorized ball valves offer precise control for on/off applications, suitable for scenarios involving high flow rates. They can be automated using electrical signals, making them ideal for remote operations. Although the upfront costs for motorized ball valves can be higher than solenoid valves, they generally require less maintenance over time, as they have fewer moving parts and don’t rely on pneumatic systems. The installation complexity is moderate, necessitating electrical connections and possibly control systems.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate solution for fluid control requires careful consideration of your specific application and operational requirements. For instances where rapid switching is crucial, the 3 way solenoid valve diagram may be ideal due to its quick actuation and low maintenance. Conversely, if your application demands high flow rates or on/off control, motorized ball valves might be more suitable. Pneumatic actuators present a robust alternative for applications requiring flexibility and speed but may involve higher initial costs and complexity. Assessing performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance will guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgets.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3 way solenoid valve diagram
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a 3 Way Solenoid Valve Diagram?
When considering the procurement of 3 way solenoid valves, understanding their technical properties is crucial for ensuring that the selected valves meet operational requirements. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a solenoid valve impacts its durability and compatibility with various fluids. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and plastic. Brass is often used for general applications, while stainless steel is preferred in corrosive environments. Choosing the right material minimizes maintenance costs and ensures longevity. -
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the valve can handle safely. This specification is vital for applications involving high-pressure systems, as exceeding this limit could lead to failure or safety hazards. Buyers should assess the operational pressure of their systems to select appropriately rated valves. -
Temperature Range
Each solenoid valve has a specified temperature range that dictates its operational limits. Understanding this range is essential for applications in extreme environments. Selecting a valve that can withstand the temperature conditions of the intended application ensures reliable performance and reduces the risk of thermal failure. -
Electrical Specifications
This includes voltage rating and power consumption of the solenoid coil. Common voltage ratings are 12V, 24V, and 220V. The power consumption affects energy efficiency and operational costs. Buyers should consider the electrical infrastructure of their facilities when selecting valves to avoid compatibility issues. -
Flow Coefficient (Cv)
The flow coefficient quantifies the flow capacity of the valve. A higher Cv indicates that the valve can pass more fluid. This specification is critical for ensuring that the valve can meet the flow demands of the system without causing pressure drops that could affect performance. -
Actuation Type
Understanding whether the valve is normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO) is essential for system integration. This affects how the valve interacts with other components in the system and can influence safety and operational efficiency.
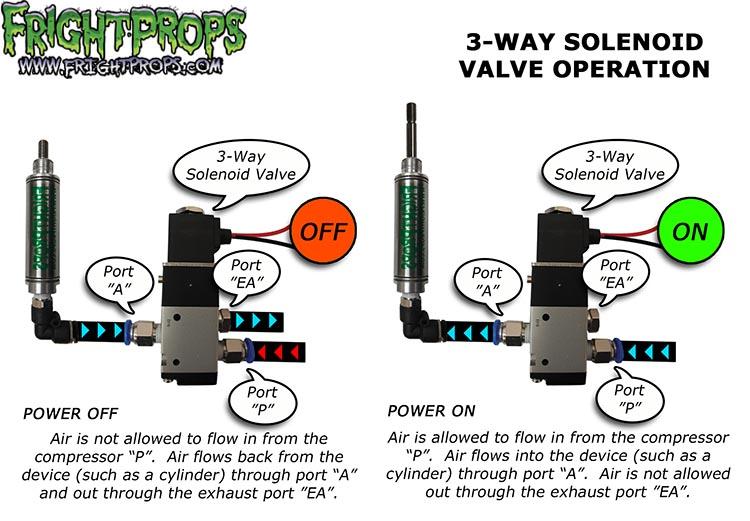
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of solenoid valves, knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can affect quality assurance and warranty conditions. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is important for inventory management and cost planning, particularly for smaller operations that may not require large quantities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotations for specific products or services. Providing detailed specifications in an RFQ ensures that suppliers can give accurate quotes, enabling better comparison and decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), helps mitigate risks related to shipping and delivery. -
P&ID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram)
A P&ID is a detailed diagram that illustrates the relationships between piping, instrumentation, and equipment. Understanding how to read P&IDs is crucial for engineers and buyers to ensure that the solenoid valves integrate properly into existing systems. -
Actuator Type
This refers to the mechanism that controls the valve. Common types include electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic actuators. Knowing the actuator type is essential for compatibility with the control systems in place, which impacts both functionality and efficiency.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminology enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring that their procurement of 3 way solenoid valves aligns with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 3 way solenoid valve diagram Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Impacting the 3 Way Solenoid Valve Diagram Sector?
