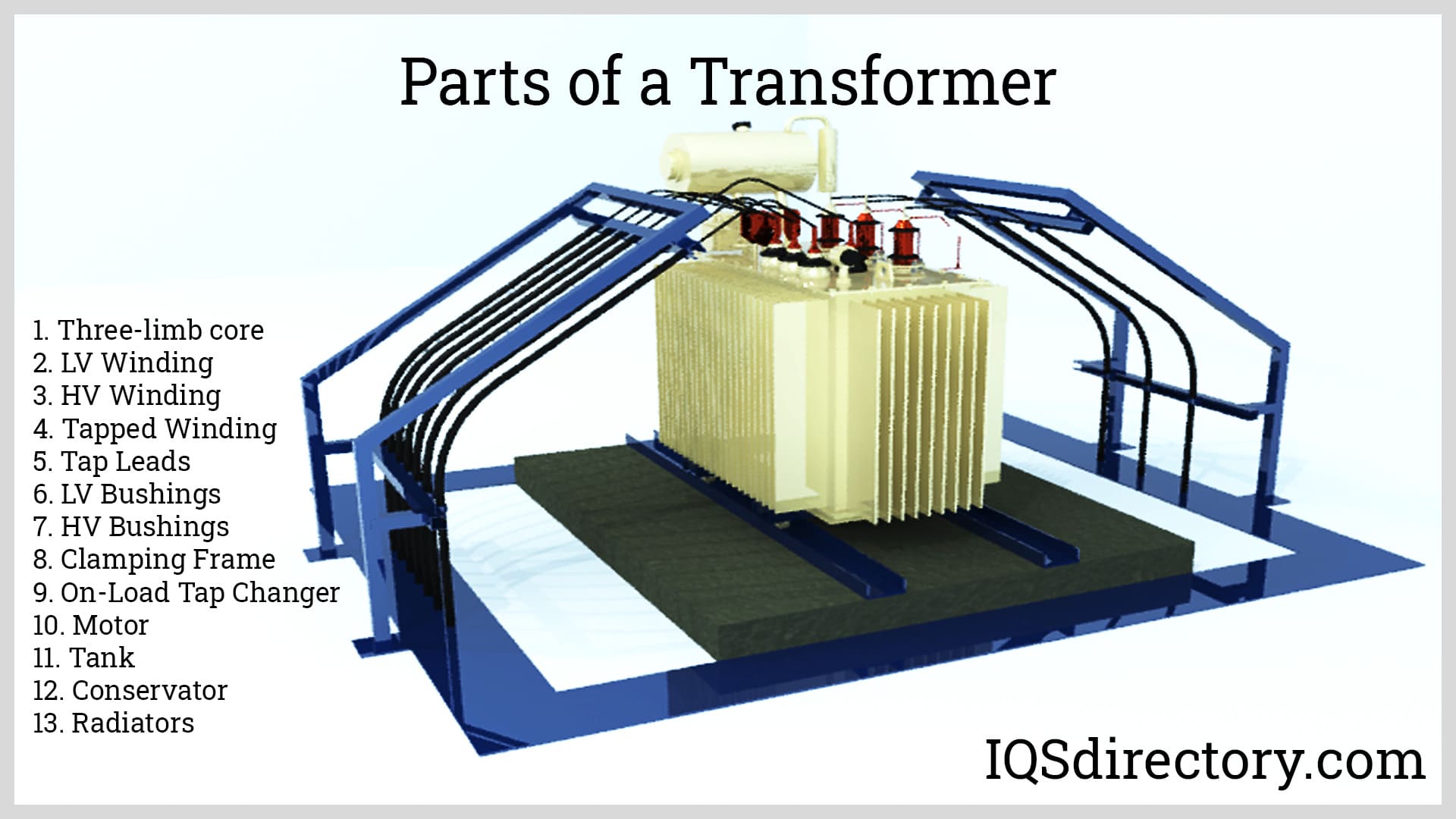
3 Transformer: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3 transformer
As global industries continue to expand, the demand for reliable and efficient three-phase transformers is on the rise. However, sourcing the right transformer can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide aims to simplify the process of navigating the global market for three-phase transformers, addressing common challenges such as identifying the appropriate transformer type for specific applications, understanding various voltage requirements, and evaluating supplier credibility.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will delve into the different types of three-phase transformers, including autotransformers and dry-type transformers, and discuss their specific uses in various industries, from manufacturing to renewable energy sectors. Additionally, we will provide actionable insights on cost factors, enabling you to make informed financial decisions while considering budget constraints.
Moreover, the guide emphasizes the importance of supplier vetting, offering criteria and best practices to ensure that you partner with reputable manufacturers and distributors. By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to confidently source the right three-phase transformers for your business needs, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and supporting your growth in the competitive global market.
Understanding 3 transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delta Transformer | Wye (Y) and Delta (Δ) configurations; handles high loads; robust. | Industrial machinery, large motors, HVAC systems. | Pros: High efficiency; good for heavy loads. Cons: More complex installation. |
| Wye (Star) Transformer | Balanced load distribution; neutral point; lower voltage. | Commercial buildings, data centers, lighting systems. | Pros: Stable voltage; easy to connect. Cons: Limited to lower power applications. |
| Autotransformer | Single winding design; voltage conversion without isolation. | Solar power systems, CNC machines, and welding equipment. | Pros: Compact size; cost-effective. Cons: Not suitable for isolation applications. |
| Dry-Type Transformer | Encapsulated design; no liquid coolant; environmentally friendly. | Urban installations, renewable energy systems. | Pros: Low maintenance; safe for indoor use. Cons: Lower power capacity compared to oil-filled types. |
| Pad-Mounted Transformer | Outdoor installation; durable enclosures; readily accessible. | Substations, commercial complexes, and industrial parks. | Pros: Easy access; weather-resistant. Cons: Higher upfront costs; space requirements. |
What are Delta Transformers and Their B2B Relevance?