The global market for 3-way solenoid valves is driven by increased automation across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and HVAC systems. As industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek efficiency and precision in fluid control, the demand for versatile solutions like 3-way solenoid valves continues to rise. The integration of IoT technologies is also transforming the landscape, with smart solenoid valves enabling real-time monitoring and control, which is particularly appealing to international B2B buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards the use of modular and customizable solenoid valves. These products allow for tailored applications, making them more attractive to businesses with specific requirements. Moreover, advancements in materials science are leading to the development of more durable and corrosion-resistant solenoid valves, which is essential for industries operating in harsh environments. As buyers become more knowledgeable about the technical specifications and performance metrics of solenoid valves, they are increasingly inclined to invest in high-quality products that offer long-term reliability.
The competitive landscape is also evolving, with manufacturers focusing on sustainability and ethical sourcing as part of their value proposition. Buyers are now more conscientious about the environmental impact of their procurement decisions, seeking suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with sustainability standards. This trend is particularly pronounced in Europe and North America but is gaining traction in emerging markets as well.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the 3 Way Solenoid Valve Diagram Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a key concern for B2B buyers in the 3-way solenoid valve sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under increasing scrutiny. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and reducing carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses aim to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitation and harmful practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming critical benchmarks for evaluating suppliers. The shift towards ‘green’ certifications has led many manufacturers to innovate, producing solenoid valves that not only meet operational requirements but also comply with environmental standards.
Furthermore, the use of eco-friendly materials, such as biodegradable plastics and sustainably sourced metals, is gaining popularity. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for products that offer both performance and a lower environmental impact, making ethical sourcing a fundamental consideration in their purchasing decisions.
What Is the Evolution of 3 Way Solenoid Valve Technology and Its Significance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of 3-way solenoid valve technology has been marked by significant advancements in design and functionality. Initially, solenoid valves were primarily mechanical devices used for simple on/off control. However, as industries evolved, the need for more complex control mechanisms became apparent. This led to the development of multi-port valves capable of managing multiple fluid circuits, enhancing operational efficiency and flexibility.
The introduction of electronic control systems has further revolutionized the industry. Today, solenoid valves can be integrated with smart technologies, enabling remote operation and automation. This shift not only improves efficiency but also reduces the likelihood of human error, thereby increasing safety in industrial applications.
For B2B buyers, understanding the historical context of solenoid valve technology is essential. It enables them to appreciate the advancements that have led to the current offerings and to make informed decisions when selecting products that align with their operational needs. As industries continue to demand more sophisticated solutions, the evolution of solenoid valve technology remains a critical factor in driving market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3 way solenoid valve diagram
1. How do I ensure the quality of 3-way solenoid valves when sourcing from suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by researching and vetting potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications or industry-specific quality standards. Request samples to evaluate the product firsthand, and consider third-party quality assurance inspections before shipment. Additionally, review customer feedback and case studies to gauge reliability. Establishing clear quality expectations in your contract can further safeguard your procurement process.
2. What is the best way to customize a 3-way solenoid valve for specific applications?
Customization can vary based on the application requirements. Begin by defining the operational parameters, such as pressure, temperature, and fluid type. Consult with suppliers about available options for port sizes, materials, and actuation methods. Many manufacturers offer design services to create tailored solutions. Ensure that all customization details are documented in your purchase agreement to avoid discrepancies during production.
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
3. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for 3-way solenoid valves?
MOQs can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Generally, for standard models, MOQs may range from 50 to 500 units. However, customized valves often have higher MOQs due to the additional production setup. Always discuss MOQs with potential suppliers upfront to align your purchasing needs with their production capabilities, and consider negotiating terms if you anticipate larger future orders.
4. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing 3-way solenoid valves internationally?
Payment terms can differ by supplier and region. Common practices include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or escrow services for larger orders to protect both parties. Always clarify payment options, currency, and deadlines before finalizing contracts to ensure smooth transactions and avoid potential disputes.