Delta transformers utilize a three-phase winding configuration that allows for the efficient handling of high loads. Their robustness makes them ideal for applications such as industrial machinery and HVAC systems. When considering a delta transformer, B2B buyers should evaluate their facility’s load requirements and installation complexities, as the initial setup can be more involved compared to simpler transformer types.
How Do Wye (Star) Transformers Benefit Commercial Applications?
Wye transformers are characterized by their balanced load distribution and the presence of a neutral point, making them suitable for lower voltage applications. Commonly used in commercial buildings and data centers, they provide stable voltage levels essential for sensitive electronic equipment. Buyers should consider the specific voltage needs of their applications, as well as the transformer’s capacity to support future expansions.
Why Choose an Autotransformer for Your Business Needs?
Autotransformers feature a single winding that serves both the primary and secondary circuits, allowing for efficient voltage conversion without isolation. This design is particularly beneficial for applications such as solar power systems and CNC machines, where space and cost savings are crucial. However, businesses should be cautious of their isolation limitations, as autotransformers are not suitable for applications requiring electrical isolation between circuits.
What Are the Advantages of Dry-Type Transformers?
Dry-type transformers are encapsulated in resin, eliminating the need for liquid coolants and making them environmentally friendly. They are commonly used in urban settings and renewable energy systems where safety and low maintenance are priorities. Buyers should weigh the lower power capacities of dry-type transformers against their advantages, especially in applications where space and safety are critical.
When Should You Consider Pad-Mounted Transformers?
Pad-mounted transformers are designed for outdoor installations, featuring durable enclosures that protect against environmental factors. These transformers are ideal for substations and commercial complexes, where accessibility and weather resistance are essential. While they may come with higher upfront costs and require more space, their robust design ensures long-term reliability for businesses looking to invest in a stable power supply solution.

Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
Key Industrial Applications of 3 transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 3 transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering CNC Machines and Robotics | Enhanced efficiency and precision in production processes | Voltage compatibility, kVA rating, and delivery timelines |
| Renewable Energy | Integrating Solar Power Systems | Increased energy reliability and reduced operational costs | Environmental ratings, grid compatibility, and certifications |
| Construction | Supplying Power for Heavy Equipment | Reliable power supply for construction operations | Load capacity, durability, and installation support |
| Data Centers | Supporting Critical IT Infrastructure | Uninterrupted power supply to ensure data integrity | Cooling requirements, redundancy features, and size |
| Agriculture | Running Irrigation Systems | Optimized water usage and crop yield improvement | Voltage specifications, weather resistance, and maintenance services |
How is a 3-Phase Transformer Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, 3-phase transformers are essential for powering CNC machines and robotics. These machines require stable and precise power to operate efficiently, ensuring high-quality production output. By converting voltage levels, these transformers help mitigate issues such as voltage drops that can lead to machine malfunctions. Buyers should consider voltage compatibility and kVA ratings to match their specific machinery needs, along with timely delivery to minimize downtime.
What Role Does a 3-Phase Transformer Play in Renewable Energy?
In renewable energy applications, particularly solar power systems, 3-phase transformers facilitate the integration of generated power into the grid. They convert the variable output from solar panels to a stable voltage suitable for commercial and residential use. This conversion enhances energy reliability and reduces operational costs by optimizing energy distribution. Buyers in this sector should focus on environmental ratings and grid compatibility to ensure that their systems meet local regulations and performance standards.
How are 3-Phase Transformers Utilized in Construction?
Construction sites often rely on heavy equipment that demands a consistent power supply, making 3-phase transformers vital for operations. They provide the necessary voltage and current to run cranes, excavators, and other machinery effectively. The reliability of these transformers ensures that construction timelines are met without interruptions. When sourcing, businesses should prioritize load capacity and the durability of the transformers, especially in rugged environments, along with access to installation support.
Why are 3-Phase Transformers Critical for Data Centers?
Data centers require a continuous and reliable power supply to maintain their IT infrastructure. 3-phase transformers play a crucial role in delivering uninterrupted power, which is vital for data integrity and operational continuity. They help manage the high electrical loads typical in data centers, ensuring that systems remain operational during peak usage. Buyers should consider cooling requirements and redundancy features to safeguard against power failures, as well as the physical size of the transformers to fit within existing infrastructure.
How Do 3-Phase Transformers Benefit Agriculture?
In agriculture, 3-phase transformers are instrumental in running irrigation systems efficiently. These systems require reliable power to ensure optimal water delivery, which directly impacts crop yield. By converting voltage levels to suit the equipment, these transformers help mitigate the risks associated with power fluctuations. Buyers should assess voltage specifications, weather resistance, and available maintenance services to ensure the longevity and reliability of their irrigation systems.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘3 transformer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Power Supply Disrupting Operations
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in manufacturing and industrial sectors, face the challenge of inconsistent power supply. This is particularly common in regions with unstable electrical infrastructure, such as parts of Africa and South America. Fluctuations in voltage can cause machinery to malfunction or become damaged, leading to costly downtime and disruptions in production schedules. Buyers often feel overwhelmed by the prospect of replacing damaged equipment and the associated costs of lost productivity.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, it is essential for buyers to invest in robust three-phase transformers that can stabilize voltage levels. When sourcing transformers, look for models designed specifically for harsh environments, featuring features such as built-in surge protection and voltage regulation. Conduct a thorough assessment of the specific power requirements of your machinery and choose a transformer that matches or exceeds these specifications. Additionally, working with a reputable supplier who can provide expert advice on installation and maintenance can ensure long-term reliability. Regular maintenance checks should also be scheduled to prevent any unforeseen issues and ensure optimal performance.
Scenario 2: Complexity in Sizing and Specifications
The Problem: Sizing and specifying the correct transformer can be a daunting task for many B2B buyers, especially those new to electrical systems. Incorrect sizing can lead to inefficiencies, overheating, and even equipment failure. Buyers often struggle to determine the appropriate kVA rating, voltage levels, and phase configuration needed for their specific applications, which can result in costly mistakes.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should utilize comprehensive kVA calculators and consult with experienced electrical engineers to accurately determine their power needs. Understanding the load requirements of connected equipment is critical; therefore, gather detailed information about the machinery’s operating characteristics, including peak loads and starting currents. When choosing a transformer, it is also beneficial to consider future scalability. Opt for models with a slightly higher capacity than current needs to accommodate potential growth or changes in operational demands. Collaborating with suppliers who offer custom solutions can also provide tailored options that fit unique specifications.
Scenario 3: Navigating Compliance and Regulatory Standards
The Problem: Compliance with local and international electrical standards can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially those operating in multiple regions like Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. Regulations regarding electrical safety, environmental impact, and energy efficiency can be complex and vary greatly from one jurisdiction to another. Buyers often find themselves stressed about the implications of non-compliance, including potential fines, project delays, and reputational damage.

Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
The Solution: To navigate these regulatory landscapes successfully, buyers should prioritize sourcing transformers that are UL Listed or compliant with relevant international standards such as IEC or ANSI. Engaging with suppliers who have experience in specific regional regulations can provide invaluable insights. Additionally, consider conducting a compliance audit as part of your purchasing process to ensure that all equipment meets the required standards. Staying informed about changes in regulations and leveraging resources such as industry associations can also help buyers maintain compliance and avoid potential pitfalls. Regular training for staff on compliance issues can further reinforce best practices and minimize risk.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3 transformer
What Are the Key Materials Used in 3-Phase Transformers?
When selecting materials for 3-phase transformers, several factors come into play, including electrical efficiency, thermal performance, and environmental compatibility. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these transformers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
How Does Copper Influence Transformer Performance?
Copper is a preferred material for windings in transformers due to its excellent electrical conductivity, which enhances efficiency. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity leads to lower energy losses, and its durability ensures a longer lifespan. Additionally, it is relatively easy to work with, which simplifies manufacturing processes.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which is higher than alternatives like aluminum. It is also susceptible to corrosion if not properly insulated, which can affect performance over time.
Impact on Application: Copper windings are ideal for applications requiring high efficiency, such as industrial motors and generators. However, in humid or corrosive environments, additional protective measures may be necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN) regarding electrical safety and material specifications. The higher cost of copper may also necessitate a cost-benefit analysis against performance gains.

Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Transformer Manufacturing?
Aluminum is often used as a cost-effective alternative to copper in transformer windings. While it has lower conductivity, it is lighter and generally less expensive, making it a popular choice for various applications.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier handling and installation. It is also resistant to corrosion, especially when treated, which can enhance its longevity in harsh environments.
Cons: The lower conductivity means that aluminum transformers may experience higher energy losses compared to copper. Additionally, aluminum’s mechanical properties can be less robust, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in portable transformers. However, energy efficiency may be compromised, particularly in high-load scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in South America and Europe should be aware of the varying standards for aluminum use in electrical applications. Compliance with local regulations is crucial to ensure safety and performance.

Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
How Do Insulation Materials Affect Transformer Reliability?
Insulation materials, such as resin and oil, are crucial for transformer performance, providing electrical insulation and thermal management.
Pros: Modern insulation materials can withstand high temperatures and provide excellent dielectric properties, enhancing safety and reliability. Resin-based insulation, for example, is often used in dry-type transformers and is known for its environmental resistance.
Cons: Some insulation materials can be expensive, and their manufacturing processes may be complex. Additionally, certain types may have limitations in high-voltage applications.
Impact on Application: The choice of insulation material can significantly affect the transformer’s operational temperature range and overall reliability. For instance, resin insulation is ideal for indoor applications, while oil insulation may be preferred for outdoor settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that insulation materials comply with international standards and local regulations, particularly in regions like the Middle East, where environmental factors can impact material performance.
What Is the Importance of Core Materials in Transformer Efficiency?
The core of a transformer is typically made from silicon steel, which enhances magnetic properties and reduces energy losses during operation.
Pros: Silicon steel cores have high magnetic permeability, which improves efficiency and reduces the size of the transformer. They also have good thermal stability, making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
Cons: The manufacturing process for silicon steel can be complex and costly. Additionally, while they are durable, cores can be susceptible to mechanical damage if not handled properly.
Impact on Application: Silicon steel cores are essential for applications requiring high efficiency and compact design, such as in renewable energy systems and industrial equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability and cost of silicon steel in their region, as well as compliance with international standards for electrical efficiency.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 3-Phase Transformers
| Material | Typical Use Case for 3 transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-efficiency windings | Excellent conductivity and durability | High cost and corrosion susceptibility | High |
| Aluminum | Cost-effective windings | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower conductivity and mechanical strength | Medium |
| Insulation (Resin/Oil) | Electrical insulation and thermal management | High dielectric strength and reliability | Potentially high cost and complexity | Medium to High |
| Silicon Steel | Transformer core | High magnetic permeability | Complex manufacturing and mechanical fragility | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in 3-phase transformers, helping them make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3 transformer
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of 3-Phase Transformers?