5. How can I assess the reliability of a supplier for 3-way solenoid valves?
Assessing supplier reliability involves several steps. Start by checking their industry experience and customer references. Look for certifications that indicate adherence to quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Engage in direct communication to evaluate their responsiveness and willingness to address your concerns. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities or conducting audits if feasible, as this can provide insight into their operational practices.
6. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing 3-way solenoid valves?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with importing industrial components to ensure smooth transportation. Research customs duties and taxes applicable in your region to avoid unexpected costs. Additionally, confirm that the supplier provides accurate documentation to facilitate customs clearance and consider potential delays in delivery due to regulatory inspections.
7. What should I know about the warranties and after-sales support for 3-way solenoid valves?
Warranties typically cover defects in materials and workmanship, and they can range from one year to several years. Ensure that you understand the warranty terms and the process for claims, including any conditions that may void the warranty. After-sales support is also crucial; inquire about the availability of technical assistance, spare parts, and repair services. A supplier with robust support can significantly enhance your experience and minimize downtime.
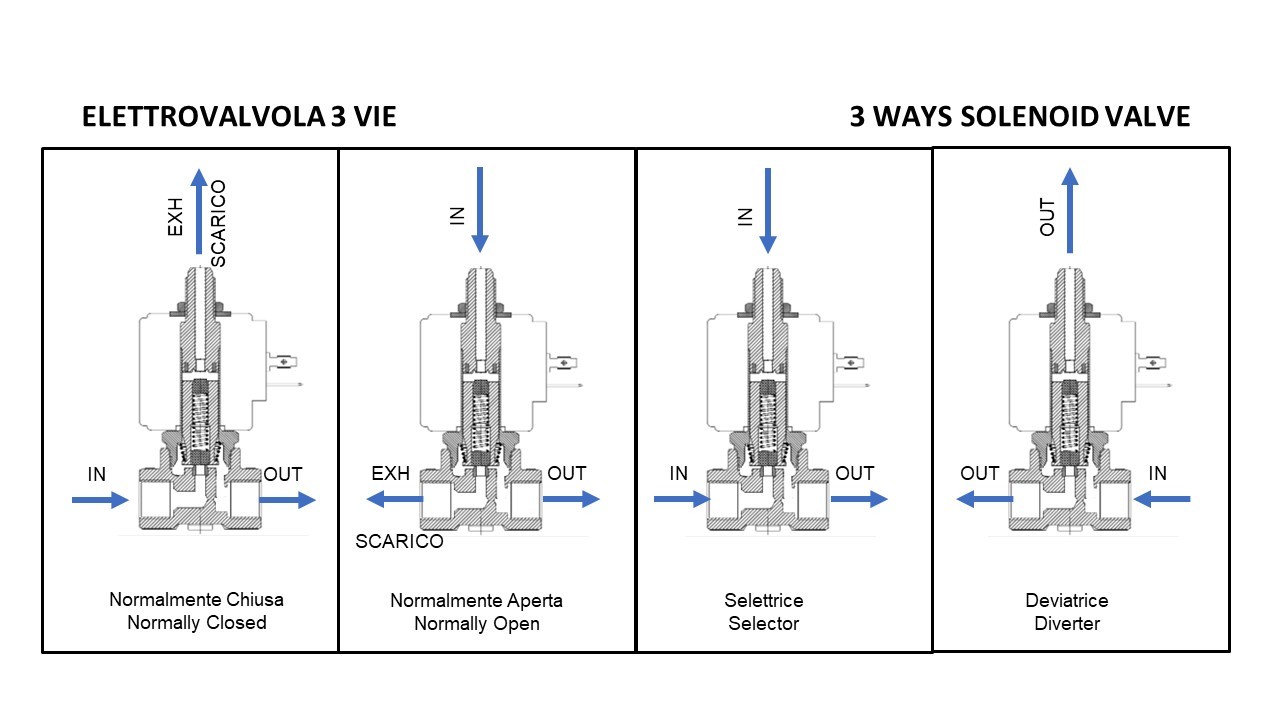
8. How do I interpret a 3-way solenoid valve diagram for effective application?
Interpreting a 3-way solenoid valve diagram requires understanding the symbols and flow directions represented. Familiarize yourself with the standard symbols for solenoid valves, as these convey operational states and flow paths. Pay attention to the port designations and switching states to ascertain how the valve interacts with your system. Consulting with your supplier or a technical expert can provide additional clarity, ensuring correct application in your specific use case.