The manufacturing of 3-phase transformers is a complex process that involves several key stages, each critical for ensuring the final product meets performance and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
Material Preparation: How Are Components for Transformers Procured and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, such as copper for windings and silicon steel for cores. Manufacturers typically procure these materials from certified suppliers to ensure compliance with international standards. Once received, materials undergo inspection and testing to verify their specifications. This stage may involve chemical analysis, dimensional checks, and electrical testing to ensure that they meet the required standards.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Transformer Components?
In the forming stage, the raw materials are shaped into the necessary components of the transformer. This includes winding copper wire into coils and cutting the silicon steel into specific shapes for the core. Advanced techniques like CNC machining and automated winding machines are often employed to ensure precision and efficiency. The quality of these components is crucial, as they directly affect the transformer’s performance and efficiency.
Assembly: How Are Components Integrated into a Finished Transformer?
During the assembly stage, the formed components are brought together to create the transformer. This involves stacking the core, winding the coils around it, and securing them in place. Quality control checkpoints are essential at this stage to ensure that all components fit correctly and that there are no defects. Proper insulation and cooling systems are also integrated to enhance the transformer’s efficiency and longevity.
Finishing: What Processes Ensure Transformers Meet Quality Standards?
The finishing stage includes testing and final inspections before the transformer is packaged and shipped. This may involve applying protective coatings and conducting electrical tests to ensure functionality under various conditions. Finishing touches, such as labeling and documentation, are crucial for compliance with international shipping and safety standards.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for 3-Phase Transformers?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of the manufacturing process for 3-phase transformers, ensuring that products meet both industry standards and customer expectations. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these practices.
Which International Standards Should Be Considered for Quality Control?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard for quality management systems, focusing on consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Compliance with this standard is essential for manufacturers aiming to export their products globally. Additionally, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be required depending on the target market and application.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints typically occur at three main stages: Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. Any materials that fail to meet these standards are rejected or returned.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections and tests are conducted to identify any defects or deviations from specifications. This might include dimensional checks, electrical testing, and thermal imaging to assess performance.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the transformers are shipped, they undergo comprehensive testing to verify their performance under load conditions. This may include high-voltage tests, insulation resistance tests, and temperature rise tests to ensure reliability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for 3-Phase Transformers?
Testing methods play a significant role in ensuring the quality and reliability of 3-phase transformers. Common testing techniques include:
Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
-
Insulation Resistance Testing: Ensures that insulation materials are effective and can withstand operational stresses.
-
Power Factor Testing: Assesses the efficiency of the transformer by evaluating the power factor at various loads.
-
Short Circuit Testing: Simulates fault conditions to evaluate the transformer’s performance during abnormal situations.
-
Temperature Rise Testing: Measures the temperature increase during operation to ensure that the transformer operates within safe limits.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Requesting supplier audits and quality control reports is a critical step. Buyers should look for:
-
Certifications: Verify that the supplier holds relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 and any industry-specific certifications applicable to the buyer’s region.
-
Audit Reports: Evaluate recent audit reports from third-party organizations to assess compliance with quality standards.
-
Production Capacity: Understand the supplier’s production capacity and their ability to meet demand while maintaining quality.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing processes. These inspections typically occur at various stages of production, ensuring that quality standards are upheld throughout.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of several nuances in quality control when sourcing 3-phase transformers. Understanding local regulations, compliance requirements, and shipping standards is crucial. For example:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must be aware of the specific certifications required in their home countries, which can vary significantly.
-
Logistics and Shipping Standards: Ensuring that transformers are packaged and shipped according to international standards is vital to prevent damage during transit.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and service. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers to ensure alignment.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select suppliers who meet their stringent quality requirements while navigating the complexities of international trade.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘3 transformer’
To aid international B2B buyers in the procurement of three-phase transformers, this guide provides a structured checklist that ensures a comprehensive understanding of requirements and supplier evaluation. The following steps will lead you through the essential considerations for a successful sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your transformer needs, including voltage ratings, power capacity (kVA), and phase configuration. This is crucial because the specifications will determine the compatibility of the transformer with your existing systems and equipment. Consider factors such as:
– Voltage Levels: Ensure the transformer can handle the voltage from your power source.
– Load Requirements: Assess the total load to avoid under or over-specification.
Step 2: Assess Application Needs
Identify the specific applications for which the transformer will be used, such as powering motors, CNC machines, or solar equipment. Understanding the application helps in selecting a transformer that can efficiently support the operational demands. Evaluate:
– Type of Equipment: Different applications may require specific transformer types (e.g., autotransformers for voltage conversion).
– Operating Environment: Consider temperature and humidity, which can affect transformer performance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. This step is vital to ensure reliability and quality. Request:
– Company Profiles: Look for established suppliers with a proven track record.
– References and Case Studies: Insights from similar industries can validate the supplier’s capabilities.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers meet relevant industry standards and certifications, such as ISO 9001 or UL listings. Certifications indicate compliance with safety and quality regulations, which is particularly important in international transactions. Check for:
– Quality Assurance Processes: Suppliers should have documented procedures for quality control.
– Product Testing Standards: Ensure transformers are tested for performance and safety.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Obtain detailed quotations from shortlisted suppliers, including pricing, terms of delivery, and warranty conditions. A comprehensive quote allows for accurate comparisons and helps in understanding the total cost of ownership. Pay attention to:
– Shipping and Handling Costs: International shipping can significantly affect the final price.
– Warranty and Support Services: Understand what support is available in case of defects or issues.

Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms, including pricing, delivery timelines, and payment options. Effective negotiation can lead to cost savings and improved service levels. Consider:
– Payment Flexibility: Ensure payment terms align with your cash flow needs.
– Delivery Schedules: Confirm that suppliers can meet your project timelines.
Step 7: Conduct a Final Review Before Purchase
Before finalizing the purchase, conduct a thorough review of all documentation and agreements. This step helps to avoid misunderstandings or potential issues post-purchase. Confirm:
– Contract Details: Ensure all terms discussed are reflected in the contract.
– Compliance with Local Regulations: Verify that the transformer meets the electrical standards required in your country.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for three-phase transformers, ensuring that their operational needs are met while minimizing risks associated with procurement.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3 transformer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Three-Phase Transformers?
When sourcing three-phase transformers, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. Key components include:

Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used (e.g., copper for windings, insulation materials) significantly influence the overall cost. High-grade materials can enhance performance but may increase the unit price.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on geographical location and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for assembly and quality control, impacting the final price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling and setup costs can be substantial, especially for custom transformers. This is often amortized over larger production runs, making volume purchasing more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that transformers meet industry standards, which can add to the cost but ultimately reduce the risk of failures and associated downtime.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, including tariffs and customs duties, can vary significantly based on the destination. This is particularly relevant for international buyers who must factor in these expenses when calculating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary widely based on market competition and the supplier’s position in the supply chain.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Transformer Costs for International Buyers?
Several factors can influence the pricing of three-phase transformers, particularly for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to significant discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their consumption needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications (e.g., voltage ratings, insulation types) can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Transformers that comply with international standards (e.g., UL, CE) may carry a premium price due to the associated testing and certification processes. Buyers should balance quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better warranties and service, which can justify a higher price point.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can significantly affect overall costs. For example, choosing DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) can simplify logistics for buyers but may come with higher upfront costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Transformer Sourcing?
To optimize costs and achieve better value when sourcing three-phase transformers, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate pricing based on volume, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a strong relationship can lead to favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors like energy efficiency, maintenance costs, and expected lifespan, which can impact long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of regional pricing variations due to local demand, tariffs, and shipping costs. Conduct market research to understand fair pricing in your specific region.
-
Supplier Diversification: Explore multiple suppliers to compare prices and terms. This not only provides options but also creates a competitive environment that can drive down costs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The prices for three-phase transformers can vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. The indicative ranges found in various sources (e.g., $578 to $5,994 for different configurations) should be seen as a starting point for negotiations rather than fixed prices. Always seek detailed quotes and consider all cost components when making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 3 transformer With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternative Solutions for Power Transformation
When it comes to electrical power distribution, businesses often seek the most efficient and cost-effective solutions. The ‘3 transformer’ serves as a robust option for converting and managing three-phase power. However, exploring alternative technologies can provide additional insights into potential benefits and drawbacks, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
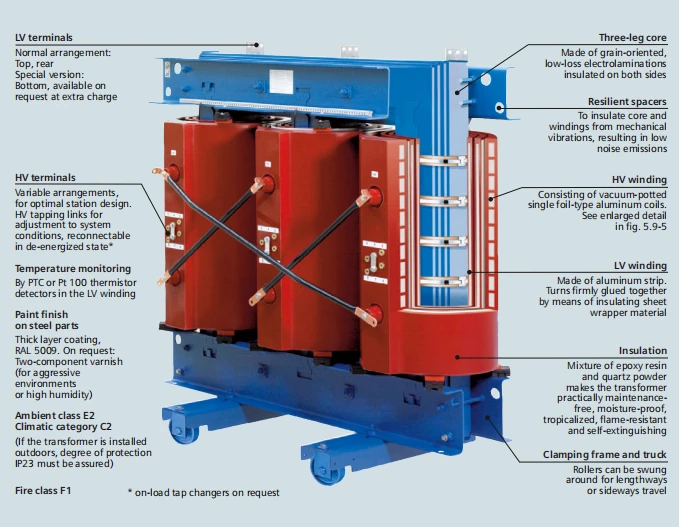
Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | ‘3 Transformer’ | Autotransformer | Phase Converter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, stable voltage | Efficient but less isolation | Moderate efficiency, variable output |
| Cost | $1,298 – $5,994 | $533 – $1,500 | $1,500 – $3,500 |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires professional installation | Easier setup; often plug-and-play | Complex; may need extensive modifications |
| Maintenance | Low; durable with minimal upkeep | Low; fewer components | Moderate; requires regular checks |
| Best Use Case | Industrial applications requiring stable and consistent power | Smaller applications; motors and equipment needing step-up/down | Converting single-phase to three-phase for various loads |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Autotransformer
Autotransformers are designed for voltage conversion and are particularly suited for applications requiring minimal electrical isolation. Their design allows for a compact form factor and reduced material costs, making them a cost-effective solution. However, the lack of isolation can be a drawback in sensitive applications where electrical interference is a concern. Autotransformers are ideal for smaller equipment, such as motors and solar inverters, where space and budget constraints are critical.