Top 6 3 Way Solenoid Valve Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tameson – Solenoid Valves Overview
Domain: tameson.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Solenoid valves are represented by unique symbols in fluid power diagrams to indicate their functions and connections. Key details include: 1. Types of solenoid valves: 2-way, 3-way, proportional valves, and pneumatic solenoid valves. 2. Valve designations: The first number indicates the number of connection ports, and the second number indicates the number of switching states (e.g., a 2/2-way val…
2. Tanghai Valve – Three-Way Valve Solutions
Domain: tanghaivalve.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Three-way valve has three inlets and outlets; can merge (two in, one out) or split (one in, two out). Controlled by the shape of the spool. Types include L-type (connects two orthogonal pipes) and T-type (connects three orthogonal pipelines). Function: changes flow direction of the medium. When open, medium flows from A to B; can reverse to C when required. Three-way solenoid valve has multiple wo…
3. Control.com – Solenoid Valves
Domain: control.com
Registered: 1990 (35 years)
Introduction: Solenoid valves are on/off valves used in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. A solenoid consists of a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when energized. Solenoid valves are classified by the number of ports: 2-way valves control flow into one port and out of another, while 3-way valves direct flow between two paths. 2-way valves operate like single-pole single-throw switches, while 3-way va…
4. Electric Solenoid Valves – 231Y-6-110VAC
Domain: electricsolenoidvalves.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“SKU”:”231Y-6-110VAC”,”Position”:”Normally Closed”,”Port Size”:”1/4″ Female NPT”,”Voltage”:”110V AC”,”Body Material”:”Brass”,”Components”:”Stainless Steel”,”Seal Material”:”NBR”,”Orifice Size”:”1.5 mm”,”Temp Range”:”25 to 195° F / -5 to 90°C”,”Pressure Range”:”0 – 115 PSI”,”Flow Rate”:”Cv 0.21 (Appx 1.5 GPM @ 60 PSI)”,”Power”:”22 Watts”,”Coil Connection”:”DIN 43650A”,”Response Time”:”Fast Acting …
5. Solenoid Solutions Inc – Custom Solenoid Valves
Domain: solenoidsolutionsinc.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Solenoid Valves: Made to Order at Catalog Prices.