Phase Converter
Phase converters are utilized to convert single-phase power to three-phase power, making them suitable for businesses that operate machinery designed for three-phase systems. While they can effectively provide the necessary power for various applications, their efficiency can vary depending on the load. Installation can be more complex, often requiring modifications to existing electrical systems. Businesses should consider phase converters when they need to operate three-phase equipment in areas where only single-phase power is available.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Power Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting a power transformation solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements. The ‘3 transformer’ offers high efficiency and reliability, making it a solid choice for industrial applications. In contrast, autotransformers are excellent for cost-sensitive projects requiring less isolation, while phase converters are ideal for adapting existing single-phase systems to accommodate three-phase machinery. By carefully evaluating these alternatives based on performance, cost, and application, businesses can optimize their electrical systems and enhance operational efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3 transformer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 3 Transformers That Buyers Should Know?
Understanding the essential technical properties of three-phase transformers is crucial for international B2B buyers. These specifications ensure that the transformers meet operational requirements and are suitable for various applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the transformer can handle. It’s typically expressed in volts (V) and is crucial for determining compatibility with existing electrical systems. For instance, common ratings include 480V, 600V, and 208Y/120V. Selecting the correct voltage rating ensures efficiency and prevents equipment damage. -
kVA Rating
The kVA (kilovolt-ampere) rating measures the transformer’s capacity to handle electrical load. This specification is vital for ensuring that the transformer can support the intended application, such as powering industrial machinery or commercial equipment. Understanding the kVA requirements helps buyers avoid under-sizing or over-sizing transformers, both of which can lead to inefficiencies or failures. -
Temperature Rise
Temperature rise refers to the increase in temperature of the transformer during operation. It is measured in degrees Celsius (°C) and is essential for assessing the cooling requirements and overall reliability of the transformer. Common temperature rise ratings include 80°C and 150°C. Selecting a transformer with an appropriate temperature rise helps prevent overheating, which can lead to premature failure. -
Winding Material
The winding material, typically copper or aluminum, plays a significant role in the transformer’s efficiency and conductivity. Copper windings are preferred for high-performance applications due to their superior conductivity and lower energy losses, while aluminum is a cost-effective alternative for lower-power applications. Choosing the right winding material affects the overall performance and longevity of the transformer. -
Insulation Class
The insulation class indicates the thermal endurance of the transformer’s insulation system. Common classes include 130°C, 150°C, and 220°C. This specification is crucial for ensuring the transformer can operate safely under specific environmental conditions. A higher insulation class allows for greater operational flexibility and longevity. -
Connection Type
Transformers can be connected in different configurations, such as Delta or Wye (Star) connections. Each connection type has unique advantages, affecting the voltage levels and phase relationships in the system. Understanding these configurations is essential for ensuring compatibility with existing electrical systems and achieving optimal performance.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand When Purchasing 3 Transformers?
Navigating the procurement process for transformers involves familiarizing yourself with specific industry jargon. Here are some common trade terms that can impact your purchasing decisions:
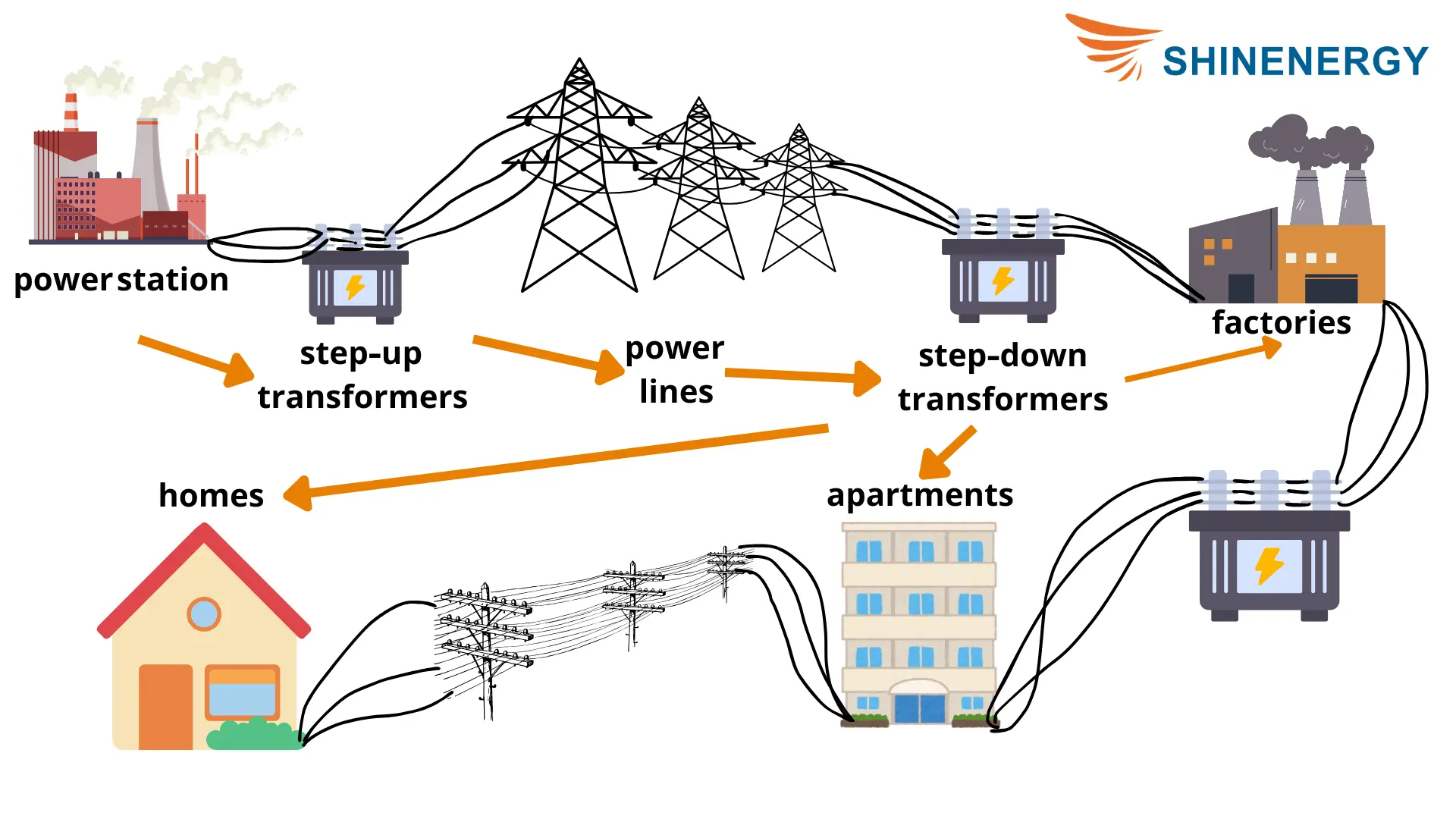
Illustrative image related to 3 transformer
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end product. Understanding whether a transformer is sourced from an OEM can assure buyers of its quality and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for international buyers who may need to meet certain order thresholds to benefit from competitive pricing. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ helps buyers receive accurate quotes and facilitates a smoother negotiation process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international transactions to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for understanding shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time required from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for project planning and ensuring that equipment is available when needed. -
Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the quality and reliability of the transformer. Knowing the warranty terms helps buyers assess the risk associated with their investment and provides recourse in case of product failures.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting three-phase transformers, ensuring they choose the right products for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 3 transformer Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the 3-Phase Transformer Sector?
The 3-phase transformer market is witnessing significant growth driven by a surge in demand for reliable and efficient power distribution systems across various sectors. Key global drivers include the increasing need for sustainable energy solutions, the expansion of industrial manufacturing, and the growth of renewable energy projects, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East. As countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil push towards industrialization and urbanization, the demand for robust electrical infrastructure, including 3-phase transformers, is set to rise.
Current sourcing trends indicate a shift towards digital procurement platforms that facilitate better transparency and efficiency in the supply chain. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging e-commerce channels to access a broader range of products and competitive pricing. Additionally, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is transforming how manufacturers operate, with smart transformers equipped with IoT capabilities becoming more prevalent. These innovations enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs for businesses.
Furthermore, the market is also influenced by geopolitical factors and trade regulations, which can impact pricing and supply chain stability. Buyers need to stay informed about tariff changes and import/export regulations that may affect their sourcing strategies, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
How is Sustainability Impacting the Sourcing of 3-Phase Transformers?
Sustainability is becoming a paramount concern for B2B buyers in the 3-phase transformer sector. The environmental impact of transformers, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and waste management, is driving demand for greener solutions. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, including the use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with businesses seeking to ensure that their supply chains are not only efficient but also socially responsible. This includes evaluating suppliers based on their labor practices and environmental impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and energy efficiency standards can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, innovations in transformer design, such as the use of dry-type transformers which are more environmentally friendly compared to traditional oil-filled models, are on the rise. These designs minimize leakage risks and are often made from recyclable materials. B2B buyers are encouraged to consider these sustainable options as they align with global initiatives aimed at reducing carbon footprints and promoting corporate social responsibility.
What is the Brief Evolution of the 3-Phase Transformer Sector?
The evolution of the 3-phase transformer sector can be traced back to the late 19th century, coinciding with the development of alternating current (AC) electrical systems. The introduction of 3-phase power systems revolutionized electrical distribution, allowing for more efficient transmission of electricity over long distances. This advancement paved the way for industrial growth, as businesses could reliably access the power needed for machinery and production.
Over the decades, technological innovations have led to the development of more efficient and compact transformer designs, including the introduction of dry-type transformers in the mid-20th century. These advancements have improved safety and reduced environmental impact, aligning with the increasing focus on sustainability in recent years. Today, the sector continues to evolve with the integration of smart technology, enabling enhanced monitoring and performance analytics that meet the demands of modern electrical grids and renewable energy applications.
This historical context underscores the importance of staying abreast of technological advancements and market shifts, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions in their sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3 transformer
-
How do I solve compatibility issues with different voltage levels in three-phase transformers?
To address compatibility issues, first, identify the voltage requirements of your equipment. Ensure the transformer you select can handle the input and output voltage levels required for your application. Consider using autotransformers if you need to step down or up voltage efficiently. Additionally, consult with your supplier about custom solutions or configurations that can accommodate specific voltage needs, particularly if you’re sourcing from regions with varying standards. -
What is the best transformer type for industrial applications?
The best transformer type for industrial applications typically depends on your specific needs. For most industrial operations, three-phase transformers are preferred due to their efficiency and ability to handle high loads. Dry-type transformers are ideal for environments where moisture and pollution may be a concern, while oil-filled transformers are suitable for outdoor applications requiring higher power ratings. Always evaluate factors such as space, load requirements, and environmental conditions when making your choice. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for three-phase transformers?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, certifications, and experience with international trade. Look for suppliers that offer comprehensive warranties and after-sales support. Assess their production capabilities and ensure they can meet your specific requirements, such as custom sizes or voltage ratings. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes and how they handle logistics, especially for international shipments to regions like Africa or South America. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for three-phase transformers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and the specific transformer model. Some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs, while others may require larger orders to justify production costs. For international buyers, it’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront to avoid unexpected costs. If you are a smaller business, look for suppliers willing to accommodate lower MOQs or explore group purchasing options with other businesses. -
What payment terms are typically available for international buyers?