– Mini-Wattmizer Solenoid Valves: Body Size: 0.75″ (19.1 mm), Port Size: #10-32 to 1/8″.
– Wattmizer Solenoid Valves: Body Size: 1″ (25.4 mm), Port Size: #10-32 to 1/4″.
– Plastic Wattmizer Solenoid Valves: Up to 85 psi, Lightweight.
– 7 Series Valves: Body Size: 1.25″ & 1.61″ (31.8 mm & 41.3 mm), Port Size: 1/8″ & 1/4″.
– 8 Series Valves: Bod…
6. IQS Directory – 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
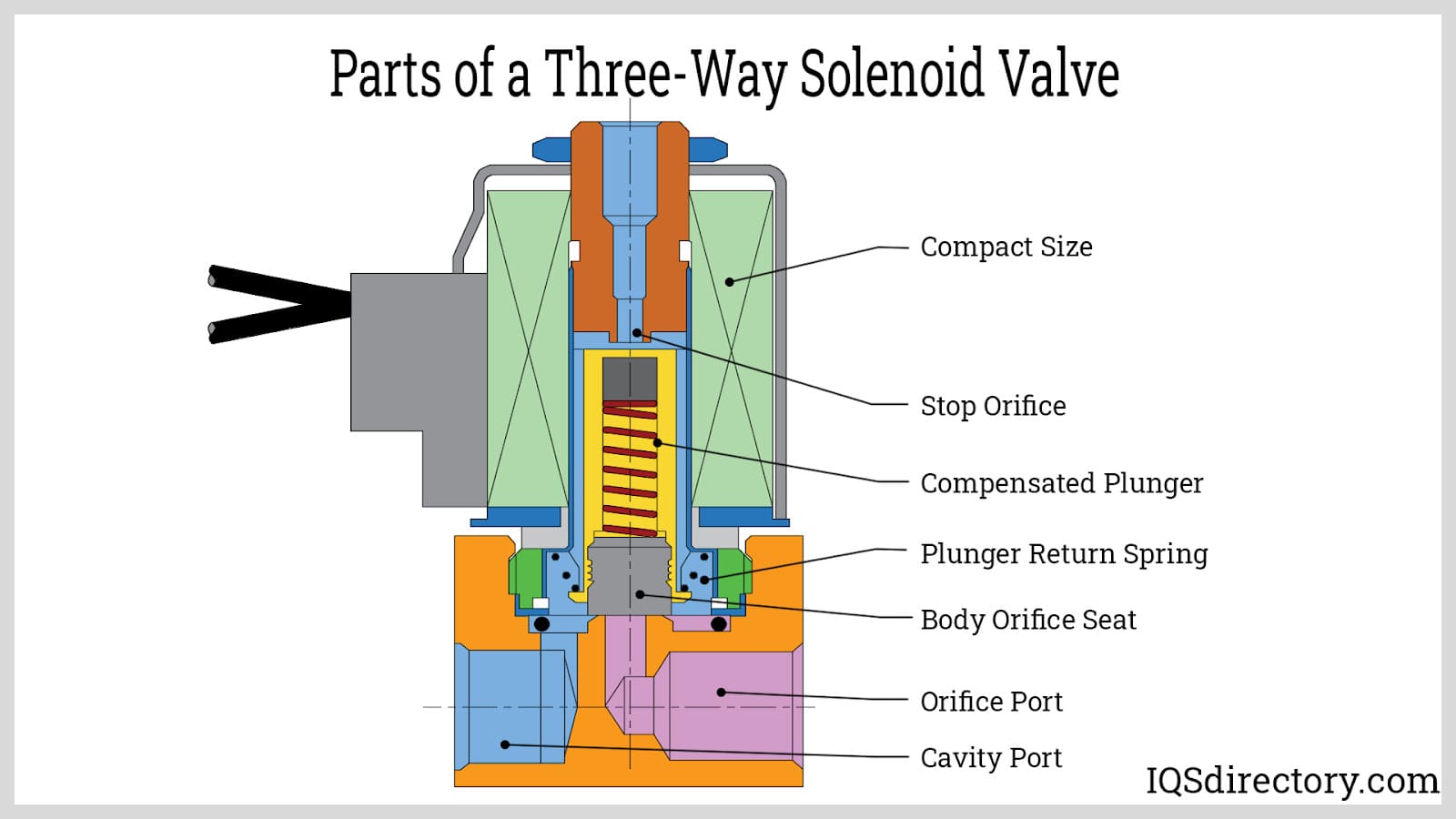
Introduction: 3-Way solenoid valves are electromechanical devices used to control the flow of liquid or gas, featuring three ports: an orifice, a cavity, and a stop port. They come in three types: normally-closed (NC), normally-open (NO), and universal. NC valves block flow until energized, NO valves allow flow when de-energized, and universal valves can be configured as either. The valves operate by using a so…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3 way solenoid valve diagram
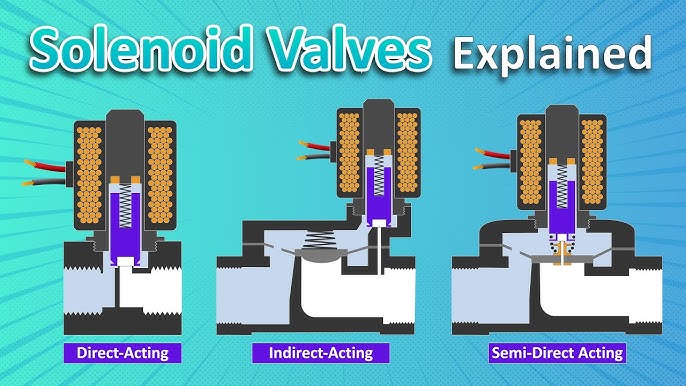
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of 3-way solenoid valve diagrams is essential for optimizing fluid control systems across various industries. The strategic sourcing of these components allows businesses to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure reliable performance in applications ranging from manufacturing to automation. By leveraging the insights gained from this guide, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
For international buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the importance of sourcing high-quality solenoid valves cannot be overstated. Engaging with reputable suppliers and utilizing detailed diagrams to visualize valve functions can significantly impact system reliability and maintenance efficiency.
As industries evolve and the demand for innovative solutions increases, proactive sourcing strategies will be key to staying competitive. We encourage buyers to explore the latest technologies and collaborate with manufacturers who prioritize quality and compliance. By doing so, you position your business to thrive in a dynamic marketplace, ensuring long-term success and operational excellence.
Illustrative image related to 3 way solenoid valve diagram
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.