Payment terms for international buyers can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation leverage. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Ensure you understand the payment structure, including any upfront deposits required, and consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection. Discuss payment terms early in negotiations to align expectations and avoid complications later. -
How can I ensure the quality of the transformers I am purchasing?
To ensure quality, request detailed specifications and certifications for the transformers, such as ISO 9001 or UL listings. Ask for test reports or compliance documentation that verifies performance standards. Additionally, consider conducting a factory audit or using third-party inspection services before shipment. Establishing a clear communication channel with your supplier can also help address any quality concerns proactively. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing transformers?
Logistics play a crucial role in the import process. Consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your country. Work with logistics partners who have experience in handling heavy equipment and understand the requirements for transporting transformers. Additionally, ensure that you have proper insurance coverage for your shipment and be prepared for potential tariffs or duties that may apply. -
Can I customize my transformer order to meet specific needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for their transformers. You can often specify voltage ratings, power capacity, and even physical dimensions based on your operational requirements. When discussing customization, be clear about your needs and the intended application of the transformer. Keep in mind that customized orders may require longer lead times and higher costs, so plan accordingly.
Top 6 3 Transformer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. North America Phase Converters – Power Converter Transformers
Domain: northamericaphaseconverters.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Single Phase to Three (3) Phase Power Converter Transformers include: 1. 240 X 480V to 120/240V Single Phase Transformers – Price range: $578.00 – $2,824.00 2. 240 Delta to 208Y/120 Volt Wye 3-Phase Transformer – Price range: $1,594.00 – $5,994.00 3. 480V to 208Y/120V Transformers – 3 Phase – Price range: $1,298.00 – $4,299.00 4. 240-480Y/277 Volt 3 Phase Transformers – Price range: $1,594.00 – $5…
2. High to Low Voltage – Isolation and Step Up Transformers
Domain: hightolowvoltage.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘208V Delta-208 Y (Isolation Transformer)’, ‘price’: ‘$3,010.00 USD’, ‘input_voltage’: ‘208’, ‘phase’: ‘3-Phase’}, {‘name’: ‘240V Delta – 416 Y (Step Up Transformer)’, ‘price’: ‘$4,080.00 USD’, ‘input_voltage’: ‘240’, ‘phase’: ‘3-Phase’}, {‘name’: ‘460 D – 460 Y 266 (Drive Isolation Transformer)’, ‘price’: ‘$1,760.00 USD’, ‘input_voltage’: ‘460’, ‘phase’: ‘3-Phase’}, {‘name’: ‘460 D – 23…
3. Maddox – 3-Phase Autotransformer
Domain: store.maddox.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “3-Phase Autotransformer 600-480-400-240-208v”, “SKU”: “MIT-AUT-110”, “available_sizes”: [“3 kVA”, “6 kVA”, “9 kVA”, “15 kVA”, “30 kVA”, “45 kVA”, “75 kVA”, “112.5 kVA”, “150 kVA”], “prices”: {“3 kVA”: “$674”, “6 kVA”: “$772”, “9 kVA”: “$1,081”, “15 kVA”: “$1,349”, “30 kVA”: “$2,279”, “45 kVA”: “$2,815”, “75 kVA”: “$3,521”, “112.5 kVA”: “$4,582”, “150 kVA”: “$5,106”}, “primary_vol…
4. The Engineering Mindset – Three Phase Transformers
Domain: theengineeringmindset.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Three Phase Transformers: Rated for 2kVA, delta primary and wye secondary configuration. Converts one AC voltage into another, producing multiple voltages (480V, 277V, 240V, 208V, and 120V). Types include pad mounted and pole mounted transformers. Used for supplying power to commercial buildings. Consists of primary and secondary coils, with the primary side connected to a single-phase AC supply a…
5. Electronics Tutorials – Three-Phase Transformers
Domain: electronics-tutorials.ws
Introduction: Three-phase transformers are essential for electrical power distribution, utilizing Delta or Star connected windings. They are used for generating and transmitting electric power over long distances for industrial and office use. Three-phase transformers can be constructed by connecting three single-phase transformers or using a pre-assembled three-phase transformer with three pairs of single-phas…
6. SE – 3T2F Transformer
Domain: se.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“model”:”3T2F”,”type”:”Transformer”,”design”:”dry type, encapsulated”,”power_rating”:”3kVA”,”phase”:”3 phase”,”primary_voltage”:”480V”,”secondary_voltage”:”208Y/120V”,”temperature_rise”:”12C, 115C rise”,”TAA_compliance”:”Yes”,”product_availability”:”Stock – Normally stocked in distribution facility”,”features”:”Resin filled transformers are epoxy encapsulated, Individual enclosures from 50VA thro…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3 transformer
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for three-phase transformers is vital for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the diverse applications and specifications of transformers, including their price ranges and configurations, equips businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. This knowledge not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters resilience in supply chains, particularly in industries reliant on robust power systems.
As buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing, prioritizing suppliers that offer comprehensive support—such as warranty services, rapid delivery options, and personalized customer service—can significantly impact the overall procurement experience. Establishing relationships with manufacturers and distributors who understand regional needs and can provide tailored solutions will further strengthen market positions.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced transformer solutions will continue to rise, driven by the global transition towards sustainable energy practices and technological advancements. International buyers are encouraged to leverage this momentum by exploring innovative transformer options that align with their operational goals. Embrace strategic sourcing to not only enhance your procurement strategy but to position your business for long-term success in a competitive landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.